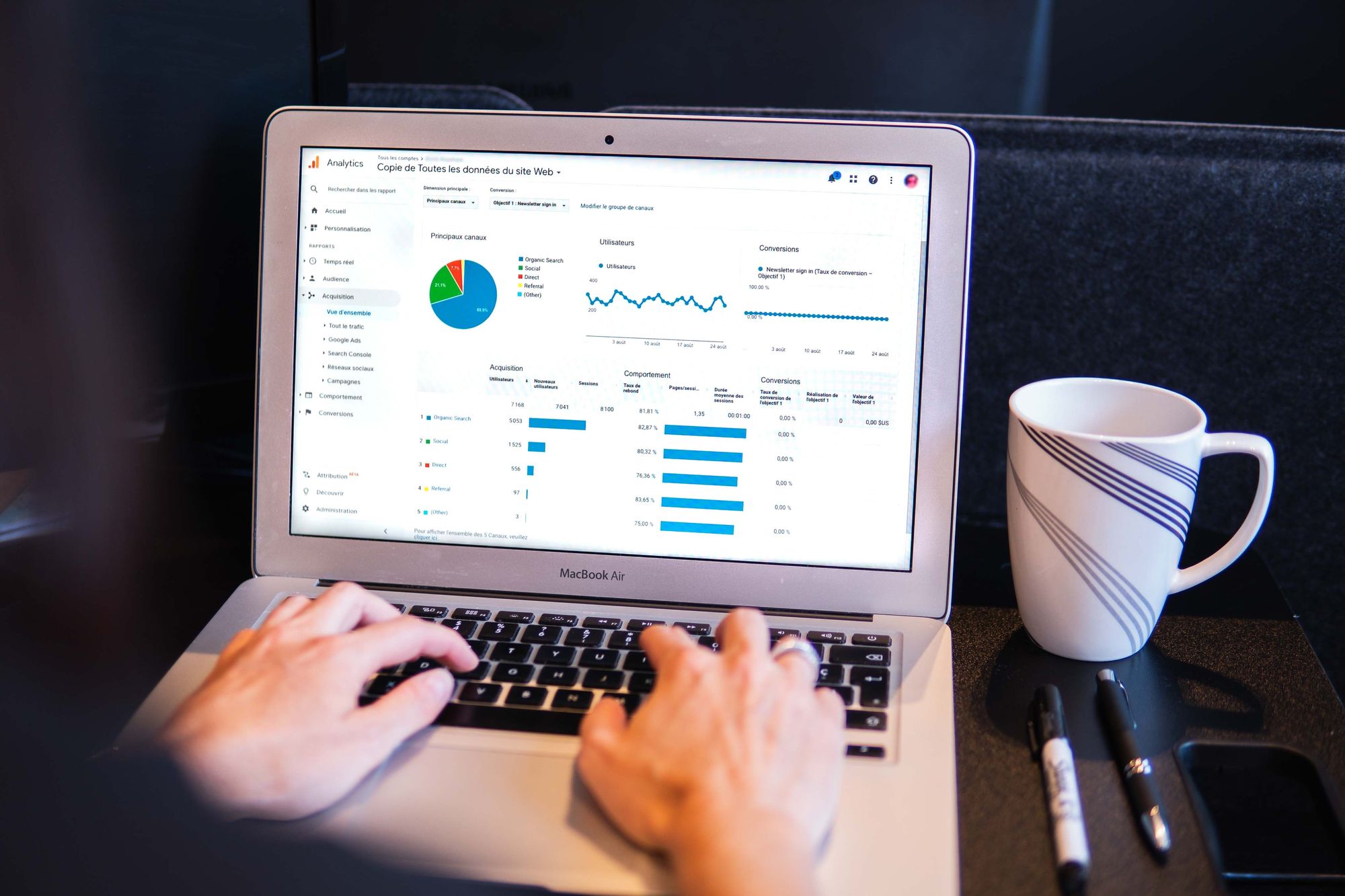
Are you a business owner trying to get a comprehensive understanding of revenue recognition in the digital age?
If yes, you are on the right page.

In the digital age, emerging technologies have revolutionized the way businesses operate and interact with customers. Along with these advancements, the methods of revenue recognition have also undergone significant changes.
Revenue recognition, the process of accounting for and reporting revenue, has become increasingly complex due to the evolving nature of digital business models and the adoption of innovative technologies.
One of the key aspects of revenue recognition in the digital age is the concept of multi-element arrangements. Many companies now offer bundled products or services that include a combination of hardware, software, maintenance, and support.
Determining the appropriate allocation of revenue among these elements requires careful analysis and consideration of various factors, including fair value assessments and standalone selling prices.
Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of subscription-based models has challenged traditional revenue recognition norms. Businesses offering subscription services must address issues related to contract duration, renewal terms, and revenue allocation over time.
This requires a shift from recognizing revenue upfront to spreading it over the subscription period, reflecting the ongoing value delivered to customers.
Revenue recognition in the digital age requires businesses to adapt to emerging technologies and implement best practices to accurately account for revenue. As technology continues to advance and new business models emerge, staying abreast of these developments and following industry standards becomes crucial for financial transparency and decision-making.
By embracing the opportunities presented by the digital age and leveraging emerging technologies, businesses can enhance revenue recognition processes and gain a competitive edge in the evolving marketplace.
This article will be your complete guide to revenue recognition in the digital age by covering the following topics:
- All About Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
- Emerging Technologies for Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
- Best Practices for Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
- FAQs related to Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
- How can Deskera Help You with Revenue Recognition?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
All About Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
Revenue recognition in the digital age refers to the process of accurately accounting for and reporting revenue generated from digital products, services, and transactions.
It involves understanding and applying accounting principles and standards to ensure proper recognition of revenue in a rapidly evolving digital business environment. Here are key aspects to consider:
- Complex Revenue Models: Digital businesses often have complex revenue models due to various factors such as subscription-based services, multi-element arrangements, usage-based pricing, freemium offerings, and bundled packages. These models require careful evaluation of performance obligations, contract terms, and pricing structures to determine the appropriate timing and amount of revenue recognition.
- ASC 606/IFRS 15 Adoption: Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606 in the United States and International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) 15 globally provide comprehensive guidelines for revenue recognition across industries. These standards establish principles-based frameworks that focus on the transfer of control of goods or services to customers. Digital businesses must understand and adopt these standards to ensure consistent and accurate revenue recognition practices.
