Enterprise operations today are under increasing pressure to move faster, operate leaner, and respond intelligently to constant change. Traditional ERP systems, once designed primarily to record transactions and standardize processes, are struggling to keep pace with this complexity. As businesses deal with volatile demand, fragmented data, and rising customer expectations, ERP platforms must evolve from static systems of record into dynamic systems of intelligence.
This shift is being driven by artificial intelligence. Nearly 85% of ERP vendors are now incorporating AI features into their platforms, signaling a fundamental transformation in how enterprise software is built and used. The impact is already visible on the ground—64% of businesses report that AI is improving productivity across their operations, enabling faster decisions, smarter forecasting, and greater automation. AI-driven ERP systems are no longer experimental; they are quickly becoming a competitive necessity.
By embedding machine learning, predictive analytics, and intelligent automation into core workflows, AI-driven ERP systems help organizations move from reactive management to proactive decision-making. Instead of relying on historical reports, leaders gain real-time insights, forward-looking recommendations, and early warnings that support better planning across finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and customer operations. The result is an ERP that not only executes processes but actively guides business outcomes.
Platforms like Deskera ERP exemplify this next generation of enterprise systems. Deskera integrates AI-powered insights across accounting, inventory, procurement, and manufacturing to help businesses make data-driven decisions with confidence. With built-in automation, predictive capabilities, and an intuitive AI assistant, Deskera enables growing enterprises to simplify complexity, improve visibility, and scale operations efficiently—positioning ERP as a true driver of future-ready growth.
What Is AI in ERP?
AI in ERP refers to the integration of artificial intelligence technologies—such as machine learning, predictive analytics, natural language processing, and generative AI—directly into enterprise resource planning systems. Since ERP software forms the backbone of core business functions like finance, supply chain, human resources, and operations, embedding AI means intelligence is no longer an add-on. Instead, it becomes woven into everyday workflows, continuously learning from data and supporting decisions across the organization.
With AI embedded at the system level, ERP platforms shift from reactive execution to proactive management. In finance, anomalies can be detected and flagged in real time instead of being discovered during manual reviews. In sales and operations, potential customer churn, demand fluctuations, or supply chain disruptions are identified early, accompanied by contextual insights that help teams act before issues escalate. This enables businesses to move faster and operate with greater confidence.
From a technical perspective, AI is integrated into ERP systems by embedding machine learning and generative AI models into core processes and user interfaces without disrupting existing workflows. Once in place, these capabilities allow ERPs to process data in real time, power predictive analytics, and support advanced decision-making. Features such as conversational AI enable users to query data using natural language, while predictive and anomaly detection tools continuously monitor transactions, operations, and performance metrics.
By infusing AI directly into ERP workflows, organizations gain an intelligent system that proactively surfaces insights, personalizes user experiences, and triggers automated actions based on roles and permissions. Crucially, all of this happens within familiar interfaces, reducing adoption friction and making AI a practical, accessible part of everyday enterprise operations rather than a standalone initiative.
Why Traditional ERP Systems Are No Longer Enough
Traditional ERP systems were designed to standardize processes and maintain operational control in relatively stable business environments. While they remain effective as systems of record, today’s enterprises operate in far more dynamic conditions—marked by volatile demand, complex supply chains, and rising expectations for speed and accuracy. As a result, rule-based, static ERP platforms are increasingly unable to deliver the agility, foresight, and intelligence modern businesses require.
Static, Rule-Based Workflows Limit Agility
Conventional ERP systems rely heavily on predefined rules and rigid workflows. While this ensures consistency, it also limits flexibility when conditions change. Adapting processes often requires manual configuration or IT intervention, slowing response times and preventing organizations from reacting quickly to market shifts, disruptions, or new opportunities.
Reactive Decision-Making Instead of Predictive Insights
Traditional ERPs focus on historical data and backward-looking reports. Decisions are typically made after issues have already occurred, such as stockouts, cost overruns, or delayed payments. Without predictive analytics or real-time intelligence, businesses are forced into a reactive mode, addressing problems after they impact operations rather than preventing them in advance.
Limited Visibility Across Data Silos
As organizations grow, data often becomes fragmented across departments, systems, and locations. Traditional ERP platforms struggle to provide a unified, real-time view of enterprise data, resulting in disconnected insights. This lack of end-to-end visibility makes it difficult for leaders to understand cross-functional impacts and align decisions across finance, supply chain, and operations.
High Dependence on Manual Effort
Despite automation at the transaction level, many traditional ERP systems still require significant manual intervention for analysis, reconciliation, and exception handling. Teams spend valuable time extracting reports, validating data, and identifying anomalies—time that could be better spent on strategic planning and optimization.
Inability to Scale with Business Complexity
As business models evolve and operations become more complex, traditional ERP systems often struggle to scale effectively. Adding new data sources, handling higher transaction volumes, or supporting advanced analytics can strain system performance and usability. Without built-in intelligence, ERP platforms become bottlenecks rather than enablers of growth.
Types of AI Technologies in ERP
Modern ERP providers are embedding a range of AI technologies across their platforms to help businesses achieve higher levels of efficiency, accuracy, and agility. Rather than operating as standalone tools, these technologies work together within ERP systems to automate workflows, analyze large volumes of data, and deliver real-time, context-aware insights across enterprise functions.
