Setting up your own company, business, or startup could be an overwhelming process. It involves a variety of operations that need to be carried out in areas such as legal, financial, sales, among others. All these operations are a part of the Business Plan. The question here is what is a business plan and how do you go about writing it?

This article takes you on a detailed journey of writing a business plan apart from the following points:
- Understanding a business plan
- Elements of a business plan
- Types of business plans
- We also see why making a business plan is important
- How to write a step-by-step business plan?
- We also look into why some business plans fail.
- Business plans FAQ
What Is a Business Plan?
The startup of a company requires knowing and addressing many problems — legal issues, finance, sales and commercialization, protection of intellectual property, protection of liability, and more.
A business plan is defined as a written document that comprises business details, the company’s goals, and methods to achieve these goals. A business plan contains a comprehensive framework for the company in terms of marketing, finance, and operations.
Business plans serve a significant purpose. They are documents that can assist in inviting potential investment before a substantiated record of success has been ascertained. It helps create a good platform for businesses to continue to pursue targets.
Drafting a business plan is specifically useful for a startup or new enterprise. Optimally, the plan will be periodically restructured to see if objectives have been achieved or changed throughout the years. The companies may also decide after some time to redraw and upgrade the business plan to give a new direction after establishment.
Understanding Business Plans
Fundamentally, a business plan is a key document that must be put in place before start-up activities. Therefore, before new companies can provide their capital, banks and risk-capital companies often make a viable business plan a necessary precondition.
It is highly advisable to define a business plan before commencing any operations of the business. There have been examples of companies not lasting long without a competent business plan. It helps the businesses take decisions on matters of investments, learn about potential risks and adapt to new trends.
A strong business plan defines a company's identity, what it does, how it does it, and where it's headed. It is easier to grasp a company plan if you keep this history in mind. The core team or the people in a company's internal dynamics shapes its policies and objectives, or participates in the capital budgeting process must be able to comprehend a business plan.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to understanding the complicated and detailed document.
Executive Summary
Being the first section in a business plan, it comprises the summary of the entire strategy of the company. This 2 to 3-page summary presents the vision statement and brings into perspective the rest of the strategy.
Table of Contents
This comes after the executive summary. This should be looked into carefully to know if there are any particular aspects you would want to know the details about.
Products
The next few sections can tell you a lot about who the adversaries are and what sort of products and services does the company offer. Any kind of issues that the company faces or even its capabilities are mentioned in this section.
Look for Management Capabilities
Within these sections, there would be information about the people playing key roles in the company. You can know about their qualifications and expertise from the document. These spaces will also consist of the description of the location of the company. It would be good to know about it to assess if it is strategically situated.
Operations Section
This section comprehensively describes the manufacturing, marketing, selling of products carried out by the business. Its customer support and other services can be assessed from this section.
Finances and Forecast Section
This could be helpful in understanding the revenue, expenditure, and other critical financial aspects of the organization. A complete chart of costs, risk analyses, and earnings estimates can be accessed through this section. This space also provides details about how these important digits were arrived at.
Final Section
This helps you understand the company’s targets and projections and the measures they wish to take for accomplishing the same. This will also share a glimpse of the ways in which the resources or funds from the investors will be used.
Elements of a Business Plan
Typically, a 20-25 page document, business plan varies hugely based on the type and size of the business. The details or the depth of the plan could be diverse and entail different kinds of elements. However, there are some crucial elements that come under the main plan and are also a part of the appendices.
Although, business plans are different, here are some common critical elements that are included in all the plans. Let’s look at them one by one:
Executive Summary
This is the point that elaborately explains the mission of the company. Besides, it also includes information about the company’s management leaders, employees, functions.
Products and Services
This point includes all the products or services that the company is offering. Apart from the names of these products, services, it also comprises the details pertaining to the product such as the pricing, longevity, and benefits that the customers can avail of from its services.
Other information that could be a part of this point, includes production and manufacturing processes. It may also showcase any patents or proprietary technology that the company has acquired. A research and development report is also a part of this element.
Market Analysis
A company must have a thorough understanding of its sector as well as its intended audience. A market analysis will show you the expected demand for the products that the company sells. It will also help you know what difficulties you could face from the competitors. This will also assist you with an insight into the expertise of the contemporaries along with their strengths and drawbacks.
