According to a recent study conducted by Statista, 76% of manufacturing executives in the United States identified inventory control optimization as a top priority for their organizations. The study also revealed that 83% of executives believe that advanced analytics and real-time data can significantly enhance inventory management capabilities.
These statistics highlight the growing recognition among manufacturing leaders of the importance of inventory control in achieving operational excellence and driving business growth.
With the availability of advanced technologies and data-driven solutions, manufacturing executives have a unique opportunity to unlock new possibilities and transform their inventory control practices.
Inventory control is a fundamental aspect of manufacturing operations, encompassing the processes and strategies employed to manage and optimize inventory levels.

It involves the balance between maintaining adequate stock to fulfill customer orders and minimizing excess inventory to avoid unnecessary costs. As a manufacturing executive, your ability to effectively control inventory can significantly impact profitability, customer satisfaction, and overall business success.
By leveraging demand-driven strategies such as just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing and lean inventory management, executives can reduce waste, improve responsiveness, and optimize inventory levels. Together, we will navigate the evolving landscape of manufacturing and equip you with the knowledge and insights to drive your organization's success.
Here is what we shall cover in this post:
- Introduction to Inventory Control
- Understanding the Four Major Inventory Control Techniques
- Leveraging Data Analytics for Actionable Insights
- Adopting Real-Time Inventory Tracking Solutions
- Exploring Cloud-Based Inventory Management Systems
- Emphasizing Collaboration and Communication Across Departments
- Exploring Robotics and Automation for Efficient Inventory Management
- Leveraging Machine Learning for Intelligent Inventory Control
- Future Trends: Innovations in Inventory Control for Manufacturing Executives
- How Deskera Can Assist You?
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
Introduction to Inventory Control
Inventory control refers to the process of managing and regulating the inventory of goods or materials within a business or organization. It involves monitoring the flow of goods from the procurement stage to the point of sale or consumption, to ensure that the right amount of inventory is available at the right time to meet customer demand while minimizing costs.
Effective inventory control is essential for businesses to optimize their operations and achieve various objectives, such as maximizing profitability, reducing carrying costs, minimizing stockouts, and improving customer satisfaction.
It involves implementing strategies, policies, and procedures to efficiently manage inventory levels, track inventory movement, and make informed decisions about replenishment and distribution.
Inventory control encompasses several key components:
- Inventory Planning: This involves forecasting and estimating future demand for products and materials to determine the appropriate inventory levels and ensure a balance between supply and demand. It includes analyzing historical data, market trends, sales projections, and other factors to make accurate inventory predictions.
- Inventory Monitoring: Regular monitoring of inventory levels is crucial to track the inflow and outflow of goods, identify any discrepancies, and ensure that inventory is maintained at optimal levels. This may involve implementing inventory tracking systems, conducting regular physical counts, and using technology such as barcoding or RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
- Replenishment and Ordering: Inventory control involves establishing reorder points and lead times to determine when and how much inventory should be reordered. This includes evaluating supplier performance, negotiating favorable terms, and optimizing order quantities to minimize costs associated with carrying excess inventory or stockouts.
- Inventory Classification: Inventory control often involves classifying items based on their value, demand patterns, and criticality. This allows businesses to prioritize their efforts and allocate resources effectively. Common classification methods include ABC analysis (based on the Pareto principle), which categorizes items into groups based on their contribution to overall sales or value.
- Inventory Accuracy and Loss Prevention: Maintaining accurate inventory records is essential for effective inventory control. This involves conducting regular audits, cycle counts, and reconciling discrepancies between physical inventory and recorded quantities. Implementing measures to prevent loss, theft, or damage to inventory is also crucial, such as implementing security measures and proper handling procedures.
- Technology and Automation: Many businesses rely on inventory management software or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to streamline inventory control processes. These systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, automate data capture and analysis, and support decision-making through advanced reporting and analytics.
Effective inventory control helps businesses achieve various benefits, including improved cash flow, reduced carrying costs, minimized stockouts and backorders, increased operational efficiency, better customer service, and enhanced profitability.
It requires a holistic approach, involving collaboration between different departments, suppliers, and customers to ensure smooth and efficient inventory management.
Understanding the Four Major Inventory Control Techniques
Inventory control techniques are essential for managing and optimizing inventory levels within a business. These techniques help businesses strike a balance between meeting customer demand and minimizing carrying costs. Here, we will discuss the four major inventory control techniques widely used by businesses:
ABC Analysis
ABC Analysis is a widely used inventory management technique that classifies inventory items into different categories based on their value and importance.
The goal of ABC Analysis is to prioritize inventory management efforts and resources by focusing on items that have the highest impact on the business's performance. The technique derives its name from the three categories used: A, B, and C.
Category A: Category A includes high-value items that contribute a significant portion of sales or profitability. These items typically have a higher value per unit and account for a substantial portion of the business's revenue. Managing these items effectively is crucial to the business's success.
Examples of Category A items may include premium products, high-demand items, or specialized components. These items require closer attention, more frequent monitoring, and potentially tighter inventory controls to ensure their availability.
Category B: Category B includes moderate-value items that have a moderate impact on the business's overall performance. These items are not as critical as Category A items but still require proper management to maintain customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
They may have a lower value per unit compared to Category A items or represent a smaller portion of the business's revenue. Examples of Category B items may include regular or popular products that have a steady demand. Balancing inventory levels and order frequency for Category B items is important to ensure adequate stock without excessive carrying costs.
Category C: Category C includes low-value items that have minimal impact on the business's performance. These items typically have a lower value per unit and contribute less to overall revenue. They may have sporadic or occasional demand and may not require the same level of attention as Category A or B items.
Examples of Category C items may include low-demand products, inexpensive components, or items with low margins. While these items may not be critical to the business, they still need to be managed efficiently to avoid stockouts or excessive inventory accumulation.
By categorizing inventory items into these three categories, businesses can allocate their resources and efforts effectively. The categorization allows for different inventory management approaches based on the value and importance of each category. It enables businesses to:
- Focus on Category A items: These items require closer monitoring, accurate demand forecasting, and potential safety stock to ensure their availability. Efficient supply chain management, including timely replenishment and inventory control measures, is crucial for Category A items.
- Balance inventory levels for Category B items: These items may have steady demand, and businesses need to maintain optimal inventory levels to meet customer needs while minimizing carrying costs. Techniques like Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) can be applied to optimize order quantities and reorder points.
- Simplify management for Category C items: While these items may not require intense monitoring, businesses should still ensure that the supply chain processes are in place to meet occasional demand and avoid stockouts.
ABC Analysis provides businesses with a framework to prioritize their inventory management efforts and allocate resources effectively. By focusing on the items with the highest impact and value, businesses can optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, minimize stockouts, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Regular review and reassessment of item classifications are essential to account for changes in demand patterns, market conditions, and business priorities.
