Have you ever wondered how your favorite chocolate, medicine, or beverage is produced with such consistent quality and taste? This marvel is achieved through process manufacturing, a method of producing goods by combining ingredients or raw materials through a specified process.
Unlike discrete manufacturing, which involves assembling distinct parts, process manufacturing is commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, chemicals, and oil and gas.
These industries rely on bulk production and typically involve chemical or biological transformations. The goal is to achieve consistency and efficiency, ensuring that each batch meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive software solution designed to streamline the complexities of process manufacturing. By automating and integrating key aspects such as production planning, inventory management, and procurement, Deskera ERP helps manufacturers improve operational efficiency and reduce costs.
This article will be your complete guide to process manufacturing.
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials or components into finished products through various methods and techniques.
This process involves several stages, including designing, producing, and assembling, and it can range from simple handcrafting to complex automated systems.
Manufacturing encompasses a wide array of industries, including automotive, electronics, textiles, food and beverage, and machinery.
The main objectives of manufacturing are to create products that meet specified quality standards, satisfy consumer demands, and generate profit. The process typically involves:
- Design and Development: Creating product designs and plans based on requirements and specifications.
- Production Planning: Organizing resources, scheduling production runs, and planning workflows to optimize efficiency.
- Material Sourcing: Acquiring raw materials or components needed for production.
- Processing: Using machinery, tools, and techniques to transform raw materials into finished products. This can include operations like cutting, molding, assembling, and packaging.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet quality standards through inspections and testing.
- Distribution: Delivering finished products to customers or retailers.
Manufacturing can be categorized into several types, including:
- Discrete Manufacturing: Producing distinct items such as automobiles or electronics.
- Process Manufacturing: Producing goods through chemical or biological processes, such as pharmaceuticals or food products.
- Batch Manufacturing: Producing items in groups or batches rather than continuous production.
- Continuous Manufacturing: Producing goods continuously, typically used for commodities like chemicals or petroleum.
The goal of manufacturing is to efficiently produce high-quality products that meet market demands while minimizing costs and maximizing profitability.
What is Process Manufacturing?
Process manufacturing is a method of production in which raw materials are transformed into finished products through a continuous or batch process.
This approach is characterized by the use of chemical, physical, or biological processes to produce goods in bulk, rather than assembling discrete parts.
Process manufacturing is commonly used in industries where products are produced in large quantities and involve complex formulations or transformations.
Key Features of Process Manufacturing
- Chemical or Biological Transformations: Process manufacturing often involves chemical reactions or biological processes. For example, in the food and beverage industry, ingredients are mixed, cooked, or fermented to create products like bread or beer.
- Continuous or Batch Production: Production can be continuous, where materials are processed without interruption, or batch, where materials are processed in specific quantities at a time. Continuous production is typical in industries like chemicals or petrochemicals, while batch production is common in pharmaceuticals and food manufacturing.
- Homogeneous Products: The end products are often homogeneous, meaning they have a consistent composition and quality throughout. This is crucial in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where precise formulations are necessary for safety and efficacy.
- Process Control: Process manufacturing relies heavily on precise control of variables such as temperature, pressure, and time to ensure product quality and consistency. Advanced technologies and automation are often employed to monitor and manage these processes.
- Equipment and Infrastructure: The equipment used in process manufacturing includes reactors, mixers, distillation columns, and other specialized machinery designed to handle the specific requirements of the production process.
In summary, process manufacturing is essential for producing bulk goods where consistency and efficiency are critical. It involves complex processes that transform raw materials into uniform, high-quality products across various industries.
Key Process Manufacturing Industries
Process manufacturing industries are sectors where goods are produced through chemical, physical, or biological processes, typically in bulk.
These industries focus on continuous or batch production and require precise control over various factors to ensure consistent quality and safety.
Here are some key examples of process manufacturing industries:
1. Chemical Industry
- Products: Fertilizers, detergents, polymers, acids, and specialty chemicals.
- Processes: Involves chemical reactions, mixing, and refining to produce substances used in various applications.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Products: Medicines, vaccines, and other healthcare products.