Agentic AI
Agentic AI refers to autonomous or semi-autonomous AI agents that can execute complex, multi-step workflows within ERP systems. These agents can draft proposals, prepare vendor evaluation criteria, compile financial reconciliations, or continuously monitor and adjust supply chain operations. Depending on governance rules, agentic AI can either act independently or route critical decisions to humans for approval, significantly reducing manual effort while maintaining control.
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection uses machine learning to continuously monitor financial transactions, operational processes, and supply chain activities. It identifies irregular patterns that may signal fraud, errors, quality issues, or inefficiencies. Within ERP systems, this capability enables real-time alerts—helping finance teams catch suspicious transactions early, manufacturers spot quality deviations, and supply chain managers respond quickly to disruptions.
Cloud-Based AI Services
Cloud-based AI services provide the computational power required for advanced AI workloads such as large-scale data analysis and real-time inference. Cloud ERP platforms benefit from frequent updates, access to the latest hardware, and rapid adoption of new AI capabilities. Compared to on-premises systems, cloud-based ERP solutions can deliver more scalable, performant, and future-ready AI functionality.
Object Recognition and Document Understanding
Object recognition and document understanding technologies allow ERP systems to extract and interpret data from unstructured and semi-structured sources. These include invoices, receipts, contracts, purchase orders, PDFs, and policy documents. By digitizing and validating information from the physical world, ERP systems can automatically classify data, trigger workflows, and reduce manual data entry.
Data Integration and ETL Tools
Data integration and ETL (extract, transform, load) tools prepare and cleanse data from multiple sources to create reliable data foundations for AI. These tools support advanced techniques such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), enabling natural language queries within ERP systems. Users can ask business questions in plain language, while the system retrieves relevant data, analyzes it contextually, and generates clear answers, charts, or summaries.
Machine Learning
Machine learning enables ERP systems to analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and detect deviations from expected behavior. It underpins use cases such as demand forecasting, scenario planning, fraud detection, and risk analysis. As models train on historical ERP data, their predictions improve over time, while generative AI layers can summarize findings and recommend actions in real time.
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardized framework that allows multiple AI models, agents, and services to share context securely and consistently. Implemented through authenticated REST APIs, MCP ensures that AI responses are relevant, accurate, and aligned with data access permissions. This is particularly valuable in ERP environments where sensitive financial, employee, and customer data must be tightly controlled.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing enables users to interact with ERP systems using written or spoken language. Through chatbots, voice assistants, and natural language queries, users can search data, generate reports, and trigger actions without navigating complex menus. NLP lowers the barrier to adoption and encourages broader use of ERP insights across roles and departments.
Predictive Analytics Engines
Predictive analytics engines analyze trends and historical patterns to forecast future outcomes such as demand, cash flow, and operational risks. When combined with NLP, these engines can explain not just what is likely to happen, but why—providing context-aware insights, visualizations, and recommendations that support informed decision-making.
Recommendation Engines
Recommendation engines deliver personalized, role-based suggestions directly within ERP workflows. These may include next-best actions, optimal inventory levels, or process improvements. By adapting to user behavior, current tasks, and historical data, recommendation engines help teams focus on high-impact decisions rather than manual analysis.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic process automation automates repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data migration, document processing, and system updates. While RPA itself is not AI-driven, it complements AI capabilities by executing recommended actions and workflows. Together, AI and RPA enable ERP systems to move beyond insights into end-to-end intelligent automation.
Collectively, these AI technologies transform ERP systems into intelligent platforms that not only execute transactions but also analyze, predict, recommend, and act—supporting smarter enterprise operations at scale.
Key Capabilities of AI-Driven ERP Systems
AI-driven ERP systems go beyond automating transactions to actively supporting smarter, faster, and more informed decision-making. By embedding intelligence directly into core workflows, these systems continuously analyze data, anticipate outcomes, and guide users with actionable insights across enterprise functions.
Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
AI-driven ERP systems use machine learning and advanced analytics to forecast demand, cash flow, inventory requirements, and operational risks. Beyond predicting what may happen, prescriptive analytics recommend optimal actions—such as adjusting reorder points or reallocating resources—helping businesses plan proactively rather than reactively.
Intelligent Process Automation
By combining AI with automation, modern ERP systems streamline complex, cross-functional processes. Tasks such as invoice processing, procurement approvals, reconciliations, and production scheduling can be automated end to end. The system learns from historical data to optimize workflows, reduce errors, and shorten cycle times.
Real-Time Decision Intelligence
AI enables ERP systems to process and analyze data continuously as transactions occur. This real-time intelligence allows businesses to detect issues early, monitor performance against KPIs, and respond immediately to changes. Contextual alerts and insights ensure that decision-makers have the right information at the right time.
Anomaly Detection and Risk Management
AI-driven ERP systems continuously monitor financial transactions, operational data, and supply chain activities to identify anomalies and risks. Whether it’s detecting potential fraud, quality deviations, or compliance issues, these systems surface exceptions early and provide context to support faster resolution.
Conversational AI and Natural Language Interaction
With built-in conversational AI, users can interact with ERP systems using natural language. Teams can ask questions, generate reports, or trigger actions without navigating complex interfaces. This capability improves accessibility, increases user adoption, and enables faster insight discovery across roles.
