Have you ever wondered how much inaccurate inventory records cost your business? Inventory accuracy is one of the most critical factors in ensuring smooth operations, yet many businesses struggle to maintain it. When stock levels don’t match what’s recorded in the system, it leads to missed sales opportunities, dissatisfied customers, and unnecessary expenses. In today’s competitive environment, even small errors can add up to big losses.
Industry data shows that inventory accuracy typically falls between 65% to 75% for average companies relying on barcodes and SKUs. While the ideal benchmark is 97% or higher, reports from ISM place the average closer to 91%. On the other hand, some studies highlight poor performers dipping as low as 65%. These discrepancies show that achieving and sustaining high accuracy isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a necessity for preventing shrinkage, avoiding overstocking, and streamlining operations.
The importance of accurate inventory extends far beyond the warehouse. It impacts demand forecasting, supply chain planning, and overall business profitability. Without reliable numbers, businesses face challenges like over-purchasing, stockouts, or even financial misreporting. That’s why improving inventory accuracy should be a strategic priority for organizations of every size, from small retailers to large-scale manufacturers.
This is where technology comes in. Modern ERP systems like Deskera ERP make it easier for businesses to maintain real-time inventory visibility, reduce manual errors, and improve accuracy rates dramatically.
With features such as automated inventory tracking, advanced reporting, demand forecasting, and even an AI-powered assistant (David), Deskera empowers businesses to move closer to the 97%+ accuracy benchmark. By leveraging such tools, companies can transform their inventory management into a competitive advantage.
What is Inventory Accuracy?
Inventory accuracy is a key performance indicator (KPI) that measures how closely the recorded level of stock in a company’s system matches the actual physical count in its warehouses or stores. Put simply, it shows whether the numbers in your inventory management system truly reflect what’s on the shelves. A high level of inventory accuracy signals efficient inventory management and lays the foundation for confident operational and financial decision-making.
In an ideal scenario, inventory records in a warehouse management system (WMS) or ERP would always align perfectly with what’s physically available. However, no business achieves 100% accuracy all the time. Issues like theft, damage, data-entry errors, or dead stock often create mismatches between digital records and actual stock. These discrepancies can lead to missed sales opportunities, customer dissatisfaction, or higher carrying costs.
Inventory accuracy expectations also vary depending on the industry. Sectors such as retail, pharmaceuticals, and construction demand especially high accuracy due to the risks of stockouts, perishability, strict compliance requirements, or project dependencies. In contrast, industries handling less-perishable or lower-value goods may tolerate slightly lower accuracy levels. Still, the ultimate goal for any business is to minimize mismatches and keep inventory levels as close to accurate as possible.
To measure accuracy, businesses often use inventory accuracy percentage. For example, if your system shows 1,000 units in stock but the physical count confirms only 800, then your accuracy rate is 80%. This metric provides a clear picture of how well your inventory is being tracked.
Maintaining a high accuracy percentage reduces the risk of stockouts, overstocking, and financial reporting errors, while also enabling better forecasting and decision-making. Achieving this requires a mix of strong operational practices—like regular cycle counts, standardized processes, and staff training—alongside technology tools such as barcoding, RFID, real-time tracking, and automation.
