As the push for more sustainable business practices grows, manufacturing executives are increasingly focused on reducing their environmental footprint without sacrificing efficiency. Sustainable inventory management offers a solution that not only benefits the planet but also improves operational performance.
One study found that sustainable inventory management can increase economic efficiency by 2.13%, demonstrating that eco-friendly practices can positively impact the bottom line. This approach involves optimizing inventory processes to minimize waste, reduce excess stock, and enhance overall resource management.
By implementing sustainable inventory management, manufacturing businesses can achieve greater control over their supply chains, improving everything from production planning to demand forecasting.
Practices such as leveraging real-time data, collaborating with suppliers, and using advanced technologies like AI and automation contribute to streamlined operations and long-term sustainability. Moreover, these practices help ensure that resources are used efficiently, aligning with both environmental goals and cost-saving measures.
Deskera ERP provides manufacturing executives with the tools needed to embrace sustainable inventory management. With features like real-time inventory tracking, automated demand forecasting, and robust reporting tools, Deskera enables businesses to reduce waste, cut costs, and improve inventory control.
By integrating Deskera ERP, companies can seamlessly implement sustainable practices, ensuring a balance between economic and environmental goals.
What is Sustainable Inventory Management?
Sustainable inventory management is the practice of managing a company’s inventory in a way that reduces environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency and profitability. This approach emphasizes minimizing waste, reducing excess stock, and optimizing resource usage throughout the supply chain.
By implementing sustainable practices, such as using inventory control software and refining inventory management processes, businesses can achieve a balance between economic efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Incorporating simple inventory control methods, like just-in-time inventory and accurate demand forecasting, helps businesses reduce their reliance on overstocking and understocking, which in turn minimizes waste and unnecessary resource consumption.
Sustainable inventory management not only benefits the environment but also improves operational efficiency by ensuring that inventory levels are optimized and aligned with demand.
By adopting sustainable inventory management practices, companies can enhance their overall inventory sustainability. This leads to reduced costs, improved supply chain performance, and a smaller carbon footprint.
Tools like inventory control software and advanced data analytics make it easier for manufacturing executives to monitor, adjust, and streamline their inventory management processes, ensuring they meet both sustainability goals and business objectives.
The Importance of Sustainable Inventory Management
Sustainable inventory management is essential for manufacturing executives seeking to strike a balance between environmental responsibility and operational efficiency.
As industries face increasing pressure to adopt environmentally conscious practices, the role of inventory control becomes even more critical. Sustainable inventory management ensures that businesses are not only optimizing their stock levels but also contributing to the broader goals of environmental sustainability.
Reducing Waste and Optimizing Resources
One of the most significant benefits of sustainable inventory management is its ability to reduce waste. Traditional inventory management methods often lead to overstocking, which results in excess inventory that eventually becomes obsolete or spoiled, especially in industries dealing with perishable goods.
By using inventory control software and integrating advanced demand forecasting techniques, companies can better align stock levels with actual demand, thus minimizing waste.
Reducing waste not only benefits the environment but also leads to cost savings. Excess inventory ties up capital and increases storage costs, while understocking can result in lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
Implementing simple inventory control techniques, such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory, allows businesses to optimize their stock levels, reducing the likelihood of both overstock and stockouts.
Improving Inventory Sustainability and Efficiency
Another key advantage of sustainable practices is the improvement in inventory sustainability. Through the use of sustainable inventory management practices, companies can reduce their carbon footprint by lowering the energy and resources needed to manage and store excess inventory.
This is especially important for manufacturing executives looking to meet both regulatory demands and the expectations of eco-conscious consumers.
Inventory control software plays a critical role in achieving this by providing real-time data that helps businesses make informed decisions. Features like automated inventory tracking, predictive analytics, and demand forecasting help streamline inventory management processes, making them more efficient and sustainable in the long run.
This technology enables companies to optimize their supply chain, reducing transportation and storage emissions, and supporting broader environmental goals.
Enhancing Brand Reputation and Compliance
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important to consumers and regulators alike. By adopting sustainable inventory management, businesses not only improve their operations but also enhance their brand reputation. Consumers today are more likely to support companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
In turn, businesses that adopt sustainable practices are more likely to remain compliant with emerging environmental regulations, which are becoming more stringent across industries.
For manufacturing executives, the implementation of sustainable inventory management practices is no longer optional but a strategic necessity. Leveraging inventory control software and other technologies not only reduces costs but positions companies as leaders in sustainability, ensuring they remain competitive in the global marketplace.
Supporting Long-Term Cost Reduction
In addition to its environmental benefits, sustainable inventory management also promotes long-term cost reduction. Efficient use of resources, reduced storage needs, and minimized waste lead to lower operational costs.
By streamlining processes through inventory control software, businesses can more accurately manage stock levels, cut down on unnecessary expenses, and prevent costly overstock situations.
This cost-saving aspect ensures that manufacturing executives maintain profitability while transitioning to more sustainable practices.
Facilitating Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow and market conditions change, the ability to scale operations and remain flexible is crucial. Sustainable inventory management practices provide the framework for scalable growth.
With tools like inventory control software and demand forecasting systems in place, companies can adapt to fluctuations in supply and demand without compromising sustainability goals. This ensures that businesses can grow efficiently while maintaining their commitment to eco-friendly practices and operational optimization.
Key Sustainable Practices for Manufacturing Executives
For manufacturing executives, adopting sustainable inventory management practices is essential to balance profitability with environmental stewardship. Implementing these key practices helps streamline operations, reduce waste, and optimize resources, all while contributing to a greener future.
