What's the point of having a warehouse if you're not going to make the most out of it? Having a well-organized warehouse can help your business achieve its goals faster and easier.
In 2023, the market for warehouse management systems reached a valuation of USD 3.94 billion and is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 19.5% from 2024 to 2030.
A warehouse is a facility where goods are stored prior to distribution or sale. Typically, warehouses are used for the storage and distribution of finished goods. They are important because they allow businesses to reduce their inventory levels and mobilize products more quickly. A well-managed warehouse can also improve production techniques and speed up customer order processing.
Thus, warehouse management is a critical component of supply chain operations, encompassing the systematic control and optimization of warehouse processes to ensure efficient handling of goods from receipt to dispatch.
Effectively managing a warehouse involves leveraging technology and strategic practices to streamline workflows, minimize costs, and maximize operational efficiency. One such technological solution that aids in comprehensive warehouse management is Deskera ERP.
Deskera ERP integrates various facets of business operations, including inventory management, order processing, and logistics coordination, providing real-time insights and facilitating informed decision-making.
By harnessing such integrated systems, businesses can enhance inventory accuracy, optimize storage space utilization, and improve overall productivity in their warehouses. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the essentials of warehouse management and the tools available to achieve operational excellence.
In this article, we'll show you how to get the most out of your warehouse and turn it into an asset for your business.
What is Warehouse Management?
Warehouse management is the process of managing the storage and movement of goods and materials within a warehouse. It’s an important part of any supply chain operation and involves the coordination of receiving, storing, and shipping activities.

Warehouse management systems are used to optimize the warehouse’s overall efficiency and accuracy. They automate and streamline processes such as inventory control, order management, shipping and receiving, and more.
What is Warehouse Management System?
A warehouse management system (WMS) is a software program created to support and improve distribution center administration and warehouse functionality.
A warehouse management system (WMS) is used to monitor, manage, and optimize the storage and flow of products. It is used to identify the exact location of goods, manage stock levels, control inventory costs, and improve customer service. WMS also makes it possible to see the entire supply chain, as from manufacturer to the client.
Software for warehouse management provides both the tools to track daily operations and those to implement long-term, strategic improvements. When a picker or packer decides what to pick or pack next on the warehouse floor using the warehouse management system, different information is displayed in the system.
Different features may be added in a warehouse management system depending on the industries it serves (for instance, the requirements of a large brick and mortar shop chain and a direct-to-consumer ecommerce seller are very different).
Significance of Warehouse Management
Since warehouse management is in charge of receiving, storing, and distributing items, it plays a significant role in the supply chain process.
It is essential for companies to have an efficient warehouse management system in place in order to ensure proper inventory control, minimize operational costs, and maximize customer service.
A well-functioning warehouse management system allows companies to gain visibility into their inventory and warehouse operations, allowing them to make better informed decisions and increase their efficiency.
Furthermore, warehouse management systems can provide insights into customer needs, helping companies to better anticipate and meet their customer's needs.
Different Types of Warehouses
Following. we have discussed different types of warehouses. Let's take a look at each and every one of those:
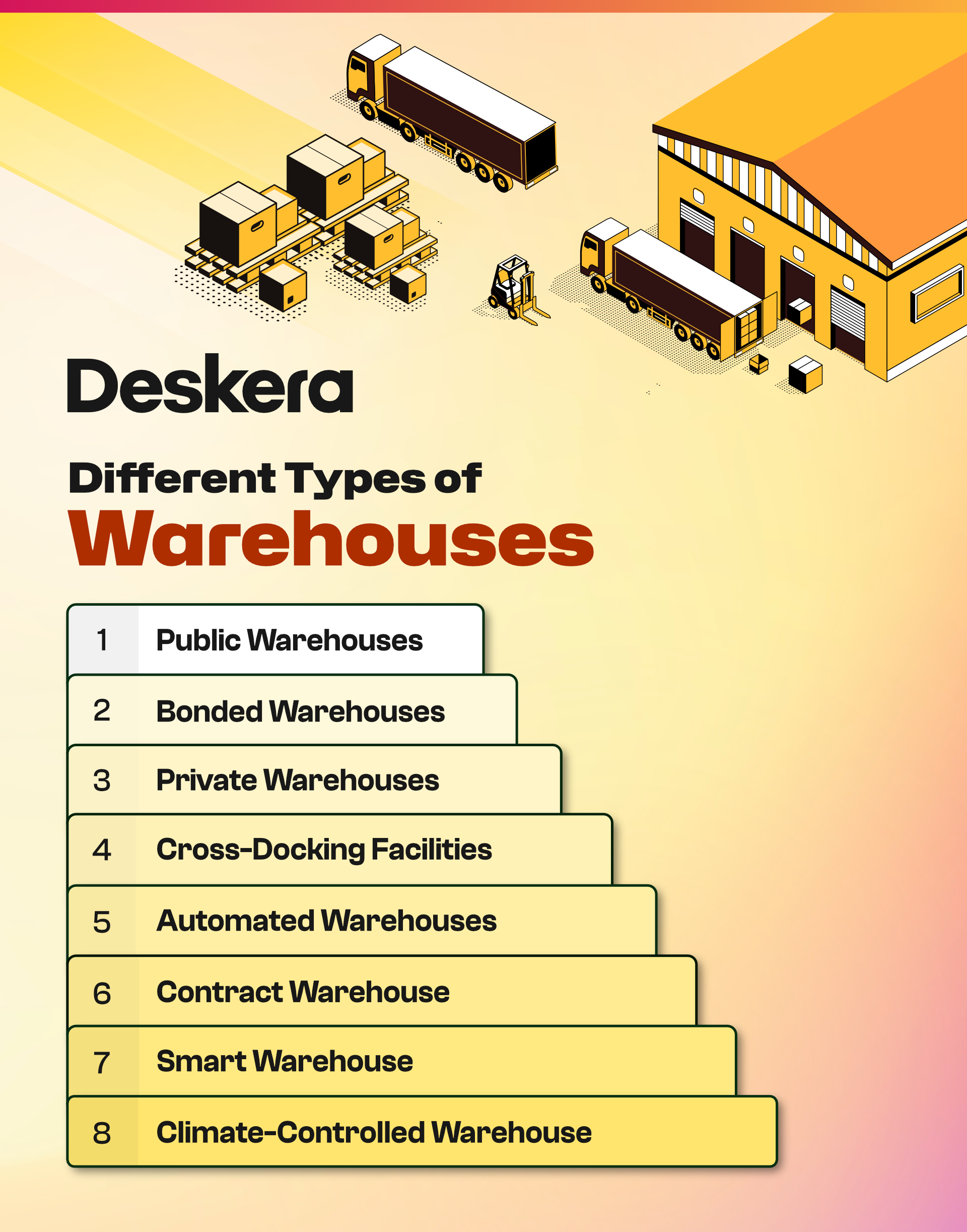
1. Public Warehouses:
A public warehouse, which is maintained by a third-party provider (3PLs), which provides storage and inventory space for businesses. They can be leased by numerous enterprises at once and are occasionally open to the general public.
