Embarking on the journey of understanding ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) accounting software is akin to unlocking the door to a realm of unparalleled efficiency and strategic advantage for businesses.
In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, the role of ERP accounting software has become increasingly indispensable. This sophisticated technology not only streamlines financial operations but also serves as a catalyst for business growth and success.
Deskera ERP accounting, for instance, offers comprehensive financial management features, an intuitive interface, and powerful automation tools, making it a standout solution for modern businesses.
According to a survey of companies poised to invest in ERP software, a staggering 89% identified accounting as the most critical ERP function. This statistic underscores the paramount importance of ERP accounting software in driving organizational performance and unlocking new opportunities for businesses across industries.
Join us as we delve into the intricacies of ERP accounting software and discover how it can propel your business to new heights with ease and precision.
What is Accounting Software?
Accounting software is a specialized type of application software designed to help businesses, organizations, and individuals manage and automate their financial transactions and accounting processes.
It provides a comprehensive platform to record, store, analyze, and report financial data, facilitating efficient and accurate financial management.
Key Functions of Accounting Software
- Transaction Recording: Automates the recording of financial transactions, including sales, purchases, receipts, and payments. This ensures accurate and timely entry of financial data.
- Ledger Management: Maintains detailed records of accounts in the general ledger. It tracks debits and credits across all accounts, providing a clear financial picture.
- Accounts Payable and Receivable: Manages the company's payables and receivables, tracking outstanding invoices and bills. This helps in efficient cash flow management and ensures timely payments and collections.
- Payroll Processing: Automates payroll calculations, tax deductions, and salary disbursements. It also handles employee benefits, bonuses, and other compensation-related tasks.
- Financial Reporting: Generates a variety of financial reports such as income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and other customized reports. These reports are crucial for internal decision-making and external financial reporting.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Assists in creating budgets and forecasts, allowing businesses to plan their finances effectively. This feature helps in setting financial goals and monitoring performance against those goals.
- Tax Compliance: Ensures compliance with tax regulations by calculating taxes, preparing tax returns, and maintaining records for audits. It helps businesses stay up-to-date with changing tax laws.
- Inventory Management: Tracks inventory levels, costs, and sales. This is particularly useful for businesses that need to manage stock and understand inventory-related expenses.
What is an ERP System in Accounting?
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system in accounting is a comprehensive software platform used to manage and integrate the core business processes of an organization.
It streamlines operations across various departments such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, services, procurement, and others.
Thus, ERP systems in accounting offer a unified platform for recording, processing, and reporting financial transactions and data. This encompasses the management of accounts payable and receivable, general ledger entries, cash flow, budgeting, forecasting, and more.
ERP software serves as a digital hub, aggregating all financial data, processing it, and making it accessible to authorized users in real-time.
ERP vs. Accounting Software: Major Differences
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems and accounting software serve distinct purposes within an organization, although there is some overlap in functionality. Here are the major differences between ERP and accounting software:
Scope and Functionality
- ERP: ERP systems are comprehensive business management platforms that integrate various functions and departments within an organization. They typically include modules for accounting, finance, human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and more.
- Accounting Software: Accounting software, on the other hand, is focused primarily on financial management tasks such as bookkeeping, invoicing, accounts payable and receivable, financial reporting, and tax preparation.
Integration
- ERP: ERP systems are designed to integrate multiple aspects of business operations into a single platform. This integration allows for seamless data flow between different departments and functions, enabling better coordination and decision-making.
- Accounting Software: Accounting software may offer some integration capabilities, but they are usually more limited compared to ERP systems. They may integrate with other financial tools or business applications, but they typically don't provide the same level of integration across all aspects of business operations.
Scalability
- ERP: ERP systems are highly scalable and can accommodate the needs of organizations of various sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises. They are designed to support growth and expansion by allowing users to add modules and functionality as needed.
- Accounting Software: Accounting software solutions vary in scalability, but they are generally more suitable for small to medium-sized businesses. While they may offer some scalability options, they may not be as flexible or customizable as ERP systems.
Customization
- ERP: ERP systems are often highly customizable to meet the specific needs and workflows of an organization. They can be tailored to accommodate industry-specific requirements and unique business processes.
- Accounting Software: Accounting software solutions may offer some degree of customization, but they are usually more standardized compared to ERP systems. They may not provide as much flexibility to adapt to specific business needs.
