Have you ever experienced the frustration of running out of stock just when customer demand peaks—or worse, realizing you’ve overstocked items that barely move? These challenges lie at the heart of why inventory planning is so crucial to business success. Effective inventory planning ensures that the right products are available at the right time, minimizing both shortages and excess while maximizing efficiency across the supply chain.
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to technology to overcome these challenges. The global inventory management software market is projected to reach $4.8 billion by 2029, underscoring the growing reliance on digital solutions to streamline operations. Yet, despite this shift, many organizations continue to struggle—34% of businesses have shipped an order late because they inadvertently sold a product that was out of stock. These inefficiencies not only hurt customer trust but also directly impact revenue and brand reputation.
Automation and intelligent planning tools are transforming the way companies manage their inventory. Research shows that businesses using automated systems can reduce stockouts by 30% and increase operational efficiency by up to 50%. By leveraging data-driven insights, AI-powered forecasting, and integrated systems, companies can predict demand more accurately, manage reorder points, and optimize storage—turning inventory from a liability into a strategic asset.
This is where Deskera ERP plays a pivotal role. Designed to simplify complex inventory processes, Deskera offers a comprehensive suite for inventory forecasting, demand planning, and real-time stock tracking. With its AI-powered assistant, David, and mobile accessibility, businesses can make faster, smarter decisions from anywhere. By unifying operations—from procurement to production—Deskera ERP helps organizations master inventory planning, ensuring every order is fulfilled accurately and efficiently.
What is Inventory Planning?
Inventory planning is the process of determining the ideal quantity and timing of stock needed to meet customer demand while aligning with production schedules and overall business objectives. It involves accurately forecasting demand, setting inventory targets, and deciding when and how much to reorder. In essence, effective inventory planning ensures that a business maintains just the right amount of stock — not too much to tie up capital or too little to cause shortages.
At its core, inventory planning is about balancing supply and demand to optimize operational efficiency. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and lead times, businesses can predict how much inventory will be required in the future. This proactive approach helps prevent both stockouts, which lead to missed sales opportunities, and overstocking, which increases carrying costs and reduces cash flow flexibility.
Inventory planning also serves as a critical part of the broader inventory management and supply chain strategy. It connects seamlessly with order management, accounting, warehouse operations, and customer service — ensuring that every stage of the product lifecycle runs smoothly. For example, an efficient plan enables businesses to purchase stock at the right time, store it effectively, and track inventory levels in real time to ensure timely replenishment.
Ultimately, successful inventory planning enhances profitability and customer satisfaction. For many businesses, inventory represents up to 80% of total assets, making proper planning vital for maintaining healthy cash flow. When done correctly, it helps reduce waste, improve demand forecasting accuracy, and ensure products are always available when customers need them — transforming inventory from a static asset into a strategic business advantage.
Key Factors for Effective Inventory Planning
Achieving effective inventory planning requires more than just maintaining the right stock levels — it involves analyzing multiple variables that influence demand, supply, and cost efficiency. From supplier performance to seasonality, each factor plays a critical role in ensuring that inventory aligns with business goals and customer expectations.
Below are the key factors that help businesses streamline their inventory planning process and maintain optimal stock levels.
1. Supplier Lead Times
The time it takes for suppliers to deliver goods after an order is placed can significantly impact inventory planning. Longer or inconsistent lead times may require businesses to maintain higher safety stock to avoid disruptions. Building strong supplier relationships, monitoring performance, and diversifying vendors can help reduce risks associated with delays and ensure timely replenishment.
2. Inventory Storage Costs
Storage and holding costs—such as warehousing, insurance, and depreciation—directly affect profitability. Maintaining excessive inventory increases these costs, while insufficient storage planning may lead to inefficiencies. Effective inventory planning involves finding the right balance between holding enough stock to meet demand and minimizing costs associated with excess inventory.
3. Inventory Turnover Rate
Inventory turnover rate measures how quickly stock is sold and replenished within a given period. A high turnover rate indicates efficient inventory use and strong demand, while a low rate may point to overstocking or obsolete products. Monitoring this metric helps businesses identify slow-moving items, optimize order quantities, and enhance overall liquidity.
4. Seasonality and Sales Trends
Seasonal fluctuations and changing sales patterns play a vital role in inventory planning. For instance, retail and manufacturing businesses often experience demand spikes during holidays or specific seasons. Analyzing past sales data helps predict these trends, allowing companies to adjust purchasing schedules and stock levels to avoid overstocking or shortages during peak periods.
5. Understocking Risks
Understocking can lead to missed sales opportunities, dissatisfied customers, and long-term reputational damage. When customers consistently find products out of stock, they may switch to competitors. By setting accurate reorder points and maintaining sufficient safety stock, businesses can minimize the risk of stockouts and maintain customer trust.
