According to the US Census Bureau, fertilizer manufacturing in the US is a $30 billion industry. In 2018, the industry employed more than 20,000 people and generated $34.1 billion in revenue. The fertilizer manufacturing industry is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7 percent from 2020 to 2025.
The market size is projected to reach $42.7 billion by 2025.
The key factors driving the market's growth include increasing demand for fertilizers in agricultural activities and rising demand for organic fertilizers.

The use of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) for fertilizer manufacturing is an essential component of any modern fertilizer manufacturing operation. MRP is a computer-based system that helps to manage the production planning process and is used to optimize inventory levels and maximize production efficiency.
This article will discuss the benefits of utilizing MRP in fertilizer manufacturing and the features of an MRP system. Additionally, it will provide an overview of the different elements of MRP and how they can be used to improve the efficiency of fertilizer manufacturing processes.
Here’s what we shall capture in this post:
- What is Fertilizer Manufacturing?
- Overview of the Fertilizer Manufacturing Process
- What is Materials Requirement Planning (MRP)?
- Features of MRP Software
- Types of Fertilizers
- MRP System Requirements for Fertilizer Manufacturing Sector
- What are the Challenges in Fertilizer Manufacturing?
- Benefits of MRP Software for Fertilizer Manufacturing
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
What is Fertilizer Manufacturing?
Fertilizer manufacturing is a process used to produce fertilizers from raw materials.
Fertilizers are essential for plant growth, providing essential nutrients for plant growth, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Fertilizers increase crop yields, improve soil fertility, and reduce the need for irrigation.
Fertilizer manufacturing typically begins with the extraction of raw materials, such as phosphate rock, sulfur, and ammonia. The raw materials are then processed to create the fertilizer. This involves mixing the materials, heating them, and treating them with chemicals to create the desired fertilizer.
Once the fertilizer is created, it is tested for quality and purity before being packaged for sale. It is then shipped to customers for use in agricultural operations. The fertilizer manufacturing process is highly regulated to ensure that fertilizers are safe.
Fertilizers must meet specific standards for purity and efficacy. Manufacturers must also adhere to specific environmental regulations to ensure the safety of their products. Fertilizer manufacturing can be a complex and costly process, but it is essential for providing farmers with the necessary nutrients to grow their crops. It is important to ensure that the fertilizer is of high quality and safe for use, as this will help ensure that crops are healthy and productive.
Overview of the Fertilizer Manufacturing Process
Fertilizers' key components are nutrients that are essential for plant growth. Nitrogen is used by plants in the creation of proteins, nucleic acids, and hormones. Reduced growth and yellowing of leaves are symptoms of nitrogen deficiency in plants.
Potassium is another important element that plants obtain from the soil. It is essential for protein synthesis and other plant activities.
Plants also require phosphorus, which is found in nucleic acids, phospholipids, and a variety of proteins. Plant growth is slowed when there is insufficient phosphorus. It is also important to supply energy to power metabolic chemical reactions. Yellowing, dead tissue patches, and weak stems and roots are all signs of potassium deficiency in plants.

Calcium, magnesium, and sulfur are other crucial plant growth components. They are only found in trace levels in fertilizers since most soils have enough amounts of these components. Other elements are required in modest amounts for plant growth.
Iron, chlorine, copper, manganese, zinc, molybdenum, and boron are examples of micronutrients that predominantly serve as cofactors in enzyme reactions. While present in small amounts, these chemicals are vital to plant growth; without them, plants will perish.
The fertilizer manufacturing process can be summarized through the following steps:
- Raw materials such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other minerals are collected.
- The raw materials are mixed and blended together.
- The blended materials are heated and processed to form a homogenous mixture.
- The homogenous mixture is cooled and dried.
- The dried mixture is ground into a powder.
- The powder is compressed into pellets or granules.
- The pellets or granules are tested for quality control.
- The fertilizer is packaged and shipped to customers.
History of Fertilizer Manufacturing
Fertilizer manufacturing is a process that has been around for centuries. Throughout the centuries, various other methods have been used to make fertilizer. In the 19th century, scientists discovered that nitrogen and phosphorus were essential nutrients for healthy crop growth, and they began to experiment with creating more effective fertilizers.
Early 1800s
The first modern fertilizer was created by German scientist Justus von Liebig in 1840. He developed a process to extract nitrogen from the air and combine it with phosphorus and potassium to create a new fertilizer. This process was later adapted by the British, who began to manufacture fertilizers on a large scale.
Early 20th Century
By the early 20th century, fertilizer production had greatly improved. Scientists were able to make fertilizer from ammonia, which could be extracted from natural gas. This process was known as the Haber-Bosch process and allowed for higher yields of fertilizer. Scientists also began to use chemical processes to create synthetic fertilizers. These fertilizers were cheaper than traditional fertilizers and could be used to increase crop yields.
