Have you ever wondered why some businesses consistently operate smoothly while others struggle with stock issues, delays, and shrinking profit margins? The answer often lies in one powerful tool: accurate, timely, and well-structured inventory reports. These reports serve as the backbone of effective inventory management, giving companies the clarity they need to make faster, smarter, and more profitable decisions.
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses can no longer rely on guesswork or fragmented spreadsheets. Inventory reports provide a comprehensive snapshot of stock levels, movement patterns, demand fluctuations, and cost structures—enabling leaders to optimize operations end to end. When used strategically, these reports reduce inefficiencies, prevent revenue leakage, and enhance overall business performance.
Inventory reports not only improve day-to-day efficiency but also play a crucial role in safeguarding profit margins. By identifying slow-moving items, monitoring valuation trends, detecting stock discrepancies, and forecasting demand, businesses can avoid unnecessary expenses and capital blockages. This makes inventory reporting essential not just for operational control, but for long-term profitability and resilience.
Modern ERP solutions like Deskera ERP make this process even more powerful. Deskera offers real-time inventory tracking, automated reporting templates, accurate valuation methods, and AI-driven insights to help businesses act quickly and confidently. With seamless integration across accounting, warehousing, purchasing, and sales, Deskera ensures that every inventory report is accurate, up-to-date, and actionable—empowering teams to drive efficiency and maximize profit margins.
What Are Inventory Reports?
Inventory reports are structured documents—either physical or digital—that provide a complete summary of the inventory a business has on hand at a specific point in time or over a defined period. They typically include total inventory counts, best-selling products, slow-moving items, stock locations, unit costs, and overall inventory value. In simple terms, an inventory report gives a clear snapshot of what a business has, where it is stored, how much it is worth, and when it needs to be reordered.
A good inventory report helps companies track, manage, and categorize their stock effectively. It outlines the items available for sale, highlights what needs replenishment, and reveals products that may require discounting or liquidation. By offering visibility into current stock levels and movement trends, inventory reports help prevent both stockouts—which lead to lost sales—and overstocking, which ties up valuable working capital.
These reports play a crucial role in efficient inventory management and business decision-making. They support procurement planning, improve demand forecasting, strengthen accounting accuracy, and enhance overall operational performance. Whether a company uses a periodic or perpetual inventory system, regular reporting—supported by at least an annual physical count—ensures that inventory values remain accurate on both the balance sheet and income statement.
Beyond simple stock counts, comprehensive inventory reports also include important data points such as item details, quantities on hand, storage locations, unit costs, total stock value, and reorder points. Together, this information helps businesses assess how well they are managing their inventory, optimize cash flow, and maintain a healthy balance between supply and demand.
Types of Inventory Reports
To manage inventory effectively, businesses rely on different types of reports—each designed to offer visibility into a specific aspect of stock performance. While the classification of these reports is somewhat flexible, grouping them into categories helps store owners understand what each report is for and where it should be used in the inventory management process. Broadly, inventory reports fall into three main types:
- Informational reports – provide raw data about all products in stock.
- Management reports – analyze inventory data to support decision-making.
- Time-based reports – show inventory trends over a defined period.
At first glance, these categories may seem similar, but their value becomes clear once you explore the individual reports below.
1. Inventory Management Report (Management Report)
An inventory management report goes beyond simple stock counts. Rather than giving raw data, it analyzes warehouse and product information automatically. This report helps you make smarter inventory decisions such as:
- How many units to order without overstocking
- Which products require more storage space
- Whether a warehouse should be expanded, consolidated, or sold
- When to prepare goods for shipment
- How many packaging materials or raw materials are needed
The biggest advantage is that the analysis is quick, accurate, and reliable—saving you time and allowing proactive planning.
2. Inventory Analysis Report (Management Report)
This report evaluates your sales, product performance, warehouse capacity, delivery timelines, and expiration periods. A common example is the ABC Analysis Report, which segments your inventory based on value contribution using the Pareto principle:
- A-items: high-value, high-profit
- B-items: moderate importance
- C-items: low-value, high-quantity
Inventory analysis reports help you focus on profitable items, reduce waste, and identify products consuming more resources than they justify.
3. Inventory Forecasting Report (Management Report)
Forecasting reports estimate future inventory requirements based on sales velocity, historical trends, promotions, seasonality, and lead times. They help answer:
- What to buy?
