In today’s fast-paced and highly interconnected business environment, traditional planning methods often fall short. Siloed functions, outdated forecasts, and reactive strategies lead to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. That’s where Integrated Business Planning (IBP) steps in. By aligning strategic, financial, and operational planning across departments, IBP enables businesses to make smarter decisions, respond to change faster, and operate more efficiently.
The impact of mature IBP processes is measurable. Organizations adopting advanced IBP practices have seen a 1–2 percentage point increase in EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) and up to 40–50% reductions in delivery penalties and missed sales. Moreover, IBP helps cut freight costs and capital intensity by 10–15%, driving not just operational performance, but also financial growth. Enhanced planning leads to 5–20 percentage point improvements in service levels, making companies more reliable partners in the supply chain.
IBP also boosts internal efficiency. According to McKinsey, businesses implementing IBP can improve planner productivity by 10–20%, while o9 Solutions reports that it can reduce time spent on forecasting by 32%, freeing up resources for more strategic initiatives. These gains highlight why more companies are moving toward an integrated approach—breaking down departmental silos and unifying planning efforts under one coordinated framework.
Deskera ERP supports this transformation by offering a fully integrated, cloud-based platform that unifies finance, inventory, sales, and production planning. With real-time data access, AI-powered forecasting, and customizable workflows, Deskera enables companies to streamline their operations and align business plans with day-to-day execution. Whether you're a mid-sized business or a growing enterprise, Deskera ERP empowers you to bring your IBP strategy to life with confidence and clarity.
What Is Integrated Business Planning (IBP)?
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a holistic process that connects a company’s strategic goals with its operational, financial, and functional planning efforts across departments. Unlike traditional planning methods that operate in silos—where sales, supply chain, finance, and marketing create isolated plans—IBP creates a unified roadmap. This ensures that every function is aligned with common business objectives, enhancing agility, coordination, and decision-making across the enterprise.
At its core, IBP integrates key business areas like demand forecasting, supply planning, product development, finance, and marketing into a continuous, collaborative planning cycle. For example, consider an automotive parts supplier that faces a sudden spike in demand due to a new vehicle launch. Without integrated planning, the company may struggle to respond in time—leading to missed revenue and unsatisfied customers. With IBP, the business can sync real-time data across production, logistics, and finance to adjust inventory levels, optimize schedules, and meet demand efficiently—preserving customer satisfaction while protecting profit margins.
A common misconception is that IBP is only a supply chain exercise. While supply chain planning is a key component, IBP extends far beyond. It bridges operational execution with financial planning and performance tracking. This connection between FP&A and operations allows for more accurate forecasting, better risk mitigation, and informed responses to challenges like raw material shortages or shifting customer behavior. When purchasing detects a potential disruption, IBP ensures that finance, operations, and procurement can quickly coordinate a response—before the issue escalates into lost sales or increased costs.
IBP isn’t a one-time event—it’s a cyclical, ongoing process. Typically operating on a rolling 24–36 month horizon, it combines strategic foresight with short-term agility. Cross-functional teams continuously review market data, analyze performance, and adjust plans as needed. Whether it’s launching a new product line, responding to a supply chain bottleneck, or reallocating budgets to meet new priorities, IBP empowers organizations to act with speed and cohesion. Ultimately, it transforms business planning from a fragmented, reactive exercise into a proactive, enterprise-wide strategy that drives long-term success.
