The size of the global waste management market, which was estimated to be worth USD 423.4 billion in 2021, would rise to USD 542.7 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 5.1% from 2022 to 2031. Governments and organizations in many nations are being forced to concentrate on improving their waste management systems by reusing, recycling, and transforming waste into energy as a result of an increase in social and environmental challenges.

ERP solutions for waste management organizations handle everything from pickup to transportation to final disposal. The system includes cutting-edge capabilities for automating these activities, documenting each step, and managing them with ease. Hence, this article will serve as a guide to ERP for Waste Management and Recycling Industry. Following are the topics covered:
- Waste Management and Recycling Market Overview
- What is ERP?
- Why do you need ERP for Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
- What are the challenges faced by Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
- What are the ERP solutions for Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
- What are the global trends in Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
- What is the impact of COVID-19 on Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
- What are the stages involved in Waste Management?
- What are some ways of managing and reducing waste?
- Key takeaways
Waste Management and Recycling Market Overview
One of the main factors fueling the market expansion is the increasing awareness of the need of waste management and waste segregation programs. With an increase in construction projects, construction and demolition (C&D) materials are being used more frequently in metropolitan areas.
Buildings, roads, and bridges are constructed, renovated, and demolished using materials used in construction and demolition (C&D). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) advocates a Sustainable Materials Management (SMM) strategy, which recognizes some C&D resources as commodities that can be used in new construction projects instead of having to mine and refine virgin materials.
Most of the demolition and construction waste produced in the US today is legally intended for disposal in landfills that are subject to Code of Federal Regulations (CFR).
Background
Early in the 18th century, the first waste management system of its kind arose in the UK. A huge increase in waste production as a result of urbanization, population growth, and the number of cities created unhygienic circumstances and sped up the spread of infectious diseases. The government offered to pick up and dispose of waste near the yards where it gathered in significant amounts as a solution to this issue. The previous waste collecting system was developed in this manner. The "3R" principle is typically the foundation of Waste Management.
- Reduce-The amount of waste you produce each day.
- Reuse- Repair, or refurbish equipment or parts.
- Recycle -Recycling old materials to create new products or substances
Reuse and recycling come in lower on the hierarchy after entirely avoiding or lowering emissions. In some areas, the entirety or a portion of the building and demolition waste stream is forcibly dumped on the ground or in natural drainage systems, including the water, in violation of laws intended to safeguard public health, industry, and the environment.
Millions of tonnes of building-related garbage are disposed of legally each year in solid waste landfills by businesses and US people. Diverse disposal methods and procedures have emerged as a result of increasing knowledge of proper waste disposal and its importance for protecting animal and human health on a global scale.
Sustainable waste management firms must promptly dispose of or recycle the waste due to the presence of significant amounts of hazardous substances, such as metals and salts, in the waste.
Waste management concept
The processes of collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal of waste, as well as monitoring and controlling the entire process, are all included in waste management.
Urban areas are developing smart cities to foster sustainable economic growth. The United Nations estimates that by 2030, 60% of the world's population will reside in urban areas, and one in three people will do so in a city with a population of at least 500,000.
There are already more than 100 smart city initiatives underway throughout the globe, which presents enormous prospects for the building industry. Roads and the need for construction present profitable opportunities for waste management market participants.
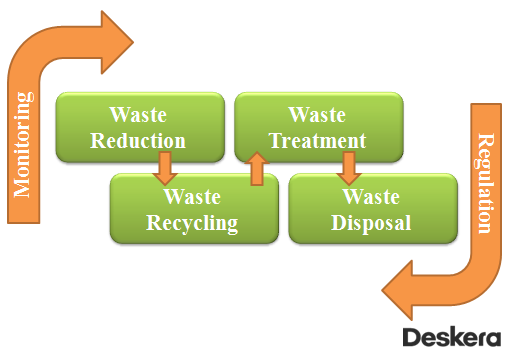
- Waste reduction. This action is to reduce waste production across society. Consider purchasing products without packaging, objects made of sustainable or recycled materials, etc.
- Waste recycling. Disposing recyclable items (such as plastic, paper, etc.) and buying products created and packaged with recycled resources. Looking for new uses for the materials that can't yet be recycled.
- Waste treatment. Actions to reduce the environmental impact of waste. Different nations use a variety of waste treatment methods (composting, sorting, trade, collection, recovery, etc.)
- Waste disposal. Specifically, the transportation of waste in tandem with the statutory regulation and oversight of this procedure, which are necessary for the subsequent management of the collected waste before its final disposal.
A rise in construction activity generates a significant volume of waste related to construction that is diverted from the waste stream. Materials that have been diverted are separated for subsequent recycling and, in certain cases, reuse. The amount of waste generated by buildings is substantially impacted by macroeconomic factors that have an impact on construction, society consumption patterns, and risks both natural and man-made.
The amount of construction and demolition waste dumped in landfills has decreased recently as a result of increased awareness about the reuse and disposal of building materials. There are numerous potential for the substantial reduction and recovery of materials that would otherwise be discarded as waste.
E-waste Management
The process of recycling, removing, and reusing valuable components and metals from the electronics wastes that are discarded in our daily lives is known as "e-waste management." Additionally, these extracted precious metals are traded on the market in accordance with governmental regulations. Over the projection period, the e-waste segment is anticipated to grow at the quickest CAGR of 7.3%.
Rapid technological development has led to the creation of new electronic devices as well as improved versions of current products, which has decreased their shelf life and increased the production of e-waste.
Market Segmentation
The waste management market is looked at from four viewpoints in order to track the effects of digitization and future development prospects:
Based on the waste type:
- Industrial Waste
- Hazardous Waste
- Bio-medical Waste
- E-waste
- Plastic Waste
- Municipal Waste
- Others
In 2021, the industrial waste sector dominated the market with a share of over 50.0%. The principal causes of the rising industrial waste creation are rapid urbanization and industrialization. Industrial waste management is necessary since improper handling of this garbage can cause damage to wildlife and plants as well as groundwater and lake pollution.
Our global research indicates that by 2050, 7 billion people will be living in cities, which will likely result in a rise in the amount of urban waste produced. In order to stop the COVID-19 pandemic from spreading, the governments of several nations, including the U.S., India, and China, had enforced a lockdown in 2020. As a result, more individuals worked from home, which led to a rise in urban waste.
In order to prevent the spread of infections and diseases like pneumonia, tuberculosis, tetanus, whooping cough, and diarrhea, waste produced by hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities must be treated using appropriate waste management practices. Due to a rise in the number of diagnostic procedures and COVID-19 patient treatments between 2020 and 2021, there was an increase in the production of biomedical waste.
Based on the service type:
- Recycling
- Open Dumping
- Collection
- Incineration/Combustion
- Landfill
- Composting & Anaerobic Digestion
Based on the end user:
- Industrial
- Residential
- Commercial
By Geography
- North America
- Latin America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
Key Market Players
Generic strategies adopted by the companies usually include mergers & acquisitions, distribution network expansion, and product portfolio expansion. Major players in the market are vertically integrated across the supply chain, wherein they provide waste collection, transportation, and disposal services.
