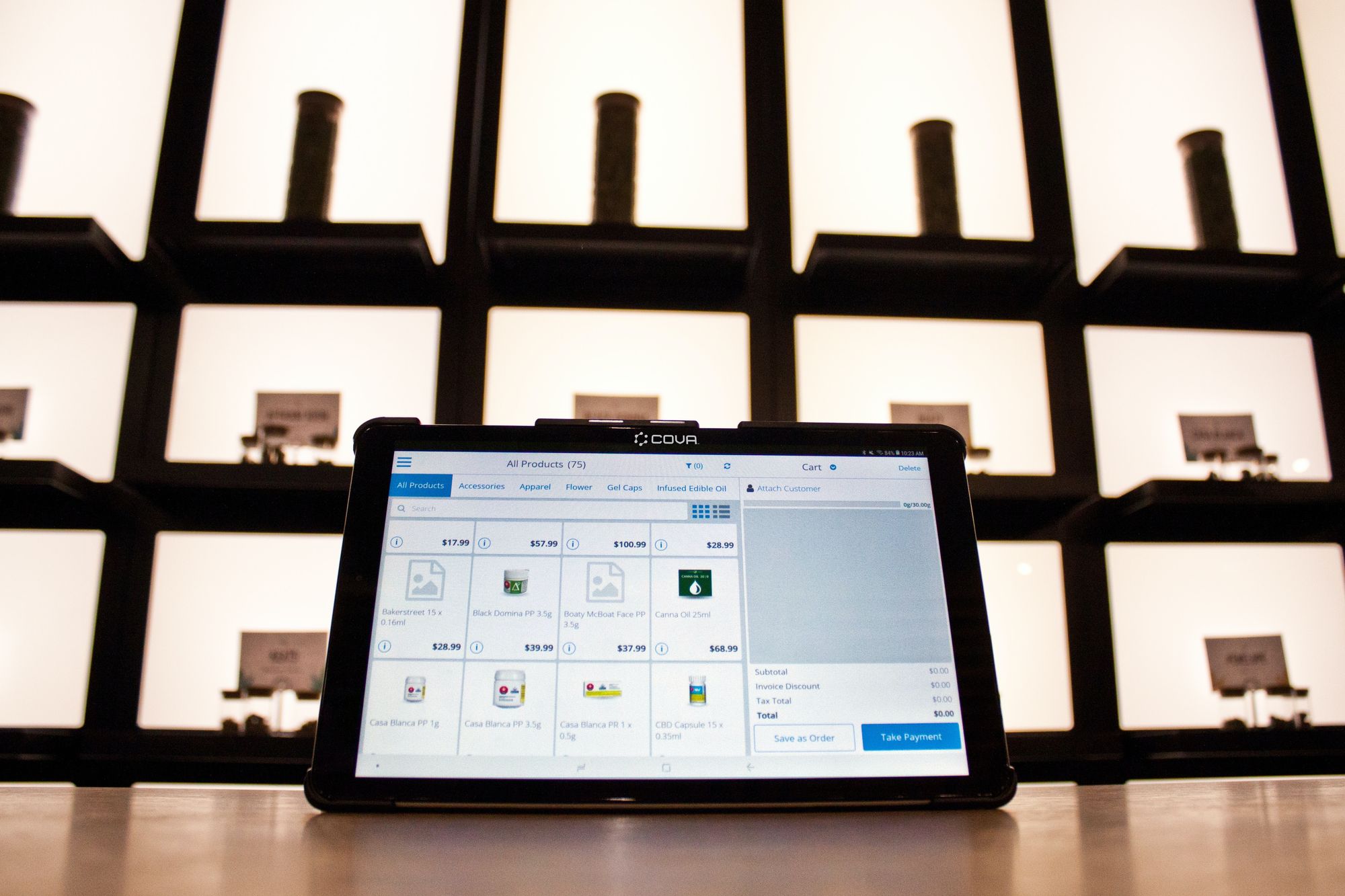
Are you facing challenges in managing and controlling inventory in your manufacturing operations? If so, you're not alone. The manufacturing industry often grapples with various inventory control challenges that can hinder efficiency, increase costs, and impact overall profitability.
In this article, we will explore the common inventory control challenges faced by manufacturers and provide valuable insights on how to overcome them.
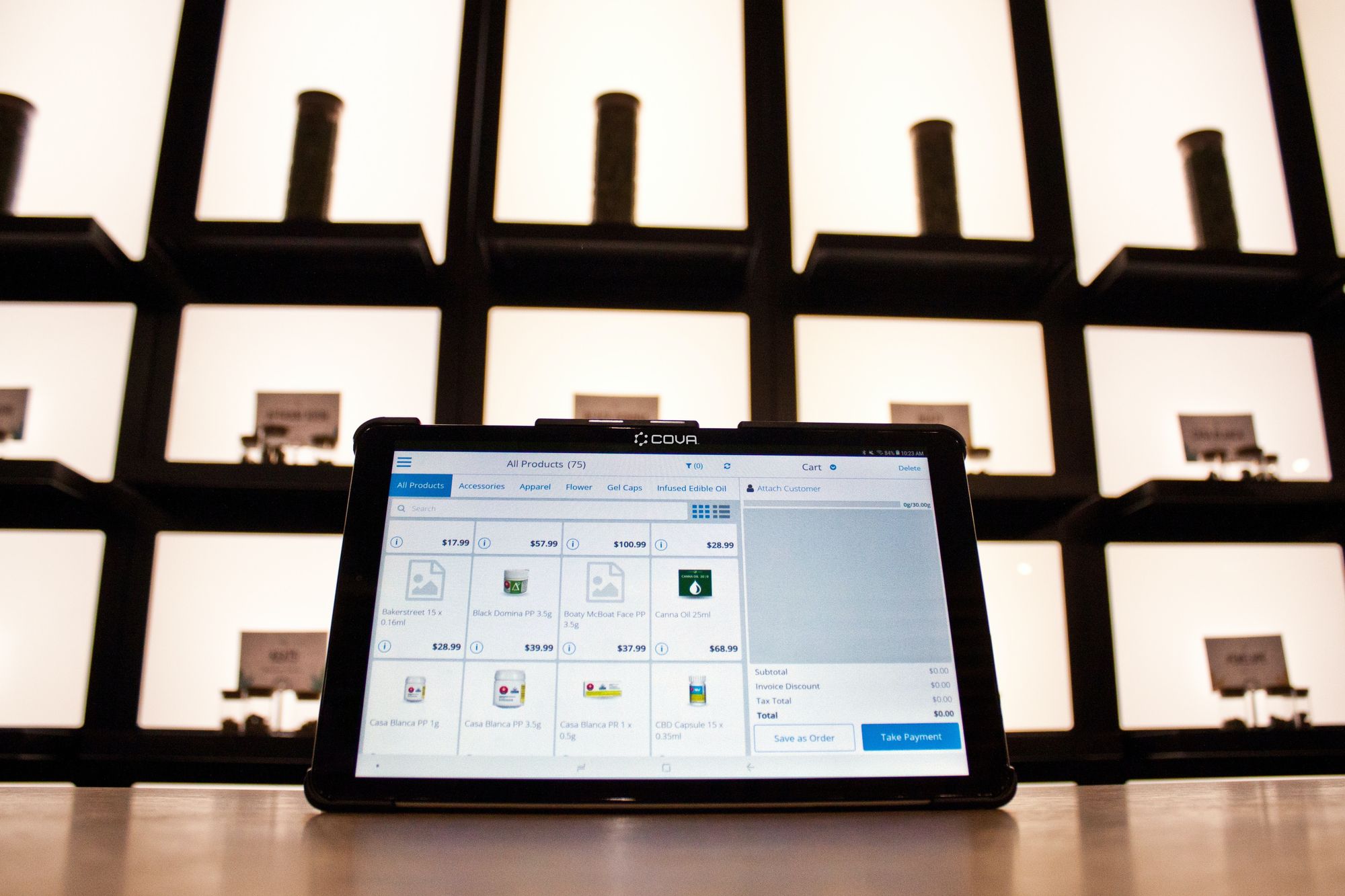
Inventory control is essential for maintaining optimal levels of stock, ensuring uninterrupted production, and meeting customer demand. However, many manufacturers face hurdles that hinder their ability to effectively manage inventory. These challenges can lead to issues such as stockouts, excess inventory, increased carrying costs, and poor customer satisfaction.
