How can manufacturers predict what their customers will need before they even ask? In today's fast-paced and competitive market, staying ahead of customer demand is critical to success.
Manufacturers who can accurately anticipate demand not only improve their production efficiency but also reduce costs and minimize waste. By understanding future needs, businesses can avoid costly overproduction, stockouts, and delays, ensuring they deliver what customers want, when they want it.
Anticipating customer demand is not a guessing game; it's a strategic process that involves analyzing data, monitoring market trends, and leveraging advanced technologies. Predictive analytics, AI, and real-time data collection have revolutionized the way manufacturers forecast demand.
This foresight helps manufacturers align their inventory, production schedules, and resources to meet evolving market needs with precision. With effective demand forecasting, companies can react faster to changing customer preferences, seasonal variations, and external factors like economic shifts.
The importance of accurate demand anticipation goes beyond efficiency; it’s also a key factor in maintaining strong relationships with suppliers and customers alike. When manufacturers can predict demand accurately, they can collaborate more effectively with suppliers to ensure timely inventory replenishment, while also ensuring customers receive their orders on time. This ability to meet demand consistently strengthens a company’s reputation and builds customer loyalty, which is essential for long-term growth.
One solution that empowers manufacturers to get ahead of demand is Deskera’s manufacturing ERP. Deskera offers advanced features like demand forecasting, real-time data analytics, and automated production planning that help manufacturers stay agile.
With tools like Deskera’s AI assistant, David, businesses can automate forecasting processes and adjust production in real time, reducing the risk of stockouts and overproduction. Deskera ERP integrates every aspect of manufacturing operations, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions that keep them ahead of the competition.
What is Customer Demand and Why Does it Matter in Manufacturing?
Customer demand refers to the quantity and type of products that customers are willing and able to purchase at a given time. In manufacturing, understanding customer demand means being aware of what products your customers need, how much they require, and when they need them.
This knowledge is crucial because it directly impacts production schedules, inventory levels, and supply chain management. When manufacturers can accurately forecast demand, they can ensure that they are producing the right amount of product without overstocking or understocking, both of which can have significant financial repercussions.
In the context of manufacturing, customer demand drives every decision—from sourcing raw materials to scheduling production runs. A clear understanding of demand helps businesses optimize their operations, ensuring that they have the resources necessary to meet customer expectations without wasting time, money, or materials.
For example, when demand is high, manufacturers can ramp up production to avoid shortages. Conversely, when demand slows, production can be adjusted to prevent overproduction, which leads to excessive inventory costs.
Failing to anticipate customer demand can lead to several negative consequences. Overstocking ties up capital in unsold inventory, while underestimating demand can lead to stockouts, resulting in missed sales opportunities and dissatisfied customers.
Moreover, inefficient demand planning can strain relationships with suppliers, disrupt supply chains, and reduce operational flexibility. This can also impact a manufacturer’s reputation, as failing to meet customer expectations can cause clients to turn to competitors.
In today’s rapidly changing market, having a strong grip on customer demand is not just beneficial—it’s essential. Manufacturers who can predict customer demand accurately gain a significant competitive advantage by delivering products more quickly, reducing lead times, and minimizing costs.
Modern tools, such as ERP systems with demand forecasting capabilities, are helping manufacturers stay ahead by providing real-time insights into customer behavior, allowing them to anticipate needs and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Key Drivers Influencing Customer Demand in Manufacturing
Customer demand in manufacturing is influenced by a complex set of factors that range from economic conditions to shifts in consumer preferences. Understanding these drivers is essential for manufacturers to forecast demand accurately and adjust their production strategies accordingly.
Below are some of the most critical factors that shape customer demand in the manufacturing sector:
1. Market Trends
Market trends play a significant role in influencing customer demand. Consumer preferences often evolve with new product innovations, technological advancements, and shifting lifestyle choices. For example, the rise of eco-friendly and sustainable products has significantly influenced demand in various industries, from electronics to packaging.
Manufacturers must stay attuned to these trends, anticipating customer interest in new product categories or emerging features to stay competitive. Failing to do so can result in missed opportunities or obsolescence in the market.
2. Seasonality
Seasonality is another key driver, particularly in industries like retail, food, and consumer goods. Manufacturers must plan for predictable demand fluctuations based on seasonal factors such as holidays, weather changes, or annual events.
For instance, a surge in demand for winter apparel during the colder months or consumer electronics during the holiday season is common. Understanding these patterns allows manufacturers to scale production efficiently, ensuring they meet demand without overstocking.
3. Customer Behavior and Preferences
The behavior and preferences of end consumers significantly influence demand. With the rise of e-commerce, customers have become more accustomed to instant access to products, which can create fluctuations in demand.
Additionally, modern consumers increasingly value personalization, ethical production practices, and sustainability, which can shape their purchasing decisions. Manufacturers that can quickly adapt to these changing preferences are more likely to succeed in maintaining steady demand for their products.
4. Economic Conditions
Economic conditions, both at the macro and micro level, have a profound impact on customer demand. During periods of economic growth, consumers and businesses are more willing to spend, increasing demand for a wide range of products.
Conversely, economic downturns or recessions often lead to reduced consumer spending, which can result in lower demand for non-essential or luxury goods. Manufacturers need to monitor economic indicators, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation, to adjust their production and pricing strategies accordingly.
5. External Factors: Geopolitics and Supply Chain Disruptions
Geopolitical events, such as trade wars, tariffs, or changes in government regulations, can significantly affect customer demand. For instance, tariffs on imported materials can lead to higher production costs, which may lower demand for products in certain markets.
Additionally, supply chain disruptions caused by natural disasters, pandemics, or political instability can create bottlenecks in production, leading to shifts in demand. Manufacturers must be agile and prepared to respond to these disruptions by having contingency plans or alternative suppliers in place.
6. Competitor Actions
The actions of competitors can also have a substantial influence on customer demand. For example, when competitors lower prices or release new features, customer interest can shift towards their products, leading to decreased demand for others in the market.
On the flip side, a competitor’s failure to meet demand or maintain product quality can create opportunities for other manufacturers to capture market share. Monitoring competitor activity and customer sentiment helps manufacturers anticipate changes in demand and adjust their offerings accordingly.
By staying ahead of these key drivers and using tools such as demand forecasting and real-time data analysis, manufacturers can more accurately predict customer demand. This allows them to streamline production, optimize inventory levels, and ultimately stay competitive in a dynamic marketplace.