Batch Tracking
Batch tracking is an inventory control technique that involves assigning unique identifiers or codes to groups of products or materials produced or received together in a batch. It allows businesses to track and trace specific batches throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution and sale.
Batch tracking provides visibility and control over individual batches, enabling businesses to effectively manage quality control, recall processes, expiration dates, and regulatory compliance.
The process of batch tracking involves several key steps:
- Batch Creation: When a batch of products is manufactured or received, a unique batch number or code is assigned to that particular group. This identifier distinguishes the batch from others and serves as a reference for tracking purposes.
- Recording Information: Relevant information about the batch is recorded, such as the production date, manufacturing facility, ingredients or components used expiration date, and any other pertinent details. This data is essential for quality control, compliance, and recall management.
- Barcode or RFID Tagging: Each product within the batch is typically labeled with a barcode or RFID tag that contains the batch number. This enables efficient scanning and tracking of the products throughout the supply chain.
- Inventory Management System Integration: The batch information is entered into the inventory management system, associating it with the specific batch number. This allows for seamless tracking and retrieval of batch-related data as products move through the supply chain.
- Tracking and Tracing: As the batch moves through various stages of production, distribution, and sale, its movement is recorded and tracked using scanning devices or RFID technology. This enables real-time visibility into the location and status of each batch.
- Quality Control: Batch tracking allows for targeted quality control measures. If a quality issue arises with a specific batch, businesses can identify and isolate affected products quickly, preventing further distribution or sale of potentially defective items.
- Recall Management: In the event of a product recall or safety concern, batch tracking enables businesses to identify the specific batches affected, locate them within the supply chain, and efficiently remove them from circulation. This helps mitigate risks and protect consumers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, such as pharmaceuticals and food manufacturing, have stringent regulations regarding batch tracking. Compliance with these regulations is facilitated through the implementation of batch tracking systems, ensuring full traceability and accountability.
Batch tracking provides several benefits to businesses, including:
- Improved Product Quality Control: Businesses can identify and address quality issues more effectively by isolating and rectifying specific batches instead of recalling entire product lines.
- Enhanced Traceability: Batch tracking enables quick and accurate tracing of products, facilitating faster response times in the event of product issues, complaints, or regulatory inquiries.
- Efficient Recall Management: Businesses can efficiently recall and remove only the affected batches from the market, reducing financial losses and preserving consumer trust.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Batch tracking helps businesses meet regulatory obligations by providing the necessary documentation and traceability required by regulatory bodies.
- Supply Chain Optimization: With batch tracking, businesses can identify trends, optimize inventory levels, and improve supply chain efficiency by analyzing batch-specific data.
Batch tracking is particularly crucial for industries where product safety, quality control, and regulatory compliance are paramount. By implementing robust batch tracking systems and integrating them with inventory management systems, businesses can ensure quality, traceability, and regulatory compliance throughout the supply chain.
Last In, First Out (LIFO) & First In, First Out (FIFO)
Last In, First Out (LIFO), and First In, First Out (FIFO) are two common inventory valuation methods used in inventory control. They determine how the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the value of remaining inventory are calculated. Let's explore each method in more detail:
Last In, First Out (LIFO): LIFO assumes that the most recent inventory items purchased or produced are the first ones sold. In other words, the last items added to the inventory are the first ones to be depleted. Under LIFO, the cost of goods sold is based on the most recent or highest cost of inventory items, while the value of the remaining inventory is based on the earlier or lower-cost items.
Benefits of LIFO:
- Tax Advantage: In periods of inflation, LIFO can result in lower taxable income and, therefore, lower taxes since higher-cost items are being matched with sales revenue.
- Reflects Current Costs: LIFO may provide a better reflection of the current cost of inventory, especially during periods of rising prices.
Drawbacks of LIFO:
- Distorted Profit Margins: LIFO can result in lower gross profit margins and distorted profitability ratios because the cost of goods sold is based on higher-cost items.
- Inventory Valuation: The value of the remaining inventory on the balance sheet may not reflect the current market value, as it is based on older, lower-cost items.
First In, First Out (FIFO): FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory items purchased or produced are the first ones sold. In other words, the items that enter the inventory first are the first ones to be depleted. Under FIFO, the cost of goods sold is based on the earliest or oldest cost of inventory items, while the value of the remaining inventory is based on the most recent or current cost items.
Benefits of FIFO:
- Reflects Actual Flow: FIFO aligns with the physical flow of inventory and represents the order in which goods are typically sold.
- Accurate Profit Margins: FIFO tends to provide more accurate gross profit margins and profitability ratios because the cost of goods sold is based on older, lower-cost items.
Drawbacks of FIFO:
- Tax Disadvantage: In periods of inflation, FIFO may result in higher taxable income and, consequently, higher taxes since lower-cost items are being matched with sales revenue.
- Reflects Historical Costs: FIFO may not accurately reflect the current cost of inventory when prices are rising, as the cost of goods sold is based on older, lower-cost items.
Choosing between LIFO and FIFO depends on various factors, including industry norms, tax regulations, inventory flow, and financial reporting requirements. It is essential to carefully evaluate the implications of each method and choose the one that best suits the business's specific needs and objectives.
It's worth noting that accounting standards and tax regulations vary by jurisdiction, so businesses should consult with accounting professionals and consider local regulations when determining which inventory valuation method to adopt.
Safety Stock
Safety stock, also known as buffer stock, is a quantity of inventory that is held by a company as a contingency measure to protect against unforeseen events or fluctuations in demand and supply. It serves as a cushion to ensure that there is an adequate supply of inventory to meet customer demand even in unexpected situations. Here are some key points about safety stock:
Purpose of Safety Stock: Safety stock is maintained to mitigate various risks and uncertainties, including:
- Demand Variability: Fluctuations in customer demand that are difficult to predict accurately.
- Lead Time Variability: Variations in the time it takes to replenish inventory due to supplier delays, transportation issues, or other factors.
- Supply Uncertainty: Unforeseen disruptions in the supply chain, such as natural disasters or production problems.
Role in Inventory Management: Safety stock acts as a buffer to provide a cushion between the average demand and the reorder point. It helps prevent stockouts and ensures that there is sufficient inventory available to fulfill customer orders even during unexpected events.
Factors Affecting Safety Stock Levels: Several factors influence the determination of safety stock levels, including:
- Demand Variability: The degree of fluctuation in customer demand and the accuracy of demand forecasting.
- Lead Time Variability: The variability in the time it takes to replenish inventory from suppliers.
- Service Level Objectives: The desired level of customer service and the acceptable risk of stockouts.
- Supply Chain Performance: The reliability and responsiveness of suppliers and the overall supply chain.
Calculating Safety Stock: Various methods can be used to calculate safety stock, including statistical approaches like standard deviation and historical demand data analysis. It is essential to consider the desired service level, lead time variability, and demand variability in determining the appropriate level of safety stock.