Leveraging technology and best practices can help manufacturers optimize inventory levels, improve accuracy, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
We will explore practical strategies, tools, and technologies that can help manufacturers overcome these hurdles and achieve efficient and effective inventory control.
Whether you are a small or large manufacturing organization, mastering inventory control is crucial for optimizing operations, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. Join us on this journey as we navigate the world of inventory control challenges and discover actionable solutions to overcome them.
Here is what we shall cover in this post:
- Introduction to Inventory Control Challenges in Manufacturing
- Addressing Stockouts and Backorders in Production
- Implementing Efficient Inventory Counting and Tracking Methods
- Overcoming Lead Time and Supplier Variability Challenges
- Reducing the Risk of Stock Discrepancies and Data Inaccuracies
- Leveraging Technology for Automated Inventory Control Systems
- Managing Seasonality and Demand Fluctuations in Inventory Control
- Future Trends: Innovative Solutions for Inventory Control in Manufacturing
- How Deskera Can Assist You?
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
Introduction to Inventory Control Challenges in Manufacturing
Inventory control plays a crucial role in the manufacturing industry. It involves managing the flow of raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods to ensure efficient production and meet customer demand. However, there are several challenges that manufacturers face in maintaining effective inventory control.
- Manufacturers must estimate the quantity of products they need to produce to meet customer requirements while avoiding excess inventory or stockouts. However, demand variability makes this task complex.
- Manufacturers often rely on multiple suppliers and face issues such as lead time variability, supplier reliability, and transportation delays. These factors can affect the availability of raw materials and components, leading to disruptions in production.
- Certain industries experience seasonal demand patterns, which pose challenges for inventory control. Manufacturers must carefully manage inventory levels to meet peak demands during high seasons while minimizing excess inventory during low seasons.
- Maintaining accurate inventory records and conducting regular stock counts is crucial for effective inventory control. However, manual counting processes can be time-consuming, error-prone, and disruptive to operations.
- Manufacturing processes often involve variability in production outputs and batch sizes. Variations in production lead times, batch sizes, or changeover times can impact inventory levels and complicate inventory control.
- Inventory carrying costs can have a significant financial impact on manufacturing companies. Costs such as storage, insurance, obsolescence, and financing tie up capital and reduce profitability.
Forecasting Demand Accurately for Effective Inventory Management
In the manufacturing industry, accurate demand forecasting is vital for effective inventory management. Manufacturers face unique challenges in predicting demand due to various factors such as supply chain complexities, changing customer preferences, and market uncertainties.
Inaccurate demand forecasts can result in costly inventory imbalances, production inefficiencies, and customer dissatisfaction.
Volatile Demand Patterns: Manufacturing companies often deal with highly volatile demand patterns. Seasonality, changing consumer preferences, economic factors, and industry-specific trends can significantly impact demand.
This makes it challenging to accurately predict demand and plan inventory levels. Traditional forecasting methods may struggle to capture these variations, leading to inventory imbalances and potential stockouts or excess stock.
Long Lead Times and Supply Chain Complexities: Manufacturing often involves complex supply chains with multiple tiers of suppliers, long lead times for raw materials, and extensive production processes.
Delays or disruptions in the supply chain can have a cascading effect on demand forecasting accuracy. Any delays in the delivery of raw materials or components can impact production schedules and ultimately affect the availability of finished goods.
New Product Introductions and Product Lifecycle Management: Manufacturing companies frequently introduce new products or variants, making it challenging to forecast demand accurately. The lack of historical data for new products or changes in existing products adds complexity to the forecasting process.
Moreover, as products move through different stages of their lifecycle, demand patterns can change, requiring continuous adjustments to demand forecasting models.
Demand Variability across Customer Segments: Manufacturing companies often serve diverse customer segments, each with unique demand patterns. Different customer segments may have distinct purchasing behaviors, order patterns, and lead time requirements.
Forecasting demand accurately for each customer segment becomes crucial to meet their specific needs while optimizing inventory levels. Failure to understand and account for these variations can lead to inventory imbalances and suboptimal customer service.
Impact of External Factors: The manufacturing industry is subject to various external factors that can significantly influence demand. Economic conditions, regulatory changes, competitor actions, and geopolitical events can all impact customer demand patterns.
Incorporating these external factors into demand forecasting models can be challenging but crucial for accurate predictions.
Strategies to Improve Demand Forecasting Accuracy
Despite the challenges, manufacturing companies can implement strategies to enhance demand forecasting accuracy and improve inventory management. Here are some key strategies:
Data-Driven Approach: Leveraging historical sales data, customer data, market trends, and other relevant information are crucial for accurate demand forecasting. Manufacturers should invest in robust data collection and management systems to capture and analyze data effectively.
Advanced analytics and machine learning techniques can help identify patterns, correlations, and demand drivers that may not be apparent through traditional methods.
Collaboration and Information Sharing: Collaboration across different departments, such as sales, marketing, production, and supply chain, is essential for accurate demand forecasting. Regular communication and information sharing enable better alignment between sales forecasts, production plans, and inventory management strategies.
Sales teams can provide valuable insights from customer interactions, while production and supply chain teams can offer expertise on lead times, capacity constraints, and supply chain risks.
Demand Sensing and Real-Time Data: Implementing demand sensing techniques, such as real-time data monitoring, can provide manufacturers with up-to-date information on customer demand patterns.
Using technologies like point-of-sale (POS) data analysis, social media sentiment analysis, and IoT-enabled sensors, manufacturers can capture real-time demand signals and adjust forecasts accordingly. This agile approach enables timely responses to demand fluctuations and reduces the reliance on historical data alone.
Managing Inventory Carrying Costs and Cash Flow
Inventory management is a critical aspect of the manufacturing industry, and effective management of inventory carrying costs and cash flow is essential for long-term success.
Inventory carrying costs, which include expenses related to holding and storing inventory, can have a significant impact on a manufacturer's profitability and cash flow. Balancing the need to maintain adequate inventory levels to minimize carrying costs presents a complex challenge.