Core Components of Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
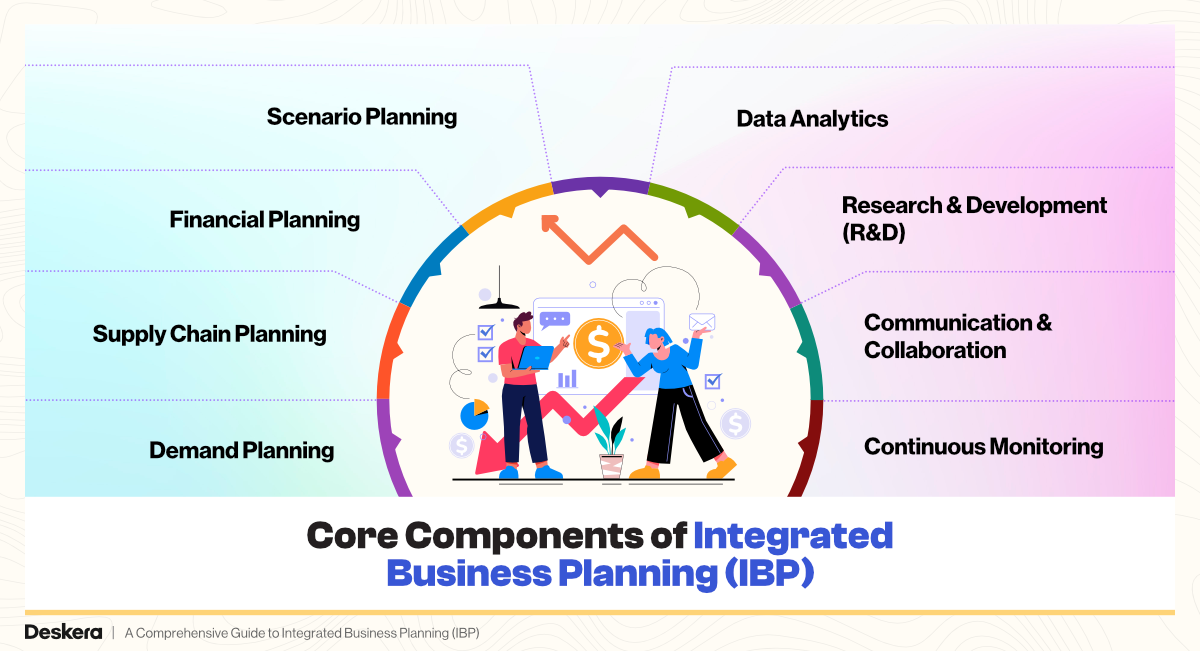
While Integrated Business Planning (IBP) may vary across industries, several core components are essential to its success. These elements work in tandem to align business functions, eliminate silos, and support a unified strategy. Understanding each component—and how they influence one another—is key to building a resilient, agile, and data-driven organization.
1. Demand Planning
This is the foundation of IBP. Demand planning leverages historical sales data, customer trends, and market insights to forecast future product demand. Accurate forecasting enables businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, avoid overstocking or stockouts, and respond quickly to shifts in customer behavior—keeping service levels high and costs low.
2. Supply Chain Planning
Once demand is understood, supply chain planning ensures the business can meet it efficiently. This involves selecting the right suppliers, manufacturing locations, and distribution networks to minimize cost and delivery time. IBP helps businesses optimize production schedules, manage capacity, and streamline logistics across the entire supply chain.
3. Financial Planning
To ensure profitability, operational plans must be tightly integrated with financial goals. Financial planning in IBP encompasses budgeting, revenue forecasting, and cash flow analysis. This integration supports smarter investment decisions, aligns spending with strategic priorities, and helps organizations maintain fiscal discipline as they scale.
4. Scenario Planning
IBP allows companies to model and evaluate multiple “what-if” scenarios, such as sudden demand surges, supplier disruptions, or market downturns. This proactive approach enables leaders to prepare contingency plans, mitigate risks, and maintain business continuity—even in the face of uncertainty.
5. Data Analytics
Robust IBP relies on timely, accurate data from across the organization. By integrating data from ERP, CRM, inventory management, and financial systems, analytics help identify patterns, uncover risks, and improve forecasting. Advanced tools provide real-time insights that guide strategic and tactical decisions across functions.
6. Research & Development (R&D)
IBP ensures that product innovation aligns with both customer demand and operational capabilities. R&D teams can use IBP insights to prioritize feasible, cost-effective product ideas and coordinate launches with marketing, supply chain, and finance—reducing time to market and improving ROI.
7. Communication & Collaboration
A critical enabler of IBP is the breakdown of departmental silos. Cross-functional collaboration ensures that every stakeholder—sales, operations, marketing, finance, and supply chain—is aligned on shared objectives. Regular collaboration cycles promote transparency, accountability, and coordinated execution.
8. Continuous Monitoring
IBP is not static—it requires ongoing tracking of key performance indicators such as inventory turnover, COGS, service levels, revenue, and margins. Continuous monitoring allows teams to detect deviations early, adjust plans swiftly, and drive continuous improvement across the business.
Together, these components form a dynamic feedback loop. For example, demand planning informs supply strategies, which influence financial projections and may prompt scenario simulations.
Data analytics supports all steps, while collaboration ensures alignment, and performance monitoring closes the loop—feeding insights back into the next cycle. This interconnected system is what makes IBP such a powerful tool for modern, high-performing organizations.