The trade-Off with Inventory Costs: Maintaining safety stock incurs additional costs, such as storage space, carrying costs, and the risk of obsolescence. Therefore, businesses need to strike a balance between ensuring adequate customer service levels and minimizing the costs associated with holding excess inventory.
Dynamic Nature of Safety Stock: Safety stock is not a static quantity and should be regularly reviewed and adjusted based on changes in demand patterns, lead times, and other relevant factors. Regular monitoring and analysis of inventory data can help identify the need for adjustments in safety stock levels.
Integration with Inventory Control Systems: Modern inventory management systems and software often include features to optimize safety stock levels. These systems consider historical data, demand patterns, lead time variability, and service level targets to determine the appropriate level of safety stock.
Importance of Collaboration: Collaboration between different functions within the organization, such as sales, operations, and procurement, is crucial for effectively managing safety stock. Sharing information and insights across departments helps ensure that safety stock decisions align with the overall business objectives.
By strategically managing safety stock, businesses can improve customer service levels, minimize stockouts, and mitigate risks associated with demand and supply uncertainties. It plays a vital role in maintaining a robust and efficient inventory management system.
Leveraging Data Analytics for Actionable Insights
In today's data-driven business landscape, leveraging data analytics has become crucial for gaining actionable insights and making informed decisions in inventory control.
By analyzing vast amounts of data related to inventory levels, demand patterns, supplier performance, and other relevant factors, businesses can optimize their inventory management strategies, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Here are some key points on leveraging data analytics for actionable insights in inventory control:
Data Collection and Integration: The first step in leveraging data analytics for inventory control is to collect and integrate relevant data from various sources. This includes data on historical sales, customer orders, inventory levels, procurement, lead times, supplier performance, and market trends. Automated systems and software can help gather and consolidate this data efficiently.
Data Cleaning and Validation: To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the insights derived from data analytics, it is crucial to clean and validate the data. This involves identifying and rectifying any inconsistencies, errors, or missing values in the data set. Data cleaning processes can include data normalization, outlier detection, and data quality checks.
Data Visualization and Dashboards: Visualizing the data through interactive dashboards and visual analytics tools enables inventory managers to gain a holistic view of their inventory performance.
Visual representations such as charts, graphs, and heatmaps provide intuitive insights into inventory trends, demand patterns, stock levels, and other key metrics. This facilitates quick identification of issues or opportunities for improvement.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization: Data analytics plays a vital role in demand forecasting, enabling businesses to predict future demand patterns accurately. Advanced forecasting models, such as time series analysis, machine learning algorithms, and predictive analytics, can help identify seasonality, trends, and demand drivers.
By integrating demand forecasts with inventory optimization techniques, businesses can determine optimal inventory levels, reorder points, and safety stock requirements.
Supplier Performance and Risk Assessment: Data analytics can be used to assess and monitor supplier performance, including factors such as on-time delivery, lead time variability, quality issues, and pricing.
By analyzing supplier data, businesses can identify potential risks and take proactive measures to mitigate disruptions in the supply chain. This includes supplier evaluation, contract management, and developing alternative sourcing strategies.
Real-Time Inventory Monitoring: Implementing real-time monitoring systems, such as IoT-enabled sensors and RFID technology, provides accurate and timely data on inventory levels, movement, and location.
This real-time visibility allows businesses to track inventory in transit, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize inventory replenishment processes. Real-time alerts and notifications help inventory managers take immediate actions to prevent stockouts or excess inventory.
Predictive Analytics for Stockouts and Demand Variability: Predictive analytics techniques, such as machine learning algorithms and predictive modeling, can help identify potential stockouts and anticipate demand variability.
By analyzing historical data, customer behavior, market trends, and external factors, businesses can make data-driven decisions on inventory replenishment, production planning, and allocation.
Continuous Improvement and Decision Support: Data analytics provides a foundation for continuous improvement in inventory control. By regularly analyzing and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover, order fill rate, stock accuracy, and carrying costs, businesses can identify areas for improvement and optimize inventory management processes.
Data analytics also provides decision support by simulating different scenarios, conducting what-if analyses, and evaluating the impact of alternative strategies.
Embracing Technology Advancements in Inventory Control
Here are some key ways in which businesses can embrace technology advancements in inventory control:
- Inventory Management Software: Implementing inventory management software is a fundamental step towards leveraging technology in inventory control. These software solutions provide centralized platforms for managing and tracking inventory levels, orders, sales, and other related data. They enable businesses to automate processes, generate accurate reports, and gain insights into inventory performance.
- Barcode and RFID Technology: Utilizing barcode and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology can significantly improve inventory control efficiency. Barcode labels and RFID tags can be applied to products, enabling easy and accurate tracking throughout the supply chain. Scanning devices and readers help capture data, update inventory records in real time, and facilitate efficient stock management.
- Automated Data Capture: Automation plays a vital role in inventory control by reducing human errors and manual effort. Automated data capture technologies, such as barcode scanners, mobile devices, and IoT sensors, streamline data entry, and update inventory systems instantly. This eliminates the need for manual data input, enhances accuracy, and saves time.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile applications offer flexibility and convenience in managing inventory on the go. Inventory control apps provide features such as scanning barcodes, checking stock levels, creating purchase orders, and generating reports. Mobile apps facilitate real-time inventory updates and enable managers to make informed decisions while being away from their desks.
- Integration with ERP Systems: Integrating inventory control with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems enables seamless data flow across different business functions. This integration ensures that inventory data is synchronized with other processes, such as sales, procurement, and accounting. It streamlines operations, reduces manual data entry, and improves overall efficiency.
- Robotics and Automation: In certain industries, robotics and automation solutions can streamline inventory control processes. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotic picking systems, and autonomous drones can help with inventory movements, stock counting, and warehouse operations. These technologies improve accuracy, reduce labor costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Adopting Real-Time Inventory Tracking Solutions
Adopting real-time inventory tracking solutions is a game-changer for businesses looking to improve their inventory control processes. Real-time tracking allows businesses to monitor inventory levels, movements, and locations with up-to-the-minute accuracy, enabling them to make informed decisions, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Here are some key benefits and considerations when adopting real-time inventory tracking solutions:
Benefits of Real-Time Inventory Tracking:
Enhanced Visibility: Real-time tracking provides businesses with complete visibility into their inventory at any given moment. They can access accurate data on stock levels, locations, and movements, enabling them to have a clear picture of their inventory status.
This visibility helps in optimizing inventory levels, reducing stockouts, and avoiding excess stock.
Accurate Demand Forecasting: Real-time tracking data allows businesses to analyze historical and current inventory data, helping them identify demand patterns, seasonality, and trends.
This accurate demand forecasting enables businesses to adjust their inventory levels, optimize reorder points, and align their supply chain accordingly. It leads to better inventory management and improved customer satisfaction.
