Successful product manufacturing operations can only be conducted by companies with precise cycle times.
But what if it's impossible to gauge or track how long it will take to manufacture and package deliverables? Manufacturing procedures are never simple. Slow turnarounds could happen and seriously impact your bottom line.
Understanding your manufacturing cycle is the only way to stop slow production and turnaround times. The worldwide business environment in which modern manufacturing companies operate is tremendously competitive.

Cycle time is one of the KPIs in manufacturing since it shows exactly how much time and resources are being used to make each item. This makes it one of the most important KPIs in a production facility. Additionally, as all businesses are aware, time is money. This is particularly true in the manufacturing industry.
In this guide, we explain everything you need to know about the manufacturing cycle time, its benefits, and its calculation. Following are the topics covered:
- What is Manufacturing Cycle Time?
- How to Calculate Manufacturing Cycle Time?
- 6 Steps in Manufacturing Cycle
- Benefits of Tracking the Manufacturing Cycle
- Reducing Manufacturing Cycle Time
- What is Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency?
- Cycle Time Vs Throughput Time
- What Are the Challenges of Calculating Cycle Time?
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
What is Manufacturing Cycle Time?
Production companies use manufacturing cycle time as a significant performance measure. It describes the length of time it took to finish a product, starting with the raw materials and ending with the finished result.
- It is used to measure the total time needed to produce a product, the efficiency of the process and the productivity of the workers.
- Divide the net production time by the total number of items to get a different perspective on the production cycle time.
- The total amount of time needed to turn raw materials into completed goods is known as the manufacturing cycle time. This covers the time required for loading, machining, assembly, inspection, moving materials, and waiting.
- Manufacturing cycle time is composed of a number of different components, including setup time, machine running time, material handling time, and quality control time.
- Manufacturing cycle time is a key metric for measuring the success of a production process. It can be used to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Manufacturing cycle time is also used to determine the cost of production and can help in making decisions on pricing and production planning.
- Manufacturing cycle time is an important factor in determining the overall productivity of a manufacturing process and should be closely monitored and managed.
It is, in essence, the period of time between receiving the customer's purchase order and/or "Start Work" notification. Then rolling the product off the production line.
How to Calculate Manufacturing Cycle Time?
Cycle Time Formula
There are several ways to compute the cycle time formula in manufacturing. It may be used for a variety of processes inside a manufacturing plant. The term is used to describe the amount of time required to process an item without taking any support procedures.
The complete production process, includes load and unload time, application changeover time per piece, and processing time. This is referred to as the "effective cycle time."
Every measurement matters and a manufacturing company can track the time it takes to complete a cycle from start to finish. The Sum of value-added time (productive hours) and non-value-added time is the manufacturing cycle time (non-productive hours).
Manufacturing cycle time = Process time + Material movement time + Inspection time + Idle waiting time
Value-added hours = Process time + Inspection time
Non-value-added hours = Movement time + Queue time constitute
Process Time- This is the amount of time needed to work on turning raw materials into final goods. Process time can be reduced by redesigning products.
- The shorter the process time, the more efficient the process is and the more cost-effective it will be.
- It is important to identify the tasks that are part of the process, how long each task takes, and which tasks are dependent on each other. This will give a good understanding of the process and allow for accurate timing of the tasks.
- In order to track process time, manufacturers should consider using a production management system. This system can track the time taken to complete each task, and provide detailed reports on the overall performance of the process.
- By measuring and analyzing process time, manufacturers can identify areas of improvement and make adjustments to ensure the most efficient production possible.
Move Time- Move time in manufacturing is an important concept that can have a major impact on the efficiency and success of any manufacturing operation. It describes the amount of time it takes for a machine or process to move from one stage of production to the next.
The shorter the move time, the more efficient the process and the more profitable the operation. Here are a few key points to consider when looking at move time in manufacturing:
- Move time should be measured and monitored on an ongoing basis. Knowing how long it takes to move from one production stage to the next can help identify potential bottlenecks. This can also help identify areas where improvements can be made.
- By measuring move time, you can also identify staff who may need additional training to become more efficient.
- Proper planning is essential to reducing move time. All steps should be planned out in advance and all machines should be configured to optimize each step. This includes ensuring that machines are set up in the most efficient order. Any necessary tools or materials are readily available and that processes are well documented and understood.
- Automation can help to reduce move time by eliminating the need for manual labor. Automation can also help to reduce errors and improve consistency.
