According to a report by MHI, the material handling and logistics industry association, 58% of warehouse operators consider improving inventory management as a top priority. Additionally, 61% of warehouses are planning to invest in technology solutions to improve inventory visibility and control.
These statistics highlight the growing recognition among warehouse managers of the importance of implementing effective inventory control strategies. With the increasing complexity of supply chains and the rise of e-commerce, optimizing warehouse efficiency has become essential to meet customer expectations and maintain a competitive edge.
In this article, we will explore the latest trends and strategies for maximizing warehouse efficiency through effective inventory control.
We will delve into key strategies such as implementing automated inventory tracking systems, adopting lean inventory management principles, optimizing warehouse layout and organization, and leveraging data analytics for demand forecasting and replenishment.
By implementing these strategies, warehouse managers can minimize stockouts and overstocks, reduce order fulfillment times, improve accuracy in picking and packing operations, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
We will also discuss the benefits of implementing real-time inventory visibility, utilizing advanced technologies such as barcode scanning and RFID, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement within the warehouse environment.
This article will provide warehouse managers and inventory control professionals with valuable insights and actionable steps to maximize warehouse efficiency. By implementing effective inventory control strategies, you can optimize space utilization, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and drive overall business success.
In this context, leveraging advanced technology and software solutions like Deskera can play a significant role. Deskera ERP integrates various business processes, including inventory management, demand forecasting, and warehouse operations, into a single platform. This integration provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, streamlines warehouse processes, and automates routine tasks.
What is Warehouse Efficiency?
Warehouse efficiency refers to the optimal performance of all warehouse operations, ensuring that goods are stored, retrieved, and handled in the most effective manner.
This involves maximizing the use of space, minimizing waste, and streamlining processes to achieve quick and accurate order fulfillment. Effective warehouse inventory management is crucial for achieving high efficiency, as it helps track and control inventory levels, locations, and movements.
A robust warehouse inventory management system can greatly enhance efficiency by providing real-time data, automating processes, and reducing manual errors.
By implementing the best warehouse inventory management software, businesses can ensure that their warehouse operations run smoothly, resulting in cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Impact of Warehouse Efficiency on Overall Business Performance
The efficiency of a warehouse directly impacts the overall performance of a business.
Efficient warehouse and inventory management lead to several key benefits:
Cost Reduction
By optimizing space and reducing waste, businesses can lower their operational costs. An effective inventory warehouse management system helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels, preventing overstocking and stockouts, which can both be costly.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Quick and accurate order fulfillment is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction. A streamlined warehouse inventory management system ensures that products are picked, packed, and shipped promptly, leading to timely deliveries.
Enhanced Productivity
Automation and advanced warehouse inventory management software can significantly boost productivity by reducing manual tasks and errors. Employees can focus on more strategic tasks, improving overall operational efficiency.
Better Decision Making
Real-time data provided by a warehouse management system (WMS) allows for informed decision-making. Businesses can analyze warehouse management system examples to understand best practices and implement strategies that enhance efficiency.
Scalability
As businesses grow, their warehousing needs evolve. An effective warehouse inventory management system provides the scalability required to handle increasing volumes without compromising efficiency.
What is Inventory Control?
Inventory control refers to the systematic approach to managing and regulating the quantity, location, and flow of inventory within a warehouse. It involves monitoring inventory levels to ensure that the right amount of stock is available at the right time to meet customer demand while minimizing excess inventory.
Effective inventory control is achieved through the use of a robust warehouse inventory management system that provides real-time visibility into inventory status and movements.
A warehouse inventory management system, often part of the best warehouse inventory management software, enables businesses to track inventory accurately, reduce manual errors, and automate replenishment processes. This ensures that inventory levels are optimized, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstock situations.
What are the Objectives of Efficient Inventory Control?
Effective inventory control is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient operation within a warehouse.
The primary objectives of inventory control include:
Maintaining Optimal Inventory Levels
One of the main goals of inventory control is to keep inventory levels balanced. This means having enough stock to meet customer demand without overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs. An efficient warehouse inventory management system helps in maintaining these optimal levels.
Reducing Holding Costs
By managing inventory effectively, businesses can reduce the costs associated with storing excess stock. This includes costs for warehousing, insurance, and obsolescence. Implementing a reliable inventory warehouse management system helps in tracking and minimizing these costs.
Enhancing Order Accuracy and Fulfillment
Accurate inventory control ensures that orders are fulfilled correctly and promptly. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business. Warehouse inventory management software aids in reducing picking and packing errors, ensuring that customers receive the correct products on time.
Improving Cash Flow
Efficient inventory control frees up capital that would otherwise be tied up in excess inventory. This improves cash flow, allowing businesses to invest in other areas. A warehouse and inventory management system provides insights into inventory turnover rates, helping businesses manage their cash flow better.
Enabling Better Decision Making
Access to real-time inventory data through an inventory management system allows businesses to make informed decisions. Whether it's adjusting reorder points, planning for seasonal demand, or identifying slow-moving items, a warehouse management system provides the necessary data for strategic decision-making.
Enhancing Warehouse Efficiency
Effective inventory control contributes to overall warehouse efficiency. By minimizing the time spent searching for items and reducing the frequency of stock checks, a warehouse inventory management system streamlines operations and boosts productivity.
Reducing Waste and Shrinkage
Inventory control helps in identifying and minimizing waste, such as damaged or expired goods, and reduces shrinkage due to theft or misplacement. Implementing the best warehouse inventory management software provides tools for tracking and managing these issues effectively.
In summary, inventory control is a fundamental aspect of warehouse management that ensures the efficient flow of goods, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
By leveraging advanced warehouse inventory management systems and software, businesses can achieve these objectives and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
What are the Key Inventory Control Strategies?
By employing the key inventory control strategies, businesses can optimize their warehouse operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Advanced warehouse inventory management systems and software play a vital role in implementing and managing these strategies effectively.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory is a strategy where inventory is ordered and received only as needed for production or customer sales. This approach minimizes inventory holding costs by reducing the amount of stock kept on hand.
The warehouse inventory management system plays a crucial role in successfully implementing JIT by providing real-time data on inventory levels and demand forecasts.
Benefits:
- Reduces holding costs and waste
- Increases efficiency and responsiveness to market changes
- Improves cash flow by minimizing capital tied up in inventory
Challenges:
- Requires precise demand forecasting and reliable suppliers
- Vulnerable to supply chain disruptions
- Can lead to stockouts if not managed carefully
Implementation Tips:
- Use advanced warehouse inventory management software for accurate tracking and forecasting.