Efficient Order Fulfillment: Real-time inventory tracking helps businesses streamline their order fulfillment processes. They can quickly check the availability of products, determine the nearest warehouse or fulfillment center with stock, and ensure prompt order processing and delivery.
This efficiency leads to faster order fulfillment, reduced lead times, and increased customer satisfaction.
Reduced Stockouts and Overstocks: Real-time tracking minimizes the risk of stockouts by providing businesses with instant notifications when inventory levels are running low. This allows them to reorder promptly, ensuring that products are always available to meet customer demand.
Similarly, real-time tracking helps prevent overstock situations by providing visibility into excess inventory and enabling businesses to adjust their purchasing decisions accordingly.
Improved Inventory Accuracy: Traditional inventory trackings methods, such as manual counts or periodic audits, are prone to errors and inaccuracies. Real-time tracking eliminates the need for manual data entry and provides accurate, up-to-date inventory information.
This improves inventory accuracy, reduces discrepancies, and ensures inventory records align with physical stock.
Considerations for Adopting Real-Time Inventory Tracking Solutions:
- Technology Investment: Implementing real-time inventory tracking solutions requires an initial investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure. Businesses need to evaluate their budget and select solutions that align with their requirements and growth plans. It's important to consider factors like compatibility with existing systems, scalability, and ease of integration.
- Data Security: Real-time tracking involves capturing and transmitting sensitive inventory data. Businesses must ensure that appropriate security measures are in place to protect this data from unauthorized access, breaches, or cyber threats. This includes encryption, access controls, regular backups, and adherence to data protection regulations.
- Training and Change Management: Adopting new technology requires training employees on how to use the system effectively. Proper training and change management strategies are crucial to ensure smooth implementation and adoption. Employees need to understand the benefits of real-time tracking, how to navigate the system, and how it integrates with their day-to-day operations.
- Scalability: Businesses should consider the scalability of real-time tracking solutions to accommodate future growth. As the business expands, the inventory volume and complexity may increase. The chosen solution should be capable of handling larger inventory volumes, multiple locations, and increased data processing requirements.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Real-time inventory tracking solutions need to integrate seamlessly with existing systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or warehouse management systems. Compatibility and integration capabilities should be evaluated to ensure data flows smoothly between different systems, avoiding manual data entry and potential errors.
Implementing RFID and Barcode Technologies
Implementing RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcode technologies is a strategic move for businesses seeking to enhance their inventory control processes. These technologies offer efficient and accurate ways to track and manage inventory, improving operational efficiency and reducing errors.
Here are the benefits and considerations of implementing RFID and barcode technologies in inventory control:
Benefits of RFID and Barcode Technologies:
Improved Inventory Accuracy: RFID and barcode technologies provide businesses with automated and precise inventory tracking capabilities. By attaching RFID tags or barcode labels to items, businesses can easily scan and update inventory information in real time.
This improves inventory accuracy, reduces discrepancies, and minimizes the risk of stockouts or overstocks.
Enhanced Efficiency: RFID and barcode technologies streamline inventory management processes. Scanning RFID tags or barcode labels is much faster than manual data entry, saving time and reducing human errors.
Inventory counts, stock transfers, and order processing can be performed more efficiently, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Real-Time Visibility: RFID and barcode technologies offer real-time visibility into inventory levels, locations, and movements. Businesses can track inventory in different warehouses, store shelves, or during transit, enabling them to make informed decisions about stock replenishment, order fulfillment, and supply chain optimization.
Real-time visibility helps prevent stockouts, improve customer satisfaction, and minimize holding costs.
Streamlined Receiving and Shipping Processes: With RFID and barcode technologies, receiving and shipping processes become more streamlined and accurate. Incoming goods can be quickly scanned and recorded in the inventory system, ensuring seamless updates and reducing manual paperwork.
Similarly, during shipping, barcode scanning or RFID readers facilitate efficient order picking, packing, and verification.
Increased Data Accuracy and Analysis: RFID and barcode technologies provide reliable and consistent data for analysis. The captured data can be analyzed to identify inventory trends, demand patterns, and areas for improvement.
This data-driven approach helps businesses optimize inventory levels, forecast demand accurately, and make informed decisions regarding procurement, production, and distribution.
Considerations for Implementing RFID and Barcode Technologies:
Infrastructure and Equipment: Implementing RFID and barcode technologies requires the necessary infrastructure and equipment. RFID systems typically involve RFID tags, readers, and antennas, while barcode systems require barcode labels, scanners, and printers.
Businesses should evaluate their needs, consider the cost of equipment, and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Integration with Inventory Management Software: RFID and barcode technologies should seamlessly integrate with inventory management software or ERP systems.
This integration ensures that captured data is automatically updated in the inventory system, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing errors. Compatibility and integration capabilities should be evaluated before implementation.
Employee Training and Change Management: Proper training and change management strategies are crucial for successful adoption. Employees need to be trained on how to operate the RFID or barcode equipment, understand the benefits of the technology, and adapt their workflows accordingly.
Clear communication and support during the transition are essential for smooth implementation.
Data Security and Privacy: RFID and barcode technologies involve capturing and storing sensitive inventory data. Businesses must ensure proper security measures are in place to protect this data from unauthorized access, tampering, or breaches.
Encryption, access controls, and data privacy regulations should be considered to safeguard inventory information.
Scalability and Future Needs: Businesses should consider the scalability of RFID and barcode technologies to accommodate future growth.
As inventory volumes and complexity increase, the technology should be able to handle larger data sets, multiple locations, and growing demands. Scalability options, such as expandable RFID systems or scalable barcode solutions, should be evaluated.
Exploring Cloud-Based Inventory Management Systems
Cloud-based inventory management systems are powerful tools that businesses can leverage to streamline their inventory control processes. These systems offer numerous benefits over traditional on-premises solutions, including accessibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, and real-time data synchronization.
Here are some key aspects to consider when exploring cloud-based inventory management systems:
Accessibility and Remote Management: Cloud-based inventory management systems provide anytime, anywhere access to inventory data.
Users can securely log in to the system from various devices, including computers, tablets, or smartphones, allowing them to manage inventory and monitor stock levels even when they are away from the office. This accessibility promotes flexibility and enables remote management.
Real-Time Data Synchronization: One of the key advantages of cloud-based systems is real-time data synchronization. Inventory information, such as stock levels, sales orders, and purchase orders, is updated in real-time across all devices and users.
This ensures that everyone has access to the most up-to-date inventory data, reducing the risk of errors, stockouts, or miscommunications.
Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based solutions often have a lower upfront cost compared to on-premises systems. Businesses can avoid the expenses associated with purchasing and maintaining servers, IT infrastructure, and software licenses.
Instead, they pay a subscription fee based on their usage and can adjust the subscription plan as needed. This cost-effective pricing model makes cloud-based systems accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Cloud-based systems typically handle software updates and maintenance tasks automatically. This relieves businesses from the burden of managing software upgrades or applying patches.