This results in optimizing the operational cost and increasing profit margins, thereby enabling the companies to obtain a significant share in the industry. Some prominent players in the global waste management market include:
- Waste Management (US)
- Veolia (France)
- Republic Services (US)
- SUEZ (France)
- Waste Connections (US)
- Biffa (England)
- Clean Harbors (US)
- Covanta Holding (US)
- Daiseki (Japan)
- Hitachi Zosen (Japan)
Drivers of waste management market
- E-waste is rising as a result of technological advancements and decreased product lifespan for electronic devices. The development, introduction, maturation, growth, and eventual disposal or recycling of an electronic product are all parts of its usual life cycle. As a result of technological improvements and shorter product lifespan, e-waste is increasing.
- Electronic products reach the recycling stage for one of three reasons: they have reached the end of their useful lives, technology has advanced, or consumer demands have changed. New electronic devices and improved versions of the current products, including laptops, mobile phones, and televisions, are produced as a result of rapid technological breakthroughs.
- Similar to this, the shelf lives of electrical devices get shorter as people's purchasing power rises. Every year, new versions of mobile phones and other electronic items are released; the older versions are either discarded or sold online for recycling. Therefore, as the lifespan of electronic products gets shorter, more and more e-waste is produced.
- The necessity for recycling electronic products is prompted by the buildup of electronic waste, which in turn fuels the demand for electronic waste management. Since the invention of PCs and mobile phones, the average lifespan of consumer goods and the parts that make them has been gradually reducing.
- Electronics now have an average lifespan of 1.5 to 13 years, compared to the initial expectation of 40+ years, with the majority lasting an average of 4-5 years.
Restraints of waste management market
- There is lack of essential infrastructure for waste collection and segregation. Waste segregation is the process of separating dry and wet waste, which makes other waste management procedures like composting, recycling, and incineration possible.
- Reducing landfill waste and finally stopping air, water, and land contamination are the objectives. For recycling waste and plastic products or any other items like paper, metals, and wood products, it is essential to collect and separate waste properly.
- Municipalities and other waste management organizations are seriously threatened by improper waste disposal. The population living close to a polluted environment or a landfill can be negatively impacted by improper waste disposal.
- Skin irritations, blood infections, respiratory disorders, development problems, and even reproductive abnormalities can all result from exposure to badly managed wastes.
- Waste management systems have been effectively adopted in developed nations including the US, Australia, Japan, and Germany, enabling efficient waste treatment and ensuring beneficial benefits from it through recycling. These instances are scarce when taking the actual scenario into account.
- Countries like Egypt, Turkey, South Africa, Nigeria, Brazil, and Middle Eastern nations are still working to standardize and organize their waste management frameworks, which has a significant negative impact on how waste is handled.
- It is important to separate different waste kinds at the source since doing so would make it easier to recover recyclable waste and would take less time and effort overall. Unscientific treatment, inappropriate waste collection, and ethical issues like dumping e-waste are the main issues with solid waste management.
- The development of the waste management market is thus constrained by risks such environmental deterioration, water pollution, soil pollution, and air pollution.
Opportunities of waste management market
- Market participants should expect to profit from rising public and governmental knowledge of the solutions as well as rising demand for the creation of waste-to-energy solutions during the projected period. Waste-to-energy technology turns non-recyclable waste into energy that can be used.
- Combustion of waste produces super-heated steam that drives turbo generators to produce electricity. The waste to energy systems offer a highly valued source of renewable energy, its power to transform garbage into ash may be their greatest advantage today, lowering the amount of waste that ends up in landfills by up to 90%.
Service Type Insights
- In 2021, the collection category dominated the market with a share of over 60.0%. Waste collection involves sorting the waste, loading and unloading the waste, choosing an appropriate location, preparing that location for waste storage at a minimal distance from the waste generation site, and maintaining the waste. The waste collection businesses must take into account routine cleaning and upkeep of these storage spaces.
- To prevent waste from spilling or leaking during transportation, proper precautions must be followed. During transportation, the liquid waste needs to be covered and leak-proof.
- Non-hazardous waste can be delivered directly to the recycling plant; however hazardous waste from commercial and industrial locations must be transported through suitable transport vehicles with a specified level of protection.
- Over the projection period, the disposal segment is anticipated to grow at the highest CAGR of 7.1%. There are several ways to dispose of waste, including open dumping, landfills, incineration, composting, and recycling. To prevent environmental deterioration and numerous illnesses like HIV and hepatitis among the population that are brought on by improper waste disposal, appropriate waste disposal is necessary.
- Incineration facilities provide energy from waste that can be used to produce heat and power.
- Depending on how much of the waste is recovered as metals from the ash for recycling, the incinerator disposal method reduces waste volume by 95%–96%. The reliance on landfills is decreased by incinerating waste.
What is ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning, or ERP, is a type of software that improves organizational management by automating and streamlining commercial procedures. It unifies numerous divisions, including HR, Manufacturing, Accounting, Sales, Inventory Management, Marketing, etc., and centrally saves all pertinent data.
The ERP solution has a user-friendly interface that is available to everyone who needs the data, but it also includes built-in authentication methods that restrict access to the pertinent parts of the system and data. ERP updates existing systems in the waste management sector to increase efficiency.
- Every single day, there is enormous garbage produced by people, offices, workplaces, hospitals, schools, restaurants, and lodging facilities.
- Our ecosystems are contaminated by toxic waste, which is a serious issue because it endangers not only our health but also the health of the entire ecosystem and a number of species.
- This issue is being caused by the quick development that we observe around us, which has no respect for efficient waste disposal or environmental damage. Therefore, it is crucial that waste management is correctly implemented by individuals, companies, nonprofit organizations, and governments alike in order to safeguard not only the health of the current population but also that of future generations.
- Waste management is a rich sector with a lot of promise, but the operators must be quick enough to adapt to the industry's shifting standards and rules.
- In this profession, constant change is the norm, thus individuals who want to work in it must be prepared to promptly comply with revised laws and regulations.
- Governments all throughout the world are strengthening the standards and laws governing garbage disposal and reporting. ERP is therefore absolutely necessary for waste management.
Why do you need ERP for Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
Waste management has become an important sector in the fight against climate change in an era when our planet is experiencing a serious environmental catastrophe. The requirement for environmental protection, which opens up chances for commercial waste management.
Both financially and operationally, waste management organizations are growing and operating smoothly. However, these businesses encounter certain difficulties when it comes to waste treatment and waste reduction.
Waste management organizations may manage waste more effectively and minimize environmental risks thanks to ERP solutions. The system includes cutting-edge technologies for automating these procedures, documenting every step, and managing them with ease, from pickup to final disposal.
Major Benefits of ERP Software
Safer Waste Disposal: Safer Waste Disposal Safe waste disposal is the main concern for people and organizations trying to maintain a healthy and clean environment.
- Only when the waste is correctly sorted according to type, the quantity is noted, and rigorously tracked from the collecting stage through carrying, all the way up to disposal, can this be accomplished.
- This entire procedure is made simple by business resource planning software.
- The solution enables you to record every detail related to disposal, including the price, the disposal technique, the quantity, the dumpsite, the transporter used, the invoice, the shipping, and so forth.
- By doing so, you can keep an eye on what was done at each level and ensure that every action was conducted in accordance with the rules and guidelines established by the relevant authorities for waste management or recycling programs.
Task Scheduling Optimized: You might frequently find yourself managing multiple projects at once, which without the aid of a reliable and efficient ERP solution can be very challenging.
You can see everything that is happening in your company thanks to a centralized system that offers real-time access to pan-organizational data and transactions.