Cost
- ERP: ERP systems tend to be more expensive than accounting software due to their comprehensive functionality and integration capabilities. Implementation costs can be significant, and ongoing maintenance and support may also be required.
- Accounting Software: Accounting software solutions are generally more affordable, especially for small businesses with limited budgets. They may offer subscription-based pricing models or one-time licensing fees, depending on the provider and features included.
Importance of ERP in Financial Operations
The significance of ERP in financial operations cannot be overstated. ERP accounting software serves as a pivotal tool in managing and integrating various financial activities within an organization. Here are key points highlighting the importance of ERP software in financial operations:
- Centralization of Financial Data: ERP accounting software centralizes financial information from different departments, ensuring consistency and accuracy. This unified data approach eliminates discrepancies and provides a single source of truth for financial data.
- Automation of Financial Processes: By automating routine tasks such as journal entries, invoicing, and payroll, accounting ERP systems reduce the burden of manual data entry. This not only improves efficiency but also minimizes the risk of human error.
- Real-Time Financial Reporting: ERP accounting software provides real-time access to financial data, enabling timely and informed decision-making. Advanced reporting capabilities allow for the generation of comprehensive financial statements, cash flow reports, and other critical financial documents.
- Regulatory Compliance and Audit Trails: ERP accounting systems ensure compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. They maintain detailed records and audit trails, which are essential for internal audits and external regulatory reviews.
- Enhanced Budgeting and Forecasting: ERP software supports robust budgeting and forecasting tools, helping organizations plan and allocate resources effectively. This capability is crucial for financial planning and long-term strategy development.
- Scalability and Adaptability: Accounting ERP systems are scalable to meet the growing needs of a business. They can adapt to new financial regulations and evolving business processes, making them a long-term solution for financial management.
- Improved Financial Control and Visibility: By providing a comprehensive view of the organization’s financial health, ERP accounting software enhances financial control. It helps in identifying potential financial issues early and allows for proactive management.
Benefits of ERP Accounting System
Implementing ERP accounting software offers a multitude of advantages that significantly enhance an organization's financial operations. Here’s a detailed exploration of these benefits:

Centralized Financial Management
Integration of Financial Data: ERP accounting software centralizes financial information from various departments into a single, unified system. This integration ensures data consistency and accuracy across the organization, eliminating data silos and providing a comprehensive view of the company’s financial health.
Example: Deskera ERP integrates data from sales, procurement, HR, and other functions, ensuring all financial information is consolidated and easily accessible.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Automation of Financial Processes: ERP software automates repetitive financial tasks such as data entry, invoicing, payroll, and ledger management. This automation minimizes human error, ensuring more accurate financial records and reducing the risk of discrepancies.
Example: Deskera ERP automates invoice processing and payroll calculations, enhancing the accuracy of financial data.
Real-Time Financial Reporting
Up-to-Date Financial Information: ERP accounting systems provide real-time access to financial data, enabling businesses to generate up-to-date financial reports and dashboards. This real-time visibility is crucial for making informed decisions quickly and effectively.
Example: Deskera ERP offers real-time dashboards and customizable reports that allow managers to continuously monitor financial performance.
Improved Compliance and Auditability
Regulatory Compliance: ERP accounting software ensures compliance with various accounting standards (e.g., GAAP, IFRS) and regulatory requirements. It provides detailed audit trails and maintains comprehensive records of all financial transactions, facilitating easier audits and regulatory reviews.
Example: Deskera ERP is designed to comply with multiple accounting standards and provides detailed audit trails to support compliance.
Efficient Budgeting and Forecasting
Advanced Financial Planning: ERP accounting systems offer robust tools for budgeting, forecasting, and financial planning. These tools help businesses set financial goals, allocate resources efficiently, and track performance against budgets, aiding in strategic planning and decision-making.
Example: Deskera ERP includes budgeting and forecasting features that allow businesses to plan for future financial needs and monitor actual performance against projections.
Enhanced Financial Control and Transparency
Comprehensive Financial Oversight: ERP software enhances financial control by providing a holistic view of the organization's finances. This transparency helps in identifying potential financial issues early, enabling proactive management and better financial oversight.
Example: Deskera ERP offers detailed financial reporting and dashboards that provide a clear picture of the company’s financial status, enhancing transparency and control.
Scalability and Flexibility
Adaptability to Business Growth: ERP accounting systems are scalable and can grow with the business. They can handle increasing transaction volumes and adapt to more complex financial processes as the organization expands, ensuring long-term viability.