- When to buy it?
- How much to buy?
A forecasting report also helps avoid costly stockouts and prevents excess inventory. It often includes critical metrics like reorder points, safety stock, replenishment quantities, and expected stockout dates.
4. Inventory Stock Report (Informational Report)
A stock report alerts businesses to two key warehouse conditions:
- Low stock levels
- Replenishment opportunities
It provides calculations for sales velocity, estimated stockout dates, stock availability per warehouse, and reorder timelines. Filters can organize data by warehouse location, price category, expiration date, product size, popularity, and more.
5. Monthly Inventory Report (Time-Based Report)
Monthly reports summarize how your inventory performed during the month. They show:
- Units sold
- Goods received
- Product popularity trends
- Monthly revenue per product
- Supply and demand fluctuations
These reports help visualize performance trends and make monthly audits faster and more accurate. They are also useful for tracking expiration dates and identifying seasonal patterns.
6. Inventory Value Report (Informational/Time-Based Report)
An inventory value report shows the total monetary worth of all items currently in stock. It helps businesses:
- Track capital tied up in inventory
- Compare warehouse inventory values
- Group products by supplier, category, or price
- Verify stock value during insurance claims or audits
This report is often referred to as an “inventory on hand” report because it represents real-time stock valuation.
7. Sales Inventory Report (Management Report)
This report connects inventory with financial data. It includes:
- Revenue
- Discounts
- Returns
- Taxes
- Shipping expenses
- Cost per sales channel
A comprehensive sales inventory report helps discover sales trends, identify top customers, evaluate product performance, and improve demand forecasting accuracy.
8. COGS (Cost of Goods Sold) Report
This report outlines the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing inventory sold within a period. It helps determine:
- Product profitability
- Pricing strategies
- Tax calculations
- Margin optimization opportunities
Understanding COGS is essential for evaluating your true bottom line.
9. Purchase Order Report
A PO report tracks incoming inventory. It shows:
- Order quantities
- Expected arrival dates
- Supplier details
- Trends in procurement behavior
This helps businesses plan warehouse space, avoid overstocking, and streamline order fulfillment.
10. Shipping Trends Report
A shipping trends report analyzes fulfillment performance across all sales channels. It helps track:
- Carrier efficiency
- Warehouse performance
- Shipping delays and bottlenecks
This report supports improvements in delivery efficiency and customer satisfaction.
11. Customer Analytics Report
Customer analytics reports reveal purchasing behaviors and patterns, such as:
- Highest-value customers
- Most frequent buyers
- Customer lifetime value
- Products often bought together
- Reasons for customer churn
These insights help shape marketing strategies, improve retention, and guide inventory planning based on customer demand patterns.
12. Stock Movement Report
A stock movement report tracks how inventory moves in and out of the warehouse. It includes:
- Opening stock
- Stock received
- Stock issued/sold
- Adjustments (damages, shrinkage, returns)
- Closing stock
This report helps identify shrinkage, theft, operational errors, and supply chain inefficiencies.
13. Stock Adjustment Report
This report records all manual changes to inventory, including:
- Damaged goods
- Expired items
- Lost or stolen stock
- Repackaging or splitting units
- Corrections from physical counts
It improves audit accuracy and helps identify systemic inventory issues.
14. Stock Aging Report (Aging Inventory Report)
This report shows how long items have been in storage. It segments inventory into age brackets—0–30 days, 31–60 days, 61–90 days, and 90+ days. It helps businesses:
- Identify obsolete or slow-moving stock
- Reduce carrying costs
- Clear deadstock through discounts or liquidation
15. Deadstock (Non-Moving Stock) Report
This report highlights items that have not moved for a specific period (e.g., 90 or 180 days). It’s critical for reducing waste, freeing up warehouse space, and cutting holding costs.
16. Inventory Turnover Report
An inventory turnover report measures how quickly stock is being sold and replenished. It typically includes:
- Turnover ratio
- Days inventory outstanding (DIO)
- Fast vs. slow-moving products
It helps assess product demand, profitability, and stocking efficiency.
17. Reorder Report / Reorder Point Report
This report shows items that have reached or are nearing their reorder point. It usually includes:
- Reorder quantity
- Required reorder date
- Safety stock levels
- Supplier lead times
It helps prevent stockouts and ensures replenishment is timely.