The 6 Pillars of Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
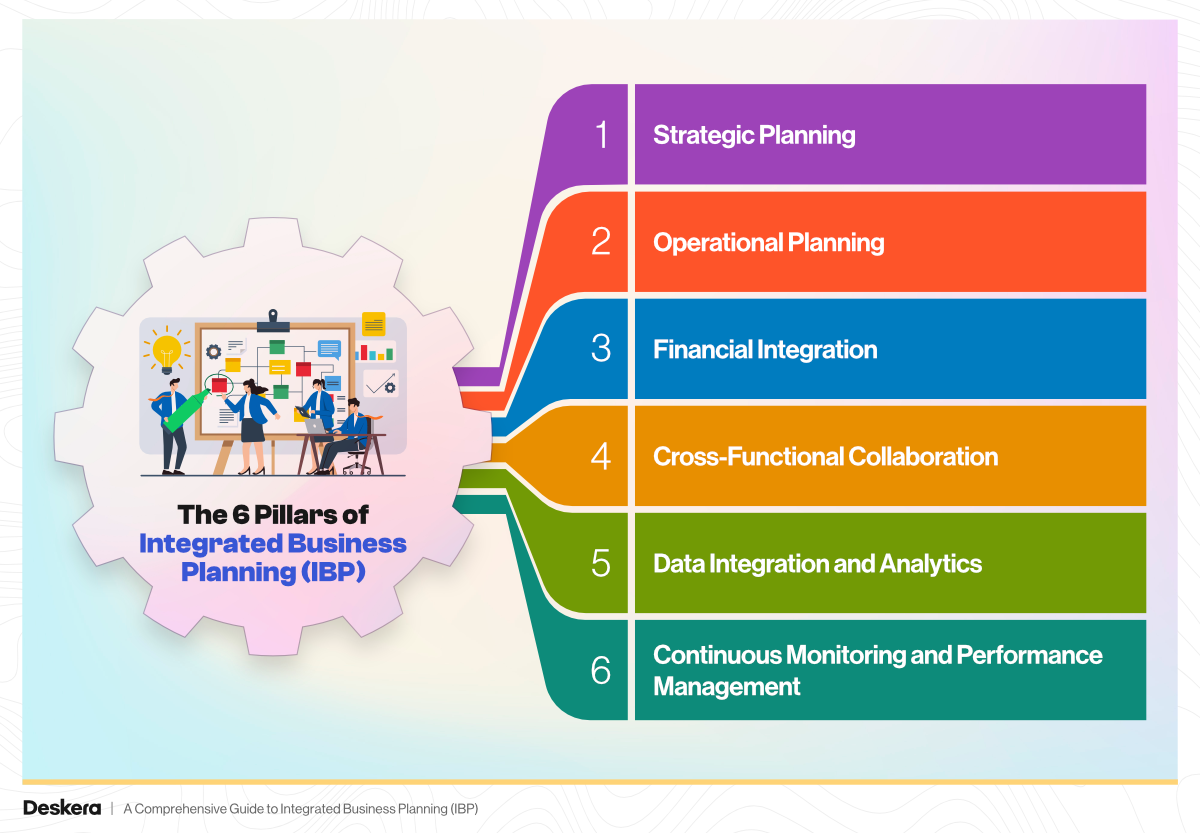
Integrated Business Planning thrives on a solid foundation of strategic alignment, functional integration, and data-driven execution. These six core pillars support the IBP framework, enabling organizations to make informed, agile decisions while aligning short-term actions with long-term goals.
1. Strategic Planning
IBP begins with strategic planning—the process of defining the company’s long-term objectives in alignment with market trends, customer needs, and competitive forces. This pillar sets the direction for the entire organization by identifying growth opportunities, potential risks, and key initiatives. With a clear roadmap in place, organizations are better equipped to navigate change and maintain a competitive edge in uncertain environments.
2. Operational Planning
Once the strategic vision is defined, operational planning transforms those goals into executable actions across departments. Sales, supply chain, marketing, and production teams translate high-level objectives into measurable initiatives—such as launching new products or optimizing inventory levels. This pillar ensures alignment between daily operations and broader business strategies, bridging the gap between planning and execution.
3. Financial Integration
No business plan is complete without financial validation. Financial integration aligns operational plans with budgeting, forecasting, and profitability targets. By incorporating financial data early in the planning cycle, organizations can better allocate resources, manage costs, and assess the feasibility of strategic initiatives. This pillar helps ensure that growth plans are both aspirational and financially sustainable.
4. Cross-Functional Collaboration
One of the most critical enablers of IBP is cross-functional collaboration. Rather than allowing departments to operate in isolation, IBP promotes alignment across sales, finance, supply chain, marketing, HR, and IT. This collaboration enables teams to share insights, resolve conflicts, and make coordinated decisions. Ultimately, it leads to stronger business outcomes and faster innovation.
