As a manufacturing executive, are you trying to understand how project accounting will facilitate better decision-making, and thus enhance your company’s productivity and profitability? If your answer is yes, then you are on the right page.
Project accounting plays a pivotal role in the manufacturing industry by providing valuable insights that enable better decision-making for executives. Manufacturing executives are tasked with managing a complex landscape of projects that involve significant resources, costs, and strategic implications. In this dynamic environment, the ability to make informed decisions is crucial to ensure efficient resource allocation, maintain financial control, and achieve overall organizational goals.

Project accounting, a specialized form of accounting that focuses on tracking and managing the financial aspects of individual projects, empowers manufacturing executives with a wealth of data and tools that facilitate strategic decision-making. From assessing project profitability to monitoring budgets, evaluating resource allocation, and managing risks, project accounting equips executives with the information needed to navigate the intricate web of manufacturing projects effectively.
This article will delve into the ways in which project accounting serves as a powerful decision-support tool for manufacturing executives.
The topics covered in this article are:
- What is Project Accounting?
- Who are Manufacturing Executives?
- How Project Accounting Facilitates Better Decision-Making for Manufacturing Executives?
- How Does Project Accounting Promote Transparency in Decision-Making?
- Can Project Accounting Help Executives Manage Resource Constraints in Manufacturing Projects?
- How Does Project Accounting Assist in Developing Contingency Plans?
- How Does Project Accounting Contribute to Continuous Improvement in Manufacturing Projects?
- How can Deskera Help You with Project Accounting?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
What is Project Accounting?
Project accounting is a specialized form of accounting that focuses on tracking, managing, and reporting financial information related to specific projects or initiatives within an organization.
This type of accounting is commonly used in industries where work is organized into projects, such as construction, consulting, engineering, software development, and research.
The primary goals of project accounting are to:
- Allocate Costs: Project accounting allows organizations to allocate costs, including labor, materials, equipment, and overhead expenses, to specific projects. This helps in understanding the true cost of each project and can aid in pricing decisions for future projects.
- Budgeting and Planning: By tracking expenses and comparing them against budgeted amounts, project accounting helps project managers and stakeholders monitor and control project costs. This allows for better planning and adjustments to be made during the project lifecycle.
- Performance Measurement: Project accounting provides insights into the financial performance of individual projects. Managers can assess whether a project is on track in terms of costs, revenues, and profitability. It also helps identify areas where cost overruns or revenue shortfalls might be occurring.
- Resource Allocation: Project accounting helps organizations allocate resources efficiently by providing data on how resources are being utilized across various projects. This can aid in resource allocation decisions and ensure that resources are distributed optimally.
- Invoicing and Billing: For businesses that bill clients based on project work, project accounting facilitates accurate invoicing. It ensures that clients are billed for the actual work completed and expenses incurred during the project.
- Compliance and Reporting: Many industries have regulations and reporting requirements specific to project-based work. Project accounting helps ensure compliance with these regulations and facilitates the generation of accurate financial reports for both internal and external stakeholders.
- Decision Making: Project accounting data provides valuable information for decision-making at various levels within an organization. It helps managers determine whether to continue, modify, or terminate a project based on its financial viability.
Project accounting often involves the use of specialized software and tools that allow for the tracking of project-related expenses, revenues, time worked by employees, and other pertinent financial data. This information is then integrated with the organization's overall financial system for reporting and analysis.
In summary, project accounting plays a crucial role in enabling organizations to effectively manage, control, and evaluate the financial aspects of individual projects, leading to better decision-making, improved resource allocation, and enhanced project profitability.
Who are Manufacturing Executives?
Manufacturing executives are senior-level professionals who hold leadership positions within manufacturing organizations. They are responsible for overseeing and managing various aspects of the manufacturing process, including production, operations, supply chain management, quality control, and strategic planning.
Manufacturing executives play a critical role in ensuring that the manufacturing processes are efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with the overall goals and strategies of the organization. Their responsibilities may vary depending on the size and complexity of the manufacturing operation, as well as the specific industry in which the organization operates.
Key responsibilities of manufacturing executives include:
- Strategic Planning: Manufacturing executives participate in the development and implementation of strategic plans for the manufacturing division. They align manufacturing goals with the overall business objectives of the organization and make decisions that contribute to the company's growth and profitability.
- Operations Management: They oversee day-to-day manufacturing operations, including production scheduling, resource allocation, capacity planning, and inventory management. Their goal is to ensure that production processes run smoothly and efficiently to meet customer demands.
- Quality Control: Manufacturing executives are responsible for maintaining high standards of product quality. They implement quality control measures, establish quality assurance processes, and ensure that products meet industry standards and customer expectations.
- Supply Chain Management: They manage the procurement of raw materials, components, and supplies needed for production. Manufacturing executives work to optimize the supply chain, reduce costs, and minimize disruptions to production.
- Cost Management: Manufacturing executives focus on cost containment and efficiency improvements in the manufacturing process. They analyze cost structures, identify areas for cost reduction, and implement strategies to enhance profitability.
- Technology and Innovation: Staying up-to-date with technological advancements is crucial for manufacturing executives. They evaluate new manufacturing technologies, automation solutions, and innovations that can improve productivity and competitiveness.
- Team Leadership: Manufacturing executives lead and manage teams of professionals, including production managers, engineers, quality control specialists, and other staff. They provide guidance, mentorship, and support to ensure a cohesive and motivated workforce.
- Risk Management: Manufacturing executives assess and manage risks associated with manufacturing operations, supply chain disruptions, regulatory compliance, and other potential challenges.
- Performance Measurement: They track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to production efficiency, quality, cost, and other relevant metrics. This data helps them evaluate the effectiveness of manufacturing strategies and make informed decisions.
- Collaboration: Manufacturing executives collaborate with other departments, such as marketing, sales, and research and development, to ensure alignment between manufacturing and other business functions.
Manufacturing executives are essential in driving the success and competitiveness of manufacturing organizations. Their leadership, strategic thinking, and operational expertise contribute to achieving high-quality products, efficient production processes, and the overall growth of the company.
How Project Accounting Facilitates Better Decision-Making for Manufacturing Executives?
Project accounting can significantly facilitate better decision-making for manufacturing executives by providing them with accurate and detailed financial information related to specific manufacturing projects.