- Processes: Includes drug formulation, chemical synthesis, and fermentation, with strict adherence to regulatory standards for safety and efficacy.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
- Products: Packaged foods, beverages, dairy products, and baked goods.
- Processes: Encompasses mixing, cooking, fermentation, and preservation to create consumable products with consistent taste and quality.
4. Oil and Gas Industry
- Products: Gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, lubricants, and petrochemical products.
- Processes: Involves refining crude oil through distillation and chemical processing to produce various fuels and chemicals.
5. Pulp and Paper Industry
- Products: Paper, cardboard, and related products.
- Processes: Includes pulping, bleaching, and papermaking, transforming wood or recycled paper into finished products.
6. Textile Industry
- Products: Fabrics, yarns, and textiles.
- Processes: Involves dyeing, weaving, and finishing processes to produce various textile products.
7. Cosmetics and Personal Care Industry
- Products: Skincare products, shampoos, perfumes, and cosmetics.
- Processes: Includes formulation, blending, and packaging of products designed for personal use.
8. Biotechnology Industry
- Products: Biopharmaceuticals, biofuels, and agricultural biotechnology products.
- Processes: Utilizes biological processes, such as fermentation and genetic engineering, to produce innovative products.
9. Plastic and Rubber Industry
- Products: Plastic containers, rubber tires, and synthetic materials.
- Processes: Includes extrusion, molding, and compounding to create durable and versatile materials.
10. Metal Processing Industry
- Products: Metal alloys, sheets, and components.
- Processes: Encompasses smelting, refining, and alloying to produce various metal products used in construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
Each of these industries relies on process manufacturing to produce high volumes of products with consistent quality, making the use of advanced technologies and strict quality control essential.
Process Manufacturing vs. Discrete Manufacturing
Manufacturing can be broadly categorized into process manufacturing and discrete manufacturing, each with distinct characteristics, methods, and applications.
Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for selecting the appropriate manufacturing strategy for specific industries and products.
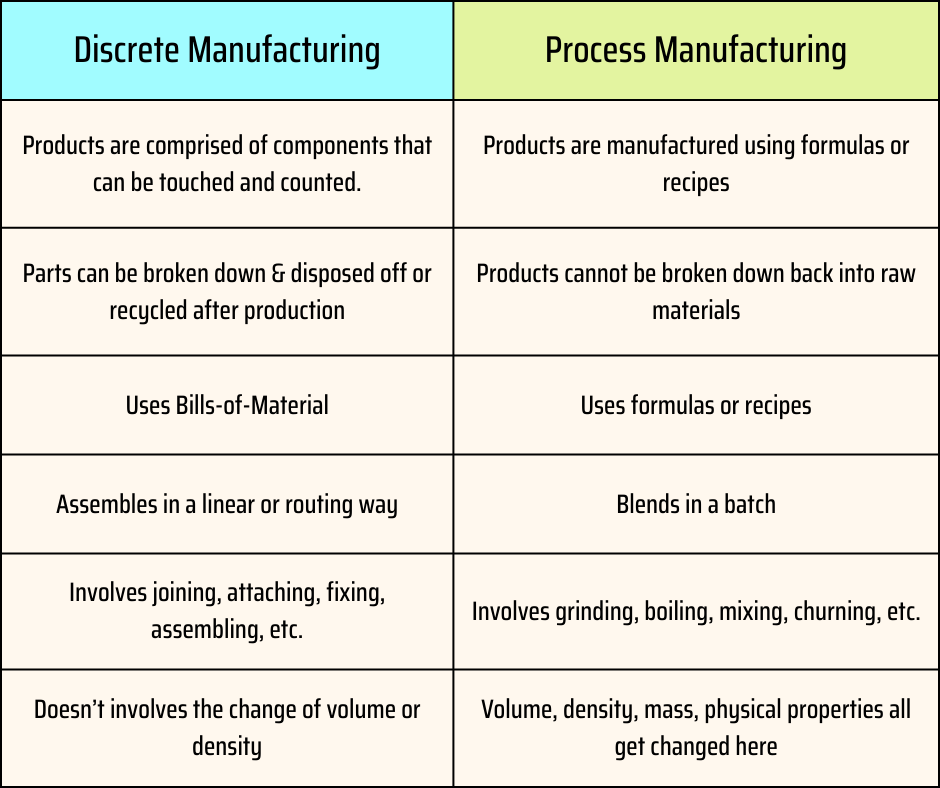
Product Nature:
- Process Manufacturing: Produces goods that are indistinguishable from one another and cannot be disassembled.
