How can businesses accurately predict the future to stay ahead in a competitive market? The answer lies in demand forecasting—a crucial process that enables companies to anticipate customer needs, optimize inventory, and make informed decisions.
Whether you're managing a small business or a large enterprise, understanding and implementing effective demand forecasting can be the key to maintaining efficiency, reducing costs, and maximizing profits.
Demand forecasting isn't just about numbers; it's about gaining insights into market trends and customer behavior. By leveraging advanced tools and methodologies, businesses can forecast demand with greater precision, leading to more strategic planning and better resource allocation.
One such powerful tool for demand forecasting is Deskera MRP. Deskera’s MRP software offers robust demand forecasting capabilities, seamlessly integrating with other business functions like inventory management, production planning, and procurement.
With features such as AI-driven analytics and real-time data processing, Deskera MRP helps businesses make accurate predictions, streamline operations, and drive growth.
In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of demand forecasting, from its foundational concepts to the advanced techniques and tools that can transform your business.
What is Demand Forecasting?
Demand forecasting is the process of predicting future customer demand for a product or service over a specific period. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors, businesses can estimate the quantity of goods or services that customers will likely purchase in the future.
This prediction is essential for various business operations, including inventory management, production planning, and financial budgeting. Accurate demand forecasting helps companies optimize their resources, reduce excess inventory, prevent stockouts, and better align their supply with customer demand, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and profitability.
Demand Planning vs. Forecasting
Demand Forecasting Methods
Here’s a detailed overview of demand forecasting methods:
1. Qualitative Methods
Market Research
- Description: Involves collecting data directly from potential customers through surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
- Best Used For: New products, markets with limited historical data, or when entering new geographic regions.
- Advantages: Provides insights based on consumer preferences and market conditions. Useful when historical data is sparse or unreliable.
Expert Opinion (Delphi Method)
- Description: A panel of experts is consulted to provide estimates and opinions on future demand. The Delphi method involves multiple rounds of questioning, with feedback provided to the experts after each round.
- Best Used For: Situations where expertise and qualitative insights are critical, and when data is limited or uncertain.
- Advantages: Leverages collective expertise and can be adjusted based on expert feedback.
Sales Force Estimates
- Description: Sales teams provide their estimates of future demand based on their interaction with customers and market knowledge.
- Best Used For: Forecasting demand for specific products or regions where sales teams have direct insight.
- Advantages: Utilizes frontline knowledge and experience of sales personnel.
2. Quantitative Methods
Time Series Analysis
- Description: Uses historical data to identify patterns or trends over time. Common techniques include moving averages and exponential smoothing.
- Best Used For: Products with consistent and stable demand patterns. Suitable for short to medium-term forecasting.
- Advantages: Provides a data-driven approach to forecast future demand based on historical trends.
Causal Models
- Description: Establishes relationships between demand and influencing factors such as economic indicators, price changes, or marketing activities. Regression analysis is commonly used.
- Best Used For: When demand is influenced by external variables that can be measured and analyzed.
- Advantages: Can account for the impact of external factors on demand, providing a more nuanced forecast.
Moving Averages
- Description: Calculates the average demand over a specific number of past periods to smooth out fluctuations and highlight trends.
- Best Used For: Products with stable demand but subject to short-term variability.
- Advantages: Simple and easy to implement, helps in identifying trends by smoothing out short-term fluctuations.
Exponential Smoothing
- Description: Assigns exponentially decreasing weights to older observations, giving more emphasis to recent data. Variants include Simple Exponential Smoothing, Holt’s Linear Trend Model, and Holt-Winters Seasonal Model.
- Best Used For: Time series data where recent observations are more indicative of future demand.
- Advantages: More responsive to recent changes in demand patterns compared to moving averages.
3. Advanced Methods
Machine Learning and AI-Based Forecasting
- Description: Utilizes advanced algorithms and models to predict demand based on large datasets and complex patterns. Techniques include neural networks, decision trees, and ensemble methods.
- Best Used For: Complex demand patterns and large volumes of data. Suitable for industries with high variability and multiple influencing factors.
- Advantages: Can handle vast amounts of data and identify complex patterns, leading to more accurate forecasts.
Simulation Models
- Description: Uses simulation techniques to model different scenarios and their impact on demand. Monte Carlo simulations are a common example.
- Best Used For: When there is significant uncertainty and variability in demand drivers.
- Advantages: Allows businesses to explore various scenarios and understand the impact of different factors on demand.
4. Hybrid Methods
Combination Forecasting
- Description: Integrates multiple forecasting methods to improve accuracy. For example, combining quantitative methods with expert judgment.
- Best Used For: When a single method is insufficient to capture all aspects of demand variability.
- Advantages: Leverages the strengths of different methods to produce a more robust forecast.
Each forecasting method has its strengths and is suited to different types of data and business contexts. The choice of method depends on factors such as data availability, the complexity of demand patterns, and the specific needs of the business.
Key Factors Affecting Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is influenced by a variety of factors that can impact the accuracy and reliability of predictions. Understanding these factors is essential for selecting the right forecasting method and making informed business decisions.
