Have you ever wondered what keeps businesses running smoothly, day in and day out? The answer lies in a critical financial aspect called operating costs. These costs represent the ongoing expenses required to keep a business functional, ranging from employee salaries to utility bills and everything in between. Understanding operating costs is essential for any business aiming to maintain profitability and achieve long-term sustainability.
Operating costs are more than just numbers on a spreadsheet—they are the backbone of operational efficiency and financial health. By managing these costs effectively, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, and investments. Whether you’re a startup owner or a seasoned entrepreneur, knowing how to calculate and optimize your operating costs is key to staying competitive in today's fast-paced market.
This is where solutions like Deskera ERP can make a significant difference. Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive platform to track, analyze, and optimize your operating expenses in real time. With features like automated expense tracking, inventory management, and financial reporting, Deskera helps businesses streamline operations, reduce unnecessary costs, and focus on growth. Its intuitive interface and customizable tools ensure that managing your operating costs is not just efficient but also hassle-free.
ERP.AI enhances this process by using artificial intelligence to uncover hidden cost patterns, forecast spending trends, and automate budgeting decisions—empowering businesses to make smarter, data-driven choices for long-term profitability.
In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into the concept of operating costs, explore their components, and provide practical strategies to manage them effectively. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to control these expenses and leverage tools like Deskera ERP to drive financial success.
What Are Operating Costs?
Operating costs are the ongoing expenses required for a business to function effectively and sustain its day-to-day operations. These costs are crucial for maintaining the infrastructure, processes, and resources that enable a company to produce goods, deliver services, and generate revenue.
Operating costs typically include two main categories:
- Fixed Costs: Expenses that remain constant regardless of production levels, such as rent, insurance, and salaries for permanent staff.
- Variable Costs: Expenses that fluctuate depending on business activity, like raw materials, packaging, and shipping costs.
In addition to these, operating costs may include utilities, maintenance, office supplies, marketing, and administrative expenses. It’s important to note that operating costs do not include one-time or capital expenses, such as purchasing new equipment or long-term investments.
By keeping track of operating costs, businesses can evaluate their profitability, identify inefficiencies, and make strategic financial decisions to optimize performance. Managing these costs effectively is essential for achieving long-term success.
What Are Fixed Operating Costs?
Fixed operating costs are business expenses that remain consistent over a specific period, regardless of the company's level of production or sales activity. These costs are predictable and do not fluctuate based on business operations, making them an essential part of financial planning and budgeting.
Examples of Fixed Operating Costs
- Rent or Lease Payments: The cost of renting office space, warehouses, or production facilities.
- Salaries for Permanent Staff: Fixed wages for employees who are not paid on an hourly or commission basis.
- Insurance Premiums: Costs for policies like liability, property, or health insurance.
- Depreciation: The gradual reduction in the value of assets such as machinery or vehicles.
- Subscription Services: Fees for software, tools, or utilities with fixed monthly rates, such as cloud storage or ERP systems.
Key Characteristics
- Consistency: Fixed costs remain the same regardless of production levels or business activity.
- Long-Term Commitment: Many fixed costs, such as leases or insurance, are tied to contracts.
- Impact on Break-Even Point: These costs play a significant role in determining the level of sales needed to cover all expenses.
Importance of Managing Fixed Costs
Effectively managing fixed costs enables businesses to:
- Ensure Financial Stability: Fixed costs remain constant, so managing them well ensures the company can meet its obligations even during low-revenue periods.
- Plan Long-Term Investments: Stable fixed costs provide a predictable expense baseline, allowing businesses to allocate resources for growth initiatives strategically.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Monitoring and reducing unnecessary fixed costs helps free up funds for other critical business operations or investments.
- Lower the Break-Even Point: By minimizing fixed costs, businesses can reduce the sales volume required to cover expenses, improving profitability.
Properly managing fixed costs creates a solid foundation for financial health and operational efficiency, allowing businesses to thrive even in fluctuating market conditions.
Effectively managing fixed operating costs is vital for businesses, as these expenses continue even during periods of low sales or production. Balancing them with variable costs ensures financial stability and operational efficiency.
What Are Variable Operating Costs?
Variable operating costs are expenses that fluctuate based on a business's production levels, sales volume, or operational activity. Unlike fixed costs, these costs increase or decrease depending on how much a company produces or sells, making them directly tied to the scale of business operations.
Examples of Variable Operating Costs
- Raw Materials: Costs of components or supplies needed for manufacturing products.
- Direct Labor: Wages for employees who are paid based on hours worked or units produced.
- Shipping and Logistics: Expenses for delivering goods to customers, which vary with order volume.
- Utilities: Energy or water costs that rise with increased production.
- Sales Commissions: Payments to sales personnel based on performance or revenue generated.
Key Characteristics
- Flexibility: These costs change in proportion to business activity levels.
- Direct Impact on Profit Margins: Variable costs influence the cost of goods sold (COGS) and overall profitability.
- Scalability: They enable businesses to adjust expenses according to demand, helping manage financial risk during fluctuations in revenue.