Techniques for Anticipating Customer Demand in Manufacturing
Accurately anticipating customer demand is critical for manufacturing businesses aiming to optimize production, reduce costs, and avoid both overproduction and stockouts. Several techniques are used to predict demand more effectively.
By combining historical data, advanced analytics, and real-time insights, manufacturers can enhance their forecasting accuracy and stay ahead of market needs.
Below are some of the most effective techniques for anticipating customer demand in manufacturing:
1. Historical Data Analysis
One of the foundational techniques for predicting customer demand is analyzing historical data. By examining past sales, production trends, and seasonal fluctuations, manufacturers can identify patterns that provide insight into future demand.
This data-driven approach enables businesses to recognize recurring trends, such as annual sales peaks during certain seasons or economic cycles. However, while historical data is valuable, it is often paired with other forecasting methods to account for market shifts or unforeseen events that past data cannot predict.
2. Market Research and Trend Analysis
Staying informed about market trends and consumer behavior is vital for demand forecasting. Conducting market research through surveys, focus groups, and industry reports helps manufacturers anticipate shifts in customer preferences and product demand.
Trend analysis can reveal changes in technology, customer preferences, or market conditions that will impact future demand. For example, growing interest in eco-friendly products can signal a need to shift production to more sustainable materials or designs.
3. Demand Sensing
Demand sensing is a real-time forecasting technique that uses current market data, such as point-of-sale (POS) information, customer orders, and inventory levels, to anticipate short-term demand.
Unlike traditional forecasting methods that rely on historical data, demand sensing captures real-time insights, making it highly effective for responding to sudden shifts in the market.
This technique is particularly useful in industries with fast-moving products, such as consumer goods or electronics. By analyzing immediate data, manufacturers can adjust production schedules or inventory orders to meet evolving customer needs.
4. Predictive Analytics and AI
Predictive analytics, often powered by artificial intelligence (AI), is revolutionizing demand forecasting in manufacturing. By using advanced algorithms to analyze large sets of data, AI can predict future demand with greater accuracy.
AI-driven tools factor in various data points, including historical sales, market trends, weather conditions, and economic indicators, to create complex demand models.
These systems can detect hidden patterns or correlations that traditional forecasting methods may overlook. AI also continuously refines its predictions as new data is introduced, making it a powerful tool for improving accuracy over time.
5. Collaborative Forecasting (CPFR)
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR) is a technique that involves manufacturers, suppliers, and retailers working together to share data and develop more accurate demand forecasts.
By collaborating across the supply chain, companies gain better visibility into customer demand at all levels, improving the accuracy of their production plans.
CPFR reduces the risk of stockouts and overproduction, as supply chain partners can adjust their operations based on shared insights. This technique also fosters stronger relationships between partners and helps synchronize production with actual demand.
6. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning involves creating multiple demand forecasts based on different potential outcomes. This technique is particularly useful in volatile or uncertain markets where sudden shifts in demand are likely.
Manufacturers develop a range of scenarios, each based on different factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, or new technological developments.
By preparing for best-case, worst-case, and moderate scenarios, manufacturers can remain flexible and adjust their production strategies quickly if demand changes unexpectedly.
7. Monitoring External Factors
External factors, such as geopolitical events, supply chain disruptions, and changes in government regulations, can heavily influence demand. Monitoring these factors allows manufacturers to anticipate potential impacts on customer demand.
For example, trade policies or tariffs may affect the cost of materials, leading to changes in demand for certain products. Manufacturers who closely monitor these external drivers can adjust their production plans accordingly, ensuring they are better prepared to meet shifts in demand.
8. Inventory Management Systems with Demand Forecasting Features
Many manufacturers use advanced inventory management systems, like ERP software, that incorporate demand forecasting features. These systems track real-time inventory levels, sales data, and market conditions to provide accurate forecasts.
For example, Deskera’s Manufacturing ERP includes tools that enable demand forecasting, production planning, and real-time data analytics. These features allow manufacturers to respond quickly to demand fluctuations and maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing both excess stock and shortages.
By leveraging these techniques, manufacturers can make better-informed decisions, optimize production processes, and ultimately align their operations with customer demand.
Whether through AI-powered analytics, collaborative forecasting, or real-time data monitoring, anticipating demand is key to maintaining a competitive edge in the manufacturing industry.
Incorporating Real-Time Data and Trends
In today's rapidly changing manufacturing landscape, relying solely on historical data to forecast customer demand is no longer sufficient. To stay competitive, manufacturers must incorporate real-time data and market trends into their demand forecasting processes.
By leveraging live data and tracking emerging trends, companies can respond swiftly to market shifts, reduce inefficiencies, and better meet customer needs.
Here are some key ways manufacturers can effectively incorporate real-time data and trends into their demand planning:
1. Real-Time Data from Supply Chain and Sales Channels
One of the most effective ways to improve demand forecasting is by gathering real-time data from various points in the supply chain, including sales channels, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and supplier information.
Modern inventory management systems, ERP platforms, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools can provide live updates on sales figures, customer orders, stock levels, and delivery statuses. By analyzing this real-time data, manufacturers can quickly identify shifts in demand and adjust their production schedules accordingly.
For example, if a manufacturer notices a spike in orders for a particular product in a specific region, they can ramp up production for that item, ensuring they meet customer expectations without delay. Real-time data enables manufacturers to react to these demand fluctuations almost instantaneously, reducing lead times and avoiding stock outs or overstocking.
2. Integrating IoT for Real-Time Insights
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed manufacturing by enabling real-time data collection across various stages of the production process. IoT sensors placed on machines, equipment, and even within supply chains can provide valuable data on machine performance, material usage, and product output.
This information allows manufacturers to monitor production in real time, identifying any potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies before they affect delivery times or output quality.
By integrating IoT data with demand forecasting tools, manufacturers gain greater visibility into their production capabilities and can more accurately adjust output based on immediate customer needs.
For instance, if demand for a product increases unexpectedly, IoT data can help identify whether the production line has the capacity to meet that demand or if additional resources are needed.
3. Predictive Analytics with Real-Time Data
Predictive analytics powered by real-time data offers manufacturers a competitive edge by enabling them to forecast demand more accurately. Predictive analytics tools analyze vast datasets in real time, identifying patterns and correlations that might go unnoticed with traditional forecasting methods.
These tools take into account factors such as current sales trends, external market conditions, and even weather patterns to predict future customer demand with greater precision.