Below are some of the critical factors that affect demand forecasting:
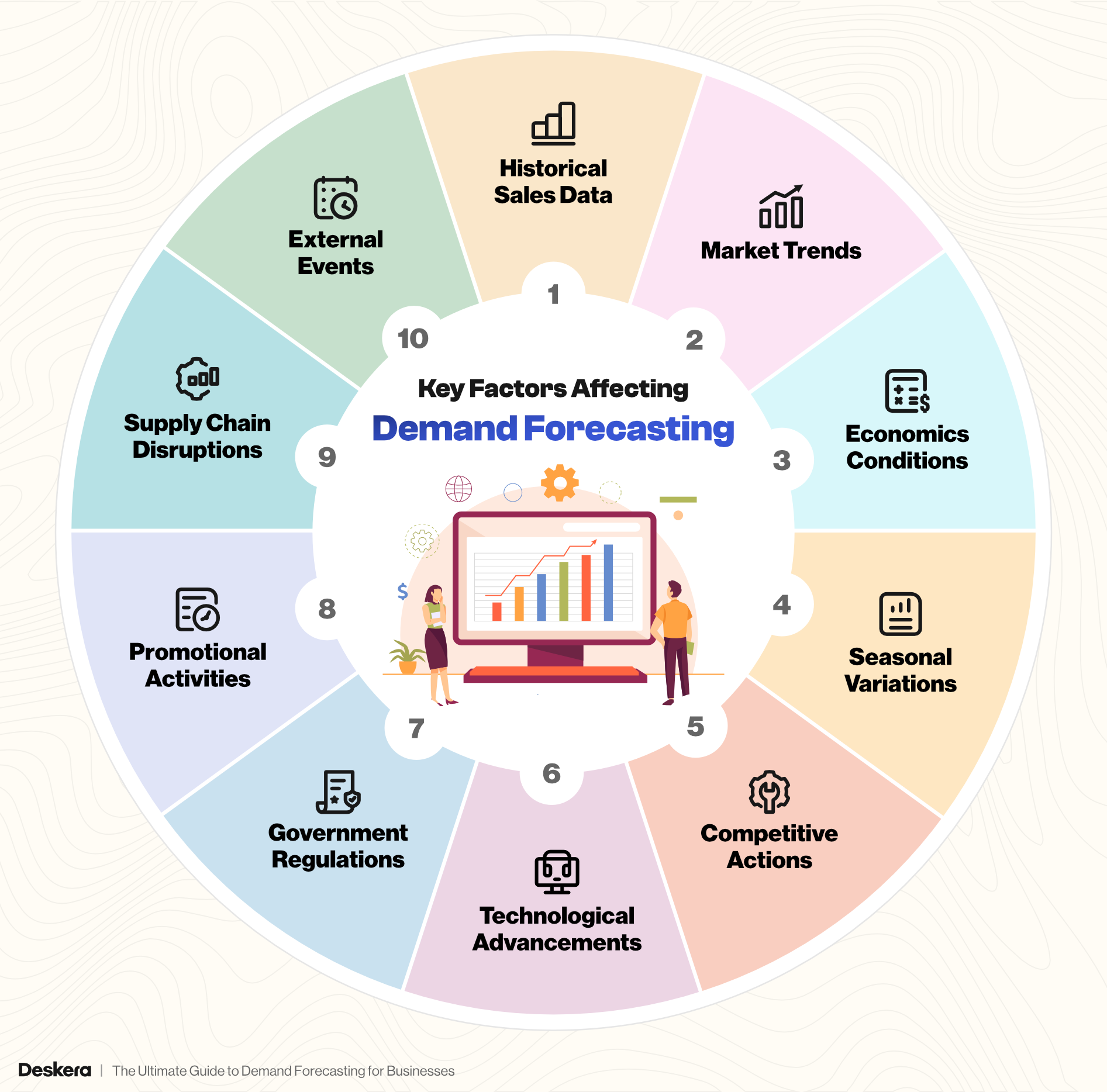
1. Historical Sales Data
- Relevance: The accuracy of demand forecasting is often dependent on the quality and quantity of historical sales data. Consistent and reliable past data allows for more accurate trend analysis and predictions.
- Challenges: Incomplete, inconsistent, or outdated data can lead to inaccurate forecasts, especially for products with irregular sales patterns.
2. Market Trends
- Relevance: Ongoing market trends, such as changes in consumer preferences, technological advancements, and competitive dynamics, can significantly influence future demand.
- Challenges: Rapid or unpredictable changes in market trends can make it difficult to rely solely on historical data, necessitating more adaptive forecasting methods.
3. Economic Conditions
- Relevance: Economic indicators such as inflation rates, interest rates, employment levels, and overall economic growth can affect consumer purchasing power and, consequently, demand.
- Challenges: Economic conditions can fluctuate due to various factors, including government policies, global events, and market disruptions, making forecasting more complex.
4. Seasonal Variations
- Relevance: Many products experience seasonal demand fluctuations based on factors such as weather, holidays, and cultural events. Accurate forecasting must account for these variations.