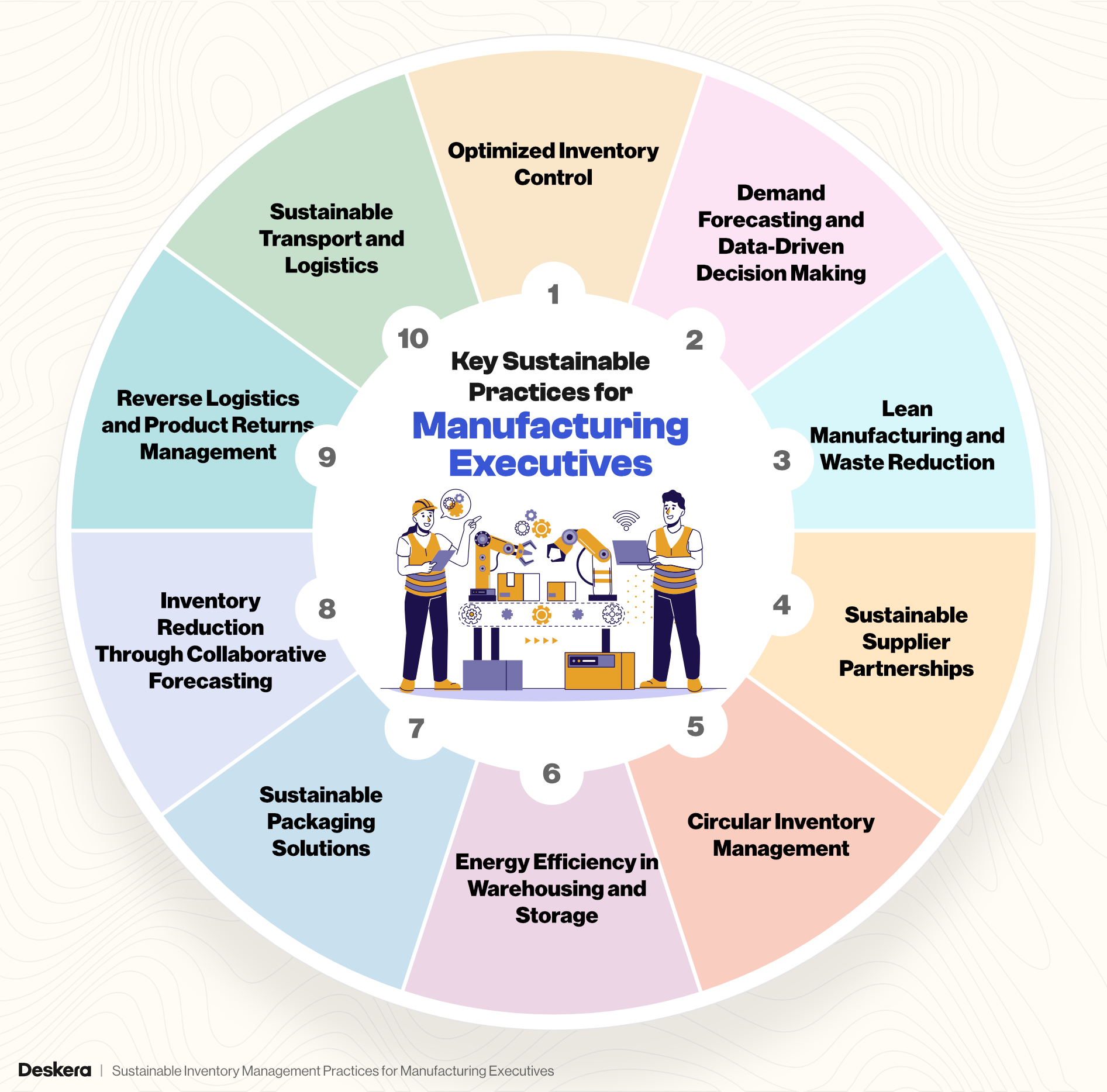
1. Optimized Inventory Control
Effective inventory control is at the heart of sustainable practices. By using advanced inventory control software, manufacturing businesses can manage stock levels in real time, reducing overstock and understock situations.
This results in lower storage costs, less waste, and more efficient resource utilization. Tools like just-in-time (JIT) inventory allow manufacturers to align stock levels closely with demand, minimizing excess inventory and reducing the risk of product obsolescence.
2. Demand Forecasting and Data-Driven Decision Making
Accurate demand forecasting is a vital part of inventory management. By leveraging predictive analytics and historical sales data, companies can anticipate customer demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
This practice ensures a more sustainable inventory approach by avoiding unnecessary stockpiling and reducing the need for emergency replenishments. Inventory control software plays a key role here by providing insights that guide data-driven decision-making, further enhancing inventory sustainability.
3. Lean Manufacturing and Waste Reduction
One of the most effective sustainable inventory management practices is the adoption of lean manufacturing principles. This method focuses on reducing waste throughout the production process, optimizing resource use, and improving efficiency.
By implementing simple inventory control measures, such as reducing overproduction and minimizing excess materials, businesses can significantly lower their environmental impact. This practice not only contributes to sustainability goals but also enhances operational efficiency.
4. Sustainable Supplier Partnerships
Building strong relationships with suppliers who prioritize sustainability is another critical practice. Manufacturing executives should work closely with their suppliers to ensure that raw materials are sourced responsibly and that their supply chains follow eco-friendly practices.
Additionally, inventory control software can be used to collaborate with suppliers in real time, reducing lead times and optimizing delivery schedules, which further minimizes waste and excess inventory.
5. Circular Inventory Management
A forward-thinking approach to inventory management involves adopting circular inventory principles, where products, parts, and materials are reused, repaired, or recycled instead of being discarded.
By incorporating circular practices into the supply chain, companies can reduce waste, lower production costs, and extend the lifecycle of materials. Sustainable inventory management not only reduces environmental impact but also aligns with global trends in resource conservation and eco-friendly manufacturing.
6. Energy Efficiency in Warehousing and Storage
Manufacturing executives should also focus on improving energy efficiency in warehousing and storage as part of their sustainable inventory management strategy.
Using energy-efficient equipment, reducing energy consumption in warehouses, and implementing smart climate control systems can help reduce the overall carbon footprint of inventory storage.
Inventory control software can also help optimize warehouse layouts, reducing unnecessary movement and energy use.
7. Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Another essential aspect of sustainable inventory management is the adoption of eco-friendly packaging solutions. Reducing reliance on non-recyclable materials and opting for sustainable alternatives, such as biodegradable or reusable packaging, can significantly lower environmental impact.
Manufacturing executives can work with suppliers to source sustainable packaging and implement simple inventory control methods to avoid excess packaging materials, ultimately leading to more sustainable operations.
8. Inventory Reduction Through Collaborative Forecasting
Collaborative forecasting with suppliers and customers is another practice that supports inventory sustainability.
By sharing real-time sales and demand data with suppliers, manufacturing companies can maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing the need for excess stock and storage space.