For example, a sudden weather change could affect demand for seasonal products such as clothing, electronics, or outdoor equipment. Predictive analytics that integrate real-time weather data can alert manufacturers to adjust production or inventory accordingly, ensuring that they are prepared for spikes in demand or unexpected lulls.
4. Tracking Market Trends and Customer Sentiment
Customer demand is not just influenced by immediate sales data but also by broader market trends and shifts in consumer sentiment. Social media platforms, industry news, and online reviews offer valuable insights into what customers are currently talking about and what they are likely to buy in the future. By actively tracking these trends, manufacturers can anticipate changes in demand before they reflect in sales numbers.
For instance, an emerging trend for sustainable or eco-friendly products may indicate an increase in demand for green manufacturing solutions. Manufacturers who monitor such trends in real time can begin adapting their processes, sourcing sustainable materials, and marketing their products to align with customer expectations before competitors do.
5. Using ERP Systems for Real-Time Demand Forecasting
Advanced ERP systems, like Deskera’s Manufacturing ERP, integrate real-time data from sales, inventory, supply chain, and customer behavior to provide up-to-date demand forecasts.
These systems allow manufacturers to gain a 360-degree view of their operations, ensuring that all departments—from procurement to production—are aligned with the most current demand forecasts.
Deskera’s ERP solution, for example, offers real-time data analytics and demand forecasting features that help manufacturers adjust their production schedules dynamically.
With tools like Deskera’s AI-powered assistant, David, manufacturers can automate demand planning, reducing manual errors and enabling faster responses to shifts in customer demand.
Real-time data analytics within ERP systems allow for constant monitoring and updating of demand forecasts, ensuring businesses remain agile and proactive in meeting customer needs.
6. Adapting to Global Trends and External Factors
Real-time data also plays a vital role in helping manufacturers adjust to broader global trends, such as economic shifts, political changes, or supply chain disruptions. By integrating real-time data from external sources, such as economic indicators or geopolitical developments, manufacturers can better anticipate how these factors will affect demand.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, manufacturers who tracked real-time data on lockdowns, supply chain disruptions, and shifts in consumer behavior were able to pivot their operations more quickly to meet the new demand for essential goods like medical supplies and home office equipment.
Incorporating real-time external data into demand planning allows manufacturers to be better prepared for unexpected challenges or opportunities in the marketplace.
Incorporating real-time data and tracking trends enables manufacturers to maintain a flexible, proactive approach to production planning. By responding quickly to shifts in demand, manufacturers can ensure operational efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver products that meet evolving customer expectations in a highly dynamic market.
Leveraging Real-Time Data and Market Trends for Demand Forecasting
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, staying ahead of customer demand requires more than just historical data and traditional forecasting methods.
To remain competitive and agile, manufacturers must harness the power of real-time data and emerging market trends. By integrating live insights into their demand forecasting processes, companies can make informed decisions, adjust production strategies, and reduce inefficiencies.
Here’s how real-time data and market trends can revolutionize demand forecasting in manufacturing:
1. Utilizing Real-Time Supply Chain and Sales Data
Real-time data from various points along the supply chain—such as sales figures, inventory levels, and customer orders—provides manufacturers with the most up-to-date information about market conditions. Rather than waiting for quarterly reports or historical trends, manufacturers can use real-time sales data to make on-the-fly adjustments to production schedules.
Modern inventory management systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, and customer relationship management (CRM) software offer real-time data tracking that informs demand forecasting.
By leveraging this data, manufacturers can quickly react to surges in demand, prevent stockouts, and avoid overproduction. For example, if a spike in orders is detected for a particular product, real-time data allows manufacturers to immediately scale up production or increase supply chain efficiency to meet customer needs.
2. Leveraging Real-Time Sales Data
Monitoring real-time sales data is crucial for manufacturers to adjust their demand forecasts quickly. E-commerce trends, in particular, can provide valuable insights into rapidly shifting consumer preferences and buying behavior.
By analyzing online sales data and browsing patterns, manufacturers can identify which products are gaining traction and which are losing popularity.
This immediate feedback loop enables manufacturers to pivot their strategies in response to changing consumer preferences. For instance, if a specific product begins to see increased online orders, manufacturers can prioritize its production to capitalize on the trend, ensuring they meet customer demand head-on.
Conversely, if sales data indicates a decline in interest for certain items, manufacturers can strategically reduce inventory and adjust production schedules accordingly.
3. Integrating IoT for Enhanced Visibility
The Internet of Things (IoT) has drastically transformed manufacturing processes by enabling real-time monitoring across the entire production line. IoT sensors placed on machinery, equipment, and supply chains continuously gather data related to production performance, material usage, and inventory status. This live data offers manufacturers an unparalleled level of visibility into their operations.
When combined with demand forecasting tools, IoT data allows for a more accurate response to shifts in demand. For example, if demand increases suddenly, manufacturers can assess machine capacity, optimize resource allocation, and adapt production plans based on real-time insights from IoT sensors. This data-driven approach minimizes downtime and ensures the production line operates at peak efficiency.
4. Predictive Analytics Powered by Real-Time Data
Predictive analytics, fueled by real-time data, is one of the most powerful tools for demand forecasting. By analyzing large volumes of data—such as sales trends, economic indicators, and even weather patterns—predictive analytics can forecast future demand with greater accuracy than traditional methods. What makes predictive analytics particularly valuable is its ability to continuously update forecasts as new data becomes available.
For instance, if sudden shifts in weather patterns affect the demand for seasonal products, real-time data can be fed into predictive models to instantly adjust forecasts.
Manufacturers can then optimize their production schedules and supply chains to avoid understocking or overproducing, ensuring they meet customer demand efficiently.
5. Tracking Market Trends and Consumer Behavior
In addition to real-time operational data, tracking external market trends and shifts in consumer behavior is essential for accurate demand forecasting. Social media platforms, industry news, and customer feedback provide valuable insights into evolving customer preferences. Monitoring these trends helps manufacturers anticipate upcoming changes in demand before they are reflected in sales data.
5.1 Social Media and Market Sentiment Analysis: Social listening tools can significantly enhance a manufacturer’s understanding of customer preferences by monitoring social media chatter and trends. By analyzing conversations around specific products or services, businesses can gauge customer interest and sentiment, allowing them to adjust their offerings accordingly.
