Did you know that the size of the global FMCG logistics market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 3.15% between 2021 and 2028? It is set to rise from USD 105.85 billion in 2021 to USD 131.54 billion in 2028.

FMCG products are widely used by people of all ages around the world. From starting the day with toothpaste to ending it with a facewash, from bread and tea for breakfast to crackers for an evening snack, almost everything packaged and ready to use is an FMCG family member.
With the world recovering from the pandemic and all the sectors beginning to look up with hope for brighter things in the pipeline, FMCG is also catching up quickly. However, the supply chain disruptions that the disease brought with it is still something that the sector is reeling with.
Within an organization, there is information pouring in from all directions, sales numbers, Human Resources, number of stock, bills, invoices, and so on. How can so much data be managed efficiently so that it can be viewed, examined, and utilized to make improvements for the future?
The older methods and manual mechanisms are no more applicable today. Not only are they inefficient, but they may also lead to errors. Bringing about cohesiveness to the overall business operations is a need of the hour. To ensure that businesses rapidly progress and recover from the pandemic's aftershocks, it is crucial to implement the new-age technologies and advanced features of the software systems like ERP.
This article focuses on the challenges of the FMCG sector and how ERP can be a powerful weapon to bring out an overhaul in the industry. Here is what we shall be learning in the article:
Here is what we shall see on this page:
- What is ERP?
- What is FMCG?
- Why do you need ERP for FMCG?
- What are the Challenges in the FMCG Sector?
- How can ERP system Resolve Problems for FMCG?
- What is the COVID-19 Impact on the FMCG sector?
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
What is ERP?
Software that streamlines all the business units – Finance, Inventory, CRM, Accounting, HR – is known as ERP or Enterprise Resource Planning. All these units are integral to a business and need to function optimally for the company to register profitability.
There are tons of information flowing in the company from various departments. The sales department summarizes and presents information, including the sales volume, revenue, leads, new accounts, and other such activities of the business. There are also some very crucial reports that the department may present. This includes the sales funnel analysis report, forecasting sales reports, cash flow forecasting, and sales goals reports, among many other crucial reports.
Accounting: The same thing goes for the accounting department, which shares the responsibility of presenting insights about the amounts, costs, and business expenses that the company is involved with. They must ensure that all these expenditures are made in time. Furthermore, the accounting team must also keep records of the payments that happen within the company. Payments to the employees must happen with coherence from the HR team.
Human Resource: The HR team updates the accounting unit about the attendance and leaves, the bonuses, and other benefits that the employees are entitled to. They are also in charge of the hiring, onboarding, training, and termination of employment. In other words, they look after the employee life cycle based on the information stored on the company database.
Inventory Management: Some companies must also closely monitor their inventory and stocks. The storage and management of raw materials, finished goods, warehousing, etc., are some of the components that affect the overall profitability of the company, and therefore, it is a must that these figures are recorded.
In order to work in coherence and eliminate wastage of time and information, these units of a business must be brought together on a single dashboard to view and analyze data and make informed decisions for business growth.
ERP makes this possible with the various modules that support the different operations of a company, thereby lowering operating costs and loss of time and reducing the wastage of efforts and other resources.
What is FMCG?
Fast Moving Consumer Goods or FMCG, as it is commonly known, comprises the goods that have high demand, are quickly consumed, and are frequently used in day-to-day life. These are the goods everybody needs and purchases for their daily activities.
We shall understand the definition of FMCG through the key features they exhibit and the associated examples.
Quickly consumable: The goods that are bought and consumed in a short span from the time of purchase are called quickly consumed goods. For example bread, biscuits, and packaged snacks are often consumed the day they are bought.
Frequently used: FMCG goods or products can almost be required for daily use. Some examples of these are soaps, shampoos, and biscuits.
Inexpensive: Most FMCG products are low-cost goods and are easily affordable by the masses. A pack of crackers or biscuits or bread are some examples here.
High Demand: Owing to their affordability and availability, FMCG goods are highly demanded products.

FMCG goods are bifurcated into the =categories or industries including the following:
- Food and Beverages
- Healthcare
- Personal Care
- Home Care
FMCG goods stretch out a lot beyond these categories. From processed foods, office supplies, and baked goods, FMCG also includes over-the-counter medicines like aspirin.
More about FMCG Industry
Owing to the high turnover rate, the FMCG market is incredibly large and competitive. FMCG products are not very expensive; however, due to high demand and soaring volume of sales, the products are able to offset the lower profit margins.
Also, since these products are very high in demand, the companies persistently strive for out-of-the-box marketing strategies for higher customer engagement.
It also includes paying close attention to the packaging during the production of these products. This also puts a lot of onus on the logistics teams which often need a helping hand for the optimal packaging process. The unit packs must contain all the information for the consumer about the product.
Why do you need ERP for FMCG?
ERPs are sophisticated systems that can single-handedly prepare you for future divergence or trends in advance. For a company that deals in the production and sale of FMCG goods, customer satisfaction is paramount. But how can they achieve this goal?
Without playing with words, we can state that all it needs to achieve customer satisfaction is streamlining all the processes involved in an FMCG. Is there a system they can land their hands on which not only provides them with existing scenarios in demand, manufacturing, supply, inventory, operating expenses, the budget, etc.?
Precisely, ERP can handle all of this. Its highly-efficient modules for handling each of the business aspects can deliver real-time data which serves as a crystal ball for the vision of the future.
This section entails all the myriad tasks which are necessary for a successful FMCG business and how ERP systems can help raise the ease with which they can be achieved. Let’s take a look at what these are.
Planning, Budgeting, and Forecasting
There are several forecasting capabilities provided by ERP that help clear up the picture of your future. Let’s visit the different forecasting capabilities of the ERP system, through this section.
Demand forecasting: This requires your team to estimate which is the best sales time of the year for a product, which are the highest demanded products, and so on. The ERP system can capably forecast the revenue and cash flow which is crucial for determining or setting up the budget for the year.