Updates are rolled out by the cloud provider, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and improvements without disrupting their daily operations.
Analytics and Reporting: Cloud-based inventory management systems often come with built-in analytics and reporting capabilities.
These features allow businesses to generate customized reports, analyze inventory performance, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and gain actionable insights. Advanced analytics can help optimize inventory levels, improve forecasting accuracy, and identify areas for improvement.
Collaborative Features: Cloud-based systems enable collaboration among team members and stakeholders. Multiple users can access the system simultaneously, collaborate on inventory-related tasks, and communicate in real time.
This facilitates efficient teamwork, enhances communication, and ensures everyone is aligned in inventory management activities.
When exploring cloud-based inventory management systems, it's important to evaluate the features, functionality, security measures, integration capabilities, and pricing models offered by different providers. Additionally, considering the specific needs of your business and industry requirements will help you choose the most suitable solution.
Utilizing Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of inventory control, as it helps businesses optimize their inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Traditional forecasting methods rely on historical data and assumptions, which may not capture the complexities of the ever-changing market dynamics. This is where predictive analytics comes into play, enabling businesses to leverage advanced algorithms and models to make accurate and data-driven demand forecasts.
Here's how businesses can utilize predictive analytics for demand forecasting:
Selection of Forecasting Models: There are several forecasting models available, and the choice of model depends on the nature of the business and the data characteristics. Some commonly used models include exponential smoothing, moving averages, linear regression, ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average), and machine learning algorithms like neural networks and random forests.
Businesses may need to experiment with different models to find the one that best fits their data and provides accurate forecasts.
Validation and Evaluation: It's essential to validate and evaluate the performance of the forecasting models to ensure their accuracy and reliability. This involves comparing the predicted demand with the actual demand over a specific time.
Statistical measures such as mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and forecast bias can be used to assess the accuracy of the forecasts. If the models perform well, they can be used for ongoing demand forecasting.
Continuous Monitoring and Refinement: Demand patterns can change over time, and businesses need to continuously monitor and refine their forecasting models. This involves updating the models with new data, assessing their performance, and making adjustments as necessary.
Regular monitoring helps businesses adapt to market changes, emerging trends, and new factors that impact demand.
Integration with Supply Chain Planning: To fully leverage the benefits of predictive analytics for demand forecasting, it's crucial to integrate the forecasts into the supply chain planning process. The demand forecasts can be used to optimize inventory levels, plan production schedules, manage procurement, and make informed decisions about capacity planning, promotions, and new product introductions.
Integration ensures alignment between demand forecasting and other supply chain activities.
Collaboration and Communication: Demand forecasting involves collaboration and communication between various stakeholders, including sales teams, marketing teams, supply chain managers, and executives.
Predictive analytics can facilitate this collaboration by providing a centralized platform where stakeholders can access and share demand forecasts, discuss assumptions, and provide input based on their domain expertise. Effective communication ensures that demand forecasts are aligned with business objectives and strategies.
Predictive analytics offers businesses the opportunity to make more accurate and informed decisions when it comes to demand forecasting.
By leveraging advanced algorithms and techniques, businesses can better anticipate customer demand, optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts and overstocks, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive business success.
Emphasizing Collaboration and Communication Across Departments
Collaboration and communication across departments play a crucial role in effective inventory control. When different departments work together and share information, it leads to better visibility, coordination, and decision-making.
Here are some key ways to emphasize collaboration and communication across departments for inventory control:
Cross-Functional Teams: Create cross-functional teams consisting of representatives from various departments involved in inventory management, such as procurement, sales, production, warehousing, and finance.
These teams can meet regularly to discuss inventory-related challenges, share insights, and collaborate on solutions. Cross-functional teams foster communication and alignment across departments, ensuring a holistic approach to inventory control.
Shared Goals and Objectives: Establish shared goals and objectives related to inventory control that align with the overall business objectives. When departments have a common understanding of the desired outcomes, it promotes collaboration and encourages them to work together toward achieving those goals.
Communicate the importance of inventory control and how it impacts the overall success of the organization.
Regular Communication Channels: Set up regular communication channels such as meetings, email updates, and collaboration platforms to facilitate ongoing communication among departments.
Encourage open dialogue, information sharing, and the exchange of ideas. This helps in identifying potential issues, addressing challenges, and fostering a collaborative environment.
Integrated Systems and Data Sharing: Integrate systems and databases across departments to enable seamless sharing of information related to inventory. This allows different departments to access real-time inventory data, sales forecasts, production schedules, and customer demand information.
Integrated systems eliminate silos and provide a holistic view of inventory, enabling departments to make informed decisions.
Inventory Planning and Forecasting: Involve different departments in the inventory planning and forecasting processes. Sales and marketing teams can provide insights into demand trends, customer preferences, and promotions, while procurement and production teams can contribute to supply availability and production capacity.
By integrating inputs from multiple departments, the accuracy of demand forecasts and inventory planning improves.
Collaborative Demand Management: Implement collaborative demand management practices that involve departments working together to align demand and supply. This involves sharing sales forecasts, promotional plans, and market insights across departments.
By integrating demand information from different sources, inventory control can be optimized, and potential supply-demand mismatches can be addressed proactively.
Continuous Improvement and Knowledge Sharing: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement and knowledge sharing among departments. Provide opportunities for cross-training and sharing best practices.
Regularly review inventory control processes and identify areas for improvement. By sharing knowledge and experiences, departments can learn from each other and implement effective strategies to enhance inventory control.
Performance Metrics and Accountability: Establish performance metrics related to inventory control and communicate them across departments. This promotes accountability and ensures that everyone understands their role in achieving inventory control objectives.
Regularly review performance metrics and provide feedback to drive continuous improvement. Recognize and reward departments that demonstrate exceptional collaboration and contribute to effective inventory control.
Emphasizing collaboration and communication across departments is essential for effective inventory control. By fostering a culture of teamwork, integrating systems and data, and involving different departments in decision-making processes, businesses can optimize inventory levels, improve supply chain efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Integrating Inventory Control With Lean Manufacturing Principles
Integrating inventory control with lean manufacturing principles is a powerful approach that can help organizations achieve operational excellence, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency. Lean principles focus on eliminating non-value-added activities and optimizing processes to achieve maximum productivity.
When applied to inventory control, lean principles can help organizations minimize excess inventory, reduce carrying costs, and enhance responsiveness to customer demand.
Here are some key strategies for integrating inventory control with lean manufacturing principles:
Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: JIT is a core principle of lean manufacturing that aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving and producing items only when needed. By synchronizing production with customer demand, organizations can reduce inventory holding costs, avoid stockouts, and enhance production efficiency.
Use Kanban Systems: Kanban is a visual signaling system that helps manage inventory levels and production flow. By using kanban cards or electronic systems, organizations can track inventory levels in real-time and signal the need for replenishment when the stock reaches a predetermined level.
