GST, or the Goods and Service Tax, is the new taxation regime that is followed in the country. Although this concept is almost five years old now, the rules that govern it are still evolving and morphing continuously into enablers and catalysers of tax payment by making the entire process simpler.
In fact, GST has brought about changes not only in the taxation regimen of the country but also increased the number of taxpayers because of the convenience it has introduced. By replacing a bunch of other individual taxes at various levels of the supply chain and sales, GST has made the collection of tax way easier and paved the way for increased penetration as well.

GST is a well-rounded taxation regime that has enough provisions to cover all kinds of businesses and entities while leaving the clutter behind. There is no more cascading or inundation of taxes at various stages, levels or in different forms anymore. One tax to replace them all - the GST.
Some of the other benefits that have come as a direct result of the introduction of GST are as follows:
- Because GST has subsumed a series of VATs and other taxes, experts believe that this taxation method has the potential to bring the cost of goods and services down in the long run.
- GST has helped onboard small businesses into the world of tax by exempting those with a turnover lesser than ₹20 lakh from paying any GST. This has simplified the taxation procedure that they would otherwise go through in the older regime.
- GST specifically targets those sales that are concluded without receipts and thus counted as corrupt transactions. By making receipts a necessary part of filing returns, GST fights tax evasion very effectively.
- With GST, industries like textile that function in an unorganised manner can now be held accountable for all their operations and be regulated properly.
- With the introduction of GST, taxes on many products such as cars and smartphones have been reduced by as much as 7.5%
- The most critical advantage of GST is seen in its elimination of border tax that impacts logistics. With e-commerce thriving today after the pandemic, GST has reflected a 20% reduction in logistics costs.
- The best part of filing returns for GST is that everything is online. You can do everything from registration to filing returns from the safety of your own home or office. Conversely, if you have hired the services of an accountant, he can do it online for you.
GST is a universal tax, you can say, and should be paid by all taxpayers registered on the GST portal. However, since not all businesses are the same, and all industries have their own workflows and operations that impact their ta returns, GST is classified into different forms. These forms differ from one another in what information needs to be filled, which, in turn, depends on what kind of business you run.
One of these forms is GSTR-7. Here is everything you need to know about filing GSTR-7 and a step-by-step guide to filling information into this form.
What is GSTR-7?
GSTR-7 is a form to be filled by a business if it deducts tax from the goods or services it purchases from other vendors, suppliers or service providers. If you deduct TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) from the payments, you make to your associates from whom you purchase, you are liable to file your GST returns along with the GSTR-7 form.
One of the most important details to include in a GSTR-7 form is the transactions where tax was deducted at the source by your business, and the details of the vendor you made that payment to. This form also contains details like TDS liability amount, TDS amount paid and pending, TDS refund amounts, etc.
In order to fully understand how GSTR-7 works, it is important to know what TDS is and who can deduct it.
Who is Required to Deduct TDS Under GST?
The concept of TDS is quite simple - it is the tax that is deducted at the source of the income. In simpler words, if you are a company that pays its employees a monthly salary, you are liable to deduct a TDS from their income and remit that fund into the account of the central government. The employees would then receive their salaries less the TDS deducted, which is eligible to be credited to them upon the filing of Form 26AS or the TDS certificate provided by the employer. When your employees file their 26AS forms, they will be credited the entitled amount into their bank accounts registered.
According to the GST law, if your business falls under any of the following categories, then you are liable to deduct TDS and file your GST returns according to the GSTR-7 form:
- If you are an establishment or a department under the Central or State governments.
- If you are a local authority.
- If you are an agency of the government.
- If you fall under the eligibilities as notified under the recommendations of the Council by the State or Central governments.
- If you are an entity established by Parliament / State /Centre / State Legislature and whose 51% equity lies with the government.
- If you are a PSU (Public Sector Undertaking).
- If you are a society registered under the Act of 1860 for Societies Registration and established by Central / State government or local authority.
Why is GSTR-7 Important?
Since GSTR-7 requires the deductor to deduct TDS from the payments he makes to his suppliers, there is a scale of balance created in the tax loop for the deductee (the vendor to whom TDS was charged).
When TDS is charged to a vendor, he is eligible to claim Input Tax Credits (ITCs). The vendor/supplier can adjust these Input Tax Credits into the output tax liabilities that he has. This gives him the benefit of paying only the balance of his output tax - thus helping him restrain his tax liabilities.