Many firms benefit from public warehouses since they lessen their management responsibilities for a warehouse. Public warehouses cover the cost of upkeep, safety, and personnel. Businesses who don't need constant inventory space can use a public warehouse for the little period that is necessary.
2. Bonded Warehouses:
Bonded warehouses are specialized warehouses in which imported goods are stored until duties or taxes are paid. Security precautions are in place, and the governments of the countries where these warehouses are located are in charge of them.
The goods stored in a bonded warehouse are considered to be held in trust for the payment of taxes or customs duties. Bonded warehouses are used for a variety of products, such as tobacco, alcohol, firearms, and other goods.
These are warehouses that have been approved and granted permission from customs authorities to store imported goods that are pending customs clearance.
3. Private Warehouses:
Private warehouses are owned and operated by a single company or individual to store their goods.
Typically, a large firm has its own warehouse where it keeps and ships its own goods. In contrast to a public warehouse, a private warehouse is not limited to retaining inventory items.
A private warehouse gives businesses the freedom to utilize the space anyway they see fit. Therefore, the entire product life cycle may occur in a single location, from brainstorming sessions through distribution center capabilities.
The ownership business is completely free to decide how to use the given resources and manage the warehouse. The cost of private storage is much higher, but the flexibility may be worth it.
4. Cross-Docking Facilities:
Cross-docking facilities are warehouses that are designed to facilitate the unloading of incoming goods and the loading of outgoing goods in a very short time frame. Goods are usually not stored in the facility but are instead quickly sorted and moved to their next destination.
Cross-docking facilities are used for both short-term storage and for long-term storage of goods. They are often used by companies to quickly move goods from one place to another, and to minimize the amount of time that goods spend in the warehouse.
Cross-docking facilities can be used for a variety of purposes, such as for short-term storage, for long-term storage, for pick-and-pack-ship operations, for order fulfillment, for product assembly, and for transportation consolidation.
5. Automated Warehouses:
Automated warehouses are warehouses that use automation technology to store, sort, retrieve, and pack goods. Automation technology includes robotic arms, automated storage and retrieval systems, goods-to-person robots, conveyor systems, automated guided vehicles, and barcode scanners.
Automated warehouses are one type of warehouse that uses automation to reduce costs, increase output, and improve customer service.
Automated warehouses have been used in many industries such as retail, e-commerce, manufacturing, and logistics. They can also be used for inventory management, order picking, and delivery. Businesses are increasingly turning to automated warehouses as a means of reducing costs and boosting productivity.
These are warehouses that use automation and robotics to store and manage goods, reducing manual labor and eliminating the need for manual sorting and picking.
6. Contract Warehouse:
Similar to a public warehouse, a contract warehouse is likewise controlled by a third-party business that provides inventory space for the duration of a contract, as negotiated. Contract warehouses differ from other types of storage since they are exclusively used by one business.
All the advantages of a private warehouse are available when renting a contract warehouse without actually owning the building. The warehouse owner signs a contract with a single company and assumes the majority of the management duties. Companies can hire warehouse employees on a contract basis or use their own internal resources.
7. Smart Warehouse:
Smart warehouses use automation to streamline activities in the warehouse. As the production industry is subjected to more technological advancements, we see robots and complex machinery entering warehouses. In some warehouses, even machines have been used to interpret orders, get items from stock, and package things for shipping.
Smart warehouses will be advantageous to businesses who can afford to invest in inventory tracking technology and seek to reduce the risk of human error. For a smart warehouse, installation, maintenance, and employee training are pricey.
8. Climate-Controlled Warehouse
Businesses should employ climate-controlled facilities when selling products that are sensitive to temperature changes.
This includes items like wine that must be maintained at a specific temperature to stay fresh as well as perishables like frozen foods. It may also comprise more basic materials like wood, which can degrade in extremely humid environments.
Climate-controlled warehousing makes an effort to create an environment that encourages the growth of commodities using dehumidifiers, heaters, and other equipment.
Important Warehouse Management Processes
One aspect of supply chain management is warehouse management. All aspects of fulfilling retail orders, including storage, inventory control, shipping, and distribution, are affected.
You can see what's happening across multiple warehouse processes, such as the reception of inventory, the packaging of orders, the labelling of shipments, and any other movement of products, in real-time using an all-in-one solution.
Inventory Tracking
Inventory tracking is the process of monitoring the quantity, location, and state of the stock held in a warehouse.
This is done to ensure that the correct amount of inventory is available when it is needed and that it is stored in the right place.
Inventory tracking also helps to identify any discrepancies between the amount of inventory in the warehouse and the amount expected. This helps to prevent losses due to theft, damage, or misplacement of items.