Marketing Strategy
This section explains how the organization plans to recruit and retain customers, as well as how it plans to reach out to them. This necessitates the creation of a distinct distribution channel. It will also detail branding, brand awareness and email marketing campaign plans, as well as the forms of media via which such efforts will be carried out.
Financial Planning
The organization should incorporate its financial planning and future estimates in order to persuade the other parties to review its business plan. The established companies may include income statements, balance sheets, and so on; On the other hand, new enterprises will include objectives and projections for the initial years of operation, as well as venture capitalists.
Budget
Every good business should have a budget in place. This comprises expenses such as employment, innovation, production, advertising, and any other business-related expenditure.
Types of Business Plans
The company management and investors can use business plans to help them start and grow their company. A company prepares a business plan to describe the objectives that will forecast and organize for expansion and to understand each area of the firm. A business plan is written by competent entrepreneurs to direct management and attract investment funds.
Business plans are drawn based on the requirements of the company. With this in mind, there are the following types of business plans:
Business Plans for Startups
A start-up business plan should outline the actions necessary to launch a new firm. It also includes a financial study with spreadsheets that describe financial concepts such as income, profit, and cash flow estimates. This may also be used by potential investors to gain an insight into the financial status of the startup. The startup business plans give clarity on market analysis, the product or service that the startup will provide besides the set goals.
Internal Business Plans
Internal plans detail project marketing, staffing, and technology costs. This document will summarise the company's present situation, including administrative performance and profitability, before determining whether and how the company would repay any project-related cash. These are written for a limited audience within the company, such as the marketing team evaluating a proposed initiative. They usually comprise a market study that shows the intended audience, competitive landscape, and the market's beneficial impact on corporate profits.
Business Plans for Strategic Business Development
A strategic business plan lays out a structural plan by providing a high-level picture of the company's objectives and how it moves to achieve them. While the framework of a strategic business plan varies per firm, typically contain five elements:
- The vision statement
- The mission statement
- Defining the key performance factors
- tactics for accomplishing objectives
- Timeframe for implementation
A strategic business plan engages personnel at all levels of the organization in the big picture, motivating them to collaborate to achieve the company's objectives
Business Plans for Scalability
A feasibility or scalability business plan considers two key issues regarding a planned business endeavor:
- If there will be buyers for the products or services that the company intends to sell.
- Whether or not the enterprise will be profitable.
This plan highlights the details of the demand of the product or service and the associated target audience for the said product. A feasibility study typically concludes by providing recommendations for the future.
Business Plans for Operations
These include features regarding the operations of the company and hence, the name. The plan specifies the deployment benchmarks and timelines for the future year. It also entails employee responsibilities.
Business Plans for Growth
These are also known as the plans for expansion and are created for both, internal as well as external use. This plan features the details around the following points:
- Management
- Detailed and specific highlights about the company
- Details of officials as the company
It is important to chalk out this plan and give the relevant corporate details to convince the potential investors.
The Importance of Making a Business Plan
Entrepreneurs frequently utilize business plans. It is doable to travel without a business strategy, but doing so will simply raise the chances of wandering aimlessly along the trip. This helps them to steer clear of any potential problems and putting themselves in a situation where they may have to keep asking for directions.
Therefore, business plans are necessary to help business owners in observing the broader picture, planning for the future, making critical decisions, and increasing their overall chances of success.
Defining organizational goals
A small business, a startup, an established business; all need a business plan. When it comes to small businesses, the business plans can be helpful in structuring the goals of the organization. It can allow you to monitor and govern everything you've strived to produce if you use it correctly and use it on a frequent basis. Finally, it can serve as a reliable tool for management to stay on track with administrative milestones.
To assist you in making important decision
The fundamental objective of a good business plan is to assist business owners in making better decisions. Companies don't always have the opportunity to take time and analyzing all of the implications of a decision. A company plan can help with this. Management frequently deals with a never-ending exercise in making decisions and dealing with crises. Developing a business plan involves estimating the outcome with some of the most important company actions.
Minimize Risks
Handling the operations of a business can involve risky steps, but it tends to become much more sustainable with a well-thought business strategy. Developing accounting period predictions, logistics planning, and a thorough knowledge of the future outlook can assist with mitigating the risk of a job that is intrinsically insecure.
A business plan makes it easier to find better solutions, leads to better decisions, and see a clearer picture of the organizational future.