Personalized Recommendations and Next-Best Actions
AI-driven ERP platforms tailor insights and recommendations based on user roles, behavior, and current tasks. From suggesting optimal inventory levels to highlighting cost-saving opportunities, the system guides users toward high-impact decisions aligned with business goals.
Continuous Learning and Optimization
Unlike traditional ERP systems, AI-driven platforms continuously learn from new data. As business conditions evolve, models refine their predictions and recommendations, ensuring the ERP system improves over time and remains aligned with changing operational realities.
How AI Transforms Core Enterprise Functions
AI-powered ERP systems can be implemented across departments to enhance daily operations and decision-making. By embedding intelligence directly into core workflows, ERP platforms move beyond transactional processing to deliver predictive insights, intelligent automation, and proactive risk management across the enterprise.
Accounting, Purchasing, and Procurement
- Automates accounting tasks such as invoice matching, expense categorization, and reconciliations, reducing manual effort and errors
- Detects anomalies and fraud risks by analyzing transaction patterns in real time
- Forecasts cash flow trends using predictive analytics to support proactive budgeting and resource allocation
- Enhances supplier selection by evaluating performance data, pricing history, and lead times
- Improves procurement workflows through automated purchase order creation, approval routing, and contract recommendations
- Anticipates supply chain disruptions early, enabling contingency planning and uninterrupted operations
Supply Chain Management
- Generates accurate demand forecasts using historical data, market trends, and external factors such as economic conditions and weather
- Continuously refines forecasts with machine learning models based on real-time sales and inventory data
- Optimizes inventory levels by automating reorder points and reducing carrying costs
- Enhances warehouse management through intelligent space utilization, optimized picking and packing, and improved stock tracking
- Improves logistics efficiency with AI-driven route optimization for cost and time savings
- Increases supply chain visibility with real-time shipment tracking and supplier performance monitoring
- Automates supplier communication using NLP-powered tools for faster coordination
- Mitigates risk by analyzing geopolitical, environmental, and market factors that may disrupt operations
Predictive Demand Forecasting
- Moves beyond historical averages by incorporating real-time data and complex interdependencies
- Analyzes seasonality, regional demand, market shifts, inflation, weather, competitor activity, and social signals
- Continuously self-corrects forecasts as new data becomes available
- Enables retailers to anticipate demand surges during local holidays or regional events
- Improves manufacturing planning efficiency, reducing waste and maintaining optimal inventory levels
- Minimizes costs, stock shortages, and excess inventory in volatile market conditions
Automated Data Entry and Document Processing
- Eliminates manual data entry using OCR and NLP to extract information from invoices, receipts, emails, and documents
- Converts unstructured and semi-structured data into structured ERP records automatically
- Learns from past corrections to improve accuracy over time
- Reduces errors that can lead to invoice delays, payment issues, or reporting inaccuracies
- Handles high document volumes efficiently as the business scales
- Frees teams to focus on higher-value work such as analysis, planning, and customer engagement
- Supports data security, access control, and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA
Customer Engagement and Sentiment Analysis
- Delivers instant customer support through AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants
- Personalizes marketing campaigns using customer purchase history, behavior, and preferences
- Anticipates customer needs with predictive analytics and proactive recommendations
- Automates CRM workflows such as follow-ups, reminders, and feedback requests
- Ensures consistency across channels through AI-driven omnichannel integration
- Analyzes customer sentiment from reviews, surveys, and social media using NLP and machine learning
- Identifies sentiment trends to understand what products or experiences resonate most
- Acts on real-time sentiment insights to address issues and strengthen customer relationships
- Informs product, marketing, and service strategies using sentiment-driven insights
Smart Inventory and Warehouse Management
- Analyzes historical sales, seasonal trends, and supplier behavior to optimize inventory planning
- Reduces overstocking and stockouts through AI-driven demand alignment
- Monitors inventory in real time using IoT-enabled data feeds
- Automates reordering and stock transfers between locations when thresholds are met
- Improves warehouse efficiency through intelligent task sequencing and space optimization
- Scales seamlessly with cloud-based ERP platforms as operations grow
- Ensures decision accuracy by maintaining clean, validated inventory data
AI-Assisted CRM and Sales Enablement
- Ranks leads based on historical behavior and buying signals to improve sales prioritization
- Surfaces timely reminders and automated follow-ups to maintain consistent engagement
- Enables proactive offers based on recurring customer purchase patterns
- Flags high-risk or high-value customers for immediate attention
- Improves sales productivity by reducing guesswork and manual analysis
- Aligns marketing efforts using insights from past purchases, web activity, and engagement data
- Centralizes customer data across sales, support, and marketing within the ERP
Manufacturing Process Optimization
- Monitors machine performance to detect early signs of failure or inefficiency
- Enables predictive maintenance to prevent unplanned downtime
- Optimizes production scheduling based on material availability, workforce capacity, and order priorities
- Detects quality deviations early to reduce scrap and rework
- Supports integration of legacy equipment through sensors and data connectors
- Improves factory-wide visibility and resource utilization
- Reduces waste and improves operational efficiency across production lines
Fraud Detection, Compliance, and Risk Management
- Monitors transactions, payments, and contracts in real time to identify suspicious activity
- Flags unusual patterns such as duplicate invoices or abnormal payment behavior
- Helps organizations stay compliant by tracking regulatory changes
- Validates internal processes against compliance and policy requirements
- Uses explainable AI to clarify why risks or anomalies are flagged
- Reduces false positives over time through continuous learning
- Acts as an early-warning system for financial, operational, and regulatory risks
AI Agents for Autonomous Decision-Making
- Deploys AI agents that monitor operations and workflows continuously
- Flags anomalies and risks in financial transactions and procurement activities
- Automates routine approvals, reorders, and operational decisions
- Generates real-time recommendations directly within ERP dashboards
- Reduces decision delays and operational bottlenecks
- Enables virtual assistants to execute tasks such as supplier checks or replenishment scheduling
- Supports human-in-the-loop governance for critical decisions
- Builds trust through explainable AI and phased adoption strategies
7 Use Cases of AI in ERP
What began as basic process automation has evolved into advanced, intelligence-driven ERP capabilities. Today, AI-integrated ERP systems combine predictive analytics, machine learning, NLP, and automation to accelerate decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and deliver measurable business value. Below are the most impactful use cases where AI is transforming ERP systems.