Inventory tracking typically involves the use of barcodes or RFID tags to identify each item in the warehouse. This information is then linked to a database that stores information about the item, such as its location, quantity, and condition. Reports that give a summary of the inventory in the warehouse can then be produced using the data recorded in the database.
Inventory tracking can also be used to automate the process of ordering, receiving, and inventorying new items.
As a result, the procedure is more effective, and the time needed to operate the warehouse is decreased. It also helps to reduce the risk of errors and losses due to inaccurate data entry.
Picking and Packing
Picking and packing are two of the most important functions within a warehouse. Picking is the process of retrieving items from shelves, bins and other storage locations in order to fulfill customer orders. Packing is the process of preparing those items for shipment.
A system for both picking and packaging must be in place for a warehouse to be managed efficiently. The personnel should be able to easily follow the system's regulations and guidelines when carrying out these duties.
A system for monitoring orders, inventory, and other goods should be included of it as well. Other elements of the system might include an automated system for order fulfillment, barcode scanning, and automated packing systems.
Having a well-designed picking and packing system in place can help ensure that orders are fulfilled quickly and accurately, and that inventory is well-managed. This may contribute to greater customer satisfaction and, ultimately, more sales. Furthermore, it can help to reduce the cost of operations by streamlining the warehouse management process.
Receiving and Stowing
Receiving and stowing are essential to warehouse management for the smooth operation of the facility. Receiving involves the physical process of unloading, sorting, and documenting the arrival of goods, while stowing involves the process of organizing and placing goods in the warehouse.
Receiving is the first step in warehouse management and involves unloading goods from trucks or other conveyances, inspecting and verifying the goods, and documenting the arrival. The process may also include separating the goods into batches and labeling them according to the inventory system.
Stowing is the process of organizing and placing goods within the warehouse. It involves finding an appropriate storage location for the goods, organizing them in an efficient manner, and labeling them according to the inventory system. The goal of stowing is to ensure easy access to the goods when needed.
The two processes of receiving and stowing are important components of warehouse management. They help to ensure efficient operations by allowing goods to be quickly and accurately stored and retrieved. By properly organizing and labeling goods, warehouse staff can quickly locate and access the goods when needed.
Shipping
Shipping in warehouse management is the process of packaging, labeling, and sending products from the warehouse to a customer or another warehouse. It involves managing inventory, coordinating with carriers, tracking shipments, and ensuring that deliveries arrive on time and in good condition.

To make sure that all orders are processed quickly and accurately, the warehouse manager is in charge. They must ensure that the right products are sent and that the shipments are properly tracked. Additionally, the warehouse manager must ensure that the necessary paperwork is completed and that all necessary fees are paid.
Shipping firms like DHL, USPS, FedEx, and UPS will pick up orders from the warehouse and deliver items to their next destination in accordance with the delivery options and shipping options you provide to clients.
Your warehouse management system should be able to transmit tracking information back to your store as soon as an order ships so that your consumers can check on the status of their purchases.
Reporting
The operational and inventory data for the entire warehouse should be available right out of the box with a warehouse management system. Order accuracy (total mis picks, mispacks, etc.), total orders fulfilled each hour to gauge staff productivity, orders dispatched on schedule, and much more may be provided.
There is also information on how people are operating, like inventory estimates to understand labor management and staffing needs. You can quickly determine which employees have completed safety training, have licenses or other credentials to operate certain equipment, and have complied with all other legal requirements necessary to operate a secure warehouse by using a warehouse management tracking system.
Warehouse management reports can provide valuable insights into operations, such as inventory levels, stock turns, product flow and employee performance. Reports can assist in identifying possibilities to enhance procedures, boost effectiveness, save costs, and enhance customer service.
Common Warehouse Management Reports include:
1. Inventory Reports: These reports provide an overview of inventory levels, such as quantity on hand, reorder points, and safety stock levels.
2. Stock Movement Reports: These reports provide visibility into how product is moving in and out of the warehouse, including details on receiving, order fulfillment, and shipping.
3. Cycle Count Reports: These reports provide insight into the accuracy of inventory levels, including the number of cycle counts performed and the accuracy of each count.
Fulfilment Strategies for Warehouse Management
By selecting fulfilment strategies that are appropriate for the size of the company as well as the volume and diversity of orders it receives, the company may send products more rapidly, decrease waste, and boost customer satisfaction.
Using choosing methods that are suitable for the types of orders you receive will help you maintain the most effective workflow.
Take into account the following when picking, packing, shipping, and your distribution strategy in general:
Optimal Picking System
An optimal picking system is a type of warehouse management system that is designed to optimize the process of picking and packaging items for shipment. This system is typically used in warehouses and distribution centers to ensure that orders are picked, packed, and shipped in the most efficient and cost-effective manner possible.
The system can include automated picking systems, such as robotic pickers and automated conveyor belts, as well as manual picking systems that involve manual selection of items by workers. The system also includes software that tracks the inventory, orders, and shipment details to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Single Order
This is the basic picking method, which is typically only used by beginners. Simply said, a picker will complete one order before going on to the next.
This would be best for small retailers who haven't yet expanded to a size where they can gain from more advanced selecting methods.
Furthermore, you must avoid using if you ship more than 20 client orders each day (or plan to in the near future).
Batch Picking
Batch picking is a warehouse fulfillment strategy that maximizes efficiency by grouping like items together into “batches” for order fulfillment.
This process allows for the combination of several orders into a single picking trip, reducing the number of times a picker needs to walk the warehouse aisles in order to fulfill orders. This can save time and increase accuracy, as well as reduce labor costs.
Batch picking is an efficient way to manage inventory in a warehouse, as it reduces the amount of time that is spent picking and packing orders.
This would be best for orders that include a lot of just one or a few products.
Furthermore, you must avoid it if your orders frequently include a lot of items (or are aiming for this in the near future).