Powerful data analytics give accurate data on what is happening in each department; taken together, all these characteristics allow for the best work scheduling for improved service.
Integrated system: Enterprise-wide integrations across all processing units are provided by ERP software. End-to-end management is achieved by consolidating all enterprise data into a single database that can be accessed via a standard interface. Thus, while each software and hardware component performs a separate duty, they may all be handled centrally. Long-term decisions are made when waste management systems' functional components cooperate.
Plan and keep track of resources allocation: ERP is often used by businesses to keep track of all transactions and generate reports based on the data gathered.
- You can obtain real-time information on the human resources assigned to each task or project when you utilize ERP in waste management programs.
- This has the advantage of allowing you to distribute resources as effectively as possible to assure better results and take corrective action as needed.
- You can use it to assign workers to tasks based on priority and to choose the best candidate for a position.
- Employees that have the ability to confirm the job they have been given to do can be assigned tasks by managers.
Work may be distributed efficiently and effectively, saving time and preventing over- or under-allocation. You can also prioritize tasks and ensure that your coworkers complete them in the proper order. This is especially useful if you are managing several sites or large projects.
Real-time management: ERP systems provide access to and real-time visibility of corporate data. Decisions are made and carried out simultaneously in real-time, guaranteeing rapidity and effectiveness. Visibility limits the potential for management error and guarantees that harmful wastes are not released until they have been properly handled.
Preventive Maintenance Plans: All of the machinery and vehicles your company uses for waste collection, treatment, transportation, and disposal must be properly maintained; this may entail servicing, tune-ups, part replacement, and other procedures.
- With ERP software, you can track and plan maintenance checks to stop serious damage because you have access to real-time information about the condition of all the vehicles and equipment utilized by your company.
- This makes it possible to make the most of your equipment's working time.
- Regular maintenance on vehicles and equipment helps prevent sudden failures, which could result in expensive repairs and have an impact on output.
Big data: Cloud computing is used by ERP systems to store data. Cloud ERP is used to protect businesses from storage problems and maintain hardware and software to keep it running. Additionally, according to the relevance to the application, enterprise data is accessible on all integrated applications in the ERP software. The ability to analyze huge datasets is made possible by the categories and subcategories of garbage as well as large-scale sources of tonnage.
This dataset's predictive analytics will show patterns in waste generation and disposal, assisting policymakers in developing sustainability strategies.
Management of prices and quotations: You must be able to provide accurate quotations or estimates for various waste management initiatives, even though it may appear unimportant.
- You can do it manually, but that could damage your reputation if the quotes are inaccurate.
- You may easily submit proposals thanks to the smart and automatic quote production provided by ERP waste management.
- There are several parameters you can include, such as return on investment and resource requirements.
- You can adjust parameters in ERP solutions to suit your particular needs.
Feedback Sharing: You can improve your services by listening to your customers' comments on waste dumping. If ERP software is not used, collecting this important data from many sources could be laborious and time-consuming.
- With the business management solution, your customers can provide feedback. The system compiles and evaluates the data, assisting you in formulating future business strategies and making educated decisions.
- ERP systems that are efficient, agile, and secure are agile due to their machine learning capabilities, and secure due to multi-step verification.
- Systems that are effective and flexible make room for creativity. Innovative waste disposal techniques are now available, which reduces the additional financial strain on businesses and governments and promotes social and economic well-being.
Better Information Management: It is essential that all the details pertaining to various dumping and collection sites are accurately documented.
- With ERP for waste management, you may establish criteria such waste kind and quantity, site location, resource requirements, and so forth and quickly input them for future needs. Additionally, you can change, modify, and add information as necessary.
- By keeping track of the company information and keeping an eye on the metrics for progress, you can quickly determine which activities are finished and which are still open.
- Employees benefit from this because they can concentrate on finishing activities that are unfinished, increasing their productivity and efficiency, and completing the collection and disposal of waste within the allotted time.
- ERP software comes with features that make waste management simple. The most recent modules meet all of your needs and raise your company's operational effectiveness.
Managing waste and going digital: Beyond its usual use, digitization opens up potential for waste management. It provides information that businesses and their clients can use to enhance operations, control waste, and pursue other environmental objectives.
- Real-time data can be collected using digital technologies, such as how quickly waste is disposed of. This information assists businesses in managing their recycling initiatives more effectively and raises the general effectiveness of the waste management process.
- In the future, it is anticipated that the international community will keep moving forward and put policies in place to address the growing waste problems in quickly developing nations through the use of digital technologies and close collaboration between businesses, communities, governments, and others.
- Digitization will make it easier to distinguish between waste and recyclables. Data will be gathered, the location and volume of recycled waste will be tracked, and waste infrastructure will be chipped and robotized, among other techniques.
- Food products will also have their complete life cycle monitored. New business models will be developed with the use of the gathered data to aid in preventing the appearance of waste.
What are the challenges faced by Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
The collection and disposal of waste are the two main challenging areas. These are difficult to manage because of irregular and delayed processes, ineffective tracking systems, communication obstacles, a lack of resources, and dispersed communities.
Well-equipped ERP systems provide solutions to all the problems affecting waste management, whether they are generated by the construction sector, urbanization, or the production of liquid and solid waste by the food industry.
Advancement of Safety Performance
The waste/recycling business has considerable safety problems. They consist of exposure to chemicals, combustible dust explosions, machine guarding risks, and contact with strong machinery with moving parts.
Industry leaders always advocate a proactive approach to safety, starting with a thorough assessment of each plant's compliance with safety regulations and continuing with strict training for all personnel to raise safety standards to necessary levels.
Asset management and legal compliance
Inappropriate asset usage results from a lack of adequate tracking tools for waste transportation trucks and equipment to separate solid waste, food waste, medical waste, and miscellaneous litter.
Poor-Quality Recyclables
Geographic location has a significant impact on recyclable quality. For instance, Seattle and the rest of the Pacific Northwest are environmentally sensitive, and their recyclable materials are typically of a very high caliber. In other parts of the nation, the quality can differ substantially.
Nowadays, you can find almost anything moving along a line, even the kitchen sink. Some of these things, notably garden hoses, have the potential to wrap around machinery and seriously harm it. Even if the quality of the recyclables is poor, having skilled onsite operations managers and well-trained staff will help you sustain production.
Costs of Developing a Consistent Solution
Waste management businesses struggle to come up with a consistent solution and wind up spending more money on a variety of ineffective ways to transport and recycle waste.
Due Diligence
It is the responsibility of the customer to confirm the veracity of the sales pitches made by many ERP suppliers rather than actual business cases.Waste Management businesses ought to have checked the projections' viability and correctness before accepting them at face value.
They may have, for instance, inquired as to what other businesses in the waste and recycling industry are now utilizing this software.
Industry Knowledge
Experience working in the waste/recycling business firsthand is unmatched. It starts with the tools. Managers of operations must understand how equipment functions and how to maintain it. Sometimes a simple fix will do.
Equally crucial are interpersonal skills. A successful operations manager must command the respect of the staff and be able to deal diplomatically with those facing both personal and professional difficulties.
Keeping Operations and Finance Sustainable
Lack of control over daily operations in waste management enterprises is caused by a lack of automated systems and tracking tools, which hinders their potential to be successful.