Example: Deskera ERP is highly scalable, making it suitable for growing businesses that need to manage increasing financial complexities.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Reduction in Manual Labor: By automating many accounting processes, ERP software reduces the need for extensive manual labor, leading to cost savings. It also streamlines workflows, making financial operations more efficient and reducing the time spent on routine tasks.
Example: Deskera ERP automates invoicing, expense tracking, and reconciliation, saving time and reducing labor costs.
Improved Decision-Making
Data-Driven Insights: With ERP accounting software, businesses can access detailed analytics and insights into their financial performance. These insights support data-driven decision-making, helping businesses make informed strategic choices based on accurate financial data.
Example: Deskera ERP provides advanced analytics and business intelligence tools that help organizations make better financial decisions.
What are the Components of an ERP System in Accounting?
ERP accounting systems are composed of various integrated modules that work together to streamline and optimize financial operations. Here are the key components of ERP accounting software:
General Ledger (GL)
Core Financial Record: The general ledger module is the central repository for all financial transactions within an ERP system. It records all debits and credits across accounts, providing a comprehensive view of the organization’s financial status.
Example: Deskera ERP includes a robust General Ledger module that tracks all financial transactions and maintains detailed financial records.
Accounts Payable (AP)
Managing Expenses: The accounts payable module handles the organization’s liabilities, including managing vendor invoices, processing payments, and tracking due dates. It ensures timely payments to suppliers and helps in maintaining good supplier relationships.
Example: Deskera ERP automates the AP process, from invoice capture to payment processing, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Accounts Receivable (AR)
Managing Revenues: The accounts receivable module tracks money owed to the organization by customers. It manages customer invoices, monitors outstanding receivables, and facilitates collection processes.
Example: Deskera ERP offers comprehensive AR functionality, including invoice generation, payment tracking, and automated reminders for overdue accounts.
Fixed Assets Management
Asset Tracking: This module manages the lifecycle of fixed assets, from acquisition to disposal. It tracks asset depreciation, maintenance schedules, and asset valuations, providing accurate financial representation of assets.
Example: Deskera ERP includes tools for managing fixed assets, ensuring precise tracking and accounting of asset-related transactions.
Cash Management
Liquidity Control: The cash management module monitors and manages cash flow, bank accounts, and liquidity. It helps in planning cash requirements, optimizing cash utilization, and ensuring sufficient liquidity for operations.
Example: Deskera ERP provides real-time cash flow tracking and bank reconciliation features, enhancing liquidity management.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Financial Planning: This module supports the creation and management of budgets and financial forecasts. It allows businesses to set financial goals, allocate resources, and track performance against budgets.
Example: Deskera ERP includes advanced budgeting and forecasting tools, enabling effective financial planning and performance monitoring.
Financial Reporting
Insightful Analysis: The financial reporting module generates various financial statements and reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. It provides insights into the organization’s financial performance and supports decision-making.
Example: Deskera ERP offers customizable reporting capabilities, allowing businesses to generate detailed financial reports tailored to their needs.
Payroll Management
Employee Compensation: The payroll management module automates the payroll process, including salary calculations, tax deductions, and disbursements. It ensures accurate and timely payment to employees and compliance with tax regulations.
Example: Deskera ERP streamlines payroll processing, ensuring accurate compensation management and compliance with payroll regulations.
Tax Management
Regulatory Compliance: This module manages tax calculations and compliance with local and international tax laws. It simplifies the preparation and filing of tax returns and maintains records for audits.
Example: Deskera ERP includes tax management features that help businesses stay compliant with tax regulations and streamline tax reporting.
Inventory Management
Stock Control: Although primarily an operations module, inventory management is crucial for financial accounting. It tracks inventory levels, costs, and movements, integrating with financial modules to ensure accurate inventory valuation and cost accounting.
Example: Deskera ERP integrates inventory management with accounting, providing a seamless flow of information for accurate financial reporting.
Audit Trails and Security
Data Integrity and Security: ERP accounting systems provide comprehensive audit trails, tracking every transaction and modification. This ensures data integrity and supports compliance with auditing standards.
Example: Deskera ERP maintains detailed audit trails and employs robust security measures to protect sensitive financial data.
Multi-Currency and Multi-Language Support
Global Operations: For organizations operating globally, ERP accounting software supports multiple currencies and languages. This feature is essential for managing international transactions and reporting.