- Establish strong relationships with suppliers for timely deliveries.
- Continuously monitor inventory levels and adjust orders based on real-time data.
Safety Stock Management
Safety stock management involves maintaining a buffer of extra inventory to protect against uncertainties in demand and supply. This ensures that there are enough products available to meet unexpected spikes in demand or delays in supply.
Calculating Appropriate Safety Stock Levels"
Calculating safety stock requires analyzing historical demand data, lead times, and variability. The formula often used is:
Safety Stock = Z × σ<sub>d</sub> × √L
Where:
- Z is the desired service level,
- σ<sub>d</sub> is the standard deviation of demand, and
- L is the lead time.
Balancing Safety Stock with Inventory Costs
To balance safety stock with inventory costs, regularly review and adjust safety stock levels based on changes in demand patterns and lead times. Utilize a warehouse inventory management system to monitor these factors and optimize safety stock levels.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is an inventory categorization technique where items are classified into three categories (A, B, and C) based on their importance:
- A items: High-value items with low frequency of sales
- B items: Moderate-value items with moderate sales frequency
- C items: Low-value items with high frequency of sales
Steps to Implement ABC Analysis
- Classify inventory items based on value and sales frequency.
- Assign items to A, B, or C categories.
- Focus on managing A items more closely due to their higher impact on the business.
Advantages of Prioritizing Inventory Items
- Improves inventory management efficiency
- Allows for better allocation of resources
- Enhances decision-making by focusing on the most critical items
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is the optimal order quantity that minimizes the total cost of ordering and holding inventory.
To calculate the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), you can use the following formula:
EOQ = √((2DS)/H)
Where:
- D is the demand rate,
- S is the order cost, and
- H is the holding cost per unit per year.
Benefits of EOQ
- Reduces total inventory costs
- Optimizes order quantity and frequency
- Balances ordering and holding costs effectively
Application in Different Warehouse Scenarios
EOQ can be applied in various warehouse scenarios by adjusting the parameters to fit different demand patterns, lead times, and cost structures. Using warehouse inventory management software can help in calculating and applying EOQ accurately.
Cycle Counting
Cycle counting is a method of auditing inventory where a small subset of inventory is counted on a rotating schedule, rather than conducting a full inventory count annually.
Benefits over Annual Physical Inventory Counts
- Reduces disruption to warehouse operations
- Improves inventory accuracy and identifies issues promptly
- Provides continuous and timely updates on inventory status
Best Practices for Cycle Counting
- Schedule counts during low activity periods.
- Use a warehouse inventory management system to track and plan cycle counts.
- Train staff to perform accurate counts and reconcile discrepancies immediately.
Implementation Tips:
- ABC Classification: Prioritize inventory items based on value and frequency of movement to determine the frequency of cycle counts.
- Technology Integration: Utilize barcode scanning or RFID technology to streamline cycle counting processes and enhance accuracy.
- Regular Review: Evaluate cycle counting results regularly to identify trends, address root causes of discrepancies, and refine counting procedures.
Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for effective inventory management. It helps in predicting future customer demand, allowing businesses to adjust inventory levels accordingly to avoid stockouts and overstock situations.
Techniques for Forecasting
- Historical Data Analysis: Using past sales data to predict future demand.
- Market Analysis: Considering market trends, economic indicators, and customer feedback.
- Advanced Analytics: Utilizing machine learning and statistical models to enhance forecasting accuracy.
Integrating Forecasting with Inventory Control
Integrating demand forecasting with inventory control ensures that inventory levels are aligned with expected demand. Warehouse inventory management software can help in automating this integration, providing real-time insights and enabling proactive inventory management.
Utilizing Cross-Docking and Efficient Order-Picking Strategies
Cross-Docking
Cross-docking is a logistics practice where incoming shipments are directly transferred to outbound transportation without long-term storage. This strategy reduces storage costs, minimizes inventory holding, and speeds up the delivery process.
Benefits of Cross-Docking:
- Reduced Storage Costs: By minimizing the time products spend in the warehouse, storage costs are significantly reduced.
- Increased Efficiency: Direct transfer of goods from inbound to outbound docks streamlines operations, reducing handling times.
- Faster Delivery: Cross-docking accelerates the supply chain, leading to quicker order fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction.
Implementation Tips:
- Strategic Dock Layout: Design the warehouse layout to facilitate seamless transfer between docks.
- Real-Time Communication: Ensure constant communication between suppliers, warehouse staff, and outbound logistics to synchronize operations.
- Advanced Scheduling: Use advanced scheduling systems to plan inbound and outbound shipments effectively.
Efficient Order-Picking Strategies
Order picking is the process of retrieving products from storage to fulfill customer orders. Efficient order-picking strategies are crucial for optimizing warehouse operations and enhancing productivity.
Types of Order-Picking Strategies:
- Batch Picking: Collecting multiple orders simultaneously to minimize travel time and increase picking efficiency.
- Zone Picking: Dividing the warehouse into zones, with pickers assigned to specific areas to reduce congestion and improve accuracy.
- Wave Picking: Coordinating picking activities in waves based on shipment schedules or carrier pick-up times to streamline processes.
Benefits of Efficient Order-Picking:
- Reduced Picking Time: Streamlined picking processes decrease the time required to retrieve items, leading to faster order fulfillment.
- Improved Accuracy: Implementing strategies like barcode scanning and RFID technology reduces errors, ensuring accurate order fulfillment.
- Enhanced Productivity: Efficient order-picking methods optimize labor usage and increase overall warehouse productivity.
Best Practices for Order-Picking:
- Utilize Technology: Implement warehouse management systems (WMS) and automated picking tools to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
- Regular Training: Continuously train staff on best practices and new technologies to maintain high performance levels.
- Optimize Layout: Design the warehouse layout to minimize travel distances and streamline picking paths.
Incorporating cross-docking and efficient order-picking strategies into your warehouse operations can significantly improve inventory management and overall efficiency. These strategies, combined with advanced warehouse inventory management systems, contribute to a leaner, more responsive supply chain.
Optimizing Storage Layout for Easy Access and Space Utilization
Efficient storage layout design is critical for maximizing warehouse space utilization and ensuring easy access to inventory. A well-organized storage layout minimizes travel time, reduces picking errors, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Key Considerations for Optimizing Storage Layout:
- Strategic Zoning: Divide the warehouse into zones based on product characteristics, demand frequency, or storage requirements to streamline operations.