Market sentiment analysis tools further deepen this understanding by providing real-time insights into how customers feel about particular products or brands. These tools can highlight potential demand spikes or declines, enabling manufacturers to make proactive adjustments to their production and marketing strategies.
For example, if social media indicates a growing interest in sustainable manufacturing practices, companies can shift their production focus to eco-friendly products, aligning themselves with customer values and driving sales.
6. Leveraging ERP Systems for Real-Time Forecasting
Modern ERP systems play a pivotal role in incorporating real-time data into demand forecasting processes. Advanced ERP solutions, such as Deskera’s Manufacturing ERP, provide manufacturers with real-time insights into inventory, sales, and production operations. These systems continuously monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), allowing manufacturers to align production with customer demand.
Deskera’s ERP platform, for example, integrates real-time demand forecasting tools, automating the process of adjusting production schedules based on live data. With AI-driven features like Deskera’s assistant, David, manufacturers can predict demand, manage inventory levels, and optimize workflows to meet evolving market conditions. By adopting ERP systems with real-time forecasting capabilities, manufacturers can stay agile and make more accurate production decisions.
7. Adapting to Global Trends and External Factors
Incorporating real-time data extends beyond internal operations—manufacturers must also consider global trends and external factors. Changes in government regulations, global trade agreements, or economic conditions can drastically influence demand. By monitoring these external drivers in real time, manufacturers can anticipate changes in customer behavior and adjust their production strategies accordingly.
For example, during times of economic uncertainty or global supply chain disruptions, manufacturers that closely monitor real-time data from external sources can pivot their production models to address new market realities. Whether it’s shifting production focus to essential goods or navigating trade restrictions, real-time data helps manufacturers remain flexible and resilient.
The Role of Customer Feedback in Anticipating Demand
In an era where customer-centricity drives business success, leveraging customer feedback has become a vital strategy for manufacturers aiming to anticipate demand effectively.
By actively seeking and analyzing feedback from customers, manufacturers can gain valuable insights into consumer preferences, identify emerging trends, and ultimately shape their production strategies to align with market demands.
Here’s a closer look at how customer feedback plays a crucial role in anticipating demand in the manufacturing sector:
1. Understanding Customer Preferences
Customer feedback provides a direct line to understanding what consumers want. By collecting feedback through surveys, product reviews, and direct interactions, manufacturers can identify specific preferences regarding features, quality, and pricing. This information allows manufacturers to tailor their products and services to meet the needs of their target market.
For example, if feedback indicates a growing demand for eco-friendly materials, manufacturers can pivot their production processes to include sustainable options. This proactive approach ensures that products resonate with consumers, driving sales and enhancing brand loyalty.
2. Identifying Emerging Trends
Monitoring customer feedback is not just about understanding current preferences; it also helps manufacturers spot emerging trends before they become mainstream. Social media platforms, online reviews, and customer interactions can reveal shifts in consumer attitudes and behaviors.
For instance, if customers start expressing interest in smart home products or automation features, manufacturers can leverage this information to innovate and develop products that align with these trends. By acting on early signals from customer feedback, manufacturers can position themselves as industry leaders and meet demand before competitors do.
3. Improving Product Development
Customer feedback plays a significant role in the product development lifecycle. By engaging with customers and soliciting their opinions during the development phase, manufacturers can create products that are more likely to succeed in the market. This iterative process allows for adjustments based on real-time input, minimizing the risk of launching products that do not meet customer expectations.
Moreover, manufacturers can conduct beta testing or focus groups to gather feedback on prototypes or new concepts. This hands-on approach not only refines product features but also builds anticipation and excitement among potential customers, creating a ready market at launch.
4. Enhancing Customer Engagement and Loyalty
Engaging with customers and valuing their feedback fosters a sense of community and loyalty. When customers feel heard and appreciated, they are more likely to remain loyal to a brand and advocate for its products. This engagement translates into repeat business and a steady demand for products.
Additionally, satisfied customers often provide positive testimonials and referrals, amplifying a manufacturer’s reach. By nurturing these relationships through active listening and responsiveness to feedback, manufacturers can create a loyal customer base that drives demand growth.
5. Utilizing Technology for Feedback Collection
With advancements in technology, manufacturers can now harness various tools to collect and analyze customer feedback efficiently. Social listening tools, online surveys, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems enable manufacturers to gather data from multiple channels and analyze it in real-time.
For example, social listening platforms can track mentions of a brand or product across social media, providing insights into customer sentiment and preferences. By integrating this data into demand forecasting models, manufacturers can make informed decisions that align with consumer expectations.
6. Adjusting Inventory and Production Strategies
Customer feedback directly influences inventory management and production strategies. By understanding which products are in demand and which are not, manufacturers can optimize their inventory levels to prevent stock outs or overstock situations.
For instance, if feedback indicates a growing interest in a particular product line, manufacturers can increase production to meet the anticipated demand. Conversely, if feedback suggests declining interest in another product, they can reduce inventory levels, minimizing waste and optimizing resources.
Collaboration with Suppliers and Distributors in Anticipating Demand
In today's interconnected manufacturing landscape, effective collaboration with suppliers and distributors is essential for accurately anticipating customer demand.
This collaboration not only enhances supply chain efficiency but also provides manufacturers with critical insights that inform demand forecasting. By fostering strong partnerships throughout the supply chain, manufacturers can better align their production strategies with market needs.
Here’s a closer look at how collaboration with suppliers and distributors plays a crucial role in anticipating demand:
1. Information Sharing and Transparency
Collaboration between manufacturers and their suppliers and distributors hinges on open communication and information sharing. When manufacturers share their demand forecasts and sales data with their suppliers, it enables them to better understand expected production volumes and timelines. In return, suppliers can provide insights about their capacity, lead times, and any potential disruptions that might affect the supply chain.
By establishing transparent communication channels, both parties can work together to create more accurate demand forecasts. For instance, if a manufacturer anticipates a surge in demand for a specific product, sharing this information with suppliers allows them to ramp up production and ensure timely delivery of materials, thereby preventing stockouts and production delays.
2. Joint Planning and Strategy Development
Engaging in joint planning sessions with suppliers and distributors can enhance demand forecasting accuracy. These collaborative efforts allow manufacturers to align their production schedules with the supply chain capabilities and market insights provided by their partners. For instance, by involving suppliers in the planning process, manufacturers can identify any potential bottlenecks in the supply chain early on.