- Effective communication between staff and between machines will help to reduce move time. This includes ensuring that all staff are aware of the production schedule. Any issues or problems are communicated quickly and effectively.
Move time in manufacturing is an important concept that can have a major impact on the success of any manufacturing operation. By understanding the concept and taking steps to reduce move time, you can ensure that your operations are as efficient and profitable as possible.
Inspection Time- This is the amount of time needed to test a product to make sure it is free of flaws. There is no need for a separate inspection function. Inspections can be incorporated into the production process.
- Inspecting products during the manufacturing process can help to reduce the cost of rework and wastage, as well as improve customer satisfaction. It can also help to ensure that products comply with industry standards and regulations.
- There are two main types of inspections that can be performed during the manufacturing process: visual inspections and functional tests.
- Visual inspections involve looking at the product closely to check for any defects or irregularities.
- Functional tests involve testing the product to ensure that it meets the required specifications.
- The inspection process usually starts with a visual inspection of the product. This is done to check for any signs of defects or irregularities. Any defects or irregularities that are found are noted, and the product is then put through a functional test.
- Quality assurance is an important part of the inspection process. Quality assurance involves testing the product to ensure that it meets the required specifications and that any defects or irregularities are caught before the product is released to the customer.
Queue Time- Queue time is the amount of time spent waiting before any task starts.
- Queue time in manufacturing can be beneficial for a company. By utilizing queue time, the company can save on labor costs and reduce production time.
- Queue time also allows for better quality control and the ability to make adjustments to the production process as needed.
- There are various factors that can influence the amount of queue time in manufacturing. These include the size of the production run, the complexity of the product and the production process, the lead time of materials and components, and the availability of resources.
- Long queue times can lead to production bottlenecks and delays in shipping. They can also increase costs and decrease customer satisfaction.
- Companies can implement various strategies to reduce queue time. These include using automation, reducing the number of steps in the production process, and using lean manufacturing methods.
Accurately tracking all constituents at once is impossible. In order to determine cycle time, the number of pieces is multiplied by the run time needed to manufacture them.
Cycle Time = Total Parts Produced / Run Time
Example of Manufacturing Cycle Time
For instance, tracking an order's cycle time yields the following outcomes: Let's consider, 60 minutes of queue time plus 10 minutes of process time plus 4 minutes of move time plus 4 minutes of the inspection time. This equals a 78-minute production cycle time. Queue time typically accounts for the majority of all time spent during the manufacturing process.
As such, it is a great place to concentrate on time-reduction efforts. This is a non-value-added activity that has no bearing on the quality of the finished product.
6 Steps in Manufacturing Cycle
Any manufacturing process entails a number of processes. Companies need resources like money, labor, and machinery to make the goods they're producing. This blog post will go over the steps you need to do after coming up with an idea for a product you want to create. The six fundamental steps of the manufacturing cycle are as follows.
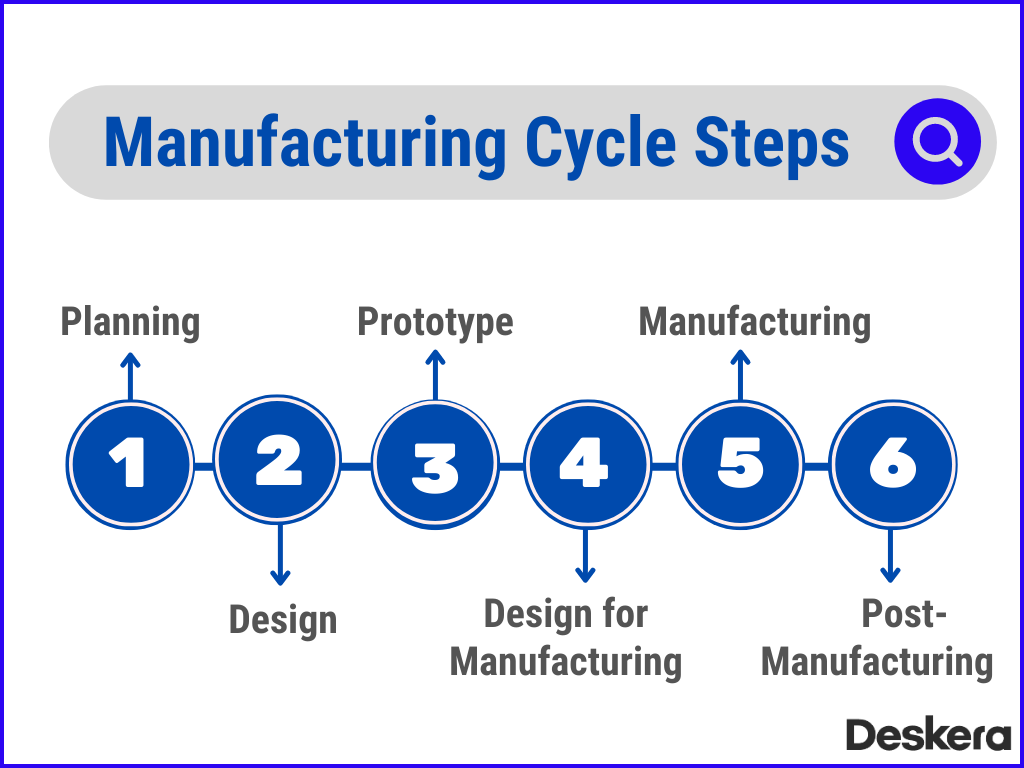
1. Planning
A clearly defined plan is required before you begin manufacturing. Any ambiguity will cause issues, which could cause a timetable delay or cost overruns. This calls for the creation of a list of the tasks, deliverables, and resources required to do them. This list must be within the constraints of your budget and time frame.