Poorly trained Employees
This is a frequent problem. Most recycling facilities eventually experience negative effects from under qualified and unmotivated employees. The truth is that many of these individuals have never received adequate management, and many of them aren't even familiar with the fundamentals of their jobs.
Because of this, a reliable labor team supplier should always make explicit the requirements of the job and then supervise the employees. Employees will be content since that is what they truly desire, so they can perform well and keep their jobs.
Employee Retention: You are familiar with the feeling; you worry about your productivity as you head into work, wondering how many employees will be absent that day. You experience a constant sense of playing "catch-up." Return to teaching and managing personnel the proper way from day one—if you want to keep good individuals. They require optimism as well, which is why it is advantageous for you to promote from within.
Excessive downtime: This will undoubtedly lower employee morale and lower production. Each employee should be responsible for managing their time because of this.
When the equipment is first turned on, they should be prepared to start working rather than just punching their time clock. You can reclaim hours of lost productive time by making little procedural adjustments like cutting back on extended phone conversations, extensive lunch breaks, and unexcused absences.
Employee recruitment in the area with low Unemployment: It's quite difficult to fill all of your open positions given the national unemployment rate of today, which is around 5%. Most hiring is frequently done at the real worksite rather than a storefront by labor team leaders. Prospects can then assess the setup's suitability for them by seeing it for themselves. Another clever idea is to hire backup pools to fill positions as soon as they become open.
Costly Recycling plastic Process
Recycling plastic Process is costlier than producing new plastic. Petrochemicals like oil and gas are the primary raw resources needed to make virgin polymers. Polyethylene terephthalate is the recycled variety of plastic (PET). The creation of a pure stream of recovered material is the issue with plastic recycling. PET plastics don't have a lasting value, but they can be recycled to make other things like new containers and fleece apparel.
While making plastic goods, a number of additives, including fillers and colorants, are added. When something is added to plastic, the recycling firms are frequently unaware of it, which has an impact on the recycling of plastic products.
In energy recovery through various thermo chemical processes, separating plastic from diverse waste streams is a challenging procedure. Plastics’ sorting is a crucial phase in many waste management processes. Additionally, the creation of fresh plastic using petrochemicals is considerably more affordable or economical than sorting and segregating plastic (according to its many classes, sorts, and the mixture of additives employed).
Maintain Open Communication
Miscommunication is the main cause of the majority of problems. It's all too simple for wires to get crossed when no one is making the difficult inquiries and everyone is assuming. You may move forward with confidence by assembling an ERP project team with both internal and external resources. This will help you communicate with your ERP vendor efficiently.
Ask your ERP provider, systems integrator, or consultant to describe their anticipated schedule and suggested strategy in your communications. When you're confident that you've identified the ideal partner for your purposes, only sign the contract.
Poor Processes
Another major industry problem is this one. Your business will function poorly if you don't use consistent practices. In order to streamline the hiring, onboarding, training, development, and performance evaluation of each employee, look for workforce providers who offer process-driven expertise. This enables you to concentrate on the crucial topics that will determine your success.
What are the ERP solutions for Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
Organizations are interested in more effective waste management due to the rise in waste production. The current market offers a wide variety of ERP that support various waste types, developing new procedures for a higher level of management and disposal in businesses. Employing ERP also gives businesses a competitive edge by increasing their transparency to regulators, clients, and staff.
Businesses can efficiently conduct all waste collection and disposal operations with the use of waste management systems. Its duties include developing workflows for procedures like sorting and destruction as well as organizing the schedule of waste collection, transportation, recycling, and disposal. It also manages contracts in terms of invoicing and pricing services.
Finance Module
A robust finance and accounting management module is included in cloud ERP for waste management companies to guarantee that no transactional data is missed. In order to make submitting tax returns simple, the system complies with local tax laws.
- Search by Area
- Search By date
- Search by Name
- Update payment received
- Options for payment Received
- Show at least 5 recent payment received Dashboard with due and time
Budget management: In the contemporary world, the waste treatment business is growing in importance. The waste treatment and recycling businesses now provide waste management for every manufacturing, service, and point-of-sale sector. With many new investors entering the waste treatment industry, effective budget management is essential to determining its success.
You can distribute funds for various projects and tasks with the help of an Enterprise Resource Planning system that is clearly specified. Software support, for instance, can be used to allocate financing for the collection process and storage management.
Expense and income tracking: ERP software for waste management that is cloud-based can help you track spending continuously. By looking at the sale paperwork, you can also determine which recycled product generates the greatest revenue.
The industry can list the various waste materials that are gathered using ERP. Additionally, it makes it simpler to list recycled goods made from various waste materials. The ERP application also aids with market forecasting and expense planning. It aids in predicting consumer demand and market developments as well. Implementing ERP can arrange revenue produced payment methods, and payment schedules. You can get a complete solution for market research and revenue development from ERP consultants.
Monitoring Resources and Waste Disposal
By assigning them in real-time with distinctive serial numbers or barcodes, you can keep track of all of your resources and assets. The remote resource management will assist you when transferring hazardous waste or managing biological or medical waste, for example.
Management of collection points: The contact module of the ERP Waste Management Software collaborates with other modules to manage collection point information. With the right ERP software, organizing disposal locations and other details is also made simple.
Based on the vicinity of waste collection stations and dumping sites, the data can be handled. Additionally, this aids in recording the specifics of organizations that buy recycled goods. The ability to edit and modify the documents as needed is provided by ERP software.
CRM for Improved Customer Services
CRM systems for waste management businesses can help you communicate and serve customers more effectively while guaranteeing that there are no gaps in the processing of service requests. Utilize the CRM system to carry out marketing initiatives, manage sales, and keep an eye on client interactions.
Sales Order & Dispatch Management Module:
- Sales Search by Date
- By Customer
- By Operator
- By Area
- By Cash Sales, Due Sales, Accounts Customer Sales, Owners Rep Sales
- Products Search
- Customer Search ( either name or mobile)
- New Customer add
- Sales Update
- Default Customer (like Walk in Customer) will be default by fill customer tab
- Discount
- Special Notes
- Cash, Due Accounts.
- Hold Sales
Monitoring of actions in real-time
ERP combines every aspect of business, including waste collection and the selling of recovered goods. It also includes managing the treatment plant workers' working hours and disposing of leftover waste materials. A monitoring tool is available in the form of open source software for various operational phases.
The ERP Software also makes it easy to track the flow of collected waste from the point of origin to recycling facilities. Once the operations are integrated with ERP Software, the investor or manager can have a clear picture of the operation.
Scheduled Tasks: ERP Projects can be used to operate the task management feature. It enables you to divide up your workload among several people who will handle the charges. Setting aside time to complete each work is made easier by scheduling activities. Work hour restructuring and labor management are two additional services that the ERP solution provides to help you successfully execute the assignment.
Personalization and Customization
Workflows and features of a smart waste management system can be customized to meet the particular needs of your waste management operations. You can personalize features and design dashboards with the info-panels you want to show.
Stock & Inventory Management
- Current Raw Products Dashboard
- Raw Materials Order Request
- Raw Materials received damage Records
- Raw Materials Received Entry Search by date Raw Materials Order Progress
- Current Raw Materials stock Dashboard
- Damage Raw Materials Records
- Search by date/products Raw Materials Received
- Current Raw Materials received Dashboard
- Total Raw Products Stock
- Search by date/products Stock
Report preparation and management
Financial accounts and reports can be generated using ERP for waste collection. Additionally, it can assist you in creating a regular report on the amount of waste collected, the recycling rate, and the effectiveness of disposal.