Manufacturers encounter various challenges when it comes to managing inventory carrying costs. Understanding these challenges is crucial for implementing effective strategies.
Let's explore some of the major challenges faced by manufacturers in managing inventory carrying costs:
Holding Costs: Holding costs encompass expenses associated with storing and maintaining inventory. These costs include warehousing expenses, such as rent, utilities, insurance, and security.
Additionally, costs related to handling, inventory tracking, and obsolescence or spoilage must be considered. Managing holding costs becomes particularly challenging when inventory levels are high or when the nature of the products requires specialized storage conditions.
Financing Costs: Financing costs are incurred when manufacturers need to finance their inventory through loans or lines of credit. The longer inventory is held, the more interest costs accumulate.
Manufacturers must carefully manage their cash flow to ensure they can meet their financial obligations and avoid excessive financing costs. Balancing the need for adequate inventory levels with the cost of financing presents a delicate challenge.
Risk of Obsolescence: In industries where products have a short shelf life or technological advancements are frequent, the risk of inventory obsolescence is high. Holding onto obsolete inventory ties up working capital and incurs storage costs without any potential for sales.
Managing the risk of obsolescence requires accurate demand forecasting, close monitoring of market trends, and proactive inventory management strategies.
Strategies for Managing Inventory Carrying Costs and Cash Flow
- Market Research and Customer Insights: Conducting market research and gathering customer insights provide valuable information about customer preferences, buying behavior, and anticipated demand. Surveys, focus groups, and customer feedback can help businesses gain a deeper understanding of their target market and make more accurate demand forecasts.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Approach: The JIT approach focuses on producing and delivering products just in time to meet customer demand. By closely coordinating production schedules with customer orders, businesses can minimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and improve cash flow. This approach requires efficient production processes, reliable suppliers, and effective communication across the supply chain.
- Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): VMI involves suppliers taking responsibility for managing inventory levels at customer locations. Suppliers monitor customer inventory levels and replenish stock as needed. VMI can help businesses reduce carrying costs by transferring some of the inventory management responsibilities to suppliers while ensuring product availability.
Addressing Stockouts and Backorders in Production
Stockouts and backorders pose significant challenges for the manufacturing industry. A stockout occurs when a company runs out of inventory for a particular product, while a backorder refers to a customer's order that cannot be fulfilled immediately due to insufficient stock.
These issues can lead to dissatisfied customers, missed sales opportunities, and damage to a company's reputation. Addressing stockouts and backorders is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction, optimizing production processes, and maximizing revenue.
The manufacturing industry faces several challenges when it comes to addressing stockouts and backorders. Understanding these challenges is essential for implementing effective strategies.
Let's explore some of the major challenges faced by manufacturers in addressing stockouts and backorders:
Supply Chain Complexity: The manufacturing industry often involves complex supply chains with multiple suppliers, production facilities, and distribution channels.
Supply chain disruptions, delays in raw material deliveries, or production issues can lead to stockouts and backorders. Lack of visibility and coordination across the supply chain can make it challenging to address these issues promptly.
Production Lead Times: Manufacturing processes often require lead times to produce and deliver products. Long production lead times can increase the likelihood of stockouts and backorders if demand exceeds production capacity or if unexpected changes occur during the lead time.
Balancing production lead times with customer demand requires careful planning and coordination.
Inventory Management and Fulfillment Challenges: Inefficient inventory management practices, such as inaccurate tracking, inadequate storage capacity, or poor order fulfillment processes, can contribute to stockouts and backorders.
Lack of real-time inventory visibility and ineffective communication between production, warehousing, and sales teams can hinder the ability to address stockouts and backorders promptly.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction and Reputation: Stockouts and backorders can result in dissatisfied customers who may seek alternative suppliers or share negative experiences, impacting a company's reputation.
Building and maintaining customer trust is crucial for long-term success. Addressing stockouts and backorders effectively is essential to ensure customer satisfaction and preserve a positive brand image.
While addressing stockouts and backorders in the manufacturing industry can be challenging, several strategies can help mitigate these challenges. Implementing these strategies can improve customer satisfaction, optimize production processes, and maximize revenue.
Let's explore some of these strategies:
- Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning: Leveraging advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning algorithms, can improve demand forecasting accuracy. These algorithms can analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and capture complex demand relationships that may not be evident through traditional forecasting methods.
- Safety Stock: Safety stock is a buffer inventory held to mitigate the risk of stockouts due to unforeseen demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions. By setting appropriate safety stock levels based on historical demand variability and lead time variability, businesses can ensure a sufficient inventory buffer to address unexpected events.
- Supplier Collaboration: Collaborating closely with suppliers can help businesses address potential supply constraints and reduce lead times. Sharing demand forecasts, production plans, and inventory data with suppliers allows them to align their production and delivery schedules, minimizing the risk of stockouts.
Optimizing Inventory Storage and Warehouse Space Utilization
The manufacturing industry encounters several challenges when it comes to optimizing inventory storage and warehouse space utilization. Understanding these challenges is crucial for implementing effective strategies. Let's explore some of the major challenges faced by manufacturers:
- Limited Warehouse Space: Many manufacturing facilities have limited warehouse space, which restricts the amount of inventory that can be stored. Maximizing storage capacity while maintaining accessibility can be a delicate balance.
- Varying Product Sizes and Characteristics: Manufacturers often deal with products of various sizes, shapes, and characteristics. Some products may be bulky, while others may be fragile or require specific storage conditions. Accommodating the diverse requirements of different products can pose challenges in efficiently utilizing warehouse space.
- Inefficient Storage Systems: Outdated or inefficient storage systems can hinder effective space utilization. Inadequate shelving, improper racking configurations, or inefficient material handling equipment can lead to wasted space and inefficient workflows.
- Inventory Visibility and Accessibility: Maintaining visibility and easy accessibility to inventory is crucial for efficient warehouse operations. Poor inventory tracking systems or disorganized storage layouts can result in wasted time, increased labor costs, and difficulty locating and retrieving inventory.
To overcome the challenges associated with optimizing inventory storage and warehouse space utilization, manufacturers can implement several strategies. By adopting these strategies, businesses can enhance their warehouse operations, increase storage capacity, and improve overall efficiency.
Let's explore some of these strategies:
- Slotting Analysis: Conducting a slotting analysis helps determine the most suitable storage locations for different products based on their characteristics and demand frequency. By placing fast-moving items closer to the shipping area and grouping similar products together, businesses can minimize travel distances, reduce picking times, and optimize space utilization.
- Vertical Space Utilization: Leveraging vertical space by installing taller racks or mezzanine floors can significantly increase storage capacity. However, careful consideration should be given to accessibility, equipment capabilities, and safety requirements.
- Aisles and Path Optimization: Optimizing aisle widths and layouts based on the types of equipment used can improve flow and maximize storage capacity. Narrower aisles or alternative storage methods such as high-density storage systems (e.g., Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems) can help achieve efficient space utilization.
- Cross-Docking and Flow-Through Operations: Implementing cross-docking or flow-through operations can minimize storage requirements by directly transferring incoming products to outgoing shipments. This approach reduces the need for long-term storage and streamlines order fulfillment processes.
