Supply Chain Management (SCM) plays a pivotal role in the seamless operation of businesses worldwide, ensuring that products reach consumers efficiently and cost-effectively.
As the backbone of global trade, SCM encompasses the planning, sourcing, manufacturing, delivery, and return of goods. The importance of effective SCM has never been more apparent, especially in today’s fast-paced and interconnected global economy.
In 2020, the global supply chain management market was valued at 15.85 billion U.S. dollars, reflecting its critical role in modern business operations. With the increasing demand for efficiency and technological advancements, this market is expected to nearly double, reaching almost 31 billion U.S. dollars by 2026 (Source: Statista) . This growth highlights the essential nature of robust SCM strategies in driving business success.
Deskera ERP is an all-in-one solution that integrates supply chain management with other crucial business functions such as accounting, inventory management, and human resources.
With advanced features like demand forecasting, production planning, and real-time analytics, Deskera ERP empowers businesses to optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the process of overseeing and managing the flow of goods, services, and information from the initial stages of production to the final delivery to the consumer.
It involves coordinating various activities, including sourcing raw materials, manufacturing products, managing inventory, and ensuring timely delivery. SCM also includes managing relationships with suppliers, distributors, and customers to optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
SCM is a critical aspect of business operations, as it helps companies streamline processes, minimize waste, and respond quickly to changes in demand or supply. By effectively managing the supply chain, businesses can gain a competitive advantage, improve profitability, and ensure that products are delivered to customers on time and in the right condition.
What is Logistics and Supply Chain Management?
Logistics and Supply Chain Management are integral concepts in the movement and management of goods and services, though they address different aspects of the overall process. Both are crucial for ensuring that products are delivered efficiently and effectively from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
Logistics Management
Logistics management is a specialized part of supply chain management that focuses on the planning, execution, and control of the efficient movement and storage of goods, services, and related information.
The primary objective of logistics management is to ensure that the right products reach the right customers at the right time, in the right condition, and at the lowest possible cost.
Central to logistics management is transportation, which involves selecting the best modes of transport—whether by road, rail, air, or sea—to move goods from suppliers to production facilities and from warehouses to customers. This process must ensure timely delivery while optimizing costs and minimizing risks.
Warehousing and storage are also crucial elements, as they involve managing the storage of goods in warehouses to ensure efficient space utilization and easy access for order fulfillment.
Effective inventory management plays a vital role here, maintaining the right amount of inventory to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs. This includes tracking and managing inventory levels, orders, and stock locations.
Order fulfillment is another critical aspect, involving the accurate processing, picking, packing, and shipping of customer orders. Packaging and handling ensure that products are protected during transport and storage, minimizing damage and losses.
Finally, logistics network design focuses on optimizing the logistics network, including the location of warehouses, distribution centers, and transportation routes, to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Supply Chain Management is a broader, more comprehensive concept that encompasses the entire process of producing and delivering a product or service. SCM covers everything from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product to the customer.
It integrates various processes across the entire supply chain, including suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers, with the aim of optimizing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction.
SCM begins with planning, which involves demand forecasting, production planning, and inventory management to align supply with customer demand. Sourcing follows, focusing on selecting suppliers, procuring raw materials and components, and managing supplier relationships to ensure quality and reliability. Manufacturing is then concerned with transforming raw materials into finished products, ensuring quality control and process optimization throughout.
Logistics, while a component of SCM, takes on a broader role in this context, encompassing the transportation, warehousing, and distribution of goods to ensure efficient movement through the supply chain.
Order fulfillment within SCM manages the entire process of receiving, processing, and delivering customer orders, ensuring customer satisfaction. SCM also includes return management, which handles the return of products from customers, including reverse logistics, refurbishment, and recycling to recover value and minimize waste.
A key aspect of SCM is integration, where activities across the entire supply chain—from suppliers to customers—are coordinated and integrated using technology and collaboration to enhance efficiency and visibility.
Relationship Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Logistics is a crucial part of Supply Chain Management, focusing specifically on the movement, storage, and flow of goods. In contrast, Supply Chain Management encompasses a broader range of activities, including sourcing, production, and overall strategy, integrating all these processes to ensure that products are delivered efficiently and meet customer demands.
Importance of Logistics and SCM
Both logistics and SCM are vital for reducing costs, improving efficiency, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Effective management of both ensures that products are delivered on time, in good condition, and at the right cost, which is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
In summary, while logistics management focuses on the movement and storage of goods, supply chain management takes a broader approach, integrating all aspects of the production and delivery process to optimize efficiency and meet customer demands.
Components of Supply Chain Management
The components of Supply Chain Management (SCM) are essential building blocks that ensure the smooth and efficient flow of goods, information, and finances across the supply chain. These components work together to create a cohesive and responsive system. Here are the key components:
1. Planning
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting customer demand to align production and inventory levels accordingly.
- Resource Planning: Allocating resources such as materials, labor, and equipment to meet production goals.
- Inventory Management: Managing stock levels to ensure adequate supply while minimizing costs.
2. Sourcing
- Supplier Selection: Identifying and evaluating suppliers that can provide the required raw materials or components.
- Procurement Strategies: Establishing contracts and procurement practices to secure the best prices and terms.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Maintaining strong relationships with suppliers to ensure reliability and quality.
3. Manufacturing
- Production Processes: Converting raw materials into finished products through efficient manufacturing techniques.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet the required standards and specifications.
- Efficiency Optimization: Continuously improving manufacturing processes to reduce waste and increase productivity.
4. Delivery
- Logistics Management: Coordinating the movement of goods from production facilities to warehouses and customers.
- Distribution Network: Designing and managing the network of warehouses, distribution centers, and transportation systems.
- Transportation Management: Selecting and managing transportation modes to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery.
5. Return
- Reverse Logistics: Managing the return of goods from customers, including handling returns, recycling, or disposal.
- Sustainability Practices: Implementing environmentally friendly practices in the return process, such as recycling and reducing waste.