Obtain Funding
While there are multiple activities for which a business plan is required, a major reason why you may need it is to secure funding from venture capitalists. The most effective means of demonstrating your competence is through a business plan, which is usually a prerequisite for anyone seeking outside funding. And anyway, anyone considering investing in your company will want to know it's in fantastic form and will be profitable in the long run.
To serve as a resource for service providers
Contractors, freelancers, and other experts are commonly a part of an organization. They are important people as they help with some of the crucial duties such as bookkeeping, legal aid, consulting, and so on. Having a business plan in place will help them get a fair idea of the key portions of areas where they are required.
To prevent unnecessary blunders
A business plan can help understand the reasons and avoid potential mistakes and blunders. Some of the most commonly observed mistakes could be:
- Capital troubles: Cash flow troubles or just running out of money are both examples of a lack of capital.
- No Appreciation: Nobody buys what you're selling since there isn't a market for it.
- Insufficient team: This emphasizes the significance of employing the correct personnel to assist you in running your company.
- Excessive competition: It's difficult to make a consistent profit when there's huge competition.
5 Quick and Easy Ways to Create an Excellent Business Plan
Let's speak about certain guidelines that will make the entire company planning process more efficient before you start writing your business plan. We have put together the following points to direct you towards writing a goal-oriented business plan.
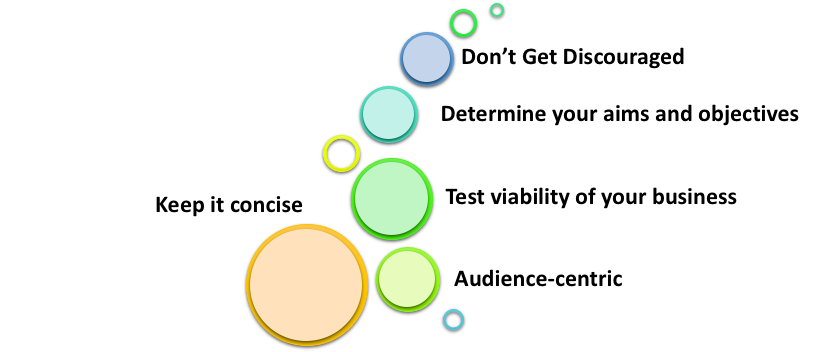
Keep it concise
A long business plan which has over 50 pages will not only consume a lot of time in drafting but may not essentially be efficient in the long run. The foundation of writing a business plan is to quickly write it and move on with the tasks defined in it.
Moreover, it is a tool to help the company grow; it will require to be fine-tuned continuously, and therefore, it is best to keep it short and precise.
Audience-centric
Make your business plan by keeping in mind the audience who would be referring to it for accomplishing their goals. An example is if the business plan is aimed at readers that consist of investors as the primary audience, it would be wise to draft it in a language that would be comprehended by them.
Test viability of your business
The more tests you conduct for the elements mentioned in your plan, the better the business plan. Elements of a business plan, as we know now, could include anything from mission and vision statement to products and services. It is recommended you get approval or feedback on the elements included in your business plan.
Determine your aims and objectives
You should have a clear idea of what you want to obtain out of your company from the start. Determine if you are looking for a complete overhaul of your business? Or if you are aiming to expand your employee base? Knowing what you want to achieve can help you design a company plan that is tailored to these objectives.
Don’t Get Discouraged
You might be a new entrepreneur who has just started to look for setting up a business plan. No matter, how daunting this may seem in the beginning, it is good you do not get intimidated by the process.
Although initially writing a business plan may seem difficult, all you need is to be confident and expert in your field. If you're an expert in your field and know everything there is to know about it, then this is all that takes to establish a business strategy.
With this information, we move on to the main section of this article which explains a step-by-step process to write a business plan.
Download Business Plan Template
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step
While writing a business plan, there could be two scenarios that could be considered:
- Traditional Business Plan
- Lean Startup Plan
Let’s look at each of these in detail:
Traditional Business Plan Format
If you're particularly looking for specifics, want a complete plan, or plan to seek funding from conventional sources, you could choose a typical business plan structure. Instead of following the conventional model, focus on the portions that are most relevant to your business and needs. You could use a combination of the sections in the conventional plan to describe how your company can benefit the reader.