Additionally, joint strategy development can help manufacturers explore new market opportunities together. For example, if a distributor identifies a growing demand for a particular product category in a specific region, manufacturers can collaborate to tailor their production and marketing strategies to capitalize on this insight.
3. Leveraging Technology for Collaboration
Technology plays a pivotal role in facilitating collaboration between manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors. Modern supply chain management software and collaborative platforms enable real-time data sharing, improving visibility across the supply chain. Tools such as cloud-based ERP systems allow all parties to access updated information on inventory levels, sales trends, and production schedules.
For example, platforms like Deskera ERP provide manufacturers with integrated tools that streamline communication with suppliers and distributors. This technology not only enhances collaboration but also empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions based on real-time data, leading to more accurate demand forecasting.
4. Supplier Performance and Capacity Monitoring
Collaborating with suppliers enables manufacturers to monitor supplier performance and capacity closely. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), manufacturers can assess suppliers' ability to meet demand effectively.
If a supplier consistently struggles to deliver materials on time, manufacturers can proactively seek alternative suppliers or adjust their production schedules to mitigate potential disruptions.
Furthermore, by understanding supplier capacity and lead times, manufacturers can make better decisions about inventory levels and production schedules. This insight allows for more agile responses to changes in customer demand, reducing the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.
5. Creating Agile Supply Chains
A collaborative approach fosters agility in the supply chain, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to shifts in demand. By maintaining strong relationships with suppliers and distributors, manufacturers can implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices, reducing carrying costs and increasing responsiveness to market changes.
For example, if customer feedback indicates a sudden increase in demand for a specific product, manufacturers with collaborative supplier relationships can quickly adjust their orders to ensure adequate material supply. This agility not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens the overall supply chain resilience.
6. Innovating Together
Collaboration with suppliers and distributors can lead to innovation that enhances demand forecasting and production processes. By working closely together, manufacturers can tap into the expertise and knowledge of their partners, leading to new product developments and improvements in existing offerings.
For instance, if a supplier has insights into emerging materials or technologies, manufacturers can collaborate to develop innovative products that meet evolving customer demands. This joint innovation not only boosts competitiveness but also helps manufacturers stay ahead of market trends.
Demand Planning and S&OP: Aligning Supply with Demand
In the realm of manufacturing, effective demand planning and Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) are critical components that ensure alignment between supply and demand.
These processes not only facilitate the efficient use of resources but also enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring that the right products are available at the right time. Here’s a detailed exploration of how demand planning and S&OP work together to synchronize supply with demand.
1. Understanding Demand Planning
Demand planning is the process of forecasting future customer demand for a product or service. This involves analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to predict future demand accurately.
Effective demand planning enables manufacturers to optimize inventory levels, reduce excess stock, and minimize stockouts, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency.
A well-developed demand plan serves as the foundation for the S&OP process, providing the necessary insights to align production and supply chain strategies. By understanding customer needs and market dynamics, manufacturers can make informed decisions regarding production schedules, inventory management, and resource allocation.
2. The Role of S&OP in Aligning Supply with Demand
Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) is a collaborative process that integrates sales, marketing, production, and supply chain functions. The primary goal of S&OP is to ensure that supply and demand are aligned, enabling manufacturers to meet customer expectations while optimizing resource utilization.
S&OP involves regular meetings and discussions among cross-functional teams to review demand forecasts, assess capacity constraints, and make necessary adjustments to production plans.
By fostering collaboration among different departments, S&OP ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding demand expectations and supply capabilities.
3. Key Components of Effective Demand Planning and S&OP
To successfully align supply with demand, manufacturers should focus on the following key components:
- Data Integration: Centralizing data from various sources, such as sales, inventory, and market trends, is essential for accurate demand forecasting and S&OP. Leveraging technology, such as ERP systems, can streamline data collection and analysis, providing a comprehensive view of demand patterns.
- Collaboration Across Functions: Encouraging collaboration between sales, marketing, production, and supply chain teams fosters a holistic approach to demand planning and S&OP. Regular communication ensures that all stakeholders are aware of demand fluctuations and can adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Scenario Planning: Developing different demand scenarios helps manufacturers prepare for uncertainties. By analyzing various “what-if” scenarios, manufacturers can identify potential risks and opportunities, allowing them to create flexible supply chain strategies.
- Continuous Improvement: The demand planning and S&OP processes should be iterative, with regular reviews to assess performance and identify areas for improvement. By learning from past outcomes, manufacturers can refine their forecasting methods and enhance their ability to respond to changing market conditions.
4. Benefits of Aligning Supply with Demand
Aligning supply with demand through effective demand planning and S&OP offers several benefits for manufacturers:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By ensuring that the right products are available when customers need them, manufacturers can enhance customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. Timely fulfillment of orders contributes to a positive customer experience.
- Optimized Inventory Levels: Effective demand planning and S&OP help manufacturers maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing carrying costs and minimizing the risk of obsolescence. This optimization leads to better cash flow and resource utilization.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: By aligning production schedules with demand forecasts, manufacturers can streamline operations and reduce lead times. This efficiency contributes to a more agile supply chain capable of responding to market changes.
- Enhanced Profitability: By minimizing stockouts and excess inventory, manufacturers can increase sales and reduce costs, ultimately leading to improved profitability. Aligning supply with demand allows manufacturers to maximize their operational effectiveness.
5. The Role of Technology in Demand Planning and S&OP
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing demand planning and S&OP processes. Advanced forecasting tools, data analytics, and ERP systems enable manufacturers to gather and analyze large volumes of data quickly.
These technologies facilitate real-time visibility into inventory levels, sales trends, and market dynamics, empowering manufacturers to make informed decisions.
For example, Deskera’s manufacturing ERP provides integrated solutions that streamline demand planning and S&OP processes, offering features such as automated forecasting, collaborative planning tools, and data analytics capabilities. By leveraging such technology, manufacturers can enhance their ability to align supply with demand effectively.
Challenges in Anticipating Customer Demand
Anticipating customer demand is a critical component of successful manufacturing operations, yet it presents a range of challenges that can hinder accuracy and responsiveness. As market dynamics evolve and consumer preferences shift, manufacturers must navigate various obstacles to create reliable demand forecasts.
Here are some key challenges in anticipating customer demand:
1. Market Volatility and Uncertainty
The manufacturing landscape is often subject to sudden changes due to market volatility, economic fluctuations, and geopolitical events. These factors can disrupt supply chains and influence customer purchasing behavior.