- Recognition over Time vs. Point in Time: Digital businesses often face the challenge of determining whether revenue should be recognized over time or at a point in time. Revenue recognition over time typically occurs when the customer simultaneously receives and consumes the benefits of a product or service over a specific period. Point-in-time recognition occurs when control of the product or service transfers to the customer at a specific moment. Understanding the nature of the performance obligations and customer consumption patterns is essential for making the correct determination.
- Contractual Considerations: Digital transactions typically involve contracts, whether explicit or implied. It is important to identify and analyze the key terms and conditions of these contracts to determine the revenue recognition approach. Digital businesses need to assess factors like contract enforceability, collectability, variable consideration, termination rights, and customer options to appropriately account for revenue.
- Performance Obligations: Digital products and services often have multiple performance obligations within a contract. Identifying and separating these obligations accurately is crucial for revenue recognition. For example, a software subscription may include software licensing, implementation services, and ongoing customer support. Each of these elements may need to be evaluated separately to determine the appropriate allocation of revenue.
- Data Management and Systems: Digital businesses generate large volumes of data related to customer transactions, usage, and engagement. Robust data management systems and processes are essential for accurate revenue recognition. It is crucial to have integrated systems that capture, process, and analyze relevant data to support revenue recognition decisions.
- Technology Enablers: Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and data analytics can enhance revenue recognition in the digital age. These technologies can help analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and automate certain aspects of revenue recognition processes. Implementing technology solutions can increase efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in revenue recognition activities.
- Regulatory Compliance and Auditing: Digital businesses need to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and undergo regular audits to validate their revenue recognition practices. Maintaining proper documentation, conducting internal controls, and engaging external auditors can help ensure accurate and transparent financial reporting.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: The digital business landscape is dynamic and continuously evolving. Revenue recognition practices need to adapt to new business models, emerging technologies, and evolving accounting standards. Ongoing education, training, and staying up-to-date with industry trends and regulatory changes are essential to navigate the digital age successfully.
Overall, revenue recognition in the digital age involves understanding the complexities of digital business models, adhering to accounting standards, leveraging technology solutions, and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
Accurate revenue recognition ensures transparent financial reporting and builds trust with stakeholders in the digital marketplace.
Emerging Technologies for Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
Emerging technologies play a significant role in enhancing revenue recognition processes in the digital age. Here are some of the key technologies that are being utilized or have the potential to transform revenue recognition:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are powerful emerging technologies that have the potential to greatly impact revenue recognition processes.
Here are some key ways in which AI and ML can enhance revenue recognition:
- Data Analysis and Pattern Recognition: AI and ML algorithms can analyze large volumes of revenue-related data, such as contracts, invoices, and transaction records. By applying advanced analytics techniques, these technologies can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data. This analysis can help in identifying revenue recognition issues, detecting potential errors or fraud, and ensuring the accuracy of revenue reporting.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: AI and ML can automate repetitive and manual tasks involved in revenue recognition, such as data entry, data validation, and reconciliation. This automation reduces the risk of human errors, improves efficiency, and frees up resources to focus on more complex tasks that require human judgment. It also allows for faster processing of revenue recognition activities, enhancing overall productivity.
- Predictive Analytics and Revenue Forecasting: ML algorithms can be trained on historical revenue data to develop predictive models. These models can forecast future revenue trends, identify potential risks, and provide insights for revenue optimization. By considering various factors like customer behavior, market conditions, and product performance, ML can help organizations make more accurate revenue projections and strategic decisions.
- Contract Analysis and Compliance: AI-powered natural language processing (NLP) techniques can extract relevant information from contracts and interpret complex contractual terms. This helps in identifying performance obligations, contract enforceability, and determining the appropriate revenue recognition approach. AI and ML can also assist in ensuring compliance with accounting standards by flagging potential contract issues and inconsistencies.
- Risk Assessment and Fraud Detection: AI and ML can play a crucial role in risk assessment and fraud detection related to revenue recognition. These technologies can analyze data patterns, detect irregularities, and identify potential instances of revenue manipulation or fraudulent activities. By applying anomaly detection algorithms and data-driven risk scoring models, AI and ML can help organizations mitigate risks and maintain the integrity of revenue recognition processes.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: AI and ML algorithms can continuously learn and improve over time as they process more data. They can adapt to evolving business models, changing customer preferences, and emerging revenue recognition practices. Through iterative learning, these technologies can enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of revenue recognition models, leading to more reliable and consistent results.
- Audit and Compliance Support: AI and ML can assist auditors and regulatory compliance teams in conducting more efficient and effective reviews. These technologies can automate the extraction and analysis of data, flag potential audit risks, and provide insights into revenue recognition practices. By leveraging AI and ML, auditors can focus on higher-value tasks such as risk assessment, validation of complex transactions, and evaluation of management judgments.
However, it's important to note that the adoption of AI and ML in revenue recognition should be done carefully and with proper consideration. Data quality, model transparency, and ethical use of AI are important factors to address. Additionally, organizations should ensure that AI and ML solutions comply with relevant regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Overall, AI and ML have the potential to revolutionize revenue recognition by improving accuracy, efficiency, and risk management. As these technologies continue to advance, organizations should explore their applicability, invest in data infrastructure, and foster a culture of data-driven decision-making to fully harness their benefits.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is an emerging technology that can significantly impact revenue recognition processes. RPA involves the use of software robots or bots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks.
Here's how RPA can enhance revenue recognition:
- Data Extraction and Validation: RPA can automate the extraction of data from various sources, such as contracts, invoices, and financial systems. Bots can read and interpret structured and unstructured data, validate the accuracy of the data, and perform data reconciliation. This automation reduces manual effort and minimizes errors in data entry, ensuring reliable revenue recognition.
- Contract Management and Analysis: RPA can streamline contract management processes by automating the review and analysis of contract terms. Bots can extract key information from contracts, such as pricing terms, performance obligations, and contract durations. By analyzing this information, RPA can support revenue recognition decisions and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
- Revenue Calculation and Recognition: RPA can automate the calculation of revenue recognition schedules based on predefined rules and guidelines. Bots can perform calculations, allocate revenue to performance obligations, and generate accurate revenue recognition entries. This automation ensures consistency and eliminates manual errors in revenue calculations.
- Integration of Systems and Data Sources: RPA can integrate multiple systems and data sources involved in revenue recognition, such as CRM, ERP, and financial systems. Bots can extract data from these systems, reconcile information, and synchronize data across different platforms. This integration enhances data accuracy, facilitates real-time visibility, and streamlines the end-to-end revenue recognition process.