Learn more about batch tracking of inventory here.
Zone Picking
Zone picking is a warehouse management fulfilment strategy that involves dividing warehouse space into distinct zones, each of which is dedicated to storing a specific type of product.
This strategy is designed to improve the efficiency and accuracy of order fulfilment by allowing workers to quickly identify and access products in the right zone. It also helps warehouses keep inventory organized and easy to access, reducing the time it takes to pick and pack orders.
Zone picking can be combined with other strategies, such as batch picking and wave picking, to further optimize order fulfilment.
This would be best for stores that regularly mail orders with a large number of items.
Furthermore, if you routinely send orders with just one or a few things or if you have few pickers, stay away from it.
Wave Picking
Wave picking is a type of order fulfillment strategy used in warehouse management. It is a method of picking orders where a group of orders are picked together, or in a “wave”, rather than picking each order individually.
This technique is used to increase efficiency and accuracy in the order fulfillment process by reducing the time spent on order picking.
Wave picking can be used in combination with other order fulfillment strategies, such as zone picking and batch picking. It is commonly used in companies with high-volume order fulfillment needs.
This would be best for retailers who frequently send orders including a large number of items but need a rapid response.
Furthermore, you must avoid if your pickers are few, you frequently send tiny or individual order packages, or cost is more essential to you than delivery speed.
Check the following table where we have summarized everything at one place. Check below:
Optimizing Packing Process
There is more to packing than rapidly putting items into a box.
It's a time to firmly state that you're making the most effective deliveries of the appropriate products to the right clients.
Below are a few concepts to think about:
Packaging Materials
Products are protected during shipping and handling by packaging materials. Common packaging materials include cardboard boxes, plastic bags, bubble wrap, foam, and shrink wrap. These materials are typically used to bundle items together and keep them safe during transit.
Warehouse managers should consider the type of products they are shipping and the best packaging materials to use in order to ensure the safety of their shipments.
Some of the most typical ones are listed below:
Box Size
The size of a box in warehouse management depends on the size and weight of the items that need to be stored inside the box. In general, the box should be larger and heavier products heavier.
To handle a variety of item sizes and weights, boxes are available in a range of sizes, from small to large.
Some warehouses may also use specialized boxes, such as pallets, to store large or heavy items.
Shipping your Orders
When it comes to shipping your orders, it is important to ensure that you are using a reliable and reputable shipping service.
You should also take into account the cost of shipping and the estimated delivery date when you are making your shipping decisions.
Additionally, you should be sure to accurately package and label your orders so that they arrive safely and on time. Finally, you should always keep records of all your shipping transactions to ensure that you are able to track the progress of your orders.
Simple warehouse management procedures comprise the following steps:
- Weigh the Package
- Make the required shipping label (and invoice, if not already done so)
- Print Labels & Invoices
- On the appropriate order management system or sales channel, mark the order as "Shipped."
- Send the customer an email to confirm delivery and provide tracking information (a good order management system will do this for you automatically)
How Can ERP Systems Help with Warehouse Management?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems play a pivotal role in modern warehouse management by integrating core business processes such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics into a centralized platform.
This integration allows businesses to streamline operations across their entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness.
ERP warehouse management modules provide functionalities like real-time inventory tracking, warehouse optimization, demand forecasting, and labor management, enabling organizations to minimize stockouts, reduce carrying costs, and improve customer service levels.
By leveraging ERP for warehouse management, businesses can achieve greater visibility, control, and synchronization across their operations, ultimately driving enhanced productivity and profitability.
Warehouse Management Software Features
Following, we've discussed some important features of warehouse management software. Let's learn:
Inventory Management
Inventory management is the practice of monitoring and controlling a company's inventory. It involves overseeing the receipt, storage, retrieval, and distribution of items and materials.
A company can raise earnings, decrease costs, and enhance customer service with the use of inventory management. It can also help to prevent stock-outs and reduce inventory carrying costs.
Proper inventory management involves tracking all inventory items, understanding inventory levels, and maintaining accurate records. It also entails setting up a productive system for placing orders, receiving deliveries, and storing inventories.
Risk Management
The process of detecting, assessing, monitoring, controlling, and minimizing risks that pertain to a business or system is known as risk management.
It is an ongoing process that involves identifying and assessing risks, implementing strategies to mitigate those risks, and monitoring and responding to any changes in the risk environment.

Risk management is a critical component of business success as it helps to identify, prevent, and mitigate potential threats that could negatively impact an organization.
Proper risk management can also help organizations better understand and manage their business operations, enabling them to make better decisions and maximize their profits.
Order Management
Order management is the process of overseeing customer orders from the moment they are placed until they are fulfilled. This includes order processing, order tracking, returns management, and customer service. It is a critical function of any business that sells products and services.
Order management is important for businesses because it helps ensure that customers get what they want when they want it. It also helps businesses optimize their supply chain and inventory management processes.
Dock Management
Dock management is the coordination of activities related to the handling of goods at a dock. This includes the loading, unloading, and storage of goods, as well as the movement of vehicles and personnel.
Dock management is typically the responsibility of a dock supervisor or manager. The goal of dock management is to ensure the efficient and safe handling of goods, as well as the protection of workers and property.
Labor Management
Labor management is the process of managing the relationship between employers and employees. It involves creating and maintaining a harmonious working environment, developing and implementing policies for employee relations, and resolving conflicts between the two.
Labor management is used to increase productivity, reduce costs, and promote a safe and healthy work environment. It also aids in ensuring adherence to rules and laws governing the labor market.
Financial Management
In order to accomplish the aims and objectives of a company, financial management is the act of managing financial resources. It includes budgeting, forecasting, financial analysis, risk management, investment decisions, and financial reporting.
Financial management is a critical component of any successful business, as it helps to ensure that resources are used efficiently and effectively to achieve the desired results. It also helps to reduce risk and maximize profits.
