World Economic Forum shared an interesting insight into digital manufacturing. The global value of digital manufacturing is estimated to reach $1.7 trillion by 2023. In 2020, the global market value of digital manufacturing was estimated to be $1.1 trillion. Digital manufacturing is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% between 2020 and 2023.
Digital manufacturing is a new technology that is transforming the way products are made. It uses computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). These tools assist in creating digital models of components and products. These components can then be produced using various fabrication processes.

Digital manufacturing allows for the rapid prototyping of components and products. Thereby reducing the cost and time involved in the development of new designs. It also allows for a much higher level of customization than traditional methods. Digital manufacturing has the potential to revolutionize the way products are made. This ranges from the automotive and aerospace industries to consumer goods and medical devices.
Digital manufacturing streamlines the design, production, and distribution processes. With that, it can make custom parts and products more cost-effective and accessible. Consequently, many more businesses can access these.
Here is all that we shall cover in this post:
- What is Digital Manufacturing?
- History of Digital Manufacturing
- Types of Digital Manufacturing
- Digital Manufacturing Processes
- Challenges and Limitations in Digital Manufacturing
- How can ERP help Digital Manufacturing?
- More about Computer-Integrated Manufacturing
- More about Product Lifecycle Management
- Top 5 Benefits of Digital Manufacturing
- How to Leverage Digital Manufacturing in Your Company?
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
What is Digital Manufacturing?
Digital manufacturing involves creating a virtual model using technology before a product is physically built. Engineers can test and iterate on the design using Industry 4.0 principles before committing resources to production.
It also enables the creation of personalized products on demand without significant minimum order quantities. This is because the product can only be manufactured when ordered. Thus, there is no need to stock finished goods.
It utilizes CAD, CAE, and CAM software to automate the entire manufacturing process. Digital manufacturing can also allow companies to produce more complex products.
History of Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing has been around since the late 20th century when the first computer-aided design (CAD) software was developed. This software allowed engineers and designers to create 3D models of products and objects, which could then be used to create physical objects.
This process of digital manufacturing revolutionized the way many products and objects are designed and manufactured, and it has become even more sophisticated over the years.
Today, digital manufacturing is used in almost every industry, from aerospace and automotive to medical and consumer products. It has become the backbone of modern manufacturing, enabling companies to design and manufacture products faster, more cost-effectively, and with greater precision than ever before. It is also helping to reduce waste and increase production yields, making it an essential tool for modern manufacturers.
Early Adopters of Digital Manufacturing
Early adopters of digital manufacturing are those who are willing to invest in new technology and reap the rewards of its efficiency and accuracy. These organizations have embraced digital transformation and sought out innovative ways to leverage new technologies to automate and streamline processes.
These companies have also invested in digital manufacturing solutions such as computer-aided design (CAD) software, 3D printing technology, and robotics to create digital twins of their products and production lines.
Additionally, these organizations are also leveraging digital manufacturing to gain greater visibility into their supply chain, manage data across various systems, and quickly respond to customer demands. As a result, early adopters of digital manufacturing are reaping the rewards of increased efficiency, decreased operational costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Types of Digital Manufacturing
We commonly come across the following types of digital manufacturing:
3D Printing
3D printing is a type of digital manufacturing technology that uses a computer-controlled printer to create three-dimensional objects from a digital model. It is also known as additive manufacturing, as the objects are created by adding materials layer by layer.