Example: Deskera ERP supports multi-currency transactions and multi-language interfaces, making it suitable for global businesses.
Key Features and Functions of ERP Systems for Accounting Department
Understanding the key features and functions of ERP systems is essential for optimizing the accounting department's performance. These systems integrate various financial processes to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and compliance in financial management.
Automated Accounting Transactions
Automated accounting transactions refer to the capability of ERP systems to conduct specific financial operations and log them into the accounting ledger without manual input.
This automation simplifies financial processes, minimizes human error, and boosts the efficiency of financial operations.
Key aspects of automated accounting transactions include:
Invoice Processing
A prevalent example of automated accounting transactions is vendor invoice processing. Traditionally, accounts payable staff manually enter invoice data, match it with purchase orders and receipts, and create journal entries. In contrast, ERP systems can automate this process.
When an invoice is received, the ERP system automatically matches it with relevant purchase orders and receipts, generates the necessary accounting entries, and updates the accounts payable ledger. This automation saves time and reduces data entry errors.
Expense Tracking
ERP systems can also automate employee expense tracking. When an employee incurs a business expense, they submit it through the ERP system.
The system verifies compliance with expense policies, allocates expenses to the correct cost centers or projects, and creates journal entries to reflect the expenses in the general ledger.
This ensures expenses are accurately recorded and properly categorized.
Payroll Management
Payroll processing involves numerous calculations, deductions, and tax withholdings. ERP systems can automate the entire payroll process.
During payroll runs, the system calculates employees' wages, deducts taxes and benefits, generates paychecks or direct deposits, and records payroll transactions in the general ledger.
This reduces payroll errors and ensures accurate and timely employee payments.
Examples of Automated Accounting Transactions
Accounts Receivable
In accounts receivable, when a customer makes a payment, the ERP system can automatically apply the payment to the corresponding invoice, update the customer's account balance, and create the necessary journal entries. This ensures payments are properly recorded and reduces the risk of discrepancies.
Inventory Management
When inventory is received or sold, ERP systems can automatically update inventory levels and generate corresponding accounting entries. For instance, when goods are received into inventory, the system increases the inventory asset account and records the corresponding accounts payable entry.
Fixed Asset Depreciation
For fixed assets, ERP systems can automate depreciation expense calculations. The system computes depreciation based on the selected method (e.g., straight-line or declining balance) and generates journal entries to reflect depreciation expense over time.
Bank Reconciliation
ERP systems can automate the bank reconciliation process by matching transactions recorded in the ERP system with bank statements, identifying discrepancies, and creating adjusting entries to reconcile accounts automatically.
Tax Compliance
ERP systems can automate tax calculation and reporting. For example, during a sales transaction, the system automatically calculates the appropriate sales tax, creates tax liability entries, and generates tax reports for compliance purposes.
Financial Analytics and Reporting
Financial analytics and reporting are essential features of ERP systems, enabling finance professionals to gain valuable insights from an organization’s financial data.
These tools extend beyond mere data entry and transaction processing, offering functionalities that support data analysis, visualization, and informed decision-making.
Here are key elements of financial analytics and reporting within ERP systems:
Custom Reports
ERP systems enable the creation of customized financial reports tailored to the specific needs of an organization. Users can set report parameters, choose data fields, and apply filters to generate reports that offer a detailed view of financial performance. Customization ensures that the reports align with an organization’s unique financial metrics and goals.
Data Analysis
ERP systems come equipped with data analysis tools that allow finance professionals to delve deeply into financial data. Users can perform trend analysis, variance analysis, profitability analysis, and more. These tools help in identifying patterns, anomalies, and opportunities within the financial data.
Visualization
Many ERP systems feature data visualization tools, including interactive dashboards and charts. These tools transform complex financial data into easily understandable visuals, making it simpler to interpret trends and insights. Examples include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and heatmaps.
Drill-Down Capability
ERP systems often include drill-down functionality, allowing users to explore financial data at various levels of detail. For instance, a finance professional can start with a high-level summary report and then drill down to view individual transactions or specific accounts for a more detailed understanding.
Forecasting and Budgeting
Some ERP systems offer forecasting and budgeting modules that enable finance teams to create financial projections and budgets. These tools use historical data, assumptions, and various scenarios to assist in long-term financial planning.