- Discrete Manufacturing: Produces distinct, countable items that can be broken down into their individual components.
Production Method:
- Process Manufacturing: Uses continuous or batch processes involving chemical, physical, or biological transformations.
- Discrete Manufacturing: Involves assembling parts or components in a specific sequence.
Consistency vs. Variety:
- Process Manufacturing: Focuses on consistency and uniformity in products.
- Discrete Manufacturing: Allows for greater variety and customization of products.
Industries:
- Process Manufacturing: Common in chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and oil and gas industries.
- Discrete Manufacturing: Common in automotive, electronics, machinery, and appliance industries.
Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right manufacturing approach to optimize production efficiency, meet quality standards, and cater to market demands.
Types of Process Manufacturing with Examples
Process manufacturing can be classified into various types based on the nature and method of production. Here is a detailed breakdown of each type, along with examples:
1. Continuous Processing
Characteristics:
- Nature of Production: Continuous and uninterrupted flow of production.
- Efficiency: High efficiency and productivity.
- Consistency: Ensures consistent product quality.
- Control: Requires precise control of process variables like temperature, pressure, and flow rate.
Examples:
- Oil Refining: Crude oil is continuously processed into gasoline, diesel, and other petroleum products.
- Chemical Production: Continuous production of chemicals like sulfuric acid, ammonia, and ethylene.
- Steel Manufacturing: Continuous casting and rolling processes in steel plants to produce sheets, coils, and other forms.
2. Batch Processing
Characteristics
- Nature of Production: Produces goods in specific quantities or batches.
- Flexibility: Allows for different product variations and smaller production runs.
- Control: Enhanced control over quality and formulation.
- Customization: Suitable for products that require specific formulations or frequent changes.
Examples
- Pharmaceuticals: Production of medicines in batches to meet specific formulations and dosages.
- Food and Beverage: Batch production of beer, yogurt, and bakery products where ingredients are processed in controlled quantities.
- Cosmetics: Production of skincare products, shampoos, and creams in batches to ensure consistency and quality.
3. Mixed-Mode Processing
Characteristics
- Combination: Integrates elements of both continuous and batch processing.
- Versatility: Provides flexibility to switch between continuous and batch modes as needed.
- Optimization: Balances the benefits of both methods to optimize production.
- Adaptability: Suitable for industries with varying production needs and product types.
Examples
- Food Industry: Production lines that can switch between continuous processing of staple items and batch processing for seasonal or specialty products.
- Chemical Industry: Plants that produce base chemicals continuously but switch to batch mode for specialized compounds or custom formulations.
4. Repetitive Processing
Characteristics
- Nature of Production: Repetitive and standardized production cycles.
- Consistency: High level of consistency and standardization.
- Efficiency: Maximizes efficiency and throughput.
- Scalability: Ideal for large-scale production with minimal variations.
Examples
- Pharmaceuticals: Continuous production of over-the-counter medications like aspirin and vitamins.
- Consumer Goods: Continuous production of personal care items like toothpaste, soap, and detergents.
- Beverage Industry: Continuous bottling and packaging of soft drinks, juices, and bottled water.
5. Discrete-Batch Hybrid Processing
Characteristics
- Combination: Combines discrete and batch manufacturing techniques.
- Customization: Allows for custom products with high consistency.
- Flexibility: Suitable for complex products that require both assembly and process manufacturing steps.
Examples
- Electronics: Production of custom circuit boards in batch processes followed by discrete assembly of electronic devices.
- Aerospace: Manufacturing of aircraft components where certain parts are produced in batches and then assembled.