- Customer Service: Ensuring that the return process is smooth and that customer satisfaction is maintained.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall effectiveness of the supply chain, contributing to a system that is responsive, efficient, and capable of meeting customer needs.
What is the Supply Chain Management Process?
The Supply Chain Management (SCM) process encompasses the planning, implementation, and control of operations related to the movement and storage of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. The goal of this process is to maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and meet customer demand effectively.
Here's an overview of the key steps in the SCM process:
1. Planning
- Demand Forecasting: Anticipating customer demand to determine the quantity of products needed, ensuring the right balance between supply and demand.
- Capacity Planning: Assessing the production capacity required to meet demand and adjusting resources accordingly.
- Inventory Planning: Determining the optimal levels of inventory to maintain, ensuring sufficient stock while minimizing holding costs.
- Supply Planning: Identifying the required raw materials, components, and suppliers to meet production goals.
2. Sourcing
- Supplier Selection: Identifying and selecting suppliers that meet the company’s requirements for cost, quality, reliability, and delivery time.
- Procurement: Acquiring the necessary materials, goods, and services from selected suppliers, including negotiating contracts and managing relationships.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Building and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers to ensure consistent supply, quality, and performance.
3. Manufacturing/Production
- Production Scheduling: Planning and controlling the production process to ensure that products are manufactured efficiently and meet quality standards.
- Quality Control: Implementing quality assurance measures throughout the production process to ensure that finished products meet specifications and customer expectations.
- Process Optimization: Continuously improving production processes to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and lower costs.
4. Inventory Management
- Inventory Control: Monitoring and managing inventory levels to avoid overstocking or stockouts, ensuring that the right products are available when needed.
- Warehouse Management: Overseeing the storage, handling, and distribution of goods in warehouses, ensuring efficient space utilization and order fulfillment.
- Order Fulfillment: Processing customer orders accurately and efficiently, ensuring timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
5. Logistics and Distribution
- Transportation Management: Planning and executing the movement of goods from suppliers to production facilities, and from warehouses to customers, using various transportation modes (e.g., truck, ship, air).
- Distribution Management: Managing the distribution network to ensure that products are delivered to the right locations at the right time.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Coordinating the final stage of delivery, from distribution centers to the end customer, ensuring timely and efficient service.
6. Return Management
- Reverse Logistics: Managing the process of returning goods from customers, including handling returns, refurbishments, and recycling.
- Return Policies: Establishing clear return policies and processes to handle customer returns efficiently and maintain customer satisfaction.
- Recovery and Disposal: Managing the recovery of value from returned products through refurbishment, resale, or environmentally friendly disposal.
7. Monitoring and Performance Measurement
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Tracking and analyzing KPIs such as order accuracy, on-time delivery, inventory turnover, and production efficiency to assess supply chain performance.
- Continuous Improvement: Using performance data to identify areas for improvement, implementing changes, and refining processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
- Risk Management: Continuously monitoring and managing risks within the supply chain to mitigate potential disruptions and ensure business continuity.
8. Integration and Collaboration
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Ensuring that all departments involved in the supply chain, such as procurement, production, logistics, and sales, work together seamlessly.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing advanced technologies, such as ERP systems, supply chain management software, and IoT, to integrate and automate supply chain processes.
- Supplier and Partner Collaboration: Collaborating closely with suppliers, logistics providers, and other partners to optimize the entire supply chain and ensure alignment with business objectives.
Key Objectives of Supply Chain Management
The key objectives of Supply Chain Management (SCM) are crucial for optimizing the performance and efficiency of the entire supply chain. These objectives ensure that businesses can meet customer demands while controlling costs and improving overall operational effectiveness.
Here are the primary objectives:
1. Cost Reduction
- Minimizing Operational Costs: Streamlining processes to reduce expenses associated with production, transportation, and inventory management.
- Optimizing Resource Utilization: Efficiently managing resources such as labor, materials, and equipment to lower costs.
2. Improved Efficiency
- Streamlining Processes: Enhancing the efficiency of supply chain activities to minimize delays and bottlenecks.
- Reducing Lead Times: Shortening the time required to move products from suppliers to customers, thus improving overall responsiveness.
3. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- Timely Delivery: Ensuring that products are delivered to customers on time and in the right condition.
- Quality Assurance: Maintaining high standards for product quality to meet or exceed customer expectations.
4. Flexibility and Adaptability
- Responding to Market Changes: Quickly adjusting to shifts in demand, supply disruptions, or changes in market conditions.
- Managing Risks: Identifying and mitigating potential risks to maintain continuity and resilience in the supply chain.
5. Inventory Management
- Optimizing Stock Levels: Balancing inventory levels to avoid stockouts and excess inventory, which can tie up capital and increase costs.
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting future demand to align inventory levels with actual needs.
6. Strategic Alignment
- Aligning Supply Chain with Business Goals: Ensuring that supply chain strategies and operations support the overall objectives and strategies of the business.
- Integrating with Other Functions: Coordinating SCM activities with other business functions such as marketing, finance, and operations.
7. Sustainability and Compliance
- Environmental Responsibility: Implementing practices that reduce environmental impact, such as reducing waste and energy consumption.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to industry regulations and standards to avoid legal issues and ensure ethical practices.
By focusing on these objectives, businesses can achieve a more effective and responsive supply chain that supports their overall success and competitive advantage.
The Role of Technology in Supply Chain Management
Technology plays a transformative role in Supply Chain Management (SCM), enhancing efficiency, visibility, and decision-making across the entire supply chain. Here’s how technology impacts SCM:
1. Enhanced Visibility and Tracking
- Real-Time Data: Technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) and GPS tracking provide real-time visibility into the movement and status of goods, enabling better tracking and management of shipments.
- Advanced Analytics: Data analytics tools analyze large volumes of data to provide insights into supply chain performance, helping businesses identify trends, predict demand, and make informed decisions.