This proactive approach to inventory control ensures more efficient operations and strengthens relationships with key supply chain partners, contributing to a more sustainable business model.
9. Reverse Logistics and Product Returns Management
Integrating reverse logistics into sustainable inventory management practices helps businesses manage product returns efficiently and sustainably. By creating systems to handle returned items for refurbishment, resale, or recycling, companies can reduce waste and recover valuable materials. This practice extends the lifecycle of products and contributes to inventory sustainability by reducing the volume of goods sent to landfills.
10. Sustainable Transport and Logistics
Sustainable transport practices, such as optimizing delivery routes, reducing fuel consumption, and using low-emission vehicles, play a crucial role in sustainable inventory practices.
Manufacturing executives can work with logistics partners to implement more efficient transportation solutions, reducing the carbon footprint associated with moving inventory.
Leveraging inventory control software to monitor and manage transportation logistics ensures that products are delivered with minimal environmental impact.
Challenges and Solutions in Adopting Sustainable Inventory Management Practices
Adopting sustainable inventory management practices presents several challenges for manufacturing executives. However, understanding these challenges and implementing effective strategies can pave the way for successful integration of eco-friendly practices into inventory management.
Common Challenges in Adopting Sustainable Inventory Management Practices
- Resistance to Change Many organizations face resistance from employees and stakeholders when shifting to new sustainable practices. This resistance can stem from a lack of understanding, fear of increased complexity, or concerns about the potential impact on existing processes.
- High Initial Costs Implementing sustainable practices often requires significant upfront investment in new technologies, such as inventory control software, energy-efficient equipment, or sustainable packaging solutions. These initial costs can be a barrier, especially for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Complex Supply Chains For businesses with complex supply chains, coordinating sustainable practices across multiple suppliers and partners can be challenging. Ensuring that all parties adhere to sustainability standards requires extensive collaboration and management.
- Limited Data and Insights Effective inventory management relies on accurate data and insights. Many organizations struggle with insufficient or outdated data, making it difficult to implement data-driven strategies and forecast demand accurately.
- Balancing Sustainability and Profitability Striking the right balance between sustainability goals and profitability can be challenging. Executives often face pressure to achieve financial targets while also meeting environmental and social responsibility objectives.
Strategies to Overcome These Challenges
- Fostering a Culture of Sustainability To address resistance to change, it is crucial to foster a culture of sustainability within the organization. Providing training, communicating the benefits of sustainable practices, and involving employees in the decision-making process can help overcome resistance. Leaders should also highlight the long-term benefits, such as cost savings and improved brand reputation, to gain buy-in.
- Leveraging Financial Incentives and Support High initial costs can be mitigated by seeking financial incentives, such as government grants or tax credits, designed to support sustainable initiatives. Additionally, businesses can start with pilot projects or phased implementations to spread costs over time and demonstrate the benefits of sustainable practices.
- Enhancing Supply Chain Collaboration Overcoming challenges in complex supply chains involves enhancing collaboration with suppliers and partners. Establishing clear sustainability criteria, conducting regular audits, and leveraging inventory control software for real-time data sharing can improve coordination and ensure adherence to sustainability standards.
- Investing in Advanced Data Solutions To address issues with limited data, investing in advanced data solutions is essential. Upgrading to modern inventory control software with robust analytics capabilities can provide better insights, improve demand forecasting, and enable more effective inventory management.
- Implementing Balanced Scorecards Balancing sustainability and profitability can be achieved by implementing balanced scorecards that integrate both financial and environmental metrics. This approach allows businesses to track performance against sustainability goals while also meeting financial objectives, ensuring that sustainability efforts contribute to overall success.
- Starting with Incremental Changes For organizations struggling with the scale of change, starting with incremental improvements can be effective. By gradually introducing sustainable practices, such as reducing packaging waste or optimizing energy use, businesses can manage the transition more smoothly and build momentum over time.
- Engaging in Continuous Improvement Embracing continuous improvement practices can help organizations adapt and refine their sustainability efforts. Regularly reviewing and updating sustainability strategies, conducting performance assessments, and incorporating feedback can lead to more effective and adaptable inventory management practices.
Future Trends and Innovations in Sustainable Inventory Management
The landscape of inventory management is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainability.
Manufacturing executives need to stay ahead of these trends to maintain a competitive edge and effectively manage their inventory in an environmentally responsible manner.
Emerging Trends in Sustainable Inventory Management
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing inventory management by providing advanced analytics and predictive capabilities. These technologies enable more accurate demand forecasting, automate inventory replenishment, and optimize stock levels.
AI-driven inventory control software can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict future demand, and recommend adjustments, leading to more efficient and sustainable inventory practices.
- Growth of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful tool for enhancing transparency and traceability in supply chains. By using blockchain, manufacturing executives can ensure the authenticity and sustainability of their inventory, from raw materials to finished products.
Blockchain’s immutable ledger provides a secure and transparent way to track inventory movements, verify supplier practices, and maintain compliance with sustainability standards.
- Advancements in IoT and Smart Warehousing
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming warehousing and inventory management with the advent of smart sensors and connected devices. IoT technology allows for real-time monitoring of inventory conditions, including temperature, humidity, and stock levels.
Smart warehousing solutions equipped with IoT sensors can optimize storage conditions, reduce waste, and enhance inventory control. These innovations support more sustainable practices by minimizing spoilage and improving efficiency.
- Circular Economy Models
Circular economy models are gaining traction in sustainable inventory management. These models focus on the reuse, repair, and recycling of products and materials rather than disposal.
Manufacturing executives are increasingly adopting circular practices, such as designing products for durability and facilitating take-back programs.
By incorporating circular economy principles into inventory management, businesses can reduce waste, extend product lifecycles, and support more sustainable operations.
- Rise of Green Logistics and Transportation
Green logistics is an emerging trend that emphasizes reducing the environmental impact of transportation and logistics.
Innovations in green logistics include the use of electric or hybrid delivery vehicles, optimization of transportation routes to reduce fuel consumption, and adoption of alternative fuels.
By integrating these practices into their supply chains, manufacturing executives can further enhance the sustainability of their inventory management processes.
- Development of Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Sustainable packaging solutions are becoming increasingly important as businesses seek to reduce their environmental footprint. Innovations in packaging include biodegradable materials, reduced packaging sizes, and reusable packaging systems.