5. Data Integration and Analytics
Robust IBP depends on timely, accurate, and centralized data. This pillar involves unifying data from ERP, CRM, inventory, and financial systems to create a single source of truth. Advanced analytics then turn this raw data into actionable insights—enabling better forecasting, early risk identification, and smarter decision-making across the organization.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Performance Management
The final pillar ensures that plans stay on track through real-time monitoring and KPI tracking. By continuously measuring performance against strategic and operational goals, companies can quickly identify deviations and adjust course. This ongoing feedback loop promotes continuous improvement and resilience in the face of disruption.
Together, these six pillars create a strong, integrated framework that enables businesses to align vision with execution, data with action, and departments with one another. By embracing each of these pillars, organizations can unlock the full potential of Integrated Business Planning and drive sustained success.
Understanding the Relationship Between S&OP and IBP
Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) and Integrated Business Planning (IBP) are often used interchangeably, but they represent different stages of business planning maturity.
S&OP is a tactical process that aligns sales forecasts with supply capabilities over a medium-term horizon—typically 12 to 18 months. It primarily focuses on balancing demand and supply to ensure operational efficiency, with participation from departments like sales, operations, and supply chain.
IBP, on the other hand, builds upon S&OP by expanding the scope both horizontally and vertically. It integrates additional functions such as finance, marketing, HR, and product development, and aligns planning with long-term strategic goals and financial targets. Where S&OP focuses on what needs to happen in the short to medium term, IBP addresses how those actions align with the company’s broader mission and profitability.
In short, S&OP is a subset of IBP. While S&OP helps businesses meet demand efficiently, IBP ensures that every decision supports enterprise-wide objectives—offering greater agility, cross-functional collaboration, and strategic foresight.
6 Essential Steps in the Integrated Business Planning (IBP) Process
While the implementation of Integrated Business Planning may differ from company to company, most successful IBP initiatives follow a consistent, structured process. These six essential steps help organizations align strategic goals with daily execution, promote cross-functional collaboration, and build the agility needed to respond to change.
1. Identify Existing Constraints
Before building an integrated plan, businesses must assess their current challenges and limitations. This could involve identifying profitability issues, inefficient operations, or overdependence on a single product or customer. For example, a manufacturer might find that excessive product complexity or reliance on one buyer is restricting growth. Recognizing these constraints provides a starting point for targeted planning and improvement.
2. Get Leadership and Employee Buy-In
Integrated Business Planning represents a cultural shift, not just a process change. Leadership must champion the effort—providing funding, direction, and active participation. Equally important is employee engagement. Without buy-in at all levels, adoption stalls. Formal communication, training, and involvement programs help ensure everyone understands the value of IBP and is invested in its success.
3. Set Up a Cross-Functional “Tiger Team”
To ensure IBP becomes an embedded practice rather than a siloed initiative, companies should create a dedicated tiger team. This cross-functional group—typically including representatives from finance, supply chain, operations, and sales—helps drive communication, resolve planning conflicts, and safeguard data accuracy. Their role is to monitor KPIs, maintain alignment, and act as change champions throughout the organization.
4. Establish a Project and Product Prioritization Process
IBP is rooted in strategic discipline. Every proposed initiative—whether it's a new product, market expansion, or operational change—must directly support business goals. Leaders should use a structured cost-benefit analysis framework to evaluate proposed projects, ensuring that only high-impact, goal-aligned initiatives receive resources. This prioritization process keeps teams focused and aligned with strategic outcomes.
5. Integrate Financial and Operational Data
One of the core strengths of IBP is its ability to link operational execution with financial outcomes. That means financial planning cannot exist in isolation. Finance teams—particularly those in FP&A roles—must participate in product planning, supply chain meetings, and sales strategy sessions. This integration enables real-time tracking of how operational metrics (e.g., production volumes) affect revenue, profitability, and cash flow.
6. Adopt Technology and Tools to Enable IBP
Successful IBP requires dynamic, data-driven decision-making—something that's nearly impossible without the right technology. Static spreadsheets and outdated forecasts won’t cut it. Businesses must adopt cloud-based tools that support rolling forecasts, integrate data from all departments, and provide real-time visibility into KPIs. Technology also enables feedback loops and performance monitoring, which are crucial for ongoing plan refinement and execution.
By following these six steps, organizations can implement an IBP process that’s not only structured and goal-oriented, but also flexible and responsive. The result is improved alignment, faster decision-making, and a planning culture built for long-term success.