Implementing Efficient Inventory Counting and Tracking Methods
The manufacturing industry encounters several challenges when it comes to implementing efficient inventory counting and tracking methods. These challenges can hinder the accuracy and timeliness of inventory information, leading to inefficiencies and operational disruptions.
Let's explore some of the major challenges faced by manufacturers:
- Inefficient Manual Processes: Many manufacturing companies still rely on manual processes for inventory counting and tracking, such as spreadsheets or paper-based systems. These manual processes are prone to errors, time-consuming, and lack real-time visibility.
- Lack of Standardization: Inconsistencies in inventory counting methods and practices across different departments or locations can lead to discrepancies and inaccuracies. Without standardized processes, it becomes difficult to consolidate and reconcile inventory data effectively.
- Limited Technology Adoption: Some manufacturing companies may be hesitant to adopt modern inventory management technologies due to cost, complexity, or resistance to change. The lack of automated systems and advanced tracking technologies can hinder the efficiency and accuracy of inventory counting and tracking.
- Inadequate Training and Education: Lack of proper training and education regarding inventory counting and tracking processes can lead to inconsistencies and errors. It is important to invest in training programs to ensure that employees understand the importance of accurate inventory management and are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Accurate inventory counting and tracking are essential for several reasons:
- Demand Planning and Forecasting: Accurate inventory data serves as the foundation for demand planning and forecasting. It helps businesses understand customer preferences, identify trends, and make informed decisions about production levels, purchasing, and inventory replenishment.
- Cost Optimization: Effective inventory counting and tracking enable businesses to minimize carrying costs. By having accurate information about inventory levels, companies can avoid overstocking, prevent stockouts, and reduce storage and holding costs.
- Streamlined Production: Accurate inventory data is crucial for production planning and scheduling. It ensures that the necessary raw materials and components are available when needed, minimizing disruptions and delays in the manufacturing process.
- Customer Satisfaction: Efficient inventory management ensures that products are available to meet customer demand. Accurate inventory counts and tracking help prevent stockouts and backorders, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
There are various inventory counting methods that businesses can employ, depending on their specific needs and operational requirements. Let's explore some of the commonly used methods:
Periodic Inventory Counting
Periodic inventory counting involves conducting physical counts of inventory at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. During these counting periods, operations may be temporarily suspended, or specific areas of the warehouse may be closed off for counting purposes.
The physical counts are compared to the inventory records to identify discrepancies and adjust the inventory levels accordingly.
Benefits:
- Provides a snapshot of inventory levels at specific points in time.
- Allows for in-depth reconciliation of inventory records.
- Helps identify and address inaccuracies or discrepancies in inventory records.
Best Practices:
- Plan counting schedules well in advance to minimize disruptions to operations.
- Implement strict security measures to prevent unauthorized access or tampering during the counting process.
- Conduct spot checks throughout the counting period to validate accuracy.
Cycle Counting
Cycle counting involves regularly counting a subset of inventory items throughout the year. Unlike periodic counting, cycle counting is an ongoing process that focuses on specific items or categories based on their importance or value.
The frequency of cycle counting may vary depending on factors such as the item's criticality or historical accuracy.
Benefits:
- Provides continuous and regular monitoring of inventory accuracy.
- Allows for the identification and resolution of discrepancies in real time.
- Reduces the need for complete shutdowns or disruptions to operations.
Best Practices:
- Define a clear cycle counting plan based on the criticality and value of items.
- Rotate the items or categories to be counted to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Analyze root causes of discrepancies and implement corrective actions.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis categorizes inventory items based on their value or importance. A-items represent high-value items with a significant impact on revenue, B-items are moderate in value, and C-items have a lower value.
By conducting frequent counts on A-items and less frequent counts on B and C-items, businesses can allocate resources effectively and prioritize accuracy for high-value items.
RFID Technology
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology uses tags or labels with embedded chips to track and identify inventory items. RFID allows for real-time data capture, enabling accurate and automated inventory tracking. It eliminates the need for manual scanning and speeds up the counting process, making it suitable for businesses with large inventories.
Barcode Scanning
Barcode scanning is a widely used method for tracking inventory items. It involves assigning a unique barcode to each item and using barcode scanners to record their movements. The barcode scanners read the barcodes and automatically update the inventory database, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels.
Advantages:
- Speed and Accuracy: Barcode scanning speeds up the inventory tracking process, reduce human errors, and improves accuracy in data recording.
- Scalability: Barcode scanning can accommodate a large volume of inventory transactions, making it suitable for businesses with high SKU counts.
- Cost-Effective: Barcode scanners are relatively affordable, and barcode labels can be easily printed and applied to inventory items.
Streamlining Procurement Processes and Supplier Management
The procurement function plays a vital role in ensuring the availability of quality raw materials and components at the right time and cost, while supplier management focuses on building strong relationships and optimizing supplier performance.
However, the manufacturing industry faces unique challenges in streamlining procurement processes and supplier management due to factors such as complex supply chains, global sourcing, and changing market dynamics.
Streamlining procurement processes and supplier management offers several benefits to manufacturing businesses:
- Supply Chain Resilience: Streamlined procurement processes and supplier management contribute to a resilient supply chain. Proactive supplier management practices help identify and address potential risks, ensuring a reliable and uninterrupted supply of raw materials and components.
- Quality Assurance: Robust procurement processes and supplier management frameworks help maintain quality standards. Effective supplier qualification, evaluation, and monitoring ensure that only high-quality materials are used in the manufacturing process, resulting in superior products and customer satisfaction.
- Innovation and Collaboration: Streamlined procurement processes and supplier management foster innovation and collaboration with suppliers. Engaging suppliers in joint product development and sharing market insights can lead to new ideas, improved product designs, and increased competitiveness.
Organizations encounter various challenges when streamlining procurement processes and supplier management. Some common challenges include:
- Global Sourcing and Supplier Diversity: With the increasing globalization of supply chains, organizations source goods and services from multiple countries. Managing suppliers from different regions, cultures, and regulatory environments can be complex, necessitating a deep understanding of global markets and customs.
- Changing Market Dynamics: Organizations operate in dynamic markets with evolving customer demands and technological advancements. Adapting to changing market conditions, identifying new suppliers, and incorporating innovative procurement practices can be challenging but necessary to stay competitive.
- Data Management and Integration: Procurement processes generate vast amounts of data, including supplier information, pricing details, contracts, and performance metrics. Ensuring accurate data collection, storage, and integration with other systems is crucial for effective procurement and supplier management.
Overcoming Lead Time and Supplier Variability Challenges
Lead time refers to the time it takes for a supplier to deliver goods or services after receiving an order, while supplier variability refers to fluctuations in supplier performance and delivery reliability.
Delays in lead times and unpredictable supplier variability can result in production disruptions, increased costs, and dissatisfied customers. Therefore, manufacturing businesses need to develop strategies to overcome these challenges and ensure a consistent and reliable supply chain.
Lead time and supplier variability directly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the manufacturing supply chain. Here are some key reasons why these factors are significant:
Meeting Customer Demand: Lead time plays a crucial role in meeting customer demand. When lead times are long or unpredictable, it becomes challenging to deliver products to customers within the expected timeframe. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction, lost sales opportunities, and damage to the company's reputation.