It is for this reason that all the details regarding TDS must be entered into a GSTR-7 form so that vendors are able to get the benefit this form was intended for.
What is The Due Date for GSTR-7?
GSTR-7 that is supposed to be filed for the current month will be due next month. It technically works like salary - you get paid in November for your work done during the month of October. By that logic, GSTR-7 forms for the month of October will be due to be filed in the month of November.
The cut-off date is typically the 10th of each month. Missing the filing of GSTR-7 incurs heavy, per-day fees which should be avoided at all costs. Therefore, it is recommended to have dedicated manpower employed/hired to take care of all tax filing duties for your company so that no deadline is ever missed.
What is The Penalty for Non-Filing of GSTR-7?
Not filing your GSTR-7 on time incurs heavy penalties to the tune of ₹5,000. It is, therefore, recommended that you file your returns in time to avoid these expenses.
A penalty for not filing your GSTR-7 is calculated on a per-day late fee basis. Typically, not filing your GST on time incurs two kinds of penalties - one levied by the Centre, and one by the State. They individually amount to ₹100. So, a total of ₹200 a day is the late fee for not filing GSTR-7 on time.
However, this amount cannot exceed ₹5,000.
When calculated annually, the late fees are charged interest at 18% per annum if not paid for the whole year. There is a dedicated section in the GSTR-7 form that asks for late fees and interest details if you have missed the deadline.
How to Revise GSTR-7?
Unfortunately, once you have filed your GSTR-7, it cannot be revised. Revisions beat the sanctity of the document. However, in case some unprecedented error has occurred inadvertently, you have the freedom to submit an amendment to the incorrect GSTR-7 form along with the next GSTR-7 that you submit in the succeeding month. For example, if there has been an error in the GSTR-7 of September, you can submit an amendment along with the GSTR-7 form for October.
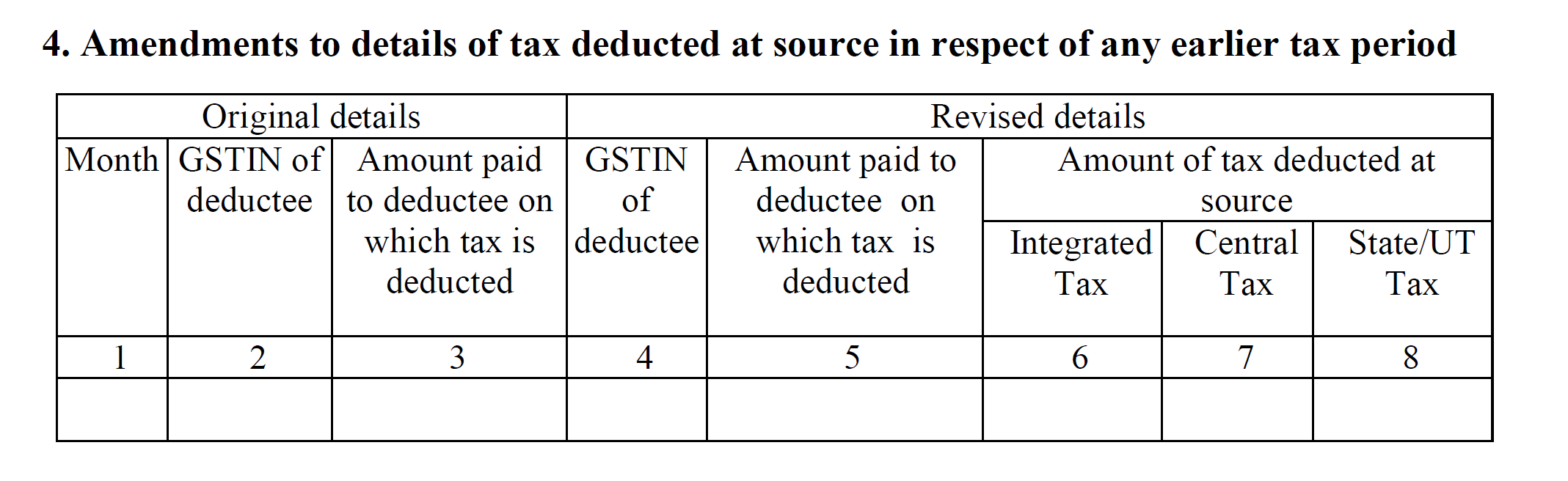
Amendments to GSTR-7 are usually included in the form under section 4. You will need to furnish the details of the original GSTR-7 filed and then in parallel submit the amendments to it in the same section. You will also need to provide the GSTIN details of the deductee since the amendment will impact the TDS deducted and thus the Input Tax Credits of the vendors.