This involves setting out the goals, objectives, and process for the production of the product. It also involves developing a plan for the procurement of the resources and materials needed for the production. Planning also includes creating a timeline for the completion of the project.
The more time and attention you put into this step, the more likely it is that the manufacturing cycle will be successful.
2. Design
After the initial planning phase, the design of the product must be considered. This includes creating a blueprint of the product and its components. You will have the guidelines to create the industrial design once the specifications for the product have been established. The strategy to get there needs to be established.
There will be evaluations and adjustments made as the product is being designed. To make sure you are adhering to the plan's specifications. To find and resolve any problems that can affect functionality or safety, you'll even need to manage risks.
3. Prototype
Once the design of the product is finalized, a prototype is created. The creation of the first prototypes marks the official start of the production cycle. Prototyping often involves three stages: alpha, beta, and pilot. The proof-of-concept model, also known as the alpha prototype, is made to test the preliminary design.
Except for a few finishing touches like color and packaging, the beta prototype reflects the full product. The purpose of the pilot production is to show the efficiency of the production procedures.
This is an important step in the manufacturing cycle. It allows for any changes or improvements to be made to the product before it enters the manufacturing process.
4. Design for Manufacturing
After the prototype has been tested and approved, the product must be designed for manufacturing. You will now make any adjustments to your product that were discovered during the prototype stage. It also involves choosing the right materials and components to reduce costs and improve the quality of the product.
The new process will be able to be used to enhance dependability and manufacturability. You can expand your production scale at this point. You are also in charge of the necessary assembly, test, and documentation procedures here.
5. Manufacturing
You're not nearly prepared for production at this point. The manufacturing step involves the actual production of the product. You will need room, tools, and labor to make your goods. You may only need a few tables, some tools, and a few technicians to do this, depending on the size and scope of your business.
This includes the assembly of the components, the application of any finishing touches, and the testing of the product. Yet, if you're engaged in larger-scale, more complex manufacturing, you'll also want equipment. Warehouse space, supplier relationships, and more.
6. Post-Manufacturing
You're not done until the thing is manufactured. You must decide how to deliver your product and, if necessary, install it. Additionally, there is any upkeep and instruction required for users to use your product.
Customer service is the main focus of post-manufacturing. You may need to spend money on a field service specialist. This is needed for installation, setup and commissioning, maintenance, repair, and other tasks. This depends on the nature of your product.
Benefits of Tracking the Manufacturing Cycle
When the manufacturing cycle time is evaluated and monitored, it might have significant business repercussions. A corporation can boost productivity and concentrate on capacity consolidation. It can also help in handling yield/loss or logistics difficulties. This can be done by reducing cycle time in manufacturing.
The cycle time is a crucial indicator for teams to know what target to strive towards, to complete a finished product. This can help businesses improve their lean manufacturing.
The more quickly a manufacturing cycle can be completed, the better for business—as long as the product's quality is not compromised. Calculating cycle time also has the following advantages:
Acquire a Competitive Edge
Want to outperform your rivals and keep customers? By being the partner who delivers within the quickest manufacturing time, you can outperform your rivals.