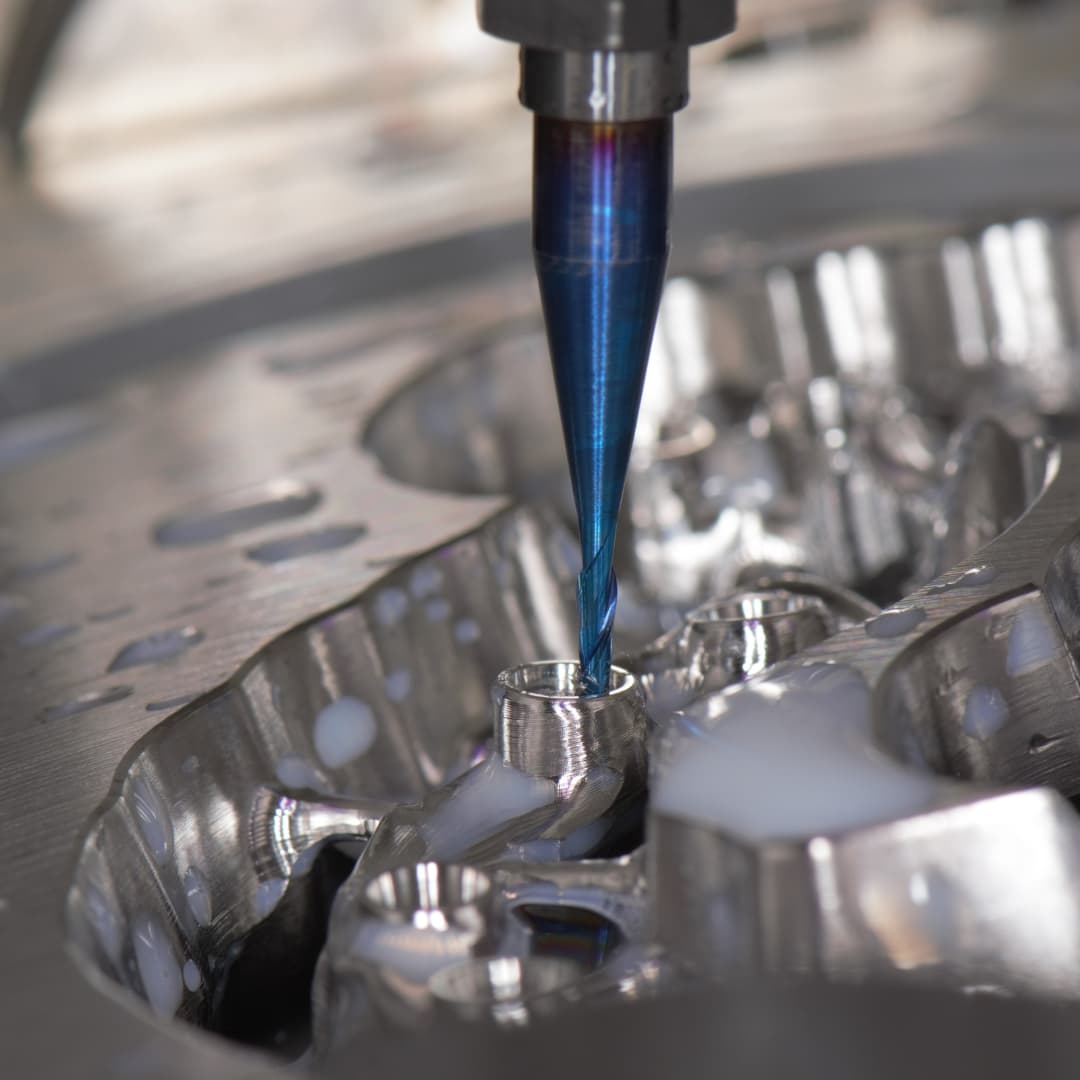
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a type of digital manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled tools to shape a workpiece. It is commonly used to create parts and components for a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products.
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a digital manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled tools to create a physical prototype of a design quickly and accurately. It is often used in product development and engineering to help designers and engineers visualize and test their ideas before moving forward with production.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a type of digital manufacturing process that uses a laser to cut materials into shapes and sizes. It is commonly used to create parts for products in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries.
Computer Numerical Control
CNC, or computer numerical control, is a type of digital manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled tools to shape a workpiece. It is commonly used to create parts and components for a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products.
Digital Manufacturing Processes
There are three main types of digital manufacturing processes that we shall see here.