1. Deep Data Analysis and Insight Discovery
- Analyzes large volumes of historical and real-time ERP data using data mining and predictive analytics
- Identifies hidden patterns, trends, and correlations that are difficult to detect manually
- Supports better forecasting of market behavior and business performance
- Enables more informed resource allocation and strategic planning
2. Personalized Customer and Employee Experiences
- Delivers personalized product recommendations based on customer purchase history and browsing behavior
- Tailors customer interactions to improve engagement and conversion rates
- Provides employees with role-based, customized dashboards that prioritize relevant tasks and insights
- Improves productivity by aligning ERP interfaces with individual work patterns
3. Enhanced Customer Service and Support
- Uses AI- and RPA-powered chatbots to handle routine customer inquiries in real time
- Supports tasks such as order tracking, billing queries, and common issue resolution
- Reduces response times and improves customer satisfaction
- Frees customer service teams to focus on complex, high-value interactions
4. Improved Forecasting and Planning
- Identifies complex patterns and demand signals that traditional forecasting methods miss
- Predicts market trends, customer behavior, and supply chain disruptions with higher accuracy
- Aligns supply more closely with demand to reduce waste and inefficiencies
- Enables proactive resource planning and opportunity identification
5. Optimized Supply Chain Operations
- Analyzes supply chain data in real time to anticipate disruptions
- Adjusts production schedules based on predicted demand fluctuations
- Improves procurement planning and supplier coordination
- Enhances order fulfillment accuracy and speed, strengthening customer satisfaction
6. Proactive Risk Management and Compliance
- Monitors financial, operational, and compliance risks continuously
- Detects potential issues early, including fraud, policy violations, and supply chain risks
- Enables organizations to shift from reactive risk handling to proactive mitigation
- Protects business continuity and safeguards critical assets
7. Continuous Improvement and Operational Optimization
- Learns continuously from structured and unstructured ERP data
- Identifies inefficiencies and process bottlenecks automatically
- Recommends improvements to increase agility and responsiveness
- Drives sustained operational efficiency and faster innovation cycles
Benefits of AI in ERP Systems
Unlike general-purpose AI tools, AI embedded within an ERP system understands your business context because it has direct access to real-time financial, inventory, sales, and operational data—securely governed by user roles and permissions. This makes AI in ERP far more powerful, actionable, and relevant. Below are the key benefits organizations gain by adopting AI-driven ERP systems.
1. Intelligent Automation and Time Savings
- Automates repetitive, rule-based tasks such as invoice processing, order entry, reconciliations, and approvals
- Combines AI with RPA and intelligent process automation (IPA) to handle more complex, judgment-based tasks
- AI agents learn from past outcomes, continuously improving accuracy and efficiency
- Reduces manual administrative burden and operational delays
- Frees employees to focus on strategic work like decision-making, relationship-building, and growth initiatives
2. More Accurate and Reliable Data
- Reduces human error through automated data capture, validation, and correction
- Flags missing, inconsistent, or anomalous data in real time
- Automatically sources missing information by cross-checking internal and external records
- Processes large datasets faster and more accurately than traditional analysis
- Ensures higher data integrity across finance, inventory, procurement, and operations
3. Advanced Insights and Predictive Analytics
- Analyzes massive volumes of historical and real-time ERP data to uncover trends and correlations
- Delivers accurate demand forecasts, revenue projections, and cost insights
- Uses third-party data such as economic indicators, market trends, and weather data to enhance predictions
- Enables proactive decision-making instead of reactive firefighting
- Helps businesses stay ahead of demand shifts, supply chain disruptions, and market changes
4. Actionable Forecasting and Future Planning
- Supports precise inventory, production, and capacity planning
- Predicts customer demand and supplier availability before issues arise
- Improves resource allocation across teams, equipment, and materials
- Identifies potential supply chain disruptions early
- Helps organizations remain agile and resilient in uncertain environments
5. Business Process Optimization and Agility
- Continuously monitors ERP workflows to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks
- Recommends process improvements based on real-time performance data
- Ensures processes operate at optimal efficiency across departments
- Enables faster responses to unexpected events or market fluctuations
- Drives continuous improvement rather than periodic optimization
6. Increased Employee Productivity
- Eliminates manual data entry and repetitive administrative tasks
- Provides role-based dashboards with prioritized, relevant insights
- Helps teams work faster with fewer errors and less rework
- Improves collaboration across finance, supply chain, sales, and operations
- Allows employees to focus on higher-value, creative, and analytical work
7. Natural Language Interaction and Accessibility
- Enables users to interact with ERP systems using plain language queries and commands