Examples of Key Financial Reports in ERP Systems
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
An income statement summarizes an organization’s revenues, expenses, and net income (or loss) over a specific period, providing a snapshot of profitability and essential insights into financial performance.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet presents an organization’s financial position at a specific point in time, listing assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. It showcases the company’s financial health and solvency.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash in and out of the organization, categorizing cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities. This report helps assess liquidity and cash management.
Accounts Receivable Aging Report
This report categorizes outstanding customer invoices by their aging status (e.g., current, 30 days overdue, 60 days overdue), helping monitor the effectiveness of credit and collections processes.
Accounts Payable Aging Report
Similar to the accounts receivable aging report, this report categorizes outstanding vendor invoices by their aging status. It assists in managing payment obligations and optimizing cash flow.
Trial Balance
A trial balance lists all accounts in the general ledger along with their current balances, essential for verifying that debits equal credits, ensuring the accuracy of financial data.
Financial Ratios Analysis
ERP systems can generate reports that calculate and display financial ratios such as liquidity ratios (e.g., current ratio), profitability ratios (e.g., return on equity), and efficiency ratios (e.g., inventory turnover). These ratios offer insights into various aspects of financial performance.
Budget vs. Actual Variance Report
This report compares budgeted figures with actual financial results, highlighting variations and helping organizations evaluate their financial performance against planned targets.
Revenue and Sales Analysis Report
For sales-focused organizations, this report breaks down sales revenues by product, region, customer, or salesperson, aiding in identifying sales trends and areas for improvement.
Expense Analysis Report
This report provides a detailed breakdown of expenses by category or department, assisting organizations in analyzing cost structures and controlling expenditures.
Audit Trail and Security Measures
An audit trail is a chronological record of all actions and changes made to financial data within an ERP system. It serves as a digital paper trail, capturing details such as who made the change, what was altered, when it happened, and why it occurred.
Here’s why it’s crucial:
Transparency and Accountability
An audit trail ensures complete transparency in the history of financial transactions and records. It allows organizations to trace every action within the ERP system, creating a clear and documented trail of financial activities, thereby fostering accountability among users.
Detection of Errors
If there are errors or discrepancies in financial data, an audit trail helps identify when and how the error occurred. This enables finance professionals to quickly detect and correct mistakes, ensuring the accuracy of financial records.
Fraud Detection
An audit trail is vital for identifying and investigating fraud or unauthorized activities. If suspicious transactions or changes are found, the audit trail can reveal who was responsible and the sequence of events, providing crucial information for fraud prevention and investigation.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries and organizations must comply with regulations that require maintaining detailed audit trails. ERP systems help organizations meet these regulatory requirements by providing comprehensive audit logs.
Historical Analysis
The audit trail acts as a historical record of changes to financial data. It allows organizations to analyze past financial activities, trends, and patterns, informing strategic decision-making and long-term planning.
Security Measures in ERP Systems
ERP systems incorporate robust security measures to protect sensitive financial data. These measures are essential for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of financial information.
Here’s why they are important:
Data Protection
ERP systems contain a wealth of sensitive financial information, including proprietary data, customer information, and employee records. Security measures such as encryption, access controls, and data masking are crucial to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have stringent regulations regarding the protection of financial data, such as GDPR and HIPAA. ERP systems must comply with these regulations to avoid legal consequences, fines, and reputational damage.
Prevention of Unauthorized Access
Access to financial data should be limited to authorized personnel. ERP systems enforce role-based access controls, ensuring users can only access data and functionalities relevant to their roles.
Data Integrity
Security measures protect the integrity of financial data by preventing unauthorized changes or deletions. This is essential to maintain data accuracy and prevent fraudulent activities.
Availability
ERP systems ensure the availability of financial data through backup and disaster recovery mechanisms, safeguarding against data loss due to system failures or external threats.
User Authentication
Users must authenticate their identities through secure login credentials, preventing unauthorized individuals from accessing the ERP system.
Importance of Financial Data Integrity and Security
The integrity and security of financial data are critical in financial management for several reasons:
Trust and Credibility
Maintaining the integrity and security of financial data builds trust with stakeholders, including investors, customers, and partners, enhancing the organization’s credibility and reputation.
Risk Mitigation
Robust security measures and audit trails reduce the risk of financial fraud, data breaches, and compliance violations, mitigating financial and legal risks associated with unauthorized activities or data breaches.
Decision-Making
Reliable financial data is the foundation of sound decision-making. Finance professionals rely on accurate and secure data to make informed strategic and operational decisions.
Compliance
Adhering to data protection regulations and demonstrating compliance through audit trails is essential to avoid regulatory fines and legal consequences.