Late 20th Century
In the late 20th century, scientists continued to improve upon fertilizer production. They developed processes to create more effective fertilizers with fewer environmental impacts. These processes included the use of organic materials such as manure and compost. Scientists also developed processes to create slow-release fertilizers, which could be applied to the soil and slowly release nutrients over time.
Fertilizer Manufacturing in Today’s Times
Today, fertilizer manufacturing is a highly advanced process. Scientists have developed various methods to create fertilizer, from organic materials to synthetic chemicals. Fertilizers are used in many industries, from agriculture to landscaping. They are vital to ensuring that crops get the nutrients they need to grow and thrive.
Importance of Raw Materials in Fertilizer Manufacturing
Fertilizer manufacturing is a process of combining various raw materials together to create a fertilizer product that can be used to increase crop yields and enhance the quality of fruits and vegetables.
- Raw materials used in fertilizer production can range from organic compounds such as manure and compost to synthetic compounds like urea and ammonium nitrate. The use of raw materials in fertilizer manufacturing is important for a variety of reasons.
- First, raw materials are essential for the production of quality fertilizer products. Different raw materials contain different nutrients and other substances that may be beneficial for crop growth. For example, manure and compost contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for healthy plants.
- Organic matter also improves soil structure, increasing the soil’s ability to retain water and other nutrients.
- Synthetic compounds such as urea and ammonium nitrate also provide nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth.
- Second, raw materials are important for the production of safe and effective fertilizer products. Synthetic compounds such as urea and ammonium nitrate must be carefully handled and stored in order to avoid potential contamination.
- Third, raw materials are essential for ensuring the cost-effectiveness of fertilizer production.
- Different raw materials have different costs associated with them, so manufacturers must choose the most cost-effective raw material for their needs. For example, manure and compost are generally more expensive than synthetic compounds like urea and ammonium nitrate, but they may be more cost-effective in the long run due to their nutrient content.
- Finally, raw materials are essential for maintaining environmental sustainability in fertilizer production. Different raw materials have different environmental impacts, and manufacturers must take this into consideration when choosing the raw materials for their fertilizer production.
For example, synthetic compounds like urea and ammonium nitrate can be harmful to the environment if not properly managed, while organic materials such as manure and compost can be beneficial in terms of soil health and carbon sequestration.
In conclusion, raw materials are essential for the production of quality, safe, and cost-effective fertilizer products. Different raw materials have different characteristics and environmental impacts, so manufacturers must carefully consider the raw materials they use in their fertilizer production. By choosing the most appropriate raw materials, manufacturers can ensure their fertilizer products are both effective and environmentally sustainable.
The Manufacturing Process
Compound fertilizers are manufactured in fully integrated plants. The manufacturing method will differ from producer to producer depending on the exact content of the finished product.
Fertilizer manufacturing is a complex process that involves several different types of equipment and processes. The primary steps in the fertilizer manufacturing process include the following:
- Raw material preparation: This includes grinding, mixing, and screening the various raw materials that are used in the production of fertilizer. The raw materials are usually a combination of organic and inorganic materials such as manure, compost, minerals, and chemicals.
- Formulation: The formulation process is used to blend the raw materials together in the correct proportions in order to create the desired type of fertilizer. This step also involves adding any necessary additives or preservatives.
- Mixing: The formulated fertilizer is then mixed together in an industrial mixer in order to achieve a uniform product.
- Granulation: The fertilizer is then placed into a granulator, where it is heated and pressed into small pellets or granules.
- Drying: The granulated fertilizer is then placed into a dryer and heated to remove any excess moisture.
- Screening: The dry fertilizer is then passed through a series of screens in order to separate it into various particle sizes.
- Packaging: The screened fertilizer is then packed into bags or containers for sale. These are the primary steps in the fertilizer manufacturing process. Each step is important in order to create a high-quality product that is safe for use on crops.
What is Materials Requirement Planning (MRP)?
Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is a manufacturing planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. It is used to effectively plan, schedule, and control the supply of materials required for production.
MRP is used to ensure that materials are available when needed and in the right quantity.
- MRP is a system used to manage the supply of materials in a manufacturing process
- It is used to plan, schedule, and control the supply of materials for production.
- It helps to ensure that materials are available when needed and in the right quantity.
- It helps to reduce inventory costs by ensuring that materials are ordered only when needed.
- It helps to maximize production efficiency by optimizing the scheduling and sequencing of production activities.
- It helps to ensure that materials are delivered on time and in the right quantities. MRP can be a complex system to implement and maintain, but it can be a powerful tool for managing a manufacturing process.
It can help to reduce costs, improve production efficiency, and ensure that materials are available when needed. With the right implementation, MRP can be a valuable asset for any manufacturing process.
