Why do manufacturers often struggle to make informed decisions despite having access to so much data? The answer lies in fragmented information spread across different systems—ERP, MES, IoT devices, supply chain portals, and more. When this data sits in silos, it becomes nearly impossible to get a unified view of operations, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and missed opportunities.
This is where manufacturing data integration comes in. By connecting and synchronizing data across multiple platforms, manufacturers can eliminate blind spots, gain real-time insights, and drive smarter decision-making. Instead of relying on outdated reports or manual reconciliations, integrated systems create a single source of truth that supports agility and competitiveness.
In today’s fast-changing manufacturing landscape, data integration is more than just a technical upgrade—it’s a strategic necessity. From predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization to improved demand forecasting and compliance reporting, integrated data is the foundation of the modern smart factory. Companies that embrace it not only streamline their operations but also unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Solutions like Deskera MRP make this possible by providing manufacturers with a unified platform that integrates production planning, inventory management, procurement, and accounting. With real-time data flow and AI-powered insights, Deskera ensures that decision-makers always have the right information at their fingertips. Its scalability and ease of use make it a powerful choice for manufacturers looking to embrace digital transformation without the complexity of traditional systems.
What is Manufacturing Data Integration?
Manufacturing data integration is the process of consolidating information from diverse production, supply chain, and business management systems into a unified platform for analysis and decision-making. Instead of allowing data to remain locked in separate departments or applications, integration connects these silos, enabling manufacturers to access, analyze, and act on all their operational data in one place.
Done correctly, this unified approach provides a 360-degree view of operations—from market research and product design to materials sourcing, production, quality management, and sales. The resulting visibility empowers manufacturers to make decisions based on complete and accurate information, rather than fragmented departmental reports. This not only accelerates production cycles but also improves product quality, enhances worker productivity, and allows faster responses to changing market conditions.
Manufacturers today generate vast amounts of data from multiple sources: production equipment, shop floor sensors, ERP systems, manufacturing execution systems (MES), customer relationship management (CRM) applications, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Business systems like ERP and CRM capture data on supply chains, inventory, sales, and customer demand, while MES platforms and IoT devices track shop floor performance—down to the efficiency of individual machines. When integrated, these diverse datasets form a single, comprehensive view of the entire manufacturing process.
Without integration, however, manufacturers are left with a fragmented and incomplete picture of their operations. Decisions become slower and less accurate, turnaround times increase, and opportunities to identify inefficiencies or predict problems are missed.
Moreover, integration is only as strong as the quality of the underlying data—good data hygiene practices such as validating accuracy, eliminating duplicates, and filling in gaps are essential. Otherwise, the insights generated from integrated systems risk being distorted, leading to poor decision-making.
Types of Manufacturing Data That Can Be Integrated
Manufacturers generate vast amounts of data every day, spanning production floors, supply chains, customer interactions, and financial systems. When this data remains isolated, it leads to inefficiencies and limited visibility.
However, integrating different types of manufacturing data provides a unified, accurate picture of the business, enabling smarter decision-making and improved operations.
Below are the key categories of data that can be integrated to deliver value:
Customer Data
Customer data is typically stored in ERP and CRM systems, covering details such as contact information, financial history, order preferences, and feedback. When integrated with demand and inventory data, it helps manufacturers anticipate customer needs, improve product forecasting, and ensure timely order fulfillment—reducing delays and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Demand Data
Demand data originates from both internal and external sources. Internally, ERP sales records, CRM insights, and website analytics reveal buying patterns. Externally, market research, social media, and economic indicators provide broader context. Integrated demand data supports accurate forecasting, smarter resource allocation, and better strategic planning for product development and market positioning.
Production Data
Collected from MES, ERP systems, IoT devices, and shop floor sensors, production data tracks efficiency, order fulfillment, and real-time machine performance. This information enables manufacturers to monitor operational health, identify potential points of failure, and optimize processes. Combined with quality and maintenance data, production data offers end-to-end visibility of the manufacturing cycle.
Supply Chain Data
Supply chain data covers supplier information, logistics, inventory, and shipping details. It is often managed through ERP, SCM, TMS, and WMS systems. Integrating supply chain data with production and inventory insights helps manufacturers identify bottlenecks, anticipate delivery delays, and make proactive sourcing or scheduling adjustments to keep operations running smoothly.