Inventory Management: Lead time directly affects inventory management. Longer lead times require manufacturers to maintain higher inventory levels to meet customer demand, which ties up capital and increases carrying costs. Conversely, shorter lead times allow for leaner inventory levels, reducing costs and improving cash flow.
Production Planning and Scheduling: Accurate lead time estimation is essential for effective production planning and scheduling. When lead times are uncertain or variable, it becomes challenging to create realistic production schedules, resulting in inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs.
Supplier Performance Evaluation: Supplier variability impacts supplier performance evaluation. Inconsistent delivery times and quality issues can hinder production processes and affect overall performance metrics.
Understanding and managing supplier variability is crucial for maintaining strong supplier relationships and optimizing supplier performance.
Manufacturing businesses face several challenges when it comes to managing lead time and supplier variability. Some common challenges include:
- Lack of Visibility: Limited visibility into supplier processes and performance can make it difficult to accurately estimate lead times and assess supplier variability. Incomplete or outdated information about supplier capacities, production capabilities, and potential bottlenecks can lead to unexpected delays and disruptions.
- Unreliable Suppliers: Some suppliers may consistently deliver goods or services late or inconsistently, leading to disruptions in the supply chain. Unreliable suppliers can result in production delays, increased costs, and potential customer dissatisfaction.
- Inaccurate Lead Time Estimation: Estimating lead times accurately can be challenging, especially when suppliers have complex production processes or rely on multiple tiers of subcontractors. Inaccurate lead time estimation can lead to inventory imbalances, production bottlenecks, and missed delivery deadlines.
To overcome lead time and supplier variability challenges, manufacturing businesses can implement several strategies and best practices. These strategies focus on improving supply chain visibility, collaboration, risk management, and operational efficiency. Here are a few key strategies to consider:
Enhance Supply Chain Visibility
Improving supply chain visibility is crucial for managing lead times and supplier variability effectively. It involves obtaining real-time data on inventory levels, order status, and supplier performance.
Businesses can leverage technology, such as advanced analytics, supply chain management systems, and supplier portals, to capture and analyze data across the supply chain. This visibility enables proactive decision-making and helps identify bottlenecks or potential disruptions early on.
Foster Collaboration with Suppliers
Collaboration and communication with suppliers are essential for reducing lead times and minimizing supplier variability. Businesses can work closely with suppliers to align production schedules, share demand forecasts, and coordinate inventory management.
Building strong relationships based on trust and transparency can lead to better collaboration, reduced lead times, and improved supplier performance.
Implement Supplier Development Programs
Supplier development programs aim to enhance suppliers' capabilities and performance. By providing training, sharing best practices, and offering technical assistance, businesses can help suppliers improve their processes, quality control, and delivery reliability.
These programs foster a culture of continuous improvement and can result in reduced lead times, increased reliability, and better product quality.
Diversify the Supplier Base
Relying on a single supplier increases the risk of lead time and supplier variability challenges. By diversifying the supplier base, businesses can spread the risk and ensure a more stable supply chain.
This includes identifying alternative suppliers, conducting thorough supplier evaluations, and developing partnerships with multiple suppliers who can provide similar products or services.
Minimizing Excess and Obsolete Inventory Through Effective Strategies
Excess and obsolete inventory pose significant challenges for manufacturing businesses. Excess inventory refers to inventory levels that exceed current demand, while obsolete inventory refers to inventory that is no longer usable or saleable due to changes in product design, technology, or market demand.
Both types of inventory tie up working capital, occupy valuable storage space and can lead to financial losses.
The Impact of Excess and Obsolete Inventory
Excess and obsolete inventory can have severe consequences for manufacturing businesses:
- Financial Impact: Excess and obsolete inventory tie up working capital, leading to increased holding costs. This ties up funds that could be invested elsewhere in the business or used for other strategic initiatives. Additionally, obsolete inventory may have to be written off, resulting in direct financial losses.
- Storage Space Constraints: Excess and obsolete inventory occupy valuable warehouse space, limiting the capacity to store more essential items. This can lead to inefficiencies in the overall supply chain and additional costs for off-site storage solutions.
- Increased Carrying Costs: Maintaining excess and obsolete inventory incurs additional carrying costs, including insurance, taxes, and potential obsolescence write-downs. These costs erode profitability and reduce the overall efficiency of the business.
- Reduced Cash Flow: Excess and obsolete inventory represent tied-up working capital that could be used for other critical business activities, such as research and development, marketing, or investments in new equipment. Reducing excess and obsolete inventory improves cash flow and allows for more agile decision-making.
- Opportunity Cost: Excess and obsolete inventory prevent businesses from capitalizing on emerging market trends or product innovations. By reducing excess and obsolete inventory, manufacturers can allocate resources to more profitable and strategic initiatives.
Reducing the Risk of Stock Discrepancies and Data Inaccuracies
Stock discrepancies occur when there are inconsistencies between the physical inventory count and the recorded inventory levels, while data inaccuracies refer to errors or inconsistencies in inventory data. These issues can result in stockouts, overstocking, poor customer service, and financial losses.
Stock discrepancies and data inaccuracies can have several negative impacts on inventory management:
- Stockouts and Lost Sales: Inaccurate inventory data can lead to stockouts, where products are not available when customers demand them. This results in lost sales, dissatisfied customers, and potential damage to the company's reputation.
- Overstocking and Excess Inventory: On the other hand, data inaccuracies can also lead to overstocking, where businesses hold excessive inventory levels beyond what is necessary. This ties up working capital, increases carrying costs, and can lead to obsolescence or spoilage of products.
- Inefficient Replenishment: Stock discrepancies and data inaccuracies can disrupt the replenishment process. Without accurate data, businesses may struggle to place timely orders or make informed decisions regarding stock replenishment, leading to supply chain disruptions and inefficiencies.
- Inaccurate Financial Reporting: Inventory is a significant asset for many businesses, and accurate inventory valuation is crucial for financial reporting. Stock discrepancies and data inaccuracies can lead to an incorrect valuation of inventory, impacting financial statements, tax liabilities, and overall financial performance.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Inaccurate inventory data can result in inefficient warehouse operations. Employees may spend excessive time searching for misplaced items or dealing with discrepancies, leading to decreased productivity, increased labor costs, and potential fulfillment errors.
To overcome the challenges associated with stock discrepancies and data inaccuracies, manufacturing businesses can implement several strategies and best practices. These strategies focus on improving data accuracy, enhancing inventory management processes, and leveraging technology solutions.
- Adopt Barcode or RFID Technology: Implement barcode or radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology to automate data capture and reduce human error. Barcode scanning and RFID tagging enable accurate tracking of inventory items, improving data accuracy and minimizing discrepancies caused by manual data entry.
- Conduct Regular Cycle Counts: Performing regular cycle counts helps identify and rectify stock discrepancies promptly. By conducting smaller, frequent counts of specific inventory items, you can verify their accuracy and reconcile any discrepancies, ensuring the recorded data aligns with the actual stock levels.
- Implement Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and implement standardized processes and SOPs for inventory management. Clear guidelines on receiving, storage, picking, and data recording procedures reduce the likelihood of errors and discrepancies. Regular training and reinforcement of these procedures among staff members are crucial to maintaining consistency.