Objectives of the MRP
MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is a computerized system used to plan and schedule materials, components, and parts in a manufacturing environment. The objectives of MRP are as follows:
- To reduce inventory levels: By accurately predicting the quantity and timing of materials and components needed, MRP can help to reduce inventory levels and prevent overstocking.
- To improve customer service: MRP can help to meet customer demands more quickly by ensuring that components and materials are available when needed.
- To reduce costs: MRP can help to reduce costs by reducing inventory levels and ensuring the most efficient use of resources.
- To improve operational efficiency: MRP can help to improve operational efficiency by accurately predicting the materials and components needed for customer orders.
- To improve planning and scheduling: MRP can help to improve planning and scheduling by providing accurate and up-to-date information about materials, components, and parts.
- To improve communication: MRP can help to improve communication between departments by providing a comprehensive view of the manufacturing process.
Overall, MRP is an effective tool for optimizing inventory levels, improving customer service, reducing costs, and improving operational efficiency. It can help to improve communication between departments and ensure that materials, components, and parts are available when needed.
Features of MRP Software
The primary features of the MRP system are described as follows:
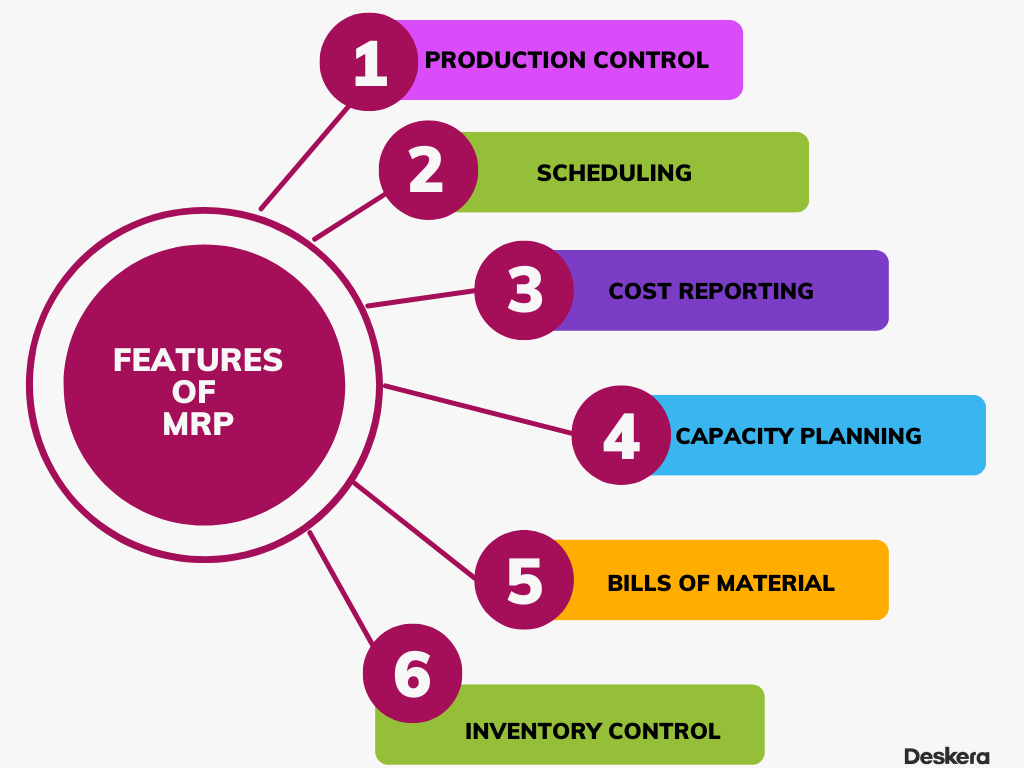
MRP software enables organizations to create and manage material plans, which helps them to balance the needs of their customers with their inventory levels.
Production Control
Production Control is a set of processes used to ensure that the production of goods and services meets customer demand. It includes planning, scheduling, and controlling the production of goods and services. It also includes forecasting, inventory management, quality control, warehousing, and cost control.
Scheduling
This is a feature of MRP software that is used to plan and manage the production of goods and services. It is used to determine when and how production resources should be allocated in order to meet customer delivery dates.
Scheduling allows companies to plan ahead, anticipate potential problems, and ensure that the production process runs smoothly. It also helps to ensure that the right resources are available at the right time to meet customer requirements.
Cost Reporting
Cost reporting is a feature of MRP software that enables the user to track and analyze the cost of materials, labor, and other expenses associated with manufacturing a product. This feature allows the user to identify areas where cost savings can be achieved, as well as monitor changes in costs over time.