- Challenges: Failing to recognize and adjust for seasonal patterns can lead to overstocking or stockouts, both of which can be costly for businesses.
5. Competitive Actions
- Relevance: Actions taken by competitors, such as new product launches, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns, can influence demand for your products.
- Challenges: Competitive actions are often unpredictable and can rapidly change the demand landscape, requiring businesses to remain vigilant and adaptable.
6. Technological Advancements
- Relevance: Technology can create new demand or render existing products obsolete. For example, innovations in production processes, distribution channels, or product features can shift demand patterns.
- Challenges: Rapid technological change can outpace traditional forecasting methods, necessitating more dynamic and flexible approaches.
7. Government Regulations
- Relevance: Regulatory changes, such as new laws, tariffs, or trade agreements, can impact the cost of goods, supply chain logistics, and ultimately consumer demand.
- Challenges: Regulatory environments can be complex and subject to change, making it difficult to predict their impact on demand accurately.
8. Promotional Activities
- Relevance: Marketing and promotional campaigns, including discounts, advertising, and product launches, can temporarily boost or reduce demand.
- Challenges: The effectiveness of promotional activities can vary, and their impact on demand can be difficult to predict, especially when combined with other influencing factors.
9. Supply Chain Disruptions
- Relevance: Disruptions in the supply chain, such as delays, shortages, or changes in supplier relationships, can affect the availability of products and influence demand.
- Challenges: Unexpected supply chain disruptions can lead to sudden changes in demand, requiring businesses to adjust their forecasts quickly.
10. External Events
- Relevance: External events such as natural disasters, pandemics, political unrest, and social movements can have a significant impact on consumer behavior and demand.
- Challenges: These events are often unpredictable and can have both short-term and long-term effects on demand, making forecasting more complex.
Demand forecasting is a complex process influenced by numerous factors. To improve accuracy, businesses must consider these factors and use appropriate forecasting methods that account for their specific industry and market conditions. By doing so, companies can better anticipate demand, optimize inventory levels, and enhance overall business performance.
Importance of Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is important for every business because:
1. Improved Inventory Management
- Demand forecasting enables businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts. By accurately predicting future demand, companies can ensure they have the right amount of inventory on hand to meet customer needs without tying up excess capital in unsold goods.
2. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- When a business accurately forecasts demand, it can better meet customer expectations by ensuring products are available when needed. This leads to higher customer satisfaction, as customers are less likely to experience delays or unavailability of products.
3. Cost Savings
- By aligning production and procurement with anticipated demand, businesses can reduce waste, lower storage costs, and avoid the expenses associated with emergency orders or expedited shipping. These efficiencies translate into significant cost savings over time.
4. Optimized Resource Allocation
- Accurate demand forecasting helps businesses allocate resources—such as labor, materials, and capital—more effectively. This ensures that resources are used where they are most needed, leading to more efficient operations and improved profitability.
5. Better Financial Planning and Budgeting
- Demand forecasting provides valuable insights that inform financial planning and budgeting. With a clear understanding of future demand, businesses can make more accurate revenue projections, plan investments, and manage cash flow more effectively.
6. Enhanced Decision-Making
- Data-driven demand forecasting supports better decision-making across the organization. From production schedules to marketing strategies, businesses can make informed choices that align with market demand, leading to better overall performance.
7. Increased Agility and Responsiveness
- Businesses that effectively forecast demand are better equipped to respond quickly to market changes. Whether it's a sudden surge in demand or an unexpected downturn, having a reliable forecast allows companies to adapt their strategies and maintain a competitive edge.
Choosing the Right Demand Forecasting Method
Choosing the right demand forecasting method is crucial for businesses to accurately predict future demand and plan accordingly. The selection of a method depends on several factors, including the nature of the product, the availability of data, the time horizon, and the specific goals of the forecasting process.
Below are key considerations and steps to guide the selection of the appropriate demand forecasting method:
1. Understand the Nature of Your Product and Market
- Product Lifecycle Stage: Consider whether your product is new, mature, or declining. New products may benefit from qualitative methods like market research, while mature products might be better suited for quantitative methods like time series analysis.
- Market Dynamics: Assess the volatility and competitiveness of your market. Highly dynamic markets might require more advanced methods, such as causal models or machine learning, to account for various influencing factors.
2. Assess Data Availability and Quality
- Historical Data: Determine the availability and reliability of historical sales data. Quantitative methods like time series analysis rely heavily on robust historical data.
- External Data Sources: Consider whether you have access to external data such as economic indicators, market trends, and customer behavior, which are essential for causal models and advanced forecasting techniques.
3. Define the Forecasting Time Horizon
- Short-Term Forecasting: If you need to forecast demand for the next few weeks or months, methods like moving averages, exponential smoothing, and sales force estimates are typically appropriate.
- Long-Term Forecasting: For forecasts extending beyond a year, consider methods that account for broader trends and external factors, such as causal models or simulation models.
4. Determine the Complexity of Demand Patterns
- Stable Demand Patterns: Products with consistent and stable demand over time may be well-served by simpler methods like time series analysis or moving averages.