- Exception Handling and Reporting: RPA can handle exceptions and discrepancies in revenue recognition processes. Bots can identify anomalies or discrepancies in data, perform investigations, and flag potential issues for further review. They can also generate exception reports, providing insights into revenue recognition errors or unusual patterns that require attention.
- Audit Support and Compliance: RPA can assist in audit preparation and support regulatory compliance. Bots can retrieve relevant documentation, perform data validations, and generate audit reports. By automating audit-related tasks, RPA can improve the efficiency of audit processes and ensure compliance with internal controls and regulatory requirements.
- Scalability and Efficiency: RPA provides scalability to handle high volumes of revenue-related transactions. Bots can work 24/7, allowing for faster processing of revenue recognition tasks and reducing the time required for manual processing. This scalability and efficiency result in cost savings, improved productivity, and enhanced overall revenue recognition operations.
It's important to note that while RPA can automate repetitive tasks, it may require human oversight for complex decision-making and exceptions that require judgment. Additionally, organizations should consider security measures, data privacy, and compliance requirements when implementing RPA solutions.
By leveraging RPA in revenue recognition processes, organizations can improve accuracy, efficiency, and compliance, allowing finance teams to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is an emerging technology that has the potential to revolutionize revenue recognition processes. Here's how blockchain can enhance revenue recognition:
- Transparent and Immutable Records: Blockchain provides a decentralized and transparent ledger where revenue-related transactions can be recorded. Each transaction is cryptographically linked, creating an immutable record that cannot be altered or tampered with. This transparency and immutability ensure the integrity of revenue recognition data, enhancing trust and auditability.
- Smart Contracts for Automated Revenue Recognition: Blockchain enables the use of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions. Smart contracts can automatically execute revenue recognition activities based on predefined criteria, such as the completion of performance obligations or the occurrence of specific events. This automation reduces manual effort, enhances accuracy, and enables real-time revenue recognition.
- Enhanced Data Integrity and Consistency: With blockchain, revenue-related data can be securely stored and shared among stakeholders. Each participant in the blockchain network has access to the same set of data, ensuring consistency and eliminating discrepancies. This improves data integrity, reduces the risk of errors or fraud, and facilitates efficient reconciliation of revenue-related information.
- Improved Revenue Sharing and Royalty Management: For industries that involve revenue sharing or royalty payments, blockchain can provide a transparent and auditable platform. Blockchain's smart contracts can automatically calculate and distribute revenue shares or royalties to the relevant parties based on predefined terms. This ensures accurate and timely revenue distribution, reducing disputes and enhancing trust among stakeholders.
- Streamlined Audits and Compliance: Blockchain's transparent and immutable nature simplifies the audit process for revenue recognition. Auditors can easily trace revenue transactions, verify the accuracy of data, and ensure compliance with accounting standards and regulations. This streamlines audits reduces the need for extensive manual documentation, and enhances the efficiency of compliance processes.
- Real-Time Insights and Analytics: Blockchain enables real-time access to revenue-related data, allowing organizations to gain valuable insights and perform analytics. By analyzing blockchain data, organizations can identify revenue trends, customer behavior patterns, and market dynamics. These insights can inform revenue forecasting, pricing strategies, and decision-making, leading to improved revenue recognition outcomes.
- Supply Chain Integration: In industries with complex supply chains, blockchain can facilitate seamless integration and traceability of revenue-related transactions. Each participant in the supply chain can contribute to the blockchain with their respective revenue data, allowing for efficient tracking of revenue flows and ensuring accuracy in revenue recognition across the entire ecosystem.
It's important to note that while blockchain technology offers significant benefits for revenue recognition, its implementation requires careful consideration. Factors such as scalability, interoperability with existing systems, data privacy, and regulatory compliance need to be addressed.
Additionally, collaboration among industry stakeholders and standardization efforts are essential for realizing the full potential of blockchain in revenue recognition.
Overall, blockchain technology has the potential to enhance transparency, accuracy, efficiency, and trust in revenue recognition processes, benefiting organizations and stakeholders involved in revenue-related transactions.
Data Analytics and Visualization
Data analytics and visualization are emerging technologies that can significantly enhance revenue recognition processes. Here's how these technologies contribute to revenue recognition:
- Advanced Data Analysis: Data analytics techniques, such as statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling, can be applied to revenue-related data. These techniques help identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in revenue data, enabling organizations to gain deeper insights into revenue streams, customer behavior, and market dynamics. Advanced data analysis enhances the accuracy of revenue recognition and supports data-driven decision-making.
- Real-time Monitoring and Reporting: Data analytics tools enable real-time monitoring of revenue-related metrics, such as revenue growth, customer acquisition, and product performance. Organizations can leverage interactive dashboards and visualizations to track revenue performance against targets, identify deviations, and take timely corrective actions. Real-time reporting provides up-to-date insights, ensuring agility in revenue recognition processes.
- Revenue Forecasting and Planning: Data analytics allows organizations to forecast future revenue trends and optimize revenue recognition strategies. By analyzing historical revenue data, market indicators, and external factors, organizations can develop predictive models to forecast revenue with higher accuracy. Revenue forecasting facilitates strategic planning, resource allocation, and revenue optimization efforts.
- Customer Segmentation and Personalization: Data analytics enables organizations to segment customers based on their revenue contribution, behavior, and preferences. By understanding customer segments, organizations can tailor pricing strategies, product offerings, and revenue recognition approaches to optimize revenue generation. Personalized revenue recognition enhances customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Fraud Detection and Risk Management: Data analytics plays a crucial role in detecting revenue recognition fraud and managing associated risks. By analyzing revenue data for anomalies, unusual patterns, or suspicious transactions, organizations can identify potential fraudulent activities and mitigate risks. Data-driven risk scoring models can help prioritize risk areas and allocate resources effectively.
- Visualization for Enhanced Insights: Data visualization tools provide intuitive and interactive representations of revenue-related data. Visualizations such as charts, graphs, and heatmaps facilitate the understanding of complex revenue patterns, trends, and relationships. Visual representations help stakeholders, including finance teams, executives, and auditors, to interpret revenue data more effectively and make informed decisions.