- Design and modeling
- Optimization
- Data Collection and Analysis
Digital manufacturing is a process that uses digital tools and technologies to create physical objects. It can involve 3D printing, CNC machining, and other forms of computer-controlled manufacturing.
Design and Modelling
The process typically starts with design and modeling, which is when a 3D model is created, or an existing model is modified to meet the customer's needs. This step requires knowledge of 3D software such as CAD and CAM.
Optimization
Once the design is complete, the next step is optimization. This involves using algorithms to determine the ideal parameters for producing the object. This includes how fast the machine should move, what materials should be used, and what processes should be used.
Data Analysis
The final step of the process is data analysis. This is when the results from the previous steps are analyzed to check the accuracy of the design and the quality of the object. This step is important for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the final product.
Challenges and Limitations in Digital Manufacturing?
The foundational challenges and limitations are enumerated in this section. We shall also be looking at them in detail.
Challenges:
- Ensuring the quality of manufactured products
- Managing the complexity of digital manufacturing processes
- Establishing secure data transfer protocols
- Overcoming the resistance to change among traditional manufacturers
- Ensuring the safety of workers in digital manufacturing environments
Limitations:
- High cost of implementation
- Availability of skilled personnel
- Long lead times for implementation
- Limited access to digital manufacturing technologies
- The limited scalability of digital manufacturing processes
Cost of Digital Manufacturing as a Challenge
The cost of digital manufacturing can be a challenge in many ways. Digital manufacturing requires a significant upfront investment in resources, software, and hardware, which can be expensive and difficult to justify.
Additionally, digital manufacturing requires personnel with specific skills and expertise, which can be difficult to find and/or costly to hire. Finally, digital manufacturing requires a significant amount of time and effort to ensure that processes are properly implemented and maintained, which can result in high overhead costs.
Skilled Labor Shortage
Lack of skilled labor is a major challenge in digital manufacturing. Digital manufacturing requires a higher level of technical skill and knowledge than traditional manufacturing processes, which can be difficult to find. Skilled labor is also expensive, and as companies move towards digital manufacturing, they may find themselves needing to invest in training or hiring more skilled personnel.
Additionally, the digital manufacturing process is constantly changing and evolving, creating a need for continual training and education for the skilled labor force. This can be a challenge, as it is not always easy to find and retain employees with the right skills and knowledge.
Data Security
The aspect of data security risks is a major challenge in digital manufacturing. As production systems become increasingly connected, the risk of cyber-attacks grows. Companies are vulnerable to malicious attacks such as malware, ransomware, and phishing, which could result in the loss of data, disruption of services, or even theft of intellectual property.
In addition, companies must also be aware of potential data breaches caused by human error, such as unauthorized access or weak passwords. Companies must take multiple steps and use various techniques, including white box pen-testing, to protect their systems and data. Encryption, access controls, and regular security updates are some of the steps.
How can ERP help Digital Manufacturing?
ERP systems can help digital manufacturing in a number of ways. They can provide better visibility and control throughout the entire manufacturing process. Thus, enabling faster decision-making and reducing production waste.
ERP systems can also help to reduce material costs by connecting suppliers with the production chain and streamlining the procurement process. Additionally, ERP systems can help to improve traceability and quality control. It achieves this by tracking materials and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Finally, ERP systems can provide useful analytics and insights. Thus, allowing manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and take corrective action.