For instance, economic downturns may lead to reduced consumer spending, while unexpected events like natural disasters or pandemics can drastically alter demand patterns. As a result, manufacturers must remain vigilant and adaptable to address these uncertainties.
2. Inaccurate Historical Data
Accurate demand forecasting relies heavily on historical sales data. However, factors such as data entry errors, incomplete records, or outdated information can lead to inaccurate forecasts.
Additionally, if past sales data do not reflect current market conditions, it can result in poor demand predictions. Manufacturers need to implement robust data collection and analysis processes to ensure they base their forecasts on reliable information.
3. Complexity of Consumer Behavior
Understanding consumer behavior is inherently complex, influenced by various factors such as seasonality, trends, marketing efforts, and social media. Customers may exhibit unpredictable purchasing patterns, making it challenging for manufacturers to anticipate demand accurately.
The rise of e-commerce and social media has further complicated this landscape, as consumer preferences can change rapidly based on trends or influencer marketing. Manufacturers must continuously monitor consumer sentiment and adapt their forecasts accordingly.
4. Limited Visibility into Supply Chain Dynamics
Effective demand forecasting requires insights into the entire supply chain, including supplier capabilities and inventory levels. Limited visibility can hinder manufacturers' ability to anticipate potential bottlenecks or disruptions that may impact their ability to meet customer demand.
For example, if a supplier faces production delays, it may affect the manufacturer's ability to fulfill orders on time. Enhancing visibility through technology and collaboration with suppliers is essential for overcoming this challenge.
5. Inefficient Collaboration Across Departments
Collaboration between sales, marketing, production, and supply chain teams is vital for accurate demand forecasting. However, silos within organizations can lead to misalignment and communication gaps.
For instance, if sales teams do not share market insights or changes in customer preferences with production and supply chain teams, it can result in inaccurate forecasts and inventory issues. Encouraging cross-functional collaboration and communication is crucial for improving demand planning processes.
6. Technological Limitations
While technology plays a pivotal role in demand forecasting, not all manufacturers have access to advanced tools and analytics. Many still rely on manual processes or outdated software, which can limit their ability to analyze data effectively and make informed decisions. Embracing modern demand forecasting software and analytics tools is essential for enhancing forecasting accuracy and responsiveness.
7. Changing Regulatory and Compliance Standards
Manufacturers must navigate an ever-evolving landscape of regulatory and compliance requirements. Changes in regulations can impact production processes, product specifications, and ultimately, customer demand.
For example, new environmental regulations may affect the availability of certain materials, leading to shifts in demand for specific products. Staying informed about regulatory changes and incorporating them into demand planning is vital for manufacturers.
8. Globalization and Supply Chain Complexity
As manufacturers expand their operations globally, they face increased complexity in managing supply chains across multiple regions. Different markets may have unique demands, preferences, and regulatory requirements, complicating demand forecasting efforts. Manufacturers must adapt their strategies to cater to diverse customer needs while maintaining efficiency in their supply chains.
The Role of Technology in Transforming Demand Forecasting
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, accurate demand forecasting is more critical than ever. With rapidly changing market conditions and consumer preferences, traditional methods of forecasting are often insufficient.
Technology plays a pivotal role in transforming demand forecasting, providing manufacturers with the tools they need to make data-driven decisions, enhance accuracy, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Here’s a closer look at how technology is reshaping demand forecasting in manufacturing.
1. Advanced Analytics and Data Processing
Modern demand forecasting relies heavily on advanced analytics and data processing capabilities. Traditional forecasting methods often rely on simple statistical techniques that may not capture the complexity of market dynamics.
In contrast, advanced analytics leverage machine learning algorithms and big data to analyze vast amounts of historical sales data, market trends, and consumer behavior.
These technologies can identify patterns and correlations that may not be apparent through manual analysis. By using predictive analytics, manufacturers can generate more accurate forecasts, helping them to anticipate demand fluctuations and respond accordingly.
For example, predictive models can analyze seasonality, promotions, and external factors such as economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of future demand.
2. Real-Time Data Integration
The ability to access and analyze real-time data is a game-changer for demand forecasting. Traditional forecasting methods often rely on historical data collected at intervals, which may not reflect current market conditions. In contrast, real-time data integration allows manufacturers to monitor sales, inventory levels, and market trends as they occur.
This capability enables manufacturers to make quick adjustments to their forecasts and production plans based on up-to-the-minute information. For example, if sales data indicates a sudden spike in demand for a particular product, manufacturers can adjust their production schedules and inventory management strategies to meet that demand. Real-time data integration is essential for enhancing agility and responsiveness in the supply chain.
3. Collaboration and Communication Tools
Effective demand forecasting requires collaboration across various departments, including sales, marketing, production, and supply chain. Technology facilitates this collaboration by providing communication tools and platforms that enable teams to share insights, data, and forecasts seamlessly.
Cloud-based collaboration tools allow stakeholders to access a centralized dashboard where they can input data, track changes, and discuss forecasts in real-time.
This improved communication helps ensure that all departments are aligned and working toward the same goals, reducing silos and enhancing the accuracy of demand forecasts.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing demand forecasting by automating data analysis and improving predictive accuracy. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from multiple sources, identifying trends and patterns that human analysts may overlook.
Machine learning algorithms can continuously learn from new data, improving their forecasting models over time. As AI-driven solutions become more prevalent, manufacturers can leverage these technologies to enhance their forecasting processes, minimize errors, and reduce the time spent on manual analysis.
5. Inventory Management Systems
Technology also plays a crucial role in inventory management, which is closely linked to demand forecasting. Advanced inventory management systems can track stock levels, sales trends, and reorder points in real-time. These systems integrate seamlessly with demand forecasting tools to provide a holistic view of inventory needs.
By aligning inventory management with demand forecasts, manufacturers can optimize their stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and minimize the risk of stockouts. Automated inventory systems can also trigger reorders based on demand forecasts, ensuring that products are available when needed without overstocking.
6. Scenario Planning and What-If Analysis
Technology enables manufacturers to conduct scenario planning and what-if analyses, helping them prepare for various demand scenarios. By simulating different conditions, such as economic downturns, market changes, or supply chain disruptions, manufacturers can better understand how these factors may impact demand.
Scenario planning tools allow manufacturers to create multiple forecasts based on different assumptions, enabling them to develop contingency plans. This proactive approach enhances resilience and agility, ensuring that manufacturers are prepared for any demand fluctuations.