Importance of Managing Variable Costs
Effectively controlling variable costs allows businesses to:
- Maintain competitive pricing by reducing production expenses.
- Increase profit margins by optimizing resource usage.
- Adapt quickly to changes in demand or market conditions.
By understanding and managing variable operating costs, businesses can achieve better cost efficiency and improved financial performance.
Semi-Variable Operating Costs
Semi-variable operating costs are expenses that contain both fixed and variable components. A portion of these costs remains constant regardless of business activity, while the other fluctuates with changes in production or sales. This dual nature makes semi-variable costs flexible yet partially predictable.
Examples of Semi-Variable Operating Costs
- Utility Bills: A fixed base charge plus additional costs based on usage.
- Salaries with Overtime: Fixed monthly wages with variable overtime pay based on extra hours worked.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regular servicing costs with additional expenses during periods of high usage.
- Telecommunications Costs: A fixed subscription fee with variable charges for extra usage like data or calls.
Key Characteristics
- Blend of Fixed and Variable: These costs are partially stable but fluctuate with operational activity.
- Scalable with Growth: The variable component increases as the business scales up its operations.
- Impact on Budgeting: Requires careful monitoring to account for both predictable and fluctuating expenses.
Importance of Managing Semi-Variable Costs
Effectively controlling semi-variable costs enables businesses to:
- Optimize Budgeting: Balancing the fixed and variable components ensures accurate financial planning.
- Improve Cost Efficiency: Adjusting variable portions during peak or low activity reduces unnecessary expenses.
- Support Scalability: Flexibility in semi-variable costs allows businesses to adapt to growth without overcommitting resources.
Managing semi-variable operating costs strategically provides businesses with both stability and flexibility, ensuring better financial performance and operational resilience.
10 Common Examples of Operating Costs in Running a Business
Operating costs encompass a wide range of expenses necessary to keep a business functioning. Here are 10 key examples:

- Rent or Lease Payments: Costs for office space, retail locations, or warehouses.
- Utilities: Expenses for electricity, water, internet, and other essential services.
- Employee Salaries and Wages: Payments to staff, including both fixed salaries and hourly wages.
- Raw Materials: Costs of supplies or components used in manufacturing products.
- Marketing and Advertising: Expenses for promoting the business, such as online ads, social media campaigns, and print materials.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Costs to maintain equipment, facilities, and vehicles.
- Insurance Premiums: Payments for policies like property, liability, or employee health insurance.
- Office Supplies: Everyday items such as stationery, printers, and software subscriptions.
- Shipping and Logistics: Expenses for delivering products to customers or managing inventory.
- Professional Services: Fees for external consultants, accountants, or legal advisors.