Importance of Inventory Accuracy
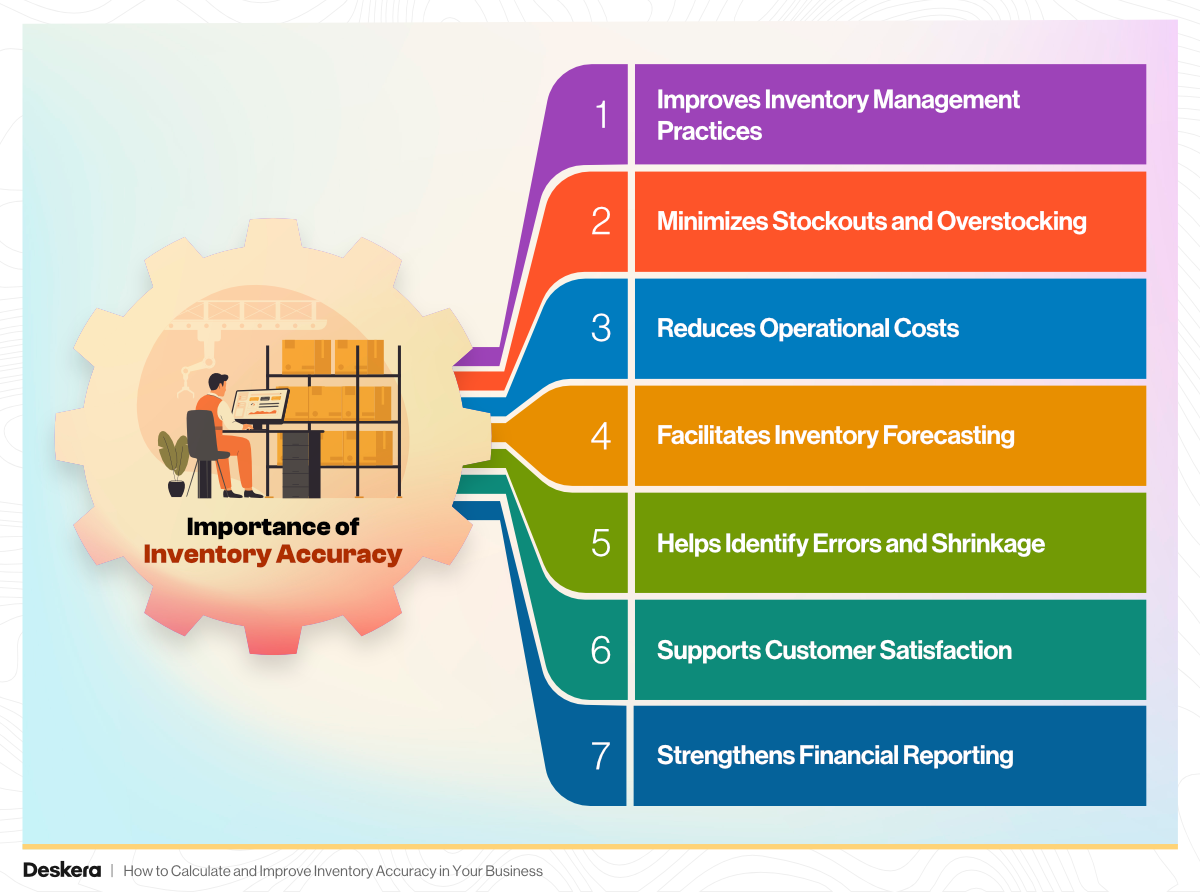
Inventory accuracy is one of the most important metrics for product-based businesses, as it directly impacts efficiency, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
When stock counts are correct, companies gain clear visibility into what’s available, how fast items are moving, and when replenishment is needed. On the other hand, inaccurate records create costly supply chain problems, from stockouts to fulfillment delays, and increase overhead costs.
Improves Inventory Management Practices
Accurate counts give businesses a reliable foundation for effective inventory management. When you know what’s in stock, where it’s located, and how fast it’s selling, you can streamline processes across replenishment, warehousing, and fulfillment. This reduces errors, ensures smoother operations, and builds better control over inventory movement.
Minimizes Stockouts and Overstocking
One of the biggest advantages of inventory accuracy is avoiding both shortages and excess stock. By aligning system records with real stock levels, businesses can make smarter purchasing decisions and reorder at the right time. This not only prevents lost sales from stockouts but also reduces the risk of tying up capital in dead stock that sits idle on shelves.
Reduces Operational Costs
Maintaining high inventory accuracy helps businesses identify underperforming SKUs and reduce carrying costs. Products that don’t move increase storage expenses and tie up valuable resources.
By spotting slow-moving items, businesses can take corrective actions such as discounts, bundling, or phasing out underperforming products. Research also shows that poor performers in inventory management face up to three times higher carrying costs compared to top performers.