- Complex Demand Patterns: Products with irregular or seasonal demand might require more sophisticated approaches like exponential smoothing (with seasonal adjustment) or machine learning models.
5. Evaluate the Need for Accuracy and Detail
- High Accuracy Required: If precise forecasting is critical (e.g., for high-cost or perishable goods), advanced methods like machine learning or combination forecasting can provide more detailed and accurate predictions.
- Moderate Accuracy Sufficient: For less critical applications, simpler methods like qualitative expert opinion or moving averages might be sufficient.
6. Consider the Resources and Expertise Available
- Technical Expertise: Advanced methods such as machine learning and causal models require specialized skills and tools. Ensure your team has the necessary expertise or access to external support if choosing these methods.
- Budget and Time Constraints: Simpler methods may be more cost-effective and faster to implement, while advanced methods may require more investment in software and analysis time.
7. Match the Method to Business Objectives
- Operational Efficiency: If the goal is to optimize day-to-day operations, such as inventory management and production scheduling, time series analysis or exponential smoothing can provide the necessary precision.
- Strategic Planning: For broader, long-term planning, methods like causal models or simulation models that consider a range of influencing factors are more appropriate.
8. Consider a Hybrid Approach
- Combining Methods: In some cases, a combination of methods may yield the best results. For example, a business might use time series analysis for short-term forecasting and supplement it with expert opinions or causal models for long-term planning.
Example Scenarios
- New Product Launch: A company launching a new product may use market research and expert opinion to forecast initial demand, as historical data is unavailable.
- Seasonal Products: A retailer forecasting demand for holiday items may rely on exponential smoothing with seasonal adjustments to capture predictable fluctuations.
- Stable, Mature Products: A manufacturer of a well-established product with consistent demand might use moving averages or simple time series analysis for routine forecasting.
Choosing the right demand forecasting method requires a careful analysis of various factors, including the nature of the product, the availability of data, and the specific goals of the forecast.
By aligning the method with these factors, businesses can improve the accuracy of their forecasts and make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to better resource allocation, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
Key Challenges in Demand Forecasting and How to Overcome Them
Demand forecasting, while essential, is fraught with challenges that can significantly affect the accuracy of predictions. However, each challenge can be addressed with specific strategies and tools.
Below are the key challenges in demand forecasting, along with actionable solutions:
1. Data Quality and Availability
- Challenge: Accurate forecasting depends on high-quality data, but businesses often deal with incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent data.
- Solution:
- Implement Data Management Systems: Use advanced data management systems to centralize and clean data, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Regular Data Audits: Conduct regular audits to identify and correct data inaccuracies.
- Invest in Data Analytics Tools: Leverage data analytics tools that can process large datasets, fill gaps in data, and identify trends more effectively.
2. Rapidly Changing Market Conditions
- Challenge: Market conditions can change quickly due to economic shifts, technological advancements, or sudden changes in consumer preferences.
- Solution:
- Adopt Agile Forecasting Methods: Implement agile forecasting techniques that allow for frequent updates based on the latest market data.
- Use Scenario Planning: Develop multiple scenarios to prepare for different potential market conditions.
- Monitor Market Indicators: Regularly monitor key market indicators and adjust forecasts accordingly.
3. Unpredictable External Events
- Challenge: External events such as natural disasters, pandemics, or political instability can drastically alter demand patterns.
- Solution:
- Build Flexibility into Supply Chains: Design flexible supply chains that can quickly adapt to sudden changes in demand.
- Create Contingency Plans: Develop contingency plans for different types of external events.
- Use Real-Time Data: Incorporate real-time data and external signals into forecasting models to adjust predictions as events unfold.
4. Long Lead Times
- Challenge: Long lead times in industries like manufacturing can make demand forecasting particularly difficult.
- Solution:
- Implement Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Systems: Adopt JIT inventory practices to reduce reliance on long forecasts and allow for more responsive production.
- Use Advanced Planning Tools: Utilize advanced planning and scheduling (APS) systems to optimize production schedules based on demand forecasts.
- Collaborate with Suppliers: Foster close collaboration with suppliers to improve the accuracy of lead time estimates and align production with demand.
5. Seasonal and Cyclical Variations
- Challenge: Distinguishing between normal seasonal patterns and other demand changes can be challenging.
- Solution:
- Apply Seasonal Adjustment Techniques: Use seasonal adjustment methods, such as exponential smoothing with seasonality, to accurately forecast seasonal demand.
- Analyze Multiple Years of Data: Review several years of historical data to identify consistent seasonal patterns.
- Integrate Marketing and Sales Input: Include insights from marketing and sales teams to account for planned promotions or events that may impact demand.
6. Product Life Cycle Variability
- Challenge: Different stages of a product’s life cycle exhibit varying demand patterns, complicating the forecasting process.
- Solution:
- Use Life Cycle-Based Forecasting Models: Apply forecasting models that account for the product life cycle stage (e.g., Bass diffusion model for new products).
- Monitor Product Performance Closely: Track product performance and adjust forecasts as the product moves through its life cycle stages.