Additionally, all these insights can be presented through sorting by customers, holidays, seasons, products, and also by geographical location. The information is vital for scheduling procurements, labor management, and making other decisions for business growth and profitability.
Supply Forecasting: Managing a well-planned supply chain is one of the most crucial aspects of maintaining an existing customer base. When should the procurement begin, or when shall the planning for production take place are some of the crucial aspects that help meet the customer demands in time. Keeping a sync between the time of supply and the time when the product reaches the shelves is significant for efficient customer relationship management as well as supplier relationships.
All of these are possible only when the companies have thorough knowledge about the process and their inventory.
Financial Forecasting: Maintain real-time records of expenses and budgets, forecast capital needs or product demands, and watch for changes in costs that can affect profit margins. When the management has access to real-time data, it can monitor operational spending expertly. Additionally, it also allows it to plan and respond to any alterations and fluctuations in real-time.
This would place the management in a comfortable seat and watch over all the income and expenditures closely.
Managing Multiple Businesses and Divisions
With a wide geographical distribution ad operation of the companies, managing them from one place is difficult. ERP makes it possible through a single database that processes transactions, closes deals and produces financial and other vital reports for each separate entity of the business.
All these reports are compiled and merged together into a centralized system that can be utilized by the owners or managers to make decisions.
Group, Multi-Level, Variant Bill Of Materials
BOMs or Bill of Materials is a list of materials that presents all the raw materials essential in the process of manufacturing the final product. There are multiple types of BOMs like single-level, multi-level, configurable, production BOMs and so on. These BOMs play an irreplaceable role in product manufacturing, and ERP systems are instrumental in the creation of BOMs.
This can be helpful in a material shortage scenario where the BOMs can be dispatched to prevent delays in production. With a real-time view of the situation, materials, parts, and assemblies, the manufacturers would be prepared to make decisions for better inventory management and improving overall efficiency.
Pick, Pack, and Ship
Picking, packing, and shipping (PPS) are the actions associated with the goods at the warehouse. As an FMCG, you must be concerned about how the different processes will align with each other and if they will be accomplished without errors.
- Picking is the process of picking up the goods from a terminal. An ERP-enabled barcode system will help in picking up only the correct order and the right number of items.
- Packing entails packing goods. ERP supports label generation software that is integrated with it. This software generates labels automatically with all the necessary details mentioned on them.
- Shipping is the process of carrying goods to their destination. ERP can integrate with a Transport Management System to ensure that the best shipping method is adopted.
Sales Order Process Management
Order processing is the most important part of order management. Once the order has been generated, resources are allocated to procure raw materials from the inventory. The implementation of an ERP system is an essential part of the sales order processing process.
The order is then directed through the ERP solution until it reaches the assembly line. A custom label and bar code are applied to the order as it is processed for packing in the packaging and shipping department. The next step involves auto-generating an invoice for the customers.
This automated process ensures that there is no confusion regarding the sales and order, and the order can be easily tracked by the people concerned.
Scheduling and Sequencing
What is Scheduling in production? Well, manufacturers have tens and hundreds of orders at the same time, and this requires them to plan well ahead. This ensures an efficient execution in the correct sequence.
When you start production planning with the help of an ERP system, it guarantees the manufacturing of orders without or negligible hurdles. It achieves this by balancing the demand-supply ratio, ensuring sufficient inventory, and avoiding unnecessary stocking of inventory.
Similarly, sequencing in production management implies grouping the relevant operations into batches and then setting them in a sequence that is beneficial to the process.
The Sequencing module of ERP helps the companies quickly recognize the sequencing pain points and also provides maximum visibility and support in the important aspects. This considerably brings down time and effort and aids preparedness in unforeseen situations.
Batch Process Management
The term – Batch Processing – is relevant to FMCG companies with products that require a set formula or recipe. In batch processing, the manufacturers gather the ingredients or components in a step-wise progression.
Chemical companies and food product companies are the two examples that need to adhere to a particular recipe for the final product. They utilize batch processing, where ingredients for the production of the final goods are monitored for their safety and quality.
The manufacturers in this zone must utilize software that deploys a consistent methodology in the database to align the fundamental elements. These elements could be associated with the finances, inventory, shop floor, etc.
Here are four ways in which an ERP can boost the operations in batch processing management:
- Quality monitoring
- Batch traceability and tracking
- Production management
- Batch recipe management
A batch activity is guided by the software in conjunction with the plant's control systems and operator interaction. In addition, standardized processes can be implemented across the organization. Furthermore, the system also helps get the activities recorded to a historical database for documentation purposes.
Capable to Promise (CTP) and Available to Promise (ATP)
CTP is the mechanism of promising or committing to an order based on the available inventory. It involves estimating if a new order can be delivered. The process follows the finite-scheduling model to understand the completion of a product.
It also takes into account any obstacles that may disrupt production by monitoring the lead times for raw materials, gauging the availability of resources, and so on. The process aims at making the production process more time-efficient and cost-efficient. Also, it helps in speeding up the orders and eliminates occurrences of inaccurate delivery-date promises.
ATP is associated with the Available capacity, which involves assessing the possibility of a unit accomplishing or completing a task in the specified time duration. The ATP can be evaluated by the company based on the number of resources available, thereby boosting the overall business planning.
Both CTP and ATP are essential elements in determining if a sales order can be met. Using CTP systems, you can determine when an order can be delivered to the customer. Using a finite schedule model, a product is determined when it will reach multiple production or distribution sites.
Cloud-based Software
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, one of which is that it is constantly accessible and has the potential to ensure easy teamwork even from a distance. Faster conversions and data-driven sales techniques are made possible owing to the handy and readily-available data. It also improves communication between coworkers in the back office and other departments.
You can foresee opportunities and hazards with excellent accuracy with business intelligence.