18. Backorder Report
A backorder report tracks items that customers ordered but are currently out of stock. It includes:
- Backordered quantities
- Customer order details
- Expected fulfillment dates
This improves customer communication and helps companies prioritize replenishment.
19. Supplier Performance Report
This report analyzes supplier efficiency using metrics like:
- Delivery timeliness
- Order accuracy
- Lead time variability
- Cost fluctuations
It helps optimize supplier selection and negotiation strategies.
20. Warehouse Utilization Report
This report measures how efficiently warehouse space is being used. It covers:
- Storage density
- Picking efficiency
- Bin/shelf utilization
- Overstock or congestion zones
Useful for planning warehouse expansion, layout redesign, or consolidation.
21. SKU Rationalization Report
A SKU rationalization report evaluates which SKUs to keep, discontinue, replace, or bundle. It examines:
- Sales performance
- Profit margins
- Warehouse space consumed
- Carrying costs
This helps optimize product catalog size and profitability.
22. Returns & Refunds Report
This report provides insights into items being returned and why. It includes:
- Return frequency
- Reasons for returns
- Cost of returns
- Supplier-related defects
It helps diagnose quality issues and reduce avoidable returns.
23. Inventory Compliance Report
Used primarily in regulated industries (pharma, chemicals, food), this report tracks:
- Batch numbers
- Expiration dates
- Regulatory documentation
- Quality checks
It ensures compliance and mitigates recall risks.
Importance of Inventory Reports
Inventory reports are far more than routine documents—they act as the foundation of effective inventory control, financial accuracy, supply chain efficiency, and customer satisfaction. By offering real-time visibility into stock levels, product movement, and inventory value, these reports help businesses make smarter decisions, reduce losses, and maximize profitability.
Here’s why inventory reports are indispensable for any product-based business:
1. Better Inventory Planning and Forecasting
Inventory reports give businesses a clear understanding of how much stock they currently hold and how much capital is tied up in each product or SKU. With accurate data, companies can:
- Set informed reorder points
- Improve demand forecasting
- Prevent stockouts and overstocking
- Plan inventory needs for peak seasons, promotions, and market trends
This leads to smarter budgeting, optimized purchasing, and more predictable inventory cycles.
2. Transparent and Accurate Inventory Tracking
Transparent tracking allows retailers to confidently ensure product availability and timely deliveries. Consistent reporting helps businesses:
- Monitor stock movement in real-time
- Identify anomalies or discrepancies quickly
- Track demand patterns and sales trends
- Improve control over stock flow and replenishment
Accurate tracking reduces operational errors and supports seamless order management.
3. Organized Inventory Categorization for Better Decision-Making
Inventory reports help businesses categorize products based on value, movement rate, profitability, and carrying costs. This segmentation allows companies to:
- Identify best-sellers and high-margin products
- Detect slow-moving or obsolete inventory
- Streamline SKU catalogs
- Implement ABC analysis or other inventory classification methods
Better organization leads to more efficient inventory strategies and fewer storage challenges.
4. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Experience
A well-maintained inventory ensures that customers find what they need, when they need it. Inventory reports help businesses:
- Keep popular items in stock
- Prevent backorders and delays
- Deliver orders faster and more accurately
- Manage returns smoothly
All of these factors strengthen customer loyalty and promote repeat business.
5. Improved Financial Management and Profitability
Inventory is a major current asset, and its accuracy directly impacts financial statements. Inventory reports enable businesses to:
- Know the exact value of stock on hand
- Detect deadstock and free up tied capital
- Manage holding and carrying costs
- Improve cash flow through optimized stock levels
By identifying products that drain profitability, companies can focus resources on high-performing items.
6. Streamlined Reordering and Procurement Processes
With clear visibility into stock levels and reorder needs, inventory reports simplify replenishment. They help businesses:
- Identify low-stock items instantly
- Automate reorder alerts
- Prevent last-minute shortages
- Ensure smooth procurement planning
This results in a more predictable and efficient supply chain.
7. Stronger Supplier Relationship Management
Inventory reports also help assess supplier performance. With detailed data, companies can:
- Evaluate delivery timelines
- Monitor order accuracy
- Analyze supplier reliability
- Negotiate better pricing and terms
Better supplier insights lead to stronger partnerships and improved purchasing efficiency.