Let’s sum up ERP actions in this table:
More about Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM)
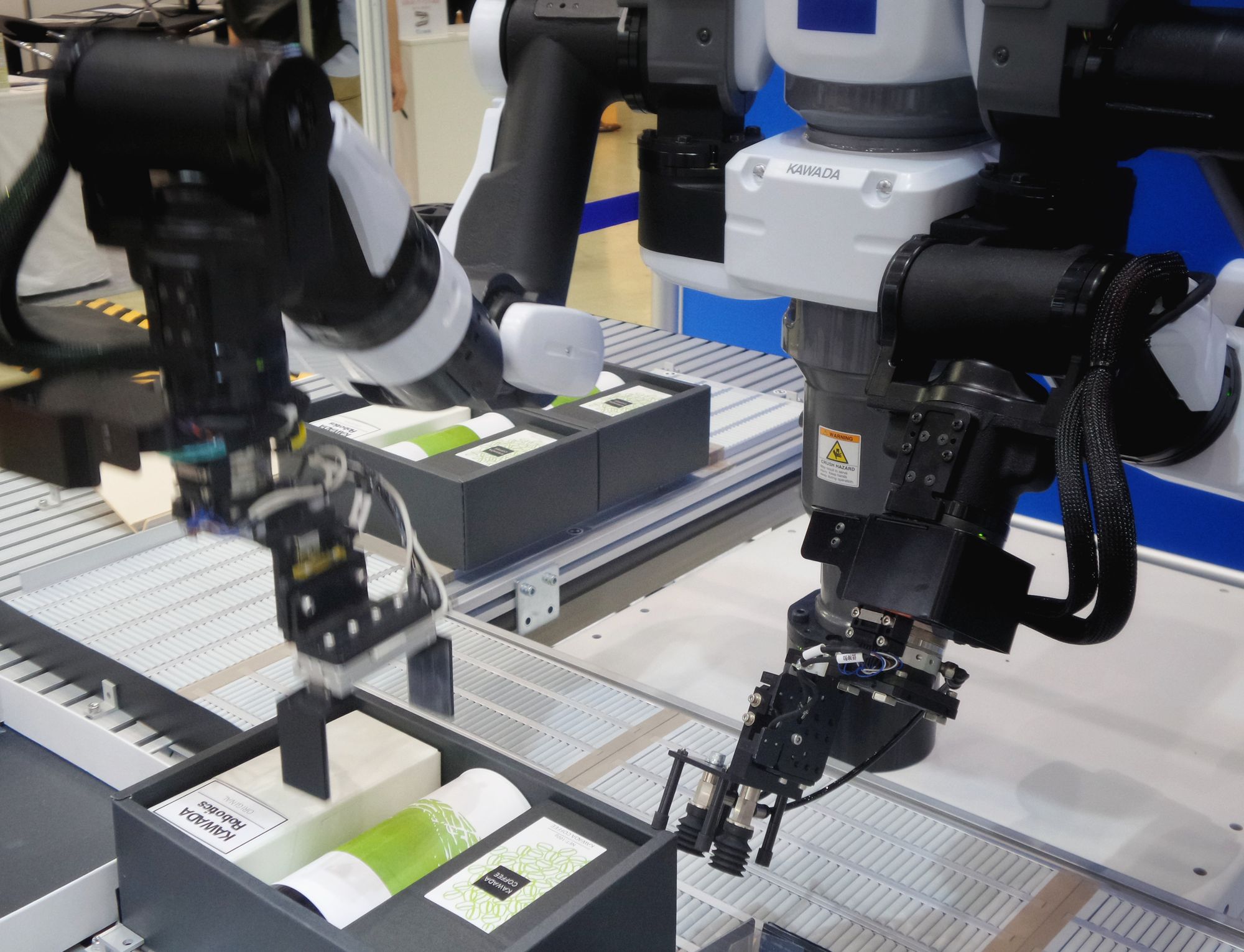
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is an approach to manufacturing that combines computer technologies. It may involve CAD, CAE, CAM, and robotics. It may also include traditional production processes.
The goal of CIM is to improve the efficiency and quality of manufacturing systems. It achieves this by automating and integrating production processes.
Automated system
CIM is a highly automated manufacturing system that links all of the components of a production process, from design, planning, and scheduling to purchase, inventory, quality control, maintenance, and delivery. The main purpose of CIM is to improve production efficiency and reduce manufacturing costs by automating and streamlining the production process.
Cheaper and Better Quality of Products
By integrating all of the components of the manufacturing process and utilizing advanced computer technology, CIM enables manufacturers to produce products faster, cheaper, and with higher quality. CIM is a key component of digital manufacturing, which is the use of digital technologies to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the entire manufacturing process.