FMCG companies can grow into new markets with the aid of cloud computing. It empowers them to gather, store, and analyze data on the spot while staying abreast of consumer behavior and market trends. This helps a sales system that moves more quickly push consumer goods that move more quickly.
FMCG organizations can utilize cloud-based field sales software to get information about micro markets and adjust their goals accordingly. They can find out which product is the most profitable one and which retailer is the best within the system. All they need to do is simply compare conversion and revenue disparities between various segments of the same market.
Payroll and HR
Human Resources unit is fundamentally associated with the management of people or employees in the company. The primary objectives are to coordinate employee hiring, manage personnel, and find solutions for problems with hiring, onboarding, departmental assignments, salary and pay slip generation, performance management, bonuses, employee benefits, allowances, and raises.
Payroll is concerned with the processes of integrating and balancing payroll data. HR operations include responsibilities including payroll management reporting, handling wage generating, deductions, and employee record keeping.
The automated ERP system enables a company to achieve the following with respect to the HR and payroll processes:
Rids the HR team of tedious paperwork: Payroll can be a painful process if done manually; however, the same process can become a lot easier with an ERP system in place. Payroll operations can be automated with the help of ERP software to produce precise results in a matter of mouse clicks. With the use of an ERP system, more information may be accessed in less time.
Time and attendance tracking: ERP systems offer a detailed description of each employee's advance and accrued leave statuses. Utilizing integrated ERP attendance systems, you may evaluate an employee's productivity in terms of working hours, late arrivals, on-time arrivals, working overtime, etc.
More transparency in HR procedures: It might be challenging to have a comprehensive view of staff resources, particularly if you need to discover employee flaws like late entries and duplicate booked holidays, and so on. The HR team can independently examine the issue, weigh their options, and undertake the steps to make improvements.
Updated employee data: The HR department needs to get data from multiple sources for the various processes they need to carry out. There is a strong likelihood that the data will be redundant, duplicated, and erroneous. However, the storage and updating of all data are made possible through the ERP software, which facilitates quicker and better decision-making.
To summarize, we can say that ERP for HR and Payroll management interfaces with all other business units and gathers all scattered employee-related data into one location. This assists in giving accurate information on every employee in the organization.
What are the Challenges in the FMCG sector?
While an FMCG product goes through numerous stages before it finally reaches the store shelves, we can identify the fundamental obstructions that an FMCG company may face. An FMCG company is all about products, and therefore, inventory management is paramount. A close second comes to the supply chain, in the absence of which the products may not reach the consumer.
The third challenge is the maintenance of customer loyalty, followed by maintaining standards and controlling the overall flow of work. We will be looking into these primary challenges that most FMCG struggle with.
Managing Inventory
While FMCG organizations are aware of the major issues surrounding the inventory and also that they need to keep stock all around the year, there are several aspects that still bother them. Here are some of the points that can provide an insight into the core issues:
- Product identification and geolocation: To identify the location of the product accurately, geolocation which is a sophisticated tool that enables us to know the real-time location of the object or product, can be utilized. Without this, the manual tracking of the products can be a time-consuming and error-prone mechanism.
- Product expiry date: It is important that the manufacturers track the products through their expiry dates as they can prepare better to deal with the expired products. Perishable products may give a tough time to the manufacturers as they require keeping track of expiry dates across multiple batches for each product.
- Manual assessment of inventory data: Trying to accomplish anything manually can be laborious and induce errors. Inventory data needs to be maintained and analyzed at various stages, but manual attempts can ruin the processes going forward.
- Managing POs (Purchase Orders): Manual management of POs can be frustrating and lead to man-made mistakes.
- Restocking decisions: Without a complete view of the stocks, restocking decisions could be difficult and may not prove fruitful in the long run.
- Logistics management: The conventional methods of tracking goods and packages, manual numbering, and labeling are not dependable methods, and the companies may have to bear the brunt of erroneous actions later.
Lowering COGS
One of the most crucial aspects of your firm that you should comprehend is the cost of goods sold or COGS. The direct costs associated with the manufacturing of the items sold by a company is how we can define COGS. This sum takes into account both the direct labor costs and the cost of the materials required to make the goods.
Companies must prioritize understanding COGS. While it is important to calculate COGS for service-providing companies, for FMCG, it becomes even more vital. COGS is used to determine taxable income, analyze a company's profitability, and help with business strategy decisions.
Businesses that rely on E-commerce or inventory have erroneous financials without proper COGS and inventory values each month, which leads to high costs and poor business decisions. This especially applies to the E-commerce FMCG companies that need to monitor their profitability every month.
Disrupted Supply Chain
From procurement to demand management, along with the correct documentation, can be some of the top challenges when FMCG firms are trying to keep their supply chains intact.
COVID-19 Impact: Aside from this, COVID-19 has influenced the supply chain tremendously. People falling prey to the disease led to the unavailability of manpower, disrupting the supply chains across businesses all over the world.
Huge Demand: While the supply chains got interrupted, at the same time, some segments of the FMCG sector witnessed a huge surge in demand; for example, medicines, toiletries, and personal hygiene. Meeting this heightened demand was close to impossible when the labor count was low.
Shipping Issues: The shipping issues have been troubling the global shipping industry owing to inordinate deadlocks. Port slowdowns due to the pandemic restrictions have only doubled up the shipping bottlenecks and problems. The other factors that add to the woes are insufficient resources to document the vital details of shipments and delivered products, etc.
While there are some factors that are beyond anyone’s control, there are others that can be effectively managed through a comprehensive automated system. We shall see how ERP can be instrumental in resolving these issues in the next section.
Maintaining High Standards of Quality
Quality has always been the top priority for most consumers. Companies frequently feel pressured to supply high-quality items in a timely and hassle-free way, especially in the consumer goods sector. This happens due to the constantly evolving and expanding client demand. It is an important aspect as the whole commercial performance of the companies can be hampered by quality alone.