8. Reduced Errors and Higher Operational Accuracy
Manual tracking is error-prone. Automated inventory reports minimize mistakes by offering:
- Real-time updates
- Accurate movement logs
- Lower risk of duplication, miscounts, or data gaps
This accuracy is crucial for critical decisions in sales, finance, and warehouse operations.
9. Compliance, Auditing, and Regulatory Support
Many industries—such as food, pharma, and chemicals—require strict documentation. Inventory reports help businesses:
- Maintain accurate stock records
- Provide supporting documents for audits
- Comply with regulatory standards
- Track expiration dates, batch numbers, or quality issues
This reduces compliance risks and helps maintain brand credibility.
10. Optimized Warehouse Efficiency and Lower Holding Costs
Accurate inventory data prevents unnecessary accumulation of stock, lowering storage, insurance, and handling costs. Inventory reports help businesses:
- Balance stock levels
- Identify space-consuming items
- Improve warehouse organization
- Reduce picking and stocking inefficiencies
This leads to a streamlined warehouse and cost savings.
11. Improved Order Fulfillment and Faster Processing
When you know what you have and where it is stored, orders can be processed more efficiently. Inventory reports help ensure:
- Faster picking, packing, and shipping
- Fewer errors in order fulfillment
- Higher customer satisfaction with delivery timelines
This is crucial for e-commerce and fast-moving retail environments.
12. Loss Prevention: Theft, Damage, and Shrinkage Control
Regular inventory reports allow early detection of:
- Pilferage
- Breakage
- Misplaced items
- Returns fraud
- Operational mistakes
Quick action minimizes losses and protects profitability.
13. Strategic Insights for Business Growth
Inventory reporting reveals long-term trends in:
- Product performance
- Seasonal demand
- Warehouse efficiency
- Supply chain bottlenecks
These insights help management refine marketing strategies, launch new products, discontinue underperformers, and scale operations.
How Inventory Reports Improve Operational Efficiency
Inventory reports play a vital role in streamlining daily operations and ensuring that every part of the supply chain flows smoothly. By offering real-time visibility into stock levels, movement, and performance, these reports help businesses eliminate inefficiencies, reduce costs, and operate with greater accuracy and speed.
1. Provide Real-Time Stock Visibility
One of the biggest contributors to operational delays is not knowing what inventory is available. Inventory reports deliver up-to-date information on quantities, locations, and stock status. This ensures:
- Faster decision-making
- Timely replenishment
- Fewer stock discrepancies
When teams have accurate visibility, processes such as picking, packing, and dispatching become significantly more efficient.
2. Improve Warehouse Organization and Layout
Inventory reports highlight top-selling SKUs, slow movers, and high-frequency picks. This information helps warehouse managers optimize storage layouts by:
- Placing fast-movers closer to dispatch areas
- Reducing travel time during picking
- Improving bin and shelf utilization
A well-organized warehouse accelerates fulfillment and reduces labor costs.
3. Streamline Order Processing and Fulfillment
With clear, accurate inventory data, teams can process orders quickly and confidently. Inventory reports support:
- Faster picking accuracy
- Reduced order errors
- Quicker turnaround times
Operational workflows—from order receipt to dispatch—become smoother, leading to faster deliveries and improved customer satisfaction.
4. Reduce Manual Errors and Operational Bottlenecks
Manual tracking often leads to miscounts, missing items, or incorrect data entries. Automated inventory reports help eliminate these bottlenecks by:
- Offering real-time updates
- Reducing dependency on manual paperwork
- Minimizing human error
This ensures all departments—sales, procurement, warehousing—work with the same accurate information.
5. Optimize Staff Productivity and Work Allocation
With clear insights into stock movement and warehouse conditions, managers can allocate labor more effectively. Inventory reports help:
- Identify peak hours requiring more staff
- Reduce idle time during slow periods
- Forecast workload accurately
This leads to better workforce planning and increased operational throughput.
6. Support Accurate Replenishment and Stock Transfers
Timely replenishment is essential for smooth operations. Inventory reports identify which items are low, which require transfers from another location, and which must be reordered. This prevents:
- Unexpected stockouts
- Emergency procurement
- Production delays in manufacturing settings
Efficient replenishment keeps workflows uninterrupted.
