The tax system and administration are different for every country. It's not unusual for a country to impose Goods and Service Tax (GST) on businesses for the government to control, regulate, and generate revenue.
In India, the tax system is unique and different compared to other countries. If you are running your business in India, I'm sure you have come across this term known as 'GST Cess.'
So, what is a 'GST Cess?' Let me start by explaining the word 'cess.' According to the dictionary, cess means tax or levy. The origin of 'Cess' came from the word assess. It's believed that Cess is originated from the Irish farmers, as those who have higher yield from their crop to pay more taxes to the government.
Why is Compensation Cess Implemented?
After the implementation of Goods and Service Tax (GST) in India, the tax of the product will eventually go to the buyer's state. This means some of the states will lose money, especially those states with high production but low consumptions.
The government then create the compensation cess to help those states to get tax revenue for them to operate. Cess is the additional levy charged in any types of goods on top of the Goods and Service Tax (GST). The revenue generated from the GST compensation cess will then be credited to Goods and Service Tax Compensation Fund, which is created to compensate tax revenue loss on the affected states. The unused fund will then be shared amongst the Central and State government at the end of the transition period.
Products with Compensation Cess
- Motor cars
- Coal and solid fuels
- Aerated waters
- Pan masala
- Motor vehicles designed to transport people
- Tobacco, tobacco products and tobacco substitute
Compensation cess applies to interstate-sales, intrastate-sales, and import. It does not apply to any export of goods and services.
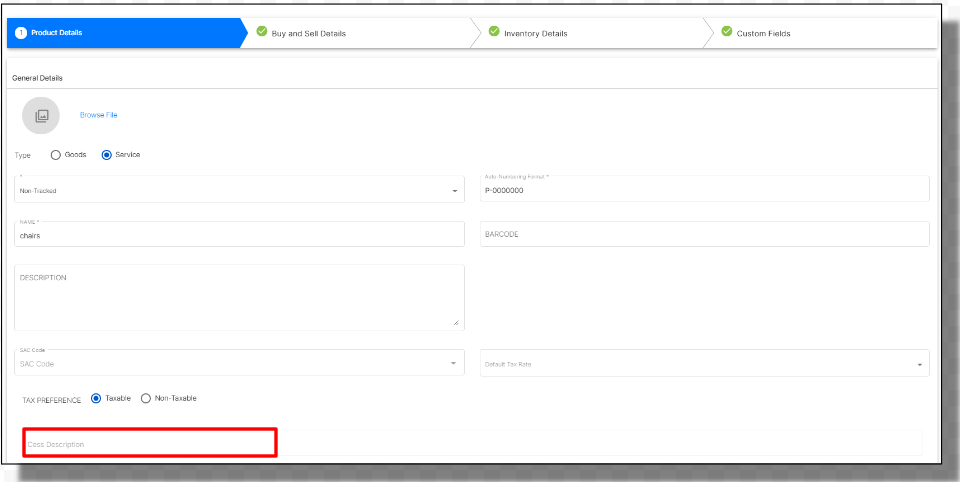
When creating a product in Deskera Books, input the compensation cess description for that particular product.
Find more about the GST Cess rates here.
How to calculate Compensation Cess?
For example, Company ABC supplies two cars that are worth Rs. 200,000 each to T&T Company in the same state, Karnataka. The cess rate is 1%, and the GST rate applicable to motor cars is 28%.
The calculation of the cess and the total cost is stated below:
Total of 2 cars: Rs. 400,000
CGST: Rs. 56,000
SGST: Rs. 56,000
Cess: Rs. 4,000
Total cost: Rs. 516,000
The GST Cess should be calculated based on the price of the goods. The GST Cess should be levied in addition to the GST taxes, i.e., CGST + SGST/UTGST in case of intrastate supplies and IGST in case of interstate supplies.