Executive Summary: Points that can go here are:
- Mission statement
- Talk about your products and services
- Information regarding the key personnel, employees
- Location of the company
- Also, some high-level plans for growth, in case you wish to seek funds.
Company Details: This includes all the minute details of your company. Talk about what kind of solutions your company provides. Points to be included here are:
- Problems that you can solve
- Enlist your consumers or businesses you wish to serve
- Mention the distinguishing feature or the USP of your company
- Mention the expertise held by the key people involved
- Include a complete overview of the strengths of your company
Market Analysis: You must closely understand your business perspective and the target market. Through thorough competitive analysis, you could assess the market trends and seek answers to the following questions:
- What are the current trends in the market?
- What are the success mantras of other companies?
- Will you be able to achieve what they are doing?
- Do you need more expertise to do it better?
Company and Management: This section is about informing your audience about how and who is in charge of the business. This would be an apt space to describe the points mentioned:
- Company’s legal structure.
- Declare of your company is a general or limited partnership.
- Determine if you want your business to be a C or S corporation
- Also, state if you are the only proprietor or a Limited Liability company.
Products and Services: This section explain the products and services that you wish to sell. Include these under this section:
- Let your audience know of your planning to get a patent, intellectual property, or copyright fr your products.
- Explain the R&D process undertaken with regards to a particular product or service.
- Also, describe the product lifecycle and the benefits of your product.
Marketing and Sales: With the varying requirements per company, the marketing strategies can be unique to all. Based on your domain and industry, you must explain the following points in this section:
- Describe the appeal and retention of customers
- How a sale really is going to take place
- Make revenue projections and forecasts
Funding Application/Request: This area will explain your funding requirements in case you apply for funding. You should also make these points clear:
- How often and how much funding you shall require
- Explain how you plan to use it over the years (providing the number of years would be appropriate)
- Mention the terms and conditions agreeable by you
- If you would want to take a debt or an equity
- Explain your expenses like your bills, employee salaries, purchase of new equipment, etc.
- Always mention your debt repayment strategies.
Financial/Revenue Projections: This goes hand-in-hand with your funding request. It brings forth your company’s stability, sustainability, and growth prospects. Here’s what should go in this section:
- All the revenue reports, balance, and income statements for the past 5 years in case yours is an established company.
- Enlist any guarantees you can levy against a loan
- Explain your financial growth plan for the next 5 years.
- Income forecasts, expenditures, and budgets
- Present a graphical analysis through charts to depict your monthly/quarterly growth plan.
Appendix: This section could be used to attach other essential documents such as:
- Legal documents
- Contracts
- Patents
- Permits
- Product pictures, if demanded.
- Credit history
- Licenses, etc.
Let’s look at the startup business plan and its design.
Startup Business Plan
Although all the business plans comprise of the nice segments, the startup business plan can touch upon each one of those without going much into the details. Moreover, as compared to the traditional plan, this one provides you a lot more agility in terms of making amendments. This would be beneficial as a startup frequently undergoes a lot of changes in its initial years.
Let’s look at the components you’ll be adding to your startup business plan:
Customer Segment: This section explains who your target customers or audience will be. While there could be numerous segments enlisted in this section, it would be wise to identify the ones that your business will most appeal to. Identifying them and naming them here is crucial.
Value Proposition: This is intended for the different audiences your business wishes to serve, The value your business holds or offers to them can be different. In this section, you describe how and what value proposition you will be making for each of those businesses/customers. It is important to figure this out and write it down here as that indicates the value-add your company holds.
Channels: This displays the communication channels you will be using to covey your propositions to your customers.
Customer Relationships: This will highlight your ways of maintaining communication with your customers. You can list down the ways through which you shall be communicating: whether they will be informed through automated emails or will you be connecting with them personally, all goes in here.
Revenue Streams: This point elaborates on where your revenue or income is coming from. An already established business may have multiple sources of income but if yours is a startup, then it may have only one. Nevertheless, you must identify and mention it here.
Key Resources: The resources in your company need to be mentioned here; this includes but is not limited to your employees, key personnel, infrastructure, among others.
Activities: Details of all the crucial activities that strengthen your business or lead it to a meritorious milestone need to go in here.
Important Partnerships: Most of the new businesses invite partnerships and have shared resources. There are certainly some other entities or businesses involved and they must find a mention in this section. These include all your vendors, suppliers, manufacturers, or other people you are working with.