Financial managers use a variety of tools and techniques to evaluate past performance and make informed decisions about future investments and activities.
Essential Components of Warehouse Management Software System
Choosing a warehouse management solution that meets your company's needs might be challenging because there are so many options available. So, the following are some of the essential components of a warehouse management software system.
Automation
This can be a great tool for an e-commerce company to save time and be more productive. By using automation, you should be able to reduce the possibility of human error in your fulfilment process.
This is because, once established, pre-defined rules govern what happens to objects, and you're picking and packing staff only needs to carry out these rules.
Digital Picking
As their businesses grow, many e-commerce companies will definitely wish to transition to digital picking from paper selection. Your warehouse management system must be set up to accommodate digital picking if you want it to be in any way future-proof.
Digital picking is the process of using digital technology to select items from a warehouse inventory. Digital picking may involve using a computer, barcode scanner, RFID tags, or voice recognition technology to identify, pick, and move items for orders. Digital picking technologies are intended to increase warehouse operations' precision, swiftness, and efficiency.
Inventory Tracking & Control
The practice of keeping track of and managing a company's inventory is known as inventory tracking and control. This includes tracking and managing the quantity, location, and value of inventory items, as well as the activities associated with managing inventory.
The goal of inventory tracking and control is to ensure that the inventory levels are accurate and up-to-date, and that the inventory is being used and managed in an effective manner. Inventory tracking and control can be done manually or through the use of an inventory management software system.
Easily Accessible Reports
Easily accessible reports are reports that are readily available and can be easily accessed, viewed, and generated by users with minimal effort. This could include reports that are generated automatically, stored in a central repository, or accessible via a web-based interface.

Examples include reports on sales, customer service, financial performance, inventory, marketing activities, and more. Reports should be designed with the user in mind and should be clear, concise, and organized in a way that makes the data easily understandable.
E-commerce is a data-driven industry. The more information you have available, the easier it is to make informed decisions. You can get all of this information from a competent warehouse management system in an intuitive style.
A warehouse management system (WMS) provides a variety of ways to monitor and provide data for controlling many elements of your warehouse operations. It includes tax systems, peak sales season, landing cost management, pricing, best-performing sales channels, most effective picker, etc.
Cloud-based for WMS
Cloud-based Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are software solutions that help warehouses manage inventory, orders, and supply chain operations. Cloud-based WMS provides users with the ability to access their WMS from any device with an internet connection, allowing for greater flexibility in warehouse operations.
Cloud-based WMS are also often more cost-effective than traditional WMS, as they often require less upfront costs, such as hardware and software licenses, as well as fewer maintenance costs, since the software is hosted on the cloud.
Additionally, cloud-based WMS are often more secure than traditional WMS, since data is stored in a secure, encrypted format.
Demand Forecasting
The technique of estimating consumer demand for a company's goods and services is known as demand forecasting. It is used to inform decisions about production, marketing, and inventory levels.
Demand forecasting involves gathering and analyzing data on past demand, current market conditions, and consumer trends. Companies use this information to develop strategies for meeting consumer needs and achieving their desired objectives.
Benefits of 3PL Warehouse Management
Due to the complexity and high cost of warehousing systems, many businesses choose to outsource the entire fulfilment process to a third-party logistics (3PL) provider.
The warehouse management practices used by 3PLs should be the same throughout all of their fulfilment centers, unlike an on-demand warehousing provider, which looks for warehouses with more capacity.
Here are some advantages of utilizing a certified logistics company to deliver out orders and keep inventory.
Logistical Optimization
3PLs have access to a wealth of data and are adept at a variety of tasks, including appraising shipping zones and forecasting demand and inventory, because they work with so many different organizations, including seasonal brands, high-growth brands, and everyone in between.
By consistently gathering data and learning from it, you may lower shipping costs, shorten customer travel times, and improve each warehouse's efficiency. These things all aid in your development.
Improved Uses for Warehouse Space
If your warehouse is likely to become too tiny, working with a 3PL might greatly simplify your life. Even after you've engaged a 3PL to manage your fulfilment, you can choose to either let the lease on your old warehouse expire or use the space for something else, such as growing your internal B2B ecommerce or wholesale fulfilment channels.
A 3PL can assist you in paying for only the space you actually require, whether you need to pay by the bin, shelf, pallet, or any other combination of those for your things. In this manner, you can rest assured that you will always be able to use the space you are paying for.
Huge Time Savings
A 3PL handles the time-consuming logistical responsibilities (picking, packing, restocking supplies, shipping, inventory storage, returns, order tracking, kitting, etc.) and the stress of operating a warehouse with its ecommerce order fulfilment services.
While they take care of these duties on your behalf, you may monitor them and use the information they provide to grow and enhance your business.
Multiple Warehouses and Larger Geographic Footprint
Having multiple warehouses allows companies to store and manage inventory more efficiently, as well as increase their geographic footprint by allowing them to deliver products to customers in different parts of the country or even the world.
This can help increase customer satisfaction by providing faster delivery times, as well as allowing companies to expand their customer base by offering products to a broader area. Additionally, having multiple warehouses can help reduce transportation costs by allowing the company to ship products directly to customers in the most cost-effective way.
Only when your warehouse is open may you ship from it. Working with a 3PL will allow you to distribute your inventory throughout several of their fulfilment centers, putting it in close proximity to more customers. If you ship nationally, you must have warehouses from coast to coast.
Real-time Insights
Even though you don't operate for the 3PL, you will be kept up to date on the advancements. They should be able to see the movement of your inventory, including when things are received, stored or put away, picked, packed, shipped, and any other actions.
With specialized warehouse management software, you can search orders based on the tracking number, the destination country, the quantity of items they contain, the sales channel, and the location of the fulfilment centre.
You can also receive total transparency into performance, including information on the timeliness, accuracy, and speed with which orders are fulfilled, the absence of disputes, and much more.