2. Automation and Efficiency
- Automated Processes: Robotics and automation technologies streamline repetitive tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting, reducing manual labor and increasing accuracy.
- Smart Warehousing: Automated warehousing systems and robotics enhance inventory management, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency in warehouse operations.
3. Improved Forecasting and Planning
- Demand Forecasting Tools: Advanced forecasting algorithms and machine learning models predict future demand more accurately, helping businesses align production and inventory levels with market needs.
- Supply Chain Planning Software: Integrated planning tools optimize resource allocation, production scheduling, and inventory management, ensuring that supply chain activities are synchronized with business goals.
4. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
- ERP Systems: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate various business functions, including supply chain management, into a unified platform, facilitating seamless communication and coordination between departments and partners.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud technologies enable real-time sharing of information and collaboration among supply chain partners, improving responsiveness and reducing the risk of disruptions.
5. Risk Management and Resilience
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics tools assess potential risks and vulnerabilities in the supply chain, allowing businesses to proactively address issues before they impact operations.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in the supply chain by providing an immutable record of transactions, which helps prevent fraud and ensure authenticity.
6. Sustainability and Compliance
- Green Technologies: Technologies that promote sustainability, such as energy-efficient transportation solutions and waste reduction systems, help businesses minimize their environmental impact and comply with regulations.
- Compliance Monitoring: Compliance management software ensures that supply chain practices adhere to legal and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
7. Customer Experience and Service
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM systems integrate with supply chain operations to provide better service and personalized experiences by tracking customer preferences and order histories.
- Omni-Channel Integration: Technologies enable businesses to manage multiple sales channels seamlessly, providing a consistent and efficient experience for customers across online and offline touchpoints.
By leveraging these technologies, businesses can optimize their supply chain operations, improve overall performance, and achieve a competitive edge in the market.
Challenges in Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) faces numerous challenges that can disrupt operations, increase costs, and negatively impact customer satisfaction. Here are some of the key challenges in SCM:
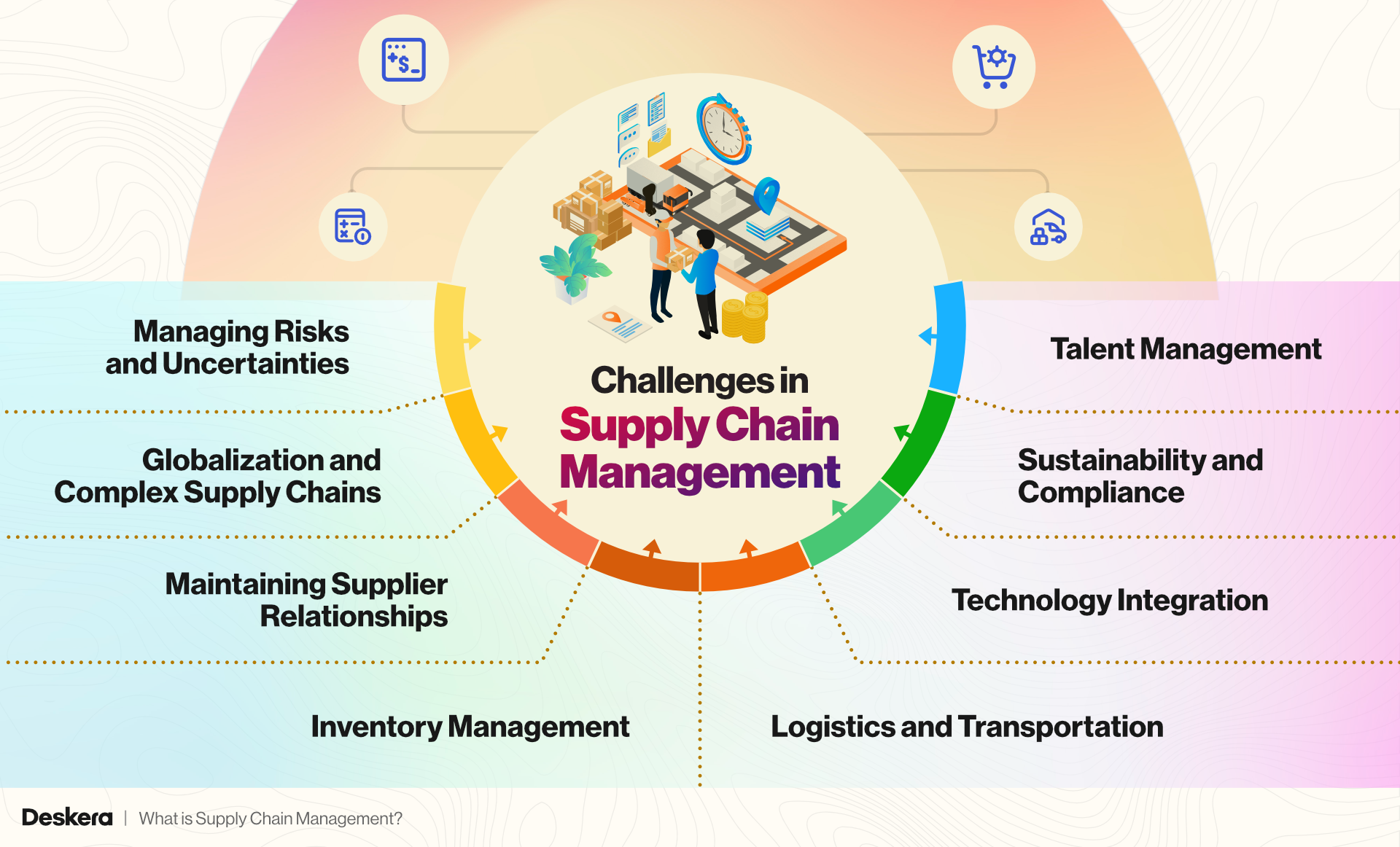
1. Managing Risks and Uncertainties
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, political instability, and pandemics can disrupt supply chains, leading to delays, increased costs, and shortages of critical materials.