- Allows employees to ask questions, generate reports, or retrieve insights conversationally
- Makes complex data more accessible to non-technical users
- Improves adoption by reducing dependency on specialized ERP training
- Learns from user interactions to deliver increasingly relevant responses
8. Personalization and Smart Recommendations
- Tailors dashboards, reports, and workflows based on user roles and behavior
- Recommends next-best actions using historical and contextual data
- Improves employee efficiency by highlighting what matters most to each role
- Enhances customer experiences through personalized offers and interactions
- Aligns ERP insights with individual and departmental goals
9. Enhanced Security and Risk Management
- Continuously monitors ERP systems for unusual or suspicious activity
- Detects financial, operational, compliance, and cybersecurity risks early
- Flags anomalies such as fraud, policy violations, or irregular transactions
- Enables proactive risk mitigation rather than reactive responses
- Strengthens business continuity and operational resilience
10. Operational Cost Savings and Quality Improvements
- Reduces waste through better forecasting and resource utilization
- Optimizes equipment lifecycle with predictive maintenance insights
- Lowers maintenance and downtime costs
- Improves quality control by tracking defects and enabling rapid corrective action
- Identifies cost-saving opportunities across procurement, production, and logistics
Challenges of AI in ERP Systems
While AI-driven ERP systems promise smarter, faster, and more adaptive operations, adopting them is not without challenges. Organizations must address data, people, technology, and governance considerations to ensure AI delivers real business value rather than added complexity.
1. Data Quality and Integration Issues
AI outcomes are only as good as the data feeding them. Many organizations struggle with inconsistent, incomplete, or siloed data across legacy systems.
- Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate forecasts and misleading insights
- Integrating AI with legacy or fragmented systems is complex
- Disparate data formats and standards slow down AI adoption
- Unified, cloud-based ERP platforms help centralize and standardize data for better AI performance
2. Change Management and User Adoption
AI introduces new ways of working, which can create resistance among employees. Concerns around job displacement or lack of familiarity with AI tools often slow adoption.
- Employees may distrust AI-driven recommendations
- Limited AI literacy reduces effective usage
- Inadequate training can lead to underutilization of AI features
- Intuitive interfaces, in-product guidance, and continuous training are critical for long-term adoption
3. Security, Privacy, and Compliance Risks
AI models in ERP systems process large volumes of sensitive financial, operational, and employee data. This raises valid concerns around security and regulatory compliance.
- Increased risk of data exposure or misuse
- Challenges in meeting region-specific compliance requirements
- Data privacy concerns in multi-country operations
- Strong encryption, role-based access controls, audit trails, and data localization capabilities are essential
4. Customization and Scalability Challenges
AI capabilities must align with an organization’s unique processes and scale as the business grows. This is especially challenging in complex or highly regulated industries.
- One-size-fits-all AI models may not fit specialized workflows
- Scaling AI across departments or global operations adds complexity
- Industry-specific requirements demand configurable AI features
- Cloud-based, modular ERP platforms offer better flexibility and scalability
5. Cost and Resource Constraints
Deploying AI—especially within on-premises ERP environments—can be resource-intensive. Organizations may face challenges justifying the investment.
- High upfront costs for infrastructure and AI tools
- Ongoing expenses for skilled talent, maintenance, and model updates
- Limited internal AI expertise slows implementation
- Cloud ERP solutions reduce capital expenditure and IT overhead
6. Organizational Privacy Concerns
Businesses handling confidential or sensitive information may hesitate to adopt AI-enabled ERP systems.
- Fear of exposing proprietary or customer data
- Uncertainty about how AI models access and process information
- Dependence on vendor trust and transparency
- Choosing a reputable ERP vendor with proven security standards is critical
7. Integration Complexities with Legacy Systems
Many organizations rely on older systems that were not designed to work with AI technologies.
- Legacy tools often lack APIs or modern integration capabilities
- Custom integrations increase project timelines and costs
- Data synchronization issues reduce AI effectiveness
- Modern ERP platforms with built-in integration layers ease this challenge
8. Risk of Over-Reliance and Loss of Human Judgment
AI-driven insights can sometimes lead to excessive dependence on automation, especially in strategic decision-making.
- AI lacks human intuition and contextual understanding in certain scenarios
- Over-automation may reduce critical thinking
- Complex decisions still require human oversight
- The most effective ERP strategies balance AI intelligence with human expertise
Best Practices for Implementing AI in ERP Systems
Successfully adopting AI in ERP is less about deploying the most advanced technology and more about aligning AI capabilities with real business outcomes. Organizations that treat AI as a strategic enabler—rather than a standalone experiment—are far more likely to realize measurable value.