Warehouse Monitoring & Reporting
Warehouse monitoring and reporting is a process used to track and report on the activities that take place within a warehouse. This can include inventory control, order fulfillment, and other operational activities.
To make sure that goods and services are delivered to clients in a timely, effective, and accurate way, warehouse monitoring and reporting is used. Warehouse monitoring and reporting can also help identify areas of improvement and provide the data necessary to make informed decisions.
Warehouse KPIs
Check the following warehouse key performance indicator (KPIs):
1. Inventory Turnover:
This metric measures how quickly a company is using and replenishing its inventory. Inventory replacement and disposal volume over a period of time. The total cost of products sold over time is divided by the normal cost of inventory over the same time period to arrive at this figure.
This KPI evaluates how effectively a warehouse manages its stock to meet client demand. More inventory turnover is frequently requested. Inventory turnover may be poor if a warehouse overestimates demand.
It can be expensive to have too much slow-moving inventory, especially for companies that deal with products with a defined shelf life.
2. Stock Accuracy:
This metric measures the ability of a company to have an accurate inventory count.
3. Lead Time:
This metric calculates how long it takes from the time an order is placed until it is shipped.
4. On-Time Deliveries:
This metric measures how often a company delivers its products on time.
5. Labor Utilization:
This metric measures how effectively the workforce is being used.
6. Space Utilization:
This metric measures how efficiently the warehouse space is being used.
7. Order Fulfillment Accuracy:
This metric measures the accuracy of order fulfillment, including the accuracy of order picking and packing.
8. Order Fulfillment Speed:
This metric measures how quickly orders are being fulfilled.
9. Return Rate:
This metric measures the rate at which customers return products. The proportion of items sold that customers return; calculated by dividing the amount of returned items by the number of items sold.
To get the full picture of this KPI, think about the causes of product returns. If customers frequently receive incorrect or damaged goods, there is room for improvement. A customer accidentally ordering the wrong product may not imply warehouse operation concerns.
10. Safety Incidents:
This metric measures the number of safety incidents that occur in the warehouse.
Warehouse Performance Evaluation
Monitoring performance and making adjustments are necessary for supply chain management in every element.
And nothing has changed in terms of warehouse management.
This mainly has to do with two things:
- accuracy of customer order fulfilment (without damage).
- rapidly completing customer orders (without damage).
In light of this, the primary KPIs you should be tracking to evaluate the success of your warehouse management process are as follows:
Receiving Efficiency
Simply explained, this is the time it takes for your team to receive and maintain a newly sent purchase order.
It's advisable to record exact timestamps for:
- Obtaining delivery of fresh stock.
- When storage of this stock is ready.
- However, once the items have been stored away.
To see how performance is trending in this section of your warehouse operations, you can then determine the time difference between each point and the average for the month.
Rate of Return
When a customer returns an order, it's possible that they simply had buyer's remorse; warehouse problems aren't always to fault.
Making the most of this hence requires segmenting based on the cause for return. The operations or warehouse manager can then start looking into the specific reasons for this KPI's probable overperformance and putting remedies in place.
Determine numerous distinct return causes, then analyze each one utilizing the following equation:
Lead Time for Orders
Order lead time is the amount of time it takes for a client to receive an order (or average order processing time).
It might be advantageous to further divide this into groups. Orders for unusual or large products, orders from distant nations, orders made through Amazon Prime, etc. are a few examples.
But typically:
Customers would be delighted with you if you can reduce order lead times, provided everything comes in perfect shape.
Picking Accuracy
By properly recording and segmenting rate of return, you can analyze picking accuracy, an important piece of data.
To assess picking accuracy, solve the following equation using data from the rate of return KPI and the total number of orders for the time period:
Warehouse Management Principles
Following, we’ve discussed crucial principles of warehouse management. Let’s learn:
1. Establish a Systematic Process:
Establishing a systematic process for warehouse management is essential for ensuring that all tasks are completed efficiently and effectively. This process should include an inventory management system, a system for tracking and managing shipments, and an efficient storage system.
2. Develop Clear Policies and Procedures:
Developing clear policies and procedures for warehouse management is important for ensuring that all tasks are completed correctly and in a timely manner. These policies and procedures should address everything from worker safety to inventory control.
3. Utilize Automation:
Automation is the secret to improving warehouse management's efficacy and efficiency. Through automation, processes can be made more effective, which also helps to reduce the need for physical labor.
4. Use Technology to Improve Efficiency:
Utilizing technology in the warehouse can help to improve the efficiency of warehouse management processes. This includes using barcode scanners, radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, and warehouse management systems (WMS).
5. Improve Communication:
Improving communication between warehouse staff and other departments is essential for ensuring that tasks are completed correctly and in a timely manner. This includes using communication systems such as emails, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
6. Invest in Quality Staff:
When it relates to warehouse management, hiring qualified employees is one of the most important expenditures you make.
Having quality staff can help ensure that the warehouse runs efficiently and that goods are shipped and stored safely and securely. Quality staff can also help improve customer service, reduce errors and increase productivity.
Investing in quality staff can also help to reduce costs associated with warehouse management, as well as help to create a safe and welcoming work environment for all employees.
Key Benefits of a Warehouse Management Software System
Below we've discussed key benefits associated with WMS. Let's learn:
1. Improved Inventory Control
A good WMS can help businesses to better manage and track inventory levels, allowing them to avoid stockouts and overstocking. This can help businesses save costs by only ordering and stocking what’s needed.
2. Increased Efficiency
A WMS can help streamline processes, such as order fulfillment, by automating and optimizing tasks. This can help reduce manual labor requirements, increase accuracy, and improve overall efficiency.
3. Reduced Labor Costs
Automating processes can help reduce labor costs, as fewer employees are needed to complete the same tasks.