They must consistently improve their services, products, and processes, which necessitates the use of cutting-edge advancements in software systems. To adopt a comprehensive approach to quality management and achieve customer excellence, consumer products companies must adopt a quality management system.
Control Workflow
Improving the way all the units in the business work tends to enhance the overall functioning and output of the company. There are so many different operations taking place in an FMCG company, such as managing the stocks, getting and sorting data from the sales, updating the financial statements based on the reports from the various departments, and whatnot!
However, in the absence of a sophisticated system, it would be difficult to maintain an agile workflow within the company, and things would turn out haywire in no time. Therefore, before the situation becomes irreparable companies must introduce modern systems that can combat this problem and provide distinguished solutions.
Here are some areas that can bring more agility to the workflow and which can be managed more efficiently:
- Maintaining fruitful communication between all the modules of the business
- Deployment of employees effectively
- Improvements through real-time data
- Having a flexible production system
- Regular machine checks
- Ensuring accurate packaging, shipping, and logistics
- Maintaining product quality
In other words, they need to introduce automation in the business processes to see visible improvements.
Transportation Management (including Freight Charges and Overhead Expenses)
Managing your supply chain and logistics presents fresh difficulties every day. Accuracy, speed, and flexibility are essential in the transportation industry if you want to increase compliance, cut costs, and make the most of your resources. This includes satisfying client needs for efficiency and improved margins, as well as managing your routes and carriers.
Then there are ever-increasing freight charges and overhead expenses. Moreover, there are repetitive tasks that, if done manually, can bring a burden of hassles. Such scenarios require the manufacturers to look carefully into optimizing route and carrier selection.
How can ERP system Resolve Problems for FMCG?
With ERP, you get these features that are essential for your FMCG business:
Multi-channel Sales Integration with E-commerce
When multiple sales channels are utilized for a company's goods or services, they are referred to as multi-channel sales. We have been a witness to an unparalleled increase in retail expenditure following the pandemic when everyone had begun to order and shop from e-commerce stations. In 2021, online retail sales in the US increased by 40% year over year, and purchasers are increasingly using multiple channels to make purchases.
Brands are seeing an increase in demand as more and more customers want contactless and secure deliveries through e-commerce channels. Enhanced product information and insightful reviews are a couple of the major things pushing people to shop online.
In recent times, the purchasing environment has seen a significant transformation. While physical stores are still very important, e-commerce has gained traction and is predicted to continue helping FMCG firms grow their market share and drive sales. FMCG companies have an advantageous position as they benefit in numerous ways, including the following:
- Better outreach to customers
- Better Monitoring
- Earn customer loyalty and trust
Here are the top ways in which ERP can resolve issues pertaining to multi-channel sales in FMCG companies.
Storage of Information
FMCG companies can use multi-channel selling software to build a single, central product catalog that can be seen and handled simultaneously in real time across all channels. All of your content, images, and photos are kept in one handy area as you expand the number of marketplaces and channels you use for your selling plan.
You need to be able to check the messaging on all channels without going to each one separately.
Cross-border transactions
ERP integration facilitates hassle-free cross-border transactions with ease. Companies can now carry out transactions and deals on international platforms using their client’s or customers’ currencies. This is possible with the order management system module of ERP.
Simplifying exchange rates
ERP makes way for automated calculations that enable you to convert international transactions into the home currency. This is greatly helpful in eliminating errors and expediting procedures.
Enabling multilingual templates
ERP helps ease communication as you can speak to your customers in their own language. Also, customizing invoices based on the native language of the customer is now feasible with ERP-integrated modules.
Integrate multiple channels
It is increasingly simple for companies to expand their reach to many more customers by integrating all the favored online sales channels, including Amazon, Shopify, and so on.
Enhanced Inventory Management
Inventory or stock is one of the most important components of FMCG, the companies must have complete control over it. By gaining control over the stocks, the companies are better positioned to prepare stock to satisfy anticipated demands and also eliminate the surplus inventory.
Here are the points that can help sum up the ways in which the ERP system can organize the inventory management for FMCG companies:
Better product identification with real-time geolocation and expiry dates
FMCG goods involve a lot of codes and numbers, which are tough to keep track of. Using codes and numbers to identify your products enables you to get a complete picture of your stock. This benefit optimizes the workflow for your professionals.
The ERP software is equipped to provide companies with real-time expiration dates. Furthermore, the product geolocation is quick and precise with an ERP system, as everything is available in real-time on one single dashboard.
Complete integration of information
Through an automated procedure, ERP software enables the integration of all pertinent data related to inventory management. This way, the company can do away with the manual assessments. This is a benefit of the system that immediately resolves the dangers of scarcity and excess inventory. The constant monitoring also offers a forecast of demand, which is essential for every business in the FMCG sector.
Better inventory management and safety
In order to secure your data and enhance the inventory management of your business, ERP software can be of great help. It enables you to keep track of each authorization granted to your staff, presenting you with any unauthorized access, if any.
Thus, managing company data adequately is paramount for the success of a business.
Automating purchase orders (PO)
You can automate your purchase orders linked to your suppliers or customers using ERP software. By doing this, you can easily determine future restocking needs based on your recent and latest accounting data.
Aside from this, it also helps in minimizing the actions to be made owing to the commercial management module of your integrated software. Thus, an ideal organization can be set up as the information gets transferred instantly between each department.
Automation of inventory restocking
FMCGs without access to the most recent data attempt to make decisions regarding inventory replenishment, which may lead to mismanaged inventory or shortages. In either case, the company does not seem to benefit in any way. By integrating real-time updated data, using ERP software enables these operations to be automated, and errors can be minimized.
Regulating the merchandise flow (flow of goods)
FMCGs need to monitor the way the inventory is flowing or moving for efficient inventory management. To assess this, they need to have the real-time scenario in front of them.