1. Start with High-Impact Use Cases (“Land and Expand”)
- Focus on business-critical priorities such as faster financial closes, demand forecasting, cash flow prediction, supply chain visibility, or AP/AR automation
- Avoid adopting AI for its own sake; tie each use case to clear business outcomes
- Begin with a small number of proven use cases and expand gradually
- Choose ERP platforms with embedded AI and partner marketplaces to support future expansion
2. Establish Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Workflows
- Use AI to recommend actions, not autonomously execute high-risk decisions at the outset
- Include human approval for critical activities like large purchase orders, budget changes, or supplier selection
- Build trust by combining AI efficiency with human judgment
- Gradually increase automation as confidence, accuracy, and governance mature
3. Invest in Data Readiness and Data Governance
- Ensure ERP data is accurate, complete, standardized, and traceable
- Cleanse historical data and define ownership for master data, transactions, and metadata
- Use cloud-based integration platforms to keep external data sources synchronized
- High-quality data directly improves AI accuracy, adoption, and user confidence
4. Build on a Modern, Scalable ERP Architecture
- Prefer cloud-native, modular, and extensible ERP systems
- Ensure support for APIs, real-time analytics, and scalable compute resources
- Enable faster experimentation, testing, and incremental AI upgrades
- Reduce dependency on rigid legacy infrastructure that limits AI capabilities
5. Encourage AI Skills Development and Change Management
- Provide continuous training and in-product guidance for users
- Develop internal AI champions and power users across departments
- Upskill employees in data literacy, AI decision support, and ethical usage
- Promote a culture of human–AI collaboration rather than replacement
6. Adopt a Phased and Incremental Rollout
- Start with assistive AI or co-pilot use cases that deliver immediate value
- Progress to predictive analytics and then to generative or agentic AI
- Use early phases to refine governance, workflows, and trust
- Reduce disruption while steadily increasing AI maturity
7. Define Clear Governance, Ethics, and Accountability
- Establish policies for data access, AI usage, transparency, and auditability
- Create a cross-functional AI governance council to oversee risk and compliance
- Monitor model behavior, data lineage, and explainability
- Ensure AI outputs align with organizational values and regulatory requirements
8. Measure ROI and Business Impact Continuously
- Track productivity gains, cost savings, error reduction, and cycle-time improvements
- Use ERP analytics to link AI outcomes directly to investment decisions
- Measure collaboration improvements across teams using shared AI insights
- Refine use cases based on real performance data
9. Prioritize Integration Strategy Early
- Align AI and ERP integrations with core business objectives
- Ensure seamless data flow between ERP and surrounding systems like CRM, POS, or ecommerce platforms
- Avoid fragmented AI deployments that dilute value
- A strong integration foundation improves both AI accuracy and scalability
10. Focus on Augmentation, Not Just Automation
- Use AI to amplify human intuition and decision-making
- Automate high-volume tasks while reserving complex judgment for people
- Let AI handle 80–90% of routine work, freeing employees to manage exceptions
- The biggest gains often come from better decisions—not just faster processes
The State of ERP with AI in 2025
By 2025, AI has moved from being an experimental add-on to a defining capability of modern ERP systems. What was once limited to basic automation and reporting has evolved into intelligent, adaptive platforms that actively support decision-making, efficiency, and resilience across the enterprise.
AI Assistants and Bots Are Becoming Standard
ERP vendors are increasingly embedding AI assistants, copilots, and chat-based interfaces directly into core workflows. These assistants help users retrieve insights, generate reports, flag anomalies, and complete routine tasks faster.
Rather than replacing users, they act as productivity multipliers—guiding decisions, surfacing insights in context, and reducing dependency on manual navigation and analysis.
Cloud ERP Is Accelerating AI Adoption
Cloud-based ERP systems have become the primary enabler of AI at scale. By 2025, the cloud is no longer just a hosting model—it is the foundation for delivering continuous AI innovation.
- Businesses can access advanced AI capabilities without heavy upfront infrastructure investments
- Vendors can roll out frequent AI updates and improvements
- Even small and mid-sized organizations can leverage enterprise-grade AI tools
As a result, AI is becoming more democratized across industries and company sizes.
AI Talent Shortages Remain a Key Constraint
Despite growing adoption, the demand for AI skills continues to outpace supply. Organizations face challenges finding talent that understands both AI and enterprise business processes.
This skills gap is pushing ERP vendors to simplify AI through low-code/no-code tools, prebuilt models, and embedded intelligence—reducing reliance on scarce specialists while still enabling meaningful AI use.
Uneven AI Maturity Across ERP Vendors
Not all ERP vendors are advancing at the same pace. While leading platforms are rapidly rolling out AI copilots, predictive analytics, and agentic capabilities, others are playing catch-up.
- Some vendors are retrofitting AI onto legacy architectures
- Strategic acquisitions are becoming a common shortcut to accelerate AI capabilities
- Customers are increasingly evaluating ERP vendors based on AI readiness, not just core functionality
This divergence is creating a clearer gap between “AI-first” ERP platforms and those struggling to modernize.
Manufacturing ERP Emerges as a Major AI Beneficiary
Manufacturing has become one of the strongest use cases for AI-enabled ERP by 2025. AI capabilities now go well beyond monitoring and reporting to support autonomous and semi-autonomous decision-making.
- Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and extends equipment life
- Computer vision enables automated quality control and inspections
- Intelligent order promising balances demand, capacity, and constraints
- Real-world deployments report 30–40% efficiency gains in AI-enabled facilities
AI-driven ERP systems are increasingly standard in advanced manufacturing environments.
AI Agents Are Emerging as Digital Workers
One of the most notable developments in 2025 is the rise of AI agents within ERP systems. These agents represent a shift from task-based automation to outcome-based execution.