Manufacturing executives should stay abreast of these developments to ensure that their packaging practices align with sustainability goals and minimize waste.
- Enhanced Data Analytics and Real-Time Visibility
Enhanced data analytics and real-time visibility are crucial for modern inventory management. Advanced analytics tools provide deeper insights into inventory performance, allowing businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their inventory practices.
Real-time visibility into inventory levels, supplier performance, and customer demand helps manufacturing executives respond quickly to changes and improve sustainability outcomes.
- Adoption of Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based solutions are transforming inventory management by offering scalable, flexible, and accessible platforms for managing inventory data.
Cloud-based inventory control software enables manufacturers to integrate their inventory systems with other business functions, such as supply chain management and financial planning.
This integration supports more efficient and sustainable inventory practices by providing a comprehensive view of operations and facilitating better decision-making.
How Manufacturing Executives Can Stay Ahead
- Invest in Technology and Training
To stay ahead of these emerging trends, manufacturing executives should invest in the latest technologies and provide ongoing training for their teams. Embracing AI, blockchain, IoT, and other innovations requires both financial investment and a commitment to upskilling staff.
Staying informed about technological advancements and understanding how they can be applied to inventory management is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Foster Innovation and Collaboration
Encouraging a culture of innovation and collaboration within the organization can help manufacturing executives identify and implement new sustainable practices.
Collaborating with technology providers, industry experts, and other stakeholders can provide valuable insights and opportunities for integrating cutting-edge solutions into inventory management.
- Monitor Industry Trends and Regulations
Manufacturing executives should continuously monitor industry trends and regulatory developments related to sustainability. Staying updated on new regulations, market demands, and technological advancements helps ensure that inventory management practices remain compliant and aligned with best practices.
- Implement Pilot Programs and Test Solutions
Testing new technologies and practices through pilot programs can provide valuable insights into their effectiveness and feasibility. Implementing small-scale trials allows businesses to evaluate the impact of emerging trends on their inventory management processes and make informed decisions before full-scale adoption.
Understanding the Role of Sustainability in Corporate Strategy
Sustainability has become an integral part of modern corporate strategy, particularly for manufacturing executives who manage complex supply chains and inventory systems.
Embracing sustainable inventory management is no longer just an environmental initiative—it is a strategic approach that can drive long-term value, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Aligning Sustainability with Business Objectives
For any sustainability initiative to be effective, it must align with the broader goals of the business. Integrating inventory management practices that reduce waste, conserve resources, and optimize efficiency not only supports environmental objectives but also enhances profitability and resilience.
Manufacturing executives need to view sustainability as a core business strategy, as it directly impacts cost reduction, risk mitigation, and long-term growth.
Adopting sustainable inventory management practices can improve operational efficiency, reduce excess inventory, and lower holding costs. It also leads to more accurate demand forecasting and simple inventory control, which minimizes the need for emergency restocking or costly expedited shipping.
By adopting sustainable practices, companies often find that they enhance their supply chain performance, all while reducing their environmental footprint.
Enhancing Corporate Reputation and Stakeholder Trust
In today’s business environment, consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies increasingly demand that companies adopt environmentally and socially responsible practices.
A strong focus on sustainability in inventory management can significantly enhance a company's reputation and brand value. Manufacturing executives who prioritize sustainability are seen as forward-thinking leaders who are committed to corporate social responsibility (CSR), which can lead to stronger relationships with customers, investors, and other stakeholders.
A reputation for sustainability can also open up new market opportunities. Many large retailers and manufacturers are now requiring suppliers to adhere to strict sustainability criteria, and businesses that do not align with these standards may lose out on key partnerships.
As a result, inventory sustainability becomes a competitive advantage, allowing businesses to remain attractive to sustainability-conscious partners and consumers.
Driving Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Sustainability drives innovation, pushing companies to find new ways to manage their inventory control and supply chains more efficiently. Businesses that incorporate sustainability into their core strategies are often at the forefront of adopting cutting-edge technologies, such as inventory control software, IoT, and artificial intelligence. These technologies not only reduce environmental impact but also lead to more streamlined operations, lower costs, and better decision-making.
Moreover, manufacturing executives who prioritize sustainable inventory management are better positioned to navigate changing market demands and regulatory requirements.
With growing global emphasis on reducing carbon footprints, those who proactively integrate sustainability into their inventory control will be better prepared to adapt to future challenges, from carbon taxes to supply chain disruptions.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations in Sustainable Inventory Management
The shift toward sustainable inventory management is not only driven by market demand but also by an increasingly stringent regulatory landscape. Governments, industry bodies, and international organizations are enforcing regulations and standards that compel businesses to adopt environmentally responsible practices. For manufacturing executives, understanding and complying with these regulations is critical to both operational efficiency and corporate reputation.
Key Regulations Impacting Sustainable Inventory Management
- Environmental Protection Laws: Numerous countries have implemented environmental protection laws aimed at reducing industrial waste, limiting carbon emissions, and conserving resources. For example, the European Union's Waste Framework Directive and Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS) require businesses to manage their waste responsibly and report on their environmental performance. Similarly, the U.S. Clean Air Act and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) impose strict guidelines on emissions and hazardous waste management, which can directly impact inventory storage and disposal processes.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Programs: EPR programs are regulatory frameworks that hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including post-consumer waste management. These laws encourage businesses to design more sustainable products and adopt practices like recycling and reusing materials. In regions such as the European Union and Canada, EPR regulations require manufacturers to manage the take-back, recycling, and disposal of their products, which in turn impacts inventory management strategies.
- Sustainability Reporting Requirements: In several countries, businesses are now required to report on their sustainability initiatives and environmental impact. For example, the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) in the European Union mandates large companies to disclose information on how they manage social and environmental challenges. Similarly, in the U.S., the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is developing rules that will require companies to disclose climate-related risks and impacts. Compliance with these regulations ensures transparency in inventory sustainability and helps businesses build trust with stakeholders.
Industry Standards and Certifications
- ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems: ISO 14001 is an international standard that provides a framework for organizations to develop and implement effective environmental management systems (EMS). This standard is particularly important for inventory control, as it requires companies to identify and mitigate environmental risks related to their operations, including energy consumption, waste production, and resource usage. ISO 14001 certification demonstrates a commitment to sustainability and helps businesses comply with various environmental regulations.