- Establish Effective Supplier Management Practices: Work closely with suppliers to improve data accuracy and reduce discrepancies caused by supplier variability. Establish clear communication channels, conduct regular performance evaluations, and collaborate on implementing electronic data interchange (EDI) systems for seamless data exchange. Supplier collaboration can help minimize errors in order quantities, delivery schedules, and product specifications.
Enhancing Communication and Collaboration Across Departments
Effective communication and collaboration are vital for the success of any organization, including the manufacturing industry. In manufacturing companies, multiple departments, such as production, procurement, sales, and logistics, must work together seamlessly to ensure smooth operations, efficient processes, and timely delivery of products.
However, challenges in communication and collaboration can hinder productivity, cause delays, and result in suboptimal outcomes.
In the manufacturing industry, effective communication and collaboration across departments have several key benefits:
- Streamlined Operations: When departments communicate and collaborate effectively, processes become streamlined, leading to improved efficiency and productivity. By sharing information and aligning their efforts, departments can work together to optimize workflows, reduce bottlenecks, and eliminate redundancies.
- Faster Decision-Making: Timely and effective communication facilitates faster decision-making. When departments share information and insights, decision-makers can access the necessary data to make informed choices promptly. This leads to more agile and responsive operations, allowing manufacturing companies to adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
- Customer Satisfaction: Effective communication and collaboration enable a customer-centric approach. When departments work together seamlessly, they can respond quickly to customer inquiries, resolve issues promptly, and deliver products on time. This enhances customer satisfaction and fosters long-term relationships.
Despite the importance of communication and collaboration, manufacturing companies face several challenges in achieving effective cross-departmental communication:
- Siloed Mindsets and Lack of Alignment: Departments may develop siloed mindsets, focusing only on their specific objectives and failing to see the bigger picture. This lack of alignment hampers communication and collaboration, as departments may not understand or appreciate the impact of their actions on other areas of the organization.
- Communication Barriers: Communication barriers such as language barriers, hierarchical structures, and physical separation between departments can impede effective information sharing. Different departments may use technical jargon or have distinct communication styles, leading to misunderstandings and misinterpretations.
- Lack of Clear Roles and Responsibilities: When roles and responsibilities are unclear, it becomes challenging to establish effective collaboration across departments. Employees may not know whom to contact for specific information or actions, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
To overcome the challenges in communication and collaboration, manufacturing companies can implement several strategies and best practices. Here are a few key strategies to consider:
- Establish Clear Goals and Expectations
One of the first steps to enhancing communication and collaboration is to establish clear goals and expectations for your teams and departments. When everyone understands the overarching objectives and their individual roles in achieving them, it becomes easier to align efforts and work collaboratively towards a common goal.
Communicate these goals and expectations effectively by providing clear instructions, guidelines, and performance metrics. Encourage open dialogue and invite feedback from employees to ensure that everyone is on the same page. Regularly revisit and reinforce these goals to maintain focus and alignment.
- Foster a Culture of Open Communication
Creating a culture of open communication is vital for effective collaboration. Encourage employees to share their ideas, concerns, and feedback freely. Implement channels that facilitate open communication, such as regular team meetings, suggestion boxes, or digital platforms for collaboration and discussion.
Promote active listening and respect for diverse opinions. Encourage transparent communication by sharing information about organizational changes, updates, and challenges. By fostering an environment where individuals feel comfortable expressing themselves, you can stimulate innovation, problem-solving, and stronger collaboration.
- Utilize Technology for Seamless Communication
In today's digital age, technology plays a crucial role in enabling seamless communication and collaboration. Implementing tools such as project management software, team messaging apps, and video conferencing platforms can enhance communication and facilitate real-time collaboration, even when team members are geographically dispersed.
Choose technology that aligns with your organization's needs and provides features for document sharing, task management, and progress tracking. Train employees on how to effectively use these tools and ensure that they have access to reliable and up-to-date technology infrastructure.
- Encourage Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Break down silos and encourage collaboration across departments. Create opportunities for employees from different teams to work together on cross-functional projects or initiatives. This can be done through interdepartmental workshops, task forces, or rotating team members across departments for short periods.
Encourage knowledge sharing and cross-training to broaden employees' understanding of the organization as a whole. Foster a spirit of cooperation and collaboration by recognizing and rewarding individuals and teams that actively contribute to cross-departmental initiatives.
- Provide Training and Development Opportunities
Investing in employee training and development can significantly enhance communication and collaboration within your organization. Offer workshops, seminars, or courses that focus on improving interpersonal skills, effective communication techniques, conflict resolution, and team building.
Leadership development programs can equip managers and team leaders with the skills needed to facilitate communication and collaboration within their teams. Encourage employees to attend industry conferences or networking events to expand their professional networks and gain insights from external experts.
Leveraging Technology for Automated Inventory Control Systems
Traditional inventory control methods are often time-consuming and prone to errors, leading to inefficiencies and financial losses. However, leveraging technology for automated inventory control systems can address these challenges and revolutionize inventory management in the manufacturing industry.
Implementing automated inventory control systems in the manufacturing industry can pose several challenges:
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating automated inventory control systems with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) or warehouse management systems (WMS) can be complex. Ensuring seamless data flow and compatibility between systems requires careful planning and coordination.
- Data Accuracy and Reliability: To function effectively, automated systems rely on accurate and reliable data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to errors in inventory tracking, resulting in incorrect stock levels and poor decision-making. Ensuring data accuracy and integrity is crucial for the successful implementation of automated systems.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Manufacturing companies often deal with dynamic and fluctuating demands. Implementing an automated system that can scale and adapt to changing inventory needs is essential. The system should be flexible enough to handle different product lines, production processes, and supply chain variations.
Implementing automated inventory control systems in the manufacturing industry can be a complex and challenging process. However, with the right strategies, these challenges can be effectively overcome. Here are a few strategies to consider:
- Conduct a Thorough Needs Assessment and System Evaluation
Before implementing an automated inventory control system, it is crucial to conduct a thorough needs assessment and system evaluation. This involves analyzing your current inventory management processes, identifying pain points and inefficiencies, and defining your specific requirements.
Consider factors such as inventory volume, product complexity, supply chain dynamics, and data integration needs. By understanding your unique challenges and requirements, you can select a system that is best suited to address them.
- Prioritize Data Accuracy and Integration
Data accuracy and integration are critical for the success of an automated inventory control system. Ensure that your data is accurate, complete, and reliable before implementing the system. This may involve conducting data cleansing activities, improving data capture processes, and establishing data governance practices.
Additionally, focus on seamless integration between the automated system and your existing ERP or WMS. Robust integration ensures real-time data synchronization and minimizes the risk of data discrepancies.
- Invest in Employee Training and Change Management
Employee buy-in and proper training are essential for the successful implementation of an automated inventory control system. Employees need to understand the benefits of the new system and how it will improve their daily tasks and overall efficiency.
Provide comprehensive training programs that cover system functionality, data entry processes, and troubleshooting. Additionally, involve employees in the implementation process by seeking their feedback and addressing their concerns. Change management initiatives, such as communication plans and user support, can facilitate a smooth transition and increase user adoption.