Operational Efficiency
ERP systems with strong security measures and audit trails enable finance teams to work efficiently and confidently, knowing that financial data is protected and accurate.
Workflow Automation in a ERP Software for Accounting
Workflow automation in ERP systems employs technology to streamline and coordinate a series of tasks, activities, or approvals within a specific business process.
Within financial management, this automation is pivotal in optimizing and standardizing financial processes, resulting in heightened efficiency, decreased errors, and improved compliance.
Here's an overview of its functionality:
Workflow Definition: Finance professionals can define and configure workflows within the ERP system, delineating the sequence of steps, tasks, and participants needed for a specific financial process. For example, an approval workflow for purchase orders might encompass requisition, approval, procurement, and payment stages.
Task Allocation: ERP systems automatically allocate tasks and responsibilities to designated individuals or roles within the organization. For instance, upon an employee's expense report submission, the system may assign tasks to their manager for approval, the finance team for verification, and accounts payable for reimbursement.
Automated Notifications: Workflow automation encompasses sending automated notifications and reminders to participants at each workflow step, keeping them informed of pending tasks, deadlines, and necessary actions. These notifications can be delivered via email, in-app alerts, or mobile notifications.
Document Routing: Documents and data pertinent to financial transactions are seamlessly routed through predefined workflows. For instance, invoices, purchase orders, and supporting documentation can be attached to the workflow for review and approval by relevant stakeholders.
Conditional Logic: ERP systems can integrate conditional logic into workflows, allowing them to adapt and follow different paths based on specific conditions or criteria. For example, an expense report may undergo a different approval path for high-value expenses compared to low-value ones.
Examples of Workflow Automation in Accounting
Expense Approval Workflow: In this scenario, an organization's expense approval process is automated. Upon an employee's expense report submission through the ERP system, a predefined workflow commences.
This workflow includes manager approval, finance team verification, and accounts payable processing. Automated notifications are sent to relevant individuals at each step, facilitating a smooth progression. Exceptions may prompt manual review.
Purchase Order Approval: ERP systems automate purchase order approval workflows in the procurement process. When a purchase requisition is generated, the system routes it through approval stages based on predefined rules, ensuring necessary authorizations before procurement and preventing unauthorized purchases.
Invoice Processing: Invoice approval workflows automate the handling of supplier invoices. In this process, invoices are digitized upon receipt and routed through predefined approval stages within the ERP system.
Approvers review the invoices against corresponding purchase orders and receipts, facilitating accurate verification. Automated notifications keep stakeholders informed of the invoice's status throughout the process, ensuring timely approvals and payments.
This automation streamlines invoice processing, reduces manual intervention, and enhances accuracy in financial transactions.
Budget Review and Revision: ERP systems have the capability to automate workflows involved in reviewing and revising budgets.
For example, when a department proposes a modification to the budget, the ERP system can trigger a workflow for evaluation by finance managers and executives.
Conditional logic enables the system to route budget revisions based on factors such as departmental considerations, expenditure types, or budgetary thresholds.
Significance of Workflow Automation in Accounting
Workflow automation holds profound significance in financial management for several compelling reasons:
- Enhanced Efficiency: By reducing reliance on manual intervention, automation accelerates financial processes, thereby diminishing processing durations and ensuring the prompt execution of financial transactions.
- Consistency: Automated workflows foster adherence to standardized processes and regulatory compliance, thereby curbing errors and ensuring that financial transactions adhere to authorized protocols consistently.
- Transparency: Workflow automation offers transparent insights into the status of financial processes, facilitating stakeholders to monitor progress, review pending tasks, and access historical data. This fosters accountability and promotes visibility across the organization.
- Compliance: Automated workflows play a pivotal role in ensuring that financial transactions undergo proper authorization and documentation, thereby aiding organizations in compliance with regulatory requirements. Compliance is imperative for sidestepping penalties and legal ramifications.
- Cost Savings: By streamlining financial operations through automation, organizations can slash operational expenses linked to manual data entry, paperwork, and repetitive tasks. Moreover, it liberates finance professionals to concentrate on high-value tasks.
- Facilitated Collaboration: Workflow automation fosters collaboration among finance professionals, departments, and external stakeholders by furnishing a centralized platform for communication and document sharing. This promotes synergy and expedites decision-making processes.
Why is Deskera ERP Accounting Software the Best Choice?