By tracking these operating costs, businesses can identify areas for optimization and ensure sustainable financial performance.
Importance of Operating Costs
Operating costs are a critical component of a business’s financial framework, impacting various aspects of operations and decision-making. Understanding and managing operating costs is vital for achieving profitability and long-term growth. Here’s why operating costs are important:
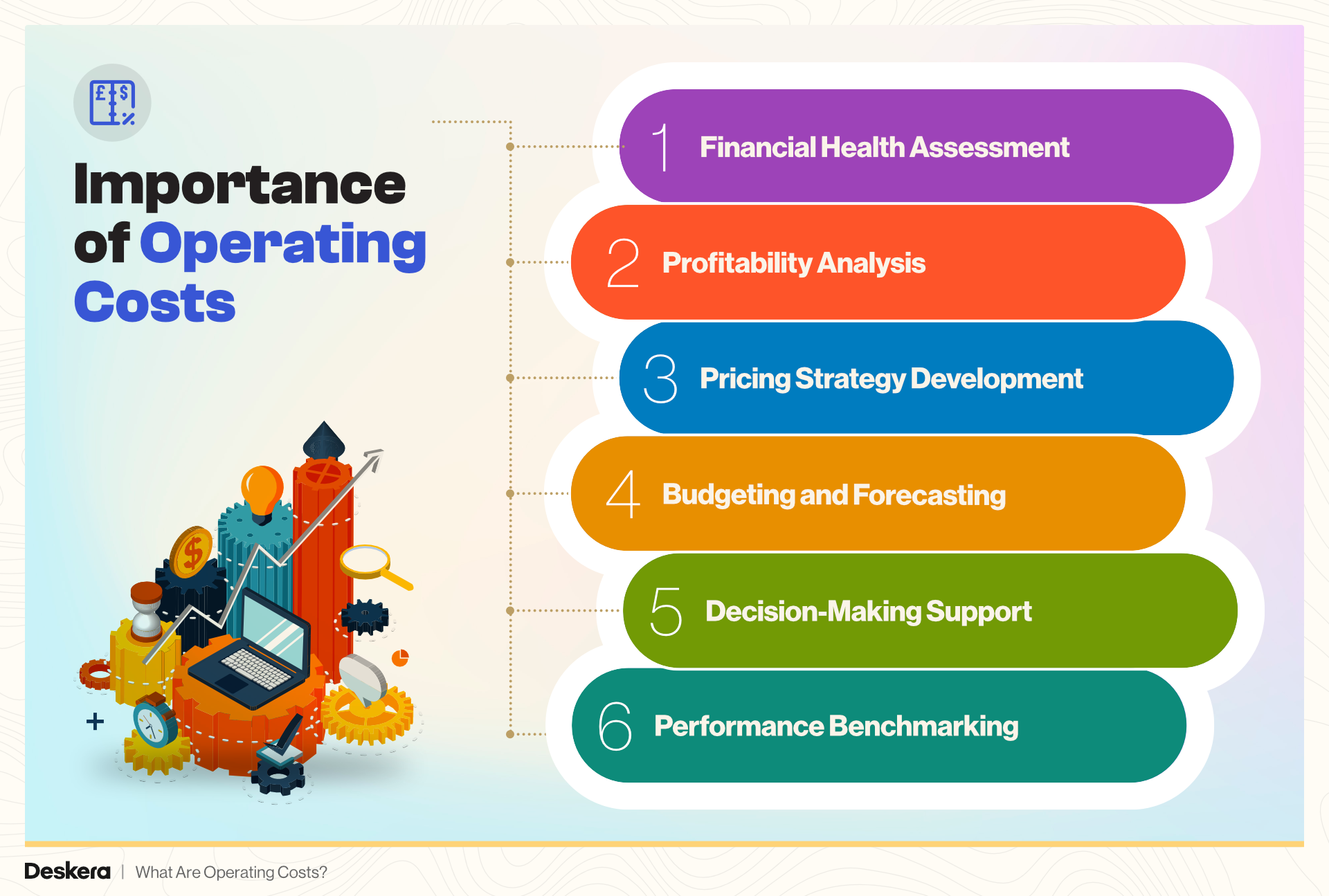
1. Financial Health Assessment
Operating costs provide a clear picture of a business's recurring expenses, helping owners evaluate financial health. By analyzing these costs, businesses can determine whether their operations are sustainable and identify opportunities to reduce unnecessary expenditures.
2. Profitability Analysis
Operating costs play a direct role in calculating a company’s profitability. Keeping these costs in check ensures that revenue generated translates into higher profit margins, which is essential for reinvestment and growth.
3. Pricing Strategy Development
Understanding operating costs is crucial for setting the right price for products or services. Businesses can ensure competitive pricing while maintaining profitability by accurately factoring in fixed and variable expenses.
4. Budgeting and Forecasting
Accurate knowledge of operating costs allows businesses to create realistic budgets and forecasts. This helps in planning for future expenses, managing cash flow, and avoiding financial surprises.
5. Decision-Making Support
By monitoring operating costs, businesses can make informed decisions about scaling operations, investing in new technologies, or launching new products. It helps determine which initiatives are financially viable.
6. Performance Benchmarking
Operating costs serve as benchmarks to measure efficiency and productivity. By comparing costs against industry standards or competitors, businesses can identify strengths and weaknesses in their operations.
Effectively managing operating costs ensures a business remains agile, competitive, and financially secure in an ever-changing marketplace.
Limitations of Operating Costs
While operating costs are essential for understanding and managing a business’s financial health, they do have certain limitations. These limitations can impact decision-making, financial analysis, and long-term planning. Here are some key challenges associated with operating costs:
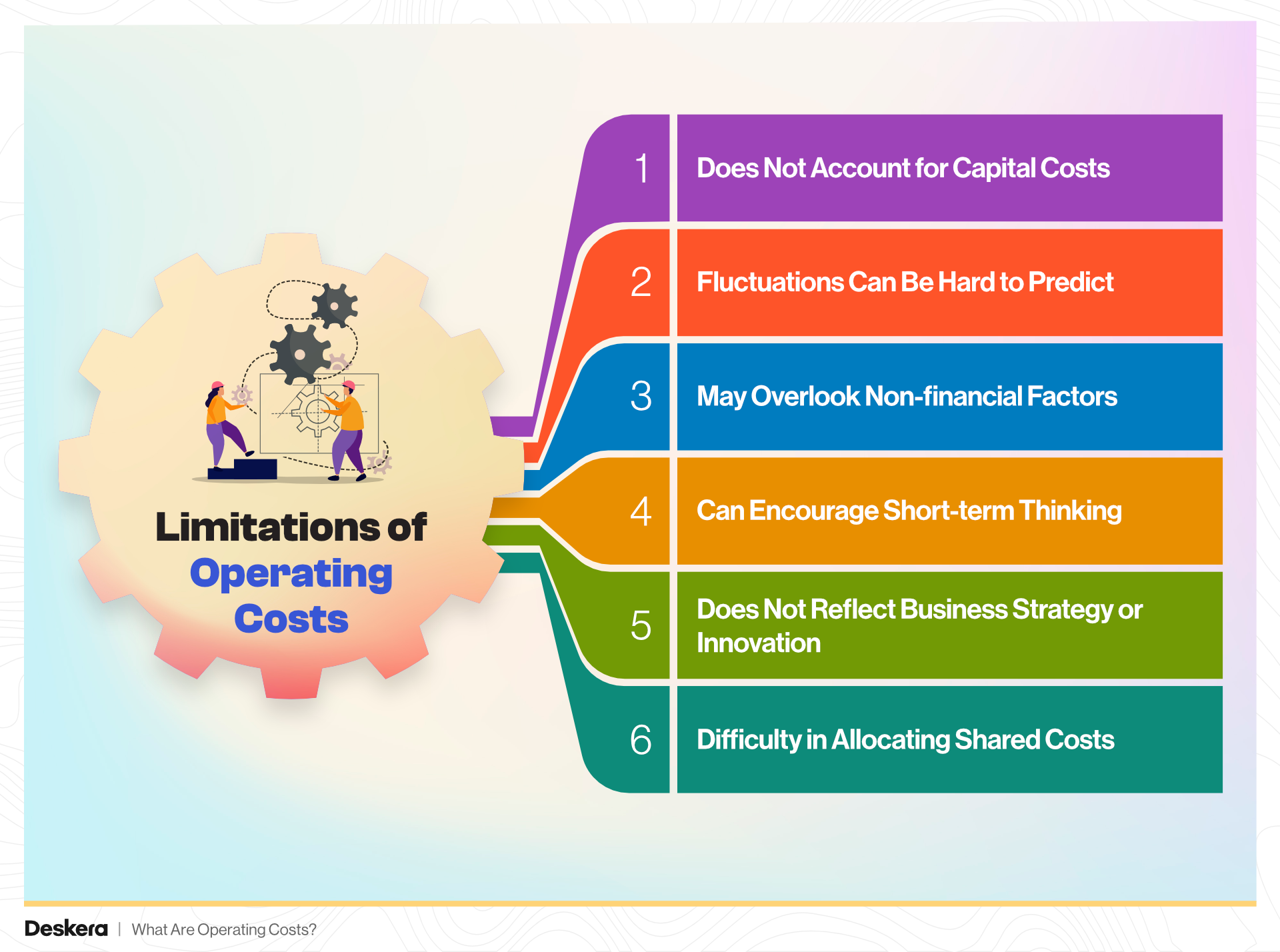
1. Does Not Account for Capital Costs
Operating costs only cover the day-to-day expenses required to run the business and exclude long-term investments like equipment purchases, property acquisitions, or capital expenditures. This means operating costs alone don’t give a complete picture of a business’s financial situation.
2. Fluctuations Can Be Hard to Predict
While fixed costs are predictable, variable costs can fluctuate significantly based on market conditions, production volumes, or consumer demand. These unpredictable changes can make it difficult to accurately forecast future costs and plan for them in the budget.
3. May Overlook Non-financial Factors