The ERP system’s real-time data allows you to create and implement the strategies that are best suited for maximizing the flow of your products.
You can derive the best outputs with advanced inventory control and by tracking your goods using distinctive numbering systems.
Efficient logistics management
Maintaining logistics can be an uphill job in an FMCG in the absence of an integrated and advanced system. ERP offers an edge over the older methods of maintaining logistics by providing a simplified interface and better accessibility of information to the logistics management team.
This way, the number of man-made errors can be brought down considerably and also help the team in increasing their productivity.
Improved and informed decision-making process
An automated system like ERP enables authorized people to access pertinent data stored in the centralized database. This eradicates the problem of manually entering and analyzing the data in spreadsheets.
The managers or users can be sure of the authenticity of the obtained reports, and thus, the process becomes time efficient. These reports can be further used to make informed decisions regarding stocks. ERP software can also incorporate accounting data from all the balance sheets and update information for an effective decision-making process.
With an ERP in place, any difficulties with the stocks at any point are very clearly identified. When any authorized person or user from the company wants to access any information about the stocks, such as restocking, reorder levels, or any other essential parameter pertaining to their inventory.
To provide users, managers, and business owners with a more exact understanding of what is kept in stock and what needs to be restocked, the system keeps detailed data about every single product that is readily available.
Additionally, by comprehending customer purchasing patterns, the tool also aids in estimating demand, giving you the ability to tailor your supply to meet future demands.
Helps Lower the COGS
According to a survey from 2010, 26% of factories have still not implemented an ERP system. The software helped manufacturing organizations with outstanding procedures lower inventory levels by 22% and the overall costs dropped by roughly 20%.
Companies often feel that they either do not need an ERP because of their smaller size or have an opinion that it may not be fruitful in terms of ROI. However, the companies must consider the amount of flawlessness and integrity brought about by the ERP integration.
Automation is the biggest advantage an ERP brings to the table. Your cost of products sold can significantly drop for each task that a machine can perform. Automating directly implies a lower requirement of labor and subsequent labor costs. When there are lesser people and resources deployed, the cost goes down and the efficiency is improved owing to the automated tasks. If the companies do not automate the tasks that heighten the COGS, they are bound to lose out on business.
Supply Chain Management
The entire procedure your company goes through to deliver a finished product to the customer falls under the process called Supply Chain Management. From raw materials to a final product that might provide value for both your business and customers, these are all a part of the SCM.
When there is so much value attached to the process, it becomes crucial to introduce ERP for better supply chain management and which can be integrated with the supply chain management module. can boost productivity and timeliness.
Strategizing and introducing ERP in your supply chain management can prove to be a game changer for the growth of the business. Let’s look at some of the areas where integration can make a tremendous difference.
Efficient procurement and demand management
FMCG companies can receive a huge boost with the implementation of an ERP system when it comes to procurements and demand management.
Among the various functionalities that ERP automates, demand planning is also automated by ERP. This generates demand when orders are received. The scheduling is carried out by the program when an order is received. This enables the team members to effectively plan production tasks and product delivery because they have access to real-time information on how resources are being used in production.
The management of warehouse resources, material transportation, and other supply chain processes can all be automated or streamlined to increase efficiency.
Accurate processing and documentation
With the automated invoice generation by the ERP system, these can be sent directly to the customer once the products have been delivered. When it comes to cross-border shipments, the supply chain team can make and send the necessary import and export papers for such shipments.
This is not all! The system also automatically compiles a history of shipments and deliveries for timely deliveries, ultimately boosting customer service while minimizing errors.
Cloud capabilities
Cloud ERP software has grown in popularity in recent times, and a variety of sectors have benefitted from it. The reasons for the cloud ERP finding a strong foothold are its mobile access and dedicated data security.
With an ERP solution that is hosted in the cloud, accessing the system from any location at any time using a mobile device is a fairly simple task. It is especially significant in the supply chain scenario owing to the fast-moving nature of supply chain goods. The ERP system enables rapid action without necessitating the presence of the entire team.
Better visibilities
ERP software gives your supply chain management team a thorough, real-time view of company operations. In other words, it enables you to gauge particular inefficiencies for better results. Eventually, it is instrumental in informing if there is anything amiss in any particular segment of the chain.
Organizations may develop smarter plans for how they use their resources. All the resources, including employees, can be managed with increased efficacy when the companies have deployed an ERP system.
Quality Control and Testing
Food manufacturers are increasingly using ERP systems to manage the critical operations necessary to maintain quality assurance and compliance in their goods. While a growing number of customers are more cautious about the information on the food labels, the concerns about maintaining higher industry standards have been the focus of the FMCG companies. Also, the companies are constantly striving to lower the frequency of food product recalls for better growth and to boost customer relationships.
Quality control is a serious issue and becomes all the more significant when companies experience a higher recall rate. Software for ERP food manufacturing may ensure that best practices are at the heart of all food production operations, lowering the likelihood of a product recall and enhancing transparency across the product life cycle.
Here are the ways in which the ERP can raise consistency and match industry standards:
Meet Industry Standards
When it comes to FMCG companies that are into food manufacturing, there are very strict regulations they must abide by. There are guidelines that cover everything from freshness to added colors, any ingredients that are frequently found allergic, and sweeteners to salt content. A single food product consists of numerous substances that must meet the set standards.
By utilizing ERP software, companies can be sure of quality control checks. This makes it simpler for manufacturers to adhere to the strict regulations that govern the sector, such as the good manufacturing practices or GMP compliance, that are regulated by the FDA.
The quality control module of the ERP system can work on and address a whole lot of issues pertaining to manufactured goods. These include issues like allergen control, lot sizes, product testing, raw materials, environmental monitoring, storage, and distribution.