- Vertical Space Utilization: Utilize vertical storage options such as mezzanines, pallet racking, or automated storage systems to maximize storage capacity.
- Clear Aisles and Pathways: Maintain clear and wide aisles for easy navigation of equipment and personnel, reducing congestion and improving safety.
- Product Segmentation: Group similar products together and arrange them based on demand patterns or SKU similarities to facilitate efficient picking and replenishment.
- Flexible Design: Design storage areas with modular and adjustable shelving or racking systems that can adapt to changing inventory needs and seasonal fluctuations.
- Integration with Technology: Incorporate RFID or barcode systems into storage locations to enhance inventory tracking accuracy and visibility.
Benefits of Optimizing Storage Layout:
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined storage layout reduces travel time for picking and replenishment activities, improving overall warehouse productivity.
- Enhanced Space Utilization: Effective space management maximizes storage capacity, allowing for more inventory without expanding physical footprint.
- Reduced Costs: Efficient storage reduces handling costs, minimizes product damage, and optimizes labor utilization.
- Improved Order Fulfillment: Easy access to inventory items enables faster order picking and fulfillment, enhancing customer satisfaction.
By optimizing storage layout for easy access and space utilization, businesses can create a more agile and efficient warehouse environment. This approach not only improves operational efficiency but also supports other inventory control strategies to meet business objectives effectively.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO) Inventory Control System
Implementing a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory control system is a fundamental strategy for efficient inventory management. FIFO ensures that the oldest inventory is sold or used first, reducing the risk of product obsolescence, spoilage, or deterioration.
Steps to Implement FIFO:
- Label and Track Inventory: Clearly label each inventory item with a unique identifier or barcode to track the product's arrival date and enable easy identification of the oldest inventory.
- Organize Storage Areas: Arrange storage areas to promote easy access and separate incoming inventory from products ready for sale or use.
- Establish Placement Rules: Define rules for product placement based on arrival date, ensuring older inventory is used before newer stock.
- Rotate Inventory: Regularly inspect and rotate stock so that older inventory is readily available for use or sale.
- Train Staff: Educate warehouse staff on FIFO principles and procedures, emphasizing accurate inventory handling and rotation.
- Use Inventory Tracking Systems: Implement inventory management software to automate tracking and facilitate FIFO management.
Utilizing Real-Time Data for Demand Forecasting and Planning
Utilizing real-time data for demand forecasting and planning is a key strategy for achieving warehouse efficiency.
Real-time data provides up-to-date insights into customer demand, market trends, and inventory levels, enabling businesses to make more accurate and proactive decisions.
Here's how to leverage real-time data for demand forecasting and planning to enhance warehouse efficiency:
- Implement Integrated Systems: Integrate your inventory management system with other data sources such as point-of-sale (POS) systems, online sales platforms, and supply chain partners. This integration allows for real-time data synchronization and provides a holistic view of customer demand and inventory levels.
- Forecasting Models: Employ advanced forecasting models, such as time series analysis, regression analysis, or machine learning algorithms, to analyze historical data and predict future demand accurately. Real-time data can be used to refine and update these models continuously, improving their accuracy over time.
- Demand Sensing: Implement demand sensing techniques to capture real-time changes in customer demand. This can be done through monitoring social media trends, tracking online conversations, or utilizing advanced analytics tools. By identifying emerging trends and customer preferences, businesses can adjust their inventory levels and production plans accordingly.
- Dynamic Replenishment Strategies: With real-time demand data, businesses can adopt dynamic replenishment strategies such as just-in-time (JIT) or vendor-managed inventory (VMI). These strategies allow for more precise inventory replenishment based on actual demand, reducing excess inventory and minimizing stockouts.
- Scenario Planning: Utilize real-time data to perform scenario planning and simulation exercises. By modeling different demand scenarios and their impact on inventory levels, businesses can proactively identify potential risks and develop contingency plans. This helps in making informed decisions and mitigating disruptions.
- Agile Production and Fulfillment: Real-time demand data enables agile production and fulfillment processes. With accurate insights into customer demand, businesses can quickly adjust production schedules, prioritize orders, and allocate resources more efficiently, improving order fulfillment and reducing lead times.
By leveraging real-time data for demand forecasting and planning, warehouses can optimize inventory levels, improve operational efficiency, and enhance overall responsiveness to market demands.
This strategic use of technology contributes significantly to achieving warehouse efficiency and maintaining competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Control in Warehouse Operations
Effective inventory control is crucial for efficient warehouse operations and offers several benefits to businesses. Let's explore some of the key advantages:
Optimal Inventory Levels
Effective inventory control helps maintain optimal inventory levels, preventing overstocking or stockouts. It ensures that the right quantity of products is available at the right time, minimizing carrying costs and avoiding potential revenue losses due to stockouts.
Improved Order Fulfillment
With accurate inventory control, businesses can fulfill customer orders quickly and accurately. This leads to higher customer satisfaction, improved retention, and a positive brand reputation.
Reduced Holding Costs
Effective inventory control helps minimize holding costs associated with storing excess inventory. By avoiding overstocking, businesses can reduce expenses related to warehouse space, utilities, insurance, and potential obsolescence.
Minimized Stock Losses
Inventory control systems enable better tracking and monitoring of stock movements, reducing the risk of theft, damage, or misplacement. This helps mitigate stock losses and enhances overall security within the warehouse.
Efficient Space Utilization
Proper inventory control allows businesses to optimize warehouse space utilization. By organizing inventory in an orderly manner and implementing efficient storage systems, such as racking and shelving, businesses can maximize storage capacity and improve operational efficiency.
Accurate Demand Forecasting
Effective inventory control facilitates accurate demand forecasting by providing insights into historical sales data, trends, and customer behavior. This enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding production planning, purchasing, and inventory replenishment.
Cost Savings
By minimizing inventory carrying costs, reducing stock losses, and optimizing space utilization, effective inventory control contributes to cost savings for businesses. This can positively impact the company's bottom line and profitability.
Streamlined Supply Chain Operations
Efficient inventory control improves the overall coordination of supply chain activities. It allows for better synchronization between production, distribution, and customer demand, resulting in smoother operations and reduced lead times.
Enhanced Decision-Making
Accurate and up-to-date inventory information provided by inventory control systems enables data-driven decision-making. Businesses can make informed choices regarding inventory management strategies, purchasing decisions, and production planning based on real-time data and insights.