Operating costs primarily focus on monetary expenditures, but they may fail to capture non-financial factors that influence operations, such as employee morale, brand reputation, or customer satisfaction. These intangible elements can significantly impact a company’s long-term success.
4. Can Encourage Short-term Thinking
Focusing too heavily on reducing operating costs might lead to short-term thinking, where businesses make cuts that harm their long-term growth prospects. For example, reducing labor costs might negatively affect productivity or service quality, which could hurt the brand over time.
5. Does Not Reflect Business Strategy or Innovation
Operating costs do not account for investment in innovation, R&D, or strategic initiatives that could drive future growth. A business might have high operating costs due to a focus on expansion or developing new products, which may not immediately yield returns but is crucial for long-term success.
6. Difficulty in Allocating Shared Costs
Many businesses incur costs that cannot be directly attributed to a single product or department, such as shared overhead expenses like administrative support or general utilities. Allocating these costs accurately can be challenging, leading to potential miscalculations in cost analysis.
In conclusion, while operating costs are a valuable tool for understanding and controlling business expenses, they should be viewed in conjunction with other financial metrics and strategic goals to ensure a balanced and sustainable approach to managing a business.
Why is it Important to Monitor Your Operating Costs?
Monitoring operating costs is crucial for businesses of all sizes, as it directly impacts profitability, sustainability, and overall financial health. Here are some key reasons why consistently tracking and managing operating costs is important:
1. Ensures Financial Control
Regularly monitoring operating costs provides businesses with a clear understanding of their financial health. It allows you to spot any unexpected expenses, track spending patterns, and make necessary adjustments. By maintaining control over costs, businesses can prevent overspending and avoid financial strain.
- Example: A business that monitors its monthly expenses can identify unnecessary expenditures, such as excess utility usage, and take corrective action before costs spiral out of control.
2. Improves Profitability
Operating costs directly impact the bottom line. The lower the operating costs, the higher the potential profit margins. By tracking these costs, businesses can identify areas where savings can be made, optimize processes, and ultimately increase their profitability.
- Example: A company that regularly reviews its operating costs may identify opportunities to negotiate better supplier rates, reducing procurement costs and increasing profits.
3. Facilitates Budgeting and Forecasting
Effective cost monitoring enables businesses to create more accurate budgets and forecasts. By understanding past and current trends, companies can predict future expenses more accurately, which helps in setting realistic goals and ensuring that cash flow remains steady.
- Example: A retail business that tracks operating costs and sales can forecast future inventory needs, helping to avoid overstocking or stockouts and improving cash flow management.