Maintain Product Consistency
From candies to cosmetics, products comprise tens of raw materials. One thing is common across FMCG goods, and that is to maintain consistency. Speaking of the eatables, the recipes must be followed to ensure that the product has the same taste and texture. These recipes and exact formulas can be fed into the ERP system for future reference and to maintain consistency.
Recipes and production procedures must be carefully duplicated for each batch in order to deliver the consistent product that consumers demand. Recipes and formulas can be recorded, stored, and managed using ERP software.
Often, substitute materials need to be added to the existing set of ingredients due to the unavailability of certain materials. The sophisticated functions of ERP will help to ensure traceability regardless of modifications or changes made in various production batches. Users can create batch tickets with exact amounts and instructions for manufacturing staff to manufacture any kind of product – simple or intricate.
Adhering to Government Guidelines
The Food Standards Agency in the UK, the FDA in the USA, and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), as well as a number of private organizations that have guidelines for food products, are among the public organizations that ensure the quality and safety of food and drink products in various markets.
The various phases of the manufacturing of food and drink, from product testing to dispatch, can be covered by the quality control features of ERP systems. The system is equipped to send out reminders for inspections, routine audits, product recalls, and reports that can all assist producers in upholding required standards.
Additionally, tasks such as recording batch schedules, recipes, compliance reports, and data for future assessment are all made easy with ERP.
Reduce Recall Rate
Higher recall rates can have serious implications on the profitability of a business and can greatly impact the product’s popularity. Needless to say, the brand name can get severely tarnished owing to the wrong headlines it makes. Furthermore, the lost trust of the customers can have long-lasting effects on all accounts.
ERP systems offer a lot of traceability at all points in the manufacturing cycle, enabling companies to monitor production issues. The thorough checking procedure can rule out any subpar or contaminated products from making it to store shelves.
Ensure appropriate labeling of products
Laws and guidelines call for food labeling to correctly disclose comprehensive nutritional information about the packaged material. It must disclose the ingredients, nutritional value (in case of food items), and any allergens in products.
ERP systems include a lot of tracking features and electronic batch records, enabling businesses to precisely create labels with the exact components and allergen. Thus, the system makes it simpler to comply with requirements.
Improves Brand Reputation
By streamlining and standardizing their operations in accordance with regulatory and customer standards, quality management software assists consumer products companies in building this confidence. A QMS also encourages a culture of gradual progress, which has a considerable positive impact on the company's bottom line, customer satisfaction, and brand image.
Regulate Industry Workflow
Workflows, which we can refer to as processes, are what drive manufacturing. Even though the technology is pervasive nowadays, several firms still manage their operations entirely manually. While this worked in the olden days, the process may throw things completely off-track in today’s scenario.
Not only does it impact the resources such as time and effort, but it also results in financial waste. In the process, industrial productivity and overall efficiency take a huge hit. This further highlights the importance of digitizing specific industrial workflows and information systems.
Here are four ways in which ERP can help improve the industry workflow:
Integrating EDI and ERP for Managing External and Internal Communication
The manufacturing industry relies completely on paper-based communication and documentation. Additionally, what follows is a lengthy process of creating a document, taking it to the concerned authority, getting it approved, and finally, it goes to the other department for further processing. This process is immensely tedious and leads to the wastage of tens of valuable office hours.
The use of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) can resolve all these issues. EDI facilitates the transfer of information or business documents from one computer to the other.
The goal of EDI and ERP integration is to automate data flow between a business' front-end EDI application and its back-end ERP system. It eliminates the need to manually re-enter messages, orders, or invoices when EDI and ERP solutions are automated.
Automating Sales, Purchase, and Inventory Management
Imagine a company that maintains its inventory manually. It also manually updates the orders, invoices, etc. When a sales order arrives, it makes decisions whether to raise a purchase order for fresh stock or to proceed with a work order. As a result of physical inventory checks and an inordinate amount of documentation, this process takes a long time.
In contrast to this, an ERP helps update changes and view insights easily. Based on previous sales trends, current sales orders, inventory levels, and future orders, an ERP calculates how much stock is required for future orders.
In response to the analysis and demand forecast, reorders of raw materials are initiated by raising Purchase Orders (POs) or Requests for Quotations (RFQs) with vendors. The system is capable of sending automatic reminders to purchasing managers and suppliers in the event of any changes in demand to delay or expedite shipments.
Work orders can also be generated quickly based on sales orders, enabling manufacturers to increase production efficiency and drastically reduce manufacturing lead times. Therefore, it is crucial to automate this workflow which helps avoid overstocking and lower storage costs.
Automating Supply Chain Management
Keeping track of products, packages, shipments, and delivery is one of the most difficult issues in supply chain management. FMCG companies can have all the vital information and insights pertaining to their supply chain by deploying an ERP linked with a tracking solution.
- Digitizing assets: ERP enables companies to digitize their physical assets, such as raw materials, semi-finished goods, and finished goods, using barcode and labeling technologies.
- Identifying clients: By connecting them with ERP, you can keep track of their movement at all times and also assess and identify the client to whom they will be delivered.
- Mill certifications: There is a lot more than the SCM team can keep track of, such as heat numbers and information about the material composition. They may also attach mill certifications to lot numbers.
- Foresee and track delivery: The businesses can predict the delivery of resources and commodities from your suppliers by tracking them online, and you can then schedule production appropriately.
- Easy detection of faults/defects: The SCM team is better positioned to determine where in the supply chain a specific component, unit, or batch originated in times when a defect is detected. This also helps in carrying out prompt product recalls.
Automating Scheduling of Production and Manufacturing
FMCG companies must have a firm knowledge of the number of materials, resources, and the timeline by which the manufacturing will be complete. This can be comfortably accomplished through ERP.
ERP can successfully forecast the number of units manufactured. With the MRP module of ERP (Material Requirements and Planning), the teams can gauge the number of materials that can be used and also initiate purchase processing in case of material shortage. This eventually speeds up the inventory movement.