Better Insights
CIM is an important part of digital manufacturing as it enables manufacturers to gain better insights into the entire production process and make the necessary adjustments in order to optimize the production process.
Real-time Data
CIM systems provide real-time data on production processes, making it easier to identify problems and inefficiencies. This data can then be used to make changes to the production process in order to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Safety and Quality Control
CIM also enables manufacturers to optimize the use of resources by automating production processes and reducing the need for manual labor. This not only helps reduce costs but also improves safety and quality control.
Track Performance
CIM systems can also be used to monitor the performance of equipment and machinery and detect any potential problems or malfunctions. CIM is a critical component of digital manufacturing and is essential for achieving the benefits of digital manufacturing.
The role of Computer-Integrated Manufacturing in digital manufacturing is explained as follows:
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) is a system that combines computers, robots, and other machinery to automate the entire production process.
- It can help in minimizing errors and maximize production efficiency by reducing the need for manual labor.
- Its systems can help to optimize inventory management, production scheduling, and quality control.
- CIM can help in facilitating digital manufacturing by providing real-time data and information to help in making decisions.
- It can help to reduce waste, increase productivity, and improve product quality.
More about Product Lifecycle Management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is a process used to track and manage the entire lifecycle of a product from its conception to its retirement. By managing the product’s lifecycle, companies can maximize their return on investment and minimize the cost of the product. PLM systems provide the visibility and control necessary to manage the product’s design, development, production, testing, and maintenance.
PLM - A Comprehensive Approach
Product Lifecycle Management in digital manufacturing is a comprehensive approach to managing the entire process of product development and manufacturing, from concept to end of life. It encompasses all aspects of the product lifecycle, including research and development, design, production, distribution, and customer service.
Reduces Cost
PLM helps manufacturers to effectively manage, track, and monitor their products and processes. It also ensures quality and efficiency in their operations. It also helps to reduce costs, increase speed-to-market, improve product quality and reliability, and provide greater visibility into the entire product lifecycle.
The role of PLM in Digital Manufacturing can be explained as follows:
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) provides a centralized platform to manage the entire lifecycle of a product from concept to retirement.
- It enables the efficient management of data related to the design, manufacturing, and lifecycle support of products.
- PLM enables digital manufacturing by providing a platform for efficient collaboration between internal and external stakeholders such as suppliers, customers, and partners.
- It helps in speeding up the product innovation process by providing accurate, up-to-date information in real time.
- PLM also helps streamline the manufacturing process by providing visibility into the entire process, enabling quicker decision-making.
Top 5 Benefits of Digital Manufacturing
The benefits of Digital Manufacturing can be enumerated in the following:
- Increased Efficiency: Digital manufacturing processes are more efficient than traditional manufacturing systems. They allow for quicker design changes, faster production rates, and more accurate production.
- Improved Quality Control: Digital manufacturing processes allow for better control over the quality of the final product as well as improved data analysis capabilities.
- Cost Savings: Digital manufacturing processes can result in significant cost savings. This is because they can reduce the need for manual labor and help to reduce the number of waste materials generated.
- Increased Flexibility: Digital manufacturing processes can enable manufacturers to quickly and easily adjust production to meet changing customer demands.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Digital manufacturing processes enable manufacturers to easily collaborate with their suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders in order to respond quickly to changing markets.
How to Leverage Digital Manufacturing in Your Company?
Digital manufacturing offers many benefits to companies that leverage its use. The first is increased efficiency and cost savings. By utilizing digital tools, companies can streamline processes, reduce manual labor and make production faster and more cost-effective.
Digital manufacturing also allows for improved quality control, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Digital manufacturing also allows for greater flexibility and scalability. Companies can quickly adjust their production processes as needed, allowing for faster response times and increased customization options.
This flexibility also allows for greater scalability, allowing companies to quickly scale up or down depending on market demand and other factors.