Cost reporting also provides insight into areas where process improvements could be made, such as reducing manufacturing times or improving inventory control. Additionally, cost reporting can be used to analyze the profitability of different products or orders, helping organizations make more informed decisions about their product lines and operations.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is an essential part of MRP software. This feature is used to ensure that manufacturers have the capacity to meet customer demand and to ensure that the production process is optimized to maximize efficiency.
Capacity planning involves forecasting future demand, assessing current capacity, and determining the resources required to meet that demand. This is achieved by analyzing the production process and mapping out the production steps and the resources required for each step.
This allows manufacturers to identify any potential bottlenecks or areas for improvement. The capacity planning feature of MRP software allows manufacturers to monitor their resources in real-time and make adjustments as needed. By tracking labor and machine utilization, manufacturers can quickly identify when production is running behind schedule or when there is an excess of available capacity.
This further allows them to make changes to the production process in order to optimize efficiency. In addition, MRP software provides visibility into the entire supply chain, allowing manufacturers to track the progress of materials and components from suppliers to the factory floor. This helps to reduce the risk of disruption due to shortages of raw materials or components.
Finally, MRP software can be used to manage the inventory of finished goods. This ensures that the right amount of product is available to meet customer demand. By understanding the amount of finished goods inventory on hand, manufacturers can make adjustments to production schedules as needed.
Overall, capacity planning is an essential feature of MRP software. The right MRP software helps to increase efficiency and reduce the risk of disruption due to shortages.
Bill of Materials
BOMs are used in MRP software to help automate the ordering process. The software can track inventory levels and suggest when new parts need to be ordered. Additionally, it can track the progress of current orders and provide a timeline for when orders should be completed. The BOM feature of MRP software can also be used to help optimize production processes.
By tracking the inventory levels and components used, the software can suggest adjustments that can reduce costs and increase efficiency. Additionally, if there are any discrepancies between the BOM and the actual product, the software can alert the user and suggest corrections.
Finally, BOMs are also used to ensure the accuracy and completeness of orders. By having a detailed list of all the necessary components, the software can help to prevent any last-minute errors that may lead to delays or additional costs.
In summary, the Bill of Materials feature of MRP software is used to track materials, optimize production processes, and ensure the accuracy and completeness of orders. It is an essential component of MRP software and can help to streamline the ordering process and reduce costs.
Inventory Control
Inventory control is a key component of most MRP software systems. The purpose of inventory control is to ensure that materials, products, and supplies are available when needed and that stock levels are maintained in order to meet customer demand and support production schedules.
Inventory control within an MRP system starts with the identification of the materials and components that are needed for production. The software will track the quantity of each item, where it is stored, and the supplier from whom it was purchased. This information is used to generate purchase orders and keep track of inventory levels. The system will also track the cost of the items and calculate the average cost of the items over time.
When inventory levels reach a predetermined reorder point, the MRP software will generate a purchase order to replenish the stock. This helps to ensure that there is always an adequate level of inventory available to meet customer demand.
Inventory control also includes tracking the movement of materials within the facility. The software will track the movement of materials from the warehouse to the production line and from the production line to finished goods storage. This information is used to help ensure efficient material flow and that the right items are available when needed.
Inventory control also includes tracking inventory levels in the finished goods warehouse. The MRP software will track the quantity of each item in the warehouse and will generate reports on the total value of the inventory. This is used to monitor the cost of inventory items and to ensure that stock levels are appropriate.
Types of Fertilizers
There are various types of fertilizers based on their composition.
- Synthetic Fertilizers: Synthetic fertilizers are created in a laboratory and contain macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Organic Fertilizers: Organic fertilizers are natural fertilizers made from plant and animal byproducts, including compost, manure, and other waste products.
- Slow-Release Fertilizers: Slow-release fertilizers are designed to release their nutrients over an extended period of time, providing long-term nutrition for plants.
- Compost: Compost is a type of fertilizer made from decomposing organic matter, such as food scraps, leaves, and grass clippings.
- Liquid Fertilizers: Liquid fertilizers are a type of fertilizer that is applied as a liquid solution or spray.
- Biofertilizers: Biofertilizers are a type of fertilizer made from beneficial microbes that help plants absorb nutrients from the soil.
Let’s dwell a little deeper into the two main categories of fertilizers which are organic and synthetic.

Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are natural, organic materials that are used to add nutrients to the soil and help plants grow. Organic fertilizers can come from plant, animal, or mineral sources and can be broken down into organic matter over time.
- They are often less expensive than chemical fertilizers and help improve the soil by increasing soil microbial activity and adding beneficial organic matter.
- Organic fertilizers can also help reduce soil erosion, improve water infiltration, and increase the soil’s ability to hold water and nutrients.
- Organic fertilizers are often used in organic farming and gardening and can be applied in a variety of ways, including composting, mulching, top dressing, and liquid fertilizers.