Here's how project accounting can contribute to informed decision-making in the manufacturing context:
Cost Visibility
Cost visibility refers to the ability to clearly see and understand the various costs associated with a manufacturing project. In the manufacturing industry, cost visibility is crucial because it allows executives to have a comprehensive view of how resources are being allocated and utilized throughout the production process.
Project accounting provides a detailed breakdown of costs, which helps manufacturing executives make informed decisions to optimize efficiency, control expenses, and enhance profitability.
Here's how cost visibility works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Granular Cost Breakdown: Project accounting captures costs at a granular level. It accounts for direct costs, such as raw materials, labor, and manufacturing equipment, as well as indirect costs like overhead expenses (utilities, facility maintenance, administrative costs). This breakdown provides a clear understanding of where the money is being spent within each manufacturing project.
- Cost Allocation: Project accounting allocates costs to specific projects based on actual usage. For instance, labor costs are allocated to a project based on the time employees spend working on that project. This ensures that costs are attributed accurately to the relevant projects.
- Comparative Analysis: Manufacturing executives can compare the costs of different projects side by side. This enables them to identify projects that are consuming more resources than anticipated and take corrective actions. They can also analyze why some projects are more cost-effective than others and apply best practices across the organization.
- Identifying Cost Drivers: Cost visibility helps executives identify the main drivers of costs within each project. This might reveal patterns, such as certain manufacturing processes being particularly expensive, which can then be optimized or modified for cost reduction.
- Real-time Monitoring: Modern project accounting systems often provide real-time cost tracking. Manufacturing executives can monitor costs as they accrue, allowing for proactive decision-making. If costs start deviating from the projected budget, executives can intervene early to avoid overruns.
- Transparency and Accountability: Cost visibility fosters transparency within the organization. Project managers and teams are aware of how their actions impact costs, encouraging accountability and responsible resource management.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Armed with accurate cost data, manufacturing executives can make data-driven decisions. For example, they can determine whether to continue a project, adjust its scope, renegotiate supplier contracts, or seek opportunities for cost optimization.
- Effective Communication: Cost visibility aids communication between different departments. Manufacturing executives can share cost breakdowns with other teams, such as finance and procurement, to ensure that everyone is aligned and informed about the financial aspects of a project.
- Cost Control: With a clear view of costs, manufacturing executives can implement cost control measures more effectively. They can set spending thresholds, establish benchmarks, and implement strategies to prevent unnecessary expenditures.
In summary, cost visibility through project accounting provides manufacturing executives with a comprehensive understanding of the financial landscape of each project. This knowledge empowers executives to make informed decisions that lead to better cost management, improved project efficiency, and enhanced overall organizational performance.
Profitability Analysis
Profitability analysis involves evaluating the financial performance of manufacturing projects to determine their level of profitability. In the manufacturing industry, profitability analysis is crucial because it helps manufacturing executives assess the financial viability of different projects, allocate resources effectively, and make informed decisions to maximize overall profitability. Project accounting plays a key role in providing the data needed for thorough profitability analysis.
Here's how profitability analysis works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Revenue and Cost Alignment: Project accounting tracks both project-specific revenues and costs. This allows manufacturing executives to directly compare the income generated by a project with the expenses incurred during its execution. By aligning revenues and costs, executives can calculate the gross profit generated by each project.
- Gross Profit Margin: Manufacturing executives can calculate the gross profit margin for each project. The gross profit margin is the difference between the project's revenue and the direct costs associated with producing the goods. This percentage indicates how efficiently a project generates profit after accounting for production costs.
- Identifying High-Performing Projects: By analyzing the gross profit margins of different projects, executives can identify which projects are generating the highest profits relative to their costs. This insight enables them to prioritize projects with the greatest potential for contributing to overall profitability.
- Low-Performing Projects: Conversely, profitability analysis highlights projects with low or negative gross profit margins. Manufacturing executives can investigate the reasons behind low profitability, such as unexpected cost overruns, inefficient processes, or pricing issues.
- Pricing Strategies: Project accounting data helps executives evaluate whether the pricing strategies for each project are appropriate. If a project's costs are exceeding its revenues, executives can consider adjusting the pricing to ensure profitability.
- Resource Allocation: Profitability analysis guides resource allocation decisions. Manufacturing executives can allocate resources such as labor, materials, and equipment to projects that have proven to be more profitable. This ensures that resources are directed toward initiatives that contribute the most to the bottom line.
- Project Evaluation and Decision-Making: Manufacturing executives can use profitability analysis to evaluate the overall value of each project. This information guides decisions about continuing, modifying or discontinuing projects. Projects that consistently demonstrate low profitability might be re-evaluated in terms of their strategic alignment.
- Comparative Analysis: By comparing the profitability of different projects, manufacturing executives can identify trends and patterns that contribute to success. These insights can be used to replicate successful strategies across other projects.
- Long-Term Planning: Profitability analysis also informs long-term strategic planning. Executives can use the insights gained from analyzing project profitability to make informed decisions about resource allocation, investment, and diversification.
In summary, profitability analysis through project accounting equips manufacturing executives with the information they need to make sound decisions about resource allocation, pricing, and project continuation. By understanding the financial performance of each project, executives can optimize the organization's portfolio of projects to maximize overall profitability and drive sustainable growth.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation involves efficiently distributing and managing resources such as manpower, materials, equipment, and funds across different manufacturing projects to achieve optimal results.
In the manufacturing industry, effective resource allocation is critical for maximizing productivity, minimizing waste, and ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget. Project accounting plays a key role in providing the data necessary for informed resource allocation decisions.
Here's how resource allocation works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Resource Tracking: Project accounting captures data on the utilization of various resources for each manufacturing project. This includes tracking the amount of labor hours, materials consumed, machine time, and other resources used during production.
- Resource Availability: Manufacturing executives can assess the availability of different resources within the organization. By understanding which resources are in high demand and which might be underutilized, they can make informed decisions about allocating resources to projects that need them the most.
- Optimizing Utilization: Resource allocation data allows manufacturing executives to identify instances of overallocation or underutilization. Overallocation of resources to a single project can lead to bottlenecks and delays, while underutilization results in inefficiency and wasted capacity.
- Balancing Workloads: Manufacturing executives can balance workloads by distributing resources evenly across projects. This prevents situations where a few projects receive excessive resources while others struggle due to resource shortages.