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive business management solution that offers a range of features across various modules, including accounting.
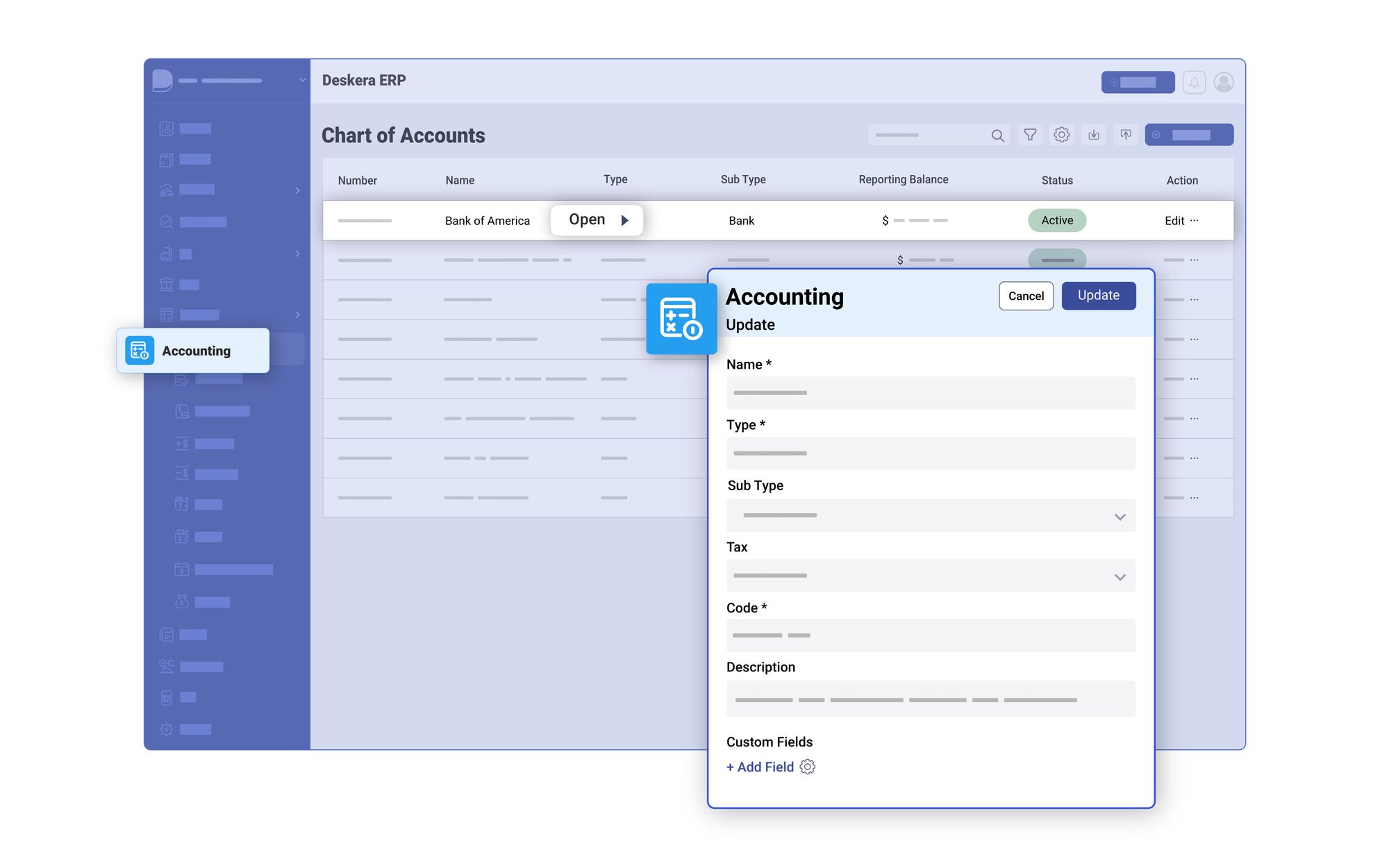
Some of the standout features of Deskera ERP accounting software include:
- Integrated Platform: Deskera ERP provides a unified platform that integrates accounting with other key business functions such as sales, inventory management, procurement, human resources, and customer relationship management (CRM). This integration ensures seamless data flow and real-time visibility across the organization.
- Financial Management: Deskera ERP accounting software enables users to manage all aspects of financial operations, including general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, bank reconciliation, budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting. Users can track income, expenses, assets, and liabilities efficiently.