Facilitates Inventory Forecasting
Accurate records are the foundation of accurate forecasting. Businesses cannot plan for future demand if their data is unreliable. With high inventory accuracy, demand forecasts reflect actual consumption trends, enabling better planning for production, purchasing, and sales. This prevents over-purchasing while ensuring stock is available when customers need it.
Helps Identify Errors and Shrinkage
Discrepancies between recorded and physical stock often point to inventory errors, shrinkage, or even fraud. Regularly comparing inventory counts helps businesses spot theft, misplacement, or data-entry mistakes before they spiral into bigger problems.
According to the 2020 National Retail Security Survey, shrinkage costs retailers an estimated $61.7 billion annually—making accuracy critical to protecting profits.
Supports Customer Satisfaction
At the end of the day, inventory accuracy directly influences customer experience. Accurate stock data prevents overselling, ensures timely fulfillment, and enables businesses to keep popular products in stock. This leads to faster deliveries, fewer order cancellations, and happier customers—all of which strengthen loyalty and customer retention.
Strengthens Financial Reporting
Finally, inventory accuracy plays a vital role in financial health. Since inventory is a major asset on the balance sheet, errors in stock records can distort financial statements and lead to incorrect profit reporting. Reliable inventory data ensures compliance, prevents audit risks, and supports confident decision-making at the executive level.
What Causes Inaccurate Inventory?

Even with modern systems in place, inventory discrepancies continue to be a challenge for many businesses. These issues are usually preventable but require attention to detail and proper processes.
Below are the most common causes of inaccurate inventory and how they affect businesses.
1. Data-Entry Errors
Manual data entry is one of the most common sources of inaccurate inventory. A single typo, transposed digit, or incorrect unit entry can ripple across records, creating serious mismatches between system data and physical stock. Since many businesses still rely on manual inputs, unchecked mistakes often pile up unnoticed.
Without verification, these errors compromise reporting accuracy and make decision-making unreliable. Automating data entry through barcode scanning or integrated systems is one of the best ways to reduce this problem.
2. Incorrect Manual Counts
When employees conduct physical counts without standardized procedures, errors are almost guaranteed. Differences in counting methods, inconsistent measurement units, or even fatigue during lengthy audits can lead to misreporting.
Inconsistent results across teams or warehouse locations make it difficult to get a reliable snapshot of inventory accuracy. Over time, this reduces trust in system data and complicates planning. Establishing strict counting standards and conducting regular cycle counts can greatly improve accuracy.
3. Spoilage and Damage
Spoiled, expired, or damaged items often remain listed in stock records unless properly removed. This is especially problematic for businesses handling perishables, chemicals, or fragile goods. If damaged inventory isn’t promptly written off, it creates an inflated sense of available stock.
The result is “phantom inventory,” where records show items that can’t actually be sold. This not only disrupts fulfillment but also misrepresents financial records. A disciplined process for documenting and removing unusable stock is essential.
4. Theft and Shrinkage
Theft—whether internal or external—is a persistent cause of inventory inaccuracies. Employee theft, shoplifting, or break-ins can create gaps between what’s recorded and what’s physically available. According to retail surveys, shrinkage accounts for billions in losses annually, significantly hurting profitability.
Weak security systems, lack of monitoring, and poor accountability structures make businesses more vulnerable. Beyond financial loss, theft also undermines trust in reported data. Implementing surveillance systems, audits, and clear accountability practices helps reduce shrinkage.
5. Misplaced Inventory
In many warehouses, stock exists but cannot be found when needed because it’s stored in the wrong place. Poor labeling, disorganized shelves, or inadequate tracking protocols lead to misplaced items. While technically still part of inventory, these items are functionally “missing,” creating the same issues as stockouts.
This problem is common in cluttered or rapidly expanding warehouses where organization hasn’t kept pace with growth. Clear labeling systems and organized storage layouts can help keep inventory accessible.
6. Disorganized Shipping and Receiving
The receiving process is the first checkpoint for inventory accuracy. When shipments are not carefully inspected, businesses risk recording incorrect quantities, mislabeled goods, or even damaged products as sellable inventory.