7. Enhance Coordination Across Departments
Inventory data plays a cross-functional role. Reports ensure that sales, procurement, finance, and warehouse teams are aligned on:
- What is available
- What needs replenishment
- What is delayed or overstocked
This alignment reduces communication gaps and improves end-to-end operational efficiency.
8. Enable Faster Issue Identification and Resolution
Inventory reports quickly highlight discrepancies such as shrinkage, damaged goods, misplacements, or unusual movement patterns. Early detection helps businesses:
- Resolve issues before they impact customers
- Prevent recurring problems
- Maintain operational accuracy
This proactive approach keeps daily operations running without interruptions.
9. Reduce Costs Through Better Utilization of Resources
By revealing inefficiencies—like excess stock, slow movers, or poor space usage—inventory reports help businesses cut unnecessary costs. Optimizing inventory levels directly reduces:
- Holding expenses
- Insurance costs
- Storage overhead
These cost savings contribute to a leaner, more efficient operation.
How Inventory Reports Boost Profit Margins
Inventory reports play a direct role in improving a company’s profitability. By helping businesses optimize stock levels, minimize waste, and focus on high-performing products, these reports enable smarter financial decisions that lead to healthier profit margins. Here’s how they contribute to sustained profitability:
1. Reduce Overstocking and Holding Costs
Carrying excess inventory locks up working capital and increases warehouse, insurance, and maintenance expenses. Inventory reports reveal slow-moving, obsolete, or excess stock early, helping businesses:
- Reduce storage costs
- Free up tied capital
- Prevent unnecessary reordering
Lower holding costs directly translate into higher margins.
2. Prevent Stockouts and Lost Sales
When products go out of stock, customers move to competitors—resulting in immediate revenue loss. Inventory reports keep businesses informed about low stock levels and upcoming shortages, enabling timely replenishment. This ensures:
- Better product availability
- Higher conversion rates
- Reduced lost-sales opportunities
Consistent availability helps protect revenue and maximize profits.
3. Identify High-Margin and Fast-Moving Products
By revealing which products sell the fastest and which contribute the most profit, inventory reports allow businesses to:
- Prioritize high-margin SKUs
- Allocate marketing and shelf space strategically
- Discontinue unprofitable or low-demand items
Focusing on high-performing products increases overall profitability.
4. Optimize Pricing and Discount Strategies
Inventory insights help businesses understand demand trends, product aging, and stock levels. This supports smarter pricing decisions, such as:
- When to raise prices on in-demand products
- When to offer targeted discounts to clear aging inventory
- How to maintain healthy markup across categories
Data-driven pricing drives higher margins while minimizing unnecessary markdowns.
5. Minimize Losses from Shrinkage, Damage, and Expiry
Shrinkage from theft, damage, or mismanagement silently drains profits. Inventory reports help detect these issues early by highlighting:
- Stock discrepancies
- Damaged or expired items
- Unusual movement patterns
Reducing shrinkage preserves inventory value and protects profit margins.
6. Improve Supplier Negotiations and Cost Control
Accurate inventory reporting helps businesses analyze supplier performance, order trends, and cost fluctuations. Armed with data, companies can:
- Negotiate better pricing and order terms
- Identify cost-efficient suppliers
- Eliminate those with frequent delays or quality issues
Better procurement control reduces COGS (Cost of Goods Sold), boosting gross margins.
7. Reduce Deadstock and Free Up Valuable Capital
Deadstock ties up cash, occupies warehouse space, and erodes profitability. Inventory reports help businesses identify non-moving inventory early so they can:
- Mark it down before it becomes obsolete
- Bundle it with fast-moving products
- Liquidate it strategically
Removing deadstock improves cash flow and increases inventory ROI.
8. Support Better Financial Forecasting
Inventory reports improve accuracy in budgeting, cost planning, and profit forecasting by offering insights into:
- Sales velocity
- Product profitability
- Seasonal demand patterns
Better financial visibility helps businesses make decisions that protect and enhance margins.