Synthetic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers are man-made chemical compounds that are designed to be used as plant nutrients.
- They are a popular choice for gardeners and farmers due to their ability to provide plants with nutrients quickly and efficiently, as well as their relatively low cost compared to other types of fertilizers.
- However, synthetic fertilizers have been linked to a number of environmental issues, such as increased nutrient runoff into waterways and groundwater, as well as soil and water acidification.
- Therefore, it is important to use synthetic fertilizers responsibly, only when necessary. One must also be aware of their potential impacts on the environment.
MRP System Requirements for Fertilizer Manufacturing Sector
MRP System Requirements for a fertilizer manufacturing company can be enumerated as follows:
- User Management System: A system to manage users, roles, and permissions to ensure secure access to the system.
- Quality Control System: A system to monitor, manage, and audit quality control processes and procedures.
- Inventory Management System: A system to track and manage raw materials, finished goods, and other inventory items.
- Production Planning System: A system to plan and manage production operations and workflow.
- Bill of Materials (BoM) System: A system to generate and manage a bill of materials for each product.
- Procurement System: A system to manage the procurement of raw materials and other items required for production.
- Scheduling System: A system to schedule production runs and ensure timely delivery of finished products.
- Sales and Distribution System: A system to manage customer orders, shipments, and invoices.
- Financial Management System: A system to track and manage finances, including accounts receivable and payable.
- Reporting System: A system to generate reports on production, inventory, and financials.
Aside from these elements, the other essential components that form the foundational strength of a fertilizer company are the BoMs. Let’s see what they are.
Bill of Materials
The bill of materials (BOM) is an important document for a fertilizer manufacturer. It is a comprehensive list of the components, parts, and materials used to manufacture the fertilizer product. The BOM is used to track the materials used in the manufacturing process and ensure that all ingredients are accounted for. It also serves as a guide for inventory and production control, helping the manufacturer to ensure that sufficient quantities of each item are available when needed.
The BOM also provides a record of the costs associated with each component, allowing the manufacturer to accurately calculate the costs of production.
Typical Bill of Materials in the Case of a Fertilizer Manufacturer
A typical bill of materials for a fertilizer manufacturer would include the raw materials needed to produce the fertilizer, such as ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, urea, phosphate, potash, and any other ingredients required.
Additionally, it would also include any other components necessary to produce the product, such as bags, labels, and containers. The bill of materials would also list the specific quantities of each material or component needed to produce one batch of fertilizer.
The BoM may include the following:
Capacity Requirements
As a fertilizer manufacturer, there are multiple aspects you will need to be mindful of. This section highlights those requirements.
- Space Requirements
A fertilizer manufacturer needs to have a large space to accommodate the production equipment, storage of raw materials, and packaging of finished products.
The space requirements for a fertilizer manufacturer will depend on the type of fertilizer being produced. Generally speaking, a plant will need adequate space for the production and storage of raw materials, the production and packaging of finished products, and the disposal of waste products. Additionally, the space must meet local zoning and safety regulations.
2. Equipment Requirements
A fertilizer manufacturer needs to have the necessary equipment to mix, blend, and package the fertilizer. This includes mixers, blending equipment, and packaging machinery.
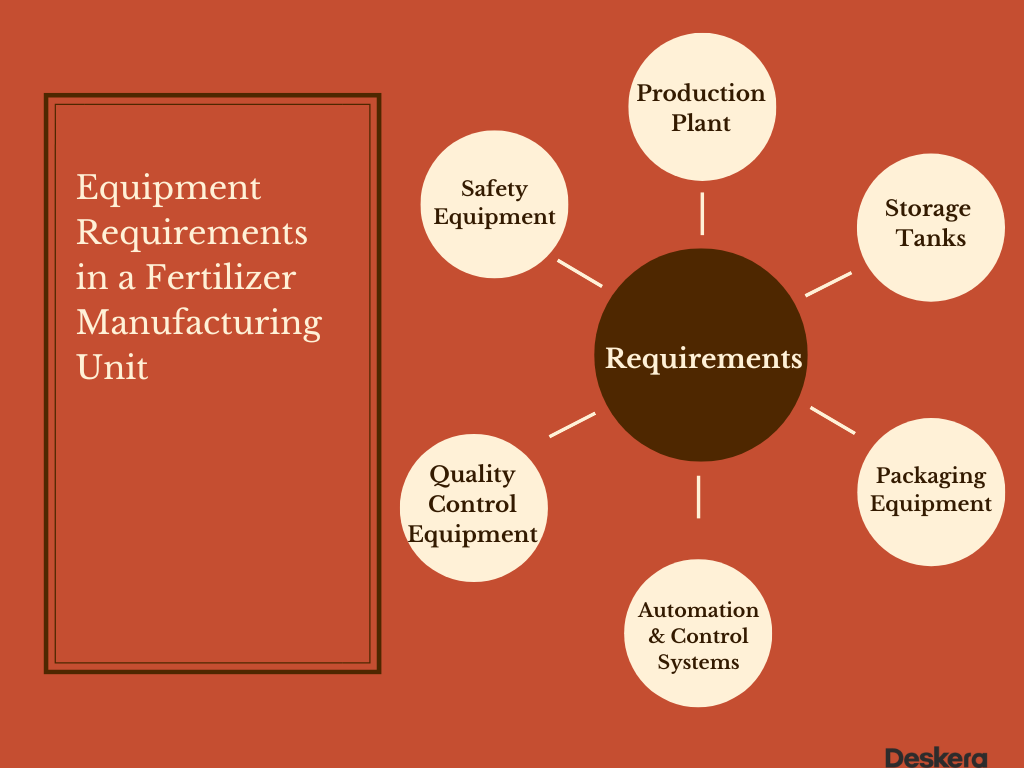
3. Personnel Requirements
A fertilizer manufacturer needs to have experienced personnel to operate the equipment and oversee the production process.