Inventory Data
Drawn from ERP, WMS, SCM, and inventory management systems, this data tracks stock levels, product returns, and purchasing patterns. Integrated inventory data prevents disruptions, minimizes stockouts, and ensures optimal stock levels. When connected with CRM and demand data, it provides stronger forecasting insights and improves order accuracy.
Quality Control Data
Quality control data is sourced from inspections, audits, product testing, and sensor readings. Integration of this data with MES and SCM systems helps manufacturers identify defects early, refine processes, and design better products. Continuous monitoring of quality metrics ensures compliance with standards and enhances overall customer trust.
Equipment and Maintenance Data
Machine sensors, production line monitoring systems, and maintenance logs generate valuable insights into equipment health. When integrated with ERP and MES systems, this data enables predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and extends machinery lifespan—supporting both efficiency and cost savings.
Operational Data
Operational data includes shop floor conditions, equipment usage, downtime, safety incidents, energy consumption, and shift productivity. By integrating operational data across systems, manufacturers can uncover bottlenecks, ensure compliance, and optimize scheduling, ultimately enhancing throughput and reducing waste.
Workforce Data
Beyond payroll and attendance, workforce data captures employee skills, certifications, and productivity. Integrated workforce data enables better resource planning, ensures coverage during critical shifts, and identifies opportunities for training and skill development—aligning labor capacity with production needs.
Financial Data
Financial data, managed through ERP or accounting systems, includes gross margins, operating expenses, inventory turnover, and industry-specific benchmarks. When combined with supply chain and production data, it reveals how disruptions impact profitability, cash flow, and long-term business performance. This integration creates a direct link between operational efficiency and financial outcomes.
Key Manufacturing Data Integration Techniques and Technologies
Manufacturing data integration relies on a range of techniques and technologies to unify diverse data sources into a single, actionable system. Each method comes with its strengths and limitations, making it important for manufacturers to choose the right approach based on their operational needs, scale, and digital maturity.
Below are the most widely used integration methods and enabling technologies in the manufacturing sector:
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
ETL is one of the most traditional yet reliable approaches to data integration. It involves extracting data from multiple sources, transforming it into a consistent format, and loading it into a central repository like a data warehouse. This process ensures clean, accurate, and structured data for advanced analytics. While highly effective, ETL can be resource-intensive and is better suited for batch processing rather than real-time needs.
ELT (Extract, Load, Transform)
ELT flips the ETL sequence by first loading data into a data lake and then applying transformations as needed. This makes it faster and more scalable, particularly for handling massive volumes of manufacturing data generated from IoT sensors, MES, and ERP systems. However, ELT requires robust infrastructure with high-performance computing and advanced transformation tools, making it ideal for digitally mature organizations.
Change Data Capture (CDC)
CDC allows manufacturers to track and apply changes in data across systems in real time. This technique is especially useful for fast-changing data like inventory, production output, or order fulfillment. By synchronizing updates across platforms, CDC ensures data accuracy and consistency. However, with very large datasets, CDC can burden system performance and slow response times.
Data Virtualization
Data virtualization provides a unified view of data across systems without physically moving it. A virtualization layer pulls data from various sources and presents it in real time, simplifying integration and reducing complexity. While this approach saves time, it can become a single point of failure and demands significant processing power and high-performance networks.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
APIs act as bridges between different systems, enabling smooth communication and real-time data exchange. In manufacturing, APIs connect ERP, MES, CRM, and IoT devices, supporting seamless workflows and reducing complexity. Their flexibility makes them scalable and adaptable to evolving business needs.
Data Warehousing
Data warehousing centralizes data from multiple sources into one repository for analysis. Manufacturers can combine historical data with real-time production data to support predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and performance monitoring. This centralized hub also facilitates business intelligence tools for deeper insights.
IoT (Internet of Things) Devices
IoT plays a critical role in modern data integration by collecting real-time data directly from the shop floor. Sensors and RFID devices track performance, quality, and output, transmitting data instantly for integration and analysis. This enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and greater visibility into production processes.
Big Data and Analytics
With the vast amount of information generated, big data technologies help process, store, and analyze integrated datasets. Advanced analytics can uncover hidden trends, support predictive modeling, and enable manufacturers to make smarter decisions. By combining big data with integration techniques like ETL or APIs, organizations can turn raw information into a strategic asset.