Since these forms cannot be revised, it is recommended that they be double-checked before filing, because they impact the entire operation chain of a business.
Details to Be Provided in GSTR-7
This form is relatively easy to fill. You can download a copy from the GSTR Portal. It is comprised of 8 distinct points in which different information is required to be provided. None of this can be skipped. Here are the 8 sections:
- GSTIN. You need to fill in this information. This is your GST Identification Number.

- Legal name of Deductor, and Trade Name. These fields will be auto-populated once you fill in the GSTIN.
- TDS Details that include the amount paid to the deductee and his GSTIN, TDS amounts of Centre, State and Integrated tax.

- Amendments, if any, to the previous GSTR-7 return filed. The details required here are the original values of the submitted GSTR-7 and the amended values. You need to furnish the GSTIN of the deductee as well here. The remaining fields are similar to section 3.
- TDS break-up and payment status. Here, you need to provide information about %TDS of State, Centre and Integrated Tax, and what amount has been paid and how much is the tax amount.

- Interest, Late Fees. This section contains information about any late fees and interest on late fees if you have incurred any. Since they may differ for Centre and all States, there are separate rows to fill in the rates applicable to your business based on where it operates.

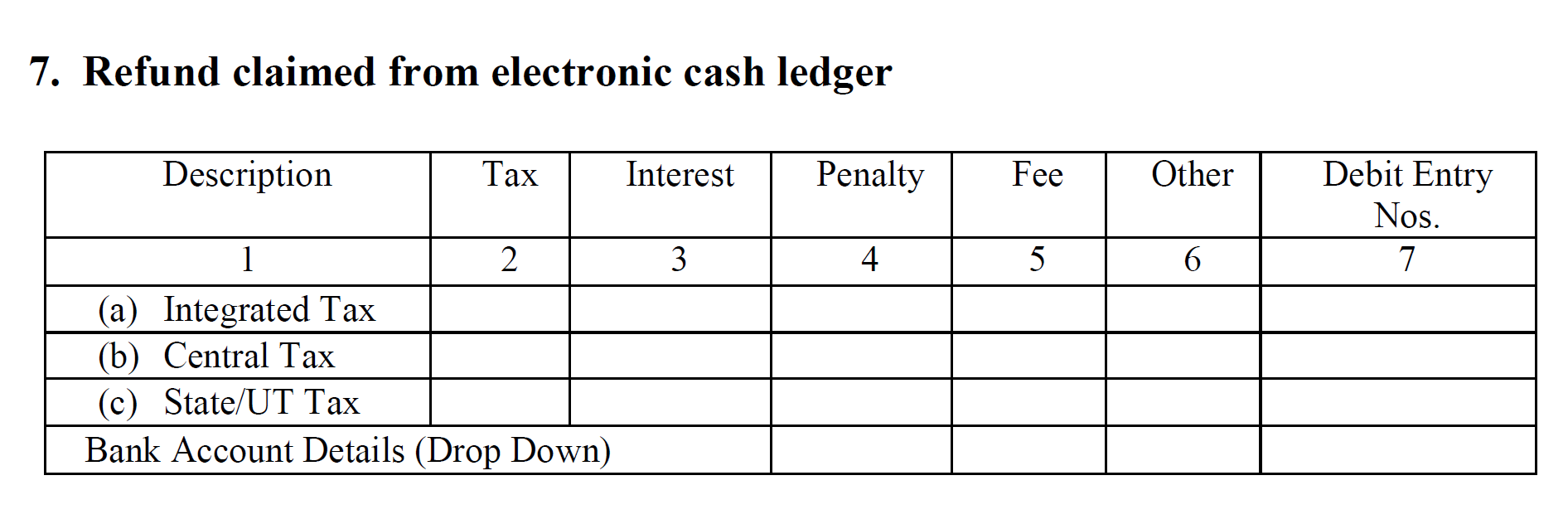
- The 7th section contains information about whether or not you have claimed refunds from the electronic cash ledger. It also contains all the details regarding the same.