You can reduce manual calculations and graph preparation with the use of ERP. Using the ERP solution, a report with graphic support may be produced quickly. To increase the productivity of the company, we may also produce a report on various waste products and repurposed goods.
Quotation Management and Flexible Pricing
An ERP system for waste management will enable you to produce custom service quotations for your clients. For more versatility, you can also include it with a built-in price list, set pricing guidelines, and various billing costs.
Machinery management
The cloud-based ERP solution aids in managing the upkeep and repair of the waste treatment equipment. The industry's efficient functioning is ensured by timely maintenance of the many equipment types utilized to recycle various sorts of waste particles. Calendars and contracts for maintenance can both be managed by it. With ERP, it is very simple to manage internal maintenance and contract out maintenance services.
Segregation & Scrap Management
The separation of collected waste is the most challenging duty in the waste management sector. With the aid of ERP software, categorizing materials into metal, glass, e-waste, plastic, and other categories can be made easier. Management of collected garbage includes segregation, organizing the storage of waste materials in warehouses, and dividing waste into recyclable and non-recyclable categories.
Management of the daily recycling limit, such as 400 tonnes; safer disposal of non-recyclable items; and reports. Management of valuable products, following recycling to get raw materials, adherence to government requirements governing waste disposal to prevent environmental problems. Establishing standards and ensuring that the standard control mechanism is implemented correctly.
The ability of the ERP to display contact information and produce an area-by-area listing of waste material providers to streamline the operations of the sector. With the use of an internet platform, an investor can obtain information about the source and the kind of waste supplied by a specific source. Additionally, it enables us to quickly and simply calculate the amount of waste and make efficient plans for disposal and recycling.
Waste treatment estimation: The success of any firm depends on the accuracy of its estimations. An investor can be confident in the forecast's accuracy with ERP. The ERP solution also provides complete support for master data preparation, operation speed control, and work centre capacity optimization.
The administration of orders for waste treatment from various businesses can also be supported by ERP. Using ERP, it can manage the costs associated with treating municipal, business, and industrial waste.
Managing multiple projects
The finest project management outcome comes from ERP. ERP can help the sector run both small-scale and large-scale waste treatment projects at once. It can assist you in establishing the needs for various tasks. An ERP program can also be used to integrate waste management across numerous units and locations.
Business Analytics and Reports
Through its intelligent reporting, the waste management ERP software system provides you with information about all processes. For instance, you might assess the contracts that bring in the most revenue and the receivables and payable for a particular time frame or customer.
ERP systems come with strong business intelligence features that empower users to gain understanding and reach decisions quickly and strategically based on reliable data. Users of this ERP Business Intelligence module can alter and examine the data in any way they see fit. The data can be sliced and diced by users to assess various indicators for complete business data analytics.
Seamless Approval Processes
You might define and adapt strong hierarchical workflows with the aid of waste management systems. These workflows help you design a smooth approval process with the appropriate levels and stages to guarantee that each approval reaches the appropriate person.
Hazardous waste management software
Follow each shipment of hazardous waste through quotation, order, and work processing to billing and required reporting.
Our software enables you to reach the greatest levels of legal compliance because it was created to specifically address the needs of the hazardous waste business.
Asset Management and Maintenance
To keep operational assets in top shape, waste management ERP software performs efficient asset maintenance. Regular maintenance increases asset longevity and reduces breakdowns during the garbage collecting process.
Managing Transportation
You could arrange the service route in the ERP system using waste management software, which would also allow you to identify the vehicle and driver for each route. In order to make planning and scheduling tracking easier, ERP offers both scheduled and ad-hoc routes.
- Bricks breaking charges management
- Gate passes Vehicle In-Out management
- Transport Charge Management
- Vehicle In-Out Time Management
- Processing Charge Management
- Other charges management if extra size like above 3.5 meter bricks
After all the routes have been planned, the information will be given to your driver via a customized screen with GPS tracking. As a result, your driver would be aware of all the unfinished jobs and/or routes that needed to be finished that day on a daily basis.
Your driver will only need to press a button once each job is finished for the system to record the completion time. Additionally, the system will use GPS to record the job's position.
Photo Taking Function: The ability to take photos comes in handy if there are ever any mishaps or damaged objects on the job site.
The technology would allow your driver to snap images directly from the tablet, and it would instantly sync those photos to the appropriate contract folder in the ERP system. The pictures would then be instantly accessible from your office.
Software for weighbridges
You may easily and swiftly manage incoming and leaving loads with the help of our Weighbridge software. With only a few clicks, you can process weights and record and access data for all of your activities.
Obtain real-time total view of all weighbridge activity and connect activity to stock control.
What are the global trends in Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
Computer technology in waste management
The creation of computerized techniques to assist with and enforce the separation of waste from recyclable materials will continue. This involves deploying waste sorting machines at recycling facilities, GPS-controlled compactors, chipped recycle bins that keep track of which homes are recycling whenever the hauler tips the bins, as well as other techniques.
Researchers will use new methods to find unusual recyclables on-site, such unused food. Data collection will be necessary to achieve sustainability and energy targets in waste and recycling systems. Products will be monitored throughout the duration of their lives. To stop the production of waste, business models based on data from the product lifetime will be developed.
E-waste leading the market
In the waste management industry, the market for e-waste is the largest by kind of waste. E-waste includes a number of dangerous or toxic compounds, including mercury, brominated flame retardants (BFRs), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), and hydro chlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs).
- The environment and even human health are seriously endangered by the rising levels of e-waste, low collection crates, improper disposal, and treatment of this wastes.
- E-waste management errors also add to global warming.
- E-waste products cannot initially replace primary raw materials or lower greenhouse gas emissions from the extraction and refinement of primary raw materials if they are not recycled.
- Next, some temperature-control equipment's refrigerants produce greenhouse gases. Unsustainable disposal of old refrigerators and air conditioners resulted in the release of 98 Mt of CO2 equivalents into the atmosphere.
High-quality resin
The existing greenhouse gas-emitting prime resin used in the plastic industry will be replaced by a high-quality resin manufactured from plastic waste. One of the most significant developments in cutting-edge technology now occurring in solid waste management is this.
Plastic waste that is both inexpensive and environmentally friendly is converted into a superior resin. The procedure produces fewer greenhouse gases than the production of prime resin does. Although the industry is now in the lead in this regard, it must continue to stay on top of things.
WTE projects
Researchers will examine methods for turning waste to energy (WTE). These include anaerobic digesters, on-demand services, and circular economy initiatives. The "energy" of wasted food can be purchased as part of circular economy initiatives, and soon technologies will be able to treat food waste on-site.
Anaerobic digestate produced by a business is converted into activated carbon using a waste-to-energy technology. The company then sells the activated carbon to businesses that produce renewable natural gas. They subsequently purchase the used activated carbon from those gas firms and market it as a soil amendment.
- WTE projects will continue to come under pressure from the recycling sector. In 2015, there were roughly 71 WTE facilities in the US that produced energy. Similar to the US, industrialized countries like Germany, Japan, and the Netherlands have witnessed a development in the recycling sector that is anticipated to put further pressure on WTE projects through 2022 and beyond.
- The lack of awareness of WTE's advantages in developing nations is anticipated to impede the expansion of the recycling sector.