Improved Collaboration
Effective inventory control fosters better collaboration between different departments within the organization, such as sales, purchasing, and logistics. Clear visibility of inventory levels and accurate information sharing facilitate smoother coordination and more efficient workflow.
Technology and Automation in Inventory Control
Technology and automation are vital for modern inventory control. Implementing these technologies as part of a broader warehouse inventory management strategy enables businesses to stay competitive and meet the demands of a dynamic market.
Implementing a Robust Inventory Management System
Implementing a robust inventory management system is essential for optimizing warehouse efficiency and ensuring smooth operations. A well-designed system enables accurate tracking, efficient inventory control, and streamlined processes.
Here are key steps to implement a robust inventory management system for warehouse efficiency:
- Assess Inventory Needs: Conduct a thorough analysis of your inventory requirements, including product demand, turnover rates, storage capacity, and lead times. This assessment helps determine the optimal inventory management approach and system requirements.
- Choose the Right Inventory Management Software: Select a comprehensive inventory management software that aligns with your warehouse's specific needs. Look for features such as real-time inventory tracking, automated order management, barcode or RFID integration, reporting and analytics capabilities, and compatibility with your existing systems.
- Set Up Proper Warehouse Organization: Optimize your warehouse layout to ensure efficient storage and retrieval of inventory. Arrange items based on their characteristics, demand patterns, and turnover rates. Implement a logical bin location system, clear signage, and aisle markings to facilitate easy navigation for warehouse staff.
- Establish Replenishment Processes: Set up streamlined replenishment processes to ensure timely restocking of inventory. Establish reorder points and safety stock levels based on demand forecasting and lead times. Automate reorder triggers to initiate purchase orders or production orders when inventory levels reach specified thresholds.
- Implement Cycle Counting and Regular Audits: Conduct regular cycle counts to verify inventory accuracy and reconcile physical counts with system records. This helps identify discrepancies and minimize inventory errors. Perform periodic audits to review inventory practices, identify root causes of discrepancies, and implement corrective actions.
- Train and Empower Warehouse Staff: Provide comprehensive training to warehouse staff on the inventory management system, including data entry, scanning procedures, and proper handling of inventory. Empower them to take ownership of inventory accuracy and encourage their active participation in continuous improvement initiatives.
- Leverage Data Analytics and Reporting: Utilize data analytics tools and reporting capabilities within your inventory management system to gain insights into inventory performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover, fill rate, order cycle time, and accuracy to measure warehouse efficiency and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuously Improve and Optimize: Regularly review and analyze inventory data to identify process bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas for improvement. Seek feedback from warehouse staff and stakeholders to identify challenges and implement process enhancements. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement to drive ongoing optimization and efficiency gains.
Role of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) play a pivotal role in modern inventory control by streamlining and automating warehouse operations.
A robust WMS integrates with other systems to provide comprehensive oversight of inventory, from receiving and putaway to picking, packing, and shipping.
By leveraging the best warehouse inventory management software, businesses can track inventory levels in real-time, optimize storage space, and improve order fulfillment accuracy.
A WMS offers features such as:
- Real-time inventory tracking and updates
- Advanced reporting and analytics
- Automated replenishment and stock transfers
- Integration with RFID and barcode systems for enhanced accuracy
- Support for Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory and safety stock management
These functionalities help businesses maintain optimal inventory levels, reduce manual errors, and improve overall warehouse efficiency.
Integrate automation and robotics technologies with a comprehensive WMS. A WMS acts as the central control system, coordinating the movement of inventory, optimizing picking routes, and providing real-time visibility into warehouse operations.
It enables seamless coordination between automation systems and other warehouse processes.
Key Components of Warehouse Management Systems:
WMS comprises several key components that collectively streamline warehouse processes:
- Inventory Management: Real-time tracking and visibility of inventory levels, locations, and movements.
- Order Fulfillment: Efficient processing, picking, packing, and shipping of customer orders.
- Warehouse Layout Optimization: Space allocation, slotting, and arrangement of products for optimal storage.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generation of reports and insights to support decision-making and performance evaluation.
Types of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
On-Premises WMS: On-premises WMS solutions are installed and maintained on-site by the organization, providing greater control over customization and data security.
Cloud-Based WMS: Cloud-based WMS solutions are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet, offering scalability, flexibility, and reduced IT infrastructure costs.
Standalone WMS: Standalone WMS focuses solely on warehouse management functionalities, suitable for organizations with specific warehouse needs.
Integrated WMS: Integrated WMS seamlessly integrates with other business systems, such as ERP and TMS, to provide end-to-end supply chain visibility and coordination.
Utilizing Barcode and RFID Technologies for Accurate Tracking
Barcode and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technologies are widely used in various industries, including warehousing and inventory management, to enable accurate tracking of products and assets.
These technologies offer several benefits and play a crucial role in enhancing inventory control and operational efficiency.
Here's how barcode and RFID technologies are utilized for accurate tracking:
Barcode Technology:
- Unique Identification: Each product or item is assigned a unique barcode, which contains encoded information such as product details, SKU, and serial number. Barcodes provide a quick and reliable method for identifying and tracking individual items.
- Scanning and Data Capture: Barcodes can be easily scanned using handheld barcode scanners or integrated scanning systems. The captured data is instantly recorded and can be transmitted to inventory management systems for real-time updates.
- Accuracy and Speed: Barcode scanning ensures accurate and fast data capture, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency in processes such as receiving, picking packing, and shipping. It enables swift identification and tracking of items throughout the supply chain.
- Inventory Control and Visibility: By scanning barcodes, inventory levels can be accurately tracked and managed. Real-time visibility into stock levels helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory control and improving overall supply chain performance.
Types of Barcode Technologies
Linear Barcodes: Linear barcodes, also known as 1D barcodes, consist of a sequence of parallel lines of varying widths and spacings. They encode data horizontally and are commonly used for product identification, pricing, and inventory management.
2D Barcodes: 2D barcodes, such as QR codes, contain both horizontal and vertical patterns, allowing them to store more data than linear barcodes. They are often used for applications requiring larger amounts of information, like URLs, contact details, or product specifications.
QR Codes: QR codes (Quick Response codes) are a type of 2D barcode that can store various types of data, including text, URLs, phone numbers, and even multimedia content. They are widely used for marketing, promotions, and mobile interactions.