- Forecast with Flexibility: Be prepared to revise forecasts frequently, especially during the introduction and decline phases.
7. Complexity of Demand Drivers
- Challenge: Demand is influenced by multiple factors like price changes, marketing efforts, and economic conditions, making it difficult to isolate their effects.
- Solution:
- Use Causal Models: Implement causal models that account for various demand drivers, such as regression analysis to understand relationships between variables.
- Leverage Machine Learning: Utilize machine learning algorithms that can handle complex, nonlinear relationships between demand drivers.
- Segment the Market: Break down demand drivers by different market segments to better understand specific influences.
8. Technological Disruptions
- Challenge: Rapid technological advancements can disrupt existing demand patterns.
- Solution:
- Stay Informed on Technological Trends: Regularly monitor technological trends and their potential impact on demand.
- Invest in Predictive Analytics: Use predictive analytics to anticipate how new technologies might influence demand for your products.
- Diversify Product Portfolio: Diversify the product portfolio to mitigate the risk of demand disruptions caused by technological changes.
9. Inaccurate Forecasting Models
- Challenge: Choosing the wrong forecasting model or relying on outdated techniques can lead to significant inaccuracies.
- Solution:
- Regularly Review and Update Models: Periodically review and update forecasting models to ensure they remain accurate and relevant.
- Conduct Back testing: Use back testing techniques to evaluate the accuracy of forecasting models against historical data.
- Experiment with Multiple Models: Test different models and methods to determine which provides the most accurate forecasts for your business.
10. Organizational Misalignment
- Challenge: Misalignment between departments (e.g., sales, marketing, supply chain) can lead to inconsistent forecasting inputs and priorities.
- Solution:
- Foster Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Encourage collaboration and communication between all departments involved in the forecasting process.
- Implement Integrated Business Planning (IBP): Adopt IBP processes that align all functions toward common forecasting goals.
- Standardize Forecasting Procedures: Develop standardized forecasting procedures and tools across departments to ensure consistency.
Demand forecasting involves navigating numerous challenges, but each can be effectively managed with the right strategies and tools. By addressing these challenges head-on, businesses can significantly improve their forecasting accuracy, leading to better decision-making, optimized operations, and enhanced financial performance.
How to Forecast Demand: A Step-by-Step Guide
Demand forecasting is a crucial process that helps businesses predict future customer demand for products or services. Accurate demand forecasting enables better inventory management, production planning, and financial decision-making.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to forecast demand effectively:
1. Define the Objectives
- Identify the Purpose: Determine why you need to forecast demand. Common objectives include optimizing inventory levels, planning production schedules, setting sales targets, or managing cash flow.
- Set Specific Goals: Establish clear goals, such as improving forecast accuracy by a certain percentage or reducing stock outs by a specific amount.
2. Collect and Analyze Data
- Gather Historical Data: Collect data on past sales, inventory levels, and other relevant metrics. Ensure that the data is accurate, complete, and representative of your business.
- Consider External Factors: Include external data such as market trends, economic indicators, competitor actions, and seasonal variations that might influence demand.
- Segment the Data: Break down the data into relevant categories, such as product lines, geographic regions, or customer segments, to create more precise forecasts.
3. Choose a Forecasting Method
- Qualitative Methods: Use qualitative methods such as expert judgment, market research, and Delphi technique when there is limited historical data or for new products.
- Quantitative Methods: Apply quantitative methods such as time series analysis, causal models, and machine learning for data-driven forecasts. Common techniques include:
- Moving Averages: Smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends.
- Exponential Smoothing: Give more weight to recent data for more responsive forecasts.
- Regression Analysis: Identify relationships between demand and other variables, like price or marketing spend.
4. Create the Demand Forecast
- Develop Multiple Forecast Scenarios: Create different forecast scenarios (e.g., best-case, worst-case, and most likely) to account for uncertainty and variability in demand.
- Use Forecasting Software: Leverage demand forecasting software that automates the process and incorporates advanced algorithms, real-time data, and predictive analytics.
- Validate the Forecast: Cross-check the forecast with historical patterns and current market conditions to ensure it aligns with business expectations.
5. Implement and Monitor the Forecast
- Integrate with Business Processes: Ensure that the forecast is integrated into key business processes like inventory management, production planning, and financial budgeting.
- Track Forecast Accuracy: Regularly compare actual demand against the forecast to assess accuracy. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) or Mean Squared Error (MSE) to measure performance. Calculate MAD or MSE to measure performance.
- Adjust as Needed: Continuously monitor the market and other external factors, and be prepared to adjust your forecast as new information becomes available.
6. Review and Improve the Forecasting Process
- Conduct Post-Forecast Analysis: After each forecasting period, analyze what worked well and where inaccuracies occurred. Identify areas for improvement.
- Update Models and Techniques: Regularly update forecasting models and techniques to reflect changes in the market, product life cycles, and customer behavior.
- Incorporate Feedback: Gather feedback from stakeholders across the organization to refine the forecasting process and improve alignment with business goals.
Forecasting demand is a dynamic and ongoing process that requires careful planning, the right data, appropriate methods, and continuous monitoring.