Your cycle time will give you visibility and real-time data that you can use to keep one step ahead of the competition. By calculating cycle time, you can make sure that your company has a competitive advantage and outperforms its rivals.
Increased Profitability
When you maximize cycle time, with delivery speed as your main priority, you lower costs and boost profitability. An easy method to identify areas where you can make cuts is to have a comprehensive picture of how and where time is being spent.
In one case study, a thorough understanding of cycle time in conjunction with other lean principles. This led to an organization's pretax profits rising from 2% to 13%.
Steady Production Rates
Organizations can reduce unnecessary waste and boost productivity. This can be done by better understanding their production flow. This is done with the aid of cycle time. You may put procedures and technologies in place to guarantee constant production rates.
If you have a thorough grasp of your production flow. You may drop the possibility of generating too little or too much by focusing on standardizing your production pace.
Customer Satisfaction
Have you ever encountered a circumstance where you have misled a consumer by promising to deliver something on time? When we don't have a clear concept of how long it takes to finish particular jobs, it happens frequently. By calculating cycle time, you may find out your production pace. This will help you generate more attainable deadlines.
Effectiveness of the Team’s Working Structure
The data provides a chance to address inefficiencies when you review and evaluate your cycle time. For instance, if your cycle time shows that you are unable to deliver promptly and offer the turnaround times you prefer.
If so, you can decide if you can increase your production batch so that you can ship more swiftly. Cycle time is a crucial factor to consider when looking for process improvements.
Improved Project Scoping
It might be difficult to scope work with your customers if you don't have a good idea of how long it takes your team to perform particular tasks in their work. This leads to frustration among your team members when they discover a project is much larger than they anticipated.
As well as among your clients when they learn you need to extend your deadline. If you use cycle time instead of just making an informed guess, your project scope will be more precise.
Explicit Information on Corporate Spending
Paid individual processes need to improve your production process, but not all of them do. By tracking cycle time, business owners, producers, and product managers may understand expense management and maximize efficiency.
In other words, cycle time enables you to gain a deeper understanding of your business operations. You can assess the value of individual processes based on the cycle time of every given activity.
You can have a better knowledge of business costs by knowing cycle time. It tells how many resources are being paid to execute production tasks within a given time frame. Then, you may concentrate on streamlining the procedures. This generates the greatest value and returns on investment.
Reducing Manufacturing Cycle Time
Setting priorities while reducing the manufacturing cycle time is crucial. It will be less disruptive to start with non-value-adding operations first, such as waiting and moving materials. Value-adding activities should only be maximized. This should be done after actions in non-value-adding activities have been exhausted.
This is because they have a tendency to have an impact on quality or continuity. Cutting the manufacturing cycle time is essential for improving customer satisfaction. It is also essential for boosting an organization's income.
Reduce Waiting and Idle Time
One of the first areas to be affected when cycle time is optimized is the availability of materials and resources to reduce idle time. Resource availability can be ensured by efficient material requirements planning (MRP).
MRP is integrated with the ERP and supply chain. The digitalization of MRP can virtually instantaneously make requirements-related data available and accessible. This leads to quicker actions.
Reduce material movement
Reduced material movement can be achieved through methodical layout planning. This can be achieved through improved route cards. Less movement can impact cycle time by reducing the time required for such movement.
Cycle Time Optimization using predictive analytics
Planning the ideal manufacturing cycle time can be accomplished by creating scenarios. This can be accomplished by creating scenarios using predictive analytics.
To make wise decisions about cycle time optimization initiatives, advanced analytics can also assist. It helps in identifying the impact of optimization on outlier products or components.
Cut down on inspection time
Inspections at the beginning and end of a production line are essential for ensuring product quality. They are also essential for minimizing waste. They take time, though, and don't really improve the result. Automation can assist or replace human intervention, which can be slowed down and worn out.
Inspection time can be sped up via guided inspection using visual cues to make decision-making easier. Having the appropriate gauges and tools on hand can also drastically cut down on inspection time.
Reviewing the order profile
Customer satisfaction is substantially affected by cycle time optimization. In order to meet client expectations, measures to optimize it should also ensure order fulfillment. This is particularly relevant when producing products with substantial variances or nonstandard specifications.
The key to minimizing cycle time is comprehending the essential elements of the order and sequencing tasks in parallel or series. This is done while guaranteeing minimal material movement.