Production scheduling is based on the manpower available for production and thus, the total time required for production can be estimated. Furthermore, ERP can present the demand due dates based on which supply planning and shipping can be accomplished smoothly.
Transportation Management
FMCG companies can effectively forecast demand and shipment volumes with the help of transportation management in ERP. The integration of modules through ERP can reasonably improve your freight management, and consolidation of orders, maximize the return on their transportation investment and gain real-time visibility into domestic and international shipping across all modes of transportation. In other words, they can resolve all of their transportation hassles with this system.
Here are some ways in which it helps:
Optimize Shipments
The ERP system lets you organize and streamline shipments by presenting all the valued information such as expenses, restrictions, and penalties in mind. You can drastically lower the amount spent for maintaining the necessary levels of customer service.
Carrier Booking
With an ERP-enabled transport management system, you can work together with carriers, organize space for shipments, and modify booking confirmations. Fundamentally, you are empowered to effectively plan transportation operations. You can also select the preferred carrier for your shipments based on optimization and ranking algorithms by bidding orders to one or more carriers through the system.
Examining all aspects of Transportation
Sending and tracking freight orders and the associated costs is made simple with the utilization of the transportation module of ERP. You can also maintain relevant documents and manage communications with carriers. This brings about an overall improvement in the process of freight handling while making it more aggressive. You can also achieve responsive logistics execution by integrating it with your warehouse management system.
Route Planning
With the help of ERP transportation management, you may assess a group of orders and choose the appropriate method, route, and carrier to reduce costs. This will also aid in maintaining the appropriate level of customer service.
Appointment Scheduling
You can stay informed about appointments and avoid problems when more than one courier comes to a particular spot at the same time. The transportation module can also update you if the docks are available for loading and unloading cargo.
Dispatch Planning
ERP transportation management aids in efficient dispatch planning; you may combine the dispatch of materials from various sales orders and acquire the necessary flexibility for efficient dispatch and loading.
Finance
The transportation management assists you with handling actual cash exchange between your business and cost or revenue centers. This includes freight invoicing and accounting with enhanced convenience and effectiveness. You can also lower errors on paid invoices and guarantee more accurate freight ratings.
Follow-up with transport
It is essential to attend to the necessary administrative or physical tasks related to transportation, and the ERP allows you to do that by syncing information. The various tasks including step-to-step tracking of shipments, customs clearance, billing, and alert setting can be managed with a few clicks by the concerned teams.
What is the COVID-19 Impact on the FMCG sector?
The FMCG sector has been as severely hit by COVID-19 as any other industry. However, the demand for consumer packaged goods increased dramatically in countries that were severely hit. This was due to the unavailability of certain goods in the local markets and also as people were restricted from moving out.
Additionally, trends also show a growth in household goods spending. As a result, the market for fast-moving consumer products saw significant changes. With the passage of time and as vaccination rates rise things have started to look better for almost all sectors.

Unprecedented Rise of E-commerce
When the pandemic began, consumers’ visits to the grocery store were brought down to a minuscule as people initially attempted to lower their risk of contracting the virus. Some also resorted to storing and hoarding food, water, and other packaged goods.
With the majority of people sticking to the online routine of purchasing goods, we witnessed an unprecedented rise in e-commerce. From household, home care, vegetables, medicines, cosmetics, and packaged food were all ordered online.
Governments Striving to Revive the situation
Diverse governments are making strong efforts to limit the outbreak. The FMCG business has, however, been severely harmed by social distance. The few examples most FMCG firms encounter globally include logistical problems, a lack of sufficient manpower, operations that only allow for the production of necessities, etc.
Food and Beverages, Cosmetics – The Most Affected
The effects of COVID-19 have also been felt in the food and beverage industry. For instance, businesses that produce processed foods and non-perishable goods have witnessed a significant rise in sales as a result of the scarcity of fresh fruits and vegetables. However, due to a lack of food supply, workers, and strict government lockdowns, restaurants, and retail food enterprises have faced tremendous hardships; some have been forced to shut down permanently.
Following the Covid-19 outbreak, American customers are altering their purchasing habits. According to 27.5% of respondents, the outbreak has caused them to limit their activities and stay away from crowds. This fact has led to a sharp fall in the demand for cosmetics.
Medicines, Personal Hygiene – The Gainers
While there are food, beverages, and cosmetics taking a hit, there are others such as medicine and hygiene products that have shot up their sales. The global demand for personal hygiene products like hand sanitizers and handwash has been increasing exponentially.
The global COVID-19 impact has primarily been on the supply chains and the logistics industry. It has been reported that approximately 76% of businesses lowered their revenue targets by over 20%. The uncertainty created by the pandemic has been giving fluctuating results to businesses.
While some companies never had any online presence have had to make a move toward E-commerce, the ones present online were surprised to receive an overwhelming response in terms of orders during the pandemic. The uncertainties in the business have been met with a response from the companies which are taking measures to implement safe and secure methods in their logistics business.
Conclusion
From all the points that we have discussed in the article, we learn that FMCG is an industry that keeps the owners and manufacturers on their toes in the context of business operations. FMCG companies have multiple and very diverse sets of units that need to work in sync with each other; it requires business owners to make quick decisions in times of high demand.
All these factors necessitate the utilization of a system that makes things easier and assembles or congregates the different business modules. When all of the processes including finance, HR, inventory, production, etc. will be present and accessible on a single dashboard, they pave the way for making critical business decisions for its profitable future.
How can Deskera Help You?
If you are looking to automate the important processes of your FMCG business that require meticulous time and attention, you are on the right page! Deskera offers you an ERP system that is not only compliant but also quick and easy to deploy.
A sector like FMCG requires quick actions from the manufacturers and also mandates them to have a bird’s-eye view in real time of all the ongoing business operations. With Deskera ERP’s cloud-based business management, you can quickly glance through all the happenings and receive real-time reports of various business modules.