Cost Structure: Once you have identified and defined your business’s requirements and infrastructure, it is time to get the details of the costs of your business. You can also give away the plans or strategies you have to optimize those associated costs.
Why do Business Plans Fail?
While there are numerous business plans drafted each year, only a few of these companies make it to the success ladder. While such business plans can include good suggestions, they fall short. The company’s projects also tend to meet the same fate; despite the brilliant ideas, the project collapses. The reasons for this failure could be many. Wouldn’t it be great if we could foresee them and avoid them before they cause failure?
Here are some reasons that could lead to a failed business plan:
Unreal objectives and ambitions
It may not always be a great idea to reach out for the highest goals in the realm of the business plan. Although high goals are important, the path to reach these goals must be realistic and achievable. You might aspire to make a grand sale of say, thousands of your products in a month but that may not always be attainable. It s, therefore, important to work out a business plan to make it realistic to avoid failures in the future.
Lack of Motivation
Businesses are driven on tonnes of motivation, which in turn is effective on the productivity of the company. The entrepreneurs with a solid determination and motivated team have been great examples of turning their ventures into grand success stories in a relatively short time. Not only does the leader need to be motivated, but the motivation also needs to flow on to his team and all employees to make a difference to the overall output. A company where the leaders lack motivation could be walking slowly towards failure.
Lack of Proper Budgeting
Budgeting is a vital aspect of a business, and a lack of real-world budgeting is a factor to avoid. It is not advisable to always go for a loan to launch the company every time. Unless you can get your theory to move in the right direction, your financial support may evaporate. Therefore, the cost of building a company must be determined and maintained through the first year. All the cost factors should be worked out much in advance to keep away disappointments in the later stages of development.
Inadequate Market Research
Market research is all about acquiring enough information and understanding the current trends in the market. Your plan should be aligned with the kind of market research you have done. Being a vital part of a new company’s business plan, market research needs to provide you a competent data to battle out the odds that you may face. Sufficient information in this regard will help you establish a plan that’s effective. Not doing so may lead you to scrap it and restart the work with greater amounts of time and effort.
Business Plans FAQ
Now that you have a fair idea of how to go about writing a business plan, let’s look around at some of the frequently asked questions:
Do I have to include all the sections?
A clear answer is No. You need not include all the sections, but work out only those that are relevant to your company and business. With the nine sections, you are trying to give away maximum relevant information in the plan; however, not all of the sections would need to be addressed.
How long should the plan be?
Your plan only needs to have all the information composed well into one document. There is no specific length or the number of pages that it should have. When you are sure that it mentions all the required information, you are good to go.
Would be a good idea to start a business in an economically challenged scenario?
Although economic ups and downs could be dissuading, especially while starting a new business. Our take is that any business that can compete well with the existing prices and offers great value to customers can make it big.
How can Deskera Help You with Your Business Plan?
Deskera offers you to learn the concepts of business and get acquainted with the top software applications for startups and can also help with accounting for startups. You may refer to Deskera’s blogs to get a better grip over business topics such as How to understand a balance sheet, Main financial statements, Why are income statements important.
Besides, you may also learn a lot from the Best Marketing Blogs 2020 and the user-friendly CRM, Business Expense, Accounting Cycles.
Take your business to the next level with Deskera All-in-One. It is a platform that offers Invoicing, Accounting, Inventory, CRM, HR & Payroll all under one roof. With Deskera Books, you can avail of online invoicing, accounting & inventory software to boost your business. It covers all the significant aspects of business such as billing, payments, warehouse management, Credit &Debit Notes, financial reports, an elaborate business dashboard apart from many other features.
Key Takeaways
Let’s look at the key points from the document:
- A business plan is a written document that describes the functional areas, goals, and the way in which a company aims to address its objectives.
- In order to attract external investors startups utilize business plans.
- Companies can develop a longer traditional business plan or a shorter startup or small business plan.
- Executive summaries, distribution channels, promotional strategies, and analytical information, wealth management, and budget should include good business plans.
- Business plans could be drafted for Startups, internal business, strategic business development, scalability, and operations.
- There are 2 major types of business plans: Traditional business plans and startup business plans.
- Unreal objectives, lack of motivation, and market research could be the reasons for the failure of a business plan
Related Links