Utilize Big Data Analytics to Achieve Minimal Cycle Time
Cycle time optimization has become more effective thanks to guided analytics that makes use of big data and machine learning.
- Data now makes it easy to pinpoint non-value-adding operations and reduce the impact they have on cycle time.
- Predictive analytics simulations that examine the effects of such activities can help. This can help to prevent costly errors and choose the best collection of initiatives.
- By providing real-time line instructions and alarm mechanisms, prescriptive analytics can help. Prescriptive analytics can also speed up the operations taken by operators and foremen.
- These big data and analytics components work together to produce the ideal cycle time in manufacturing today.
What is Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency?
The percentage of production time that is spent on value-added activities is manufacturing cycle efficiency. This is known as manufacturing cycle efficiency. Manufacturers can find tasks that don't bring value to the operation and cut expenses by eliminating them.
This is a key factor in determining what proportion of cycle time is taken up by value-added operations. The little portion of the entire cycle time that is effective in this data is frequently surprising to manufacturers.
- Manufacturing cycle efficiency is measured by the ratio of actual output to theoretical output. The theoretical output is the maximum output that can be produced with the available resources and time.
- It is important to measure manufacturing cycle efficiency. This is in order to ensure that a manufacturing process is as efficient as possible. If a process is inefficient, it can lead to wasted resources and time, which can negatively affect the profitability of a business.
- Improving manufacturing cycle efficiency involves identifying areas of inefficiency and then finding a way to reduce or eliminate them. This can involve improving the design of a process, improving the training of workers, or changing the way that resources are allocated.
- Manufacturing cycle efficiency is an important metric for manufacturers to measure. It is important to ensure that their processes are as efficient as possible.
- By improving manufacturing cycle efficiency, manufacturers can reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction. They can also increase profits and stay competitive in the marketplace.
How to Calculate Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency?
Value-Added Production Time divided by Total Cycle Time is used to determine cycle efficiency. As a point of reference, Total Cycle Time is the total of all actions taken over the course of producing a whole unit.
Remember that the term can also be used to refer to the time it takes for a piece of equipment to complete a movement or process, depending on who you ask.
Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency = Value-Added Production Time / Total Cycle Time
5 Steps to Improve Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency
The five steps that must be explored in order to conduct a successful cycle time analysis are reviewed below. For a manufacturer to fully comprehend and maximize the nature of their production, it's crucial to participate at each stage.
Step 1: Conceptualization and Development
During a new product's conception and development phases, there is a substantial potential for waste and redundancy. This is a major problem in the development of new products. The key to solve this is by implementing lean manufacturing efficiency.
- Consider the end user when designing a product. This will help to ensure that the product is designed to meet the customer’s needs and is easy to manufacture.
- Design components to minimize the number of parts required to construct the product. This will help save time and cost in production.
- Analyze the production process and identify areas for improvement. This will help to streamline the manufacturing process and reduce waste and inefficiency.
Step 2: Ordering Process
Demand for completed goods and manufacturer supply are the two main factors in efficient production. Placing orders for the creation of a specific number of products is one of the important early steps in the manufacturing cycle.
Without a simplified ordering process that takes into consideration potential complicating elements, such as the amount of stock that is already held, the volume of sales, or potential future trends. The efficiency of this manufacturing cycle is easily impaired.
- Develop a system for tracking and managing orders that is accurate and up to date. This will help to ensure that orders are filled quickly and efficiently.
- Automate the ordering system to reduce manual errors and streamline the process.
- Utilize a system for reordering parts and materials to ensure that components are available when needed.
Step 3: Production Scheduling
Production should be planned once the order is received to make the most of a company's manufacturing capacity. Products manufactured in the allotted time frame enable a business to meet the demand created throughout the ordering process. A well-organized manufacturing cycle is created by a closely controlled production scheduling procedure.
- Develop a production schedule that takes into account the availability of raw materials, labor, and other resources.
- Utilize technology to track and monitor production processes in real time. This will enable you to respond quickly to changes in demand or delays in production.
- Automate the scheduling process to reduce manual errors and ensure that production is scheduled efficiently.
Step 4: Manufacturing
The real manufacturing process can start on the machines and production lines that are currently available. Once the production scheduling procedure has been optimized.
Smart businesses use machine monitoring software. A modern, secure cloud analytics platform program that is accessible from anywhere. It requires no servers, automated upgrades, or significant IT expenditure to become leaner and remove waste.