Steps of Process Manufacturing
Process manufacturing involves a series of steps to transform raw materials into finished products. These steps are essential for ensuring consistency, quality, and efficiency in production.
Here is a detailed outline of the manufacturing process steps:
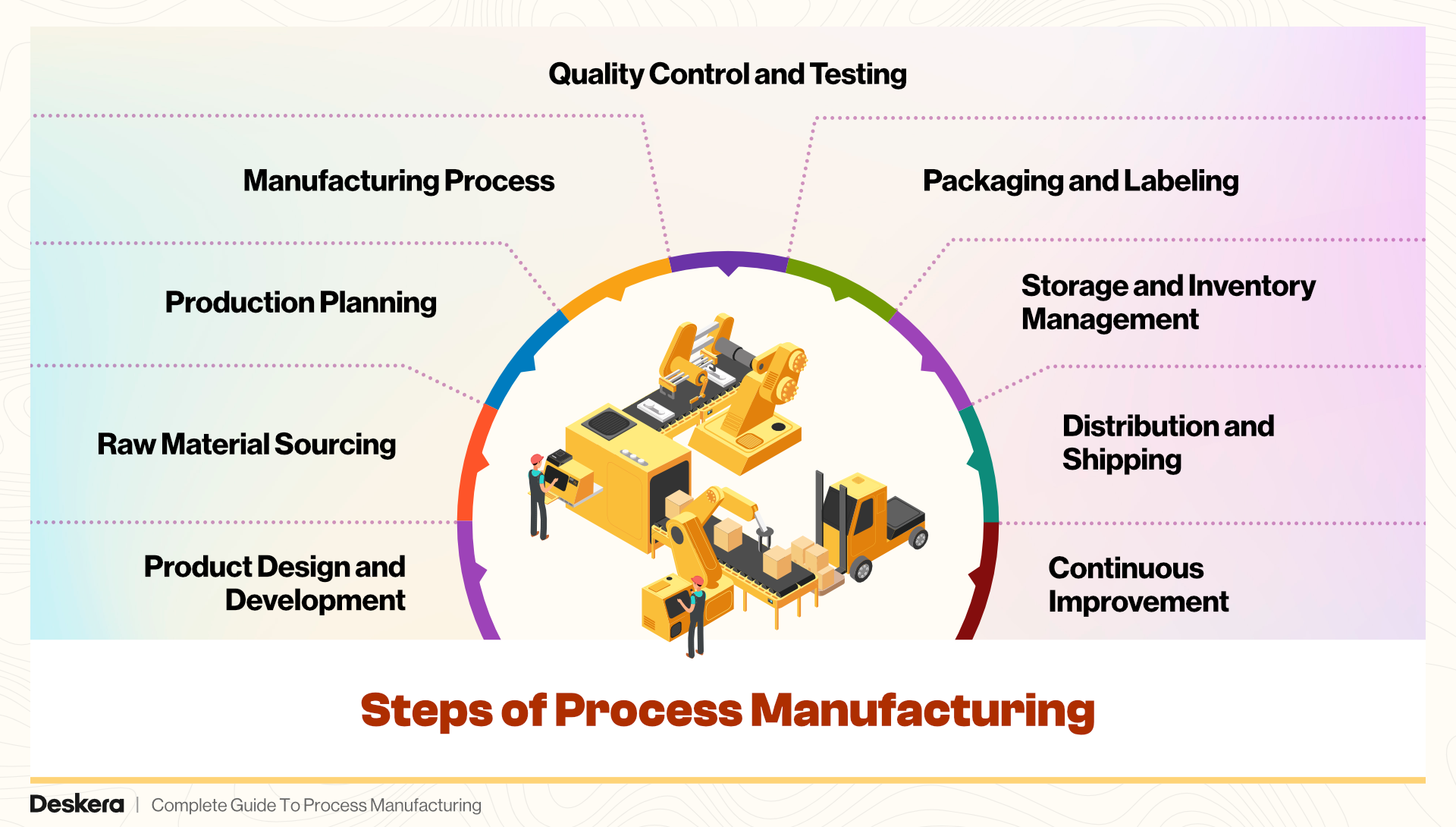
1. Product Design and Development
- Step Description: This is the initial phase where product specifications and formulations are developed.
