In business and accounting, net profit is a company's income minus the cost of goods sold (COGS), expenses, depreciation and amortization, interest, and taxes for an accounting period.

Calculating your companies profits shows you how much money your business brings in. You can compare profits from previous accounting periods to determine your growth. There are two types of profit that companies must deal with and calculate: gross profit and net profit.
Understand gross profit and net profit will help you to make business decisions, create accurate financial statements, and monitor your financial health.

Net profit is computed as the residual of all revenues and gains less all expenses and losses for the period. It has also been defined as the net increase in shareholders' equity that results from a company's operations. Thus, it is different from gross profit, which only deducts the cost of goods sold from revenue. For households and individuals, net profit can refer to the gross profit minus taxes and other deductions e.g. mandatory pension contributions.
What is Net Profit?
Net profit or net income is synonymous with a company's profit for the accounting period. In other words, net profit includes all of the costs and expenses that a company incurred, which are subtracted from revenue. Net profit is usually referred to as the bottom line due to its positioning at the bottom of the income statement.
Many items can be listed on a company's income statement, depending on the industry they are in, usually net profit is derived by subtracting the following expenses from revenue:
- General and administrative expense (SG&A)
- Income taxes
- Interest on debt and loans
- Operating expenses
- Overhead or selling,
- Depreciation
Additional income sources are also included in the net profit. For example, companies often invest their cash in short-term investments, which is considered a form of income. Also, proceeds from the sale of assets are considered income.

Net profit is an accounting metric and does not represent the economic profit or cash flow of a business. Since net profit includes a variety of non-cash expenses such as depreciation, amortization, stock-based compensation, etc., it is not equal to the amount of cash flow a company produced during the period.
How To Calculate Net Profit?
Net profit is the result of subtracting all expenses and costs from revenue, while also adding income from other sources. Based on the industry, a company could have multiple sources of income besides its revenue and various types of expenses. Some of those income sources or costs can be listed as separate line items on the income statement.
For example, a company with a factory would likely have the COGS listed, while a company in the service industry will not have COGS but instead, their costs can be listed under operating expenses.
The general formula for net profit could be expressed as:
- Net Profit = Total Revenue — Total Expenses
A more detailed formula could be expressed as:
- Net Profit = Gross Profit — Operating Expenses — Other Business Expenses — Taxes — Interest on Debt + Other Income
Investors look at a company's posted bottom-line or top-line growth. Top-line growth means a growth in revenue since revenue is the first or top line of the income statement. Bottom line growth refers to a growth in net profit since net income is listed on the bottom line of the income statement.