This ensures that inventory is replenished only as needed, avoiding excess stock and reducing waste.
Employ Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): TPM focuses on maximizing the operational efficiency of equipment and machinery.
By implementing preventive maintenance practices, organizations can minimize unplanned downtime, reduce the need for spare parts inventory, and improve overall equipment effectiveness. This reduces inventory costs associated with maintenance and repairs.
Embrace Continuous Improvement: Lean manufacturing promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Apply this philosophy to inventory control by regularly reviewing and optimizing inventory management processes. Conduct value stream mapping exercises to identify areas of waste and develop strategies to eliminate them.
Continuously monitor inventory levels, lead times, and order quantities to identify opportunities for improvement.
Value Stream Analysis: Analyze the end-to-end value stream, from supplier to customer, to identify bottlenecks, delays, and non-value-added activities that impact inventory control. By optimizing the flow of materials, information, and processes, organizations can reduce inventory levels, improve throughput, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Implement Visual Management: Visual management techniques, such as color-coded inventory systems, visual cues, and standardized labels, can enhance inventory control.
These visual tools make it easy to identify inventory levels, reorder points, and production requirements at a glance, facilitating quick decision-making and reducing the risk of errors.
Optimize Production Scheduling: Align production schedules with customer demand to avoid overproduction and excess inventory. Use tools like demand forecasting, capacity planning, and production leveling to ensure that production is synchronized with actual customer requirements.
This minimizes the need for excessive finished goods inventory and reduces the risk of obsolescence.
Collaborate with Suppliers: Lean principles encourage close collaboration with suppliers to establish mutually beneficial relationships. Work with suppliers to implement vendor-managed inventory (VMI) or consignment stock arrangements. This allows suppliers to monitor inventory levels and replenish stock directly, reducing the burden on the organization's inventory control.
Implement Lean Six Sigma: Lean Six Sigma combines the principles of lean manufacturing with statistical process control methodologies to drive process improvement and minimize defects. By applying Lean Six Sigma techniques to inventory control, organizations can identify and eliminate waste, reduce lead times, and improve inventory accuracy.
Employee Empowerment and Training: Lean manufacturing emphasizes employee involvement and empowerment. Engage employees in inventory control initiatives and provide them with training on lean principles and tools. Empowered employees can contribute ideas for process improvement, identify inefficiencies, and actively participate in inventory management activities.
Integrating inventory control with lean manufacturing principles enables organizations to achieve optimal inventory levels, reduce waste, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Exploring Robotics and Automation for Efficient Inventory Management
Robotics and automation have revolutionized various industries, and inventory management is no exception. By employing robotics and automation technologies, organizations can achieve higher levels of efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in their inventory management processes.
Here are some key areas where robotics and automation can be utilized for efficient inventory management:
Automated Material Handling: Robots can be employed for efficient material handling tasks such as sorting, picking, and placing inventory items. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) or autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can navigate warehouse aisles and transport goods between different locations.
This reduces manual labor, minimizes errors, and improves the speed and accuracy of inventory movement.
Warehouse Automation: Automated systems such as conveyor belts, robotic arms, and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) can streamline warehouse operations.
These systems can efficiently store and retrieve inventory items, eliminating the need for manual searching and reducing the risk of errors. Warehouse automation improves inventory visibility, optimizes space utilization, and enhances order fulfillment speed.
Inventory Counting and Auditing: Robots equipped with barcode scanners or RFID readers can automate the inventory counting process. These robots can move through the warehouse, scan barcodes or RFID tags on inventory items, and update inventory records in real time.
This eliminates the need for manual counting, reduces human errors, and provides accurate and up-to-date inventory information.
Order Picking and Packing: Robotic systems can automate the order fulfillment process by picking and packing items. Robots equipped with vision systems and grippers can identify and handle different products, ensuring accurate and efficient order fulfillment.
This speeds up order processing, reduces errors, and improves customer satisfaction.
Automated Replenishment: Robotics and automation can automate the replenishment process by automatically sensing and restocking low inventory levels. Smart shelving systems equipped with sensors can detect when inventory levels are low and trigger replenishment orders.
This ensures timely replenishment, reduces stockouts, and optimizes inventory levels.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers, assisting them in inventory management tasks. These robots can perform repetitive and physically demanding tasks, such as lifting heavy items or reaching high shelves while ensuring the safety of human workers.
Cobots improve productivity, reduce the risk of injuries, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Integration with Inventory Management Systems: Robotics and automation can be seamlessly integrated with inventory management systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and other business applications.
This integration enables real-time data exchange, automated order processing, and seamless inventory tracking. It ensures accurate inventory records, reduces manual data entry, and improves overall system efficiency.
Demand-Driven Automation: By integrating robotics and automation with demand forecasting and planning systems, organizations can achieve demand-driven automation.
Robots and automated systems can adjust their operations based on real-time demand fluctuations, ensuring optimal inventory levels, efficient order fulfillment, and reduced inventory holding costs.
Incorporating robotics and automation in inventory management enables organizations to achieve higher levels of efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. By automating material handling, warehouse operations, inventory counting, order fulfillment, and replenishment processes, organizations can streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Implementing Agile Inventory Control Strategies
Agile inventory control is an approach that emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and responsiveness in managing inventory. It draws inspiration from the Agile methodology commonly used in software development, focusing on iterative and incremental improvements to meet changing customer demands.
Agile inventory control aims to optimize inventory levels while maintaining the ability to quickly adjust to market dynamics and customer requirements. Here are key principles and practices of agile inventory control:
- Iterative Planning and Forecasting: Instead of relying on long-term forecasts, agile inventory control promotes iterative planning and forecasting. Organizations regularly review and update demand forecasts, considering market trends, customer feedback, and other relevant factors. This enables them to make more accurate inventory decisions based on the latest information.
- Small Batch and Quick Response: Agile inventory control favors smaller batch sizes and quick response times. Instead of carrying large amounts of inventory, organizations focus on smaller, more frequent replenishments. This reduces the risk of excess inventory and enables faster adaptation to changes in customer demand.
- Dynamic Inventory Allocation: Agile inventory control involves dynamically allocating inventory based on customer demand. Organizations prioritize the availability of products that are in high demand or have shorter lead times. By continuously monitoring customer demand patterns, organizations can make informed decisions on inventory allocation and fulfillment priorities.
- Kanban System: Kanban is a visual signaling system that helps manage inventory levels and production flow. By using kanban cards or electronic kanban systems, organizations can establish pull-based inventory control. Inventory is replenished only when signaled by downstream processes or customer demand, reducing waste and optimizing inventory levels.
Here are some steps to consider when implementing agile inventory control in your organization:
- Assess Current Inventory Management Practices: Evaluate your existing inventory management practices, including forecasting methods, order quantities, lead times, and inventory holding costs. Identify areas that can be improved through agile inventory control.