- Utilize the latest technology to improve the speed and accuracy of the production process.
- Streamline the production process to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Identify and eliminate bottlenecks in the production process to maximize efficiency.
Step 5: Transportation
It is the effective delivery of finished items to various physical and geographic locations. These locations may be warehouses, distributors, dealers, or retailers.
- Establish a system for tracking and managing shipments. This will help ensure that products are delivered on time and in good condition.
- Utilize technology to track shipments in real time. This will enable you to respond quickly to any delays or issues.
- Utilize a system for reordering parts and materials to ensure that components are available when needed.
This is the final step in the production process. The real action starts here, so to speak.
Customer expectations are higher than ever. Therefore even the smallest hiccup in the process of getting a product from the factory floor to the consumer could have fatal results. Only two outcomes, cancellations and payment delays are risky. It can jeopardize all your efforts to improve manufacturing cycle efficiency.
Cycle Time Vs Throughput Time
Cycle time and throughput time are sometimes mistaken for one another because of their close relationship. The latter adds up all the time a product spends in the manufacturing process as a whole. The former measures the length of time for individual jobs. The components of throughput time are as follows:
- Queue time
- Processing time
- Move time
- Inspection time
Cycle time and throughput time can only be used interchangeably. It can be used if your entire manufacturing process consists of a single operation. Which is typically not the case.
- The primary difference between Cycle Time and Throughput Time is that Cycle Time is the time required for the completion of a single cycle, whereas Throughput Time is the total amount of time required for the completion of all cycles in a given process.
- Throughput Time takes into account all the steps involved in the process. Whereas Cycle Time only measures the time required for the completion of one cycle.
- Additionally, Cycle Time is mainly used to measure the efficiency of an assembly line or manufacturing process, while Throughput Time is used to measure the efficiency of a system or process as a whole.
In conclusion, cycle time and throughput time are two important measurements in industrial process management. Both measurements are important for understanding the overall efficiency and speed of the production process. Manufacturers should strive to optimize both measurements to improve production efficiency and increase productivity.
Cycle Time Vs Takt Time
Takt time refers to the processing rhythm being used on the shop floor at a particular moment. Cycle time and demand are both taken into account while making the decision. To ensure that products are completed on time and that there is a minimum amount of idle time when goods are produced consecutively.
Takt time is used to specify how much time should be spent on one unit. Takt Time is what the manufacturing "needs to accomplish," while Cycle Time is what it "can do." Given that extra processing times during Lead Time will remain constant for all Cycle Time rates, these two figures can be utilized. The data can be used to determine if production can fulfill consumer needs.
- Usage: Cycle time is used to measure the overall performance of a manufacturing process. Takt time is used to measure the rate of production required to meet customer demand.
- Calculation: Cycle time is calculated by measuring the total time taken to complete a given cycle of production. Takt time is calculated by dividing the total available production time by the demand for a given product.
- Goal: Cycle time is used to measure efficiency in a production process and identify areas for improvement. Takt time is used to ensure that customer demand is met in a timely manner.
- Flexibility: Cycle time is relatively static, as it is based on the cycle time of the production process. Takt time is more flexible, as it can be adjusted based on changes in customer demand.
In conclusion, cycle time and takt time are both important metrics for measuring the performance of a manufacturing process. However, there are important distinctions between the two that should be taken into account when evaluating the performance of a system.
Cycle Time Vs Lead Time
The Cycle Time is a portion of the overall Lead Time. Lead Time is measured from the viewpoint of the client, whereas Cycle Time is measured from the viewpoint of the internal process.
- Duration: Cycle time is the total duration of a process or task, while lead time is the duration between initiation of an order and its delivery.
- Measurement: Cycle time is measured from the start to the finish of a particular task or process. Lead time is measured from the initiation of an order to its delivery.
- Relation: Cycle time is related to the efficiency of a process or task, while lead time is related to customer service.
- Cost: Cycle time helps to reduce the cost of production, while lead time helps to reduce the cost of customer service.
- Performance: Cycle time helps to improve the overall performance of a process or task, while lead time helps to improve the customer service level.
- Optimization: Cycle time can be optimized by reducing the number of steps in the process or task, while lead time can be optimized by improving the delivery process.
What Are the Challenges of Calculating Cycle Time?
Cycle time is an important metric for businesses to track, as it measures the amount of time it takes for a process or task to be completed. While there are many advantages to using the cycle time formula in your project, doing so correctly might be challenging.