- Demand Volatility: Fluctuating customer demand makes it challenging to forecast accurately, leading to overproduction or stockouts.
- Supplier Reliability: Dependence on a limited number of suppliers can create vulnerabilities if a supplier fails to deliver on time or meets quality standards.
2. Globalization and Complex Supply Chains
- Complex Network Management: As supply chains become more global, managing the complexity of multiple suppliers, manufacturers, and distribution channels across different countries becomes increasingly difficult.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Navigating different cultural practices, regulations, and trade laws across regions can create compliance challenges and affect the flow of goods.
3. Maintaining Supplier Relationships
- Communication Barriers: Poor communication with suppliers can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and quality issues.
- Supplier Performance Management: Ensuring that suppliers meet performance standards, such as on-time delivery and product quality, requires ongoing monitoring and collaboration.
- Negotiation Challenges: Balancing cost efficiency with maintaining good relationships with suppliers can be difficult, especially when negotiating contracts and prices.
4. Inventory Management
- Balancing Inventory Levels: Maintaining the right amount of inventory is challenging, as holding too much can increase costs, while holding too little can lead to stockouts and lost sales.
- Obsolescence: In industries with rapid product cycles, managing inventory to prevent obsolescence is crucial, as outdated products can lead to significant financial losses.
- Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting is difficult but essential for managing inventory levels effectively.
5. Logistics and Transportation
- Transportation Costs: Rising fuel prices, labor costs, and regulatory fees can increase transportation costs, affecting the overall cost structure of the supply chain.
- Delivery Delays: Unpredictable factors such as weather, traffic, and customs clearance can cause delivery delays, impacting customer satisfaction.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Managing the complexities of last-mile delivery, especially in urban areas, can be challenging and expensive.
6. Technology Integration
- Legacy Systems: Many companies still rely on outdated legacy systems that are not integrated with modern SCM technologies, creating inefficiencies and data silos.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As supply chains become more digital, they are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks that can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data.
- Data Management: The sheer volume of data generated by modern supply chains can be overwhelming, and managing this data to extract actionable insights is a significant challenge.
7. Sustainability and Compliance
- Environmental Impact: Meeting sustainability goals while managing costs and maintaining efficiency is a growing challenge, as consumers and regulators demand greener practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to an ever-increasing array of regulations across different regions requires constant monitoring and adaptation, which can be resource-intensive.
8. Talent Management
- Skills Shortage: The growing complexity of supply chains requires specialized skills, but there is often a shortage of qualified professionals with the necessary expertise.
- Employee Retention: Retaining skilled workers in a competitive job market is challenging, particularly in roles that require high levels of technical knowledge and experience.
- Training and Development: Continuously training and upskilling employees to keep pace with technological advancements and industry changes is essential but resource-intensive.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach, leveraging technology, fostering strong supplier relationships, and continuously adapting to the evolving landscape of global supply chains.
Benefits of Effective Supply Chain Management
Effective Supply Chain Management (SCM) offers numerous benefits that enhance a company's overall performance and competitiveness. Here are the key benefits:
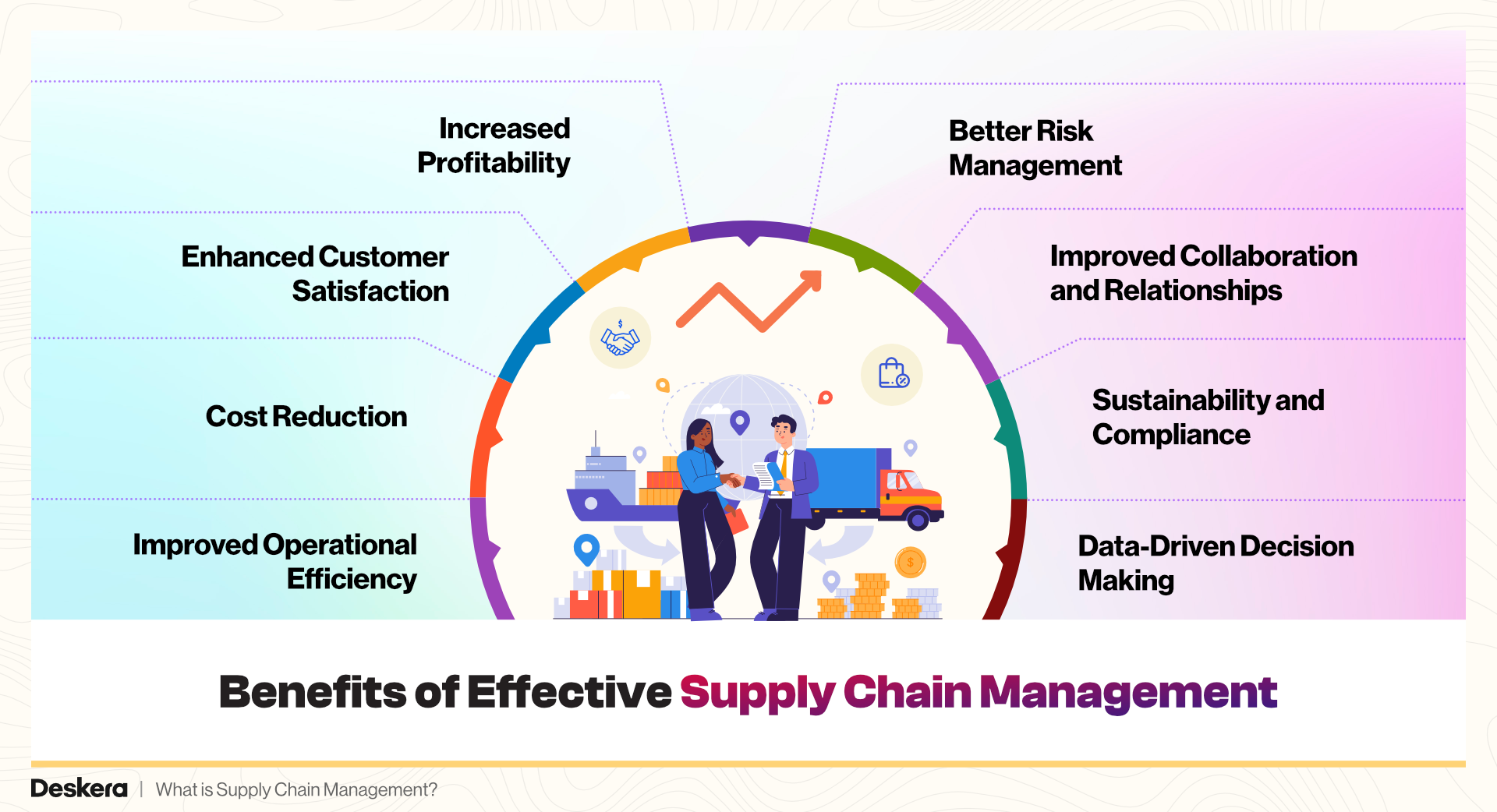
1. Improved Operational Efficiency
- Streamlined Processes: Effective SCM optimizes the flow of goods, information, and finances, reducing delays and inefficiencies across the supply chain.