- AI agents can manage end-to-end workflows across finance, supply chain, and operations
- They understand business context, policies, and constraints
- Multiple agents can collaborate, adjusting plans in real time when disruptions occur
Potential applications gaining traction include invoice reconciliation, inventory reordering, maintenance coordination, early risk detection, and first-level customer support. While still early, AI agents are increasingly viewed as “digital workers” that augment teams rather than replace them.
From Automation to Adaptive Enterprises
Overall, the state of ERP with AI in 2025 reflects a clear shift: ERP systems are no longer passive systems of record but active systems of intelligence. Organizations are using AI-enabled ERP to move from reactive operations to predictive, and increasingly autonomous, enterprise management.
The next phase will be less about whether AI belongs in ERP—and more about how effectively businesses govern, scale, and balance AI-driven automation with human judgment.
How Deskera ERP Enables AI-Driven Enterprise Operations
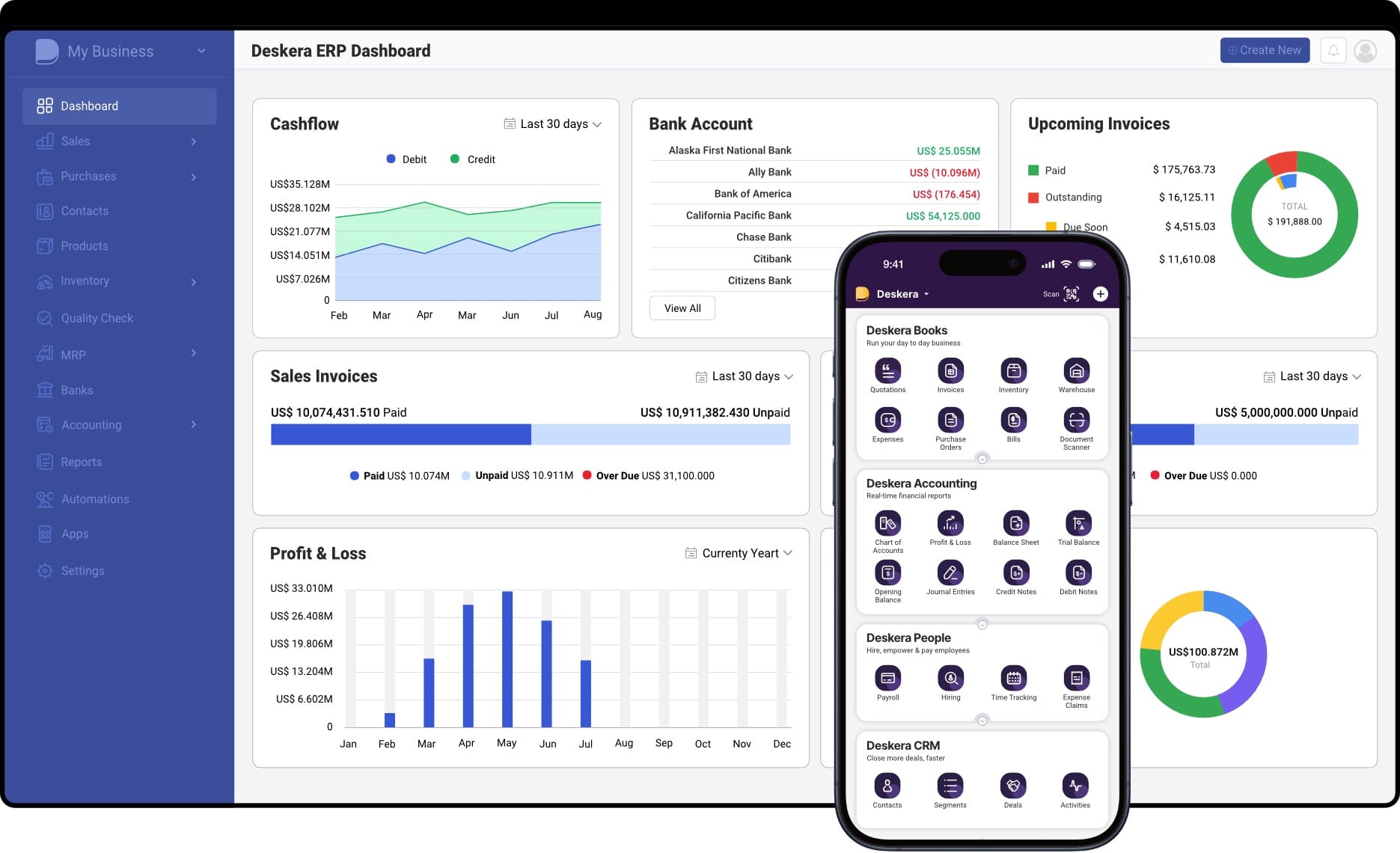
Deskera ERP integrates artificial intelligence directly into core business workflows, empowering organizations to automate routine tasks, gain real-time insights, and make smarter decisions—all within a unified, cloud-native platform. Instead of treating AI as an add-on, Deskera embeds intelligence across finance, inventory, supply chain, sales, and operations so teams can work faster, with greater accuracy and agility.