- High-Priority Projects: Resource allocation helps prioritize high-priority projects by ensuring they receive the necessary resources. Manufacturing executives can direct critical resources to projects aligned with strategic goals, allowing them to achieve desired outcomes more effectively.
- Resource Constraints: If a manufacturing organization has limited resources, project accounting helps executives identify where resource constraints might occur. This enables proactive planning to address potential shortages and prevent project delays.
- Effective Scheduling: Resource allocation data supports effective project scheduling. Executives can schedule projects based on the availability of key resources, ensuring that projects are sequenced in a way that optimizes resource utilization.
- Mitigating Risks: Manufacturing executives can use resource allocation data to assess the risks associated with resource shortages or dependencies. They can develop contingency plans to address resource-related risks and ensure project continuity.
- Adaptive Resource Allocation: As project circumstances change, manufacturing executives can adapt resource allocation in real time. For instance, if a project requires additional resources due to unexpected demand, executives can allocate resources accordingly.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Data on resource allocation empowers manufacturing executives to make data-driven decisions. They can evaluate resource needs based on historical data and make well-informed choices to enhance efficiency and project success.
- Maximizing ROI: By allocating resources strategically to projects with the highest potential return on investment (ROI), manufacturing executives contribute to overall profitability and ensure that resources are used where they generate the most value.
In summary, resource allocation through project accounting enables manufacturing executives to optimize the use of resources, prevent bottlenecks, and enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing projects. By allocating resources based on accurate data, executives ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and with the highest possible quality.
Budget Monitoring
Budget monitoring involves tracking and managing project expenditures in comparison to the approved budget. In the manufacturing industry, where projects can involve significant costs and resources, effective budget monitoring is crucial for maintaining financial control, preventing overspending, and ensuring that projects remain financially viable. Project accounting provides the tools and data needed to closely monitor project budgets.
Here's how budget monitoring works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Budget Allocation: At the beginning of a manufacturing project, a budget is established that outlines the expected costs for various components, such as labor, materials, equipment, and overhead. This budget serves as a baseline against which actual expenses are measured.
- Real-time Tracking: Project accounting systems allow manufacturing executives to track expenses in real time. As costs are incurred, they are recorded and compared to the budgeted amounts.
- Expense Categories: Budget monitoring categorizes expenses according to different cost categories, making it easier for executives to identify where costs are being incurred and whether they align with the budgeted allocations.
- Variance Analysis: Manufacturing executives can conduct variance analysis, which involves comparing actual expenses to the budgeted amounts. Positive variances indicate that costs are lower than budgeted, while negative variances signify that costs are higher.
- Early Detection of Issues: Budget monitoring allows executives to identify budget overruns or deviations from the plan early in the project lifecycle. This enables them to take corrective actions promptly to avoid larger financial problems down the line.
- Informed Decision-Making: Armed with real-time budget data, manufacturing executives can make informed decisions about resource allocation, adjustments to project scope, and necessary cost-cutting measures.
- Risk Management: Budget monitoring helps identify potential financial risks. If a project's expenses are consistently exceeding the budget, executives can address the underlying causes and implement risk mitigation strategies.
- Project Performance Assessment: Budget monitoring is an integral part of evaluating project performance. By comparing actual costs with budgeted costs, executives can assess whether a project is meeting its financial targets and making progress toward profitability.
- Transparency and Accountability: Budget monitoring promotes transparency within the organization. Project managers and teams are accountable for managing expenses within the allocated budget, fostering responsible financial management.
- Accurate Reporting: Budget monitoring data contributes to accurate financial reporting. Manufacturing executives can provide stakeholders with up-to-date information on project costs, ensuring that all parties are well-informed about the financial status of projects.
- Adjustments and Revisions: Based on budget monitoring insights, manufacturing executives can revise budgets if necessary. Changes in project scope, unexpected events, or new opportunities might require adjustments to the budget to reflect the evolving reality of the project.
- Continuous Improvement: Budget monitoring data from past projects can be used to refine future project budgets. Insights gained from analyzing budget variances can inform more accurate cost estimations for similar projects in the future.
In summary, budget monitoring through project accounting enables manufacturing executives to maintain financial control, make informed decisions, and ensure that projects are executed within the allocated budget. It helps prevent budget overruns, supports effective cost management, and contributes to the overall financial health of the organization.
Decision Support for New Projects
Project accounting provides valuable decision support for manufacturing executives when considering the initiation of new manufacturing projects. The financial data and insights generated through project accounting can help executives make well-informed choices about whether to proceed with new projects, how to structure them, and how to ensure their financial viability.
Here's how decision support for new projects works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Cost Estimation: Project accounting data from past projects can serve as a reference point for estimating the potential costs of new projects. Manufacturing executives can analyze historical cost trends and use them to develop accurate cost projections for the new project.
- Resource Allocation: Based on the resource allocation data collected from previous projects, manufacturing executives can determine the resource requirements for the new project. This includes identifying the amount of labor, materials, equipment, and other resources needed.
- Risk Assessment: Manufacturing executives can use project accounting data to assess the potential financial risks associated with the new project. They can identify risk factors, anticipate potential challenges, and develop strategies to mitigate risks before the project begins.
- Profitability Projections: Using profitability analysis insights, executives can project the potential profitability of the new project. They can estimate revenue based on expected pricing and sales volume, and then deduct the projected costs to determine the potential gross profit.
- Investment Decision: Armed with accurate cost estimates, resource allocation plans, risk assessments, and profitability projections, manufacturing executives can make an informed investment decision about the new project. They can assess whether the potential returns justify the costs and risks associated with the project.
- Comparative Analysis: Project accounting allows for comparative analysis between the new project and similar past projects. Manufacturing executives can evaluate whether the new project aligns with the organization's goals and whether it has the potential to outperform or replicate the success of previous endeavors.
- Strategic Alignment: Manufacturing executives can assess whether the new project aligns with the organization's overall strategic objectives. They can ensure that the project contributes to the company's growth, competitiveness, and long-term vision.
- Budget Planning: Decision support for new projects involves developing an accurate budget that considers both expenses and potential revenues. Manufacturing executives can set realistic budgetary targets based on data-driven estimates.
- Scenario Analysis: Project accounting data can be used to conduct scenario analysis for the new project. Executives can model different scenarios, such as variations in resource allocation, pricing strategies, or market conditions, to understand how changes might impact the project's financial outcomes.
- Continuous Improvement: Insights from decision support for new projects can be used as feedback for continuous improvement. Lessons learned from previous project decisions can inform the refinement of decision-making processes for future projects.