- Integration of Multiple Data Sources: Data analytics enables the integration and analysis of data from multiple sources relevant to revenue recognition. This includes data from sales systems, financial systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and external data sources. Integrating diverse data sources provides a holistic view of revenue-related information, improving accuracy and completeness in revenue recognition.
- Compliance and Audit Support: Data analytics supports compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Organizations can use analytics tools to validate revenue recognition practices, perform internal audits, and generate audit reports. Data-driven insights and analytics provide evidence for regulatory compliance, ensuring transparency and accuracy in revenue recognition.
It's important for organizations to invest in data analytics capabilities, including skilled resources, robust data infrastructure, and user-friendly analytics tools. Additionally, organizations should prioritize data privacy and security to ensure compliance with regulations and protect sensitive revenue-related information.
By leveraging data analytics and visualization, organizations can gain valuable insights, improve revenue recognition accuracy, optimize revenue strategies, and mitigate risks, ultimately leading to enhanced financial performance.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a powerful emerging technology that can significantly impact revenue recognition processes. Here's how cloud computing enhances revenue recognition:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing provides a scalable infrastructure that can accommodate varying workloads and data storage requirements. Organizations can easily scale up or down their computing resources based on the volume of revenue-related data and processing needs. This scalability and flexibility enable efficient revenue recognition processes, especially during peak periods or when handling large datasets.
- Data Centralization and Accessibility: Cloud-based platforms allow organizations to centralize revenue-related data from multiple sources, such as CRM systems, financial systems, and transaction records. This centralization improves data accessibility for revenue recognition purposes, enabling real-time access to up-to-date data by authorized stakeholders. Cloud platforms also facilitate data integration, ensuring seamless data flow between different systems involved in revenue recognition.
- Collaboration and Remote Work: Cloud computing enables collaboration among teams and stakeholders involved in revenue recognition, regardless of their physical locations. Cloud-based platforms provide secure access to revenue-related data, documents, and applications, allowing finance teams, auditors, and other stakeholders to collaborate in real-time. This flexibility supports remote work environments and enhances efficiency in revenue recognition processes.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing offers cost advantages by eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and reducing hardware and maintenance costs. Organizations can leverage cloud services on a pay-as-you-go model, only paying for the resources and services utilized for revenue recognition. This cost efficiency enables organizations to allocate resources more effectively and invest in other revenue-generating activities.
- Data Security and Compliance: Cloud service providers prioritize data security and invest in robust security measures to protect revenue-related data. They often have advanced security protocols, encryption techniques, and regular data backups to ensure data integrity and availability. Cloud providers also comply with industry standards and regulations, relieving organizations from the burden of maintaining their own compliance infrastructure.
- Integration with Third-Party Applications: Cloud platforms offer integration capabilities with third-party applications and services relevant to revenue recognition. Organizations can integrate their cloud-based revenue recognition systems with CRM systems, financial systems, payment gateways, and other applications, ensuring seamless data flow and process automation. This integration enhances accuracy, reduces manual effort, and improves overall efficiency in revenue recognition.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting: Cloud computing enables organizations to leverage advanced analytics and reporting tools for revenue recognition. Cloud-based analytics platforms provide robust capabilities for data analysis, visualization, and reporting. These tools allow organizations to generate comprehensive revenue reports, perform data-driven analysis, and gain actionable insights for revenue optimization.
It's important for organizations to assess the security measures, reliability, and compliance capabilities of cloud service providers before adopting cloud computing for revenue recognition. Additionally, organizations should consider data governance, data privacy, and backup and recovery strategies to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of revenue-related data.
Overall, cloud computing offers numerous benefits for revenue recognition, including scalability, data centralization, collaboration, cost efficiency, data security, and advanced analytics capabilities. By leveraging cloud technologies, organizations can streamline revenue recognition processes, improve accuracy, and make data-driven decisions to optimize revenue generation.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an emerging technology that can have a significant impact on revenue recognition processes. Here's how IoT enhances revenue recognition:
- Improved Data Collection and Accuracy: IoT devices, such as sensors and connected devices, can collect real-time data on various aspects of revenue generation, such as product usage, customer behavior, and service performance. This data can be automatically captured and transmitted to revenue recognition systems, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information for revenue calculations. IoT enables organizations to gather more granular and detailed data, leading to more precise revenue recognition.
- Enhanced Asset Tracking and Usage Monitoring: IoT enables organizations to track and monitor the usage of revenue-generating assets. For example, IoT sensors embedded in products or equipment can capture data on their utilization, location, and condition. This information can be leveraged in revenue recognition processes to determine when revenue should be recognized based on usage or performance milestones. IoT-powered asset tracking ensures accurate and timely revenue recognition based on the actual usage of assets.
- Real-Time Revenue Monitoring: IoT devices enable real-time monitoring of revenue-related metrics and events. For instance, IoT sensors in retail environments can track sales transactions and inventory levels, providing instant visibility into revenue generation. This real-time monitoring allows organizations to respond promptly to revenue-related events, make data-driven decisions, and optimize revenue recognition processes accordingly.
- Personalized Revenue Generation: IoT data can provide valuable insights into customer preferences, usage patterns, and buying behavior. By leveraging this data, organizations can personalize revenue generation strategies, such as dynamic pricing, cross-selling, and targeted promotions. IoT enables organizations to deliver personalized experiences that drive revenue and optimize revenue recognition based on individual customer preferences.
- Maintenance and Service Revenue Opportunities: IoT devices can facilitate the monitoring and predictive maintenance of revenue-generating assets. By collecting data on asset performance, organizations can proactively identify maintenance needs and offer timely services to customers. This creates new revenue opportunities through service contracts, warranties, or subscription models. IoT-powered maintenance and service revenue can be accurately recognized based on usage, performance, or contract terms.
- Integration with Revenue Recognition Systems: IoT can integrate with revenue recognition systems, such as ERP or CRM platforms, enabling seamless data flow and automated revenue recognition processes. IoT data can be directly fed into revenue recognition systems, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors. This integration ensures efficient and accurate revenue recognition, streamlining financial operations.
- Compliance and Audit Support: IoT data provides a transparent and auditable trail of revenue-related activities. Auditors can access IoT-generated data to verify revenue recognition processes and compliance with accounting standards. IoT enhances the accuracy and transparency of revenue recognition, facilitating audits and regulatory compliance.
It's important for organizations to consider data privacy, security, and compliance when implementing IoT for revenue recognition. Protecting IoT devices, securing data transmission, and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations are crucial considerations.