Applications of Barcode Technology
Retail and Point of Sale (POS): Barcodes revolutionized the retail industry by enabling efficient product scanning, price lookup, and quick checkouts. They ensure accurate pricing and inventory management.
Inventory Management: Barcodes facilitate accurate and real-time tracking of inventory levels, leading to optimized stock replenishment, reduced overstock, and improved order fulfillment.
Supply Chain and Logistics: Barcodes enhance visibility and traceability throughout the supply chain by tracking shipments, monitoring transit, and improving supply chain efficiency.
Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, barcodes are used to manage patient records, track medications, and ensure accurate specimen identification, reducing errors and improving patient safety.
Manufacturing and Production: Barcodes streamline manufacturing processes by identifying work-in-progress, tracking components, and facilitating quality control checks.
Library and Document Management: Barcodes simplify library operations by cataloging and managing books, documents, and other resources, making tracking and lending more efficient.
RFID Technology:
- Contactless Identification: RFID technology uses radio frequency signals to identify and track items without the need for direct line-of-sight scanning. RFID tags can be attached to products, pallets, or containers, enabling contactless data capture.
- Automated Data Capture: RFID readers or scanners emit radio waves that activate and read the information stored in RFID tags. This automated data capture allows for fast and simultaneous scanning of multiple items, improving efficiency and reducing labor requirements.
- Real-time Tracking and Visibility: RFID technology provides real-time tracking and visibility of inventory. As items pass by RFID readers, their location and status are instantly recorded, allowing for accurate and up-to-date inventory information.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: RFID technology eliminates the risk of human error associated with manual barcode scanning. The automated nature of RFID data capture ensures high data accuracy, reducing discrepancies and improving overall inventory accuracy.
- Increased Read Range and Durability: RFID tags have a longer read range compared to barcodes, enabling faster and more convenient scanning. RFID tags are also more durable, making them suitable for harsh environments and reusable containers.
Components and Types of RFID Technology
RFID Tags: RFID tags are small devices comprising a microchip and an antenna. They come in various forms, including passive, active, and semi-passive tags, each with distinct capabilities and applications.
Passive RFID Tags: Passive tags do not have their own power source; they derive energy from the radio frequency signals emitted by RFID readers. They are cost-effective and suitable for short-range applications.
Active RFID Tags: Active tags are equipped with an internal power source (battery), enabling longer read ranges and real-time tracking. They are commonly used for tracking high-value assets and monitoring temperature-sensitive goods.
Semi-Passive RFID Tags: Semi-passive tags combine elements of both passive and active tags. They have a battery for powering the microchip but rely on external RF signals for communication.
Benefits of RFID and Barcode Systems
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcode systems are essential components of an effective warehouse inventory management system. They provide numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Accuracy: Both RFID and barcode systems significantly reduce human errors in inventory tracking. Automated data capture ensures that inventory records are precise, leading to fewer discrepancies and stockouts.
- Real-Time Visibility: RFID and barcode technologies enable real-time tracking of inventory movements. This visibility allows for immediate updates to the warehouse inventory management system, ensuring that stock levels are always current.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Scanning barcodes or using RFID readers speeds up the processes of receiving, picking, packing, and shipping. This automation reduces the time and labor required for manual data entry and stock checks.
- Improved Inventory Control: With accurate and real-time data, businesses can better manage their inventory. This includes optimizing reorder points, implementing cycle counting, and enhancing demand forecasting accuracy.
Streamlining Receiving and Put-Away Processes
Streamlining the receiving and put-away processes in a warehouse is crucial for achieving efficiency and maintaining optimal inventory control. These processes are the initial steps in the warehouse operation and can greatly impact overall productivity and accuracy.
Strategies for Streamlining Receiving and Put-Away Processes
Preparing for Incoming Shipments
- Establish clear procedures for receiving and inspecting incoming shipments.
- Communicate with suppliers to ensure they provide advanced shipment notices (ASNs) or packing lists.
- Prepare receiving areas with necessary tools, equipment, and space for efficient handling.
Dock Management
- Implement an organized dock management system to prioritize incoming shipments and allocate resources effectively.
- Utilize technology like dock scheduling software or RFID-based systems to optimize dock space and streamline unloading.
Standardized Receiving Processes
- Develop standardized procedures for receiving goods, including verification of quantities, inspection for damages, and checking against purchase orders.
- Utilize barcode or RFID technology for automated data capture and error reduction.
Efficient Put-Away Strategies
- Optimize put-away processes with efficient storage location strategies.
- Use barcode or RFID scanning to guide operators and ensure accurate item placement.
- Implement slotting techniques to organize high-demand items for faster access.
Automation and Technology Integration
- Explore automation solutions such as conveyor belts or robotic systems to enhance receiving and put-away efficiency.
- Integrate these technologies with your inventory management system (WMS) for seamless data capture and improved operational efficiency.
Implementing Efficient Inventory Replenishment Strategies
Implementing efficient inventory replenishment strategies is essential for maintaining warehouse efficiency and ensuring optimal inventory levels.
These strategies prevent stockouts, minimize excess inventory, and streamline replenishment processes.
Strategies for Efficient Inventory Replenishment
Set Reorder Points
- Determine reorder points based on historical demand and lead time to avoid stockouts.
- Utilize inventory management software for automatic reorder alerts and optimized inventory control.
Implement Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
- Calculate EOQ for items with predictable demand to minimize ordering and carrying costs.
- Ensure orders are placed at optimal quantities to balance inventory levels effectively.
Use Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
- Collaborate with suppliers to implement VMI for automated inventory monitoring and replenishment.
- Transfer replenishment responsibilities to suppliers to streamline inventory management processes.
Adopt Just-in-Time (JIT) Replenishment
- Synchronize inventory replenishment with customer demand using JIT principles.
- Minimize holding costs and improve inventory turnover by aligning supply with actual demand.
Consider Kanban Systems
- Implement visual inventory control with Kanban systems to signal replenishment needs.
- Use Kanban cards or electronic signals to maintain optimal inventory levels and facilitate lean practices.
Utilize Demand-Driven Replenishment
- Analyze real-time demand data to adjust replenishment orders and align inventory levels with customer needs.
- Utilize POS data and customer orders for accurate demand forecasting and responsive inventory management.
Implement Automated Replenishment Systems
- Utilize automation technologies such as barcode scanners or RFID systems to streamline replenishment activities.
- Improve accuracy and efficiency in data capture and replenishment processes.