In summary, decision support for new projects through project accounting empowers manufacturing executives to assess the financial feasibility and potential success of new initiatives.
By leveraging historical data, resource allocation insights, and risk assessments, executives can make informed decisions that contribute to the organization's growth and profitability.
Performance Measurement
Performance measurement involves evaluating the progress, achievements, and outcomes of manufacturing projects to determine how well they are meeting their objectives and contributing to the organization's overall goals.
In the manufacturing industry, effective performance measurement is essential for ensuring that projects are on track, identifying areas for improvement, and making informed decisions to optimize project outcomes. Project accounting provides the data necessary for comprehensive performance measurement.
Here's how performance measurement works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Objective Assessment: Manufacturing executives use project accounting data to objectively assess the progress of each project. They compare actual project performance against the initial goals, milestones, and key performance indicators (KPIs) set for the project.
- Financial Metrics: Project accounting provides financial metrics, such as revenue, costs, gross profit, and net profit, which executives can use to evaluate the project's financial health and overall profitability.
- Schedule Adherence: Performance measurement involves tracking project timelines and schedules. Manufacturing executives can determine whether projects are staying on schedule or if there are delays that need to be addressed.
- Resource Utilization: Executives can analyze how effectively resources are being utilized within each project. This includes assessing whether labor hours, materials, and equipment are being used efficiently and whether there are any bottlenecks.
- Quality Assessment: Performance measurement considers the quality of the products or outputs generated by the project. Manufacturing executives can evaluate whether the project is delivering outputs that meet or exceed quality standards.
- Risk Monitoring: Project accounting data helps executives monitor and assess risks throughout the project lifecycle. By tracking project risks and their potential impact on project outcomes, executives can take proactive steps to mitigate risks and prevent negative consequences.
- Variance Analysis: Executives conduct variance analysis to compare actual project performance with the initial plans or budgets. This analysis reveals where deviations from the plan are occurring and helps executives understand the reasons behind these deviations.
- Continuous Improvement: Performance measurement provides insights into areas for improvement. Manufacturing executives can identify recurring challenges, inefficiencies, or bottlenecks and use this information to implement process improvements in future projects.
- Decision-Making: Performance measurement data informs decision-making. If a project is underperforming or experiencing issues, executives can make informed decisions about corrective actions, resource reallocation, or project adjustments.
- Stakeholder Communication: Manufacturing executives use performance measurement data to communicate project progress and outcomes to stakeholders, including senior management, investors, and customers. Transparent communication fosters trust and alignment.
- Lessons Learned: Performance measurement involves analyzing the outcomes of completed projects. Executives can extract valuable lessons from both successful and unsuccessful projects to improve future project planning and execution.
- Strategic Alignment: Performance measurement ensures that projects are aligned with the organization's strategic objectives. If a project's performance deviates from these objectives, manufacturing executives can take corrective actions or adjust project priorities.
In summary, performance measurement through project accounting allows manufacturing executives to monitor and evaluate the progress, efficiency, and outcomes of manufacturing projects.
By using data-driven insights, executives can make informed decisions, optimize project performance, and contribute to the organization's overall success.
Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring potential risks that could impact the success of a manufacturing project. In the manufacturing industry, where projects can be complex and involve various uncertainties, effective risk management is crucial for minimizing negative impacts, ensuring project continuity, and achieving desired outcomes. Project accounting provides the data and insights necessary for comprehensive risk management.
Here's how risk management works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Risk Identification: Manufacturing executives use project accounting data to identify potential risks associated with the project. This includes identifying factors that could lead to cost overruns, delays, quality issues, safety concerns, and other negative outcomes.
- Quantitative Analysis: Project accounting allows executives to quantitatively analyze risks by estimating their potential impact on project costs, timelines, and overall objectives. This analysis helps prioritize risks based on their potential severity.
- Risk Assessment: Manufacturing executives assess the likelihood of each identified risk occurring and the potential consequences if they do occur. This assessment helps executives understand the overall risk profile of the project.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Based on the assessment, manufacturing executives develop strategies to mitigate identified risks. These strategies might involve contingency planning, resource reallocation, process improvements, or the development of alternative scenarios.
- Resource Allocation for Risk Management: Project accounting supports resource allocation for risk management activities. Executives allocate resources to implement risk mitigation strategies, such as setting aside contingency budgets, assigning personnel to address specific risks, or investing in technologies that reduce certain risks.
- Monitoring Risk Indicators: Manufacturing executives use project accounting data to monitor key risk indicators. Early warning signs of potential risks can be identified through deviations from expected costs, timelines, or quality standards.
- Scenario Analysis: Executives use project accounting data to conduct scenario analysis, evaluating how different risks might impact the project. By modeling various scenarios, they can develop response strategies for different risk scenarios.
- Communication and Transparency: Risk management involves clear communication with stakeholders about potential risks, their likelihood, and the mitigation strategies in place. Project accounting data helps provide accurate and transparent information for stakeholder communication.
- Contingency Planning: Manufacturing executives allocate contingency budgets based on potential risks. These budgets are set aside to address unforeseen events or challenges that might arise during the project.
- Lessons Learned: Project accounting data from past projects contributes to lessons learned for risk management. Executives can identify risks that were successfully mitigated and incorporate those strategies into future projects.
- Adaptive Risk Management: As project conditions change, manufacturing executives can adapt risk management strategies accordingly. Project accounting data enables them to respond to new risks that emerge during the project lifecycle.
- Overall Project Resilience: Effective risk management contributes to the overall resilience of the project. By addressing potential risks proactively, executives ensure that the project can withstand challenges and disruptions without derailing its progress.
In summary, risk management through project accounting enables manufacturing executives to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that could impact the success of manufacturing projects.
By using data-driven insights, executives can make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and ensure project continuity even in the face of uncertainties.
Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis involves the creation and examination of different possible scenarios or outcomes that could impact a manufacturing project. This analytical technique allows manufacturing executives to assess how various factors, including risks, uncertainties, and changes, might influence the project's financial performance, timeline, and overall success. Project accounting data plays a vital role in conducting scenario analysis and helping executives make informed decisions.
Here's how scenario analysis works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Multiple Scenarios: Manufacturing executives consider multiple scenarios that represent different potential situations that could affect the project. These scenarios may include best-case, worst-case, and moderate-case situations, as well as variations that account for specific risks or uncertainties.