Key Benefits of Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
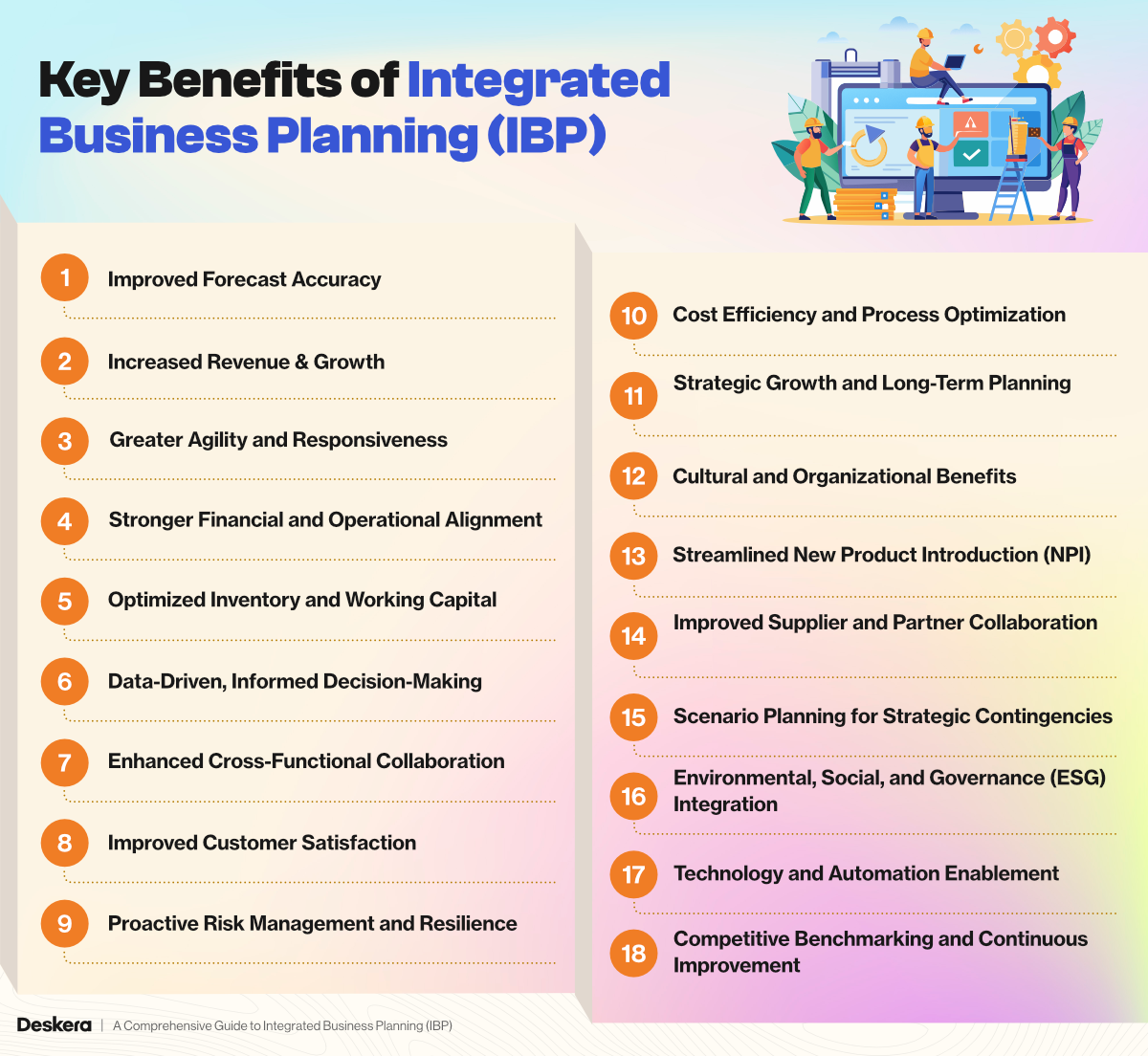
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) goes beyond traditional Sales & Operations Planning (S&OP) by integrating financial, strategic, and operational planning into a unified, cross-functional process. While implementing IBP requires effort and resources, the benefits are both immediate and long-term—driving performance, agility, and profitability across the business.
1. Improved Forecast Accuracy
IBP combines inputs from sales, marketing, operations, and finance—supported by advanced analytics—to deliver more reliable and refined forecasts. This leads to:
- Reduced forecasting errors
- Better inventory and production planning
- Fewer stockouts and overstocks
Example: A global CPG company reduced forecast errors by 20% after IBP implementation, improving delivery performance and customer satisfaction.
2. Increased Revenue & Growth
With better demand sensing, synchronized planning, and aligned pricing/promotions, IBP enables companies to:
- Seize market opportunities faster
- Improve order fulfillment rates
- Avoid revenue loss due to misalignment
Research shows that the primary financial outcome of IBP is higher revenue growth through coordinated execution.
3. Greater Agility and Responsiveness
IBP enables rapid scenario planning and real-time adjustments to market shifts, customer demands, or supply chain disruptions.