- Key Activities: Research, formulation development, prototyping, and testing.
- Importance: This step lays the foundation for all subsequent stages.
2. Raw Material Sourcing
- Step Description: Acquiring the necessary raw materials or ingredients required for production.
- Key Activities: Vendor selection, procurement, quality checks, and inventory management.
- Importance: Ensures the availability of high-quality raw materials for a smooth manufacturing process.
3. Production Planning
- Step Description: Organizing resources, scheduling production runs, and planning workflows.
- Key Activities: Capacity planning, scheduling, and resource allocation.
- Importance: Ensures that the manufacturing process runs efficiently and meets production targets.
4. Manufacturing Process
- Step Description: The actual transformation of raw materials into finished products through various processes.
- Key Activities: Mixing, reacting, heating, cooling, fermenting, or other processing steps specific to the industry.
- Importance: This step is the core of process manufacturing where value is added to raw materials.
5. Quality Control and Testing
- Step Description: Ensuring that the products meet the required quality standards and specifications.
- Key Activities: Sampling, testing, and inspections at various stages of production.
- Importance: Critical for maintaining product consistency and safety.
6. Packaging and Labeling
- Step Description: Packaging the finished products in appropriate containers and labeling them with necessary information.
- Key Activities: Filling, sealing, labeling, and coding.
- Importance: Protects the product, ensures compliance with regulations, and provides necessary information to consumers.
7. Storage and Inventory Management
- Step Description: Storing the finished products before distribution.
- Key Activities: Warehousing, inventory management, and logistics planning.
- Importance: Ensures that products are stored safely and are readily available for shipping.
8. Distribution and Shipping
- Step Description: Delivering the finished products to customers or retailers.
- Key Activities: Order processing, transportation, and delivery.
- Importance: Ensures timely and efficient delivery of products to the end-users.
9. Continuous Improvement
- Step Description: Ongoing efforts to improve the efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness of the manufacturing process.
- Key Activities: Analyzing production data, implementing new technologies, and refining processes.
- Importance: Enhances productivity, reduces waste, and improves overall competitiveness.
Understanding the steps of process manufacturing is essential for optimizing production and ensuring high-quality outcomes.
From the beginning steps in the manufacturing process, such as product design and raw material sourcing, to the final stages of distribution and continuous improvement, each step plays a crucial role in the overall manufacturing process.
By focusing on these steps and integrating keywords like manufacturing process automation and process manufacturing examples, companies in process manufacturing industries can enhance their operations and achieve greater success.
Benefits of Process Manufacturing
Process manufacturing offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive method for producing goods in various industries. Here are the key benefits:
1. Efficiency and Productivity
- Continuous Operation: Process manufacturing often involves continuous production processes, leading to higher efficiency and productivity.
- Automation: The integration of manufacturing process automation reduces manual intervention, speeds up production, and minimizes errors.
2. Consistency and Quality Control
- Uniform Products: Ensures that products are consistent in quality and composition, which is crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals and food and beverages.
- Strict Quality Control: Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process ensures that all products meet specified standards.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
- Economies of Scale: Producing goods in bulk reduces the cost per unit, making process manufacturing cost-effective.
- Resource Optimization: Efficient use of raw materials and energy helps in reducing overall production costs.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
- Adaptability: Batch processing allows for flexibility in production, enabling manufacturers to produce different products or adjust formulations as needed.
- Scalability: Continuous processes can be easily scaled up to meet increasing demand without significant changes to the production setup.
5. Improved Inventory Management
- Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced inventory management systems enable real-time tracking of raw materials and finished products, reducing the risk of stockouts or overproduction.
- Lean Inventory: Just-in-time inventory systems can be implemented to minimize waste and reduce storage costs.
6. Enhanced Safety and Compliance
- Regulatory Compliance: Process manufacturing industries, such as pharmaceuticals and food and beverages, often adhere to strict regulatory standards to ensure product safety and quality.