- Key Variables: Scenario analysis focuses on key variables that can impact the project, such as changes in resource availability, fluctuating costs, shifts in market demand, regulatory changes, and technological advancements.
- Quantitative Assessment: Project accounting provides data that allows manufacturing executives to quantitatively assess the financial impact of each scenario. They can model how changes in variables might influence project costs, revenues, and profitability.
- Resource Allocation: Executives consider how different scenarios could affect resource allocation. For instance, if a scenario involves unexpected demand, they might assess whether the organization has the capacity to meet that demand without overstretching resources.
- Risk Mitigation: Scenario analysis helps executives develop strategies to mitigate risks. By exploring how different risks might unfold, they can identify appropriate risk mitigation measures for each scenario.
- Decision-Making: Manufacturing executives use scenario analysis to inform decision-making. They can evaluate the potential outcomes of each scenario and decide on the best course of action based on the organization's goals, risk tolerance, and available resources.
- Contingency Planning: Scenario analysis contributes to contingency planning. By identifying potential challenges or disruptions, executives can allocate contingency budgets and resources to be used in case a specific scenario materializes.
- Strategic Alignment: Executives assess whether each scenario aligns with the organization's strategic objectives. They consider how each scenario impacts long-term goals and whether it's worth pursuing despite potential challenges.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Sensitivity analysis is a subset of scenario analysis that focuses on how changes in individual variables affect project outcomes. Manufacturing executives can identify which variables have the most significant impact on project success.
- Stakeholder Communication: Scenario analysis results are often communicated to stakeholders to provide insights into the potential risks and opportunities associated with the project. This transparent communication fosters alignment and informed decision-making.
- Continuous Improvement: Insights gained from scenario analysis contribute to ongoing improvement of decision-making processes. Lessons learned from past scenarios help executives refine their approach to managing uncertainties.
- Project Planning: The insights gained from scenario analysis can guide project planning and resource allocation strategies. Executives can create plans that are flexible and adaptable to different potential outcomes.
In summary, scenario analysis through project accounting empowers manufacturing executives to anticipate and prepare for various potential outcomes. By exploring different scenarios, executives can make proactive decisions, allocate resources effectively, and develop strategies to address challenges and capitalize on opportunities that may arise during the course of a manufacturing project.
Informed Investment Decisions
Informed investment decisions involve assessing the potential return on investment (ROI) and evaluating the financial feasibility of various manufacturing projects. Manufacturing executives use project accounting data to make well-informed choices about where to allocate resources, invest capital, and initiate new projects. This process helps ensure that investments are aligned with the organization's strategic objectives and have the potential to contribute to long-term growth and profitability.
Here's how making informed investment decisions works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- ROI Evaluation: Manufacturing executives use project accounting data to evaluate the potential ROI for each project. This involves estimating the expected returns in terms of revenue and profitability compared to the costs and resources invested.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Executives conduct cost-benefit analyses to compare the projected benefits of a project with its estimated costs. This analysis helps assess whether the benefits outweigh the costs and if the project is financially viable.
- Risk Assessment: Project accounting data contributes to risk assessment for potential investments. Executives identify and evaluate risks associated with each investment opportunity, considering how risks might impact the potential returns.
- Resource Allocation: Manufacturing executives assess the resource requirements for each investment opportunity. This includes analyzing the amount of capital, labor, materials, and equipment needed to initiate and complete the project.
- Strategic Alignment: Executives evaluate how each investment opportunity aligns with the organization's overall strategic objectives. They consider whether the investment supports the company's growth, competitive positioning, and long-term vision.
- Scenario Analysis: Executives conduct scenario analysis to explore different potential outcomes of an investment. By modeling various scenarios, they can assess the range of possible outcomes and make decisions that consider different risks and uncertainties.
- Comparative Analysis: Project accounting data supports comparative analysis between different investment opportunities. Executives can compare potential ROIs, risks, resource requirements, and strategic fit to determine which opportunity is the most promising.
- Decision Framework: Manufacturing executives develop decision frameworks that consider both quantitative and qualitative factors. They weigh financial data alongside strategic goals, market trends, competitive landscape, and other relevant considerations.
- Resource Allocation Strategy: Based on the investment opportunities available, executives determine the optimal allocation of resources to achieve the desired balance between projects that generate quick returns and those that contribute to long-term growth.
- Project Portfolio Management: Informed investment decisions contribute to effective project portfolio management. Executives select a mix of projects that collectively align with the organization's objectives and balance short-term gains with long-term strategic investments.
- Budget Planning: Investment decisions are factored into budget planning. Executives allocate budgets to different investment opportunities based on their projected ROI, alignment with strategic goals, and available resources.
- Continuous Evaluation: The process of making informed investment decisions is iterative. Manufacturing executives continually evaluate ongoing projects and potential opportunities, ensuring that investments remain in line with changing market conditions and organizational priorities.
In summary, making informed investment decisions through project accounting empowers manufacturing executives to allocate resources wisely, prioritize projects with the highest potential for returns, and ensure that investments contribute to the organization's growth and profitability.
By leveraging data-driven insights, executives can enhance their decision-making process and maximize the value generated from investments in manufacturing projects.
Alignment with Business Goals
Alignment with business goals involves ensuring that manufacturing projects are strategically aligned with the broader objectives, mission, and vision of the organization. Manufacturing executives use project accounting data to assess how well individual projects contribute to the organization's overall strategic direction, growth, and long-term success. This process helps prioritize projects that have the most significant impact on achieving the organization's goals.
Here's how alignment with business goals works within the realm of project accounting for manufacturing:
- Strategic Objectives: Manufacturing executives begin by identifying the strategic objectives of the organization. These objectives could include goals related to market expansion, product innovation, cost reduction, quality improvement, customer satisfaction, and more.
- Project Selection: Executives use project accounting data to evaluate potential projects based on how well they align with the identified strategic objectives. Projects that directly support these objectives are given higher priority.
- Strategic Fit Analysis: Executives assess how each project contributes to the organization's strategic fit. This involves analyzing how the project aligns with the organization's core competencies, target markets, competitive advantage, and overall value proposition.
- Resource Allocation: Projects that align closely with business goals receive favorable resource allocation. Manufacturing executives allocate resources such as capital, manpower, and materials to projects that have the potential to deliver the most significant strategic impact.