Intelligent Process Automation
- Automates repetitive, time-consuming tasks such as invoice processing, order entry, reconciliations, and approvals
- Reduces manual errors and accelerates cycles across accounts payable, accounts receivable, and procurement
- Allows teams to focus on higher-value work—such as strategic planning, supplier negotiations, and analysis—by offloading routine operational work
Real-Time Insights and Predictive Analytics
- Continuously analyzes business data across modules to surface trends, anomalies, and forecasts
- Uses predictive analytics to support demand forecasting, cash flow planning, inventory optimization, and risk mitigation
- Delivers actionable insights directly to dashboards so leaders can act proactively rather than reactively
Conversational AI and Natural Language Interaction
- Enables users to interact with the ERP using natural language queries
- Lets teams ask questions like “What were sales last quarter?” or “Which products are low in stock?” and receive instant, contextual answers
- Lowers the barrier to data access for non-technical users, improving adoption and reducing reliance on IT support
Personalized Dashboards and Recommendations
- Provides role-based dashboards tailored to individual user needs (e.g., finance, operations, supply chain)
- Surfaces recommendations such as optimal reorder points, cost-reduction opportunities, and production adjustments
- Helps users stay focused on what matters most to their role, rather than sifting through generic reports
Enhanced Supply Chain and Inventory Management
- Leverages real-time data and AI intelligence to refine demand planning and inventory control
- Automates reorder triggers, warehouse task planning, and inventory allocation
- Reduces stockouts, excess inventory, and carrying costs while improving service levels and fulfillment accuracy
AI-Assisted Financial Accuracy and Risk Detection
- Monitors financial transactions continuously to flag anomalies, suspicious patterns, and reconciliation issues
- Supports compliance tracking through audit logs, role-based access, and real-time alerts
- Improves financial governance while minimizing risk related to fraud or accounting inconsistencies
Collaboration and Cross-Functional Intelligence
- Breaks down data silos across finance, operations, and sales using a unified, cloud-first architecture
- Facilitates cross-team collaboration by providing shared insights, alerts, and workflows
- Helps teams work from the same trusted data source, reducing miscommunication and improving alignment
Cloud-Native Scalability and Continuous Innovation
- As a cloud-based platform, Deskera delivers regular AI enhancements and performance upgrades without costly infrastructure investments
- Scales easily with business growth, user count, and changing operational needs
- Keeps organizations current with the latest AI capabilities through continuous delivery and updates
Built-In Data Governance and Security
- Ensures that AI models and analytics run on secured, audited, and role-restricted data
- Offers encryption, permissions management, and compliance features to protect sensitive business information
- Supports responsible AI use by managing data access and operational transparency
Deskera ERP transforms traditional enterprise systems into AI-driven operations hubs—helping businesses automate tasks, improve accuracy, harness predictive insights, and unlock strategic value from data.
Key Takeaways
- Traditional ERP systems are built for historical reporting and rigid workflows, while AI-driven ERPs enable real-time intelligence, adaptability, and proactive decision-making in fast-changing business environments.
- AI-driven ERP systems combine automation, predictive analytics, NLP, and machine learning to transform ERP from a transactional system into an intelligent, self-learning operational platform.
- By embedding AI across finance, procurement, supply chain, manufacturing, and customer engagement, ERP systems shift from siloed execution tools to connected, insight-driven business ecosystems.
- AI-powered demand forecasting enables businesses to anticipate market shifts, reduce waste, and balance inventory more accurately by continuously learning from real-time and external data.
- AI enhances supply chain resilience by predicting disruptions, optimizing logistics, and enabling proactive planning rather than reactive problem-solving.
- AI-driven automation eliminates manual data entry bottlenecks, improves data accuracy, and frees teams to focus on higher-value strategic work.
- AI chatbots simplify ERP adoption by providing instant, natural-language assistance, reducing dependency on training and support teams.
- AI strengthens financial control by detecting anomalies in real time and ensuring continuous compliance with evolving regulatory requirements.
- AI-driven ERP systems optimize inventory levels and warehouse operations by combining predictive insights with real-time tracking and automation.
- AI transforms ERP-based CRM from a static data repository into a proactive system that predicts customer needs and personalizes engagement at scale.
- In manufacturing, AI-enabled ERP systems improve efficiency, quality, and uptime through predictive maintenance, intelligent scheduling, and real-time production insights.
- AI-driven risk management shifts ERP systems from reactive monitoring to proactive early-warning systems that safeguard business continuity.
- AI agents represent the next evolution of ERP, enabling autonomous execution of routine decisions while keeping humans in control of strategic oversight.
- From deep data analysis to personalized experiences and continuous improvement, AI use cases demonstrate ERP’s transition into a system of intelligence rather than administration.
- AI delivers measurable business value through automation, smarter insights, improved accuracy, higher employee productivity, and better forecasting.
- Data quality, integration complexity, security concerns, and user adoption remain key hurdles that must be addressed for successful AI-driven ERP implementations.
- Organizations succeed with AI in ERP by focusing on high-impact use cases, ensuring data readiness, adopting phased rollouts, and maintaining human-in-the-loop governance.
- By 2025, AI-powered ERP systems—especially in manufacturing—are becoming standard, with AI assistants, agents, and cloud platforms driving efficiency gains of 30–40%.
- Deskera ERP embeds AI across finance, inventory, supply chain, and analytics to help businesses automate operations, gain real-time insights, and scale intelligently.
Related Articles