6. Demand Forecasting with Inventory Planning Software
Modern inventory planning relies heavily on data analytics and automation. Advanced inventory planning software uses AI and predictive algorithms to forecast demand, track stock levels, and automate reordering. This not only reduces manual errors but also ensures that businesses make informed decisions backed by real-time insights and historical data.
7. Shipping and Logistics Costs
Shipping costs can fluctuate based on fuel prices, carrier rates, and delivery distances. These expenses should be factored into the overall inventory planning strategy to maintain profitability. Optimizing shipment schedules, consolidating orders, and using data-driven logistics tools can help reduce transportation costs while ensuring timely product delivery.
By accounting for these factors, businesses can strengthen their inventory planning framework, enhance forecasting accuracy, and maintain an agile supply chain capable of adapting to market shifts.
Inventory Planning vs. Assortment Planning
While inventory planning and assortment planning are closely related and often overlap, they serve distinct purposes within a company’s supply chain and merchandising strategy.
Both rely on accurate data, forecasting, and a deep understanding of customer behavior, but their focus areas differ. Understanding how they complement each other can help businesses maintain healthy stock levels while offering the right mix of products to maximize sales and customer satisfaction.
1. Focus and Objective
Inventory planning focuses on optimizing stock levels to ensure there’s always enough inventory to meet demand without incurring excess holding costs. It involves making strategic decisions about when to reorder, how much to order, and where to store inventory. The goal is operational efficiency — balancing availability and cost while maintaining a steady flow of goods through the supply chain.
Assortment planning, on the other hand, focuses on selecting the right mix of products to offer at any given time. It determines which products to sell, through which channels, and in what quantities — based on customer preferences, seasonality, and sales performance. The objective is to curate a product range that drives profitability and enhances the customer experience.
2. Data and Decision Drivers
Both types of planning rely on data, but the kind of data they use differs. Inventory planning depends heavily on sales forecasts, supplier lead times, and stock movement data to decide replenishment schedules and quantities.
In contrast, assortment planning uses customer behavior insights, product performance metrics, and trend analysis to decide which SKUs should be included or excluded from the assortment. It helps businesses rationalize their product range and allocate resources toward high-demand, high-margin products.
3. Operational Impact
Inventory planning ensures products are available when and where they’re needed, minimizing the risks of stockouts or overstocking. It directly impacts logistics, warehouse management, and order fulfillment efficiency.
Assortment planning, meanwhile, impacts what products are available and how they align with consumer expectations. It helps businesses optimize their shelf space or online catalog, ensuring customers find relevant and appealing products based on market trends or regional demand variations.
4. Interrelationship Between the Two
While distinct, inventory planning and assortment planning are interdependent processes. A well-designed assortment plan informs what needs to be stocked, while effective inventory planning ensures that the chosen assortment is available to customers when they want it.
For example, during a festive season, assortment planning helps select high-demand items, and inventory planning ensures those items are available in sufficient quantities across all channels.
In essence, assortment planning defines what to sell, while inventory planning determines how much to stock and when to replenish. Together, they create a synchronized strategy that maximizes sales opportunities, reduces waste, and enhances the overall customer experience.
Benefits of Inventory Planning
Effective inventory planning delivers a wide range of advantages that extend beyond stock optimization—it strengthens supply chain performance, enhances customer satisfaction, and directly impacts profitability.
By leveraging accurate data, forecasting tools, and automation, businesses can transform inventory from a cost burden into a strategic asset. Below are the key benefits of implementing a well-structured inventory planning strategy.
1. Cost Optimization
One of the most immediate benefits of inventory planning is the reduction of unnecessary costs. By preventing both overstocking and understocking, businesses minimize storage expenses, reduce product obsolescence, and eliminate the need for costly last-minute replenishment. Approaches like Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and Just-in-Time (JIT) models further help balance order frequency and volume, driving overall operational cost efficiency.
2. Improved Cash Flow
When inventory levels are aligned with actual demand, less capital is tied up in unsold stock. This frees up financial resources that can be redirected toward other business priorities, such as marketing, innovation, or expansion. Efficient inventory planning ensures a smooth cash flow, enabling companies to maintain liquidity even during periods of fluctuating demand.
3. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Customers expect timely deliveries and product availability. Effective inventory planning minimizes stockouts, delays, and backorders—factors that directly influence brand trust and repeat purchases. By maintaining the right balance of inventory across locations, businesses can fulfill orders faster, reduce cancellations, and ensure a superior customer experience.
4. Increased Forecast Accuracy
Accurate demand forecasting lies at the core of successful inventory planning. By analyzing historical sales data, seasonal trends, and market behavior, companies can better anticipate fluctuations in demand. This leads to more precise purchasing decisions, reduced waste, and improved responsiveness to sudden changes in customer preferences or supply chain conditions.