- Reduced Waste: By closely monitoring and managing resources, companies can minimize waste, including excess inventory and overproduction.
- Better Resource Utilization: Efficient SCM ensures that materials, labor, and equipment are used effectively, maximizing productivity and reducing costs.
2. Cost Reduction
- Lower Operational Costs: By optimizing procurement, production, and logistics processes, companies can significantly reduce their operating costs.
- Inventory Cost Savings: Effective inventory management prevents overstocking and understocking, reducing storage costs and minimizing capital tied up in inventory.
- Transportation Savings: Optimized logistics and transportation management lead to lower shipping costs and more efficient distribution.
3. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- Timely Delivery: Effective SCM ensures that products are delivered to customers on time, meeting or exceeding their expectations.
- Product Quality: By maintaining high standards throughout the supply chain, companies can deliver products that consistently meet quality requirements, leading to increased customer trust and customer loyalty.
- Responsive Service: A well-managed supply chain allows companies to respond quickly to customer inquiries, order changes, and market shifts, improving overall customer service.
4. Increased Profitability
- Revenue Growth: Efficient SCM enables faster time-to-market, allowing companies to capitalize on market opportunities and increase sales.
- Margin Improvement: Cost savings achieved through effective SCM translate directly into higher profit margins.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with well-managed supply chains can offer better prices, higher quality, and faster service, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
5. Better Risk Management
- Proactive Risk Identification: Effective SCM includes robust risk management practices that identify potential disruptions and vulnerabilities before they impact operations.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Companies with strong SCM practices can quickly adapt to disruptions, minimizing their impact and maintaining continuity in operations.
- Supplier Diversification: By managing a diversified supplier base, companies reduce their dependence on a single supplier, mitigating risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
6. Improved Collaboration and Relationships
- Stronger Supplier Relationships: Effective SCM fosters closer collaboration with suppliers, leading to better terms, improved quality, and more reliable supply.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Integrated SCM systems enhance communication and collaboration between different departments, ensuring alignment with overall business goals.
- Enhanced Partner Collaboration: A well-coordinated supply chain allows for better collaboration with logistics providers, distributors, and other partners, leading to smoother operations and shared efficiencies.
7. Sustainability and Compliance
- Environmental Benefits: By optimizing resource use and reducing waste, effective SCM supports sustainability goals and reduces the environmental impact of business operations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Well-managed supply chains are more likely to comply with industry regulations and standards, avoiding costly penalties and ensuring ethical practices.
8. Data-Driven Decision Making
- Informed Decisions: Effective SCM leverages data analytics to provide insights into supply chain performance, helping managers make informed decisions that drive continuous improvement.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced SCM systems allow for real-time tracking and monitoring of supply chain activities, enabling quicker responses to changes and issues.
By focusing on effective SCM, businesses can enhance their overall operational performance, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and build a sustainable competitive advantage in the marketplace.
What is Supply Chain Risk Management?
Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks within the supply chain to ensure continuity and resilience in operations.
These risks can stem from various sources, including suppliers, logistics providers, natural disasters, geopolitical events, market fluctuations, and internal inefficiencies.
The goal of SCRM is to minimize the impact of these risks on the supply chain, thereby protecting the business from potential disruptions, financial losses, and damage to its reputation.
Key Aspects of Supply Chain Risk Management
The key aspects of supply chain risk management are:
Risk Identification
- Mapping the Supply Chain: Understanding the entire supply chain, including all suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and distribution channels, to identify potential risk points.
- Risk Categorization: Classifying risks into categories such as operational, financial, environmental, geopolitical, and cyber risks to better understand their nature and potential impact.
Risk Assessment
- Probability and Impact Analysis: Evaluating the likelihood of each identified risk occurring and its potential impact on the supply chain.
- Prioritization: Ranking risks based on their severity and the urgency of addressing them, allowing businesses to focus on the most critical threats.
Risk Mitigation
- Diversification: Reducing reliance on a single supplier or region by diversifying sources and creating alternative supply routes.
- Contingency Planning: Developing backup plans, such as alternative suppliers, emergency stockpiles, or flexible production processes, to quickly respond to disruptions.
- Contractual Safeguards: Including clauses in contracts with suppliers and partners to address potential risks, such as penalties for late deliveries or quality issues.
Risk Monitoring
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing systems to continuously monitor supply chain activities and external factors, allowing for early detection of potential risks.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conducting periodic audits of suppliers and partners to ensure compliance with standards and identify emerging risks.
Collaboration and Communication
- Partner Collaboration: Working closely with suppliers, logistics providers, and other partners to share risk information and develop joint risk mitigation strategies.
- Internal Coordination: Ensuring that all departments within the organization, including procurement, logistics, finance, and legal, are aligned in their risk management efforts.
Crisis Management and Recovery
- Emergency Response Plans: Having clear plans in place to respond to and manage crises, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or supplier failures, to minimize downtime and disruption.