By leveraging IoT in revenue recognition, organizations can gain real-time insights, improve accuracy, optimize revenue strategies, and enhance customer experiences. IoT enables organizations to move towards more data-driven and proactive revenue recognition processes, resulting in improved financial performance.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an emerging technology that can significantly impact revenue recognition processes. Here's how NLP enhances revenue recognition:
- Contract Analysis and Extraction: NLP can analyze and extract relevant information from contracts, such as sales agreements, service contracts, or licensing agreements. By automatically extracting key terms and conditions related to revenue recognition, NLP can assist in identifying performance obligations, pricing terms, payment terms, and other critical information. This automation reduces manual effort, improves accuracy, and ensures consistency in revenue recognition across contracts.
- Automated Data Extraction and Validation: NLP techniques can be applied to extract revenue-related data from unstructured sources, such as invoices, sales orders, or customer communication. NLP algorithms can interpret and extract relevant information, such as transaction details, customer names, product descriptions, and pricing information. This automated data extraction improves efficiency, reduces errors, and speeds up the revenue recognition process.
- Sentiment Analysis and Customer Insights: NLP can analyze customer feedback, reviews, and support tickets to gain insights into customer satisfaction, preferences, and sentiment. By analyzing customer sentiment related to revenue-generating activities, organizations can identify areas for improvement, optimize pricing strategies, and tailor revenue recognition approaches to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Revenue Recognition Compliance and Audit: NLP can assist in ensuring compliance with revenue recognition standards and regulations. By analyzing financial documents, disclosures, and revenue-related communications, NLP can help identify potential non-compliance or discrepancies. NLP-powered compliance checks enable organizations to proactively address revenue recognition issues, improve accuracy, and simplify the audit process.
- Voice-Enabled Revenue Recognition: NLP technologies enable voice-activated interfaces and voice assistants that can assist with revenue recognition tasks. Users can interact with the system using natural language commands to perform functions such as querying revenue data, retrieving revenue reports, or initiating revenue recognition processes. Voice-enabled interfaces improve user experience, accessibility, and efficiency in revenue recognition activities.
- Revenue Reporting and Insights: NLP techniques can be applied to analyze revenue-related data and generate meaningful insights. By processing large volumes of revenue data, NLP algorithms can identify revenue trends, anomalies, or patterns that may impact revenue recognition decisions. NLP-powered analytics and reporting tools facilitate data-driven decision-making, revenue forecasting, and optimization of revenue recognition strategies.
- Multilingual Revenue Recognition: NLP technologies enable organizations to process revenue-related data in multiple languages. NLP algorithms can understand and analyze text in different languages, facilitating revenue recognition in global markets. This capability is particularly valuable for organizations operating in multinational environments or dealing with revenue recognition across diverse language regions.
It's important to note that while NLP can automate and assist with revenue recognition processes, human review, and oversight are still crucial. Organizations should validate the output generated by NLP systems and ensure compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
By leveraging NLP in revenue recognition, organizations can automate data extraction, gain valuable insights from unstructured text, improve compliance, and enhance decision-making processes. NLP empowers organizations to efficiently process and analyze revenue-related data, leading to more accurate and effective revenue recognition outcomes.
Advanced Visualization and Reporting Tools
Advanced visualization and reporting tools are indeed emerging technologies that can greatly enhance revenue recognition processes. Here's how these tools contribute to revenue recognition:
- Interactive Dashboards: Advanced visualization tools enable the creation of interactive dashboards that provide a comprehensive view of revenue-related metrics and trends. Users can customize and drill down into the data, exploring different dimensions and visualizing revenue performance in real time. Interactive dashboards facilitate data exploration, quick identification of revenue patterns, and informed decision-making.
- Data Visualization Techniques: These tools employ various data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, heatmaps, and geospatial visualizations, to present revenue data in a visually compelling and intuitive manner. Visualization techniques make it easier to understand complex revenue relationships, identify outliers or anomalies, and communicate revenue insights effectively to stakeholders.
- Real-time Reporting: Advanced reporting tools enable the real-time generation of revenue reports and performance indicators. With automated data feeds and integration with revenue systems, these tools can generate up-to-date reports on revenue growth, revenue by product or service, revenue by region, and other relevant metrics. Real-time reporting enhances agility and responsiveness in revenue recognition processes.
- Predictive Analytics: Advanced visualization and reporting tools often incorporate predictive analytics capabilities. By applying machine learning algorithms and statistical models to revenue data, these tools can generate forecasts and predictions for future revenue trends. Predictive analytics enables organizations to anticipate revenue patterns, identify potential risks or opportunities, and optimize revenue recognition strategies accordingly.
- Comparative Analysis: Visualization tools facilitate comparative analysis of revenue data across different time periods, product lines, customer segments, or geographical regions. Users can easily compare revenue performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions based on these comparisons. The comparative analysis enables organizations to gain insights into revenue drivers and optimize revenue recognition practices.
- Storytelling and Data Narratives: Advanced visualization tools often include features that allow users to create data stories and narratives around revenue data. Users can build compelling narratives using visualizations, annotations, and annotations to communicate revenue insights effectively. Data narratives help stakeholders understand the context and implications of revenue data, facilitating collaboration and alignment in revenue recognition processes.
- Mobile and Remote Access: Modern visualization and reporting tools are designed to be accessible on multiple devices, including mobile devices. This mobility allows stakeholders to access revenue dashboards and reports remotely, enabling real-time decision-making, collaboration, and monitoring of revenue performance from anywhere. Mobile access enhances flexibility and productivity in revenue recognition activities.
It's important for organizations to choose visualization and reporting tools that are user-friendly, scalable, and compatible with their data infrastructure. Organizations should also ensure data security and privacy when using these tools, particularly when sharing sensitive revenue-related information.
By leveraging advanced visualization and reporting tools, organizations can gain actionable insights, improve data-driven decision-making, and optimize revenue recognition processes. These tools enable stakeholders to visualize revenue data effectively, identify trends, and communicate revenue insights, ultimately enhancing revenue generation and financial performance.
Best Practices for Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
Implementing best practices for revenue recognition is crucial to ensure accurate and transparent financial reporting. Here are some key best practices to consider:
Understand and Apply Relevant Accounting Standards
Understanding and applying relevant accounting standards is indeed a crucial best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Revenue recognition is governed by specific accounting standards, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the United States. Adhering to these standards ensures consistency, comparability, and transparency in revenue recognition practices. It helps organizations meet regulatory requirements, maintain financial credibility, and build trust with stakeholders.