Impact of Automation on Inventory Accuracy and Efficiency
Automation in inventory control has a profound impact on both accuracy and efficiency. Implementing advanced warehouse and inventory management technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), conveyor systems, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can revolutionize warehouse operations.
Accuracy:
- Error Reduction: Automation minimizes human intervention, reducing the risk of errors in inventory handling and data entry.
- Consistent Performance: Automated systems perform tasks with consistent precision, ensuring that inventory counts and locations are always accurate.
Efficiency:
- Speed: Automation accelerates processes such as order picking, packing, and shipping, leading to faster order fulfillment.
- Labor Optimization: Automated systems handle repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, freeing up warehouse staff to focus on more strategic activities.
- Scalability: Automation allows warehouses to scale operations efficiently to meet increasing demand without compromising performance.
Using a comprehensive warehouse inventory management system that integrates automation technologies ensures that businesses can maintain high levels of inventory accuracy and operational efficiency. This integration leads to better resource utilization, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Implementing Proper Labeling and Bin Location Systems
Proper labeling and bin location systems play a crucial role in enhancing warehouse efficiency. They provide clear identification and organization of inventory, making it easier for warehouse staff to locate and retrieve items quickly and accurately.
Key considerations of implementing proper labeling and bin location systems:
- Standardized Labeling: Establishing a standardized labeling system ensures consistency and clarity throughout the warehouse. Labels should include essential information such as product name, SKU, barcode, and any other relevant details to facilitate accurate identification and tracking.
- Barcode and RFID Technology: Utilizing barcode or RFID technology allows for efficient and automated data capture. This enables faster scanning and reduces the likelihood of errors during inventory management tasks, such as receiving, picking, and stock counting.
- Bin Location System: Implementing a well-structured bin location system helps organize inventory and provides a systematic arrangement of products within the warehouse. This can be achieved through a combination of alphanumeric codes, color-coded labels, and logical grouping based on product characteristics or demand patterns.
- Clear Signage and Markings: Proper signage and markings aid in navigation within the warehouse. Clear indicators of aisle numbers, bay numbers, and bin locations help employees quickly locate the desired items, reducing search times and improving productivity.
- Integration with Warehouse Management System (WMS): Integrating the labeling and bin location systems with a WMS or inventory management software provides real-time visibility and accurate inventory tracking. This enables better inventory control, efficient order fulfillment, and timely replenishment.
- Employee Training and Communication: Proper training and ongoing communication with warehouse staff are essential for successful implementation. Training programs should cover label reading, scanning procedures, and the overall bin location system to ensure that employees are familiar with the processes and can navigate the warehouse efficiently.
Benefits of Proper Labeling and Bin Location Systems:
- Increased Efficiency: Clear labeling and well-organized bin locations minimize search times and reduce errors, resulting in faster and more accurate inventory retrieval and storage processes.
- Enhanced Inventory Accuracy: Proper labeling and bin location systems contribute to improved inventory accuracy and visibility. This leads to better inventory control, reduced stockouts, and improved order fulfillment rates.
- Space Optimization: Organizing inventory with a bin location system allows for efficient use of warehouse space. It enables proper categorization and stacking of items based on size, weight, and demand, maximizing storage capacity.
- Error Reduction: Barcode or RFID technology reduces the likelihood of manual errors and enhances data accuracy during inventory tracking, picking, and stock counting activities.
- Improved Safety: Clear signage and markings contribute to a safer working environment by providing clear directions and ensuring that employees can navigate the warehouse without confusion or hazards.
Utilizing Automation and Robotics for Efficient Inventory Handling
Utilizing automation and robotics in warehouse operations is a key strategy for achieving efficient handling of inventory and improving overall warehouse efficiency. Automation and robotics technologies can streamline processes, increase productivity, and enhance accuracy.
Here are some ways to leverage automation and robotics for efficient handling in a warehouse:
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Implement AGVs to transport goods within the warehouse. AGVs can navigate predetermined paths, avoiding obstacles and safely moving inventory from one location to another.
They reduce manual handling and increase the speed and accuracy of material transportation.
Types of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Forklift AGVs: Forklift AGVs are designed to lift, transport, and stack loads like traditional forklifts. They are commonly used for pallet handling and stacking in warehouses.
Tow AGVs: Tow AGVs are used to transport multiple trailers or carts in a train-like fashion, making them ideal for moving heavy loads within manufacturing and distribution facilities.
Unit Load AGVs: Unit Load AGVs are versatile vehicles designed to move individual loads or materials on a platform. They are suitable for tasks such as moving raw materials, finished products, and containers.
Custom-Designed AGVs: Custom AGVs are tailored to specific applications and requirements, ranging from specialized handling to complex operations within unique environments.
Applications of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Warehousing and Distribution: AGVs optimize warehousing and distribution by automating tasks such as order picking, packing, and inventory movement, leading to increased efficiency and accuracy.
Manufacturing and Assembly: AGVs streamline manufacturing processes by automating material supply, assembly line feeding, and work-in-progress transportation.
Automotive Industry: AGVs play a crucial role in the automotive sector by transporting components and vehicles along assembly lines, reducing cycle times, and enhancing production efficiency.
Food and Beverage: AGVs ensure hygienic material handling in food and beverage industries, moving ingredients, finished products, and packaging materials while adhering to strict safety standards.
Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, AGVs facilitate the movement of raw materials, chemicals, and finished products while maintaining clean and controlled environments.
E-Commerce and Fulfillment Centers: AGVs are used in e-commerce fulfillment centers for order fulfillment, inventory replenishment, and shipping operations, enabling rapid and accurate order processing.
Robotic Palletizing and Depalletizing
Utilize robotic systems to automate palletizing and depalletizing processes. Robots can handle heavy loads, stack and unstack pallets, and optimize the arrangement of goods.
This minimizes manual labor and improves efficiency while ensuring proper stacking and reducing the risk of errors.
Technologies in Robotic Palletizing and Depalletizing
Robotic Arms: Robotic arms are the core components of palletizing systems, available in various configurations, including articulated, SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm), and delta robots.
End-Effectors and Grippers: End-effectors, such as vacuum grippers, mechanical grippers, and clamp grippers, enable robots to securely pick up and manipulate different types of products.
Vision Systems: Vision systems use cameras and image processing software to identify and locate items, ensuring accurate positioning and alignment during palletizing and depalletizing.