By following these steps, businesses can create accurate and reliable demand forecasts that drive better decision-making, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Best Practices for Effective Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is essential for optimizing supply chain operations, managing inventory, and ensuring that your business can meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking. Implementing best practices can significantly improve the accuracy and effectiveness of your demand forecasting efforts.
Here are some key best practices:
1. Use Multiple Forecasting Methods
- Diversify Techniques: Don’t rely on a single forecasting method. Combining qualitative (expert judgment, market research) and quantitative (time series analysis, regression models) approaches can provide a more balanced and accurate forecast.
- Test and Compare Models: Regularly test different forecasting models against historical data to determine which method produces the most accurate results for your specific situation.
2. Incorporate Real-Time Data
- Leverage Real-Time Analytics: Use real-time data analytics to adjust forecasts based on the latest market conditions, sales data, and other relevant factors.
- Integrate with Sales and Marketing Data: Connect your forecasting models with real-time sales and marketing data to capture the impact of promotions, advertising campaigns, and other initiatives.
3. Segment Your Forecast
- Breakdown by Product or Region: Segment your forecast by product category, customer segment, or geographic region to increase accuracy and relevance.
- Customize Strategies: Apply different forecasting methods to different segments based on their unique demand patterns and variability.
4. Regularly Review and Adjust Forecasts
- Monitor Accuracy: Continuously monitor the accuracy of your forecasts by comparing them with actual sales and demand data. Use metrics such as Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) to evaluate performance.
- Adjust for Changes: Be agile and ready to adjust your forecasts in response to changes in the market, new product launches, or unexpected events.
5. Collaborate Across Departments
- Integrate Insights from All Stakeholders: Engage sales, marketing, finance, and operations teams in the forecasting process to gather a comprehensive view of demand drivers.
- Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between departments to ensure that the forecast aligns with overall business objectives and strategies.
6. Account for External Factors
- Include Macroeconomic Indicators: Consider the impact of economic trends, such as inflation rates, unemployment, and consumer confidence, on demand.
- Monitor Competitor Actions: Stay aware of competitor activities, such as pricing strategies, product launches, and market expansions, which can influence demand for your products.
7. Incorporate Seasonality and Cyclicality
- Adjust for Seasonal Variations: Use historical data to identify and account for seasonal demand patterns, such as holiday shopping spikes or back-to-school demand.
- Plan for Cyclical Demand: Recognize and plan for cyclical demand patterns that occur regularly, such as economic cycles or industry-specific trends.
8. Utilize Advanced Forecasting Tools
- Invest in Technology: Implement advanced forecasting software that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to analyze large datasets and predict demand with greater accuracy.
- Automation: Automate repetitive forecasting tasks to save time and reduce human error, allowing your team to focus on strategic analysis.
9. Build Flexibility into Your Supply Chain
- Maintain Buffer Stocks: Keep buffer stock levels to accommodate unexpected demand spikes or supply chain disruptions.
- Agile Supply Chain Management: Develop a flexible supply chain that can quickly respond to changes in demand, reducing lead times and increasing responsiveness.
10. Conduct Scenario Planning
- Develop Multiple Scenarios: Prepare for different demand scenarios (e.g., best-case, worst-case, and most likely) to be better equipped to handle uncertainties.
- Use Sensitivity Analysis: Perform sensitivity analysis to understand how changes in key variables (such as price or economic conditions) can impact demand.
Effective demand forecasting is a blend of art and science, requiring the right mix of data, techniques, tools, and collaboration. By adopting these best practices, businesses can improve the accuracy of their forecasts, leading to better inventory management, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Continuous improvement and adaptability are key to maintaining an effective forecasting process in a dynamic business environment.
The Future of Demand Forecasting
As businesses navigate an increasingly complex and dynamic marketplace, the future of demand forecasting is set to undergo significant transformation.
Advances in technology, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping how companies predict customer demand, enabling more accurate, agile, and proactive decision-making.
Here’s a look at the key trends and innovations that will define the future of demand forecasting:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- AI-Driven Insights: The integration of AI and machine learning into demand forecasting processes is revolutionizing how businesses interpret and act on data. These technologies can process vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns and trends that human analysts might miss.
- Predictive Accuracy: Machine learning algorithms continuously improve by learning from historical data, leading to more accurate forecasts. They can also adapt to changes in consumer behavior, market conditions, and other external factors, enhancing the reliability of predictions.
- Automation: AI-powered tools can automate the forecasting process, reducing the time and effort required to generate accurate predictions while minimizing the risk of human error.
2. Real-Time Data Integration
- Dynamic Forecasting: Future demand forecasting will increasingly rely on real-time data from various sources, including sales channels, social media, and IoT devices. This data allows companies to make instant adjustments to their forecasts based on the latest market developments.
- Enhanced Responsiveness: With real-time data integration, businesses can respond more quickly to changes in demand, such as sudden spikes or drops, ensuring that inventory levels are always aligned with current needs.