5. Greater Operational Efficiency
Inventory planning aligns production schedules, purchasing processes, and warehouse operations for optimal performance. When stock levels are optimized, warehouse layouts become more efficient, order fulfillment becomes faster, and labor costs are reduced. The result is a streamlined workflow that enhances productivity across every stage of the supply chain.
6. Strengthened Supplier Relationships
Consistent inventory planning creates predictability in procurement cycles, allowing businesses to collaborate closely with suppliers. This not only leads to favorable pricing and shorter lead times but also fosters stronger partnerships based on trust and reliability. Sharing demand forecasts with vendors enables smoother coordination and mutual growth.
7. Increased Profitability
Retailers worldwide lose nearly $1.75 trillion annually due to overstocking, shortages, and product returns. With accurate inventory planning, businesses can reduce such losses and increase profitability. Optimized stock levels lower holding costs, improve turnover rates, and enhance overall financial health—turning inventory into a revenue driver rather than a liability.
8. Improved Transparency and Control
With proper planning and real-time tracking systems, businesses gain greater visibility into their inventory across multiple locations. This improved transparency reduces the risk of shrinkage, theft, or misplaced stock and ensures accountability at every level. Enhanced visibility empowers decision-makers to act quickly when addressing discrepancies or optimizing stock movement.
9. Better Demand Responsiveness
Modern inventory planning allows businesses to respond quickly to market shifts. Whether it’s a sudden surge in demand or an unexpected supply chain disruption, proactive planning backed by intelligent software ensures agility. Businesses can reallocate resources or adjust reorder points dynamically, maintaining continuity even in volatile markets.
In essence, effective inventory planning is not just a logistics necessity—it’s a strategic advantage. It optimizes costs, strengthens supplier collaboration, boosts forecasting accuracy, and elevates customer satisfaction. By combining these benefits, businesses can achieve a resilient, data-driven, and highly profitable supply chain.
Key Methods of Inventory Planning
Inventory planning isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. Different businesses require different models depending on their operational scale, supply chain complexity, demand variability, and cost structure. The right inventory planning method ensures that companies balance availability with cost efficiency, minimize waste, and maintain seamless operations.
Below are some of the most widely adopted methods that organizations use to optimize their inventory.
1. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model helps determine the ideal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, including ordering and holding expenses. It assumes a constant demand rate and fixed replenishment costs, making it best suited for stable, high-volume products. By calculating EOQ, businesses can avoid over-purchasing, reduce carrying costs, and maintain steady inventory turnover.
2. ABC Analysis
ABC Analysis categorizes inventory items into three classes based on their importance and value contribution.
- A items: High-value, low-quantity goods that require strict monitoring.
- B items: Moderate value and volume products with balanced control.
- C items: Low-value, high-quantity items that need minimal oversight.
This method allows inventory planners to allocate resources strategically—focusing attention and control on the items that have the greatest financial impact on the business.
3. Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
The Just-in-Time (JIT) approach emphasizes lean inventory management by ensuring that materials arrive exactly when they are needed for production or sales. JIT minimizes storage costs and reduces waste but requires accurate forecasting and reliable suppliers. It is particularly effective in environments with predictable demand and stable supply chains, such as automotive and electronics manufacturing.
4. FIFO and LIFO Inventory Models
These models define how inventory costs are accounted for and managed:
- FIFO (First-In, First-Out): The oldest inventory is sold or used first, which aligns with the physical flow of goods and is essential for perishable items like food or pharmaceuticals.
- LIFO (Last-In, First-Out): The newest inventory is sold first, often used in inflationary environments to reduce taxable income.
Choosing between FIFO and LIFO influences both cost accounting and profitability, depending on market conditions and product type.
5. Deterministic Inventory Model
In the Deterministic Inventory Model, demand, lead time, and costs are assumed to be constant and known. This model is useful for stable, predictable environments and allows planners to set straightforward reorder policies. While idealized, it serves as a foundation for modeling basic inventory scenarios before introducing real-world variability.
6. Work-in-Progress (WIP) Inventory Model
The Work-in-Progress (WIP) model deals with partially completed goods still in production. Managing WIP effectively is critical in manufacturing, as it impacts production efficiency, cost allocation, and throughput. The WIP model helps balance raw materials, labor, and machine capacity, preventing production bottlenecks and ensuring smooth workflow continuity.
7. Perpetual Inventory Model
The Perpetual Inventory Model continuously updates inventory records in real time using technologies like barcode scanners, RFID systems, or ERP software. It provides constant visibility into stock levels, supporting proactive decision-making and reducing errors. This model is ideal for large-scale or multi-location operations where accuracy and responsiveness are key.
8. Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) Model
The Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) model represents the smallest quantity a supplier will sell. Businesses must consider MOQs in procurement decisions, balancing bulk purchase discounts with storage costs and demand variability. This model is especially important when dealing with supplier-imposed constraints or managing low-demand items efficiently.