- Start with a Pilot Project
Implementing an automated inventory control system across your entire organization in one go can be overwhelming and risky. Instead, consider starting with a pilot project in a specific department or product line.
This approach allows you to test the system's effectiveness, identify any issues or challenges early on, and make necessary adjustments before rolling it out on a larger scale. By starting small, you can mitigate risks and gain valuable insights that can inform the broader implementation plan.
- Collaborate with Experienced Vendors and Consultants
Engaging with experienced vendors and consultants can greatly support the successful implementation of an automated inventory control system. Look for vendors who specialize in inventory management solutions and have a proven track record in the manufacturing industry.
Collaborate with them to design a tailored system, implement best practices, and address specific challenges. These experts can provide valuable insights, guidance, and ongoing support throughout the implementation process, increasing the chances of a successful outcome.
Implementing Effective ABC and XYZ Inventory Classification Methods
One of the key challenges in inventory management is classifying inventory items appropriately to prioritize resources and optimize operations. Two widely used inventory classification methods are ABC analysis and XYZ analysis.
ABC and XYZ inventory classification methods provide valuable insights into the inventory value, usage, and importance, allowing companies to allocate resources efficiently. Here's a brief overview of each method:
- ABC Analysis: ABC analysis categorizes inventory items into three categories based on their value and contribution to overall inventory costs. Category A includes high-value items that contribute to a significant portion of total inventory costs. Category B consists of medium-value items, and Category C includes low-value items that contribute to a minimal portion of inventory costs. By categorizing items based on their value, companies can prioritize resources, such as inventory control efforts, procurement decisions, and demand forecasting.
- XYZ Analysis: XYZ analysis classifies inventory items based on their demand variability. Category X items have high demand variability and are often unpredictable. Category Y items have moderate demand variability, and Category Z items have stable and predictable demand. By classifying items based on demand variability, companies can apply different inventory management strategies for each category. This helps in optimizing inventory levels, reducing stockouts, and minimizing excess inventory.
Implementing ABC and XYZ inventory classification methods in the manufacturing industry can pose several challenges:
- Classification Criteria and Thresholds: Establishing appropriate classification criteria and thresholds can be a challenge. Determining the cutoff values for categorizing items as high, medium, or low value (in ABC analysis) or high, medium, or low demand variability (in XYZ analysis) requires careful consideration. Companies need to analyze historical data, consider business objectives, and make informed decisions regarding classification criteria and thresholds.
- Continuous Monitoring and Updating: Inventory classification is not a one-time activity. It requires continuous monitoring and updating as market conditions, demand patterns, and business priorities change. Many companies struggle with maintaining the accuracy and relevance of inventory classifications over time. Establishing robust processes for monitoring and updating classifications is necessary to ensure their effectiveness and relevance.
- Employee Understanding and Adoption: Implementing inventory classification methods requires employee understanding and adoption. Employees involved in inventory management, procurement, and supply chain functions need to understand the rationale behind the classification methods and how to apply them effectively. Providing training and education programs to employees, coupled with effective change management initiatives, can facilitate understanding and encourage the adoption of classification methods.
Here are a few strategies to consider:
- Ensure Data Accuracy and Availability
To implement ABC and XYZ inventory classification methods successfully, it is crucial to ensure the accuracy and availability of data. Establish robust data collection processes and invest in data cleansing activities to improve data quality. Implement systems that capture data in real-time to ensure up-to-date information for classification.
Additionally, integrate data from various sources, such as ERP systems, WMS systems, and sales databases, to obtain a comprehensive view of inventory and demand patterns.
- Define Clear Classification Criteria and Thresholds
Defining clear and consistent classification criteria and thresholds is essential for accurate inventory classification. Analyze historical data to understand the distribution of values or demand variability and establish appropriate cutoff points for each category.
Involve key stakeholders in the decision-making process to ensure alignment with business objectives. Document the criteria and thresholds in a clear and accessible manner to provide guidance to employees involved in the classification process.
Managing Seasonality and Demand Fluctuations in Inventory Control
Seasonality refers to the predictable patterns of demand variation that occur at certain times of the year, such as holidays or specific seasons. Demand fluctuations, on the other hand, can occur due to various factors such as market trends, economic conditions, or unexpected events.
Seasonality and demand fluctuations significantly impact inventory control in the manufacturing industry. Here's a brief overview of each:
- Seasonality: Many industries experience seasonal demand patterns, where the demand for certain products or services increases or decreases at specific times of the year. For example, retailers may see increased demand for holiday-related products during the festive season. Managing seasonality involves accurately forecasting demand during peak seasons and ensuring sufficient inventory levels to meet customer demand without excess inventory during slower periods.
- Demand Fluctuations: Demand fluctuations can occur due to various factors such as changing market trends, economic conditions, or unexpected events. These fluctuations can be unpredictable and require agile inventory control strategies. Manufacturers need to be prepared to adjust inventory levels quickly to meet increased demand or scale back during periods of decreased demand.
To effectively manage seasonality and demand fluctuations in inventory control, manufacturing companies can employ the following strategies:
- Inventory Optimization: Optimize inventory levels to strike the right balance between meeting customer demand during peak seasons and minimizing excess inventory during slower periods. Utilize inventory management techniques such as safety stock levels, economic order quantity (EOQ), and reorder points to maintain optimal inventory levels. Leverage demand planning software and inventory management systems to monitor and track inventory levels in real time and make data-driven decisions.
- Promotions and Marketing Strategies: Develop targeted promotions and marketing strategies to leverage seasonal demand peaks and stimulate demand during slower periods. Offer discounts, bundle deals, or limited-time promotions during peak seasons to capitalize on increased customer demand. Implement marketing campaigns and customer engagement initiatives to generate demand during slower periods and maintain a consistent flow of sales.
Implementing Continuous Improvement Initiatives in Inventory Management
In today's competitive business landscape, manufacturing companies face the challenge of continuously improving their inventory management practices to drive operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Continuous improvement initiatives in inventory management can face various challenges in the manufacturing industry. Understanding these challenges is essential for organizations to develop appropriate strategies to overcome them. Here are some common challenges:
Organizational Silos: Inventory management involves multiple departments and stakeholders within an organization. However, organizational silos can hinder effective collaboration and communication.
Different departments may have conflicting priorities or may not share information and insights, leading to suboptimal inventory management practices. Breaking down silos through cross-functional collaboration, shared goals, and effective communication channels is essential for successful continuous improvement initiatives.
Lack of Metrics and Performance Measurement: Without appropriate metrics and performance measurement systems in place, organizations struggle to evaluate the effectiveness of their inventory management practices. A lack of clear performance indicators and targets can make it challenging to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Implementing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to inventory turnover, stock accuracy, order fulfillment rates, and customer satisfaction is crucial for measuring performance and identifying improvement opportunities.
To overcome the challenges of implementing continuous improvement initiatives in inventory management, manufacturing companies can adopt the following strategies:
Create a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Establishing a culture of continuous improvement is crucial for the success of any initiative. This involves fostering a mindset of seeking improvement in all aspects of the organization's operations.
Encourage employees at all levels to actively participate in identifying areas for improvement and providing suggestions. Develop a system for recognizing and rewarding employees' contributions to continuous improvement efforts.