Common Mistakes Businesses Make When Using Inventory Reports
Even the most sophisticated inventory reports can fall short when businesses fail to use them correctly. Misinterpretation, outdated data, and inconsistent processes often lead to poor decisions that affect efficiency and profitability. Here are some of the most common mistakes companies make when working with inventory reports—and why they matter.
1. Relying on Inaccurate or Outdated Data
One of the biggest mistakes is relying on stale or incorrect data. When inventory reports are not updated in real time—or only refreshed manually—businesses risk:
- Reordering items they already have
- Running out of stock unexpectedly
- Making decisions based on inaccurate valuations
Outdated data leads to cascading inefficiencies across procurement, sales, and fulfillment.
2. Ignoring Slow-Moving or Deadstock Items
Many businesses focus on fast-moving inventory but overlook slow sellers. Failing to analyze deadstock data causes:
- Blocked working capital
- Higher holding costs
- Reduced warehouse space efficiency
Regularly reviewing slow-mover trends helps address problems before they become costly.
3. Overlooking Reorder Point Insights
Some companies treat inventory reports as simple stock lists, ignoring critical indicators such as reorder points and safety stock levels. This results in:
- Frequent stockouts
- Panic-based reordering
- Poor alignment with demand patterns
Using these insights correctly helps maintain optimal inventory levels.
4. Not Segmenting Inventory Properly
Failing to categorize products (e.g., by value, demand, profitability, or ABC classification) limits the usefulness of reports. Without proper segmentation, businesses struggle to:
- Prioritize high-value or high-margin SKUs
- Identify items that require tighter control
- Improve warehouse layout and picking efficiency
A one-size-fits-all approach reduces the strategic value of inventory reporting.
5. Misinterpreting Report Metrics
Many users misunderstand key metrics such as turnover rate, carrying costs, or demand trends. Misinterpretation can lead to:
- Ordering too much or too little
- Misjudging product performance
- Incorrect forecasting decisions
Proper training ensures teams interpret the data accurately.
6. Using Reports Only Reactively, Not Proactively
Some businesses only check inventory reports when problems arise. This reactive approach often leads to:
- Delayed replenishment
- Overspending on emergency purchases
- Missed opportunities for cost savings
Proactive, routine analysis drives better planning and smoother operations.
7. Lack of Integration Between Departments
Inventory reports lose value when sales, finance, purchasing, and warehouse teams are not aligned. Poor integration leads to:
- Mismatched data
- Duplicate reordering
- Confusion over stock availability
Cross-functional collaboration ensures everyone works from the same accurate information.
8. Failing to Conduct Regular Physical Inventory Counts
Even with automated systems, businesses must verify inventory physically. Skipping annual or periodic counts results in:
- Undetected shrinkage
- Inaccurate valuation
- Gaps between recorded and actual stock
Physical checks keep reports reliable and audit-ready.
9. Overdependence on Manual Reporting
Manual inventory reports increase the risk of errors, delays, and inconsistencies. Businesses relying heavily on spreadsheets often face:
- Mistyped data
- Version control issues
- Time-consuming processes
Automating reports through an ERP system ensures accuracy and saves significant time.
10. Not Utilizing Advanced Insights for Decision-Making
Many businesses generate reports but fail to use deeper analytics such as:
- Forecasting trends
- Margin analysis
- Supplier performance
- Seasonal demand insights
Ignoring these advanced metrics limits the strategic impact of inventory reporting.
Best Practices for Leveraging Inventory Reports Effectively
Before inventory reports can truly drive efficiency and profitability, businesses must know how to use them strategically. Simply generating reports isn’t enough—what matters is how consistently, accurately, and intelligently the data is interpreted and applied.
By following proven best practices, companies can transform raw numbers into actionable insights, streamline operations, and support smarter decision-making across procurement, sales, and finance.
Below are some of the most effective ways to maximize the value of your inventory reports.
1. Automate Inventory Tracking to Minimize Errors
Manual tracking increases the risk of mistakes, delays, and inconsistent data. Automating inventory updates through an ERP or inventory management system ensures real-time accuracy, faster reporting, and fewer stock discrepancies.
2. Standardize Reporting Formats Across Departments
Using uniform templates and metrics helps teams interpret inventory data consistently. Standardized reporting also eliminates confusion, ensures comparability over time, and strengthens inventory-related decision-making.