- Stay Up-to-Date with Accounting Guidance: Accounting standards for revenue recognition are periodically updated to reflect changing business practices and emerging issues. It is essential for organizations to stay informed about the latest accounting guidance, interpretations, and amendments related to revenue recognition. This can be achieved through continuous professional education, engagement with accounting bodies, and regular monitoring of accounting updates.
- Interpret and Apply Standards Appropriately: Interpreting and applying accounting standards correctly is critical for accurate revenue recognition. Organizations should have a deep understanding of the principles, concepts, and guidelines outlined in the accounting standards. This includes understanding the criteria for recognizing revenue, determining the transaction price, allocating revenue to performance obligations, and recognizing revenue over time or at a point in time, depending on the nature of the revenue arrangement.
- Document Revenue Recognition Policies: Organizations should develop comprehensive revenue recognition policies that align with accounting standards. These policies should clearly outline the criteria and procedures for revenue recognition, including specific scenarios and exceptions. Documenting the policies ensures consistency in revenue recognition practices, provides guidance to employees involved in revenue recognition, and supports audit and compliance processes.
- Regular Training and Education: Providing regular training and education to finance and accounting personnel is crucial for understanding and applying accounting standards effectively. This ensures that employees involved in revenue recognition are knowledgeable about the relevant accounting guidance and are equipped with the skills to make appropriate revenue recognition decisions. Ongoing training helps maintain a high level of expertise and reduces the risk of errors or non-compliance.
- Internal Controls and Review Processes: Implementing robust internal controls and review processes is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of revenue recognition. Organizations should establish control activities, such as the segregation of duties, approval workflows, and reconciliation procedures, to mitigate the risk of fraudulent or erroneous revenue recognition. Regular reviews and audits of revenue recognition processes help identify weaknesses, assess compliance, and ensure adherence to accounting standards.
- Engage Professional Advisors: In complex revenue recognition scenarios or when significant judgment is required, organizations may benefit from engaging professional advisors, such as external auditors or accounting consultants. These experts can provide guidance on interpreting and applying accounting standards, offer insights on industry-specific considerations, and assist with complex revenue recognition issues. Their expertise and experience help ensure accurate and compliant revenue recognition.
By understanding and applying relevant accounting standards, organizations can establish consistent and accurate revenue recognition practices. Compliance with accounting standards enhances financial reporting integrity, provides transparency to stakeholders, and mitigates the risk of non-compliance.
It is essential to establish strong internal controls, provide ongoing training, and engage professional advisors to effectively implement best practices for revenue recognition in accordance with accounting standards.
Document Contracts and Key Terms
Documenting contracts and key terms is indeed a critical best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Establishing Evidence of Revenue Arrangements: Documenting contracts provides tangible evidence of revenue arrangements between the organization and its customers. It helps establish the terms and conditions agreed upon, including the scope of goods or services to be provided, pricing, payment terms, and any specific provisions or commitments. Having clear and well-documented contracts ensures transparency and provides a foundation for accurate revenue recognition.
- Identification of Performance Obligations: Contracts often outline the specific performance obligations that the organization has committed to deliver to the customer. These obligations may include the delivery of goods, provision of services, or a combination of both. By documenting contracts and key terms, organizations can clearly identify and understand the performance obligations associated with each revenue arrangement, enabling appropriate revenue recognition.
- Determining Transaction Price and Variable Consideration: The contract documentation is crucial for determining the transaction price, which is the amount the organization expects to be entitled to in exchange for transferring goods or services. Contracts may include variable considerations, such as discounts, rebates, or contingent payments. Documenting the contract terms allows organizations to accurately assess the transaction price and account for any variable consideration appropriately.
- Allocation of Revenue to Performance Obligations: Revenue recognition standards require the allocation of revenue to each distinct performance obligation identified in the contract. By documenting contracts and key terms, organizations can allocate revenue accurately based on the relative standalone selling prices of the goods or services promised. Clear documentation helps ensure proper revenue allocation and prevents over- or under-recognition of revenue.
- Ensuring Consistency and Compliance: Documenting contracts and key terms promotes consistency in revenue recognition practices across the organization. It enables finance and accounting teams to follow standardized procedures, interprets contractual terms consistently, and apply revenue recognition policies in compliance with accounting standards. This consistency supports accurate financial reporting and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
- Facilitating Review and Audit Processes: Well-documented contracts provide a clear audit trail and facilitate review processes. During internal or external audits, contract documentation allows auditors to verify the accuracy of revenue recognition and assess compliance with accounting standards. Documenting contracts and key terms saves time and effort during audits and helps ensure the accuracy and completeness of revenue recognition disclosures.
- Supporting Dispute Resolution: In situations where disputes or disagreements arise with customers regarding revenue recognition, having well-documented contracts and key terms serves as valuable evidence to resolve conflicts. Clear documentation helps clarify the intentions and commitments of both parties, reducing the potential for disputes and supporting efficient resolution if they do occur.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should establish robust contract management processes. This may involve implementing a centralized contract repository, ensuring contracts are reviewed and approved by relevant stakeholders, and establishing procedures for maintaining and updating contract documentation as needed.
By documenting contracts and key terms, organizations can ensure accurate revenue recognition, promote consistency, support audit processes, and facilitate dispute resolution. It is an essential best practice to establish a solid foundation for revenue recognition and financial reporting.
Identify and Separate Performance Obligations
Identifying and separating performance obligations is indeed a crucial best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Accurate Revenue Allocation: Revenue recognition standards require the allocation of revenue to distinct performance obligations in a contract. By identifying and separating performance obligations, organizations can allocate revenue accurately based on the relative standalone selling prices of the goods or services promised. This ensures that revenue is recognized in a manner that reflects the transfer of control to the customer for each obligation.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Proper identification and separation of performance obligations ensure compliance with accounting standards, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards provide guidance on identifying separate performance obligations within a contract and specify criteria for their recognition and measurement. Adhering to these standards ensures consistency, comparability, and transparency in revenue recognition practices.
- Enhanced Financial Reporting: Separating performance obligations enables organizations to provide more detailed and transparent financial reporting. By disclosing revenue recognized for each distinct performance obligation, stakeholders gain a clearer understanding of the revenue sources and the nature of goods or services being provided. This transparency builds trust and facilitates decision-making for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
- Improved Revenue Forecasting: Identifying and separating performance obligations can contribute to more accurate revenue forecasting. By understanding the specific goods or services to be provided, their timing, and the associated revenue recognition, organizations can better project future revenue streams. Accurate revenue forecasting supports effective budgeting, planning, and resource allocation within the organization.