- Faster response to disruptions (e.g. supplier issues, demand spikes)
- Shorter decision-making cycles
- Real-time plan revisions
One firm improved its response to market changes by 30% with IBP, giving it a significant edge over slower competitors.
4. Stronger Financial and Operational Alignment
IBP connects strategic financial goals with operational execution, ensuring resources are deployed where they matter most:
- Aligned budgets, forecasts, and operations
- Better visibility into cost structures and margins
- Improved return on investment (ROI)
FP&A integration within IBP gives executives accurate, up-to-date insights into spending, revenue, and profitability.
5. Optimized Inventory and Working Capital
By eliminating planning silos, IBP helps reduce unnecessary inventory buffers and optimize working capital:
- Leaner, more efficient operations
- Reduced carrying costs and waste
- Improved cash flow
Companies using IBP have reported annual cost savings of $50M+ by aligning inventory and production with actual demand.
6. Data-Driven, Informed Decision-Making
IBP offers a single source of truth by integrating data across all functions:
- Better use of historical, market, and internal data
- Scenario modeling and predictive insights
- Faster, more confident executive decisions
7. Enhanced Cross-Functional Collaboration
IBP fosters a “one plan” culture that breaks down functional silos:
- Sales, operations, marketing, and finance work toward shared goals
- Greater transparency and accountability
- Less finger-pointing and misalignment
Cross-functional tiger teams within IBP drive continuous collaboration and collective ownership of outcomes.
8. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Better forecasting and synchronized operations result in more reliable deliveries and service:
- Higher on-time, in-full (OTIF) rates
- Fewer backorders and missed SLAs
- More personalized customer offerings
IBP empowers businesses to understand and anticipate customer needs more effectively, building loyalty and trust.
9. Proactive Risk Management and Resilience
With regular performance monitoring, scenario planning, and predictive analytics, IBP helps mitigate operational and financial risks:
- Better supply chain continuity planning
- Early warning for demand/supply shifts
- Resilience to economic and geopolitical disruptions
10. Cost Efficiency and Process Optimization
IBP streamlines workflows and eliminates redundant planning processes:
- Lower production and logistics costs
- More efficient labor and asset utilization
- Scalable processes for business growth
11. Strategic Growth and Long-Term Planning
IBP ensures daily execution supports long-term strategic objectives:
- Clear line-of-sight from operational decisions to strategic KPIs
- Supports innovation and market expansion
- Builds sustainable competitive advantage
12. Cultural and Organizational Benefits
Beyond process improvements, IBP fosters a performance-driven, accountable culture:
- Employees feel more empowered and engaged
- Clear role in achieving company goals
- Improved morale and organizational trust
13. Streamlined New Product Introduction (NPI)
IBP facilitates better coordination across R&D, marketing, and supply chain for product launches:
- Faster time-to-market for new products
- Improved alignment between demand and production capabilities
- Reduced risk of launch failures
Companies using IBP frameworks for NPI have achieved 15–25% faster rollout timelines with higher product adoption rates.
14. Improved Supplier and Partner Collaboration
IBP extends planning visibility to suppliers and external partners:
- Better coordination on lead times, capacity, and replenishment
- Shared accountability for meeting demand and service levels
- Lower risk of supply chain disruptions
Global manufacturers report stronger supplier performance through collaborative IBP planning platforms.
15. Scenario Planning for Strategic Contingencies
IBP enables “what-if” simulations to test the impact of market changes, regulatory shifts, or M&A activities:
- Proactive identification of strategic risks
- More robust contingency plans
- Data-backed decisions under uncertainty
For example, a pharma firm used IBP scenario planning to realign global supply chains in response to geopolitical tensions—avoiding millions in potential losses.
16. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Integration
IBP helps companies embed sustainability goals into operational planning:
- Visibility into carbon footprint and resource consumption
- Alignment of ESG targets with financial plans
- Enhanced reporting and compliance
IBP supports sustainable decision-making, critical for companies pursuing net-zero and circular economy goals.
17. Technology and Automation Enablement
IBP acts as a foundation for digital transformation by leveraging AI, machine learning, and automation:
- Automated demand sensing and replenishment
- Continuous data integration and updates
- Reduced manual intervention and errors
Companies report up to 50% planning cycle time reduction when IBP is combined with AI and advanced analytics.
18. Competitive Benchmarking and Continuous Improvement
IBP provides a framework for tracking internal performance and comparing it to industry benchmarks:
- Identification of performance gaps
- Continuous refinement of planning processes
- Clear metrics to drive accountability and innovation
Organizations using IBP consistently outperform peers in key areas such as forecast accuracy, OTIF delivery, and profit margins.