9. Reorder Point (ROP) Model
The Reorder Point (ROP) model helps determine the optimal time to reorder inventory before stockouts occur. It factors in current inventory levels, average demand, lead time, and often includes a safety stock buffer to handle unexpected fluctuations. The ROP model ensures continuity in operations and is widely used in demand-driven and fast-moving industries.
In summary, selecting the right inventory planning method depends on a company’s operational complexity, demand patterns, and cost considerations.
Whether through data-driven models like EOQ and ABC or dynamic systems like JIT and Perpetual Inventory, each approach helps businesses strike the right balance between availability and efficiency—ensuring long-term resilience and profitability.
Essential Tools and Solutions for Inventory Planning
Modern inventory planning goes far beyond manual spreadsheets. With the increasing complexity of supply chains, businesses now rely on advanced software tools and automation solutions to forecast demand, monitor stock levels, and optimize procurement.
The right tools help minimize costs, prevent stockouts, and improve decision-making through real-time data visibility and analytics. Below are some of the most essential tools and solutions that support efficient inventory planning.
1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
An ERP system integrates various business functions—such as procurement, production, accounting, and inventory—into a single unified platform. For inventory planning, ERP software provides:
- Real-time inventory visibility across multiple locations
- Automated reorder alerts and purchase order generation
- Integration with sales and production data for accurate forecasting
Tools like Deskera ERP offer comprehensive inventory modules with demand forecasting, MRP (Material Requirements Planning), and built-in analytics, enabling businesses to plan efficiently and reduce manual intervention.
2. Inventory Management Software
Dedicated inventory management solutions are designed to track and control stock levels, warehouse operations, and fulfillment processes. They help businesses:
- Monitor inventory movements in real time
- Identify slow-moving or obsolete items
- Optimize reorder points and safety stock levels
These systems often integrate with POS, e-commerce, and logistics platforms, ensuring that every sale or shipment automatically updates inventory records for accurate stock visibility.
3. Demand Forecasting and Predictive Analytics Tools
Accurate demand forecasting is at the heart of effective inventory planning. Predictive analytics tools use historical data, market trends, and seasonality patterns to predict future demand.
This allows planners to adjust inventory levels proactively and minimize both overstocking and understocking. AI-driven forecasting solutions can also account for external factors like weather patterns, promotions, and economic conditions to enhance forecast accuracy.
4. Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Systems
MRP systems are essential for manufacturers managing raw materials and production schedules. These systems calculate material requirements based on current inventory, production plans, and lead times.
MRP ensures that the right materials are available at the right time to meet production demands—preventing costly delays and excess inventory buildup.
5. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) optimizes warehouse operations—from receiving and storage to picking and shipping. Key features include:
- Barcode and RFID tracking
- Space optimization and slotting
- Labor and equipment utilization tracking
WMS tools help maintain high levels of accuracy, reduce handling time, and ensure efficient movement of goods across the supply chain.
6. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) Tools
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) tools enable businesses to manage procurement and supplier performance effectively. These systems provide visibility into supplier lead times, reliability, and costs—helping inventory planners choose the best vendors and negotiate favorable terms. By integrating SRM with ERP or MRP systems, companies can automate purchase orders, monitor deliveries, and reduce procurement risks.
7. Cloud-Based and Mobile Inventory Solutions
Cloud-based and mobile inventory tools allow teams to access, update, and monitor inventory data anytime, anywhere. They are especially useful for businesses with multiple warehouses, field teams, or remote operations. Real-time synchronization ensures that all departments—from sales to procurement—have up-to-date inventory information for faster decision-making.
8. Business Intelligence (BI) and Reporting Tools
BI tools help transform raw inventory data into actionable insights through dashboards, trend analysis, and performance metrics. These reports assist managers in identifying inefficiencies, tracking KPIs like turnover rate or carrying cost, and making data-backed strategic decisions. Integrating BI with ERP or inventory management systems provides a holistic view of operational performance.
In summary, effective inventory planning relies on integrated, data-driven tools that connect forecasting, procurement, warehouse management, and analytics into a single ecosystem. By leveraging ERP systems, MRP software, and predictive analytics, companies can achieve greater accuracy, reduce costs, and ensure the right products are always available to meet customer demand.
Step-by-Step Process for Effective Inventory Planning
Effective inventory planning is not a one-time task—it’s a continuous, data-driven process that ensures your business maintains the right stock levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs.
A structured approach helps synchronize demand forecasting, procurement, and supply chain management for optimal efficiency. Below is a detailed seven-step process to help you build and refine your inventory planning strategy.
1. Analyze Historical and Real-Time Data
Every strong inventory plan begins with data analysis. This includes examining sales history, seasonality patterns, and current market conditions.
- Identify your top-performing and slow-moving SKUs.
- Review supplier lead times, order cycles, and stock turnover rates.