- Risk Mitigation: Separating performance obligations can help mitigate the risk of over- or under-recognition of revenue. By clearly delineating the promises made to the customer and the corresponding revenue recognition, organizations can ensure that revenue is recognized when control over goods or services is transferred. This reduces the risk of revenue manipulation or misstatement, which could have legal, financial, and reputational consequences.
- Facilitates Contract Analysis: Identifying and separating performance obligations requires a thorough analysis of contracts and an understanding of the promised goods or services. This process enables organizations to evaluate the terms, conditions, and obligations within the contract, ensuring alignment with revenue recognition principles. Contract analysis facilitates better risk assessment, contract structuring, and negotiation to optimize revenue recognition outcomes.
- Internal Control and Audit Compliance: Separating performance obligations contributes to strong internal control and audit compliance. It supports the establishment of control activities, such as segregation of duties, approval workflows, and periodic reviews, to ensure accurate revenue recognition. Clear separation of obligations helps auditors verify compliance with accounting standards, providing assurance to stakeholders and reducing the risk of non-compliance.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should analyze contracts thoroughly to identify distinct promises and performance obligations. This may involve engaging legal and finance teams, understanding customer expectations, and considering the nature of goods or services being provided.
Clear documentation of the identified performance obligations is essential for transparency, compliance, and effective revenue recognition.
By identifying and separating performance obligations, organizations ensure accurate revenue allocation, compliance with accounting standards, improved financial reporting, and risk mitigation.
This best practice establishes a solid foundation for revenue recognition, enabling organizations to meet regulatory requirements and provide transparent and reliable financial information.
Determine Transaction Price and Variable Consideration
Determining the transaction price and variable consideration is indeed a critical best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Accurate Revenue Recognition: The transaction price represents the amount an organization expects to be entitled to in exchange for transferring goods or services to the customer. It is essential to determine the transaction price accurately as it forms the basis for recognizing revenue. Variable considerations, such as discounts, rebates, or contingent payments, can impact the transaction price. By properly determining the transaction price and accounting for variable considerations, organizations can ensure accurate and reliable revenue recognition.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Determining the transaction price and handling variable consideration aligns with accounting standards such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards provide guidance on how to estimate, allocate, and recognize revenue when variable consideration exists. Complying with these standards ensures consistency, comparability, and transparency in revenue recognition practices.
- Evaluation of Contractual Terms: Determining the transaction price requires a thorough evaluation of contractual terms and conditions. It involves assessing the agreed-upon price, considering any variable or contingent amounts, and accounting for any significant financing components. By carefully reviewing and understanding the contract terms, organizations can ensure the accurate determination of the transaction price and avoid potential revenue recognition errors or omissions.
- Estimation and Probability Assessment: In cases where the transaction price includes variable consideration, organizations need to make reasonable estimates and assess the probability of different outcomes. This involves considering historical data, market conditions, customer behavior, and any relevant performance obligations. Applying appropriate estimation techniques and assessing the probability of different scenarios allows organizations to determine the most accurate transaction price.
- Monitoring and Adjusting Estimates: The determination of the transaction price and variable consideration is an ongoing process. Organizations should continuously monitor and evaluate the estimates made and adjust them as necessary. This includes reassessing variable consideration, updating estimates based on changes in circumstances, and considering any constraints or changes in customer expectations. Regular monitoring and adjustment of estimates ensure revenue recognition remains accurate and up to date.
- Documentation and Disclosure: Proper documentation of the determination of the transaction price and variable consideration is essential. Organizations should maintain clear and comprehensive records of the factors considered, estimation techniques used, and the rationale behind the determination. Documentation serves as evidence of the organization's compliance with accounting standards, supports audit processes, and provides transparency to stakeholders. Additionally, appropriate disclosure of the transaction price and variable consideration in financial statements enhances transparency and helps stakeholders understand the revenue recognition process.
- Internal Control and Audit Compliance: Establishing robust internal controls and review processes is crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of determining the transaction price and handling variable considerations. Organizations should implement control activities such as the segregation of duties, approval workflows, and periodic reviews to mitigate the risk of misstatement or fraud. Strong internal controls and compliance with audit requirements provide assurance to stakeholders and demonstrate a commitment to accurate revenue recognition.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should involve finance, sales, and legal teams in the evaluation and determination of the transaction price and variable consideration. Collaboration and clear communication among these teams are essential to ensure accurate and consistent revenue recognition practices.
By determining the transaction price accurately and handling variable considerations appropriately, organizations can ensure compliant revenue recognition, reliable financial reporting, and transparency in their revenue recognition practices.
This best practice helps organizations meet regulatory requirements, maintain financial credibility, and provide meaningful information to stakeholders.
Allocate Transaction Price
Allocating the transaction price is indeed a critical best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Accurate Revenue Recognition: The allocation of the transaction price involves assigning the total consideration from a customer contract to the various performance obligations identified within that contract. Each performance obligation represents a distinct good or service to be provided to the customer. By properly allocating the transaction price, organizations can ensure that revenue is recognized in a manner that reflects the transfer of control for each obligation, resulting in accurate revenue recognition.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Allocation of the transaction price aligns with accounting standards such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards provide guidance on how to allocate the transaction price when multiple performance obligations exist within a contract. Complying with these standards ensures consistency, comparability, and transparency in revenue recognition practices.
- Standalone Selling Prices: To allocate the transaction price, organizations must determine the standalone selling price of each distinct performance obligation. The standalone selling price represents the price at which the organization would sell the good or service on a standalone basis in the market. It is crucial to estimate the standalone selling prices accurately to allocate the transaction price appropriately.
- Relative Allocation Basis: In situations where the standalone selling prices cannot be directly observed, organizations need to use an appropriate allocation method to allocate the transaction price to each performance obligation. The allocation method should be based on the relative standalone selling prices or another systematic and rational basis. The method chosen should reflect the organization's best estimate of the value delivered to the customer.