4. Improved Customer Service
A WMS can help businesses to better manage customer orders and provide timely order fulfillment. This can help improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Increased Visibility
Businesses can get real-time information on the status of their inventory, orders, and warehouse activity through the use of a WMS. Businesses may be able to plan better and make better decisions as a result.
Important Tips to Arrange your Warehouse
Making ensuring everything is set up as efficiently as possible is perhaps the most crucial initial step in optimizing your warehouse operations.
What you should consider is this:
Warehouse Layout
Warehouse layout is the organization of different areas within a warehouse. It typically involves the placement of storage racks, shipping and receiving areas, office spaces, and other related components within the facility.
An effective warehouse architecture can boost production, lower expenses, and increase operational effectiveness. The design of the warehouse layout should be based on the size and type of products being stored and the operational needs of the business.
Labelling Areas
Warehouse management cannot be successful without properly labelled stock with established locations and names.
Your staff should have access to your warehouse system and be able to locate any goods with accuracy.
Practicality is key in this situation.
If you keep to straightforward alphanumeric combinations, it will be simpler to grasp and decipher for pickers seeking to access that web location.
Arranging Inventory in Warehouse
We now have a warehouse that is set up and labelled in the best way for your business. However, this raises the following issue:
How can you determine the exact location where each product should be stored?
Keep higher margin items close to the packaging station as a solution.
We conducted research on more than 20 Veeqo stores and discovered that just 20% of a company's products frequently account for 60% of its sales.
You can drastically reduce the amount of time pickers spend walking by selecting the 20% of products that make up your company's historical sales data and placing them as close to the packing desk as you reasonably can.
The usage of instruments like ABC Analysis is becoming prevalent in inventory management. However, this can also offer some useful information regarding this facet of warehouse management.
Re-arranging your Warehouse
Re-arranging your warehouse can help improve its efficiency. Here are some tips to help you get started:
1. Begin by evaluating your current layout: Determine which areas require more space and which could benefit from reorganization.
2. Take inventory of your existing warehouse products and equipment: Make sure to note any items that are no longer in use or need to be replaced.
3. Make a Plan: Lay out a rough sketch of how you want the warehouse to be organized and which areas need more space.
4. Start Organizing: Reorganize your warehouse by grouping items according to their use and purpose.
5. Utilize the Right Equipment: Make sure to use appropriate tools and machinery to help streamline the process.
6. Label Everything: Label items, shelves, and racks to help workers quickly find what they need.
7. Implement Safety Measures: Make sure all items are properly secured and that there are no tripping hazards.
8. Adjust as Needed: Your warehouse layout may need to be adjusted in the future, so be prepared for that.
9. Use Technology: Utilize warehouse management software to help you manage your inventory and warehouse operations.
Warehouse Equipment
Warehouse equipment typically includes items such as shelving, storage bins, pallet racks, forklifts, conveyor belts, racking systems, scales, sorting systems, automated conveyor systems, compactors, and robotic arms. Other items may include ladders, hand trucks, carts, and packaging materials.
Choosing a Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Following, we've discussed things you should consider while choosing a warehouse management system.
1. Determine your Needs
The first step in selecting a Warehouse Management System (WMS) is to clearly define your warehouse objectives and requirements. Consider factors like inventory management, order fulfillment, warehouse layout, and labor management.
2. Research WMS Vendors
Once you’ve determined your needs, research the various WMS vendors that provide warehouse solutions that meet your requirements. Consider factors like cost, scalability, and the vendor’s reputation.
3. Evaluate the Features
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of vendors, evaluate the features each WMS offers. Consider features like barcode scanning, automated data collection, and real-time reporting.
4. Test the System
Once you’ve selected a vendor, it’s important to test the system to ensure it meets all of your warehouse needs. Ask for a demonstration or a trial period to get an idea of how the system works.
5. Monitor Performance
Once you’ve implemented the system, monitor its performance to ensure its meeting your objectives. Make sure to ask for feedback from warehouse staff to get an accurate picture of how the system is performing.
FAQs Related to Warehouse Management
Que 1: Which warehouse management system is preferable for you: a standalone or integrated one?
Ans: If you utilize a standalone, you must integrate it with the rest of your operating systems. However, an integrated solution will address every stage of your order management process.
Furthermore, you should weigh the benefits and drawbacks of both options before deciding which is best for your company.
Standalone WMS
A standalone WMS is a WMS that just focuses on warehouse management. Even if it might interface with other systems, the features will be tailored toward warehouses.
Advantages
- Give warehouse operations a wide range of features, including cycle inventory counts, warehouse reports, and multiple picking options.
- Should be able to integrate with operational solutions. It includes inventory management software, point-of-sale systems, and ERP programs.
Disadvantages
- Lack of procedural openness Because your reports are just interested in warehouse operations, they can have gaps when trying to analyze the complete fulfilment process.
- Standalone solutions can be cumbersome to use because the ecommerce fulfilment process requires logging into multiple separate items.
- Since they commonly do not offer substantial inventory tracking and control tools or real-time contact with sales channels, these are typically insufficient for multichannel ecommerce. making it more difficult to monitor your stock levels.
- They cannot be cost-effective because you will need to buy additional goods to handle your fulfilment.
Integrated WMS
This type of WMS and the rest of your order management system will both use the same database. This suggests that the management of your orders will be coordinated throughout the entire procedure.
Advantages
- Integrated systems offer a single, centralized method for order fulfilment. This suggests that the information about your orders, inventory, and delivery is always current.
- Detailed reporting and forecasts. This kind of system keeps track of all the information on the fulfilment of your orders, enabling more thorough reporting and precise estimates.
- Saves both money and time. The time it takes to manage your fulfilment process is reduced because there is only one software to log into.
- Because they only need to learn how to utilize one system, your team will likewise find it easier. Additionally, you simply need to pay for one solution and interact with one support staff.
Disadvantages
The integrated solution may include fewer warehouse functions or be less specialized, depending on the standalone and integrated solutions you choose.