- Multi-Currency and Multi-Company Support: Deskera ERP supports multiple currencies and allows users to manage finances across multiple companies or subsidiaries from a single platform. This feature is particularly beneficial for organizations operating globally or with diverse business entities.
- Automation and Workflow: Deskera ERP automates routine accounting tasks and workflows, such as invoice processing, expense management, and payment approvals. Automated workflows help streamline processes, reduce manual errors, and improve efficiency.
- Bank Reconciliation: The bank reconciliation feature in Deskera ERP helps users reconcile their bank accounts with their accounting records. It automatically matches transactions from bank statements with corresponding entries in the accounting system, streamlining the reconciliation process and reducing errors.
- Audit Trail: Deskera ERP maintains a detailed audit trail of all financial transactions and changes made to financial data. This audit trail provides transparency and accountability, allowing users to track the history of transactions and identify any discrepancies or unauthorized changes.
- Customizable Reports: Deskera ERP accounting software offers customizable reporting capabilities, allowing users to generate financial reports tailored to their specific requirements. Users can create income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and other financial reports with ease.
- Tax Compliance: Deskera ERP helps ensure tax compliance by providing features for tax calculation, reporting, and filing. The software supports various tax regimes and enables users to generate tax reports accurately and efficiently.
- User-Friendly Interface: Deskera ERP features an intuitive and user-friendly interface that makes navigation and use straightforward for users of all levels. The software is designed with a focus on usability and accessibility.
- Cloud-Based Accessibility: Deskera ERP is a cloud-based solution, allowing users to access the software from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility enables remote work, collaboration, and real-time access to financial data.
- Scalability: Deskera ERP is scalable and can grow with the needs of the organization. Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, Deskera ERP can accommodate your requirements and scale accordingly.
- Security: Deskera ERP prioritizes data security and provides robust security measures to protect sensitive financial information. The software employs encryption, access controls, and data backups to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Deskera ERP accounting software incorporates role-based access control, allowing administrators to define access levels and permissions for different user roles within the organization. This feature ensures that users have access only to the information and functionality relevant to their roles, enhancing security and data privacy. Administrators can configure granular access controls based on job responsibilities, departments, or hierarchies, providing an additional layer of protection for sensitive financial data.
Overall, Deskera ERP accounting software offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline financial operations, improve efficiency, and facilitate informed decision-making for businesses of all sizes.
Key Takeaways
ERP accounting software stands as a cornerstone of modern business management, offering a myriad of benefits that can propel organizations to new heights of success.
These are:
- Streamlined Financial Operations: ERP accounting software integrates various financial functions such as general ledger management, accounts payable and receivable, and financial reporting into a unified platform, streamlining operations and reducing manual effort.
- Real-Time Insights: By providing real-time access to financial data, ERP accounting software enables businesses to make informed decisions quickly and effectively, enhancing agility and responsiveness.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation of routine accounting tasks and workflows improves efficiency, minimizes errors, and frees up valuable time and resources for strategic initiatives.
- Scalability: ERP accounting software is scalable and can accommodate the evolving needs of businesses as they grow and expand, providing flexibility and adaptability.
- Improved Compliance: With built-in compliance features and robust security measures, ERP accounting software helps businesses adhere to regulatory requirements and safeguard sensitive financial information.
- Cost Savings: Despite initial investment costs, ERP accounting software can deliver significant long-term cost savings by optimizing processes, reducing operational expenses, and enhancing productivity.
- Competitive Advantage: By leveraging ERP accounting software, businesses can gain a competitive edge by improving operational efficiency, enhancing decision-making capabilities, and fostering innovation.
- Tailored Solutions: ERP accounting software solutions can be customized to meet the specific needs and workflows of businesses, ensuring alignment with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
By investing in ERP accounting software, businesses can unlock opportunities for growth, mitigate risks, and stay ahead of the competition in today's dynamic and evolving marketplace.
As organizations continue to harness the power of technology to drive innovation and efficiency, ERP accounting software emerges as a catalyst for business transformation, enabling businesses to skyrocket towards their goals with ease and confidence.
Deskera ERP accounting is a powerful example of ERP accounting software's benefits. It offers comprehensive financial management, including general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, and advanced financial reporting.
Its user-friendly interface and automation tools streamline processes, reduce errors, and provide real-time financial insights. Being cloud-based, Deskera allows seamless operation from anywhere, enhancing collaboration and efficiency.
Related Articles