4. Raw Material Requirements
A fertilizer manufacturer needs access to the necessary raw materials, such as fertilizers, binders, and other ingredients.
5. Safety Requirements
A fertilizer manufacturer needs to have safety measures in place to protect personnel and products from potential hazards. This could include safety gear, personal protective equipment, ventilation systems, and other measures.
What are the Challenges in Fertilizer Manufacturing?
Fertilizer manufacturing can face a number of challenges, like any other sector. MRP can be instrumental in resolving most of these problems. These include the following:
Quality Control
This is a major challenge for fertilizer manufacturers. It is essential to ensure that the products meet the standards of the relevant regulatory bodies. It is a complex process that involves numerous steps and processes.
Ensure Safety Standards are Met
Quality control involves ensuring that fertilizer products meet safety, performance, and environmental standards, which can be difficult to achieve and maintain. Manufacturing fertilizer requires quality control to ensure that the products meet industry standards and are safe for use.
Standard Ingredients
Quality checks must be applied during the production process to ensure that all ingredients are of the highest quality. It also involves ensuring that the manufacturing process is efficient and that any issues that arise are quickly and effectively addressed. In addition, quality control must be applied to ensure that the fertilizer is not contaminated by any foreign substances, such as metals, insecticides, or herbicides.
Ensure no Contamination
Contamination of fertilizer can lead to health and environmental risks, making quality control a priority for fertilizer manufacturers. Finally, quality control must be applied to ensure that the fertilizer is properly labeled and that any instructions or warnings are accurately communicated to the user.
Ensure no Environmental Hazards
This is especially important regarding proper handling and storage of fertilizer, as improper handling can lead to safety and environmental risks.
In conclusion, quality control is a critical aspect of fertilizer manufacturing, and it can be a major challenge for fertilizer manufacturers. Quality control must also be applied to ensure that any instructions and warnings are accurately communicated to the user.
Cost Control
In order to remain competitive, fertilizer manufacturers must focus on reducing costs and improving efficiency. Cost control can be a challenge for fertilizer manufacturing companies due to the numerous factors involved in the production process.
Consider Market Volatility
Fertilizer production requires raw materials, labor, energy, and other inputs, all of which can be subject to price fluctuations and market volatility. Additionally, the manufacturing process itself can be complex and energy-intensive, resulting in high costs for production. The cost of raw materials is a major factor in cost control for fertilizer production. Prices for these materials can fluctuate depending on changes in global demand for fertilizer, as well as the availability of the materials themselves.
Electricity and Fuel Expense
The cost of energy inputs, such as electricity and fuel, can also fluctuate and be difficult to predict.
Wages and Salaries
Labor costs are another factor that can affect cost control in fertilizer production. Companies must balance their labor costs with the need to keep production costs low while still providing a safe working environment and paying a competitive wage.
Training Expenses
Additionally, companies must ensure that their labor force is properly trained and up to date on the latest technology and processes. The complexity of the production process can also pose a challenge to cost control. Fertilizer production often involves numerous steps, such as mixing, blending, and drying, that require significant resources and energy. Companies must ensure that their processes are efficient.
Market Volatility
Finally, market volatility and the cyclical nature of the fertilizer industry can make cost control difficult. Fertilizer prices can be influenced by global supply and demand, as well as weather conditions, making it difficult to predict future prices and costs.
In summary, cost control can be a challenge for fertilizer manufacturing companies due to the numerous factors involved in the production process. Companies must monitor and manage the costs of raw materials, labor, energy, and other inputs while ensuring that their processes are efficient and meet the necessary safety and quality standards.