- Integrate data from POS systems, e-commerce platforms, and warehouses for a unified view.
This analysis highlights key trends in customer demand and exposes inefficiencies in your current inventory strategy.
2. Forecast Future Demand
Once you understand your historical performance, use demand forecasting techniques to predict future sales.
- Apply forecasting models such as time-series analysis, moving averages, or AI-driven predictive analytics.
- Consider external factors like seasonality, promotions, or market shifts.
- Regularly update forecasts as new data comes in.
Accurate demand forecasting enables you to anticipate customer needs, plan replenishment schedules, and reduce costly stock imbalances.
3. Define Inventory Goals and KPIs
Set clear objectives for your inventory plan, focusing on both service levels and cost efficiency. Key inventory KPIs include:
- Inventory turnover ratio – how quickly stock is sold and replaced.
- Stockout rate – frequency of running out of products.
- Fill rate – percentage of orders fulfilled on time.
- Carrying cost – cost of storing unsold inventory.
These KPIs help measure progress and align your team’s efforts with business goals.
4. Calculate Reorder Points and Safety Stock
Determine when and how much to reorder by setting reorder points (ROP) and maintaining safety stock.
- Use historical data to calculate average lead time and demand during lead time.
- Apply the safety stock formula: (Maximum Daily Sales × Maximum Lead Time) – (Average Daily Sales × Average Lead Time)
- Adjust safety stock levels for high-demand or high-risk SKUs.
This ensures you can handle supply chain disruptions or sudden demand spikes without overstocking.
5. Build a Replenishment and Supplier Plan
A robust replenishment strategy keeps your production and sales processes running smoothly.
- Identify reliable suppliers and negotiate terms based on consistent order volumes.
- Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) or Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) models if suitable.
- Consider Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) when planning purchases.
Collaborating closely with suppliers ensures timely deliveries and reduces the risk of production halts due to material shortages.
6. Optimize Warehouse Capacity and Tracking Systems
Before finalizing your plan, assess your storage capacity and ensure you have the right inventory tracking systems in place.
- Implement barcode scanning, RFID tagging, or ERP-integrated tracking tools for real-time visibility.
- Use Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to optimize layout, picking routes, and space utilization.
- Plan for seasonal demand peaks to prevent storage bottlenecks.
These practices streamline warehouse operations, reduce manual errors, and improve order fulfillment accuracy.
7. Monitor, Review, and Adapt Continuously
Inventory planning is an ongoing process that requires regular performance reviews and data-driven adjustments.
- Monitor deviations between forecasted and actual demand.
- Revisit safety stock levels and supplier performance periodically.
- Track KPIs to identify improvement areas and refine your models.
Staying agile helps your business respond quickly to market changes and continuously improve inventory efficiency.
The key to mastering inventory planning lies in integrating data analytics, forecasting models, and automation tools. From analyzing demand and setting KPIs to supplier coordination and warehouse optimization, each step contributes to a well-balanced, cost-effective, and customer-centric inventory management strategy.
Common Challenges in Inventory Planning
Even with the best strategies and tools, businesses often face obstacles that can disrupt the balance between supply and demand. These inventory planning challenges can lead to overstocking, stockouts, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction. Understanding these hurdles is the first step toward developing a more resilient inventory system.
1. Inaccurate Demand Forecasting
One of the biggest challenges in inventory planning is forecasting demand accurately. Even a small error in projections can lead to significant overstock or shortage.
- Fluctuating consumer preferences, seasonality, and market volatility make accurate forecasting complex.
- Relying solely on historical data without factoring in current trends or real-time insights can skew predictions.
Solution: Use AI-driven forecasting tools and ERP systems that combine real-time sales, market data, and predictive analytics for better accuracy.
2. Supplier and Lead Time Variability
Suppliers often have inconsistent lead times, affecting the availability of materials or products.
- Delays in procurement can halt production or delay customer deliveries.
- Global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical issues, or transportation delays further compound the risk.
Solution: Maintain strong supplier relationships, track performance metrics, and consider safety stock or multi-sourcing strategies to mitigate risk.
3. Overstocking and Understocking
Finding the right inventory balance is a constant struggle.
- Overstocking ties up capital and increases storage costs.
- Understocking leads to missed sales opportunities and dissatisfied customers.
Solution: Implement automated reorder point systems and use inventory optimization software to maintain ideal stock levels based on demand variability and lead times.
4. Poor Data Visibility and Integration
Many businesses still rely on spreadsheets or disconnected systems for tracking inventory, which causes data silos and inaccuracies.
- Lack of real-time visibility leads to misinformed decisions.
- Teams across departments may operate on outdated or inconsistent data.
Solution: Use cloud-based ERP software that integrates sales, procurement, and inventory data in real time to ensure accuracy and transparency.
5. Inefficient Warehouse Management
Even with accurate planning, poor warehouse organization can disrupt order fulfillment.