3. Advanced Analytics and Big Data
- Leveraging Big Data: The explosion of big data offers unprecedented opportunities for demand forecasting. By analyzing large datasets from multiple sources, companies can gain deeper insights into customer preferences, buying patterns, and market trends.
- Advanced Statistical Models: The future will see the adoption of more sophisticated statistical models and analytics techniques that can handle the complexity of big data, leading to more nuanced and accurate forecasts.
4. Collaborative and Integrated Forecasting
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Demand forecasting will become more collaborative, involving input from multiple departments, such as sales, marketing, finance, and supply chain. This approach ensures that forecasts reflect a comprehensive view of the business and market environment.
- Integration with ERP Systems: Forecasting will increasingly be integrated with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, allowing for seamless communication and data sharing across the organization. This integration helps ensure that all departments are aligned and working towards common goals.
5. Scenario Planning and Risk Management
- Enhanced Scenario Planning: The future of demand forecasting will involve more sophisticated scenario planning, allowing businesses to prepare for a range of potential outcomes. This approach enables companies to develop contingency plans for various market conditions, reducing risk and improving resilience.
- Risk Mitigation: By incorporating risk management into the forecasting process, companies can identify potential threats to demand, such as economic downturns or supply chain disruptions, and take proactive measures to mitigate their impact.
6. Personalized and Customer-Centric Forecasting
- Personalized Forecasts: Advances in technology will enable businesses to create more personalized demand forecasts based on individual customer data. This approach allows for more precise targeting and inventory management, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Customer-Centric Strategies: Future demand forecasting will focus more on understanding and anticipating customer needs and preferences, helping businesses tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to meet specific demand segments.
7. Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
- Sustainable Forecasting Practices: As sustainability becomes a key business priority, demand forecasting will increasingly incorporate environmental and ethical considerations. Businesses will aim to optimize supply chains and inventory levels in ways that minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints.
- Ethical AI: The future will also see a greater emphasis on the ethical use of AI and data in demand forecasting, ensuring that technologies are deployed responsibly and with respect for consumer privacy.
8. Increased Focus on Forecast Accuracy
- Continuous Improvement: Companies will invest more in improving the accuracy of their demand forecasts by adopting new technologies, refining models, and continuously monitoring performance.
- Feedback Loops: The use of feedback loops, where actual demand data is used to adjust and improve forecasting models, will become more common, leading to progressively more accurate predictions over time.
The future of demand forecasting promises to be more intelligent, responsive, and integrated than ever before. As businesses embrace new technologies and data-driven approaches, they will be better equipped to anticipate customer needs, manage resources efficiently, and navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing market.
By staying ahead of these trends, companies can turn demand forecasting into a powerful competitive advantage, driving growth and success in the years to come.
How can Deskera MRP Help You With Demand Forecasting?
Deskera MRP can significantly enhance your demand forecasting capabilities by leveraging advanced tools and features designed to improve accuracy and efficiency.
Here's how Deskera MRP can help with demand forecasting:
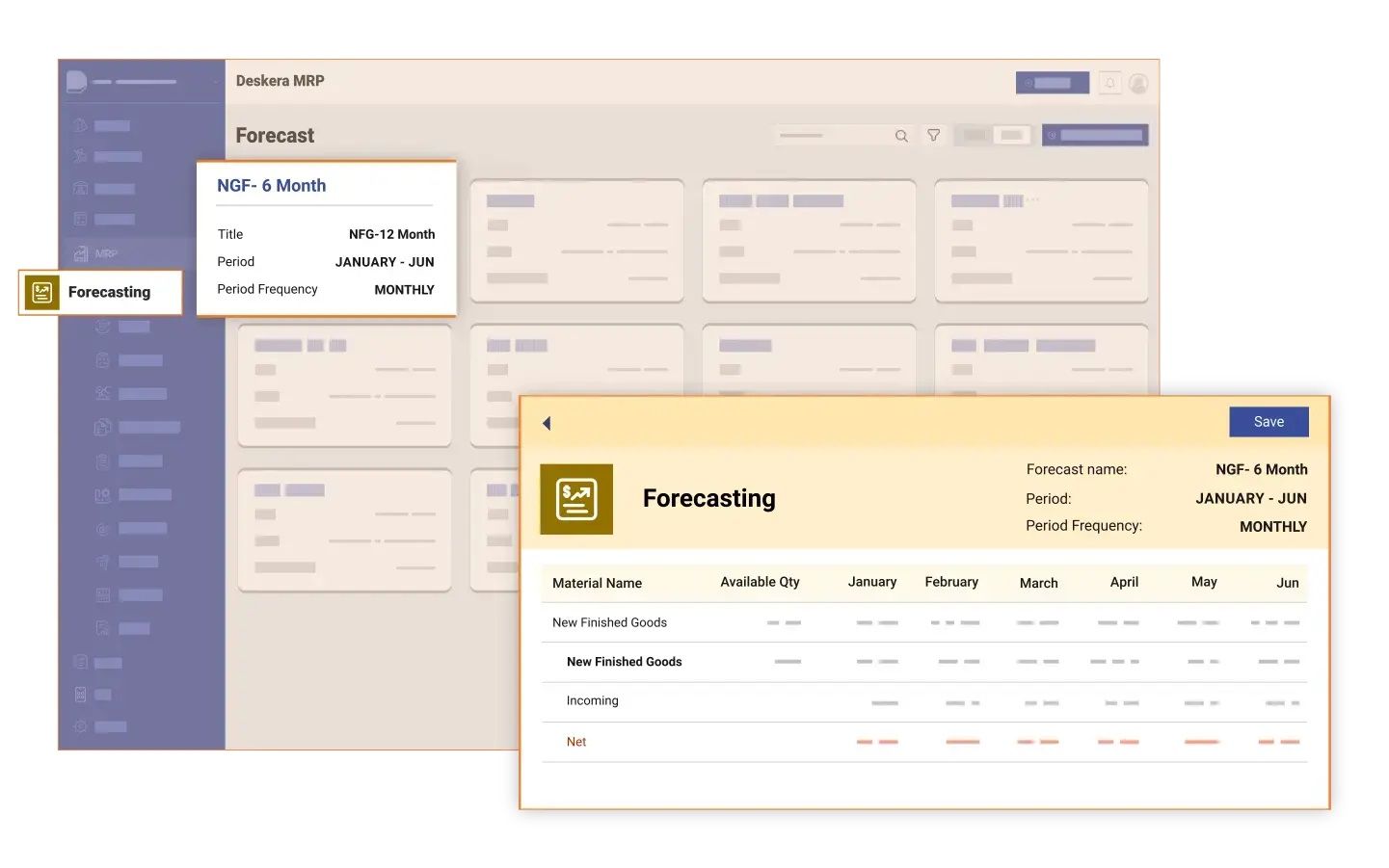
1. Automated Data Collection and Integration