- LEED Certification for Warehousing and Storage Facilities: The Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification is a globally recognized standard for green building practices. Manufacturing executives who operate large warehouses or storage facilities can pursue LEED certification to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. LEED-certified facilities are designed to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and optimize resources, all of which contribute to more sustainable inventory management.
- Green Supply Chain Certifications: Certifications such as the Green Supply Chain Certification (GSCC) and the Sustainable Green Printing Partnership (SGP) validate a company’s efforts to implement sustainable practices across its supply chain. These certifications focus on reducing environmental impact, optimizing resource use, and promoting responsible sourcing. Achieving these certifications can help manufacturing executives align their inventory control processes with global sustainability goals.
Strategies to Ensure Compliance
- Conduct Regular Audits and Assessments: To maintain compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability standards, businesses must regularly audit their inventory management practices. Audits should focus on waste management, energy consumption, material handling, and emissions, ensuring that all aspects of the inventory lifecycle align with relevant regulations. By identifying areas of non-compliance early, businesses can implement corrective actions to avoid penalties and maintain regulatory adherence.
- Implement a Comprehensive Environmental Management System (EMS): Implementing an EMS in accordance with ISO 14001 or similar frameworks helps manufacturing executives monitor and manage the environmental impacts of their inventory operations. An EMS offers a structured approach to setting sustainability goals, tracking performance, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. It also provides a mechanism for continuous improvement, enabling businesses to adapt to new regulations as they emerge.
- Engage in Ongoing Employee Training: Ensuring compliance requires the full involvement of employees across all levels of the organization. Providing regular training on regulatory requirements, sustainability best practices, and inventory control procedures empowers employees to make informed decisions that align with the company’s sustainability goals. Engaging employees in sustainability efforts also fosters a culture of environmental responsibility, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Sustainability Success
To ensure the success of sustainable inventory management efforts, manufacturing executives need to track and evaluate key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect their impact on sustainability.
These metrics provide actionable insights into the efficiency, environmental footprint, and cost-effectiveness of inventory management strategies.
Below are the essential KPIs and metrics that manufacturing executives should use to assess the success of their sustainable inventory management initiatives.
1. Waste Reduction Metrics
One of the primary goals of sustainable inventory management is to reduce waste throughout the supply chain. Measuring waste reduction not only lowers operational costs but also minimizes environmental impact. Key waste reduction metrics include:
- Percentage of Inventory Waste: This KPI tracks the amount of waste generated as a percentage of total inventory, including unsold goods, packaging waste, and expired or damaged products. A lower percentage indicates more efficient inventory control and better management of resources.
- Product Disposal Rate: This metric measures how often products are disposed of or written off due to expiration, damage, or obsolescence. Reducing the disposal rate signals effective inventory management practices, such as better demand forecasting and streamlined order quantities.
- Recycling and Reuse Rate: This KPI tracks the percentage of materials that are recycled or reused in the manufacturing process or supply chain. A higher recycling rate contributes to overall inventory sustainability by reducing the consumption of raw materials and minimizing landfill waste.
2. Energy Efficiency Metrics
Energy consumption is a critical factor in assessing the environmental footprint of inventory management operations. By monitoring energy usage, manufacturing executives can identify opportunities to reduce costs and enhance energy efficiency. Key energy efficiency metrics include:
- Energy Consumption per Unit of Inventory: This KPI measures the amount of energy used to store, manage, and transport inventory on a per-unit basis. A lower energy consumption rate indicates greater efficiency in warehousing, logistics, and supply chain management.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Manufacturing executives should track the reduction in carbon emissions related to their inventory control and logistics activities. This KPI measures the effectiveness of energy-saving initiatives, such as adopting eco-friendly transportation methods, optimizing warehouse layouts, or using energy-efficient equipment.
- Renewable Energy Usage: This metric tracks the percentage of total energy consumption derived from renewable sources, such as solar or wind power. Increasing renewable energy usage is an important aspect of sustainable inventory management and aligns with broader corporate sustainability goals.
3. Supply Chain Sustainability Metrics
The sustainability of a company’s supply chain plays a significant role in the overall success of sustainable inventory management. KPIs related to supplier practices, resource efficiency, and environmental impact help executives monitor and improve supply chain sustainability. Key metrics include:
- Sustainable Sourcing Rate: This KPI tracks the percentage of materials and products sourced from suppliers who adhere to environmental and social responsibility standards. Sustainable sourcing ensures that inventory is produced with minimal environmental impact and supports ethical labor practices.
- Supplier Compliance with Sustainability Standards: Manufacturing executives should measure the percentage of suppliers that meet sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001 or the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC). Monitoring supplier compliance ensures alignment with the company’s sustainability objectives and promotes responsible practices across the supply chain.
- Green Transportation Usage: This metric measures the proportion of goods transported using eco-friendly methods, such as electric vehicles, hybrid trucks, or rail transport. Increasing the use of green transportation reduces the carbon footprint of logistics and supports broader sustainability goals.
4. Inventory Optimization Metrics
Efficient inventory control is key to reducing waste, minimizing excess stock, and ensuring sustainability. Manufacturing executives can use the following metrics to track inventory optimization and sustainability efforts:
- Inventory Turnover Rate: This KPI measures how quickly inventory is sold and replaced over a given period. A higher turnover rate indicates that inventory is being managed efficiently, with minimal overstocking or obsolescence, which reduces waste and storage costs.
- Stockout Rate: The stockout rate measures the frequency of stockouts or instances when products are unavailable due to insufficient inventory. A lower stockout rate suggests that simple inventory control methods, such as better demand forecasting, are being applied to balance supply with demand while minimizing excess inventory.
- Carrying Costs of Inventory: This metric tracks the costs associated with holding inventory, including storage, insurance, and depreciation. Reducing carrying costs indicates more sustainable inventory management practices, such as reducing excess stock and optimizing storage space.
5. Social and Ethical Metrics
Beyond environmental metrics, sustainable inventory management also considers the social impact of inventory operations, including labor practices, worker safety, and community engagement. Key social and ethical metrics include:
- Employee Training on Sustainability: This KPI measures the percentage of employees trained in sustainability practices, including inventory control procedures that promote environmental responsibility. Engaged and knowledgeable employees contribute to more effective sustainability initiatives.