- Inventory misplacement, manual tracking errors, and inefficient space utilization lead to slow operations.
- Lack of proper labeling or tracking systems increases picking and dispatching times.
Solution: Deploy Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) with barcode scanning, RFID tagging, and real-time tracking to streamline inventory movement and storage efficiency.
6. Ignoring Seasonality and Market Trends
Failing to account for seasonal demand fluctuations or sudden market shifts can cause severe mismatches in inventory levels.
- Seasonal spikes may leave you underprepared, while off-season overstocking increases holding costs.
Solution: Analyze past seasonal sales trends and integrate dynamic forecasting models that adjust predictions based on real-time demand signals.
7. Limited Collaboration Across Departments
Inventory planning requires coordination between sales, procurement, finance, and warehouse teams.
- Poor communication or siloed decision-making leads to mismatched goals and inaccurate plans.
Solution: Adopt centralized planning tools that allow cross-departmental collaboration, ensuring that all teams work with synchronized, up-to-date data.
8. Rising Holding and Logistics Costs
As warehouse space, labor, and transportation costs rise, holding excess inventory becomes more expensive.
- Inefficient logistics further amplify these costs, eroding profit margins.
Solution: Optimize warehouse layouts, use route planning tools for logistics, and consider Just-in-Time (JIT) approaches to minimize excess inventory.
The most common inventory planning challenges—ranging from inaccurate forecasting to supplier delays and poor data visibility—can significantly impact profitability and customer satisfaction.
By embracing ERP-integrated solutions, automation, and real-time data analytics, businesses can overcome these issues and build a more agile, demand-responsive inventory management process.
Best Practices for Successful Inventory Planning
Achieving efficiency in inventory planning requires more than just software and spreadsheets—it calls for a strategic, data-driven approach that aligns demand, supply, and business goals.
By following a set of proven best practices, businesses can minimize costs, prevent stockouts, and maintain a healthy balance between operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
1. Use Data-Driven Forecasting Techniques
Accurate demand forecasting forms the foundation of effective inventory planning.
- Go beyond historical sales data—integrate real-time analytics, market trends, and customer insights.
- Use AI and machine learning models to predict seasonal variations, demand spikes, and product life cycles.
Tip: Deskera ERP helps automate demand forecasting using predictive analytics, ensuring businesses plan inventory more accurately and efficiently.
2. Maintain Safety Stock Levels
Unexpected delays or sudden demand surges can disrupt your inventory balance. Maintaining safety stock ensures you can meet orders even when supply chain disruptions occur.
- Calculate optimal safety stock using lead time variability and demand uncertainty.
- Review and adjust these levels regularly to reflect changing business conditions.
Tip: Incorporate safety stock calculations into your ERP system to automate reorder triggers and minimize manual intervention.
3. Implement Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Visibility is key to informed decision-making. Real-time inventory tracking allows businesses to monitor stock levels, movement, and usage across all channels.
- Use barcode scanning, RFID tags, or IoT-enabled systems for precise monitoring.
- Sync all channels—warehouses, retail, and e-commerce—to ensure a unified view of inventory.
Tip: Deskera ERP offers real-time inventory tracking and instant updates across all locations, ensuring total visibility and control.
4. Optimize Supplier Relationships
Strong supplier collaboration directly influences your ability to maintain a smooth inventory flow.
- Share forecasts and inventory data with suppliers to reduce lead times and improve responsiveness.
- Maintain a mix of primary and secondary suppliers to mitigate disruption risks.
Tip: Regular performance reviews and automated communication workflows can strengthen supplier reliability and transparency.
5. Regularly Review Inventory Performance Metrics
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) helps assess the effectiveness of your inventory strategies.
- Track metrics such as inventory turnover rate, carrying cost, order accuracy, and fill rate.
- Identify underperforming SKUs or storage inefficiencies and make timely adjustments.
Tip: Deskera ERP provides built-in reporting templates and customizable dashboards for detailed inventory analytics.
6. Classify Inventory with ABC Analysis
Prioritize your resources and efforts by categorizing inventory based on value and movement.
- A items: High-value, low-quantity items requiring strict control.
- B items: Moderate value and quantity, monitored periodically.
- C items: Low-value, high-volume products with minimal oversight.
Tip: Use this classification to allocate management attention, optimize stock levels, and improve cash flow.
7. Integrate Inventory with Other Business Functions
Inventory planning doesn’t operate in isolation—it must align with sales, finance, and production.
- Ensure seamless integration between these functions for consistent data flow.
- Use ERP systems to unify processes and enhance decision-making across departments.
Tip: Deskera ERP connects inventory, sales, and accounting modules for a single source of truth, helping you streamline planning and execution.
8. Conduct Regular Audits and Cycle Counts
Regular inventory audits ensure data accuracy and uncover discrepancies early.