Environmental Regulations
Fertilizer production often involves hazardous materials and activities, so meeting environmental regulations is a constant challenge. Environmental regulations can be a significant challenge for a fertilizer manufacturing company.
Keeping Soil Pollution in Check
Fertilizer production is a highly regulated industry, as the use of fertilizers can result in environmental damage, such as water and soil contamination, air pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. In order to comply with environmental regulations, a fertilizer manufacturing company must implement stringent safety measures, invest in pollution control technologies, and adhere to strict environmental standards.

Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
The most significant environmental regulations for a fertilizer manufacturing company include the Clean Air Act, Clean Water Act, and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. The Clean Air Act regulates air pollution from fertilizer production, such as the release of volatile organic compounds, and requires manufacturers to install pollution control equipment. The Clean Water Act regulates the discharge of pollutants from fertilizer production into bodies of water and requires manufacturers to obtain a National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System permit.
Local and Federal Regulations
In addition to the regulations outlined above, fertilizer manufacturing companies must also comply with a variety of local, state, and federal regulations. These regulations can be costly and time-consuming to comply with and can significantly increase the operating costs of a fertilizer manufacturing company.
Failure Penalties
Furthermore, failure to comply with environmental regulations can result in costly fines or other penalties. Overall, environmental regulations are a significant challenge for a fertilizer manufacturing company.
Companies must invest in pollution control technologies and adhere to a variety of stringent regulations in order to comply with environmental standards.
Supply Chain
Fertilizer manufacturers must have efficient supply chains in order to ensure the timely delivery of the products. Supply chain management is a challenge for fertilizer manufacturing companies because of the complexity and cost associated with managing the production and distribution of the product.
Have Reliable Suppliers
Fertilizer is typically produced in large quantities and requires specialized equipment and facilities to manufacture. This means that the company must have access to reliable suppliers of raw materials, as well as the ability to store and transport the product. Additionally, fertilizer is a highly regulated product and must meet certain standards in order to be sold legally.
Significant Costs associated with Supply Chain
The costs associated with the supply chain can be significant for fertilizer manufacturing companies. In addition to the costs of raw materials, the production process itself is expensive and requires a lot of energy and resources.
Storage Costs
Additionally, the company must invest in distribution networks and storage facilities in order to get the product to the customer. This can add up to high costs over time.
Transportations Charges
The transportation of fertilizer is also a challenge due to its hazardous nature. It is typically transported by truck but must be handled with care in order to prevent accidents and spills. This means that fertilizer companies must invest in specialized transportation and handling equipment in order to ensure the safe delivery of their product.
Market Fluctuations
Finally, fertilizer companies must be able to respond quickly to changing market conditions. As markets fluctuate, fertilizer companies must be able to adjust their production and distribution strategies in order to remain competitive. This requires a great deal of flexibility and agility in the supply chain.
Overall, managing the supply chain of a fertilizer manufacturing company can be a challenge due to the complexity and cost associated with production and distribution. Companies must have access to reliable suppliers, invest in specialized equipment, and be able to respond quickly to changing market conditions in order to remain competitive.
Increasing Competition
With the globalization of fertilizer markets and the emergence of new players, competition is increasing and putting pressure on companies to differentiate themselves and remain competitive.
Results in a Drop in Selling Price
Increasing competition can be a challenge for a fertilizer manufacturing company in many ways. For one, as competition increases, it is likely that prices will drop. This might lead to a decrease in profit margins and make it difficult for the company to remain competitive.
Higher Marketing and Advertising Costs
Furthermore, increased competition could lead to increased marketing and advertising costs. As other businesses invest in marketing campaigns to promote their products, the fertilizer manufacturing company will have to invest in similar efforts to keep up.
More Research and Development Required
As competition increases, the fertilizer manufacturing company will be forced to innovate and offer unique products and services in order to differentiate itself from the competition. This may involve investing in research and development, which could be costly. Moreover, the company may be at a disadvantage if it does not keep up with new technologies and trends.
Decrease in Customer Loyalty
Furthermore, increased competition could lead to a decrease in customer loyalty. As customers have more options to choose from, they may be inclined to switch to another company if they find a better deal elsewhere. This could lead to a loss of customers and a decrease in revenue for the company.
Lower Quality Products
Finally, increased competition could lead to a decrease in the quality of the products being produced. As companies try to cut corners in order to remain competitively priced, they may not be able to maintain the same standards of quality that they had prior to increased competition. This could lead to unhappy customers and a decrease in sales.
In conclusion, increased competition can be a challenge for a fertilizer manufacturing company in many ways. It can lead to decreased profit margins, increased marketing costs, product innovation, customer loyalty issues, and a decrease in quality. As such, it is important for companies to be prepared for increased competition and have strategies in place to remain competitive.