In summary, IBP delivers a unified, data-driven planning approach that enables businesses to align strategy and execution, adapt quickly to change, and drive profitable, customer-centric growth.
Common Challenges of Implementing Integrated Business Planning
Adopting IBP is not simply a software implementation—it’s a cultural and operational shift that requires commitment across departments. Here are some of the most frequent hurdles businesses face when transitioning to IBP:
1. Siloed Business Functions
IBP demands a unified approach, yet many companies still operate with departments functioning in isolation. Breaking down these silos to foster collaboration between sales, finance, operations, and supply chain teams is often the first and biggest hurdle.
2. Poor Data Management
Without accurate, timely, and integrated data, planning loses its value. Inconsistencies in data sources, lack of transparency, and outdated reporting systems can severely undermine decision-making and strategy alignment.
3. Limited Technology Infrastructure
Legacy systems may lack the capability to aggregate, analyze, and visualize enterprise data. When critical data is locked away in departmental silos, it becomes difficult to achieve real-time visibility and collaboration—key elements of IBP.
4. Unclear Assessments and Metrics
Measuring the success of an IBP program is often challenging due to its cross-functional nature. Establishing the right KPIs that reflect financial, operational, and customer performance requires deliberate planning and coordination.
Best Practices for IBP Adoption
To successfully implement IBP and overcome organizational and technical roadblocks, businesses should focus on these proven best practices:
1. Harmonize Team Processes
Encourage cross-functional alignment by unifying workflows, clarifying roles, and fostering collaborative planning. Establish clear communication protocols and shared goals to maintain consistency and efficiency across teams.
2. Focus on Data Quality
Ensure your organization prioritizes clean, consistent, and accessible data. Reliable data is foundational to building forecasts, analyzing performance, and making informed decisions in real time.
3. Leverage Advanced Technology
Invest in scalable planning tools and ERP systems that support automation, predictive analytics, and real-time data integration. Modern platforms enable agility and adaptability in your IBP process.
4. Assess and Manage Risks
Build flexibility into your planning by incorporating risk assessment and scenario analysis. This allows your team to anticipate disruptions and pivot strategies proactively based on market conditions.
5. Measure and Track Performance
Define relevant KPIs across departments—covering finance, supply chain, operations, and customer service—to monitor progress and drive accountability throughout the organization.
6. Conduct Regular Reviews
Establish frequent planning and review cycles to assess what’s working, what needs adjustment, and how strategies can evolve with changing customer demand, market shifts, or internal developments.
How Deskera ERP Supports Integrated Business Planning
Integrated Business Planning is only as strong as the tools that power it—and Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive platform to bring your IBP strategy to life. Here’s how:
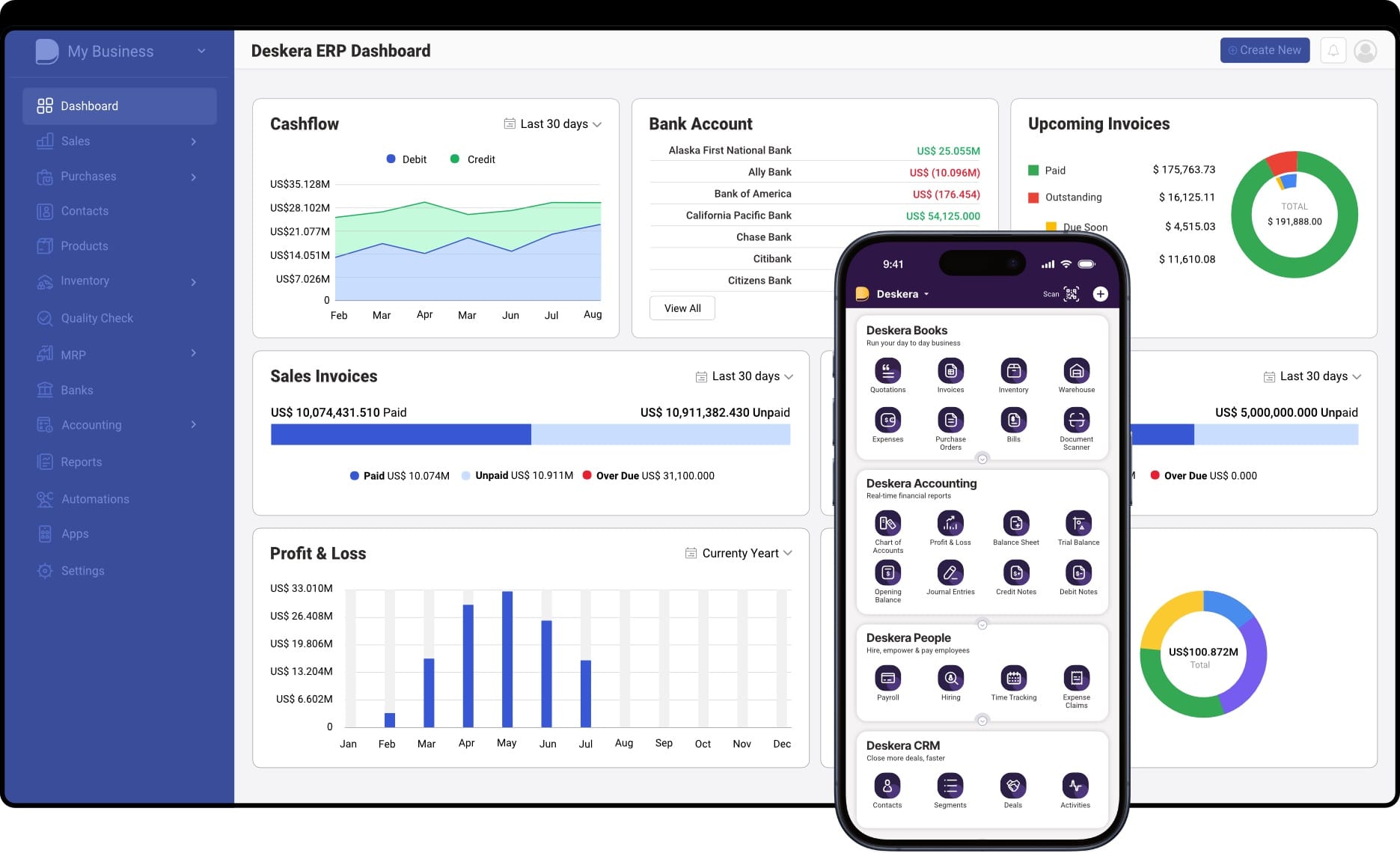
1. Unified Platform for Cross-Functional Planning