- Implement cycle counting—periodic checks of specific items rather than full inventory counts—to maintain accuracy without disrupting operations.
- Use automation tools to flag inconsistencies and update stock levels in real time.
Tip: Combining Deskera ERP with barcode scanning simplifies the auditing process and reduces manual errors.
Successful inventory planning depends on accurate forecasting, real-time visibility, integrated systems, and data-driven decisions. By adopting these best practices—and leveraging modern ERP solutions like Deskera ERP—businesses can optimize inventory performance, reduce costs, and consistently meet customer demand with confidence.
How Deskera ERP Simplifies Inventory Planning
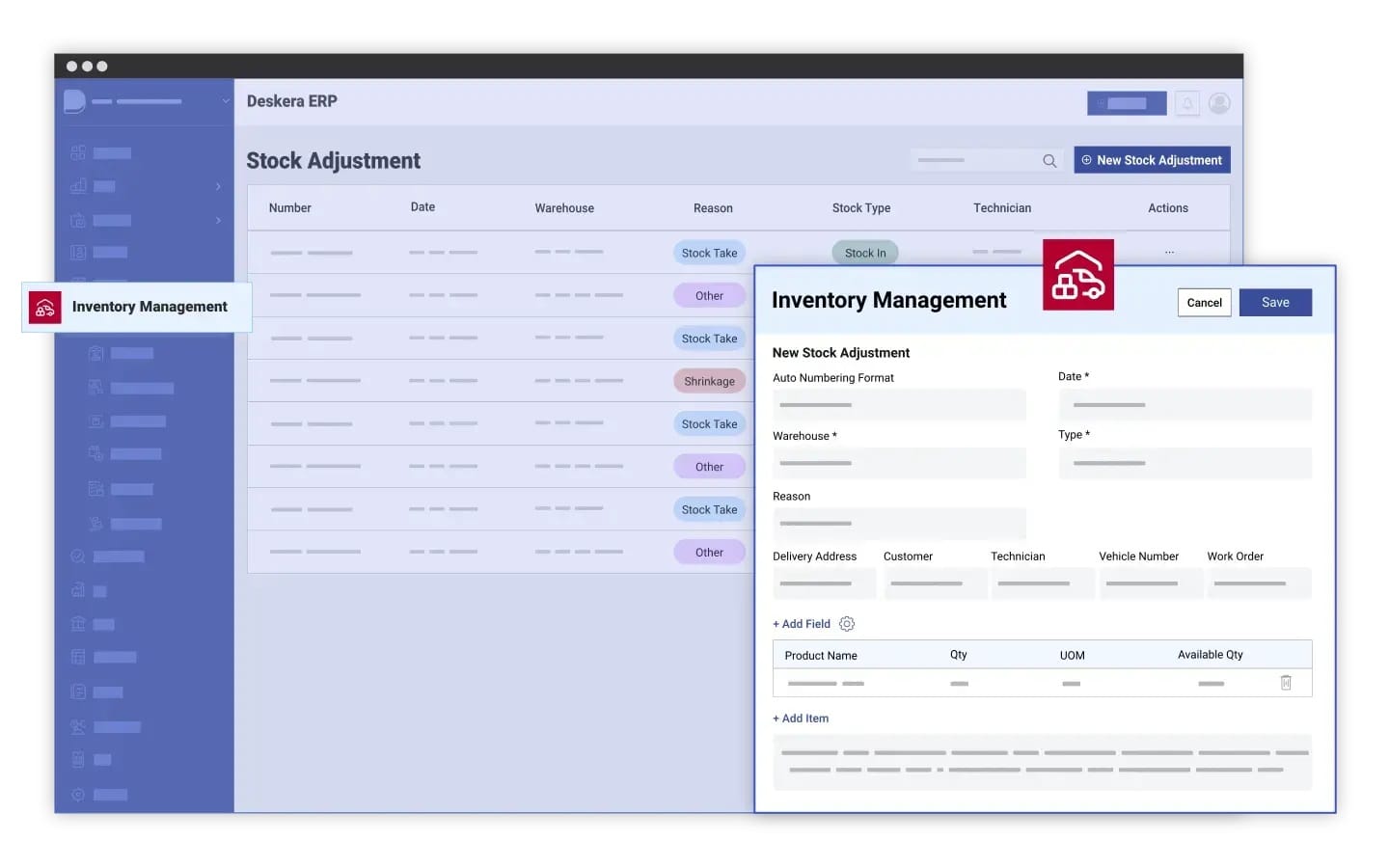
Effective inventory planning requires precision, agility, and real-time data—three things that Deskera ERP delivers seamlessly. By integrating forecasting, order management, and analytics into a unified platform, Deskera ERP empowers businesses to make smarter, faster, and more accurate inventory decisions. Whether you’re managing raw materials for production or finished goods for retail, Deskera helps you strike the perfect balance between supply and demand.