Deskera MRP simplifies the process of data collection by automatically gathering data from various sources, including sales orders, inventory levels, and production schedules. This real-time data integration allows you to generate accurate demand forecasts quickly, reducing manual effort and the risk of errors.
2. Advanced Forecasting Models
The platform offers robust forecasting models that analyze historical data to predict future demand. Deskera MRP uses machine learning algorithms and statistical methods to identify trends and patterns, providing you with reliable forecasts that can adapt to changes in the market.
3. Scenario Planning and What-If Analysis
Deskera MRP enables you to create multiple forecast scenarios to plan for different market conditions. Whether you're preparing for a best-case, worst-case, or most likely scenario, the platform allows you to simulate various outcomes and adjust your strategies accordingly.
4. Integration with Supply Chain Management
By integrating demand forecasts with supply chain management, Deskera MRP helps you align production schedules, optimize inventory levels, and reduce lead times. This integration ensures that your business is always prepared to meet customer demand without overstocking or stockouts.
5. Real-Time Reporting and Dashboards
Deskera MRP provides real-time reporting and interactive dashboards, giving you instant access to key metrics and insights. These tools allow you to monitor demand forecasts, track accuracy, and make data-driven decisions that support your business goals.
6. Collaborative Planning
Deskera MRP facilitates cross-departmental collaboration by allowing teams to share data and insights within a unified platform. This collaboration ensures that sales, marketing, finance, and operations are aligned, leading to more accurate and cohesive demand forecasts.
Key Takeaways
Demand forecasting is a dynamic and critical process that plays a pivotal role in a company's success.
- Importance of Demand Forecasting: Effective demand forecasting is crucial for optimizing inventory management, production planning, and financial decision-making. Accurate forecasts help businesses meet customer demand without overstocking or understocking.
- Diverse Forecasting Methods: Utilize both qualitative and quantitative forecasting methods to achieve the best results. Techniques such as moving averages, exponential smoothing, and regression analysis can provide valuable insights depending on the nature of your data and business needs.
- Real-Time Data Integration: Incorporate real-time data and advanced analytics to enhance the accuracy of your forecasts. Leveraging technologies like AI and machine learning can significantly improve forecasting precision and adaptability.
- Collaboration and Integration: Effective forecasting requires collaboration across departments and integration with other business systems. Aligning sales, marketing, finance, and supply chain teams ensures that forecasts reflect a comprehensive view of the market and organizational goals.
- Handling Challenges: Address common challenges such as data quality, external events, and model accuracy with strategic solutions. Implementing data management systems, scenario planning, and flexible supply chains can help mitigate these issues.
- Future Trends: The future of demand forecasting will be shaped by advancements in AI, real-time analytics, and personalized forecasting. Embrace these trends to stay competitive and responsive to market changes.
By understanding and applying best practices, utilizing advanced tools, and continuously refining forecasting methods, businesses can enhance their ability to predict future demand with greater accuracy.
Implementing a robust forecasting strategy not only helps in managing inventory effectively but also enables better decision-making and improved operational efficiency. As technology evolves, staying abreast of innovations and trends in demand forecasting will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge and ensuring long-term success in an ever-changing market.
By utilizing Deskera MRP, businesses can improve their demand forecasting accuracy, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency. This comprehensive approach helps companies stay ahead of market trends and better meet customer needs.
Related Articles