- ROI Evaluation: Project accounting data is used to evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI) of each project in the context of its alignment with business goals. Projects that offer both financial benefits and strategic alignment are prioritized.
- Risk Assessment: Executives consider how each project's alignment with business goals might impact its associated risks. They assess whether the strategic benefits outweigh the potential risks and challenges.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Executives ensure that key stakeholders, including senior management, investors, and board members, are aligned with the strategic goals of the projects. Project accounting data helps communicate how each project contributes to the organization's long-term vision.
- Long-Term Impact: Manufacturing executives consider the long-term impact of each project on the organization's growth trajectory and competitive positioning. They assess whether the project's outcomes will positively shape the company's future.
- Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term: Project accounting supports executives in striking a balance between short-term gains and long-term strategic investments. Executives allocate resources to projects that deliver immediate results while also investing in initiatives that pave the way for sustained success.
- Project Portfolio Management: Alignment with business goals guides project portfolio management decisions. Executives create a balanced portfolio of projects that collectively contribute to the organization's strategic vision and address various aspects of business growth.
- Strategic Adjustments: Manufacturing executives continually assess project alignment as business goals evolve. They may adjust project priorities, reallocate resources, or even discontinue projects that no longer align with the organization's changing strategic direction.
- Clear Communication: Alignment with business goals is communicated to project teams to ensure that everyone understands the broader context of their work and its significance to the organization's success.
In summary, alignment with business goals through project accounting enables manufacturing executives to make decisions that prioritize projects with the greatest potential to contribute to the organization's strategic objectives.
By ensuring that projects align with the company's mission and vision, executives drive growth, enhance competitiveness, and ensure that resources are invested in initiatives that align with the long-term success of the organization.
How Does Project Accounting Promote Transparency in Decision-Making?
Project accounting promotes transparency in decision-making through its ability to provide accurate, detailed, and real-time financial data related to manufacturing projects. This transparency is crucial for manufacturing executives as it enables them to make well-informed decisions based on a clear understanding of project performance, costs, and risks.
Here's how project accounting promotes transparency:
- Accurate Financial Reporting: Project accounting captures and records financial transactions, expenses, and revenues associated with each manufacturing project. This data is presented in a structured and standardized format, ensuring that executives have reliable information for decision-making.
- Real-Time Tracking: Project accounting systems allow for real-time tracking of project expenses, budgets, and financial performance. This means executives have access to up-to-date information that reflects the current status of projects.
- Budget Visibility: Manufacturing executives can compare actual project expenses against approved budgets. This visibility helps them identify any budget overruns or deviations early on and take corrective actions as needed.
- Cost Allocation: Project accounting categorizes costs based on different project components, such as labor, materials, equipment, and overhead. This breakdown provides a clear view of where resources are being allocated and helps prevent misallocation.
- Variance Analysis: By comparing actual financial data with the budgeted amounts, executives can perform variance analysis. Positive or negative variances can be explained and understood transparently, leading to data-driven decision-making.
- Risk Identification: Project accounting highlights potential risks that could impact project finances. This transparency enables executives to assess and address risks proactively, minimizing their negative effects.
- Stakeholder Communication: Transparent project accounting data is crucial for communication with stakeholders, such as senior management, investors, and board members. Clear financial information fosters trust and understanding among stakeholders.
- Scenario Modeling: Transparent project accounting allows for scenario analysis where different financial scenarios are modeled based on changes in project parameters. This provides a clear picture of potential outcomes under various conditions.
- Decision Documentation: Transparent project accounting records decisions made during the project lifecycle, along with the rationale behind them. This documentation provides an audit trail that ensures accountability and transparency.
- Continuous Monitoring: Executives can continuously monitor project financials through project accounting, making it easier to detect any deviations or issues. Transparent monitoring ensures that corrective actions can be taken promptly.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Project accounting fosters collaboration between different teams and departments involved in a project. Shared financial data allows everyone to be on the same page, reducing misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Transparent project accounting helps executives evaluate how well each project aligns with the organization's strategic objectives. This assessment ensures that decisions are consistent with the organization's overall mission and vision.
In summary, project accounting enhances transparency in decision-making by providing accurate, timely, and comprehensive financial information about manufacturing projects. This transparency empowers manufacturing executives to make informed choices, communicate effectively with stakeholders, and steer projects toward successful outcomes while maintaining financial integrity.
Can Project Accounting Help Executives Manage Resource Constraints in Manufacturing Projects?
Yes, project accounting can indeed help manufacturing executives manage resource constraints in manufacturing projects. Resource constraints can arise due to limitations in terms of labor, materials, equipment, or other critical resources needed for project completion. Project accounting provides insights and tools that allow executives to effectively address these constraints and optimize resource utilization.
Here's how project accounting helps in managing resource constraints:
- Resource Allocation Planning: Project accounting systems allow executives to allocate resources based on project requirements and availability. By having a clear overview of resource demands across various projects, executives can make informed decisions about allocating resources to projects with the highest priority.
- Resource Tracking: Project accounting enables real-time tracking of resource usage and availability. Executives can monitor how resources are being utilized, identify potential bottlenecks, and take corrective actions to prevent resource shortages.
- Efficient Scheduling: Project accounting data provides insights into project timelines, dependencies, and resource needs. Executives can use this information to schedule tasks and allocate resources in a way that minimizes conflicts and optimizes resource utilization.
- Resource Leveling: When there are resource constraints, project accounting helps executives balance resource demands across different projects. By strategically reallocating resources, executives can avoid overloading certain projects while underutilizing resources in others.
- Scenario Analysis: Project accounting supports scenario analysis where executives can model different resource allocation scenarios. This helps them understand the impact of resource constraints on project timelines, costs, and overall outcomes.
- Priority Setting: In cases of severe resource constraints, executives can use project accounting insights to prioritize projects based on their strategic importance and potential impact on the organization's goals.
- Resource Procurement: Project accounting data can aid executives in making informed decisions about when and how to procure additional resources. This ensures that resources are available when needed without causing unnecessary delays.
- Risk Management: Resource constraints are often associated with risks of project delays and cost overruns. Project accounting allows executives to assess these risks and develop mitigation strategies to address potential resource shortages.
- Budget Control: Resource constraints can impact project budgets due to expedited procurement or the need for additional resources. Project accounting enables executives to track these budget adjustments and make sure they align with the overall financial plan.