Alternative fueled vehicles
With approximately 30% of the fleet converted, solid waste took the lead on CNG. The transition to electric vehicles, which are a blend of CNG and EV and have now surpassed CNG in the overall routing fleet, is the next significant step. However, in order to compete with CNG and diesel, the capital cost, servicing hours and weight restrictions must be made more flexible.
- Solid waste is ready to adopt entirely electric cars based on declared pledges (EV). Hours of Service (HOS) (battery life) and payload are the current restrictions.
- A directed vehicle must be able to run for 10 to 11 hours without refueling.
- Currently, the payload trade-off is around 3,000 pounds, or 10% to 20% less than a diesel/CNG equivalent's permitted payload.
- The car is significantly more expensive (almost twice as expensive), but we anticipate that the cost gap will close considerably if EV manufacturing capacity is increased and economies of scale can be utilized.
Sorting and treatment
Without proper sorting and treatment, it has long been customary to dispose of residential and industrial garbage in landfills and waterways, causing significant environmental harm. Additionally, it has caused a number of health problems in many human groups.
Sorting waste has grown to be of utmost importance in today's society in order to distinguish between biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste, solid and liquid waste, and to sort and treat various types of hazardous waste to render it non-hazardous before disposal. The impact on the environment and communities will be reduced as a result.
Collection and Post Collection
Less than 1,300 landfills remain in operation, and as a result, the national average tip rate has increased to waste than $75 per tonne (a 3.5% annual increase).
- In the US, there are around 1,280 active non-hazardous waste landfills, and 25 corporations handle about half of them (and two-thirds of that group is controlled by the five public companies).
- Over the next ten years, we anticipate that tiny private and small- to medium-sized municipal landfills will gradually close.
- Lack of available space for expansion, increased leachate management costs, and financial assurance duties (closing and post closure commitments) are the trends that are driving this development.
Collection at the loading dock and curb: The amount and nature of waste generation remain constant, as do the methods of stop-by-stop, incremental collection. Where possible, technology enables more automated collection, dynamic routing, and on-demand pick-up, but otherwise, equipment does not alter materially.
Better routing, less labor, and greater safety will be made possible by technology. The fact that every day there are hundreds of different pickups does not change as a result. Additionally, no technology is available today that will change the collection model.
When utilized to adapt changes in the cab to increase the role of female drivers, who now make up around 10% of the direct labor force, technology helps to alleviate the labor pool limits and has the potential to increase the size of the addressable labor pool.
Landfill Gas (LFGTE)/Organics: Solid waste currently generates roughly 11 mil MWh of base load electricity into the Grid from 480 low/medium Btu LFGTE systems, according to landfill gas (LFGTE)/Organics.
- The next step is to build new hi-Btu plants and convert existing high volume sites to produce sustainable natural gas. However, until a technique that is effective, scalable, and profitable on its own merits is developed, nothing significant will happen with respect to the diversion of organic materials.
- Solid Waste will continue to take a royalty and outsource the majority of its Low/Medium Btu LFG development.
- The Hi-Btu may be entirely owned by one person or jointly developed with a partner. Because running an LFG plant is so unique, working with an operator or developer makes a lot of sense.
- The waste management industry's landfill sector is anticipated to have the largest market by service type.
- Solid waste is disposed of in well-managed, well-engineered landfills nowadays. To ensure adherence to stated regulations, landfills are planned, situated, run, and monitored. Additionally, they are made to safeguard the environment against toxins that could be found in the waste stream.
- Landfills are located using on-site environmental monitoring systems, and they cannot be constructed in environmentally sensitive locations. These monitoring devices look for any indication of landfill gas and groundwater contamination.
- The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) established strict guidelines for the construction, operation, and closure of landfills.
Biodegradable waste
Instead of burning or discarding the bio-waste, composing offers a better way to use it as valuable resources. Composting can be used to create bio-fuels and fertilizers from the bio-waste produced by homes, businesses, hospitals, and restaurants, among other sources. The idea of waste to energy (WTE) is becoming increasingly popular.
Building infrastructure for compost has received more attention recently, both in urban and agricultural settings. This would not only result in improved exploitation of bio-waste but also lessen the traditional environmental impact of disposal.
Residential segment
In the waste management market, the residential segment is anticipated to be the largest by end user. In terms of end users, the residential sector accounted for the greatest portion of the waste management market in 2020.
- This category includes waste gathered from single- and multi-family homes.
- The waste produced by households is made up of discarded plastic bags, consumer durables, toys, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), e-waste, household hazardous wastes, and other packaging materials.
- The amount of plastic waste produced by the residential sector has also increased dramatically as a result of rising disposable income and customers' preference for online shopping.
- Inhabitants of large housing units, such apartment buildings, are more conscientious about sorting waste before disposal than residents of neighborhoods of single homes.
- The Government of Korea claims that recycling companies from the private sector thoroughly process pollutants such paper, waste metals, cans, and bottles that are disposed of separately for recycling purposes.
- Typically, these organizations recycle 30 to 50 percent of the overall amount of these commodities. Due to a lack of plastic recycling facilities, just 13% of plastics are collected. Therefore, recyclable plastics are kept on hand at collection points run by local governments and the Korea Resource Recovery and Re-utilization Corporation.
Recycling business model
Recycling is saved by large solid waste. There are currently roughly 800 MRFs. At least a $2 billion renovation is required to meet the demand for greater and higher-quality output.
The collecting of recyclables and the fees associated with it, as well as the processing of recyclables at material recovery facilities (MRF), are the two places where the business model is changing. Nearly half of the municipal collection contract adjustments have been made to reflect the processing fees charged to collect and unload the recycling collection.
The remaining contract clauses are anticipated to be handled during routine contract renewals, which might take an additional three to five years.
Largest share by Asia Pacific
In 2020, Asia Pacific accounted for the greatest portion of the waste management market. Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, and the rest of Asia Pacific are among the nations that make up the region. Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and the rest of Asia-Pacific make up the majority of the region. It is anticipated that the generation of solid waste would increase quickly as more people move from rural to urban regions in the Asia Pacific region.
- By 2050, there will be 5.1 billion people living in Asia and the Pacific, with urban areas estimated to make up at least 64.0% of that total.
- Through the emigration of rural populations to urban regions and the transformation of towns into cities, industrialization has accelerated urbanization in the Asia Pacific region.
- Additionally, consumers in the Asia-Pacific region are seeing an increase in their disposable income due to the region's consistent economic expansion, which has ultimately fueled demand for waste management services. The waste management market in this nation has been significantly impacted by the growing awareness regarding the effects of non-eco-friendly packaging, such as plastic packaging and other plastic product components, on the environment.
- Some of the countries in the region's local and national governments do not effectively support waste management recycling, and some local governments do not impose rigorous laws on the crucial parts of recycling, like source segregation. The region faces difficulties managing plastic waste because of a lack of infrastructure and funding.
- The e-retailing boom in Asia Pacific's developing nations is anticipated to hasten the growth of the packaging industry, which is anticipated to fuel the growth of the waste management market over the course of the forecast period.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
There is no national EPR program, but state programs grow in states with a strong blue population and resemble the Canadian model more than either the Oregon or Maine schemes. We do not observe a federal EPR requirement. The US Congress would likely find that hill to be too high. Instead, the state level will address this. Maine and Oregon both passed laws.