Similarly, disorganized outbound shipping leads to items being miscounted or mis-shipped, disrupting accuracy. Vendor mistakes, such as incorrect packing or labeling, compound the issue. Without thorough verification at both ends of the supply chain, discrepancies take root early and cause persistent problems throughout operations.
7. Inaccurate Picking
Errors during the picking process—such as grabbing the wrong item, wrong quantity, or similar-looking product—directly impact both customer satisfaction and inventory accuracy. Misread labels, poor training, or unclear picking instructions are often to blame.
When the wrong products leave the warehouse, system records no longer align with physical stock. These mistakes also increase return rates, further complicating records. Investing in clear labeling, training, and technology like barcode scanners or pick-to-light systems can significantly reduce picking errors.
8. Undocumented Inventory Loss
Inventory loss, also known as shrinkage, often goes unrecorded when products are damaged or misplaced but never officially written off. For example, if damaged goods are left in system records as available stock, they create phantom inventory.
This causes mismatches during audits and disrupts order fulfillment. Unreported loss also distorts financial reporting, since unsellable products inflate asset values. Documenting all losses immediately—whether due to damage, theft, or errors—ensures records reflect true availability.
9. Supplier and Fulfillment Errors
Even before inventory reaches a business, errors at the supplier or fulfillment partner level can set accuracy off track. Common issues include suppliers shipping the wrong quantities, mislabeling products, or packing damaged goods. These mistakes, if not caught during receiving, immediately create discrepancies.
Since businesses often assume supplier accuracy, these errors can go unnoticed for weeks. Establishing strict verification protocols at receiving and working with reliable partners helps minimize supplier-related inaccuracies.
10. Disorganized Warehouses
A cluttered or poorly managed warehouse is one of the biggest contributors to inaccurate inventory. If products are stored in random locations, mislabeled bins, or inconsistent pallets, employees struggle to track stock reliably.
Items can be easily misplaced, counted twice, or skipped during audits. Disorganization also slows down picking and fulfillment, increasing the chance of human error. A clean, organized, and standardized warehouse layout with consistent labeling reduces mistakes and improves both efficiency and accuracy.
11. Mismanaged Returns
Returns are often overlooked as a source of inventory inaccuracies. When returned goods are coded incorrectly—such as damaged products being marked “available”—they create phantom stock that doesn’t actually exist.
Without proper inspection and categorization, unsellable items re-enter system records as if they were sellable. This not only distorts accuracy but also leads to failed fulfillment when items can’t actually be shipped. Training staff to handle returns correctly and implementing strict return procedures helps eliminate this issue.
How to Calculate Inventory Accuracy
Inventory accuracy measures how closely your recorded stock levels match the actual physical inventory in your warehouse. It’s usually expressed as a percentage, and there are a few methods to calculate it depending on how detailed you want to be.
1. Standard Formula (Simple Count Method)
The most common way to calculate inventory accuracy is to compare the number of items physically counted to the number recorded in your inventory management system.
Formula:
Inventory Accuracy = (Counted Items / Recorded Items) × 100
Example: A company sells phone cases. After counting stock, they find 1,000 cases physically in storage, while the system shows 1,020 cases.
Inventory Accuracy = (1,000 / 1,020) × 100 = 98%
This means the company’s inventory accuracy rate is 98%, which is very good (industry benchmarks aim for 97% or higher).
2. Variance-Based Formula
The standard method allows shortages and overages to cancel each other out, which can make results look better than they actually are. To get a truer picture, many businesses use a variance-based method. This approach looks at the absolute variance between expected and actual quantities for each SKU.