- Safety Protocols: Implementation of stringent safety measures and protocols protects workers and minimizes the risk of accidents.
7. Environmental Sustainability
- Waste Reduction: Efficient processes and automation help in minimizing waste generation and energy consumption.
- Sustainable Practices: Adoption of environmentally friendly practices, such as recycling and the use of sustainable materials, contributes to sustainability goals.
8. Technological Advancements
- Innovation: Continuous improvement and integration of new technologies lead to innovation in manufacturing processes.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging data analytics for process optimization and predictive maintenance enhances overall efficiency.
The benefits of process manufacturing are manifold, encompassing efficiency, consistency, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility.
With advancements in manufacturing process automation and continuous improvement strategies, process manufacturing continues to evolve, offering enhanced quality control, safety, and sustainability.
These benefits make process manufacturing a preferred choice for many industries, ensuring that products are produced efficiently and to the highest standards.
What is Process Manufacturing ERP Software?
Process Manufacturing ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a comprehensive solution designed to manage and optimize all aspects of process manufacturing operations.
Unlike traditional ERP systems that are often geared towards discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing ERP software addresses the unique needs and challenges of process-based industries. Here is an overview of its key features and benefits:
Key Features of Process Manufacturing ERP Software
Recipe and Formula Management
- Description: Manages detailed recipes or formulas for products, including ingredients, proportions, and processing instructions.
- Benefit: Ensures consistency and accuracy in product formulation.
Batch Tracking and Traceability
- Description: Tracks production batches from raw materials to finished products, enabling traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
- Benefit: Enhances quality control and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Inventory Management
- Description: Manages raw material and finished product inventory, optimizing stock levels and reducing waste.
- Benefit: Ensures timely availability of materials and reduces holding costs.
Production Planning and Scheduling
- Description: Plans and schedules production runs, balancing demand with manufacturing capacity.
- Benefit: Improves efficiency and reduces manufacturing lead times.
Quality Management
- Description: Implements quality control measures and monitors product quality at every stage of production.
- Benefit: Ensures products meet quality standards and reduces defects.
Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
- Description: Manages compliance with industry regulations and generates required documentation.
- Benefit: Helps maintain regulatory compliance and reduces risk of fines or legal issues.
Manufacturing Process Automation
- Description: Automates various manufacturing processes, from mixing and blending to packaging and labeling.
- Benefit: Increases efficiency, reduces human error, and enhances productivity.
Real-Time Data and Analytics
- Description: Provides real-time visibility into production data, inventory levels, and operational performance.
- Benefit: Enables informed decision-making and proactive management.
Benefits of Process Manufacturing ERP Software
Improved Operational Efficiency
- Description: Streamlines production processes and optimizes resource utilization.
- Benefit: Reduces operational costs and increases throughput.
Enhanced Product Quality
- Description: Ensures consistent product quality through robust quality control measures.
- Benefit: Builds customer trust and meets regulatory standards.
Better Compliance Management
- Description: Helps manage compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Benefit: Reduces the risk of regulatory penalties and enhances reputation.
Increased Flexibility and Scalability
- Description: Adapts to changing production needs and scales with business growth.
- Benefit: Supports business expansion and innovation.
Real-Time Insights
- Description: Provides actionable insights through real-time data and analytics.
- Benefit: Improves decision-making and operational responsiveness.
How Can Deskera Help You with Process Manufacturing?
Deskera is a robust ERP software platform designed to streamline and enhance various aspects of process manufacturing.
By leveraging its comprehensive suite of tools, process manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency, quality, and compliance in their operations.
Here’s how Deskera supports process manufacturing, including its MRP (Material Requirements Planning) capabilities:
Batch Tracking and Traceability
- Feature: Tracks every batch of production from raw materials to finished goods, providing complete traceability.
- Benefit: Enhances quality control and compliance with industry regulations, making it easier to trace and address any issues that arise.
Advanced Inventory Management
- Feature: Manages raw material and finished product inventory in real-time, optimizing stock levels and reducing waste.
- Benefit: Ensures that materials are available when needed and reduces the costs associated with excess inventory.