- Supplier Fair Labor Practices: Manufacturing executives should track the percentage of suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices, ensuring ethical treatment of workers in the production and delivery of goods. Ethical sourcing is a key component of supply chain sustainability.
- Community Engagement Initiatives: This metric tracks the company’s involvement in community sustainability programs, such as recycling drives, environmental education, or local reforestation efforts. Community engagement enhances corporate reputation and fosters positive relationships with stakeholders.
Building a Sustainable Supply Chain Ecosystem
Creating a sustainable supply chain ecosystem is essential for manufacturing executives looking to reduce their environmental impact and meet growing demands for sustainability. A sustainable ecosystem extends beyond individual inventory management efforts and requires collaboration with suppliers, partners, and customers.
By fostering transparency, aligning on shared sustainability goals, and implementing eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain, companies can significantly enhance their inventory sustainability while driving business value.
1. Collaborating with Suppliers for Sustainable Sourcing
Sustainable sourcing is the foundation of an eco-friendly supply chain. By working closely with suppliers who adhere to ethical and environmental standards, manufacturing executives can ensure that raw materials and components are sourced responsibly.
Key strategies for promoting sustainable inventory management with suppliers include:
- Engaging in Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of supplier operations ensures compliance with sustainability certifications and environmental regulations. Audits help identify areas where suppliers may need to improve their sustainability practices, such as reducing emissions or minimizing waste.
- Adopting a Sustainable Procurement Policy: A formal procurement policy sets clear guidelines for selecting suppliers based on their sustainability performance. This policy should prioritize vendors that use renewable resources, minimize energy consumption, and adhere to fair labor practices.
- Long-Term Partnerships for Innovation: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers encourages collaboration on innovative solutions for sustainability. Joint efforts can lead to the development of new materials, processes, or technologies that improve environmental performance across the supply chain.
2. Enhancing Transparency in the Supply Chain
Transparency is key to building trust and ensuring accountability across the supply chain. By increasing visibility into sourcing, production, and distribution processes, manufacturing executives can monitor and address sustainability challenges more effectively. Important transparency strategies include:
- Implementing Digital Tracking Tools: Using digital tools like blockchain or RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology allows companies to track products throughout the supply chain. This provides real-time data on the environmental footprint of goods, including resource use, energy consumption, and emissions.
- Supply Chain Reporting and Disclosure: Manufacturing executives can foster greater transparency by publishing sustainability reports that outline the environmental impact of their operations. Reporting on key metrics, such as energy usage and waste reduction, not only satisfies regulatory requirements but also demonstrates a commitment to responsible business practices.
- Supplier Engagement on Transparency Goals: Encouraging suppliers to share their sustainability data and reporting standards can help create a more cohesive and transparent supply chain ecosystem. This collaborative approach ensures that all stakeholders are working toward the same sustainable inventory management practices.
3. Aligning on Shared Sustainability Goals with Partners
Collaboration with supply chain partners is essential to aligning sustainability goals and promoting eco-friendly practices. When all parties share a common commitment to sustainability, companies can more easily implement sustainable inventory control strategies and improve overall efficiency. Key approaches to achieving this include:
- Setting Joint Sustainability Targets: By working with partners to establish joint sustainability targets, manufacturing executives can ensure that everyone is committed to reducing environmental impact. These targets may include reducing carbon emissions, cutting down on packaging waste, or optimizing transportation logistics.
- Developing Green Transportation Solutions: Collaborating with logistics providers to develop green transportation options, such as using electric vehicles or optimizing routes for fuel efficiency, can reduce the carbon footprint associated with product distribution. This also supports broader sustainability goals and contributes to a more environmentally friendly inventory management system.
- Partnering on Circular Economy Initiatives: Circular economy initiatives focus on extending the lifecycle of products by promoting recycling, reusing, or remanufacturing materials. Manufacturing executives can partner with suppliers and customers to create closed-loop systems that reduce waste and conserve resources, thereby fostering a more sustainable supply chain ecosystem.
4. Engaging Customers in Sustainability Efforts
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a key factor for consumers when making purchasing decisions. By engaging customers in sustainability initiatives, manufacturing executives can not only meet consumer expectations but also drive broader environmental awareness throughout the supply chain. Strategies for engaging customers include:
- Providing Eco-Friendly Product Options: Offering products made from recycled or sustainable materials and clearly communicating their environmental benefits allows customers to make informed choices that align with their sustainability values.
- Customer Education on Sustainability: Educating customers about sustainable inventory practices—such as reducing waste, using eco-friendly packaging, and promoting product recycling—builds a stronger connection between the brand and its environmentally conscious audience.
- Incentivizing Sustainable Behavior: Companies can encourage customers to participate in sustainability efforts by offering incentives, such as discounts for recycling products or using eco-friendly packaging. These initiatives not only promote sustainability but also enhance customer loyalty and brand reputation.
Employee Engagement and Training for Sustainability
The successful implementation of sustainable inventory management practices requires more than just technological advancements and strategic planning—it also depends on the active participation and engagement of employees at all levels. Fostering a culture of responsibility and environmental consciousness within the workforce is crucial for achieving long-term sustainability goals.
Engaging employees through education, training, and empowerment can significantly improve the effectiveness of sustainability initiatives, helping companies reduce waste, optimize resource use, and achieve eco-friendly objectives.
1. Educating Employees on Sustainability Goals
The first step to fostering a sustainable culture is ensuring that employees understand the company’s sustainability objectives and how their roles contribute to achieving them.
Effective communication about the importance of sustainable inventory management practices should be a core part of onboarding and ongoing training programs.
Best practices for educating employees include:
- Clear Communication of Sustainability Goals: Manufacturing executives should clearly define and communicate the company’s sustainability targets and how they impact daily operations. This helps employees recognize the broader context of their efforts and align their work with the company's environmental mission.
- Incorporating Sustainability into Training Programs: Sustainability training should be integrated into existing programs to provide employees with the necessary knowledge to implement sustainable inventory management techniques. This may include learning about energy-efficient processes, reducing material waste, or adopting eco-friendly technologies.