1. Automated Demand Forecasting
Deskera ERP uses AI-driven demand forecasting to help businesses predict future inventory needs accurately.
- It analyzes historical sales data, seasonal trends, and market dynamics to generate data-backed demand projections.
- This enables businesses to order the right quantities at the right time, reducing overstocking and stockouts.
Result: Optimized inventory levels and improved cash flow through accurate, proactive planning.
2. Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Deskera ERP provides real-time visibility into every stage of the inventory lifecycle—from procurement to dispatch.
- Users can monitor stock movement, reorder points, and item aging across multiple locations through a centralized dashboard.
- Barcode and RFID integrations ensure quick tracking and error-free updates.
Result: Complete transparency and control over stock availability, minimizing miscounts and fulfillment delays.
3. Seamless Integration Across Business Functions
Inventory planning is most effective when connected with other functions such as sales, accounting, and production.
- Deskera ERP unifies these workflows, ensuring that changes in sales orders or production schedules automatically reflect in inventory data.
- This eliminates silos and helps maintain consistent, up-to-date information across departments.
Result: A synchronized supply chain where planning, purchasing, and sales operate in perfect alignment.
4. Intelligent Reorder Management
Never worry about running out of stock again—Deskera ERP automates reorder points based on real-time demand and lead times.
- You can set custom reorder thresholds for each SKU, automatically triggering purchase orders when stock dips below the set limit.
- Built-in supplier management tools make replenishment quick and efficient.
Result: Zero missed orders and optimized restocking without manual intervention
5. Comprehensive Reporting and Analytics
Deskera ERP offers powerful inventory analytics and reporting tools that turn raw data into actionable insights.
- Track KPIs such as inventory turnover, carrying costs, order accuracy, and fill rates through customizable dashboards.
- Identify slow-moving or obsolete items to fine-tune purchasing and storage strategies.
Result: Data-backed decision-making that enhances efficiency and profitability.
6. Multi-Location and Multi-Channel Support
Managing inventory across warehouses, retail outlets, or online platforms can be challenging—but Deskera simplifies it.
- It consolidates data from multiple locations and sales channels into a single view.
- Businesses can allocate stock efficiently and fulfill orders from the most optimal location.
Result: Faster fulfillment, reduced logistics costs, and better customer satisfaction.
7. AI Assistant “David” for Smarter Planning
Deskera’s built-in AI assistant, David, simplifies daily inventory tasks.
- David can help users analyze inventory trends, suggest reorder points, and generate reports instantly.
- The assistant learns from usage patterns, improving accuracy and efficiency over time.
Result: Simplified decision-making and reduced manual workload for inventory planners.
Deskera ERP transforms inventory planning from a manual, reactive process into an automated, intelligent system. With real-time insights, AI forecasting, and seamless integration across business functions, it enables organizations to maintain optimal stock levels, minimize costs, and ensure uninterrupted operations—all from a single, user-friendly platform.
Key Takeaways
- Effective inventory planning is essential for achieving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. With the global inventory management software market projected to reach $4.8 billion by 2029, automation and data-driven insights—like those offered by Deskera ERP—are becoming critical to reducing stockouts and improving fulfillment accuracy.
- Key factors such as supplier lead times, storage costs, turnover rates, demand forecasting, and shipping costs directly impact inventory efficiency. Balancing these variables helps maintain optimal stock levels while minimizing costs.
- While inventory planning focuses on maintaining the right stock quantity to meet demand, assortment planning is about selecting the right mix of products for each channel. Together, they ensure product availability and customer satisfaction.
- Strategic inventory planning drives cost savings, improved cash flow, reduced stockouts, and higher customer satisfaction, ultimately boosting long-term profitability and operational resilience.
- Techniques like EOQ, ABC Analysis, JIT, FIFO/LIFO, and Reorder Point models help businesses choose the right inventory strategy based on product demand, cost structure, and supply chain reliability.
- Businesses should leverage inventory management software, demand forecasting tools, barcode systems, and cloud-based ERPs to automate tracking and enhance accuracy in decision-making.
- A structured approach—covering data analysis, demand forecasting, supplier coordination, safety stock calculation, and performance monitoring—ensures consistency and agility in managing inventory across all stages.
- Businesses often face hurdles like inaccurate forecasting, supply chain disruptions, high carrying costs, and lack of visibility. Overcoming these challenges requires real-time analytics and integrated digital tools.
- Implementing best practices such as regular audits, adopting just-in-time models, tracking KPIs, and improving supplier collaboration helps achieve greater efficiency and profitability.
- Deskera ERP streamlines every aspect of inventory planning through AI-powered forecasting, real-time tracking, automated reordering, and intelligent analytics. Its AI assistant, David, further enhances decision-making by offering actionable insights for smarter inventory management.
Related Articles