Production Planning and Scheduling
- Feature: Automates production planning and scheduling, balancing demand with production capacity.
- Benefit: Improves operational efficiency, reduces lead times, and ensures timely delivery of products.
Quality Management
- Feature: Implements and monitors quality control measures at every stage of the manufacturing process.
- Benefit: Guarantees that products meet quality standards, reducing defects and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
- Feature: Helps manage compliance with industry-specific regulations and generates required documentation and reports.
- Benefit: Reduces the risk of non-compliance, fines, and legal issues by ensuring adherence to regulatory standards.
Real-Time Data and Analytics
- Feature: Provides real-time visibility into production data, inventory levels, and operational performance.
- Benefit: Enables data-driven decision-making, proactive management, and continuous process improvement.
Operational Efficiency
- Automation: Deskera automates routine tasks and processes, freeing up resources and reducing manual errors.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with other systems and processes, ensuring smooth operations.
Cost Management
- Cost Tracking: Tracks production costs in real-time, helping to identify and reduce waste and inefficiencies.
- Resource Optimization: Optimizes the use of materials and labor to reduce overall production costs.
Compliance and Safety
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps maintain compliance with industry regulations through comprehensive documentation and reporting.
- Safety Protocols: Incorporates safety protocols to protect workers and ensure safe production processes.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Scalable Solutions: Deskera’s ERP system can scale with your business, accommodating growth and expansion.
- Flexible Processes: Allows for flexible production processes to adapt to changing market demands and product variations.
Key Takeaways
A complete guide to process manufacturing reveals the intricacies and benefits of this production method, essential for industries where continuous or batch processing is prevalent.
Definition and Scope
- Process Manufacturing: Involves the production of goods through continuous or batch processing where raw materials are transformed into finished products, often in industries like chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and cosmetics.
Types of Process Manufacturing
- Continuous Processing: Produces goods in a continuous flow, ideal for high-volume and consistent products.
- Batch Processing: Produces goods in batches or groups, allowing flexibility and variation in product formulations.
- Mixed-Mode Processing: Combines elements of continuous and batch processing to optimize production efficiency and adaptability.
- Repetitive Processing: Focuses on repetitive tasks and production runs for consistent, high-volume output.
Steps of Process Manufacturing
- Product Design and Development: Establishing product specifications and formulations.
- Raw Material Sourcing: Procuring and managing raw materials.
- Production Planning: Organizing resources and scheduling production.
- Manufacturing Process: Transforming raw materials into finished products.
- Quality Control: Ensuring products meet required standards.
- Packaging and Labeling: Preparing products for distribution.
- Storage and Inventory Management: Managing inventory levels and storage.
- Distribution and Shipping: Delivering products to customers.
- Continuous Improvement: Enhancing processes and efficiency over time.
Benefits of Process Manufacturing
- Efficiency and Productivity: Higher efficiency through automation and continuous processes.
- Consistency and Quality Control: Uniform product quality and stringent quality control.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Economies of scale and resource optimization.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Adaptability to changes and scalability for growth.
- Enhanced Safety and Compliance: Adherence to regulatory standards and safety protocols.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reduction in waste and implementation of sustainable practices.
Role of ERP Software in Process Manufacturing
- Batch Tracking and Traceability: Comprehensive tracking from raw materials to finished products.
- Inventory Management: Real-time management of inventory levels.
- Production Planning and Scheduling: Efficient scheduling and planning.
- Quality Management: Ensuring product quality and compliance.
- Compliance and Regulatory Reporting: Managing regulatory requirements and documentation.
- Real-Time Data and Analytics: Data-driven decision-making and process optimization.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Optimizing inventory and material availability.
Deskera’s ERP software provides a comprehensive and integrated solution for process manufacturing, including advanced MRP functionality.
By implementing Deskera, process manufacturers can benefit from enhanced recipe management, batch tracking, inventory optimization, and production efficiency.
Deskera’s tools support high-quality standards, regulatory compliance, and scalable growth, ensuring that manufacturers can meet their operational goals and achieve long-term success.
Related Articles