- Post-Disruption Recovery: Strategies to quickly restore normal operations after a disruption, including reassessing risks and making necessary adjustments to prevent future issues.
Benefits of Supply Chain Risk Management
- Enhanced Resilience: SCRM helps businesses build more resilient supply chains that can withstand disruptions and continue to operate effectively.
- Cost Savings: By proactively managing risks, companies can avoid the high costs associated with supply chain disruptions, such as lost sales, expedited shipping fees, and reputational damage.
- Improved Decision-Making: SCRM provides the data and insights needed to make informed decisions about sourcing, logistics, and other supply chain activities.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with strong SCRM practices can respond more quickly to market changes and disruptions, gaining an edge over competitors.
By implementing effective SCRM, businesses can safeguard their supply chains, ensuring they remain agile, responsive, and capable of meeting customer demands even in the face of unforeseen challenges.
What is Supply Chain Management in eCommerce?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) in e-commerce refers to the coordination and management of all activities involved in the flow of goods, services, information, and finances across the entire supply chain, specifically tailored for online businesses.
In the context of e-commerce, SCM plays a crucial role in ensuring that products are delivered to customers efficiently, quickly, and cost-effectively.
Key Aspects of Supply Chain Management in E-Commerce
The key aspects of supply chain management in eCommerce are:
Order Processing and Fulfillment: In e-commerce, order processing and fulfillment are critical, as they involve receiving online orders, processing them quickly, and ensuring timely delivery to customers. Efficient SCM ensures that the order fulfillment process is streamlined, reducing delays and errors.
Inventory Management: Managing inventory in e-commerce involves maintaining the right balance of stock to meet customer demand without overstocking.
SCM helps in optimizing inventory levels by using data-driven approaches like demand forecasting and just-in-time inventory, which reduce holding costs and minimize stockouts.
Warehouse Management: E-commerce businesses often rely on multiple warehouses located strategically to ensure fast delivery. SCM in e-commerce involves optimizing warehouse operations, such as picking, packing, and shipping, to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Automation and advanced technologies like warehouse management systems (WMS) play a significant role in this process.
Transportation and Logistics: Transportation and logistics are vital components of e-commerce SCM, as they determine how quickly and cost-effectively products are delivered to customers.
This includes choosing the right shipping carriers, optimizing delivery routes, and managing last-mile delivery. E-commerce businesses often need to manage complex logistics networks to meet customer expectations for fast shipping.
Supplier and Vendor Management: E-commerce businesses rely on a network of suppliers and vendors for their products.
SCM involves managing relationships with these suppliers to ensure consistent quality, timely deliveries, and cost efficiency.
Effective SCM helps in building strong partnerships with suppliers, enabling better negotiation and collaboration.
Technology Integration: E-commerce SCM heavily relies on technology to manage and optimize supply chain operations. This includes using integrated software systems like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supply Chain Management Systems (SCMS) to provide real-time data, automate processes, and improve decision-making.
Technology also enables better visibility across the supply chain, helping e-commerce businesses respond quickly to changes in demand or supply disruptions.
Customer Experience: In e-commerce, customer experience is a critical factor in success. SCM directly impacts customer satisfaction by ensuring that orders are delivered on time, products are available when needed, and returns are handled efficiently.
Effective SCM also supports personalized customer experiences, such as offering multiple shipping options, tracking orders in real-time, and providing easy return processes.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing: E-commerce businesses are increasingly focusing on sustainability in their supply chains. This includes sourcing products ethically, reducing carbon footprints in transportation, and using eco-friendly packaging. SCM plays a key role in implementing and managing sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
Importance of SCM in E-Commerce
Supply Chain Management is vital for e-commerce businesses as it directly influences operational efficiency, cost management, and customer satisfaction. A well-managed supply chain enables e-commerce companies to:
- Reduce Operational Costs: By optimizing inventory, transportation, and warehouse operations, businesses can lower costs and increase profitability.
- Enhance Customer Satisfaction: Timely deliveries, accurate orders, and easy returns lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improve Scalability: Effective SCM allows e-commerce businesses to scale operations smoothly, handling increased order volumes without compromising on quality or speed.
- Increase Flexibility: A robust supply chain can adapt to market changes, new product launches, and varying customer demands with minimal disruption.
In summary, Supply Chain Management in e-commerce is the backbone of online retail operations, ensuring that products are delivered efficiently from suppliers to customers while maintaining a focus on cost-effectiveness, customer satisfaction, and sustainability.
Tips to Improve Supply Chain Management
Improving Supply Chain Management (SCM) is crucial for enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and boosting customer satisfaction.
Here are some key tips to improve SCM:
1. Embrace Technology and Automation
- Implement SCM Software: Use advanced SCM software to automate and optimize supply chain operations. This includes inventory management, order processing, and logistics.
- Leverage Data Analytics: Utilize data analytics to gain insights into supply chain performance, forecast demand, and identify areas for improvement.
- Adopt IoT and AI: Integrate Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, and decision-making.
2. Enhance Supplier Collaboration
- Strengthen Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers through regular communication, collaboration, and long-term partnerships.
- Supplier Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor supplier performance using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to ensure reliability and quality.
- Diversified Supplier Base: Reduce risk by diversifying your supplier base, ensuring that you have multiple sources for critical materials and components.
3. Optimize Inventory Management
- Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Adopt JIT inventory practices to reduce holding costs and minimize waste by receiving goods only when needed.
- Use Demand Forecasting: Utilize advanced forecasting techniques to predict customer demand accurately, allowing for better inventory planning and management.
- Regular Inventory Audits: Conduct regular inventory audits to ensure accuracy and identify discrepancies early.
4. Improve Logistics and Transportation
- Route Optimization: Use route optimization software to reduce transportation costs, improve delivery times, and enhance fuel efficiency.
- Use Third-Party Logistics (3PL): Consider outsourcing logistics to 3PL providers who can offer specialized services and expertise.