Finally, digital manufacturing can provide invaluable insights into customer preferences and behaviors, allowing companies to better understand their target audience and create more tailored products and services.
- Invest in digital technologies: Invest in digital technologies such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) software to improve product design, prototyping, and manufacturing processes.
- Automate processes: Use robotics and automation to streamline and optimize your production processes.
- Track data: Implement a system to track production data, such as product inventory, production times, and quality metrics.
- Connect operations: Connect all machines and systems to create a connected production line.
- Increase connectivity: Use the Internet of Things (IoT) to connect machines, sensors, and other devices to each other to improve data collection and analysis.
- Implement 3D printing: Use 3D printing to produce quick, high-quality prototypes and parts for low-volume production runs.
- Analyze data: Use data analytics to gain meaningful insights into your production processes and make informed decisions.
- Invest in staff training: Invest in training and upskilling your employees to effectively use digital technologies and understand data analytics.
Conclusion
Digital manufacturing has revolutionized the way products are made. It manages processes from the production line to the end user. It has enabled products to be made faster, cheaper, and more precisely than ever before. Additionally, it has allowed manufacturers to have access to real-time data. Thus, allowing them to respond quickly to customer needs. Also, they can make the most of the resources they have available.
Digital manufacturing has made the production process more efficient. It is instrumental in broadening the possibilities for product customization. Digital manufacturing has positively affected the industry by making it more efficient and agile.
It has opened up new possibilities for manufacturers as well as customers. They can now get the products they need faster. As digital manufacturing technology continues to evolve, businesses can expect even more efficiency. It is clear that digital manufacturing is here to stay. It will continue to revolutionize and improve the way products are made.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera's cloud-based ERP solutions help streamline the entire manufacturing process by providing real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, from raw material purchases to finished goods delivery.
Here are some of the ways Deskera ERP and MRP systems can help you:
- Make a manufacturing schedule
- Maintain a Bill of Materials
- Produce detailed reports
- Create your own dashboard, among other things!
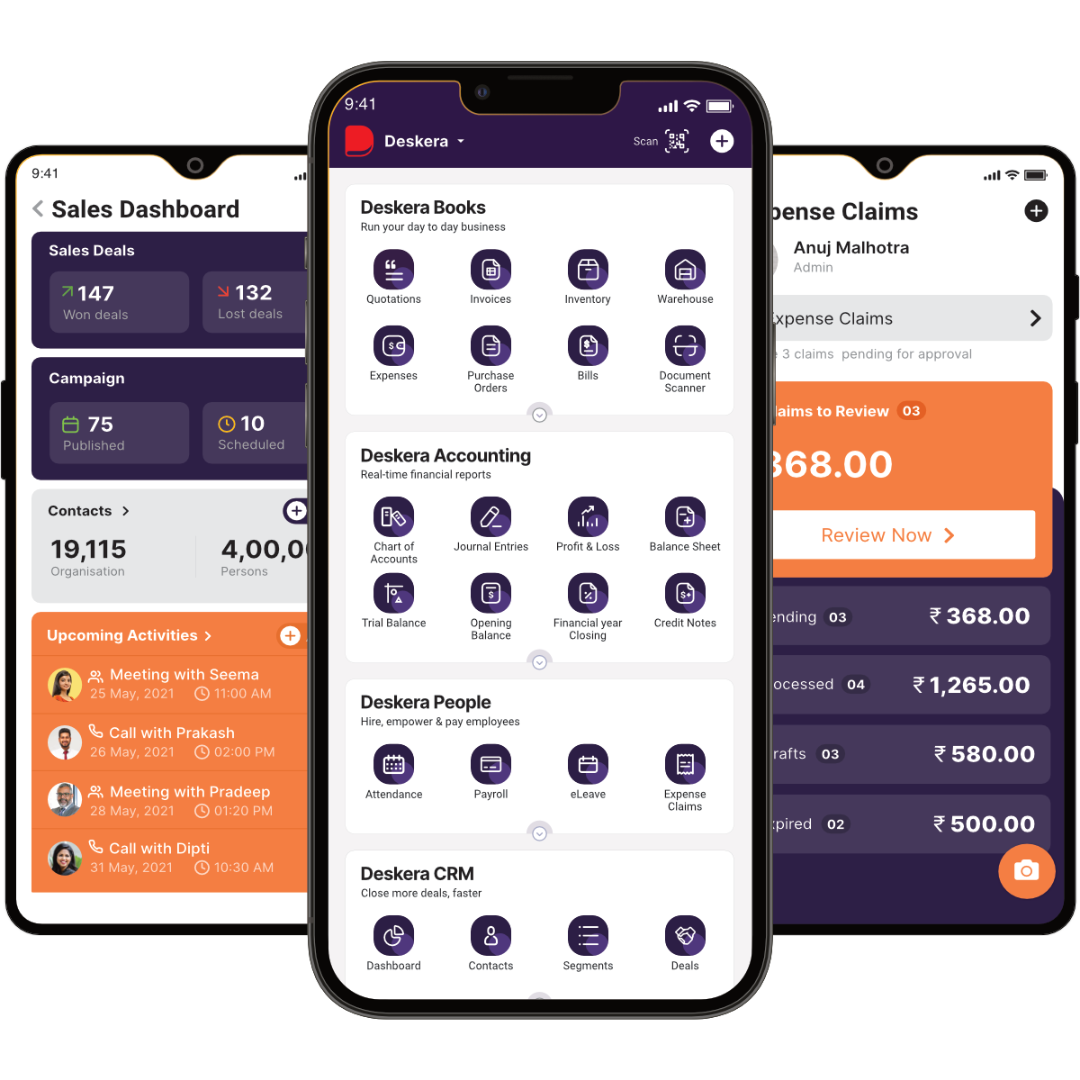