Manufacturing Data Integration Use Cases
Virtually every manufacturer can benefit from integrating its data, but the real value comes from how that data is applied. By connecting systems and breaking down silos, manufacturers unlock insights that drive efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage.
Below are some of the most impactful use cases of manufacturing data integration, with real-world applications:
Predictive Maintenance
By analyzing IoT sensor data, machine performance logs, and maintenance histories, predictive maintenance helps anticipate equipment failures before they occur. Data integration ensures that information from MES, ERP, and IoT devices flows into one platform for real-time analysis. The result is reduced downtime, extended equipment life, and lower repair costs.
Example: General Motors uses predictive maintenance across its assembly plants by integrating IoT sensor data with AI models, allowing them to detect anomalies in robots and machinery before breakdowns occur—saving millions in downtime annually.
Defect Analysis
Product quality depends on the ability to identify and eliminate flaws quickly. Defect analysis draws on data from product lifecycle management systems, ERP, MES, and quality control systems to uncover the root causes of defects. With integrated data, manufacturers can detect patterns, take corrective actions, and ensure higher product reliability.
Example: Samsung integrates defect analysis into its semiconductor manufacturing by analyzing data from inspection equipment, MES, and ERP systems. This helps the company quickly trace defects back to specific processes and improve product yield.
Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting requires consolidated insights from ERP, CRM, sales data, and customer feedback. With integrated data, manufacturers can better predict product demand, align production schedules, and manage inventory more efficiently. This prevents overproduction, reduces waste, and ensures that supply chains stay responsive to customer needs.
Example: Procter & Gamble leverages integrated ERP and CRM data with retail analytics to improve demand forecasting. This enables them to adjust production based on shifting consumer behavior and seasonal trends, reducing excess inventory.
Audit Tracing (Traceability)
Traceability is critical for both compliance and operational excellence. By integrating data from RFID tags, barcodes, ERP, MES, and SCM systems, manufacturers can track raw materials, components, and finished goods across the entire supply chain. This provides transparency for regulatory reporting and builds customer trust with full product history records.
Example: Nestlé uses end-to-end traceability to comply with food safety regulations by integrating supplier data, production data, and logistics tracking. This allows them to trace any product back to its origin in minutes during audits or recalls.
Supply Chain Visibility
Integrated data from ERP, IMS, CRM, and TMS systems allows manufacturers to gain complete visibility into their supply chains. This visibility enables them to identify potential bottlenecks, such as shipping delays or inventory shortages, before they impact production. Enhanced visibility leads to better coordination with suppliers and smoother operations overall.
Example: Siemens uses supply chain visibility solutions by integrating supplier data, ERP, and logistics systems. This real-time view helps them proactively manage disruptions, such as delayed shipments, and optimize production schedules.
Data Syncing and Collaboration
Siloed data often leads to misalignment between departments. Integration ensures that sales, operations, finance, and production teams all work from the same accurate dataset. This synchronization fosters collaboration, increases productivity, and improves decision-making across the entire organization.
Example: Boeing integrates data from design, engineering, and production systems into a unified platform, enabling cross-functional teams to collaborate more effectively. This has reduced errors in aircraft assembly and improved production speed.
Energy Optimization
Energy efficiency is a growing priority in manufacturing. Integration of shop floor sensor data with energy management systems (EMS) and MES platforms allows real-time monitoring of energy consumption. By analyzing this data, manufacturers can identify opportunities to reduce waste, cut costs, and meet sustainability goals without sacrificing output quality.
Example: BMW integrates energy usage data from IoT sensors across its factories into an EMS. By doing so, they have reduced energy consumption by over 30% in some plants, aligning with their sustainability goals while maintaining production efficiency.
Benefits of Data Integration in Manufacturing
The consolidation of business and production data into a unified system gives manufacturers a holistic view of their operations. By connecting previously isolated systems, data integration eliminates silos, enhances transparency, and enables faster and more informed decision-making. This unified approach not only streamlines operations but also drives innovation, reduces costs, and improves responsiveness to market changes.
Below are the key benefits of manufacturing data integration:
Empowers Better Decisions
With integrated data, manufacturers gain access to real-time, accurate information across the organization. This makes it easier to identify market trends, forecast demand, and adapt to shifting customer preferences.