- Define Inventory Objectives: Set clear objectives for your inventory management, such as reducing stockouts, minimizing excess inventory, improving order fulfillment rates, or reducing lead times. These objectives will guide your agile inventory control implementation.
- Adopt Iterative Planning and Forecasting: Shift from traditional long-term forecasting to iterative planning and forecasting. Regularly review and update demand forecasts based on market trends, customer feedback, and other relevant data. Incorporate the feedback loop into your planning process to refine forecasts over time.
- Implement Lean Principles: Apply lean principles to your inventory control processes. Identify and eliminate waste, streamline workflows, and optimize inventory flow. Value stream mapping can help identify areas for improvement and guide process optimization efforts.
- Embrace Data-Driven Decision Making: Collect and analyze relevant data to make informed inventory decisions. Utilize advanced analytics tools and techniques to identify demand patterns, analyze lead times, and optimize inventory levels. Leverage real-time data to monitor inventory performance and identify potential risks or opportunities.
- Establish Pull-Based Inventory Control: Implement a pull-based inventory control system, such as a Kanban system. Use visual signals or electronic kanban systems to trigger replenishment based on actual customer demand or downstream process needs. This approach helps reduce overproduction and minimizes inventory carrying costs.
- Invest in Technology: Leverage technology solutions to enhance your agile inventory control capabilities. Implement inventory management software that provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, automates data collection, and supports demand forecasting and analysis. Consider utilizing RFID or barcode technologies for accurate tracking and inventory control.
- Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define and track relevant KPIs to measure the effectiveness of your agile inventory control strategies. Key metrics may include inventory turnover rate, order fulfillment rate, stockout rate, lead time, and customer satisfaction. Regularly review and analyze these metrics to identify areas for improvement.
Leveraging Machine Learning for Intelligent Inventory Control
Leveraging machine learning for intelligent inventory control can significantly enhance decision-making and optimization processes. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate valuable insights to improve inventory management.
Here are some ways machine learning can be applied to intelligent inventory control:
- Seasonal Demand and Trend Analysis: Machine learning models can identify seasonal demand patterns and trends by analyzing historical data. This information can help organizations proactively adjust inventory levels, plan promotions, and optimize production schedules to meet anticipated demand fluctuations.
- Supplier Performance Monitoring: Machine learning algorithms can assess supplier performance by analyzing factors such as delivery times, quality metrics, and pricing. This data can help identify reliable suppliers, optimize supply chain partnerships, and mitigate risks associated with supplier disruptions.
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Machine learning algorithms combined with IoT technologies, such as RFID or barcode scanning, can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and locations. This enables organizations to track inventory movements, monitor stock levels, and quickly identify discrepancies or potential issues.
- Exception Management: Machine learning algorithms can flag and prioritize exceptions in inventory management, such as stockouts, excess inventory, or unusual demand patterns. This allows organizations to focus on critical issues and take proactive measures to address them.
- Dynamic Pricing and Revenue Optimization: Machine learning algorithms can analyze market dynamics, competitor pricing, demand patterns, and other factors to optimize pricing strategies. By adjusting prices based on real-time demand and supply conditions, organizations can maximize revenue and profitability.
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning algorithms can detect anomalies in inventory transactions, such as fraudulent activities or theft. By continuously monitoring data patterns, machine learning models can identify unusual behaviors and generate alerts, enabling organizations to take timely action.
However, it's important to note that implementing machine learning for intelligent inventory control requires clean and reliable data, robust algorithms, and skilled data scientists or analysts. Organizations should also ensure data privacy and security measures are in place when handling sensitive inventory-related data.
By leveraging machine learning, organizations can make data-driven decisions, optimize inventory levels, improve demand forecasting accuracy, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency in their inventory control processes.
Future Trends: Innovations in Inventory Control for Manufacturing Executives
Inventory control is a critical aspect of manufacturing operations, and as technology continues to advance, innovations are transforming the way inventory is managed.
Manufacturing executives need to stay informed about these trends to ensure they can adapt and leverage the latest solutions for efficient and effective inventory control. Here are some future trends and innovations to watch out for:
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technologies enable real-time tracking of inventory through connected devices and sensors. Manufacturing executives can leverage IoT to gain visibility into inventory levels, location, and condition, allowing for accurate and proactive inventory management.
IoT also facilitates automated data collection, reducing manual efforts and enabling faster decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are revolutionizing inventory control by providing advanced analytics and predictive capabilities. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make accurate demand forecasts.
AI-powered algorithms can also optimize inventory levels, replenishment strategies, and order management, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers transparency and security in supply chain management, including inventory control. By using a decentralized ledger, blockchain can provide a tamper-proof and immutable record of inventory transactions, ensuring trust and preventing fraud.
It can enhance traceability, facilitate authentication, and streamline inventory reconciliation processes.
Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation play a crucial role in inventory control by automating repetitive tasks such as picking, sorting, and inventory tracking. Robotic systems can work alongside human operators, increasing accuracy and efficiency while reducing errors and labor costs.
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can navigate warehouses independently, optimizing inventory movements and streamlining order fulfillment processes.
Predictive Analytics and Demand Sensing: Predictive analytics utilizes historical and real-time data to forecast demand accurately. By incorporating external factors like market trends, social media, and weather patterns, manufacturers can make data-driven decisions and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
Demand sensing techniques, such as point-of-sale data analysis and sentiment analysis, enable faster response to changing customer demands.
Cloud-Based Inventory Management Systems: Cloud-based inventory management systems offer flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. They allow manufacturers to centralize inventory data, collaborate in real time, and gain insights from anywhere.
Cloud-based systems also facilitate integration with other business applications, enabling seamless data flow and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are transforming inventory control by providing visual aids and virtual simulations.
They can assist in warehouse layout optimization, improve inventory visibility through virtual overlays, and enhance training and onboarding processes for inventory management personnel.
Advanced Analytics and Data Visualization: Advanced analytics techniques, such as data mining, predictive modeling, and optimization algorithms, help uncover hidden insights and optimize inventory control strategies.
Coupled with interactive data visualization tools, manufacturing executives can gain actionable insights from complex inventory data and make informed decisions.
Mobile Applications and Wearable Devices: Mobile applications and wearable devices provide on-the-go access to inventory information, allowing manufacturing executives to monitor inventory levels, track shipments, and receive real-time alerts.
These technologies enhance mobility and enable quick decision-making, improving overall inventory control efficiency.
Integration with Supplier and Customer Systems: Seamless integration between inventory control systems and supplier/customer systems enhances supply chain visibility.
By sharing real-time data on inventory levels, demand forecasts, and production schedules, manufacturers can collaborate with suppliers and customers for better coordination, reduced lead times, and optimized inventory management.