4. Identifies Opportunities for Cost Reduction
When businesses regularly monitor their operating costs, they can spot inefficiencies, redundancies, or areas where waste is occurring. This opens up opportunities for cost-saving initiatives, such as process improvements, automation, or renegotiating supplier contracts.
- Example: By monitoring labor costs, a company might realize that certain processes can be automated, reducing the need for manual work and lowering staffing expenses.
5. Enhances Decision-Making
Having real-time insights into operating costs provides managers and executives with the data they need to make informed decisions. Whether it’s deciding on new investments, expanding product lines, or scaling operations, knowing the cost structure helps mitigate risk and optimize decision-making.
- Example: A business considering an expansion can use operating cost data to assess whether it has the financial capacity to handle additional overhead and whether the potential revenue will justify the increased expenses.
6. Promotes Business Growth and Sustainability
Consistently monitoring operating costs allows businesses to adapt and remain flexible in a competitive market. By keeping operating costs in check, businesses can reallocate resources to growth initiatives, innovate, or improve customer service, ensuring long-term sustainability.
- Example: A technology startup may monitor its operating costs closely to invest savings into research and development, helping it stay competitive and innovative in the marketplace.
7. Helps with Tax and Compliance Planning
Properly tracked operating costs are essential for accurate financial reporting, tax filings, and ensuring compliance with regulations. By maintaining detailed records of all operating expenses, businesses can avoid errors in tax reporting and take advantage of eligible deductions, ultimately reducing tax liabilities.
- Example: A business that monitors and categorizes all its operating expenses will have accurate records for tax purposes, making it easier to claim deductions for business-related costs and avoid penalties.
In conclusion, monitoring operating costs is not only vital for financial control but also for optimizing profitability, making informed decisions, and ensuring long-term success. Regular cost analysis allows businesses to remain agile, competitive, and financially sustainable in a dynamic business environment.
How Do Operating Costs Affect Profit?
Operating costs directly impact a business's profitability by influencing both revenue generation and expense management. Understanding how these costs affect profits is crucial for maintaining financial health and optimizing business operations. Here's how:
1. Impact on Profit Margins
Operating costs are subtracted from a company’s total revenue to determine its profit. The higher the operating costs, the lower the profit margins. If operating costs increase without a corresponding increase in sales or revenue, it reduces the amount of profit left after expenses.
- Example: If a company’s revenue is $100,000 and its operating costs are $70,000, the profit will be $30,000. However, if operating costs rise to $80,000, the profit decreases to $20,000.
2. Control Over Costs Leads to Higher Profit
Effectively managing and reducing operating costs can lead to improved profitability. By finding ways to streamline operations, cut unnecessary expenses, and optimize resource usage, businesses can keep costs under control, thus increasing their bottom line.
- Example: A company that invests in energy-efficient equipment to reduce utility costs can lower its overall operating expenses and keep more revenue as profit.
3. Breakeven Point
Operating costs play a key role in determining the breakeven point, which is the level of sales needed to cover all fixed and variable expenses. If operating costs are too high, the business will need to generate more revenue to break even. Reducing operating costs lowers the breakeven point and helps a company become profitable faster.
- Example: A company with lower operating costs will require fewer sales to cover its expenses, allowing it to achieve profitability with lower sales volume.
4. Impact of Rising Costs
When operating costs increase, businesses face higher financial pressures. If they cannot raise prices or increase sales proportionally, the increase in operating costs will eat into profits.
- Example: If the cost of raw materials rises unexpectedly, and a company can’t pass on the higher costs to consumers, its profit margins will shrink, reducing overall profitability.
5. Scalability of Profits
Operating costs, especially variable costs, scale with production or sales. A business that efficiently manages its variable operating costs can increase its profits as it grows. However, poorly controlled costs can lead to diminishing returns as the business expands.
- Example: A business that can negotiate bulk discounts on raw materials or streamline its production process will see increasing profits with each additional unit sold, despite higher production volumes.
In conclusion, operating costs have a significant impact on a business's profitability. Efficiently managing these costs allows a company to maintain healthy profit margins, grow sustainably, and navigate financial challenges with greater flexibility.
How to Calculate Operating Costs
Calculating operating costs involves summing up all the expenses a business incurs during its normal operations. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to calculate them:
- Identify Fixed Costs: Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production or sales volume. These typically include:
- Rent or lease payments
- Salaries for permanent employees
- Insurance premiums
- Depreciation of equipment
Formula: Fixed Costs = Rent + Salaries + Insurance + Depreciation
- Identify Variable Costs: Variable costs change based on production or sales levels. These include:
- Raw materials
- Direct labor costs (e.g., hourly wages)
- Utilities based on usage
- Shipping and delivery expenses
Formula: Variable Costs = Raw Materials + Direct Labor + Utilities + Shipping
- Add Semi-Variable Costs: Semi-variable costs have both fixed and variable components. Examples include:
- Utility bills (base fee + additional charges based on usage)
- Salaries with overtime pay
- Equipment maintenance
Formula: Semi-Variable Costs = Base Fee + Variable Portion (e.g., overtime pay or usage-based charges)
- Sum of All Operating Costs: Add together fixed, variable, and semi-variable costs to get the total operating costs.