- Collaboration and Communication: Transparent resource allocation data provided by project accounting facilitates collaboration among project teams. Teams can work together to identify resource needs and communicate effectively about potential constraints.
- Continuous Monitoring: Project accounting supports ongoing monitoring of resource utilization. Executives can adjust resource allocation as needed based on real-time data, ensuring that projects stay on track despite changing circumstances.
In summary, project accounting equips manufacturing executives with the tools and insights necessary to effectively manage resource constraints in manufacturing projects. By optimizing resource allocation, addressing bottlenecks, and making data-driven decisions, executives can navigate resource limitations while ensuring successful project outcomes.
How Does Project Accounting Assist in Developing Contingency Plans?
Project accounting plays a crucial role in developing effective contingency plans for manufacturing projects by providing the necessary financial insights and data to anticipate potential risks and uncertainties. Contingency plans are strategies put in place to address unexpected events or challenges that could impact a project's progress, timeline, or budget.
Here's how project accounting assists in developing contingency plans:
- Identifying Risks: Project accounting helps executives identify potential risks that could affect project outcomes. By analyzing historical project data and assessing current project conditions, executives can pinpoint risks that may require contingency planning.
- Quantifying Risk Impact: Project accounting allows executives to quantify the potential impact of identified risks on project costs, schedules, and resources. This helps prioritize risks that require contingency plans.
- Cost Estimation: Project accounting data aids in estimating the potential financial impact of risks. This estimation is crucial for determining the amount of resources that should be allocated to contingency plans.
- Resource Allocation: Executives use project accounting insights to allocate resources specifically for contingency plans. These resources can include additional budget, personnel, materials, or tools that may be needed in case a risk materializes.
- Scenario Analysis: Project accounting supports scenario analysis where different risk scenarios are modeled to assess their potential effects on the project. This analysis guides the development of appropriate contingency strategies.
- Budget Planning: Project accounting facilitates the creation of contingency budgets. Executives can allocate a portion of the project budget to cover unforeseen expenses that may arise due to risks.
- Communication: Transparent project accounting data enables executives to communicate the need for contingency planning to stakeholders, project teams, and other relevant parties. This fosters understanding and support for the plan.
- Mitigation Strategies: Project accounting provides insights into the effectiveness of different risk mitigation strategies. These insights guide the selection of appropriate actions to be taken in case risks materialize.
- Responsibility Assignment: With project accounting data, executives can assign responsibilities for executing contingency plans to specific team members or departments. This ensures that everyone is aware of their role in managing risks.
- Tracking Contingency Actions: Project accounting allows executives to track the implementation of contingency plans and associated actions. This monitoring ensures that the plans are being executed effectively when needed.
- Impact on Project Schedule: Project accounting helps assess the potential impact of contingency plans on the project schedule. Executives can evaluate how these plans might extend the project timeline.
- Documentation: Project accounting contributes to documenting the entire contingency planning process, including risk assessments, strategies, budget allocation, and ongoing actions taken. This documentation aids in learning and improvement for future projects.
In summary, project accounting provides the financial data and insights necessary to develop comprehensive contingency plans for manufacturing projects. By understanding potential risks, quantifying their impact, and allocating resources effectively, executives can ensure that their projects are prepared to navigate unforeseen challenges and disruptions.
How Does Project Accounting Contribute to Continuous Improvement in Manufacturing Projects?
Project accounting contributes significantly to continuous improvement in manufacturing projects by providing valuable data and insights that facilitate learning, refinement of processes, and better decision-making.
Here's how project accounting supports continuous improvement:
- Data-Driven Insights: Project accounting captures detailed data about project costs, revenues, resource utilization, and performance. Analyzing this data helps identify areas for improvement, inefficiencies, and trends over time.
- Variance Analysis: Executives can perform variance analysis by comparing actual project performance with the initial plans or budgets. Deviations from the plan can highlight opportunities for improvement in processes, resource allocation, and cost management.
- Lessons Learned: By analyzing past project accounting data, executives can extract valuable lessons from both successful and unsuccessful projects. These lessons guide future decision-making and project planning.
- Root Cause Analysis: Project accounting data can help executives identify the root causes of project delays, cost overruns, or quality issues. This knowledge enables targeted improvements to address underlying issues.
- Process Refinement: Continuous improvement often involves refining existing processes. Project accounting insights can highlight areas where processes can be streamlined, automated, or made more efficient.
- Resource Optimization: With access to resource utilization data, executives can optimize the allocation of labor, materials, and equipment across projects, avoiding bottlenecks and resource shortages.
- Benchmarking: Project accounting data allows executives to benchmark projects against each other or industry standards. This helps identify best practices and areas where projects can be enhanced.
- Technology Adoption: Executives can use project accounting insights to identify opportunities for adopting new technologies that can improve project management, resource allocation, and cost control.
- Continuous Monitoring: Project accounting supports ongoing monitoring of project performance. Executives can identify issues early and take corrective actions promptly, ensuring continuous project improvement.
- Feedback Loop: Project accounting data provides feedback on the effectiveness of previous improvement initiatives. This feedback guides adjustments and ensures that improvements are sustained over time.
- Risk Management Enhancement: Lessons learned from past projects aid in refining risk management strategies. Executives can develop more effective contingency plans based on historical data and experiences.
- Strategic Alignment: Project accounting data helps executives assess how well projects align with business goals. This evaluation guides project selection and prioritization for better strategic alignment.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Transparent project accounting data encourages collaboration between different teams and departments involved in projects. Shared insights facilitate collective problem-solving and continuous improvement efforts.
- Decision-Making Refinement: Project accounting insights enhance the quality of decision-making. By understanding the outcomes of past decisions, executives can refine their decision-making processes for better results.
- Cultural Improvement: Consistent use of project accounting data for continuous improvement can foster a culture of learning, adaptation, and innovation within the organization.
In summary, project accounting acts as a continuous improvement catalyst by providing data-driven insights, promoting learning from past experiences, and enabling executives to make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and success of manufacturing projects over time.
How can Deskera Help You with Project Accounting?
Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive suite of cloud-based business software solutions that can assist organizations with various aspects of project accounting.