Outstanding accounting solutions with Deskera Books help you automate your accounting tasks including invoicing, expenses, billing, payments, multiple currency payments, and much more!
With Deskera CRM, you can access software that helps you expand your customer base through CTAs, landing pages, email marketing, and also walk through the relevant stages of your sales pipeline.
Last but not the least, manage all your HR processes and payroll with Deskera People. It makes handling your staff, their deductions, bonuses, attendance management, and overtime remarkably simple.
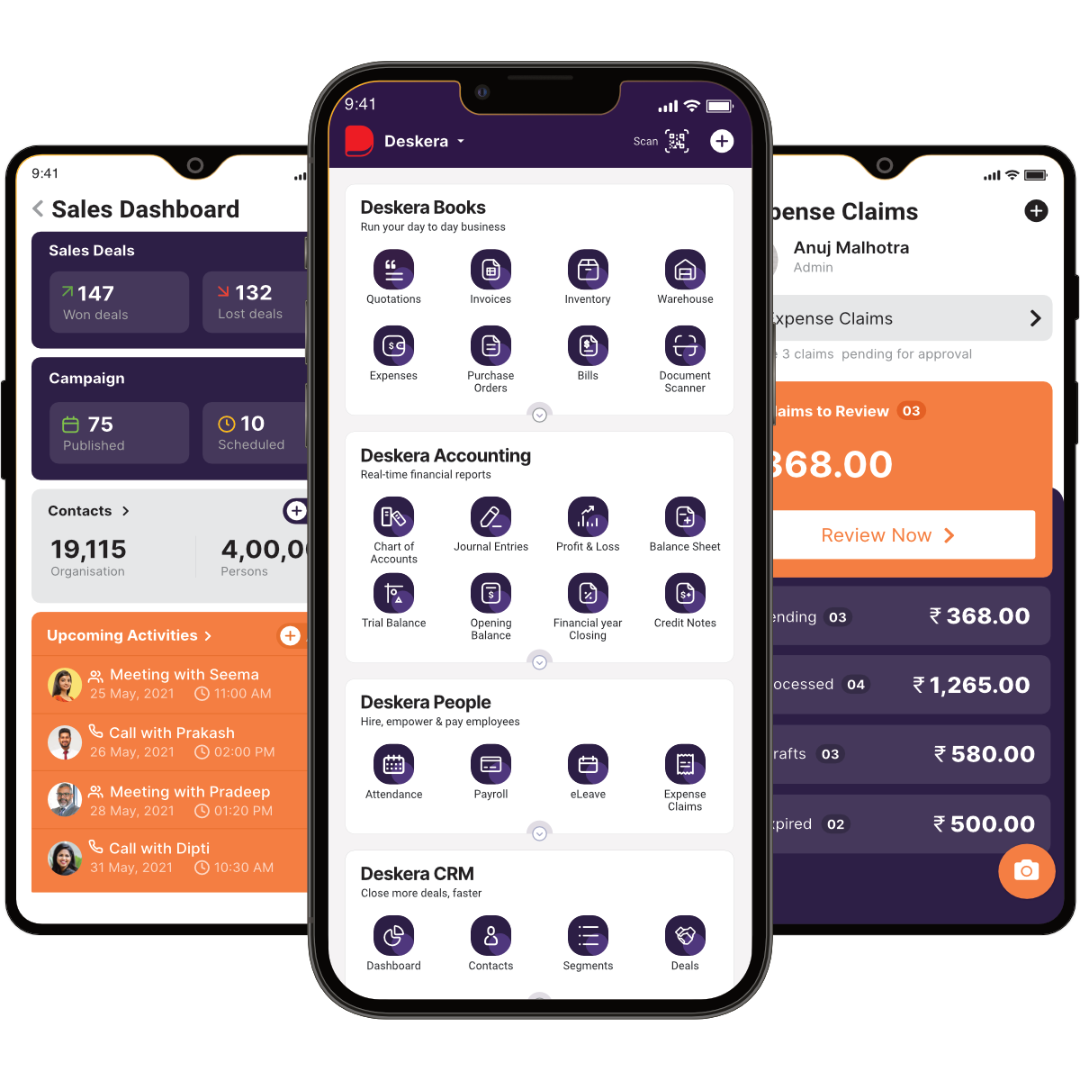
With Deskera’s ERP, here is what you shall enroll for:
- Connect with a centralized database
- Manage multiple locations and business units
- Shoulder seamless process flows
Key Takeaways
In order to work in coherence, and eliminate wastage of time and information. If and when all these modules are present on a single dashboard, managing the business becomes peaceful.
- Software that streamlines all the business units – Finance, Inventory, CRM, Accounting, HR – is known as ERP or Enterprise Resource Planning.
- Fast Moving Consumer Goods or FMCG, as it is commonly known, comprises the goods that have high demand, are quickly consumed, and are frequently used in day-to-day life.
- The FMCG products are characterized by features such as quickly consumed, frequently used, inexpensive, and having a high demand.
- Budgeting, Shipping, Sales Order Management, Scheduling & Sequencing, Batch process management, payroll are some of the ways in which an ERP system can benefit the FMCG companies.
- Managing inventory, lowering COGS, disrupted supply chains, maintaining standards, controlling workflow, and transportation management are some of the areas of business that most FMCG companies struggle with.
- Multi-channel sales integration, enhanced inventory management, lowering COGS, efficient supply chain management, regulating industry workflow, and transportation management can be efficiently handled with an integrated ERP system.
- COVID-19 disrupted the supply chain for FMCG while paved the way for unmatched E-commerce transactions. While cosmetics and grooming products segment of FMCG took a hit, personal hygiene products and medicine were some of the biggest gainers in the pandemic years.
- When all of the processes including finance, HR, inventory, production, etc. will be present and accessible on a single dashboard, they pave the way for making critical business decisions for its profitable future.
Related Articles