Formula: Total Operating Costs = Fixed Costs + Variable Costs + Semi-Variable Costs
Example Calculation
- Fixed Costs: Rent = $2,000Salaries = $5,000Insurance = $500Depreciation = $300Total Fixed Costs = $2,000 + $5,000 + $500 + $300 = $7,800
- Variable Costs: Raw Materials = $1,000Direct Labor = $1,500Utilities = $200Shipping = $150Total Variable Costs = $1,000 + $1,500 + $200 + $150 = $2,850
- Semi-Variable Costs: Utility Base Fee = $100Overtime Pay = $300Total Semi-Variable Costs = $100 + $300 = $400
- Total Operating Costs = $7,800 (Fixed) + $2,850 (Variable) + $400 (Semi-Variable) = $11,050
By following this process, businesses can calculate their total operating costs and gain valuable insights into their financial performance.
Need to Monitor Operating Costs
Monitoring operating costs is essential for businesses to stay competitive, ensure profitability, and make informed decisions. Here are several reasons why consistent tracking of operating costs is crucial:
1. Prevent Financial Overspending
By keeping a close eye on operating costs, businesses can prevent excessive spending in areas that do not contribute directly to revenue generation. Tracking expenses allows for the early detection of wasteful practices, helping to avoid unnecessary costs that can erode profits.
- Example: A business may notice a rise in office supply expenses, prompting a review of purchasing practices and helping avoid further overspending.
2. Improve Profitability
Controlling operating costs is one of the most effective ways to boost profitability. If businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities while maintaining quality and service, they can maximize profit margins without increasing revenue.
- Example: By reducing energy consumption through energy-efficient practices, a company can lower utility bills, thereby increasing profit margins.
3. Optimize Resource Allocation
Monitoring operating costs enables businesses to allocate resources more effectively. When companies know where money is being spent, they can redirect funds toward high-impact activities, such as marketing, product development, or improving customer experience, which contribute more directly to growth.
- Example: A business that identifies high spending on a non-essential service may choose to reallocate that budget to a more impactful area, like investing in software that automates operations, leading to long-term savings.
4. Enhance Decision-Making
Accurate cost data provides valuable insights for decision-making. Whether you're deciding to scale operations, adjust pricing strategies, or invest in new projects, understanding operating costs ensures that business decisions are financially sound and sustainable.
- Example: A business considering a new product launch can calculate the projected operating costs to ensure that the venture is profitable before moving forward.
5. Facilitate Better Budgeting and Forecasting
Regular monitoring of operating costs allows businesses to build more accurate budgets and forecasts. It helps predict future costs, assess potential financial risks, and ensures that sufficient funds are available for essential operations.
- Example: A company that tracks its quarterly operating costs can predict future increases in raw material costs and adjust the budget accordingly, avoiding unexpected financial strain.
6. Drive Business Efficiency and Innovation
When businesses track operating costs, they are often prompted to look for ways to optimize operations. This focus on cost control leads to efficiency improvements, process innovations, and smarter ways to do business that enhance overall performance.
- Example: A company that tracks its labor costs may realize that automating routine tasks can free up employees to focus on higher-value work, increasing productivity and reducing long-term costs.
7. Ensure Financial Stability
Monitoring operating costs helps businesses maintain healthy cash flow and ensures that there is enough capital to cover day-to-day operations. By identifying and reducing unnecessary costs, businesses can remain financially stable even during lean times.
- Example: By carefully managing its operating costs, a retail business can maintain consistent profitability, even during seasonal downturns, and remain financially resilient.
8. Support Compliance and Tax Efficiency
Accurate tracking of operating costs ensures businesses comply with financial reporting standards and tax regulations. This also allows companies to claim tax deductions for legitimate business expenses, reducing tax liabilities and avoiding compliance issues.
- Example: A business that monitors operating costs will have precise records for tax reporting, helping to maximize eligible deductions and avoid costly penalties from the IRS.
In conclusion, monitoring operating costs is essential for business success. It helps prevent overspending, improves profitability, supports decision-making, and drives growth and innovation. By keeping costs in check, businesses can maintain financial health, operate more efficiently, and navigate economic challenges effectively.
10 Strategies to Reduce Operating Costs
Reducing operating costs is essential for improving profitability and maintaining long-term business sustainability. Here are several strategies that businesses can implement to effectively reduce their operating expenses:
1. Optimize Workforce Efficiency
Investing in employee training and adopting efficient workflows can help reduce labor costs without sacrificing productivity. Implementing automation tools and software can also streamline tasks and minimize the need for additional staff.
- Example: Automating data entry or customer support processes with AI tools can reduce the need for extra administrative staff.
2. Negotiate Better Supplier Contracts
Reviewing and renegotiating contracts with suppliers and service providers can result in lower raw material, shipping, or service costs. Consider bulk buying, loyalty discounts, or switching suppliers to secure better pricing.
- Example: A business may negotiate a discount with a supplier by committing to a higher volume of orders or by consolidating shipments.