7. Cloud Computing and Scalability
Cloud computing has transformed the way manufacturers manage their data and forecasting processes. Cloud-based demand forecasting tools provide scalability, allowing manufacturers to access powerful analytics without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware or software.
These cloud solutions enable real-time collaboration, data sharing, and access to advanced analytics tools from anywhere, fostering a more agile and responsive forecasting environment. As manufacturers grow and their data needs evolve, cloud technology provides the flexibility to scale their forecasting capabilities accordingly.
Benefits of Accurate Demand Anticipation in Manufacturing
Accurate demand anticipation is a cornerstone of successful manufacturing operations. By effectively forecasting customer demand, manufacturers can align their production processes, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Here are the key benefits of accurate demand anticipation in manufacturing:
1. Enhanced Inventory Management
Accurate demand forecasts allow manufacturers to maintain optimal inventory levels. By anticipating customer needs, manufacturers can reduce excess stock and minimize the risk of stockouts.
This leads to better inventory turnover rates and lower carrying costs, as manufacturers only hold what is necessary to meet demand. Enhanced inventory management ensures that products are available when needed without tying up capital in unsold inventory.
2. Improved Production Planning
Accurate demand anticipation enables manufacturers to develop more effective production plans. With a clear understanding of future demand, manufacturers can schedule production runs, allocate resources, and streamline operations to meet customer requirements efficiently. This leads to reduced lead times, minimized downtime, and improved overall production efficiency.
3. Cost Reduction
Accurate demand forecasting helps manufacturers identify and eliminate inefficiencies in their operations. By producing the right amount of products at the right time, manufacturers can reduce waste, lower labor costs, and optimize resource utilization. Furthermore, minimizing the need for expedited shipping or last-minute production adjustments can lead to significant cost savings.
4. Increased Customer Satisfaction
Meeting customer demand consistently is crucial for maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction. Accurate demand anticipation enables manufacturers to deliver products on time, reducing backorders and delays.
This reliability builds trust with customers and enhances brand loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to return for repeat business and recommend the brand to others.
5. Agility and Responsiveness
In a rapidly changing market environment, the ability to respond quickly to fluctuations in demand is essential. Accurate demand forecasting equips manufacturers with the insights needed to adapt to market changes promptly.
Whether responding to seasonal trends, unexpected spikes in demand, or shifts in consumer preferences, manufacturers can adjust their operations to stay ahead of the competition.
6. Optimized Supply Chain Management
Effective demand anticipation improves collaboration and communication within the supply chain. Manufacturers can share accurate forecasts with suppliers and distributors, allowing them to align their production schedules and inventory levels accordingly. This synchronization leads to a more streamlined supply chain, reducing lead times and enhancing overall efficiency.
7. Better Financial Planning
Accurate demand forecasting provides manufacturers with valuable insights for financial planning. By understanding future sales trends, manufacturers can make informed decisions regarding budgeting, investment, and resource allocation. This strategic approach enables manufacturers to allocate resources more effectively, maximizing their return on investment.
8. Competitive Advantage
Manufacturers that excel in demand anticipation gain a competitive edge in the market. By accurately predicting customer needs and trends, they can introduce new products or adjust existing offerings ahead of competitors. This proactive approach allows manufacturers to capture market share and respond to opportunities more effectively.
9. Risk Mitigation
Accurate demand forecasting helps manufacturers identify potential risks associated with demand fluctuations. By understanding the factors that influence customer behavior, manufacturers can develop contingency plans to mitigate risks related to supply chain disruptions, changing market conditions, or unexpected demand shifts.
10. Sustainable Practices
Accurate demand anticipation contributes to more sustainable manufacturing practices. By minimizing waste and optimizing resource use, manufacturers can reduce their environmental impact.
Furthermore, understanding demand patterns enables manufacturers to implement sustainable sourcing and production practices that align with customer expectations for environmentally friendly products.
How Deskera Manufacturing ERP Can Help You Anticipate Customer Demand in Manufacturing
In the dynamic world of manufacturing, anticipating customer demand is crucial for optimizing operations and maintaining competitive advantage. Deskera's manufacturing ERP software offers a range of features designed to enhance demand forecasting and improve overall efficiency.
Here’s how Deskera manufacturing ERP can assist manufacturers in anticipating customer demand:
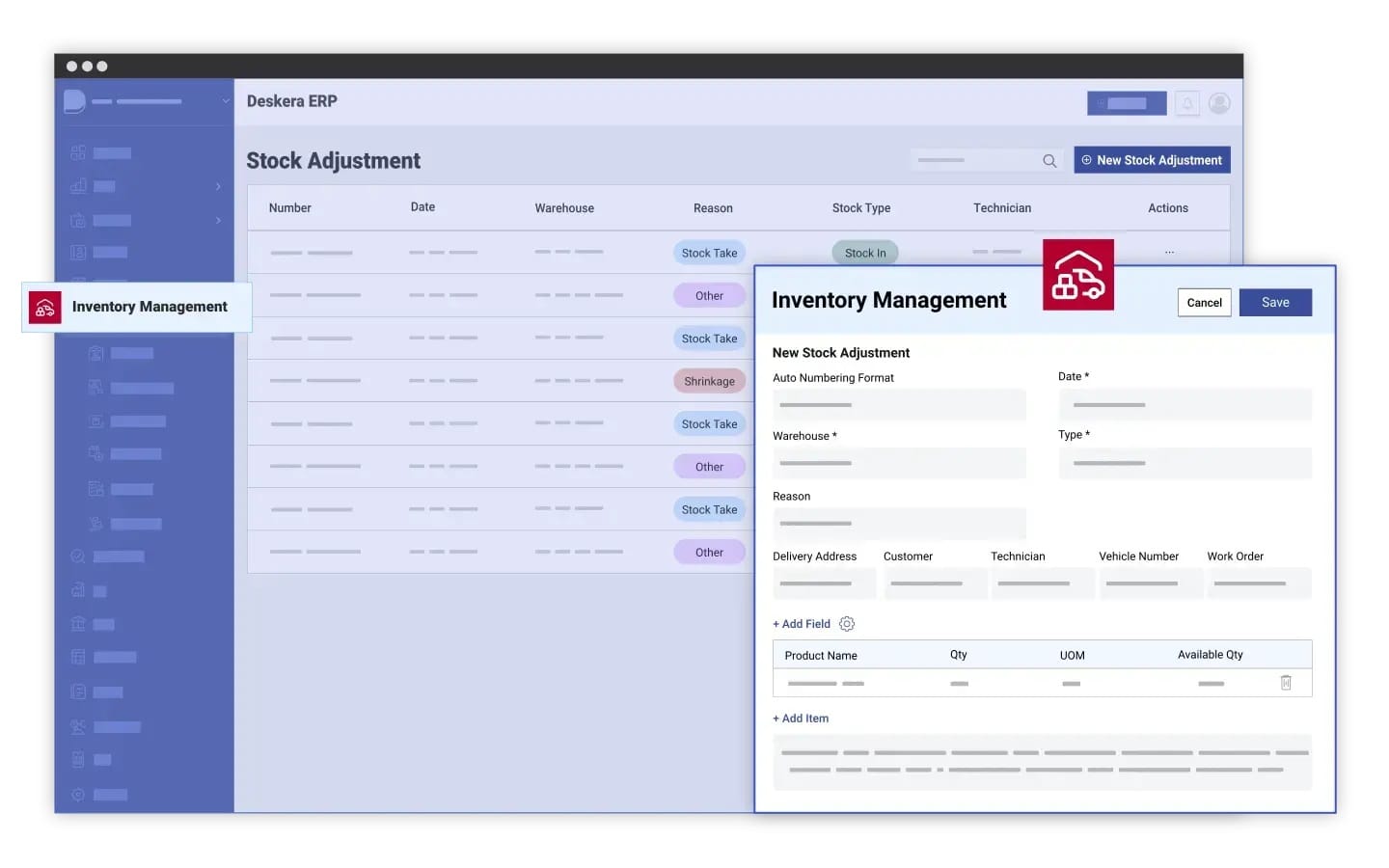
1. Integrated Data Analysis
Deskera MRP integrates data from various sources, including sales history, inventory levels, and market trends. This centralized data access allows manufacturers to analyze historical performance and identify patterns that inform future demand. By utilizing advanced analytics tools, manufacturers can make informed predictions based on comprehensive data insights, helping them anticipate customer needs more accurately.