Decision-makers no longer rely on incomplete departmental reports but instead use a single source of truth to coordinate operations more effectively, boosting productivity and confidence in every strategic move.
Identifies Cost-Saving Measures
Integration enables manufacturers to spot inefficiencies, minimize downtime, and eliminate waste. For example, consolidating machine sensor data with maintenance logs may reveal recurring bottlenecks.
By adopting predictive maintenance strategies, companies can reduce unplanned breakdowns, avoid costly repairs, and improve productivity—directly enhancing profitability.
Optimizes Resource Utilization
From labor scheduling to inventory management, integrated data ensures better resource allocation. Accurate forecasting helps avoid overstocking or understocking materials, while workforce management improves factory line efficiency.
This optimization reduces delays, lowers storage costs, and strengthens profit margins through more effective use of time, materials, and human resources.
Improves Data Accuracy and Reliability
When systems operate in isolation, each team often ends up with conflicting versions of data. Integration solves this by centralizing and standardizing information, ensuring consistency across the organization.
With reliable data at hand, manufacturers can make timely, accurate decisions that enhance operational performance and build trust across departments.
Enables Automation of Processes
Data integration makes it possible to automate workflows across ERP, MES, WMS, PLM, and even e-commerce systems. Automation reduces repetitive manual tasks, cuts down on errors, and frees employees to focus on higher-value activities such as process optimization and innovation.
Accelerates Time to Market
By providing real-time visibility and seamless collaboration across engineering, production, and supply chain teams, data integration shortens development cycles. This allows manufacturers to bring products to market faster, respond swiftly to customer demands, and gain a competitive edge.
Enhances Compliance and Quality Control
Integrated systems automate compliance tracking, making it easier to meet industry regulations. By continuously monitoring process and equipment data, manufacturers can identify correlations that affect product quality, enabling proactive improvements and reducing the risk of defects reaching customers.
Reduces Operational Costs
Through automation, optimized resource allocation, and improved collaboration, data integration significantly reduces operational costs. Manufacturers can streamline supply chains, cut energy usage, and minimize material waste, translating to a stronger bottom line and long-term competitiveness.
Facilitates Predictive Maintenance
Analyzing historical and real-time machine data enables predictive maintenance strategies. This approach prolongs equipment life, reduces repair expenses, and ensures smooth production schedules. Predictive insights minimize downtime while maximizing equipment effectiveness, supporting consistent production quality.
Challenges in Manufacturing Data Integration and How to Overcome Them
While manufacturing data integration offers immense benefits, the road to achieving it is not without obstacles. From legacy systems to compliance issues, these challenges can slow down transformation efforts if not addressed strategically.
Below are the key hurdles manufacturers face—and practical ways to overcome them.
1. Data Quality and Consistency
The Challenge: The old saying “garbage in, garbage out” applies perfectly to manufacturing data. Poorly captured, fragmented, or outdated data leads to flawed analytics and misguided decision-making. Errors, duplicates, and inconsistent entries further degrade the value of integrated systems.
The Solution: Implement strong data governance frameworks, including validation checks, automated cleaning tools, and standardized data entry practices. Regular audits and monitoring ensure that all data remains accurate, complete, and reliable.
2. Data Formatting and Compatibility Issues
The Challenge: Manufacturing data often originates from multiple sources—ERP, MES, IoT sensors, CRM, and SCADA systems—each with its own formats and protocols. Without uniformity, integration becomes complex and error-prone.
The Solution: Use middleware, APIs, and standardized integration platforms to harmonize disparate formats. Adopting industry-wide data standards like OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) helps ensure smoother interoperability across systems.
3. Legacy Systems Integration
The Challenge: Many manufacturers still operate on decades-old systems that were never designed with integration in mind. These systems are often siloed and difficult to connect with modern tools, leading to incomplete or inaccessible data.
The Solution: Instead of a costly rip-and-replace, manufacturers can use data connectors, gateways, or virtualization layers to bridge legacy systems with newer platforms. A phased modernization approach, supported by ERP systems like Deskera MRP, allows companies to integrate gradually while minimizing disruptions.
4. Security and Compliance Risks
The Challenge: As more systems are integrated and data is shared across departments and partners, manufacturers face heightened cybersecurity risks. Sensitive information can become vulnerable, while regulatory requirements (such as ISO standards, GDPR, or industry-specific compliance rules) add extra complexity.