Deskera seamlessly connects finance, inventory, sales, procurement, and manufacturing into one unified system. This integration ensures that every department is working from the same real-time data, enabling synchronized planning and execution.
2. Real-Time Data for Faster Decision-Making
With real-time dashboards and reporting, Deskera gives decision-makers instant access to business-critical insights. This agility helps you respond to market fluctuations, demand changes, and supply chain disruptions without delay.
3. Demand Forecasting & Scenario Planning
Deskera’s AI-powered forecasting tools help you anticipate future demand with greater accuracy. You can run "what-if" scenarios, model outcomes, and plan inventory or production accordingly—supporting proactive rather than reactive decision-making.
4. Enhanced Collaboration and Visibility
Deskera promotes transparency across the organization. Role-based access, cloud-based accessibility, and mobile-friendly interfaces ensure that teams—from the shop floor to the boardroom—are aligned and informed.
5. Built-In Automation for Productivity
Routine tasks like invoice generation, order tracking, procurement scheduling, and financial reporting can be automated within Deskera, freeing up your team to focus on strategic planning and innovation.
6. Scalability for Growing Businesses
Whether you're a small enterprise or a growing manufacturer, Deskera ERP is designed to scale. As your business evolves, so can your planning capabilities—without needing to switch platforms or overhaul systems.
Key Takeaways
- IBP is a holistic approach that aligns strategic, operational, and financial plans across departments, ensuring all business units work toward shared goals using a unified framework.
- IBP enables organizations to remain competitive in dynamic markets by improving cross-functional collaboration, enhancing agility, and ensuring responsiveness to changing demand and supply conditions.
- The main building blocks of IBP include demand planning, supply planning, financial planning, scenario modeling, and performance tracking—all working together to support strategic goals.
- IBP is built on six essential pillars: strategy alignment, operational planning, financial integration, cross-functional collaboration, advanced analytics & technology, and continuous monitoring—ensuring a holistic and scalable planning system.
- A strong IBP process involves assessing current capabilities, securing executive sponsorship, unifying data sources, integrating planning tools, training teams, and continuously refining based on KPIs.
- Integrated Business Planning boosts forecast accuracy, increases operational efficiency, improves financial visibility, and supports better risk management across the enterprise.
- Organizations often face resistance from siloed departments, poor data quality, limited infrastructure, and difficulty setting measurable outcomes during IBP adoption.
- Overcome implementation hurdles by fostering cross-functional collaboration, ensuring high-quality data, using modern forecasting tools, managing risk with scenario planning, and conducting regular performance reviews.
- Deskera ERP streamlines IBP with built-in forecasting, cross-departmental integration, real-time data, and automation—enabling faster, smarter decision-making across the organization.
Related Articles