Sensors and Safety Mechanisms: Force sensors, proximity sensors, and safety barriers ensure safe interaction between robots, humans, and the surrounding environment.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Implement AS/RS to automate the storage and retrieval of inventory. These systems use robotic mechanisms to move and retrieve items from designated storage locations.
AS/RS maximizes space utilization, increases picking speed, and reduces errors associated with manual retrieval.
Types of Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Unit-Load AS/RS: Unit-load AS/RS handles large quantities of uniform items, such as pallets or containers, and uses stacker cranes or robotic arms to store and retrieve them.
Mini-Load AS/RS: Mini-load AS/RS is designed for smaller items and uses automated shuttles or robotic systems to manage trays or totes.
Vertical Lift Modules (VLMs): VLMs are vertical storage systems that use a lift mechanism to access and retrieve trays or shelves containing items.
Horizontal Carousels: Horizontal carousels are circular shelving units that rotate to bring items to a picking station, reducing the time required for manual picking.
Pick-and-Place Robots
Employ pick-and-place robots to handle individual items or packages during order fulfillment. These robots can precisely pick items from bins or conveyors and place them in designated containers.
They improve accuracy, speed, and consistency in picking processes, resulting in higher throughput and reduced errors.
Types of Pick-and-Place Robots
Cartesian Robots: Cartesian robots, also known as gantry robots, operate along a linear axis system and are well-suited for applications requiring precise linear movements.
Articulated Robots: Articulated robots have multiple joints that mimic human arm movements, offering versatility and flexibility in reaching objects from various angles.
SCARA Robots: Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (SCARA) robots are designed for fast and precise horizontal movements, making them ideal for pick-and-place tasks.
Delta Robots: Delta robots have a unique parallel-link structure that enables high-speed and precise movements, making them suitable for rapid pick-and-place applications.
Conveyor Systems
Install conveyor systems to automate the movement of goods within the warehouse. Conveyors facilitate the seamless flow of items from one area to another, eliminating the need for manual carrying or pushing of carts. They optimize workflow, reduce labor requirements, and minimize the risk of damage or loss.
Types of Conveyor Systems and Their Applications
Belt Conveyors: Belt conveyors consist of a continuous loop of material that moves items along a flat or inclined path. They are widely used in industries like manufacturing, mining, and agriculture for transporting bulk materials and packaged goods.
Roller Conveyors: Roller conveyors use a series of rollers to move items along the conveyor path. They are commonly used for material handling, order picking, and assembly line processes.
Chain Conveyors: Chain conveyors utilize chains to move items along the conveyor path. They are suitable for heavy-duty applications and can transport large and bulky items.
Screw Conveyors: Screw conveyors use a rotating helical screw to move granular or powdery materials. They are often used for bulk material handling and processing.
Gravity Conveyors: Gravity conveyors rely on the force of gravity to move items along a downward slope. They are used for simple and cost-effective material transportation.
Overhead Conveyors: Overhead conveyors are suspended from the ceiling or overhead structure, allowing items to move along elevated paths. They are ideal for space-saving and high-capacity applications.
Robotic Sorting Systems
Utilize robotic sorting systems to automate the sorting and categorization of inventory. These systems can scan and identify items, sort them based on predetermined criteria, and direct them to the appropriate storage or shipping locations.
Robotic sorting improves accuracy, speeds up sorting processes, and reduces labor-intensive manual sorting.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Deploy cobots, which are designed to work alongside human operators, to perform repetitive or physically demanding tasks. Cobots can assist with picking, packing, and assembly processes, enhancing worker productivity, reducing fatigue, and improving overall efficiency.
Future Trends: Innovations in Warehouse Efficiency and Inventory Control
The world of warehouse efficiency and inventory control is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer demands.
As businesses strive to optimize their operations and stay competitive, several future trends are emerging that will shape the landscape of warehouse efficiency and inventory control.
Here are some key innovations to watch out for:
Automation and Robotics
The use of automation and robotics in warehouses is expected to increase significantly. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), and robotic picking systems can enhance efficiency and accuracy in material handling and order fulfillment processes.
These technologies can streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and improve overall warehouse productivity.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT is revolutionizing warehouse management by enabling real-time monitoring and control of inventory and equipment.
IoT sensors and devices can track and collect data on inventory levels, temperature, humidity, and other factors, providing valuable insights for inventory control and decision-making.
IoT-powered solutions also enable predictive maintenance, improving equipment uptime and reducing downtime.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated and are being applied to optimize warehouse operations.
AI-powered demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and route planning can help businesses make more accurate predictions and decisions. ML algorithms can analyze historical data, identify patterns, and improve inventory control strategies.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are transforming warehouse training and picking processes. AR glasses or headsets can provide real-time visual guidance, reducing errors and improving picking accuracy.
VR simulations can be used for employee training, allowing them to practice tasks and familiarize themselves with the warehouse environment.
Cloud-Based Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Cloud-based WMS solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. They allow businesses to access real-time data, collaborate with partners and suppliers, and manage inventory from anywhere.
Cloud-based systems can also integrate with other software solutions, such as ERP systems, to streamline data sharing and enhance overall visibility.
Predictive Analytics and Big Data
The availability of vast amounts of data in the warehouse environment enables the use of predictive analytics to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Big data analytics can identify patterns, trends, and correlations, helping businesses make data-driven decisions and proactively respond to changing market conditions.
Drones and Autonomous Vehicles
Drones and autonomous vehicles have the potential to transform warehouse operations, especially in large-scale facilities.
Drones can be used for inventory counting, surveillance, and monitoring, while autonomous vehicles can optimize material movement and reduce manual labor requirements.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers enhanced security, transparency, and traceability in supply chain operations.
By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain can help track and verify the movement of goods, reducing the risk of counterfeiting, enhancing product authenticity, and improving inventory control.
Green and Sustainable Warehousing
As environmental concerns continue to grow, the adoption of sustainable practices in warehousing is becoming more prominent. This includes energy-efficient lighting, renewable energy sources, eco-friendly packaging materials, and waste reduction initiatives.
Green warehousing not only benefits the environment but also improves cost efficiency and brand reputation.
How Can Deskera Help in Maximizing Warehouse Efficiency?