When determining cycle time, the following typical problems can happen:
Establishing the Start and End Points- The first challenge of calculating cycle time is determining when the process or task starts and when it ends. This can be difficult, especially when the process involves multiple steps. To accurately measure cycle time, businesses must ensure they are tracking the right start and end points.
Defining the Process- The challenge of calculating cycle time is determining the production process and associated tasks. In order to accurately measure cycle time, the process must be well-defined and all tasks must be identified. This requires careful analysis of the production process and identifying all the steps involved in completing a task.
Disrupt Supply and Distribution Channels- It's crucial to be aware of the possibility that changing cycle times could tip the supply and distribution balance of your project.
Keeping Track of Data- The next challenge of calculating cycle time is tracking the data required to measure it. This can include the start date, end date, and any other relevant data points. Businesses must ensure they have the right data available to accurately measure cycle time
Communication Silos- When team members work independently on their jobs without regularly and successfully collaborating. It can cause problems with the project's workflow.
Analyzing the Data- This can be difficult, as businesses must consider any delays or inefficiencies in the process to accurately calculate cycle time.
Poor Job Prioritization- With so many projects underway at once, it can be challenging to determine where the team should concentrate its efforts.
Determining the Right Metrics- The last challenge of calculating cycle time is determining the right metrics to measure it. Businesses must decide which metrics are most relevant to their processes and tasks, in order to accurately calculate their cycle time.
Overall, calculating cycle time can be a challenging process for businesses. However, with the right data, metrics, and analysis, businesses can accurately measure their cycle time and identify areas of improvement.
How can Deskera Help You?
As a manufacturer, you must keep track of your inventory stock. The condition of your inventory has a direct impact on production planning, people and machinery use, and capacity utilization.
Deskera MRP is the one tool that lets you do all of the above. With Deskera, you can:
- Control production schedules
- Compile a Bill of Materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboard.
Deskera ERP is a complete solution that allows you to manage suppliers, track supply chain activity in real time, and streamline a range of other company functions.
Deskera Books allows you to manage your accounts and finances better. It helps maintain good accounting standards by automating billing, invoicing, and payment processing tasks.
Deskera CRM is a powerful tool that organizes your sales and helps you close deals rapidly. It enables you to perform crucial tasks like lead generation via email and gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward application for centralizing your human resource management activities. Not only does the technology expedite payroll processing, but it also helps you to handle all other operations such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more.
Using ERP for Calculating Manufacturing Cycle Time
No matter how precise your calculations are, there are situations when you might miss important information. This would result in expensive downtime. The good news is that utilizing ERP to calculate cycle time makes it possible to reduce cycle time losses.
Deskera is an excellent solution for ERP production. It provides useful real-time insights into the manufacturing cycle time. Deskera assists in tracking the relevant data and information connected to the manufacturing process. These reports point out problem areas so that the required adjustments can speed up the cycle time.
Conclusion
Manufacturing cycle time is used as a KPI to gauge how long it takes to complete the process of turning raw materials into completed goods. The production cycle can be determined by combining the productive or value-added hours with the unproductive or non-value-added hours.
Movement and queue time are both non-value-added times. It sounds like this would be a difficult task. It is impossible to attempt an exact estimation of every one of those variables. Because of this, figuring out production cycle time is as simple as dividing the number of parts by the time needed to make them.
It might have significant business repercussions. When the manufacturing cycle time is evaluated and monitored. A company can boost productivity, concentrate on capacity consolidation, and handle yield/loss or logistics difficulties.
This can be done by reducing cycle time in manufacturing. The cycle time is a crucial indicator for teams to know what target to strive towards in order to complete a finished product.
Key Takeaways
- Manufacturing cycle time refers to the amount of time it takes to execute one manufacturing operation on one unit. It can be several at once, from beginning to end.
- The overall manufacturing cycle time is calculated using four factors. Process time, inspection time, move time, and queue time are each one of them.
- The time indicators give you a comprehensive picture of how your team is using its time. It is the most important takeaway. This enables you to spot any workflow issues.
- Both the productive and non-productive hours must be taken into account when calculating the manufacturing cycle time. Manufacturing cycle time is the amount of time needed to finish manufacturing.
- Lead time and manufacturing cycle time are two of the most crucial indicators you can compare. How they differ can reveal a lot about the effectiveness of your team.
Related Articles