2. Real-Time Inventory Tracking
With Deskera MRP, manufacturers benefit from real-time inventory tracking, which provides up-to-date information on stock levels and product availability. This feature allows manufacturers to adjust their forecasts based on current inventory data, reducing the risk of stockouts or overproduction. Real-time insights enable quick decision-making, ensuring that production aligns with customer demand.
3. Forecasting Tools
Deskera MRP offers built-in forecasting tools that leverage historical data and market trends to generate accurate demand forecasts. These tools can analyze seasonal trends, historical sales data, and other influencing factors to project future demand more reliably. By utilizing sophisticated forecasting algorithms, manufacturers can better prepare for fluctuations in demand, ensuring they meet customer expectations effectively.
4. Collaboration Features
Deskera MRP promotes collaboration across various departments, including sales, production, and supply chain management. By facilitating communication and information sharing, the platform ensures that all stakeholders are aligned with demand forecasts. This collaborative approach enhances overall operational efficiency, as everyone involved in the manufacturing process can respond to changes in customer demand promptly.
5. Scenario Planning
Deskera MRP supports scenario planning, enabling manufacturers to create different demand forecasts based on various market conditions. By simulating different scenarios, manufacturers can assess the potential impact of changes in customer preferences, economic factors, or industry trends on demand. This capability allows businesses to prepare for uncertainty and make strategic decisions that align with anticipated customer needs.
6. Supplier and Distributor Collaboration
Deskera MRP enhances collaboration with suppliers and distributors by providing accurate demand forecasts that inform their production and inventory management strategies. By sharing insights and forecasts with partners, manufacturers can synchronize their supply chains, ensuring that raw materials and products are available when needed. This collaboration minimizes lead times and improves overall responsiveness to customer demand.
7. Mobile Accessibility
With Deskera MRP’s mobile accessibility, manufacturers can monitor and manage demand forecasts and inventory levels from anywhere. This flexibility enables decision-makers to stay informed about market trends and customer behavior in real time, allowing them to make adjustments as necessary. Mobile access enhances agility, ensuring that manufacturers can respond swiftly to changes in customer demand.
8. Comprehensive Reporting and Analytics
Deskera MRP provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities that allow manufacturers to evaluate their performance against demand forecasts. By generating detailed reports on sales trends, inventory turnover, and production efficiency, manufacturers can gain valuable insights into their operations. This data-driven approach helps identify areas for improvement and informs future demand forecasting strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding customer demand is crucial for manufacturers, as it drives production schedules, inventory management, and overall operational efficiency, ultimately impacting customer satisfaction and business profitability.
- Factors such as market trends, economic conditions, consumer preferences, and competitive landscape significantly influence customer demand; staying attuned to these drivers is essential for accurate forecasting.
- Employing various forecasting techniques, including historical analysis, market research, and predictive analytics, allows manufacturers to anticipate demand accurately and align their production strategies accordingly.
- Utilizing real-time data from sales, e-commerce, and social media trends enables manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing consumer preferences, enhancing their ability to predict and meet demand.
- Actively seeking and analyzing customer feedback provides valuable insights into preferences and expectations, allowing manufacturers to adjust their offerings and better anticipate future demand.
- Fostering collaboration with suppliers and distributors ensures a synchronized supply chain, enabling manufacturers to respond effectively to shifts in customer demand and maintain product availability.
- Implementing effective demand planning and Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) processes allows manufacturers to align supply with anticipated demand, optimizing resource allocation and production efficiency.
- Manufacturers face various challenges in demand anticipation, including market volatility, data inaccuracies, and shifting consumer preferences; addressing these challenges requires robust forecasting strategies and agile processes.
- Leveraging advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and MRP systems significantly enhances demand forecasting accuracy, providing manufacturers with the tools needed to stay ahead of market changes.
- Accurately anticipating customer demand leads to improved inventory management, reduced costs, increased customer satisfaction, and a stronger competitive advantage, ultimately driving long-term business success.
- In a competitive manufacturing landscape, accurately anticipating customer demand is essential for operational success. Deskera MRP offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance demand forecasting, streamline inventory management, and promote collaboration across the supply chain. By leveraging Deskera MRP’s capabilities, manufacturers can improve their ability to anticipate customer needs, optimize production processes, and ultimately drive business growth.
Related Articles