Deskera ERP, a cloud-based platform offering integrated business management software, can significantly contribute to maximizing warehouse efficiency through several key functionalities:
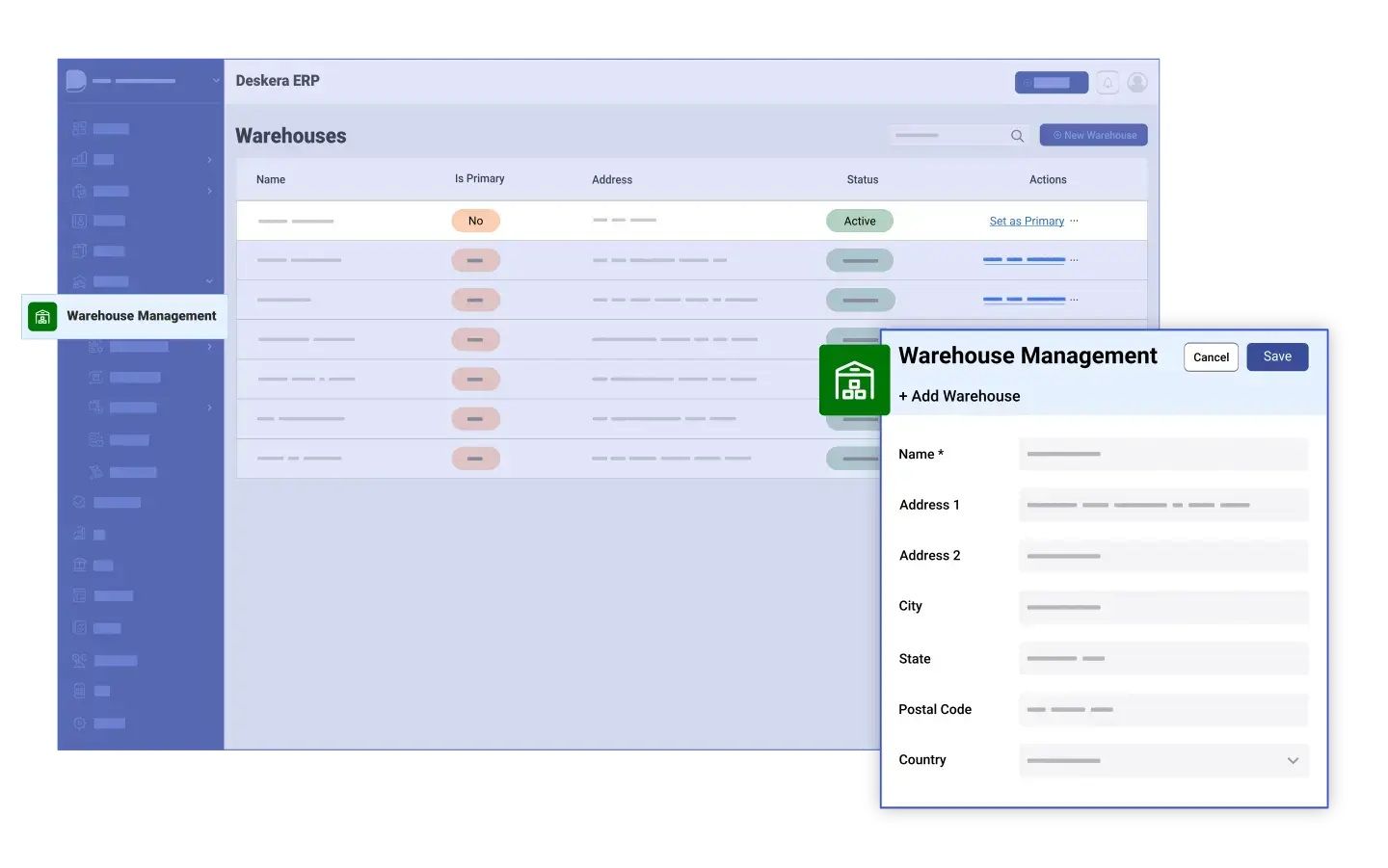
- Inventory Management: Deskera ERP provides robust inventory management capabilities that allow businesses to track inventory levels in real-time. This feature helps in optimizing stock levels, reducing excess inventory, and preventing stockouts by ensuring items are replenished at the right time.
- Warehouse Management System (WMS): Deskera ERP offers WMS functionalities that streamline warehouse operations. This includes organizing warehouse layout, optimizing storage space, and improving picking, packing, and shipping processes. It also facilitates barcode scanning and RFID integration for accurate inventory tracking.
- Demand Forecasting and Planning: Deskera's software includes tools for demand forecasting and planning. By analyzing historical data and trends, businesses can make informed decisions about inventory levels and procurement, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking items.
- Integration with Other Business Processes: Deskera ERP integrates seamlessly with other business processes such as sales, purchasing, and accounting. This integration ensures that inventory data is synchronized across departments, enhancing overall operational efficiency and accuracy.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: Deskera ERP automates routine warehouse tasks, such as generating purchase orders, receiving goods, and updating inventory records. This automation reduces manual errors, speeds up processes, and allows warehouse staff to focus on more strategic activities.
- Reporting and Analytics: Deskera ERP provides customizable reports and analytics dashboards that offer insights into warehouse performance, inventory turnover rates, stock movement, and more. These insights enable businesses to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
- Mobile Accessibility: Deskera's mobile app allows warehouse managers and staff to access real-time inventory data, update records on the go, and manage warehouse operations remotely. This flexibility enhances responsiveness and agility in managing warehouse activities.
By leveraging Deskera's comprehensive suite of tools and functionalities, businesses can optimize warehouse operations, improve inventory accuracy, reduce costs, and ultimately enhance overall warehouse efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Maximizing warehouse efficiency through effective inventory control strategies is crucial for businesses to achieve operational excellence, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Accurate inventory tracking and labeling, along with regular audits, contribute to higher inventory accuracy and reduced errors.
- Efficient layout design and space utilization help minimize travel time, reduce picking errors, and maximize storage capacity.
- Adopting lean principles in warehouse operations eliminates waste, improves productivity, and shortens lead times.
- Leveraging technology and automation, such as barcode scanning and robotics, enhances picking and packing processes and reduces manual errors.
- Effective demand forecasting and demand-driven replenishment strategies optimize inventory levels and ensure timely replenishment to meet customer needs.
- Proper training and development programs for warehouse personnel improve overall efficiency and reduce operational errors.
- Continuous monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) helps identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
- Regular review and optimization of warehouse processes ensure ongoing improvement and efficiency gains.
- Implementing sustainable practices in warehouse operations, such as energy efficiency and waste reduction, aligns with environmental goals.
- Close coordination with suppliers and partners improves supply chain efficiency and reduces stockouts.
Related Articles