3. Leverage Energy-Efficient Technology
Investing in energy-efficient equipment, lighting, and systems can significantly lower utility bills. Additionally, implementing energy-saving policies, such as turning off unused equipment or using smart thermostats, can reduce overhead costs.
- Example: Replacing old lighting systems with LED lights and investing in energy-efficient machinery can lead to substantial savings in the long run.
4. Outsource Non-Core Functions
Outsourcing tasks such as payroll processing, IT support, or marketing can reduce the costs associated with maintaining in-house departments. It can also allow businesses to focus on their core competencies.
- Example: Hiring a third-party logistics provider for shipping and warehousing can reduce overhead expenses related to inventory management and shipping infrastructure.
5. Adopt Remote Work and Flexible Hours
Allowing employees to work remotely or offering flexible work hours can reduce office space, utilities, and other associated costs. With advancements in digital communication tools, many businesses can maintain productivity with fewer physical resources.
- Example: Switching to a remote or hybrid work model can save on costs such as office rent, utilities, and commuting allowances.
6. Reduce Waste and Increase Efficiency
Streamlining processes and minimizing waste can lower operating costs. This includes managing inventory more efficiently, reducing scrap in manufacturing, and eliminating unnecessary steps in business workflows.
- Example: Implementing lean manufacturing techniques can help reduce excess inventory and waste, lowering production costs.
7. Utilize Cloud-Based Software
Switching to cloud-based software for accounting, customer management, and project collaboration can reduce the need for expensive on-premise IT infrastructure and support staff. Cloud platforms often offer scalability and flexibility at a lower cost.
- Example: Using cloud-based ERP systems like Deskera can help streamline business operations, saving on IT maintenance costs and improving efficiency.
8. Optimize Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management reduces storage costs, minimizes excess stock, and ensures that businesses only purchase what they need. This can be achieved through techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory management or using automated inventory tracking systems.
- Example: Implementing inventory management software can help track stock levels and reduce the costs associated with overstocking or stockouts.
9. Implement Preventative Maintenance
Regular maintenance and inspections of equipment can prevent costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns. Scheduling routine checks can extend the lifespan of machinery and ensure smooth operations, reducing downtime and repair costs.
- Example: Using a predictive maintenance system to monitor equipment health and prevent major breakdowns can lower repair and replacement expenses.
10. Streamline Marketing Expenses
Reviewing marketing strategies and focusing on low-cost, high-impact methods can significantly reduce marketing spend. Digital marketing, social media, and content marketing can be more cost-effective than traditional advertising methods.
- Example: Shifting from traditional print ads to targeted social media campaigns or influencer partnerships can lower marketing costs and improve ROI.
By adopting these strategies, businesses can reduce their operating costs, increase their profit margins, and improve their financial stability in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
How AI Streamlines Cost Management
By automatically analyzing financial data, AI uncovers inefficiencies, flags wasteful expenses, and suggests areas for cost optimization. AI-driven insights also help teams forecast upcoming expenses and plan budgets with greater accuracy.
Through automation, companies can minimize manual tracking, reduce human error, and allocate resources more strategically. Instead of reacting to cost overruns after they happen, AI enables proactive cost control—making it easier to maintain profitability and improve operational efficiency.
How Can Deskera ERP Help You with Operating Costs?
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive enterprise resource planning solution designed to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and reduce costs across various business functions. By integrating key business processes into a single platform, Deskera helps businesses manage and optimize their operating costs more effectively.
Here's how Deskera ERP can assist in controlling and reducing operating costs:
1. Streamlined Financial Management
Deskera ERP provides businesses with a centralized financial management system that simplifies accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. By automating financial processes, businesses can gain real-time insights into their operating costs, track expenses more accurately, and make data-driven decisions to minimize unnecessary spending.
- Example: Deskera’s automated invoicing and expense tracking features allow businesses to easily monitor operational expenses, identify discrepancies, and eliminate redundant costs, leading to greater financial control.
2. Improved Inventory Management
With Deskera ERP's advanced inventory management features, businesses can optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and improve the efficiency of procurement processes. By minimizing excess inventory and ensuring that products are available when needed, Deskera helps businesses avoid unnecessary storage costs and stockouts.
- Example: Deskera's real-time inventory tracking enables businesses to maintain optimal stock levels, reducing overstocking and the associated holding costs, as well as preventing stockouts that could lead to lost sales.
3. Enhanced Resource Allocation
Deskera ERP's resource planning capabilities allow businesses to allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that labor, materials, and time are used effectively across various departments. By monitoring resource usage and identifying inefficiencies, Deskera helps businesses make more informed decisions about resource allocation, which can lead to reduced operating costs.
- Example: Deskera’s resource scheduling tools can help companies optimize employee shifts and machine usage, avoiding idle time and maximizing productivity.
4. Automation of Routine Tasks
Deskera ERP automates routine tasks such as order processing, payroll, and customer invoicing, reducing the need for manual intervention and cutting labor costs. This automation not only saves time but also ensures that tasks are completed accurately and on time, reducing operational errors that can result in additional expenses.