The Solution: Strengthen integration frameworks with encryption, access controls, and role-based permissions. Conduct regular compliance audits and adopt secure-by-design principles to protect sensitive data while meeting regulatory obligations.
5. Data Silos and Organizational Resistance
The Challenge: Beyond technical barriers, cultural resistance to change can block integration efforts. Departments may be reluctant to share data, leading to silos that weaken collaboration and obscure the bigger picture.
The Solution: Foster a data-driven culture by highlighting the benefits of integration for all stakeholders. Leadership must champion cross-functional collaboration, supported by clear policies and training to ensure smooth adoption.
Best Practices of Manufacturing Data Integration
When done right, manufacturing data integration can become a powerful enabler of efficiency, innovation, and growth. To fully realize these benefits, manufacturers must follow a set of best practices that ensure smooth implementation and sustainable success.
1. Review Your Existing Data Infrastructure
Before starting any integration project, take stock of your current data ecosystem. Identify all data sources—ERP, MES, CRM, IoT devices, and more—and evaluate how information is being captured, stored, and accessed. Address gaps in formatting, governance, and security protocols early on to avoid blind spots or disruptions during integration.
2. Define a Clear Data Strategy
Successful integration efforts begin with a well-defined strategy aligned to business goals. Ask: What challenges is the organization trying to solve? For example, improving demand forecasting, reducing downtime, or enhancing vendor visibility. Understanding current data flows between systems also helps identify redundancies and gaps, laying the foundation for a streamlined approach.
3. Identify Potential Synergies Between Data Sets
Not all data is equally valuable. The real advantage of integration comes from uncovering synergies between datasets—for example, connecting production data with quality control results to predict defects, or linking supply chain data with financial data to evaluate cost impacts. Focusing on meaningful overlaps creates actionable insights without overcomplicating systems.
4. Prioritize High-Impact Integrations
Rather than trying to integrate everything at once, manufacturers should start with projects that deliver the most immediate value. Early wins—such as integrating predictive maintenance data from IoT sensors with ERP systems—can boost organizational confidence and build momentum for larger, more complex initiatives.
5. Don’t Overdo It
More data isn’t always better. Overloading teams with unnecessary data streams can overwhelm decision-making instead of improving it. Focus on integrating only the data that supports core business objectives and enhances operational visibility.
6. Build Integrations to Scale
Data integration should be future-proof. As businesses grow, so will the volume and complexity of data. Scalable, cloud-based solutions provide the flexibility to add new data sources, applications, or processing capabilities without costly infrastructure overhauls. This adaptability helps manufacturers remain agile in a fast-changing market.
7. Prioritize Security and Compliance
Integration expands data accessibility, but it also introduces new risks. Strong encryption, role-based access controls, and regular audits are essential to protect sensitive manufacturing and customer data. Compliance with regulations—such as ISO, GDPR, or industry-specific standards—should be embedded into the integration process from the start.
8. Continuously Monitor and Improve
Data integration is not a one-time project; it requires ongoing monitoring and refinement. Regularly evaluate the performance of integration systems, update protocols as new technologies emerge, and train teams to adapt to changes. Continuous improvement ensures that the integration strategy remains effective and aligned with evolving business goals.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Data Integration
The future of manufacturing is being shaped by how effectively organizations can harness and integrate data across systems, processes, and partners. With Industry 4.0 continuing to evolve, manufacturers are moving beyond simple system-to-system connections toward intelligent, predictive, and fully automated data ecosystems. Below are some of the key trends driving the next wave of manufacturing data integration.
1. AI-Driven Data Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how data is connected and processed. AI-powered integration platforms can automatically map data fields, identify anomalies, and optimize workflows without manual intervention. This not only accelerates deployment but also improves the accuracy and reliability of manufacturing data.
2. Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
Machine learning (ML) goes a step further by analyzing historical and real-time data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes. When integrated into manufacturing systems, ML and predictive analytics can forecast demand fluctuations, predict machine failures before they occur, and optimize inventory levels. These capabilities help manufacturers reduce downtime, lower costs, and boost overall efficiency.
3. Expansion of Industrial IoT (IIoT) Connectivity
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) continues to grow, with machines, sensors, and devices producing massive amounts of operational data. Future integration platforms will increasingly focus on seamless ingestion and processing of IIoT data, enabling predictive maintenance, energy efficiency monitoring, and real-time quality control.