Formula:
Inventory Accuracy = [1 – (Total Absolute Variance / Total Recorded Inventory)] × 100
Example: A bike parts manufacturer physically counts inventory and compares it with system records:
- Spokes: 875 vs 1,000 → Variance = 125
- Tires: 198 vs 200 → Variance = 2
- Chains: 97 vs 100 → Variance = 3
- Handlebars: 100 vs 100 → Variance = 0
- Pedals: 212 vs 200 → Variance = 12
Total variance = 142
Total recorded = 1,600
Inventory Accuracy = [1 – (142 / 1,600)] × 100 = 91.1%
This number is slightly lower than the simple method (92.6%) but provides a more realistic measure of performance.
3. Inventory Valuation Method
Instead of counting units, some businesses calculate inventory accuracy by comparing the value of actual stock against the value of recorded stock. This is especially useful for high-volume businesses where manual counting is too time-consuming.
Formula:
Inventory Accuracy = (Actual Inventory Value / Recorded Inventory Value) × 100
Example: If a business has 1,000 phone cases worth $5 each ($5,000 actual value), but records show 1,020 cases ($5,100 value), then:
Inventory Accuracy = (5,000 / 5,100) × 100 = 98%
This method aligns with unit-based calculations but is easier when working with valuation systems or barcode scanning.
What is a Good Inventory Accuracy Rate?
- Average companies: ~83% (CAPS Research, 2024)
- Best-in-class: 95–97% or higher
- Industry variations: Highly regulated industries (pharma, food, aviation) often require near-perfect accuracy, while others may accept slightly lower benchmarks.
In practice, most companies use cycle counts and variance-based accuracy to keep numbers reliable. High accuracy not only prevents stockouts and overstocking but also ensures better forecasting, customer satisfaction, and financial reporting.
How to Improve Inventory Accuracy

Organizations have real opportunities to improve inventory accuracy by following proven, actionable steps. By addressing common challenges and leveraging the right blend of technology, processes, and training, businesses can significantly reduce errors and streamline warehouse operations.
Below are key strategies that can help boost inventory accuracy.
Implement Cycle Counting for Continuous Accuracy
Cycle counting involves checking a portion of inventory regularly rather than waiting for a full annual count. This approach helps businesses detect errors early, adjust discrepancies promptly, and maintain higher accuracy throughout the year. By incorporating cycle counts into daily or weekly routines, companies can prevent issues from snowballing and reduce the workload of massive stock audits.
Leverage Barcode Scanning and RFID Technology
Manual data entry often leads to mistakes that reduce accuracy. Barcode scanning and RFID systems minimize human error by automating stock tracking. Each item movement is instantly recorded, ensuring real-time visibility of inventory levels. These technologies not only improve speed but also reduce shrinkage and misplacements, leading to more reliable data and smoother operations.
Automate Inventory Tracking with ERP Software
ERP systems centralize and automate inventory management across procurement, sales, and warehousing. By eliminating data silos and manual updates, ERP tools like Deskera provide real-time accuracy and insights into stock movement. Automated alerts for low stock, demand forecasting, and seamless integration with sales channels help businesses maintain near-perfect accuracy while reducing operational inefficiencies.
Train Employees on Standardized Processes
Employees play a critical role in inventory management. Without proper training, even the best systems fail. Training ensures that staff follow standardized practices for receiving, labeling, storing, and recording stock. A well-trained workforce reduces the chances of miscounts, misplaced items, and incorrect entries, leading to greater consistency and accuracy in day-to-day operations.
Set Clear Reorder Points and Stock Thresholds
Unclear reorder points often lead to stockouts or overstocking. By defining reorder levels based on demand history and lead times, businesses can prevent errors in replenishment. Setting thresholds ensures that orders are placed only when necessary, reducing excess inventory while guaranteeing availability. This balance enhances both accuracy and efficiency in managing stock levels.
Conduct Regular Inventory Audits and Reconciliations
Audits and reconciliations allow businesses to validate their system data against physical stock. Regular checks, whether weekly, monthly, or quarterly, help catch discrepancies early. Reconciling data builds confidence in reports used for decision-making, reduces financial risks, and ensures that shrinkage or misplacements are promptly identified and corrected.