- Example: By automating payroll and invoicing, Deskera reduces the need for administrative staff, cutting labor costs and improving operational efficiency.
5. Real-Time Data and Analytics
Deskera ERP provides businesses with real-time data and detailed analytics on various aspects of their operations, from sales to production. This data-driven approach allows businesses to monitor their operating costs closely and make informed decisions to optimize expenses. Additionally, the system can highlight areas where cost-cutting measures can be implemented.
- Example: Deskera’s dashboards provide a clear view of cost trends, allowing businesses to pinpoint areas where cost reduction initiatives can be applied, such as in marketing spend or production processes.
6. Supplier and Vendor Management
With Deskera ERP, businesses can streamline their procurement and supplier management processes. The software helps businesses track supplier performance, negotiate better contracts, and ensure that they are paying competitive prices for goods and services. By improving vendor relationships and managing procurement more efficiently, Deskera reduces procurement-related operating costs.
- Example: Deskera’s vendor management tools allow businesses to review supplier terms and prices regularly, ensuring they are getting the best deals and avoiding unnecessary overpayments.
7. Cost-Effective Project Management
Deskera’s project management tools allow businesses to track project costs in real-time, ensuring that projects are completed within budget and on schedule. By monitoring labor costs, material usage, and other project expenses, businesses can avoid cost overruns and improve overall project efficiency.
- Example: Deskera can track labor and material costs for each project, ensuring that expenses stay within budget and identifying opportunities to reduce costs in future projects.
8. Cloud-Based Accessibility
Deskera ERP’s cloud-based platform offers accessibility from anywhere, reducing the need for expensive on-site IT infrastructure and maintenance costs. The software’s scalability means businesses only pay for the features and resources they need, helping them control software-related expenses while benefiting from the latest technology.
- Example: A growing business can scale its Deskera ERP solution as needed without incurring the high costs of additional servers or IT staff, making it a cost-effective solution for companies of all sizes.
9. Real-Time Collaboration
Deskera ERP facilitates real-time communication and collaboration across departments. This reduces operational bottlenecks, speeds up decision-making, and improves overall efficiency. By enhancing collaboration, Deskera helps businesses minimize delays and inefficiencies that can lead to increased costs.
- Example: Deskera’s real-time collaboration tools allow teams to work together more efficiently, eliminating delays in decision-making and reducing the time spent on administrative tasks, ultimately lowering operating costs.
10. Enhanced Compliance and Reporting
Deskera ERP helps businesses stay compliant with financial and regulatory standards by offering built-in compliance tools and customizable reporting. This reduces the risk of penalties and fines, ensuring that businesses avoid the costs associated with non-compliance.
- Example: Deskera’s automated tax calculations and compliance features ensure that businesses meet regulatory requirements without incurring extra costs from manual compliance checks or penalties.
Key Takeaways
- Operating costs are the expenses a business incurs as part of its regular operations, including costs for production, maintenance, and day-to-day functioning. These costs are essential for running the business but need to be carefully managed to ensure profitability.
- Operating costs can be categorized into fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, while variable costs change in direct proportion to production or sales volume.
- Fixed costs are expenses that do not fluctuate with changes in business activity. These costs, such as rent and insurance, are predictable and need to be managed to maintain financial stability.
- Variable costs, such as raw materials and labor, fluctuate based on production volume or sales. Effectively managing these costs can help businesses stay agile and responsive to market changes, ultimately increasing profitability.
- Semi-variable costs have both fixed and variable components. Examples include utility bills that have a base cost with additional charges depending on usage. Managing these costs requires a strategic approach to minimize fluctuations.
- Common examples of operating costs include wages, raw materials, rent, utilities, and marketing. Understanding these costs helps businesses make more informed decisions and optimize their overall financial performance.
- Monitoring operating costs is crucial for maintaining profitability, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring efficient business operations. It helps businesses prevent overspending and improve cash flow.
- Operating costs alone do not provide a complete financial picture. They don’t account for capital expenditures, depreciation, or non-operating income, which must also be considered when evaluating a business's financial health.
- Operating costs can be calculated by adding fixed costs and variable costs together. This provides an overall picture of the costs required to maintain day-to-day operations and helps identify areas for cost-saving opportunities.
- Operating costs have a direct impact on profit margins. Reducing operating costs increases profitability, while higher operating costs can eat into profits. Balancing costs while maintaining business efficiency is key to sustained growth.
- Businesses can reduce operating costs through automation, optimizing resource allocation, renegotiating supplier contracts, and reducing waste. Cost control strategies are essential for improving profitability and competitiveness.
- Regular monitoring of operating costs ensures businesses stay within budget, avoid overspending, and adapt quickly to market fluctuations. Tracking these costs helps maintain financial stability and enables more informed decision-making.
- Deskera ERP empowers businesses to reduce operating costs through automation, improved resource management, and data-driven insights. By streamlining financial, inventory, and supplier management processes, Deskera not only helps businesses optimize their operations but also provides the tools necessary to make cost-effective decisions that lead to greater profitability.
Related Articles