- Sustainability Workshops and Seminars: Organizing workshops or seminars focused on environmental responsibility helps employees stay informed about the latest sustainability trends and best practices in inventory control. These sessions can offer insights into new approaches, regulations, and innovations that can help the company enhance its environmental performance.
2. Involving Employees in Sustainability Initiatives
For sustainability practices to succeed, employees need to feel empowered to contribute to these efforts.
By involving them in decision-making and encouraging active participation, manufacturing executives can cultivate a sense of ownership and accountability for sustainability initiatives.
Strategies for promoting involvement include:
- Sustainability Committees and Employee Ambassadors: Establishing sustainability committees or designating employee ambassadors for sustainability allows workers to take an active role in shaping the company’s green initiatives. These committees can lead efforts to improve inventory management efficiency, reduce waste, and identify opportunities for further eco-friendly practices.
- Encouraging Employee Feedback: Soliciting feedback from employees about existing inventory control practices and sustainability measures can lead to valuable insights and innovative solutions. Front-line workers often have a deep understanding of operational challenges and can offer practical suggestions for improving sustainability.
- Incentivizing Sustainable Behavior: Providing incentives, such as recognition programs or rewards, for employees who actively contribute to sustainability goals fosters a positive and engaged workforce. Whether it’s reducing energy use, optimizing production processes, or minimizing material waste, recognizing these efforts can motivate others to follow suit.
3. Developing a Culture of Responsibility and Sustainability
A successful sustainability strategy goes beyond individual actions—it requires building a company-wide culture of environmental responsibility.
This involves instilling sustainability values into the company’s mission, reinforcing them through leadership, and continuously promoting eco-friendly behavior.
Best practices for creating this culture include:
- Leadership by Example: Leaders play a crucial role in shaping the company’s sustainability culture. When executives and managers visibly prioritize sustainable inventory practices, employees are more likely to follow suit. Leading by example through initiatives like energy conservation, waste reduction, and responsible procurement can inspire the entire workforce to engage in sustainability efforts.
- Embedding Sustainability in Corporate Values: Integrating sustainability into the company’s core values helps reinforce the importance of environmental responsibility across all levels of the organization. This can be reflected in decision-making processes, employee performance evaluations, and daily operations.
- Sustainability Challenges and Campaigns: Launching company-wide sustainability challenges or campaigns can engage employees in friendly competition and teamwork while promoting eco-friendly behaviors. These initiatives encourage employees to think creatively about reducing waste, improving efficiency, or adopting sustainable technologies in their work.
4. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Sustainability is an evolving field, and companies need to keep pace with new developments in sustainable inventory management.
Encouraging continuous learning and adaptation helps employees stay up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies that can enhance sustainability efforts.
Ways to promote continuous learning include:
- Ongoing Sustainability Training: Regularly updating training programs to reflect new sustainability standards, regulations, and technologies ensures that employees remain informed and prepared to implement the latest eco-friendly practices.
- Collaborating with Industry Experts: Partnering with industry experts or environmental organizations can provide valuable insights and resources to help companies improve their sustainability efforts. These collaborations offer access to cutting-edge research and best practices that can be shared with employees.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between different departments, such as procurement, logistics, and production, helps employees understand how their roles intersect with sustainability objectives. This integrated approach fosters a holistic view of inventory control and sustainability across the organization.
How Can Deskera ERP Help You with Sustainable Inventory Management?
Deskera ERP offers a comprehensive suite of tools that support sustainable inventory management by enhancing visibility, improving efficiency, and reducing waste across the entire supply chain.
Its features are specifically designed to help manufacturing executives implement eco-friendly practices, streamline operations, and make data-driven decisions that contribute to sustainability goals.
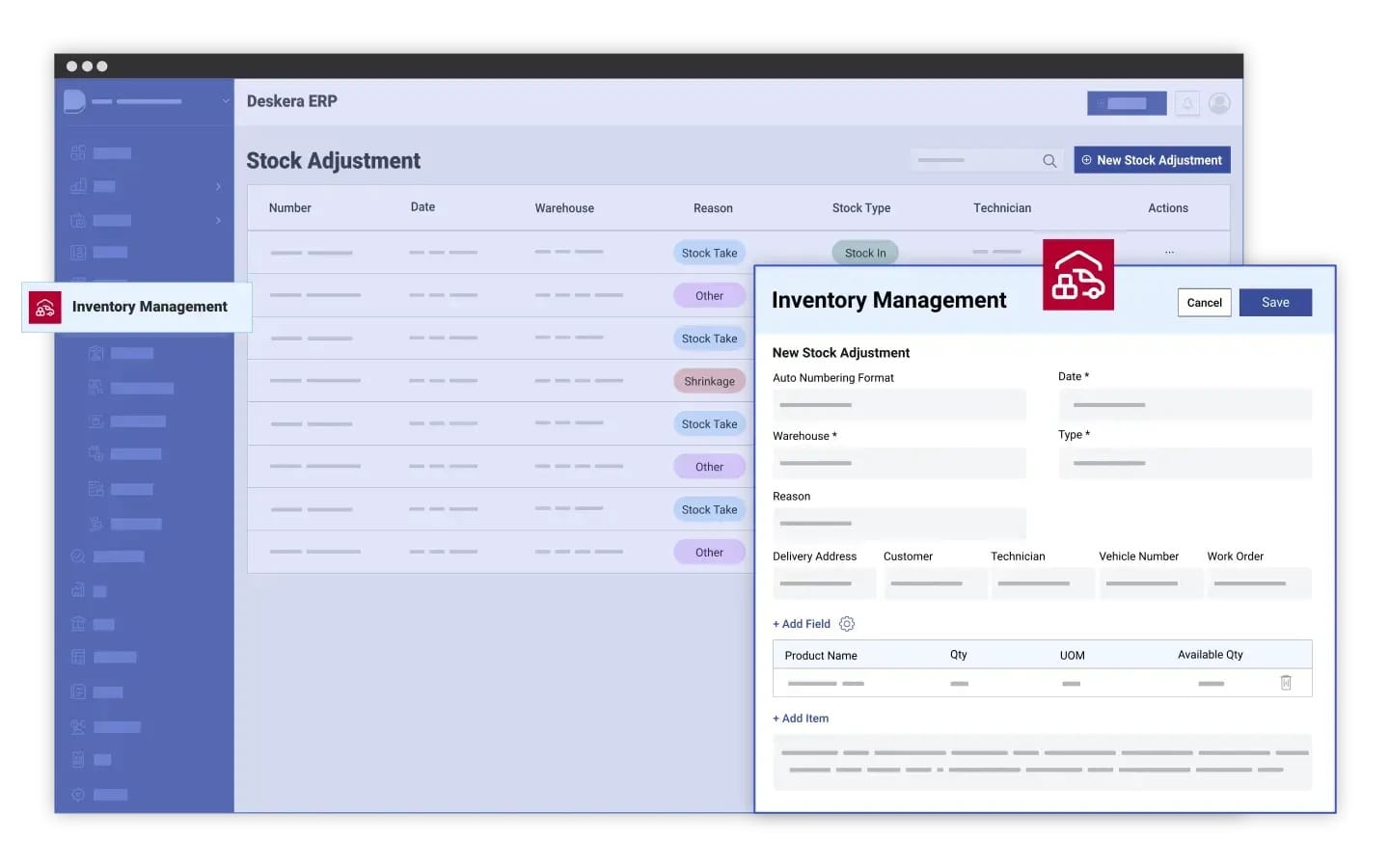
Here’s how Deskera ERP can assist with sustainable inventory management:
1. Real-Time Inventory Tracking and Control
With Deskera ERP’s real-time inventory control capabilities, businesses can monitor stock levels, track product movement, and reduce overstocking or understocking. This helps eliminate excess inventory, minimizing waste and optimizing resource usage. By having accurate insights into stock levels, companies can better manage raw materials and finished goods, ensuring they only store what’s necessary, which directly contributes to sustainable inventory management.