4. Cloud-Native and Hybrid Integration Platforms
As manufacturers adopt cloud-based ERP, MES, and supply chain solutions, integration strategies will also move to cloud-native platforms. These solutions allow manufacturers to connect cloud and on-premises systems seamlessly, supporting scalability, agility, and cost efficiency. Hybrid integration is emerging as a key enabler for enterprises transitioning gradually to the cloud.
5. Edge Computing for Faster Processing
For time-sensitive processes such as robotics, production line automation, and defect detection, data integration at the edge is becoming critical. By processing data closer to where it is generated, edge computing reduces latency and minimizes reliance on centralized servers. This trend will complement cloud integration to deliver both speed and scale.
6. Data Fabric and Unified Architecture
Manufacturers are moving toward building a data fabric—a unified architecture that integrates data across diverse systems, whether structured or unstructured. This approach improves visibility, consistency, and accessibility, ensuring that decision-makers at all levels can rely on a single source of truth.
7. Greater Focus on Data Security and Compliance
With more systems being connected, data privacy and compliance are becoming even more important. Future integration solutions will embed stronger security protocols, including end-to-end encryption, zero-trust access, and AI-driven threat detection, to ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and industry-specific standards.
8. Integration of Digital Twins
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets and processes—are gaining momentum in manufacturing. Their effectiveness relies on real-time, integrated data streams from machines, sensors, and enterprise systems. As adoption grows, seamless data integration will be essential to create accurate, dynamic twins for optimization and scenario planning.
How Can Deskera MRP Help You with Manufacturing Data Integration?
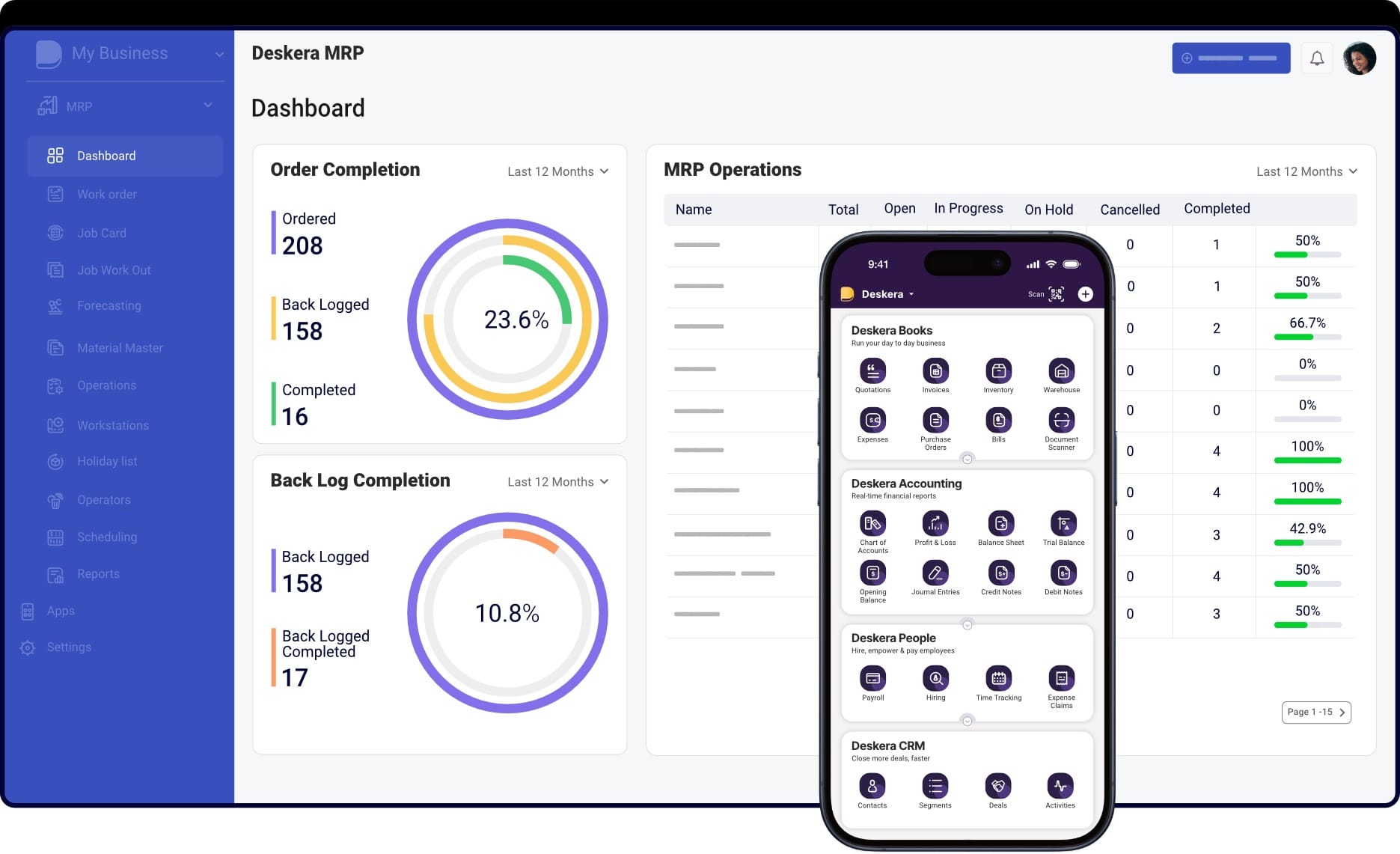
Successful manufacturing data integration requires a system that not only connects different data sources but also provides actionable insights for decision-making. Deskera MRP, with its modern cloud-based architecture and intuitive design, makes this process seamless by bringing together production, inventory, procurement, and sales data into a unified platform. Here’s how it helps:
1. Centralized Data Management
Deskera MRP consolidates data from various manufacturing processes—such as production planning, raw material procurement, and finished goods tracking—into a single platform. By eliminating silos, it ensures that teams across departments can access accurate and real-time information without manual intervention.
2. Real-Time Data Synchronization