Deskera Books is an automated bookkeeping software. It can help businesses streamline their financial operations. It helps automate the bookkeeping process, from creating invoices to tracking expenses. It can be used to generate financial statements. With Deskera Books, businesses can save time, reduce errors, and improve visibility into their finances.
Deskera People is a cloud-based HR software. It is designed to help organizations manage their human resources. It has features such as employee onboarding, a self-service portal, time tracking, performance review, payroll management, leave management, and an employee directory. With Deskera People, organizations can streamline and automate their HR processes.
Deskera CRM is an easy-to-use customer relationship management software solution. It helps build and maintain relationships with your customers, prospects, and partners. It also helps you track customer data and interactions. You can create customized sales and marketing campaigns and manage all aspects of customer service. It also allows you to track customer feedback and monitor customer satisfaction. Finally, you can optimize customer service processes.
Key Takeaways
- Digital manufacturing involves creating a virtual model using technology before a product is physically built. Engineers can test and iterate on the design using Industry 4.0 principles before committing resources to production.
- Digital manufacturing allows for the rapid prototyping of components and products. Thereby reducing the cost and time involved in the development of new designs.
- 3 D Printing, CNC machining, rapid prototyping, and laser cutting are some types of digital manufacturing.
- The cost of digital manufacturing can be a challenge in many ways. Digital manufacturing requires a significant upfront investment in resources, software, and hardware, which can be expensive and difficult to justify.
- Lack of skilled labor is a major challenge in digital manufacturing. Digital manufacturing requires a higher level of technical skill and knowledge than traditional manufacturing processes, which can be difficult to find.
- The aspect of data security risks is a major challenge in digital manufacturing. As production systems become increasingly connected, the risk of cyber-attacks grows.
- Companies are vulnerable to malicious attacks such as malware, ransomware, and phishing, which could result in data loss, disruption of services, or even theft of intellectual property.
- Increased efficiency, cost control, and improved quality control are some of the major benefits of digital manufacturing.
- ERP systems can help digital manufacturing in a number of ways. They can provide better visibility and control throughout the entire manufacturing process. Thus, enabling faster decision-making and reducing production waste.
Related Articles