Provide Training and Development: Invest in training and development programs to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to drive continuous improvement.
Offer training on lean methodologies, problem-solving techniques, data analysis, and project management. This will empower employees to identify process inefficiencies, implement improvement initiatives, and sustain the gains over time.
Use Lean Principles and Tools: Lean principles and tools provide a systematic approach to process improvement. Implement lean methodologies such as value stream mapping, 5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), and Kaizen events to identify and eliminate waste, streamline processes, and improve efficiency.
Use tools such as Kanban boards, visual management, and standardized work procedures to enhance transparency and enable continuous improvement.
Implement a Robust Measurement System: Establish a robust measurement system to track the progress of continuous improvement initiatives. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the organization's goals and objectives.
Regularly collect and analyze data to measure performance, identify areas for improvement, and monitor the impact of implemented changes. Use visual dashboards and reports to communicate performance metrics and progress to all stakeholders.
Future Trends: Innovative Solutions for Inventory Control in Manufacturing
Internet of Things (IoT) and Real-time Data Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way manufacturers manage their inventory. By connecting physical objects to the internet, manufacturers can gather real-time data on various inventory-related parameters, such as stock levels, location, condition, and usage. This enables organizations to have complete visibility and control over their inventory, leading to improved accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making.
IoT devices, such as RFID tags, sensors, and smart shelves, can automatically capture and transmit data, eliminating the need for manual data entry. Integrating this real-time data with inventory management systems allows manufacturers to track inventory movements, monitor stock levels, and proactively address issues such as stockouts, overstocking, and the expiration of perishable goods.
Real-time data integration enables organizations to make informed decisions, optimize inventory levels, and enhance supply chain collaboration.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are revolutionizing inventory control in manufacturing. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate actionable insights to optimize inventory management practices. AI-powered algorithms can forecast demand, identify optimal reorder points, and automate replenishment processes, minimizing stockouts and excess inventory.
Machine learning algorithms can also detect anomalies and predict demand fluctuations based on historical data, market trends, and external factors. This allows organizations to adjust inventory levels and production schedules accordingly, ensuring efficient utilization of resources and reducing inventory holding costs.
AI and ML enable organizations to make data-driven decisions, improve forecast accuracy, and enhance overall supply chain performance.
Blockchain Technology for Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in the manufacturing industry, offering enhanced transparency and traceability in inventory control. Blockchain is a decentralized and immutable ledger that records transactions transparently and securely.
By implementing blockchain in inventory management, manufacturers can ensure the authenticity and integrity of inventory-related data, minimizing the risk of counterfeit products and unauthorized changes.
Blockchain technology enables end-to-end visibility of the supply chain, allowing manufacturers to track the movement of goods from suppliers to customers. This transparency enhances trust among stakeholders and facilitates quick identification and resolution of issues such as product recalls, quality control, and compliance violations.
Blockchain also enables the implementation of smart contracts, automating inventory-related transactions and streamlining processes.
Robotics and Automation for Efficient Material Handling
Robotic systems and automation technologies are increasingly being utilized in inventory control to streamline material handling processes. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic arms can handle repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, such as picking, packing, and moving inventory.
These systems can operate 24/7, improving efficiency, reducing errors, and enhancing safety in warehouse operations.
With the integration of advanced technologies like computer vision and machine learning, robots can identify and classify inventory items accurately, optimizing storage and retrieval processes. Collaborative robots, or cobots, can work alongside human operators, further enhancing productivity and flexibility in inventory control.
The use of robotics and automation reduces operational costs, minimizes human error, and enables organizations to adapt to changing demand patterns effectively.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting
Predictive analytics and forecasting techniques are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling manufacturers to anticipate demand patterns, optimize inventory levels, and minimize stockouts or overstocking. Advanced analytics models can analyze historical data, market trends, social media sentiment, and external factors to provide accurate demand forecasts.
This empowers manufacturers to align production and inventory levels with anticipated demand, improving customer satisfaction and reducing holding costs. Predictive analytics can also identify seasonality trends, identify potential supply chain disruptions, and enable proactive mitigation strategies, ensuring a smooth and efficient inventory control process.
Cloud-Based Inventory Management Systems
Cloud-based inventory management systems offer flexibility, scalability, and real-time access to data, revolutionizing the way manufacturers manage their inventory.
With cloud-based systems, manufacturers can centralize inventory data, enable collaboration across departments and locations, and streamline inventory control processes. These systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, demand trends, and supplier performance, empowering manufacturers to make data-driven decisions.
How Deskera Can Assist You?
Deskera ERP and MRP system can help you:
- Manage production plans
- Maintain Bill of Materials
- Generate detailed reports
- Create a custom dashboard
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive system that allows you to maintain inventory, manage suppliers, and track supply chain activity in real-time, as well as streamline a variety of other corporate operations.
Deskera MRP allows you to closely monitor the manufacturing process. From the bill of materials to the production planning features, the solution helps you stay on top of your game and keep your company's competitive edge.
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology not only speeds up payroll processing but also allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more. This is your chance to grow your business, increase earnings, and improve the efficiency of the entire production process.
Conclusion
Effective inventory control is a crucial aspect of successful manufacturing operations. However, the manufacturing industry often faces numerous challenges when it comes to inventory management. This article has explored some of the common inventory control challenges faced by manufacturers and provided strategies to overcome them.
The article also highlighted the challenge of poor inventory visibility. By implementing advanced inventory management systems that provide real-time insights into inventory levels, locations, and movement, manufacturers can gain better visibility and control over their inventory, leading to improved decision-making and operational efficiency.
We also explored the challenge of supply chain complexity. By establishing strong relationships with suppliers, implementing collaborative planning processes, and embracing technology-driven supply chain solutions, manufacturers can overcome the complexities of their supply chains and ensure a smooth flow of materials and components.
Additionally, we explored the challenge of warehouse organization and layout. By adopting efficient warehouse design principles, optimizing storage space utilization, and leveraging technology solutions such as barcode scanning and RFID tracking, manufacturers can enhance their warehouse operations and improve inventory control.
Overcoming common inventory control challenges requires a combination of proactive strategies, effective use of technology, and continuous process improvement.
By addressing these challenges head-on, manufacturers can improve their inventory control processes, optimize their supply chain, reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in the market. Manufacturers must prioritize inventory control and invest in the right tools and practices to overcome these challenges and achieve efficient and effective inventory management.
Key Takeaways
- Accurate demand forecasting is crucial to overcome inventory control challenges in the manufacturing industry.
- Implementing real-time inventory tracking systems helps to prevent stockouts and overstocking.
- Streamlined order management processes enhance order accuracy and reduce lead times.
- Improved inventory visibility leads to better decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Effective inventory optimization strategies minimize carrying costs and optimize working capital.
- Strong supplier relationships and collaborative planning processes address supply chain complexity.
- Proactive inventory assessment and disposition techniques mitigate the impact of obsolete inventory.
- Robust data management practices ensure data accuracy and integrity for inventory control.
- Efficient warehouse design principles and technology solutions improve warehouse operations.
- Adopting automation and digitization reduces manual errors and improves inventory control accuracy.
Related Articles