They have adopted two totally different strategies. While Maine places the responsibility on the producers but specifically exempts paper products, Oregon splits the financial responsibility with the producers.
What is the impact of COVID-19 on Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
Waste management has been greatly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic containment effort as well as restrictions on business operations, travel, and the manufacturing sector. In particular during the COVID-19 pandemic, waste management is essential for human growth and health consequences.
The essential service offered by the waste management industry makes sure that strange piles of waste that are hazardous to health and accelerate the development of COVID-19 are prevented.
U.S. creation of solid waste
Despite some WFH volume movement, there is now a structural shift of about five pounds per individual. Solid waste volumes recovered in 2021 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic's peak effects having subsided and people becoming accustomed to the work-from-home (WFH) shift.
All public waste companies reported positive FY21 year-over-year volume growth ranging from 1.6% to 3.4% with a simple average of 2.6% and median 2.8%.
Medical waste
In particular during crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, sustainable management of medical waste is challenging and made worse. Given the novelty of the global pandemic, it is necessary to have adequate knowledge of the volume of medical waste produced, hot-spots for waste generation, and available treatment facilities in order to modify existing waste facilities to control the unusual medical waste and its associated viral spread effect.
- In order to make the most of the existing infrastructures and prepare for emergencies, a variety of technical skills in sorting, segregating, transport, storage, and sustainable waste management technologies are needed.
- Medical waste management mistakes could put patients, healthcare professionals, and waste managers at risk for harm, infections, harmful side effects, and air pollution.
- Non-hazardous, pathological, radioactive, infectious, chemical, cytotoxic, sharps, and pharmaceutical waste is only a few of the several types of medical waste and its byproducts.
- An unusually large amount of recorded medical waste has been caused by the global epidemic.
Non-medical and household waste
The production and consumption of non-medical and domestic goods like masks, gloves, thermometers, sanitizers and cleaning products, toilet paper, and foodstuffs increased as a result of the implementation of lock-down, the stay-at-home policy, and other preventive measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
- Single-use product usage increases as a result of the sudden lock-down and virus fear, which also causes panicky shopping.
- According to reports, the manufacturing of COVID-19 rose due to the unprecedented use of masks to prevent exposure, which raised global sales by US$166 billion.
- The COVID-19 pandemic appears to have impeded attempts to reduce plastic pollution because of the existing function of protective gear such disposable masks and gloves.
- The World Health Organization forecasts a monthly global spending of 1.6 million protective eyewear made of plastic, 76 million inspection masks made of plastic, and 89 million medical masks made of plastic to stop the spread of COVID-19.
- China produced 116 million more plastic-based masks per day in February than in January, an increase of 12 times.
What are the stages involved in Waste Management?
A waste management company will go through these five steps in the waste management process. Waste management involves more than merely bringing waste to a landfill. To make waste management as efficient as possible, it is a continual process that includes things like evaluating your household's needs, recycling, and using a waste compactor to utilize less garbage bags.
1. Identifying Your Waste Management Requirements
Every home is unique, and a good waste management firm will ensure that all of your household's waste demands are properly met. When disposing of waste, this should be taken into account if your business handles hazardous items.
Bins for waste processing and recycling are also provided at these locations. You might choose to own compaction tools like a waste compactor as an organization or a household.
2. Waste Collection
To prevent waste from remaining outside for too long, the waste pickup process incorporates logistics planning. Long-term exposure to the elements could cause the bins to spill or begin to smell, creating an ugly mass of waste. To guarantee that safety standards are met, personnel handling waste for collection should be trained professionals.
3. Moving the Waste to a Processing Facility
It is taken to be processed the waste that has been gathered from various collection places. Your waste collection provider should have a permit to deliver waste to these locations. For the sake of safety, waste management businesses and their personnel should abide by the government's compliance regulations.
There is no waste at a processing facility since non-recyclable waste is turned to electricity. Taking waste to a dumpsite and burying it there is the classic waste management strategy. However, burning the waste is another option.
4. Waste Processing
Waste that can be recycled and waste that cannot be recycled are sorted during the processing step of the collected waste. The company in question's waste management procedures determine what happens to the non-recyclable waste. To treatment facilities set up to handle this kind of waste, hazardous waste is transported.
5. Disposal and Recycling
All recyclable waste is reorganized into various commodities, such as plastics and metals, as part of this process. Recycling should be done safely and effectively. If the waste cannot be recycled, it may be disposed of or turned into energy for future use. Particular processing facilities turn waste into electricity. The final stage of waste management is this.
However, every time a cycle is finished, often on a weekly, biweekly, or monthly basis, monitoring for each of the phases should be carried out. This guarantees that the procedure will get better over time.
What are some ways of managing and reducing waste?
Significant volumes of materials and waste are produced by office buildings, schools, retail establishments, hotels, restaurants, and other commercial and institutional facilities. Here are some tools and resources to aid facility managers, building owners, tenants, and other interested parties in enhancing sustainability while also improving waste management in their buildings.
Track Waste
Wastes and materials present a sometimes ignored chance to increase an organization's sustainability, stop greenhouse gas emissions, and cut costs. As the saying goes, "you can't manage what you don't measure." Tracking your waste and recycling offers the crucial foundation for a successful waste reduction program. The first step is determining how much waste your firm produces.
An easy-to-use web platform called ERP can be used to track waste, energy, and water data over time. Utilize it to securely compare the performance of a single building or a large portfolio of buildings. A set of consistent measures are provided by Portfolio Manager to help you evaluate your waste management operations.
Set a high bar
Your waste reduction campaign will be more successful if you include others and follow an action plan.
Team up
Make use of a current team. Think about expanding the green team in your company to include someone who specializes in waste reduction. This can entail adding more team members who are focused on recycling and waste.
Form a brand-new team. If your company doesn't already have a green team, think about forming one to organize, develop, and carry out waste reduction initiatives. Following are some pointers for organizing your team:
- Obtain the management's backing.
- Select people from various divisions within your company. A diverse team will provide a range of viewpoints, innovative problem-solving methods, and probably find more potential for improvement.
- Match the number of team members you have to the number of employees in your company, and try to include people from as many different divisions, tenants, or functions as you can.
It is crucial to establish the team's responsibilities as it comes together. These duties could include:
- Collaborating with the management of your firm to establish both short- and long-term waste reduction goals.
- Collecting and evaluating data pertaining to the creation and execution of your scheduled actions.
- Securing management support for the program's objectives and implementation, emphasizing the value of waste reduction within the company, managing and maintaining the program, and promoting and rewarding employee commitment and involvement in the endeavor.
- Promoting the program and instructing other staff members on how to take part.
- Providing incentives to employees to cut waste.
- Engaging employees to develop recognition and award programs and solicit comments.
- Tracking the development.
- Letting management know how the planned activities are going.
- Letting all staff members know about the organization's waste reduction activities.
Set Goals
Teams are better equipped to communicate their objectives and progress when they have clear, measurable goals.
- Analyze your tracking information to create a baseline and guide your goal-setting.
- Analyze your tracking information to create a baseline and guide your goal-setting.
- Setting goals enables you to prioritize actions for waste reduction and growing recycling initiatives. After then, use your benchmark to monitor your progress toward the targets.
- Conduct a waste assessment to pinpoint the precise actions that can help you achieve your goals most successfully. You can target specific areas for waste reduction using the information gathered.