3. Conduct Regular Audits to Validate Report Accuracy
Periodic stock counts—cycle counts, ABC analysis checks, or annual physical inventories—help verify that system records match actual stock. This prevents inaccurate reorder decisions, revenue leakage, and financial misstatements.
4. Track Inventory KPIs That Align With Business Goals
Metrics such as Days of Inventory Outstanding (DIO), inventory turnover, carrying costs, stockout rate, and fulfillment accuracy reveal underlying operational performance. Monitoring the right KPIs ensures reports support strategic objectives.
5. Use Segmentation to Prioritize High-Impact Items
Classifying inventory using ABC analysis, demand patterns, or profitability segments helps focus attention on items that matter most. This ensures resources aren’t wasted on products with minimal operational or financial impact.
6. Review Reports Frequently to Identify Trends Early
Instead of relying on monthly or quarterly reviews, analyzing weekly or even daily reports enables quicker responses to fluctuations in demand, supplier delays, or stock inconsistencies. Early intervention reduces losses and improves service levels.
7. Integrate Reports With Purchasing and Sales Functions
Connecting inventory reporting with procurement, sales forecasting, and financial planning creates a unified view of operations. This ensures better replenishment decisions, reduced surplus inventory, and improved cash flow.
8. Leverage Forecasting Tools to Plan More Accurately
Pairing inventory reports with demand forecasting software helps businesses anticipate customer needs, align production schedules, and avoid stock imbalances. It also reduces emergency purchases and associated rush costs.
9. Visualize Inventory Data for Faster Interpretation
Dashboards, charts, and real-time visual trackers make complex data easier to understand. Visualizations highlight trends and anomalies that traditional spreadsheets often hide.
10. Train Staff to Understand and Utilize Reports Properly
Even the best reports fail if teams don’t know how to interpret them. Training employees on metrics, report formats, and decision workflows ensures data is used effectively to improve performance.
How Deskera ERP Helps Businesses Optimize Inventory Reporting
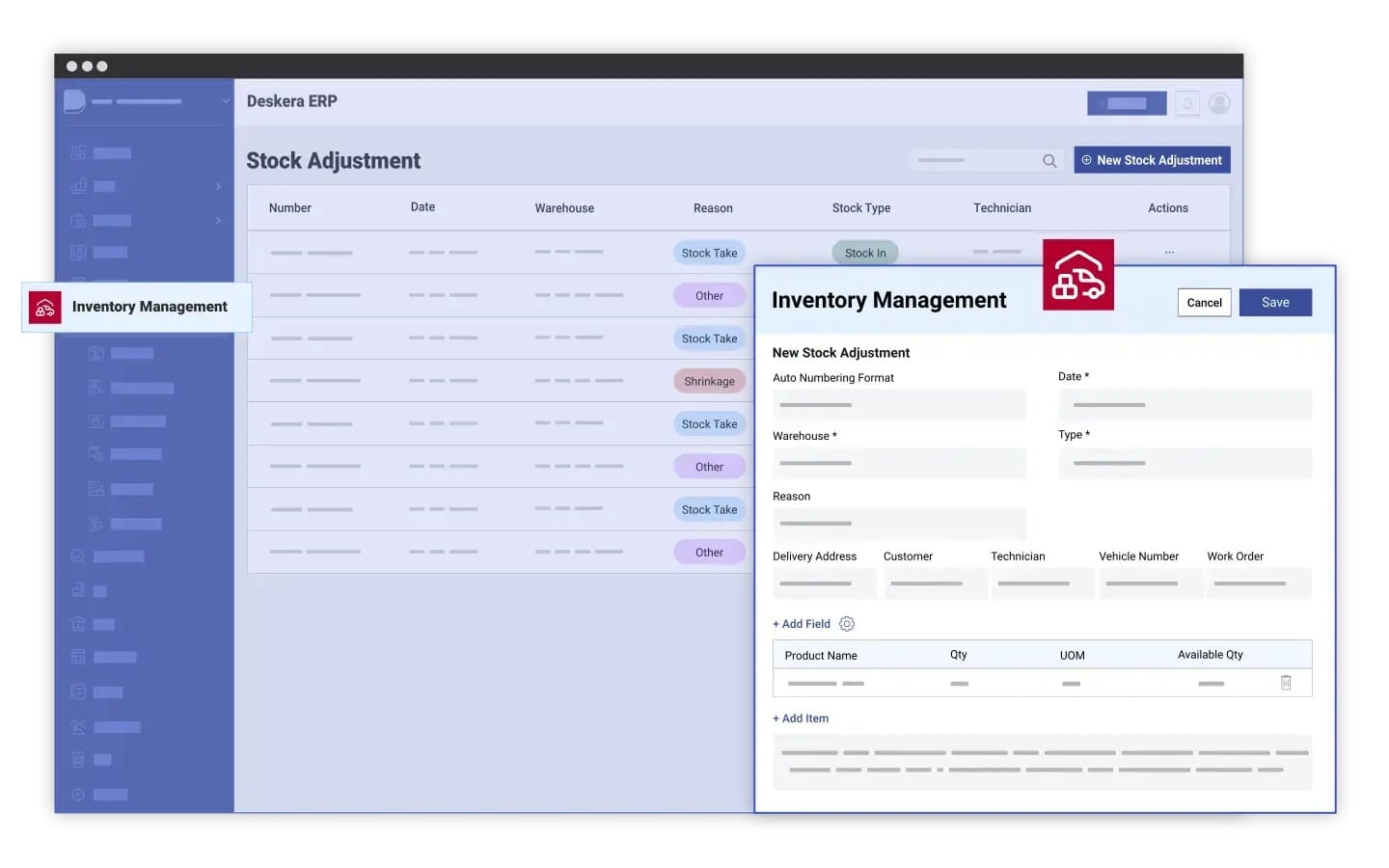
Accurate, real-time reporting is only possible when businesses have the right tools in place—and this is where Deskera ERP stands out. Designed to simplify complex inventory operations, Deskera provides automated, data-rich reports that empower companies to make faster, smarter decisions. With its unified platform for inventory, accounting, sales, and procurement, Deskera ensures that every report reflects up-to-date information across the entire supply chain.
Here’s how Deskera ERP enhances and streamlines inventory reporting:
- Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Automatically updates stock levels across warehouses, locations, and channels for accurate reporting.
- Automated Report Generation: Generates inventory valuation, stock movement, reorder level, and aging reports instantly without manual work.
- Demand Forecasting Insights: Uses historical data and built-in analytics to predict future demand, helping you plan purchases more effectively.
- Integrated Accounting & Inventory: Ensures inventory numbers flow directly into financial reports, improving accuracy in costing and COGS calculations.
- Reduction of Manual Errors: Minimizes human error with standardized templates and automated data capture.
- Alerts & Threshold Notifications: Sends automatic alerts when stock reaches reorder points, preventing stockouts.
- Batch & Serial Tracking: Offers precise traceability for industries dealing with batches, serials, or perishable goods.
- Multi-Warehouse Management: Consolidates stock movement data across different warehouses for unified reporting.
- Mobile-First Access: Lets teams view reports and approve actions anytime through Deskera’s mobile app.
- Advanced Dashboards & Analytics: Provides visual insights that help decision-makers identify trends, bottlenecks, and improvement areas quickly.
Key Takeaways
- Inventory reports play a strategic role in improving both operational efficiency and profitability by offering clear, data-backed visibility into stock performance.
- Inventory reports provide a comprehensive snapshot of stock levels, movements, value, and performance, enabling businesses to maintain balance, prevent stock issues, and make informed decisions.
- Different inventory reports—such as stock movement, valuation, reorder level, demand forecasting, aging, ABC analysis, shrinkage, and multi-warehouse reports—serve unique functions that collectively enhance end-to-end inventory control.
- Accurate reporting streamlines workflows, reduces manual checks, minimizes errors, and equips teams with real-time insights that improve day-to-day inventory operations.
- By preventing stockouts and overstocking, improving demand planning, and optimizing procurement, inventory reports directly support higher profit margins and better financial outcomes.
- Incomplete data, irregular reporting, poor categorization, and disconnects between departments often reduce the effectiveness of inventory insights.
- Standardizing report formats, reviewing data regularly, integrating systems, and using technology-driven tools help businesses extract maximum value from their inventory reports.
- Deskera ERP automates reporting, enhances real-time visibility, improves accuracy, and provides advanced analytics—making it easier for businesses to optimize inventory performance and make data-driven decisions.
Related Articles