2. Demand Forecasting for Efficient Resource Use
Deskera ERP’s powerful demand forecasting tools allow manufacturers to predict future demand accurately. By analyzing historical sales data and market trends, companies can optimize their procurement and production processes, reducing the risk of overproduction and waste. Efficient demand forecasting ensures that resources are used responsibly and inventory is kept at optimal levels, supporting both economic efficiency and sustainability goals.
3. Automated Procurement and Vendor Management
Deskera ERP simplifies procurement processes by automating purchase orders and enabling better coordination with suppliers. It also allows companies to source materials from eco-friendly vendors, promoting sustainable sourcing practices. By automating and streamlining vendor relationships, businesses can ensure they’re working with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, contributing to a sustainable supply chain ecosystem.
4. Reducing Energy and Material Waste
Deskera ERP integrates production planning and inventory management in ways that reduce energy consumption and minimize material waste. With automated systems that optimize manufacturing schedules and production processes, businesses can avoid unnecessary energy usage, minimize downtime, and make better use of materials. This reduction in waste contributes directly to sustainable inventory management practices.
5. Reporting and Analytics for Sustainability Metrics
Sustainability success is measured through key metrics such as waste reduction, energy efficiency, and supply chain sustainability. Deskera ERP’s robust reporting and analytics tools provide detailed insights into these areas, enabling manufacturing executives to track their environmental performance. Customizable reports allow businesses to monitor their sustainable inventory management efforts, adjust strategies, and ensure compliance with sustainability goals.
6. Integration with Green Supply Chain Initiatives
Deskera ERP seamlessly integrates with supply chain systems to create a unified approach to sustainability. Its advanced supply chain management features allow for the tracking of eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain, such as reducing carbon emissions during transportation or choosing energy-efficient logistics providers. This integration ensures that inventory sustainability is part of a broader company-wide initiative to reduce environmental impact.
Key Takeaways
Sustainable inventory management integrates environmental responsibility into traditional inventory practices, reducing waste, conserving resources, and improving economic efficiency by 2.13%.
Importance of Sustainable Inventory Management: Key benefits include enhanced operational efficiency, reduced costs, minimized environmental impact, and alignment with corporate sustainability strategies. It also addresses consumer expectations for eco-friendly business practices.
Key Sustainable Practices for Manufacturing Executives:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory minimizes overstocking, reducing waste.
- Eco-friendly Packaging limits waste and supports sustainability.
- Circular Economy encourages reuse and recycling within inventory practices.
- Energy-Efficient Warehousing lowers energy consumption, reducing carbon footprints.
- Optimized Transportation supports sustainable logistics and inventory distribution.
- Responsible Supplier Selection promotes collaboration with suppliers who adopt green practices.
- Inventory Forecasting leverages data for efficient resource planning.
- Waste Reduction Initiatives minimize material wastage throughout the supply chain.
Challenges and Solutions: Common challenges in adopting sustainable inventory management include resistance to change, high initial costs, and lack of expertise. Solutions include investing in technology like ERP systems, employee training, and collaboration with eco-friendly partners.
Future Trends and Innovations: Upcoming trends in sustainable inventory management include AI-driven demand forecasting, green technologies, blockchain for transparency, and increased reliance on eco-friendly supply chain partners.
Understanding the Role of Sustainability in Corporate Strategy: Embedding sustainability in corporate strategy is key to meeting consumer expectations, regulatory compliance, and improving long-term profitability.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations: Businesses must comply with sustainability-related regulations, such as ISO standards, and adhere to certifications like LEED and ISO 14001. Ensuring compliance is essential to maintaining a competitive advantage and avoiding legal pitfalls.
Metrics and KPIs for Measuring Sustainability Success: Key performance indicators such as waste reduction, energy consumption, carbon footprint, and sustainable sourcing rates should be measured to evaluate the success of sustainable inventory management initiatives.
Building a Sustainable Supply Chain Ecosystem: A sustainable supply chain ecosystem requires collaboration with suppliers, partners, and customers. This involves fostering transparency, aligning sustainability goals, and working collectively toward minimizing environmental impact.
Employee Engagement and Training for Sustainability: Engaging employees through education and empowerment is essential for the successful implementation of sustainable inventory practices. Leadership should encourage sustainability initiatives, offer training, and build a culture of responsibility.
How Deskera ERP Helps with Sustainable Inventory Management: Deskera ERP enhances sustainable inventory management by offering real-time tracking, demand forecasting, automated procurement, and reporting features. It reduces material waste, energy consumption, and helps businesses meet their sustainability goals.
Related Articles