Streamline Data Entry and Reduce Manual Errors
Every manual entry increases the risk of inaccuracies. Simplifying data capture with scanners, mobile apps, or automated forms minimizes mistakes. Businesses should eliminate redundant data points and use real-time syncing across platforms. Streamlined entry ensures that updates are timely, consistent, and accurate, forming the backbone of reliable inventory data.
Integrate Inventory Across Sales and Supply Channels
In multi-channel operations, siloed systems often create mismatched data. Integrating inventory across e-commerce platforms, retail outlets, and supply chains ensures a single source of truth. Unified systems provide real-time visibility and prevent overselling, backorders, or inaccurate stock projections. This synchronization enhances customer satisfaction while protecting profitability.
Monitor Key Metrics Like Shrinkage and Stock Variance
Monitoring metrics such as shrinkage, stock variance, and turnover rates helps identify accuracy gaps. Businesses that track these KPIs gain insights into inefficiencies and patterns of error. By setting benchmarks and reviewing performance, companies can adopt corrective actions quickly. Ongoing measurement ensures continuous improvement in maintaining inventory accuracy.
Adopt Cloud-Based Inventory Management for Real-Time Updates
Cloud-based solutions allow instant access to inventory data from anywhere. They ensure updates are reflected across departments in real-time, reducing delays and discrepancies. With features like mobile access, automatic backups, and scalability, cloud systems improve transparency and accuracy. This real-time visibility is especially crucial for growing businesses managing multiple locations.
Optimize Warehouse Layout and Signage for Efficiency
A well-organized warehouse layout directly improves inventory accuracy by minimizing errors during picking, stocking, and counting. Clear pathways, properly labeled shelves, and strategic product placement reduce confusion and speed up item retrieval.
Signage with clear identifiers ensures employees can quickly locate SKUs, preventing misplaced stock. Optimizing layout not only improves accuracy but also enhances operational flow, safety, and overall warehouse productivity.
How Can Deskera ERP Help Improve Inventory Accuracy?
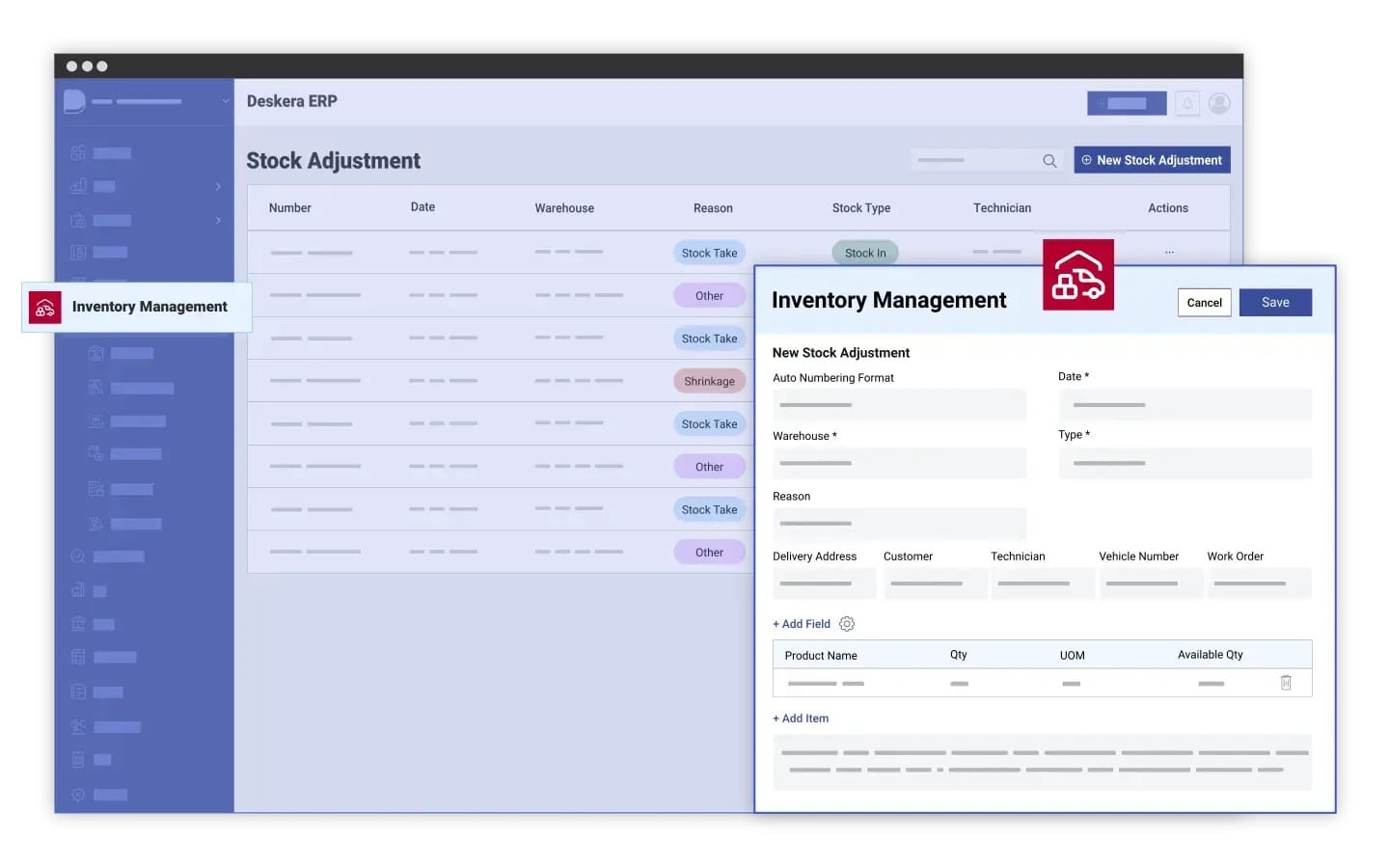
Improving inventory accuracy requires more than manual checks—it needs automation, integration, and real-time visibility. Deskera ERP equips businesses with the right tools to track, monitor, and optimize inventory while reducing human errors. Here’s how it helps:
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Deskera ERP automatically updates stock levels as sales, purchases, or returns occur. This eliminates discrepancies caused by delayed updates and ensures businesses always work with accurate data.
- Barcode and RFID Integration: By supporting barcode scanning and RFID tracking, Deskera minimizes manual entry errors and speeds up stock movement recording, improving accuracy at every warehouse touchpoint.
- Demand Forecasting and Planning: Using advanced analytics, Deskera predicts inventory needs to prevent overstocking or stockouts. This improves alignment between supply and demand while reducing waste.
- Centralized System Integration: Inventory, purchasing, sales, and accounting are seamlessly connected. This ensures that any movement in one system reflects across all business functions, avoiding miscommunication or mismatches.
- AI-Powered Assistant – David: Deskera’s AI assistant provides actionable insights, highlights anomalies, and generates quick reports to monitor accuracy KPIs, enabling managers to take corrective action swiftly.
With these capabilities, Deskera ERP not only streamlines workflows but also helps businesses reach the industry gold standard of 97%+ inventory accuracy while reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaways
- Accurate inventory is the backbone of smooth operations, reducing costs, avoiding stockouts, and keeping customers satisfied.
- Importance of Inventory Accuracy: High inventory accuracy helps businesses minimize shrinkage, improve demand forecasting, cut holding costs, and maintain strong customer trust.
- Causes of Inventory Inaccuracy: Issues like manual data entry errors, poor warehouse practices, and lack of system integration lead to costly discrepancies that can be prevented.
- How to Measure Inventory Accuracy: Regularly tracking metrics such as cycle count results, order fulfillment rates, and stock discrepancies ensures businesses identify and fix problems early.
- How to Improve Inventory Accuracy: Adopting better practices—such as real-time tracking, cycle counts, training staff, and optimizing warehouse layout—ensures long-term accuracy and efficiency.
- Deskera ERP boosts inventory accuracy with real-time tracking, barcode scanning, AI insights, and integrated workflows, helping businesses achieve efficiency and cost savings.
Related Articles