Que 2: Warehouse Management Vs Inventory Management?
Ans: Following, we've discussed warehouse management and inventory management. Let's learn:
Warehouse Management:
Warehouse management is the process of managing the receiving, storage, retrieval and shipping of goods and materials within a warehouse. This includes the planning and organization of the space, equipment, labor and inventory control.
Inventory Management:
Inventory management is the process of overseeing and controlling the ordering, storage, and use of materials and products in an organization. It includes the tracking of material and product purchases, costs, usage and inventory levels throughout the entire supply chain, from raw material acquisition to the finished product. Inventory management also includes the management of stock levels, reorder points and order quantities.
In addition to these two, there is stock management. Let's study it, too:
Stock Management
Although "stock management" and "inventory management" are frequently used interchangeably, it's important to know the difference between the two, particularly for companies that manufacture things. A finished good that is ready for distribution or sale is often referred to as stock.
However, inventory includes all items in the warehouse, including unfinished goods, products that are still in the process of being manufactured, and raw materials (stock).
Stock management is a subset of inventory management that is therefore primarily concerned with maintaining the least amount of stock while still being able to satisfy customer demand. Space and money are saved in this way.
Que 3: Warehouse vs. Distribution Center
Ans: Distribution centers and warehouses are facilities used to store and deliver goods. The main differences between a warehouse and a distribution centre are their size and purpose.
A warehouse is typically a large facility used to store goods for a longer period of time, while a distribution center is a smaller facility used to quickly move goods from one location to another. Warehouses are typically used for long-term storage, while distribution centers are used for shorter-term storage and distribution.
Que 4: When you should switch to a warehouse management system?
Ans: Your individual business needs will determine whether and when you opt to upgrade your warehouse management systems, as is the case with many other decisions.
When should your warehouse management system be improved? Here are some queries to think about:
- Does your current process have a 99.9% picking accuracy rate? If not, how much does each wrongly chosen order cost the business?
- And would it be more cost-effective to replace some of them with software or a warehouse management system?
- Have you been meeting your growth objectives? And how swiftly do you anticipate expanding in the coming short to medium term?
- How many employees does your current company need?
- What does the other warehouse KPI look like? How beneficial would it be to enhance each one?
- What number of orders do you process each day? And how much money does this bring in?
Que 5: Points that I Should Keep in Mind before Choosing Warehouse Management System?
Ans: Using warehouse management systems or some kind of warehouse management software can eliminate a sizable percentage of the manual labour involved in all the aforementioned tasks.
Everything they can be automated and digitalized. aiding significantly:
- Organize, keep an eye on, and document everything.
- Pick something that is close to perfection with accuracy.
- Speed up every step of your logistical procedure.
But sorting through all the data to determine whether to upgrade and what to really look for in your management software can be challenging.
How Can Deskera ERP Assist You with Warehouse Management?
Deskera ERP offers several features and benefits that can significantly enhance warehouse management:
- Inventory Management: Deskera ERP provides robust tools for tracking inventory levels in real-time. It allows businesses to monitor stock movements, manage stock locations, and automate reorder points. This capability ensures optimal inventory levels, minimizes stockouts, and reduces carrying costs.
- Order Processing: The ERP system streamlines order fulfillment processes by integrating sales orders with inventory data. It facilitates efficient order picking, packing, and shipping operations, leading to faster order processing times and improved customer satisfaction.
- Warehouse Optimization: Deskera ERP includes features for warehouse layout planning, space utilization optimization, and bin/rack management. By organizing the warehouse layout effectively and utilizing space efficiently, businesses can reduce storage costs and enhance operational efficiency.
- Real-time Analytics: The ERP system provides powerful reporting and analytics capabilities, offering insights into warehouse performance metrics such as inventory turnover, fill rates, and order accuracy. These insights enable data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement in warehouse operations.
- Integration with Supply Chain: Deskera ERP integrates seamlessly with other modules like procurement, sales, and logistics. This integration ensures smooth coordination between different aspects of the supply chain, from procurement of raw materials to delivery of finished goods, optimizing overall supply chain efficiency.
- Mobile Accessibility: Deskera ERP is often accessible via mobile devices, allowing warehouse managers and staff to access real-time data, perform inventory counts, and manage operations from anywhere. This flexibility enhances agility and responsiveness in warehouse management.
Final Takeaways
We've arrived at the last section of this guide. Let's have a look at some of the most important points to remember:
- Warehouse management is the process of managing the storage and movement of goods and materials within a warehouse. It’s an important part of any supply chain operation and involves the coordination of receiving, storing, and shipping activities.
- A warehouse management system (WMS) is used to monitor, manage, and optimize the storage and flow of products. It is used to identify the exact location of goods, manage stock levels, control inventory costs, and improve customer service. WMS also makes it possible to see the entire supply chain, as from manufacturer to the client.
- Utilizing technology in the warehouse can help to improve the efficiency of warehouse management processes. This includes using barcode scanners, radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, and warehouse management systems (WMS).
- An optimal picking system is a type of warehouse management system that is designed to optimize the process of picking and packaging items for shipment. This system is typically used in warehouses and distribution centers to ensure that orders are picked, packed, and shipped in the most efficient and cost-effective manner possible.
- Products are protected during shipping and handling by packaging materials. Common packaging materials include cardboard boxes, plastic bags, bubble wrap, foam, and shrink wrap. These materials are typically used to bundle items together and keep them safe during transit.
- 3PLs have access to a wealth of data and are adept at a variety of tasks, including appraising shipping zones and forecasting demand and inventory, because they work with so many different organizations, including seasonal brands, high-growth brands, and everyone in between.
- Deskera ERP empowers businesses with the tools and capabilities needed to streamline warehouse operations, improve inventory accuracy, reduce costs, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction through efficient order fulfillment and supply chain management.
Related Articles