Manufacturing requires agility, and Deskera MRP ensures that data is updated across systems instantly. Whether it’s a change in demand forecast, machine downtime, or updated supplier timelines, Deskera automatically syncs this data so managers can make quick, informed decisions.
3. Improved Data Quality and Accuracy
Deskera MRP enforces standardized data entry and process workflows, reducing errors caused by manual updates or fragmented systems. This improves data accuracy across inventory, production, and procurement, which in turn leads to better reporting and analytics.
4. Scalable and Cloud-Based Integration
As businesses grow, so does the complexity of their data. Deskera MRP’s cloud-native infrastructure ensures that data integration can scale effortlessly without requiring heavy IT investments. It also integrates smoothly with other enterprise applications, enabling a flexible and future-ready data ecosystem.
5. Actionable Insights with AI Assistant
Deskera’s built-in AI assistant, David, adds another layer of intelligence to data integration by providing predictive insights, personalized recommendations, and instant answers to operational queries. This empowers decision-makers with contextual information derived from integrated data.
Key Takeaways
- Manufacturing data integration eliminates silos and provides a single source of truth, enabling manufacturers to make faster and more accurate decisions. It is the process of consolidating data from diverse systems—such as ERP, MES, IoT, and CRM—into a unified platform for real-time visibility and smarter decision-making.
- Importance of Manufacturing Data Integration: Integration enhances operational efficiency, boosts collaboration, and strengthens competitiveness by giving organizations a holistic view of their operations.
- Use Cases of Manufacturing Data Integration: From predictive maintenance and defect analysis to demand forecasting and supply chain visibility, integration powers critical use cases that improve efficiency, quality, and responsiveness.
- Challenges in Manufacturing Data Integration and How to Overcome Them: Data silos, poor quality, legacy systems, and compliance issues are major barriers, but they can be overcome with governance, standardization, and secure integration strategies.
- Best Practices of Manufacturing Data Integration: Building a clear data strategy, prioritizing high-impact projects, ensuring scalability, and focusing on security are essential best practices for successful integration.
- Future Trends in Manufacturing Data Integration: Cloud adoption, IIoT, predictive analytics, machine learning, and blockchain will drive the next wave of integration, making manufacturing smarter and more resilient.
- How Deskera MRP Helps with Manufacturing Data Integration: Deskera MRP unifies production, inventory, procurement, and sales data with real-time synchronization, AI-powered insights, and scalable cloud-based integration.
Related Articles