Net profit indicates a company's profit after all of its expenses has been deducted from revenues.
Net profit is an all-inclusive metric for profitability and provides insight into how well the management team runs all aspects of the business.
Net profit is often referred to as the "bottom line" due to its positioning at the bottom of the income statement.
Net Profit or Net Income, we need know Net Income, also called net earnings, is calculated as the net sales minus cost of goods sold (cogs), selling, administrative and general expenses, depreciation, operating expenses, taxes, interest, and other expenses.
It is the number used by investors to assess how much revenue exceeds the expenses of an organization. This number appears on a company's income statement and is also an indicator of a company's profitability.
Net Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold − Operating Expenses − Other Expenses − Interest − Taxes
Let us look at an example of Net Profit:
A company has $450,000 in revenue with a cost of goods sold of $40,000. That leaves them with a gross profit of $410,000. If $60,000 is allocated for salaries, $35,000 to operating expenses and $5,000 to taxes, those numbers are then subtracted from the gross profit, leaving a net income of $315,000.
$450,000 - $40,000 - $60,000 - $35,000 - $5,000 = $310,000
Let us look at another hypothetical income statement for Company X:
Income Statement for Company X, Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2021
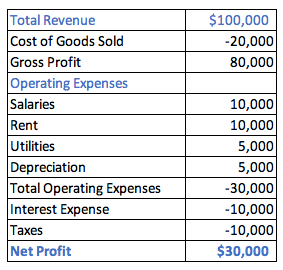
By using formulas we can see that Net Profit = 100,000 - 20,000 - 30,000 - 10,000 - 10,000 = $30,000
What Expenses Factor into Net Profit?
Net profit includes both variable and fixed expenses. Variable expenses is also known as cost of goods sold and can change based on the amount of products being made or sold and are incurred as a direct result of acquiring or creating the product. They can include:
- Packaging
- Materials
- Shipping
- Depreciation of the equipments used
- Wages for people who create the product
- Machinery to create a product
- Utilities for space where the product is created
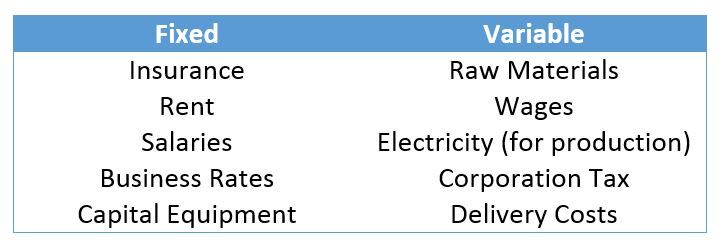
For an e-commerce business owners who don't manufacture their products, it is much simpler. The variable expenses are just how much you pay to purchase the product you are selling. Fixed costs are, just how they sound, more stable and are not likely to change significantly over time. They can include:
- Wages for employees not involved in creating the product
- Office expenses
- Marketing expenses
- Taxes
- Rent
- Employee benefit costs
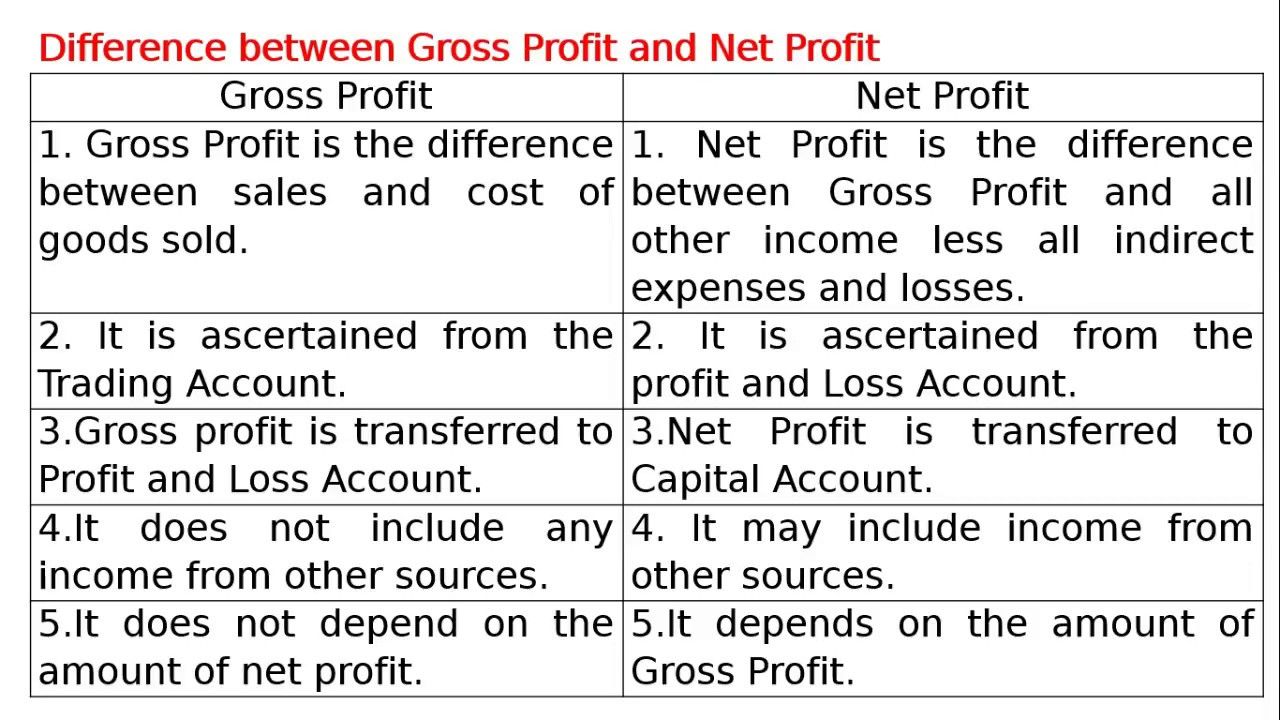
What is the Difference Between Gross Profit and Net Profit?
Gross profit is the profit a company makes after substracting the costs that are associated with selling and making its products, or the costs associated with providing the services.
Gross profit appears on a company's income statement and can be calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue or sales. Gross profit can be found on a business's income statement. Gross profit may also be referred to as sales profit or gross income.
Gross Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold
Net Profit or Net Income, we need know Net Income, also called net earnings, is calculated as the sales minus cost of goods sold (cogs), selling, administrative and general expenses, depreciation, operating expenses, taxes, interest, and other expenses.
It is the number used by investors to assess how much revenue exceeds the expenses of an organization. This number appears on a company's income statement and is also an indicator of a company's profitability.
Net Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold − Operating Expenses − Other Expenses − Interest − Taxes
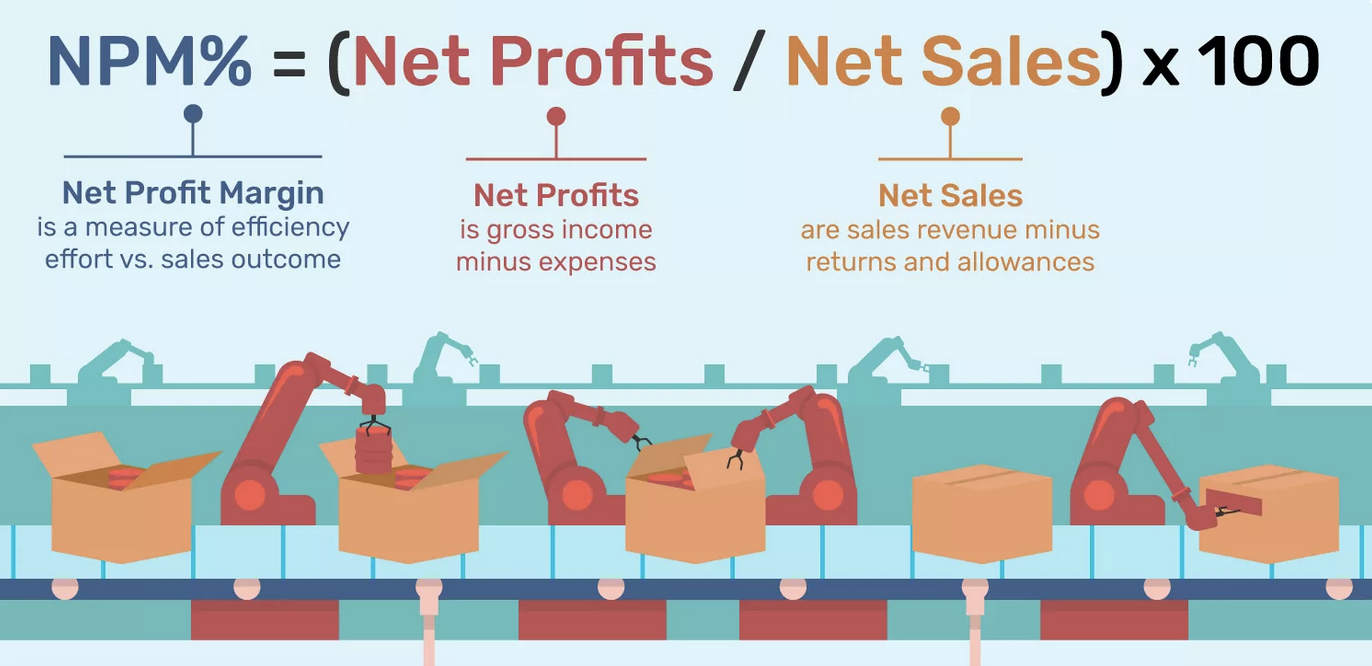
What is Net Profit Margin?
Net profit is the income left over after all expenses, including taxes and interest have been paid. There are many kind of profit margins. The net profit margin, or simply the net margin, measures how much net profit or income is generated as a percentage of revenue. It is the financial ratio of net profits to revenues for a company or business segment.
Net Profit or Net Income = Operating Profit − Taxes & Interest
Net Income or Net Profit = Revenue − Cost of Goods Sold − Operating Expenses − Other Expenses − Interest − Taxes
Net Profit Margin = Net Profit/ Revenue
Net profit is calculated by deducting both taxes and interest, of these from operating income or operating profit. In the example of Company X, the answer is $20,000 minus $10,000, which equals $10,000. Divide the net profit by sales for the net profit margin, which is 10%.
How to Improve Net Profit?
If you are hoping to improve your company's net profit, here are some tips to consider:
- Get rid of products or services that are not making a profit
- Review the pricing of your company's products or services
- Reduce your company's ongoing expenses
- Reduce costs

Which Financial Report Shows the Net Profit?
Net profit will appear on a business's income statement and can be calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the revenue (sales). Calculating the net margin of a business is a routine part of financial analysis. It is part of a type of analysis known as the vertical analysis. This takes every line item on the income statement and divides it into revenue.
These figures can be found on a company's income statement. Net profit may also be referred to as net income.
Calculating your net profit could mean switching between analytics platforms, advertising platforms, your e-commerce platform and more. With Deskera Book's accounting software for invoicing, bookkeeping and sales management, discovering the net profit is easy, since all your data is pulled into one central location and platform.
Key Takeaways
- Net profit indicates a company's profit after all of its expenses have been deducted from revenues
- Net profit is the income left over after all expenses, including taxes and interest, have been paid
- Net profit is an all-inclusive metric for profitability and provides insight into how well the management team runs all aspects of the business
- The net profit margin, or simply net margin, measures how much net profit or income is generated as a percentage of revenue
- Net profit is often referred to as the bottom line due to it's positioning at the bottom of the income statement
- Net profit includes both variable and fixed expenses