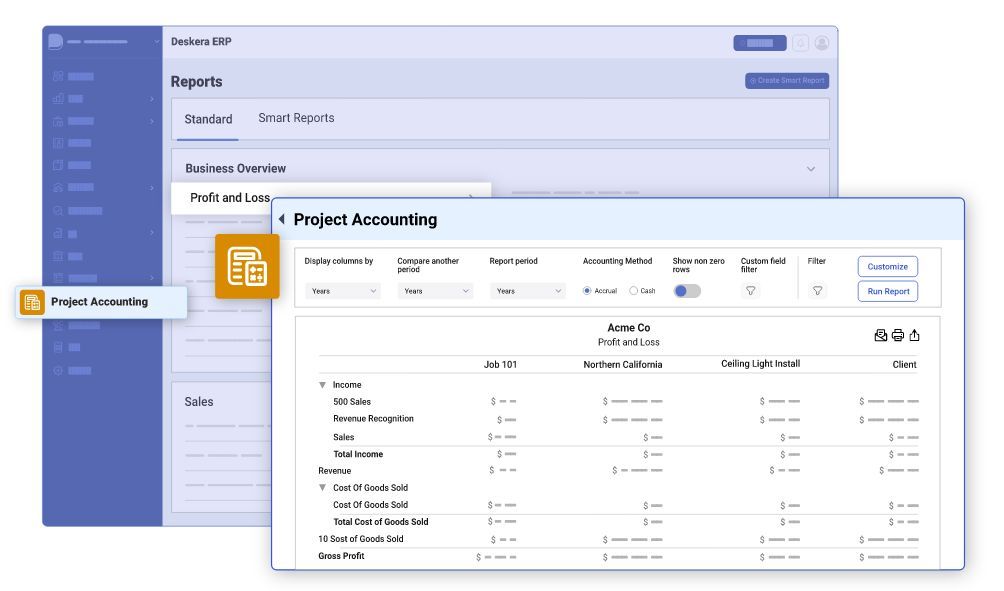
Here's how Deskera can help you with project accounting:
- Bill of Quantities: This will help you accurately track project costs and revenue. This is because Deskera automatically calculates prices, discounts, taxes, and other factors for each item, while also ensuring real-time updates of a project’s bill of quantities.
- Project Time Tracking: Through Deskera, you would be able to monitor your project progress because it automatically logs time spent on tasks and projects. It also ensures accurate billing based on actual project time. Deskera ERP also enables efficient project tracking and management.
- Payment Milestones: With Deskera, you will be able to create payment milestones to streamline accounts payable, set custom payments with specific dates and amounts, and ensure timely payments by setting reminders and notifications.
- Revenue Recognition: With Deskera you will be able to ensure timely invoicing because it enables upfront recognition of revenue. It also allows cost-based accounting for revenue recognition. Lastly, Deskera ERP ensures accurate reporting of revenue.
- Project Costing and P&L: Deskera will assist you in tracking financial health by monitoring, managing, and tracking project costs. It will also help in identifying and analyzing cost overruns, as well as monitoring and reviewing budget performance. Deskera ERP will also generate real-time Profit and Loss reports, and analyze cost and benefit performance, while also giving you financial visibility.
Moreover, you can use these features to create detailed reports and dashboards that provide you with an in-depth understanding of your project finances. With Deskera ERP, you can easily keep track of your project's financials and make better decisions that lead to increased profitability.
Key Takeaways
Project accounting is a specialized approach to tracking and managing the financial aspects of individual manufacturing projects. It provides insights into project costs, revenues, profitability, and resource allocation.
Project accounting equips manufacturing executives with data-driven insights that support informed decision-making, enabling them to allocate resources effectively, assess project profitability, and manage risks.
The 10 ways in which project accounting facilitates better decision-making for manufacturing executives are:
- Cost Visibility: Project accounting allows manufacturing executives to track and analyze the costs associated with individual manufacturing projects. They can see the allocation of expenses, including labor, materials, equipment, and overhead, for each project. This visibility helps executives understand the true cost of production and identify areas where cost-saving measures can be implemented.
- Profitability Analysis: Manufacturing executives can use project accounting to assess the profitability of different manufacturing projects. By comparing project revenues against project-specific costs, they can identify which projects are the most profitable and which might need adjustments to improve profitability.
- Resource Allocation: Project accounting provides insights into how resources, such as manpower and materials, are being utilized across various manufacturing projects. Executives can identify underutilized resources and allocate them more effectively to optimize production capacity.
- Budget Monitoring: Manufacturing projects often have specific budgets allocated to them. Project accounting enables executives to monitor project expenses in real time against the budgeted amounts. This helps prevent budget overruns and ensures that projects stay on track financially.
- Decision Support for New Projects: When considering the launch of new manufacturing projects, project accounting can provide historical data from similar past projects. This data can assist executives in estimating costs, setting pricing strategies, and making informed decisions about resource allocation.
- Performance Measurement: Project accounting helps manufacturing executives measure the performance of ongoing projects. They can assess whether projects are meeting their financial goals, identify any deviations from the plan, and take corrective actions as needed.
- Risk Management: By tracking financial data at the project level, executives can identify potential risks early on. If a project starts to show signs of cost overruns or revenue shortfalls, executives can intervene to mitigate the risks and make adjustments to the project plan.
- Scenario Analysis: Project accounting enables manufacturing executives to conduct scenario analysis by modeling different financial scenarios for a project. They can simulate the impact of changes in variables such as resource allocation, pricing strategies, or production volumes to make more informed decisions.
- Informed Investment Decisions: Manufacturing executives can use project accounting data to evaluate the return on investment (ROI) for different manufacturing projects. This information helps them prioritize projects with higher potential returns and aligns investment decisions with the organization's strategic objectives.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Project accounting data can be used to ensure that manufacturing projects are aligned with the overall business goals and strategies. Executives can make decisions that support the organization's long-term growth and competitiveness.
In essence, project accounting empowers manufacturing executives with actionable financial insights that enable them to make informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle. This leads to more effective resource allocation, better cost control, improved project profitability, and the ability to respond promptly to changes and challenges in the manufacturing environment.
By harnessing the power of data-driven insights, manufacturing executives can steer their projects toward success, drive growth, and propel their organizations to new heights in the competitive landscape of the manufacturing industry.
Deskera ERP will help you with project accounting by tracking, monitoring, and analyzing project revenue, expenses, and billable hours. It will help you leverage real-time visibility into project finances and performance to ensure cost control and profitability. It will also help you in entering timesheets, monitoring profit and loss, and managing bills of quantities.
Related Articles