Evaluating Your Program
Monitoring the quantity of recyclables and wastes removed from your building gives you information on the amount of waste produced and the recycling rate, as well as how well your waste management program is working. However, a waste assessment is essential to gaining knowledge about how to improve. A waste assessment will give you crucial information to find waste reduction options.
- A waste assessment or audit is a methodical examination of your facility and its activities to determine the volume and make-up of the waste stream.
- Your waste reduction program can be effectively tailored if you are aware of what is in waste.
- You can also consider contacting your waste hauler or the recycling organization in your city or county for help with a waste assessment.
- Businesses can get free waste audits from some local governments and waste transporters.
Using the Results of the Waste Assessment
Use the findings of your waste assessment to guide your waste-reduction efforts. For instance, you might discover that your recycling stream has a high level of contamination, highlighting the need for more education and communication on what belongs in the recycling bin. Or the findings might show that participants frequently discard recyclable materials in the waste.
Consider organizing a team brainstorming session to come up with new waste reduction initiatives after studying the waste assessment's findings. Make a list of your best possibilities, and then assess their viability and compatibility with your objectives. As you evaluate and pick your activities:
- Prioritize waste prevention, which will aid in eradicating waste at its source, conserving resources, energy, and money.
- Analyze your alternatives for recycling and composting to handle garbage that cannot be avoided.
- Implement the waste reduction strategies that are most appropriate for your company. To get others involved, you might want to start with one or two distinct activities. Then, as some of the early waste prevention and recycling activities become second nature, introduce other programs.
Enhance Your Methods
By actively involving and training staff and finding markets for your recovered items, waste prevention and recycling programs can be greatly improved.
Prevention of Waste
Creating less waste in the first place is the best strategy to reduce waste in your company. The greatest economic reductions and environmental advantages come from waste prevention.
- Reduce: By altering the design, manufacture, acquisition, or use of materials or products, organizations can change their current procedures to lessen the quantity of waste produced. For instance, to save paper, your business could advise staff to print only what is necessary and make sure that double-sided printing is the printer's default setting.
- Reuse: Using items and packaging again extends their useful lives, delaying their eventual disposal or recycling. Reuse is the process of repairing, renovating, washing, or simply recovering discarded or worn goods, including furniture, appliances, and building materials. You can avoid managing the disposal of a large number of coffee cups, for instance, by encouraging residents to utilize reusable coffee mugs rather than single-use, throwaway cups.
- Donate: Businesses can give goods or materials to people in need or who can use them. For instance, restaurants, lodging facilities, and cafeterias quickly provide prepared and perishable foods to the hungry members of their local communities. You can avoid paying for storage and disposal by taking advantage of the free pickup services offered by many local food banks.
Recycling
Recycling provides raw materials for the creation of new products while also conserving energy and keeping waste out of landfills and incinerators. Recycling is the next best thing if waste cannot be avoided. Recycling does more than just make landfills last longer. It involves utilizing our resources as efficiently as possible and preserving them for future generations. It is about preserving resources such as raw materials, energy, and land.
Recycling for organics is composting. It transforms organic wastes like food scraps and grass clippings into a useful soil supplement that improves soil health and prevents organic waste from ending up in landfills. The availability and engagement of recyclables are two interrelated factors that must be addressed in order to promote recycling.
Availability
This refers to the recycling possibilities that are influenced and affected by the collection methods, markets, and equipment that are available to you. Your organization's ability to expand recycling depends on where it is located and how much waste it produces. There are various layers to availability:
- Regional - If you have a lot of commodities, what regional markets and processing facilities can you access?
- Local - Which materials are accepted for recycling or composting by your municipalities or county's programs? What services are provided by haulers in your area? Are there any other companies or groups that could benefit from your waste products, such as waste exchanges and donation centers?
What services does your hauler provide for your building within a building? Bins for recycling and composting are they accessible and visible?
Engagement
When composting or recycling is a possibility, it's crucial to inform and involve people. People can easily and visibly participate in a company's sustainability efforts by recycling. Top practices consist of:
- Make an announcement and hold a program kick-off whether you're beginning a new recycling program or reviving an existing one. Have a senior leader in the organization proclaim the objectives, the significance of this initiative, and the implementation strategy.
- Highlight the role that individuals have had in helping the organization achieve its waste reduction objectives by using challenges, zero waste lunches, recognition, and more.
- Use pictures instead of words when posting information about waste, recycling, and composting bins. Waste and recycling containers work best when placed close to one another so that people have access to both options in one location. Recycling ought to be as simple as throwing anything away. To prevent misuse, make sure that all waste cans and recycling bins are clearly marked.
- If your waste bins are black, your compost bins are green, and your recycling bins are blue, maintain the colors the same throughout your program.
- The effectiveness of a program depends on ongoing communication and marketing. To keep the initiative moving forward, take advantage of special emphasis days like Earth Day (April 22) and America Recycles Day (November 15).
Advantages of Reducing Waste
You might not have given your company's waste much thought up until lately. Many businesses are pleased to only set up a waste removal system. Waste management is receiving more and more attention, and proactive businesses are seeing the advantages of starting a waste reduction program.
- Save Money - Recycling more can save disposal expenses and boost your revenue.
- Knowledge is power - By being aware of the quantity and kind of the wastes your company generates, you'll be in a better position to find solutions to save hauling expenses and bargain for waste and recycling services that truly meet your requirements.
- Streamline reporting and information sharing - Sharing and reporting information with stakeholders is made simpler by tracking your waste management activities on a single platform and utilizing a set of uniform indicators.
- Promote sustainability - Among sustainability's essential elements is the efficient management of waste, water, and energy. Enhancing your company's sustainability can enhance your brand, draw desirable tenants to your facilities, and motivate employees.
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions - Recycling and waste prevention have a big potential to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Preserve resources - Recycling and reuse help preserve natural resources like water, metals, and trees.
How can Deskera help with ERP for Waste Management and Recycling Industry?
Deskera is proud to offer ERP software to enterprises operating in Waste Management and Recycling Industry. Deskera's all-in-one platform combines accounting, CRM, and HR software for the expansion of your organization. It is the finest option in ERP for SMEs as it is a reliable software solution.
Deskera CRM helps you monitor and engage with your customer base through e-mail marketing, CTAs, customer service, and also receive real-time information on your dashboard.
Lastly, with Deskera People, which is an HR specialized software, you will be able to handle not only your employees’ deductions, bonuses, overtime pays, and payrolls but also the industry specification of the payroll frequency.
Key takeaways
- Businesses can efficiently conduct all waste collection and disposal operations with the use of waste management systems. Its duties include developing workflows for procedures like sorting and destruction as well as organizing the schedule of waste collection, transportation, recycling, and disposal. It also manages contracts in terms of invoicing and pricing services.
- A successful waste management company needs capable ERP software to handle personnel, finances, inventories, and other activities from a single platform and to promote best practices in the sector.
- Conscious waste management is crucial for every firm and is growing in popularity across the globe. Organizations are beginning to pay more attention to waste management procedures as governments strive to control waste more strictly in order to protect the environment and enhance population quality of life.
- Digitization opens up potential for waste management. It provides information that businesses and their clients can use to enhance operations, control waste, and pursue other environmental objectives. Real-time data can be collected using digital technologies, such as how quickly waste is disposed of.
Related articles