Other Common Challenges
Aside from these, there are other aspects that could pose challenges. These are:
- Difficulty sourcing raw materials and meeting regulatory requirements
- Inadequate access to technology and infrastructure
- Rising energy costs
- Environmental concerns and pollution
- Product quality control and safety issues
- Competition from substitute products
- Increasing consumer demand for sustainable fertilizers
- Limited access to capital and financing
Benefits of MRP Software for Fertilizer Manufacturing
Now that we have a fair idea of what an MRP system is, let’s look at the benefits for the fertilizer manufacturing sector.
Improved Inventory Management
The primary benefit of an MRP system is its ability to provide accurate inventory forecasting. The system uses data from past sales, current customer orders, and projected sales to create an accurate forecast of future demand. This helps businesses better manage their resources and reduce the risk of stock-outs.
With an MRP system, businesses can plan for and order exactly the right amount of inventory, which reduces costs associated with overstocking and dead stock. MRP software can help fertilizer manufacturing businesses improve their inventory management by providing real-time tracking of inventory levels and automating the process of ordering new supplies when needed. This can help reduce costs associated with overstocking and ensure that production is never delayed due to a lack of supplies.
MRP systems provide businesses with a means of effectively managing their inventory levels and streamlining their supply chain processes. In essence, an MRP system uses inventory data to forecast future demand and plan for production, procurement, and inventory levels.
Streamlined Production Planning
MRP software can also help fertilizer manufacturing businesses streamline production planning by providing a complete view of the entire production process. It allows businesses to easily keep track of production schedules, materials needed for production, and other important aspects of the production process.
Increased Efficiency
MRP software can also help improve efficiency in fertilizer manufacturing businesses by providing detailed reports and analyses. This can help businesses identify areas that are inefficient and take corrective action to improve them.
Better Quality Control
MRP software can also help fertilizer manufacturing businesses improve their quality control efforts by providing detailed information about the production process. This can help businesses identify areas where quality control can be improved and take corrective action accordingly.
Improved Tracking and Reporting
MRP software also makes it easier for fertilizer manufacturing businesses to track and report their production data. This can help businesses quickly identify problems and remedy them to ensure that production remains efficient and cost-effective.
Conclusion
The MRP system for fertilizer manufacturing provides a number of advantages over traditional production methods. It helps streamline the production process, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve product quality.
Additionally, the system allows for better forecasting and planning capabilities. This helps to reduce inventory costs, improve customer satisfaction, and provide a better understanding of the production process.
Overall, MRP for fertilizer manufacturing is a great tool for manufacturers to utilize. It can help increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Additionally, it provides better forecasting and planning capabilities and improves customer satisfaction. With all these benefits, it's no surprise that the MRP system has become an integral part of the fertilizer manufacturing process.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera provides an integrated suite of cloud-based ERP, CRM, and HRMS solutions that can help fertilizer manufacturing companies streamline their business processes and improve efficiency. It enables them to automate their financial, production, supply chain, and customer management operations while tracking their inventory, orders, and customer relationships.
Deskera MRP is the one tool that lets you do all of the above. With Deskera, you can:
- Track raw materials and finished goods inventory
- Manage production plans and routings
- Maintain bill of materials
- Generate detailed reports
- Create custom dashboards
Deskera Books is a simple cloud-based accounting and bookkeeping software that assists small and medium-sized businesses in better managing their money.
Deskera People is a comprehensive human resource management solution that assists you in managing your workforce and HR activities. Employee profiles, attendance tracking, payroll integration, performance reviews, leave management, and reporting are all included.
Deskera CRM is a customer relationship management (CRM) software that is cloud-based and meant to assist organizations to optimize their sales and customer management activities.
Key Takeaways
- Fertilizer manufacturing is a process used to produce fertilizers from raw materials.
- Fertilizer manufacturing typically begins with the extraction of raw materials, such as phosphate rock, sulfur, and ammonia. The raw materials are then processed to create the fertilizer.
- This involves mixing the materials, heating them, and treating them with chemicals to create the desired fertilizer.
- Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is a manufacturing planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. It is used to effectively plan, schedule, and control the supply of materials required for production.
- Reducing inventory levels, improving customer service, and improving operational efficiency are some of the key objectives of an MRP system.
- BoMs, cost reporting, capacity planning, and inventory control are some of the prime features of MRP.
- There are various MRP system requirements. These include user management system, quality control system, BoM system, and procurement system.
- Quality control, cost control, environmental regulations, and supply chain are some of the challenges faced commonly by the fertilizer manufacturing sector.
- The sector often struggles with increasing competition.
- An MRP can be helpful in improving inventory management, quality control, production planning, and tracking.
- Overall, MRP for fertilizer manufacturing is a great tool for manufacturers to utilize. It can help increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
Related Articles