- Focus on Last-Mile Delivery: Optimize last-mile delivery by implementing strategies like local warehousing, delivery drones, or crowd-sourced delivery models.
5. Increase Supply Chain Visibility
- Real-Time Tracking: Implement real-time tracking systems to monitor the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, enabling quick responses to any disruptions.
- Blockchain Technology: Consider using blockchain for greater transparency and traceability in the supply chain, ensuring the authenticity and origin of products.
- Collaborative Platforms: Use collaborative platforms that allow all stakeholders, including suppliers and logistics providers, to share information and coordinate activities seamlessly.
6. Focus on Sustainability
- Sustainable Sourcing: Source materials and products from sustainable and ethical suppliers to reduce environmental impact and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
- Reduce Carbon Footprint: Optimize transportation routes, use eco-friendly packaging, and adopt green logistics practices to minimize the supply chain’s carbon footprint.
- Implement Circular Economy Practices: Embrace the circular economy by focusing on recycling, reusing, and refurbishing products to extend their lifecycle.
7. Enhance Risk Management
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Regularly assess potential risks in the supply chain, including natural disasters, geopolitical issues, and supplier bankruptcies.
- Develop Contingency Plans: Create contingency plans for various scenarios, such as supplier failures or transportation disruptions, to ensure business continuity.
- Insurance Coverage: Ensure adequate insurance coverage for different aspects of the supply chain, including inventory, transportation, and supplier reliability.
8. Invest in Workforce Training
- Continuous Learning: Provide ongoing training for employees involved in supply chain management to keep them updated on the latest tools, technologies, and best practices.
- Cross-Functional Skills: Encourage cross-functional training to improve collaboration and understanding between different departments, such as procurement, logistics, and sales.
- Empower Decision-Making: Empower employees with the tools and authority to make quick, informed decisions that can improve supply chain efficiency.
9. Measure and Monitor Performance
- Use KPIs: Establish clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your supply chain operations, such as order accuracy, delivery times, and cost efficiency.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of supply chain performance to identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes.
- Benchmarking: Compare your supply chain performance against industry standards and competitors to identify opportunities for improvement.
10. Improve Customer Communication
- Transparent Order Tracking: Provide customers with real-time tracking information and updates on their orders to enhance trust and satisfaction.
- Feedback Loops: Implement feedback loops that allow customers to provide input on delivery performance, product quality, and overall satisfaction, helping you identify areas for improvement.
- Proactive Issue Resolution: Address potential issues proactively by communicating with customers in advance about delays, stock shortages, or other disruptions.
By implementing these tips, businesses can significantly enhance their supply chain management processes, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and a more resilient and customer-centric supply chain.
How Can Deskera ERP Help You With Supply Chain Management?
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive software solution that offers powerful tools for effective Supply Chain Management (SCM). It integrates various processes across the supply chain, helping businesses manage everything from procurement to inventory, production, and distribution.
Here’s how Deskera ERP can assist with SCM:
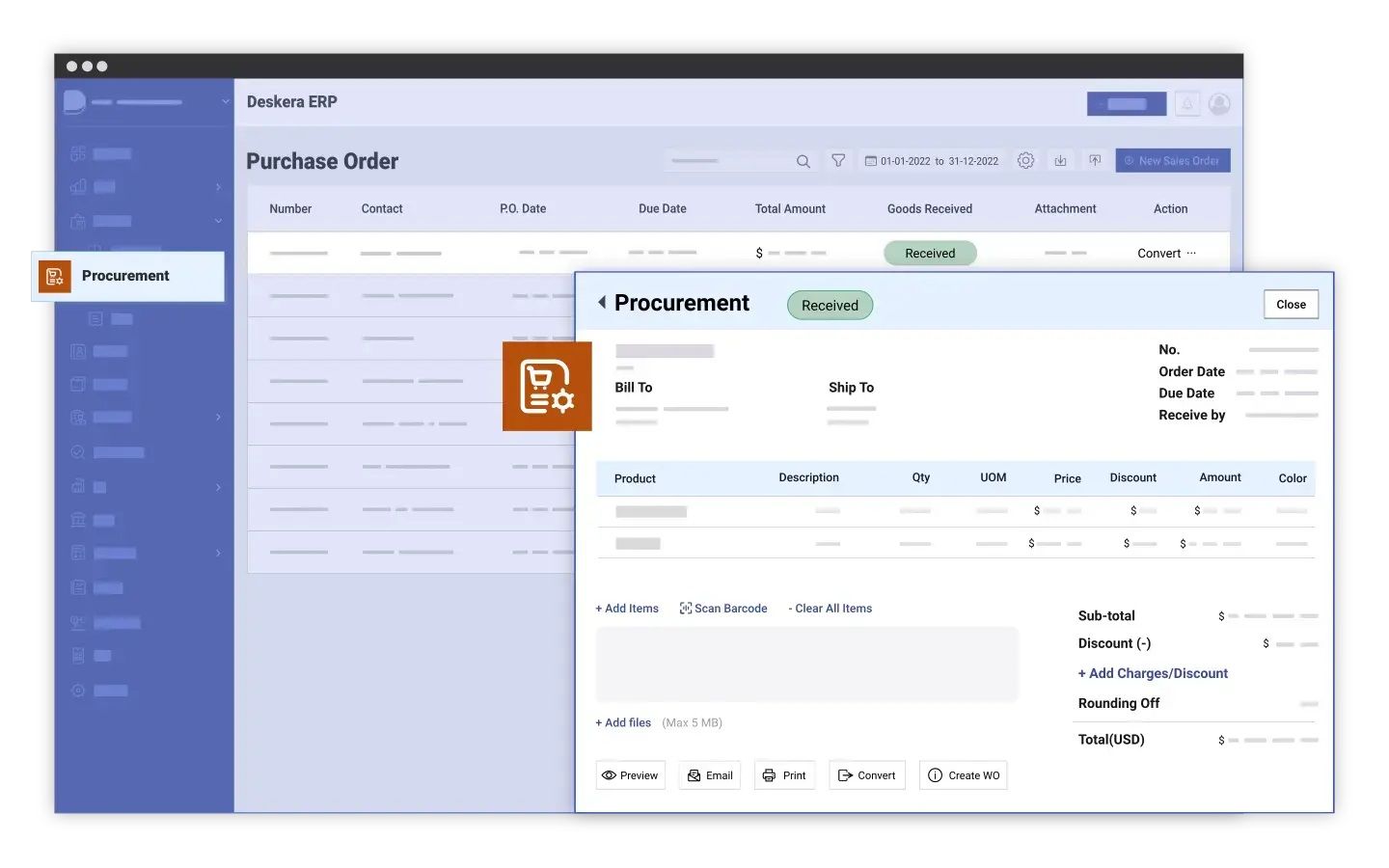
1. Streamlined Procurement and Vendor Management
- Automated Purchase Orders: Deskera ERP automates the creation of purchase orders based on inventory levels, demand forecasts, or production needs, ensuring that you always have the right materials when needed.