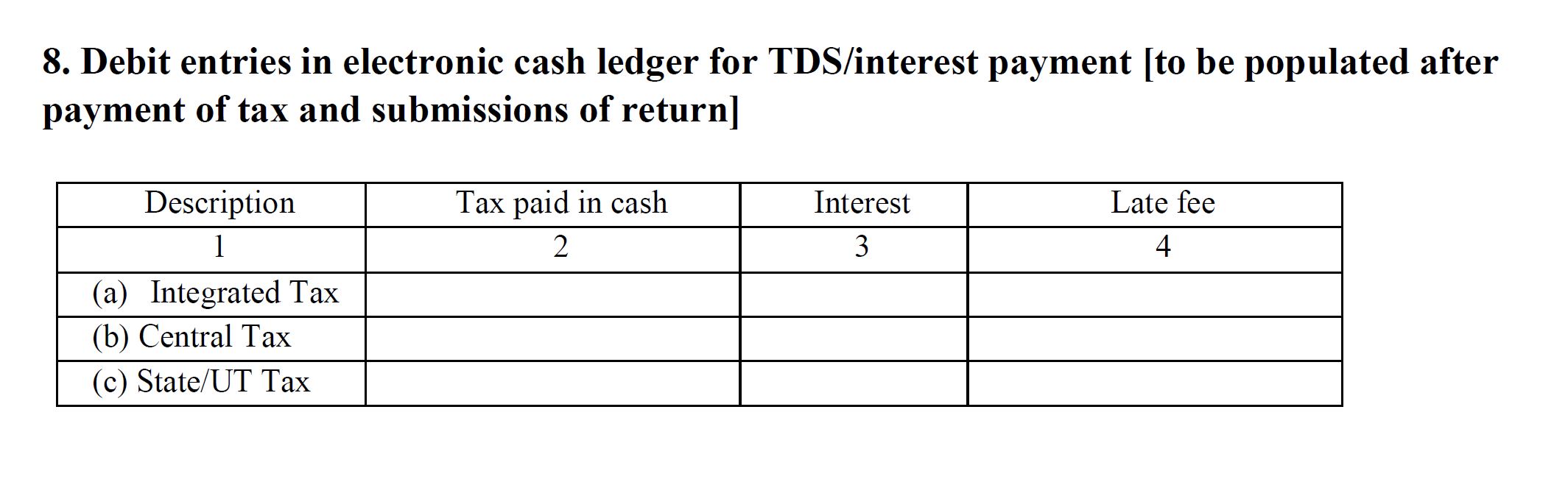
- The last section contains information about your debit entries to the electronic cash ledger. It is supposed to be populated after you have submitted the GSTR-7 and the filing is complete.
Prerequisites for Filing GSTR-7
As stated earlier, not everyone needs to fill out this form and file returns according to it. Only a certain category of entities need to be filled out in the GSTR-7 and filed monthly. Here is a list of criteria that you must fulfil if you want to check eligibility for filing GSTR-7:
- You need to have a GSTIN number and must be a registered taxpayer on the GST Portal.
- Your business/company must have a turnover (aggregate) that is greater than ₹20 lakh.
- If you deduct TDS on payments you make for inward supplies
How can Deskera Help You?
Discover how you can combine accounting, finances, inventory, and much more, under one roof with Deskera Books. It's now easier than ever to manage your Journal entries and billings with Deskera. The remarkable features, such as adding products, services, and inventory, will all be available to you from one place.
Experience the ease of implementation of the tool and try it out to get a new perspective on your accounting system.
With the guiding and informative videos on how to manage and set up India GST, you can learn about and familiarize yourself with the process in just a few minutes.
Deskera Books is a time-saving strategy for managing your work contacts, invoicing, bills and expenses. In addition, opening balances can be imported and chart accounts can be created through it.
Deskera Books can handle every aspect of the organization, including inviting colleagues and accountants.
Key Takeaways
GSTR-7 form isn't difficult to understand, especially if you are a meticulous person who maintains the transaction details of every TDS that you deduct. GSTR-7 form is ultimately aimed at reducing fraudulent sales (sales without receipts or reference IDs) and meant to encourage businesses to start paying their due taxes by making the entire process simpler.
While stopping corruption is one of the major ideologies behind GSTR-7, it does attempt to make the process simpler by encouraging firms to keep a track of all the paperwork they generate regarding TDS. You could say it clears up some of the workflows at a company by encouraging healthy record-keeping and data management habits.
Additionally, the GSTR-7 form makes it possible for the vendors to offset their outward tax liabilities a little bit by claiming Input Tax Credits through the GSTR-7 forms that you submit. This form is a win-win all around.
Related Articles