As manufacturing executives embrace these future trends and innovations, they can gain a competitive edge by improving inventory control, reducing costs, enhancing customer satisfaction, and optimizing overall supply chain performance.
It is crucial to evaluate the specific needs of the organization and select the most relevant technologies to align with business goals and strategies.
How Deskera Can Assist You?
Deskera ERP and MRP system can help you:
- Manage production plans
- Maintain Bill of Materials
- Generate detailed reports
- Create a custom dashboard
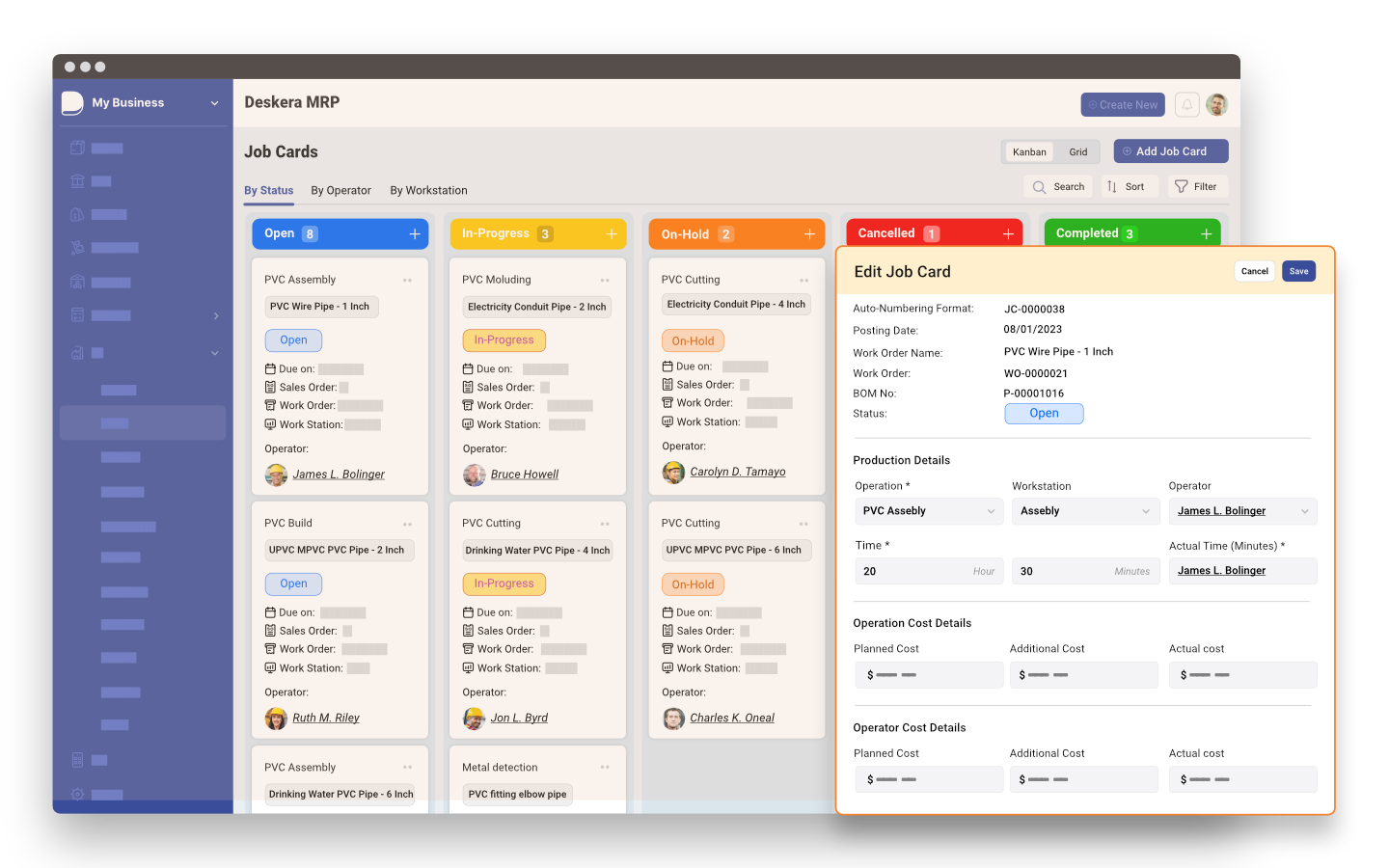
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive system that allows you to maintain inventory, manage suppliers, and track supply chain activity in real-time, as well as streamline a variety of other corporate operations.
Deskera MRP allows you to closely monitor the manufacturing process. From the bill of materials to the production planning features, the solution helps you stay on top of your game and keep your company's competitive edge.
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology not only speeds up payroll processing but also allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more. This is your chance to grow your business, increase earnings, and improve the efficiency of the entire production process.
Conclusion
Effective inventory control is a critical aspect of successful manufacturing operations, and manufacturing executives have a significant role to play in unlocking new opportunities in this field. The rapidly evolving business landscape, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations, has brought about both challenges and opportunities for inventory control in the manufacturing industry.
By embracing innovative strategies and leveraging advanced technologies, manufacturing executives can transform their inventory control practices and unlock new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and profitability.
The key takeaway from this article is that embracing modern inventory control practices is essential for manufacturing executives to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
By adopting real-time inventory tracking systems, implementing demand forecasting models, optimizing warehouse operations, and leveraging data analytics, manufacturing executives can gain valuable insights into their inventory levels, demand patterns, and supply chain dynamics. This enables them to make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and unlock new opportunities for growth and profitability.
By optimizing inventory levels, improving demand forecasting accuracy, and streamlining supply chain processes, manufacturing executives can achieve greater operational efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
By continuously adapting and evolving their inventory control practices, investing in employee development, and staying abreast of industry trends, manufacturing executives can unlock new levels of success and drive their organizations to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Key Takeaways
- Implementing effective demand forecasting models can help manufacturing executives make informed decisions and align inventory levels with customer demand.
- Optimizing warehouse operations, including layout design and process automation, can lead to improved inventory control and operational efficiency.
- Leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling can enable manufacturing executives to anticipate future demand and proactively adjust inventory levels.
- Collaborating with suppliers and implementing supplier management strategies can help optimize inventory levels and reduce lead times.
- Effective communication and collaboration across departments, such as procurement, production, sales, and finance, are essential for successful inventory control.
- Embracing emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) can enhance inventory visibility and enable more accurate demand forecasting.
- Continuous monitoring and analysis of inventory metrics, such as turnover rate, carrying costs, and stockouts, can help identify areas for improvement and cost reduction.
- Implementing just-in-time (JIT) or lean manufacturing principles can help reduce inventory levels while ensuring the timely availability of materials and products.
- Conducting regular inventory audits and cycle counts can help identify discrepancies and maintain accurate inventory records.
- Investing in employee training and development on inventory management best practices and data analysis tools can enhance inventory control capabilities.
Related Articles