- Supplier Management: The platform allows you to manage and evaluate suppliers, track performance, and maintain strong relationships, helping you secure better terms and ensure reliable deliveries.
2. Efficient Inventory Management
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Deskera ERP provides real-time visibility into your inventory levels across multiple locations, helping you avoid stockouts and overstocking.
- Demand Forecasting: With built-in forecasting tools, you can predict demand more accurately, enabling better inventory planning and reducing the risk of excess or obsolete stock.
- Just-in-Time Inventory: The software supports just-in-time inventory practices by aligning procurement and production schedules with demand, minimizing holding costs and waste.
3. Optimized Production Planning
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Deskera ERP’s MRP feature helps you plan and optimize production by ensuring that the necessary materials are available when needed, reducing production delays.
- Production Scheduling: The platform allows you to schedule production runs efficiently, manage resources, and track work orders, leading to better use of manufacturing capacity and reduced lead times.
4. Enhanced Logistics and Distribution
- Warehouse Management: Deskera ERP includes robust warehouse management tools that help you optimize space utilization, streamline picking and packing processes, and reduce errors in order fulfillment.
- Shipping and Delivery Tracking: The software integrates with various shipping providers, allowing you to manage and track shipments from within the platform. This ensures timely deliveries and enhances customer satisfaction.
5. Improved Supply Chain Visibility
- Integrated Platform: Deskera ERP provides a single, integrated platform that connects all parts of your supply chain, from procurement to production, inventory, and distribution, offering a comprehensive view of operations.
- Real-Time Data and Reporting: The platform offers real-time data and reporting capabilities, allowing you to monitor key metrics, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions quickly.
- Supply Chain Analytics: Deskera ERP includes powerful analytics tools that help you analyze supply chain performance, track trends, and identify opportunities for improvement.
6. Risk Management and Compliance
- Compliance Management: The software helps ensure that your supply chain processes comply with industry regulations and standards, reducing the risk of penalties and improving operational transparency.
- Risk Mitigation: Deskera ERP allows you to assess and manage risks within the supply chain, such as supplier reliability, inventory shortages, and logistical challenges. By providing real-time insights, it enables you to respond proactively to potential disruptions.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
- Scalable Solutions: Deskera ERP is scalable, meaning it can grow with your business. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, the platform can be customized to meet your specific supply chain management needs.
- Cloud-Based Accessibility: Being a cloud-based solution, Deskera ERP offers the flexibility to access your supply chain data from anywhere, enabling remote management and collaboration across teams and locations.
8. Enhanced Collaboration
- Collaborative Tools: Deskera ERP facilitates collaboration between different departments and supply chain partners, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and working towards common goals.
- Communication and Workflow Automation: The platform automates communication and workflows, reducing the chances of errors and delays, and ensuring smooth coordination across the supply chain.
9. Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
- Process Automation: Deskera ERP automates routine supply chain processes, reducing manual labor, minimizing errors, and cutting operational costs.
- Resource Optimization: By providing insights into inventory, production, and logistics, Deskera ERP helps you optimize the use of resources, leading to cost savings and efficiency improvements.
Key Takeaways
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is a fundamental aspect of modern business operations, encompassing the comprehensive coordination of activities involved in producing and delivering products from suppliers to customers.
- End-to-End Coordination: Supply Chain Management (SCM) encompasses the entire process of producing and delivering a product or service, from sourcing raw materials to final delivery to customers. It involves the integration and coordination of various activities to ensure efficiency and effectiveness across the supply chain.
- Key Components: SCM includes several critical components such as procurement, inventory management, production planning, logistics, and order fulfillment. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that products are delivered to customers on time and at the right cost.
- Objectives of SCM: The primary objectives of SCM are to reduce operational costs, enhance efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ensure smooth, uninterrupted operations. Effective SCM aims to align supply and demand, optimize resource utilization, and minimize risks.
- Technological Integration: Technology plays a crucial role in modern SCM, with tools such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, data analytics, and real-time tracking helping businesses manage their supply chains more effectively. Technologies enhance visibility, automate processes, and improve decision-making.
- Challenges and Risks: SCM faces various challenges, including managing supply chain disruptions, maintaining inventory levels, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Effective risk management and contingency planning are essential to address these challenges and ensure continuity.
- Benefits of Effective SCM: A well-managed supply chain can lead to significant benefits, including cost reductions, improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and greater scalability. Businesses that excel in SCM can gain a competitive advantage by meeting customer demands more effectively and efficiently.
In summary, supply chain management is a comprehensive discipline that involves managing the flow of goods and services across the entire supply chain. By focusing on key components, leveraging technology, addressing challenges, and aiming for specific objectives, businesses can optimize their supply chains and achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive suite of tools that can significantly improve supply chain management by enhancing visibility, optimizing processes, reducing costs, and ultimately delivering better customer experiences.
Related Articles