- Adjustments and Constraints: Allocation of the transaction price may require adjustments or consideration of certain constraints. For example, organizations may need to consider discounts, volume rebates, or other variable consideration elements that impact the allocation. Additionally, organizations need to assess any significant financing components or potential contract constraints that could affect the allocation process.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments: The allocation of the transaction price is not a one-time exercise. Organizations should monitor and evaluate the allocation continually, considering changes in circumstances, customer expectations, or performance obligations. Adjustments to the allocation should be made as necessary to reflect updated information and ensure accurate revenue recognition.
- Documentation and Disclosure: Proper documentation of the allocation of the transaction price is essential. Organizations should maintain clear and comprehensive records of the factors considered, the allocation method used, and the rationale behind the allocation decisions. Documentation serves as evidence of compliance with accounting standards, supports audit processes, and provides transparency to stakeholders. Appropriate disclosure of the allocation methodology and significant judgments made enhances transparency and helps stakeholders understand the revenue recognition process.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should establish robust processes and controls around the allocation of the transaction price. This may involve collaboration among finance, sales, and legal teams, as well as the use of appropriate systems and tools to facilitate accurate allocation.
By allocating the transaction price accurately, organizations ensure compliant revenue recognition, reliable financial reporting, and transparency in their revenue recognition practices. This best practice helps organizations meet regulatory requirements, maintain financial credibility, and provide meaningful information to stakeholders.
Recognize Revenue Over Time or at a Point in Time
Recognizing revenue over time or at a point in time is indeed a crucial best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Alignment with Performance: Revenue recognition over time or at a point in time ensures that revenue is recognized when control of goods or services is transferred to the customer. Recognizing revenue over time is appropriate when the customer receives the benefits of the organization's performance as it occurs. On the other hand, recognizing revenue at a point in time is suitable when control is transferred at a specific moment or milestone.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Determining whether revenue should be recognized over time or at a point in time aligns with accounting standards such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards provide guidance on recognizing revenue based on the transfer of control concept and the criteria for revenue recognition over time or at a point in time. Complying with these standards ensures consistency and comparability in revenue recognition practices.
- Enhanced Financial Reporting: Recognizing revenue over time or at a point in time can provide more meaningful and accurate financial reporting. It allows stakeholders to understand the timing and pattern of revenue recognition, providing insights into the organization's performance and revenue streams. Transparent and informative financial reporting builds trust and facilitates decision-making for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
- Proper Evaluation of Performance Obligations: Determining the appropriate timing of revenue recognition requires a thorough evaluation of the performance obligations identified within a contract. Understanding the nature of the obligations and the criteria for recognizing revenue over time or at a point in time is essential. Proper evaluation ensures that revenue is recognized in a manner that reflects the transfer of control and aligns with the organization's contractual commitments.
- Measurement of Progress: Recognizing revenue over time requires measuring the progress toward the completion of performance obligations. Organizations need to establish reliable methods to assess the extent of completion, such as input or output measures. Accurate measurement of progress ensures that revenue is recognized proportionally to the organization's performance and the value provided to the customer.
- Documentation and Disclosure: Proper documentation of the determination of whether revenue should be recognized over time or at a point in time is crucial. Organizations should maintain clear records of the evaluation process, the rationale behind the decision, and the methods used to measure progress. Documentation serves as evidence of compliance with accounting standards, supports audit processes, and provides transparency to stakeholders. Appropriate disclosure of the timing of revenue recognition enhances transparency and helps stakeholders understand the revenue recognition approach.
- Internal Control and Audit Compliance: Establishing robust internal controls and review processes is essential to ensure the accurate and reliable recognition of revenue over time or at a point in time. Organizations should implement control activities, such as the segregation of duties, approval workflows, and periodic reviews, to mitigate the risk of misstatement or fraud. Strong internal controls and compliance with audit requirements provide assurance to stakeholders and demonstrate a commitment to accurate revenue recognition.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should involve finance, sales, and legal teams in the evaluation and determination of when revenue should be recognized over time or at a point in time. Collaboration and clear communication among these teams are essential to ensure consistent and accurate revenue recognition practices.
By recognizing revenue over time or at a point in time, organizations ensure compliant revenue recognition, reliable financial reporting, and transparency in their revenue recognition practices. This best practice helps organizations meet regulatory requirements, maintain financial credibility, and provide meaningful information to stakeholders.
Regularly Review and Update Revenue Recognition Policies
Regularly reviewing and updating revenue recognition policies is indeed a crucial best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Compliance with Changing Standards: Revenue recognition standards and regulations may evolve over time. By regularly reviewing and updating revenue recognition policies, organizations can ensure compliance with the latest accounting standards, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Staying up to date with regulatory changes helps maintain consistency and accuracy in revenue recognition practices.
- Alignment with Business Changes: Business models, product offerings, and customer contracts may change over time. Regularly reviewing revenue recognition policies allows organizations to assess whether existing policies align with current business practices. This ensures that revenue recognition policies accurately reflect the nature of goods or services provided and the corresponding revenue recognition criteria.
- Enhancing Consistency and Comparability: Consistency and comparability are essential for financial reporting. Regularly reviewing and updating revenue recognition policies promotes consistency in how revenue is recognized across different contracts and periods. It helps avoid inconsistencies, confusion, and potential misinterpretations. Consistent revenue recognition practices enable stakeholders to make meaningful comparisons and assessments of an organization's financial performance.
- Adapting to Industry Trends: Industries and markets are subject to ongoing changes, such as emerging business models, technological advancements, or new revenue streams. Regular policy review allows organizations to adapt to these industry trends and align revenue recognition practices with evolving business realities. This ensures that revenue recognition policies remain relevant and appropriate for the organization's specific industry context.
- Addressing Internal Control Considerations: Regular policy review provides an opportunity to evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls related to revenue recognition. Organizations can identify any gaps or areas for improvement in the control environment and implement necessary changes to strengthen internal controls. Effective internal controls provide assurance that revenue recognition is accurate, reliable, and in compliance with policies and standards.
- Incorporating Lessons Learned: Regularly reviewing revenue recognition policies allows organizations to incorporate lessons learned from past experiences. It enables the organization to identify any challenges or issues encountered during the revenue recognition process and make appropriate adjustments to policies. Incorporating lessons learned helps improve the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of revenue recognition practices.
- Documentation and Communication: During policy reviews and updates, organizations should document the rationale, considerations, and changes made to revenue recognition policies. Clear documentation provides a record of policy updates and supports transparency and accountability. Additionally, effective communication of policy changes to relevant stakeholders, such as finance teams, sales teams, and auditors, ensures that everyone is aware of the updated policies and can apply them consistently.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should establish a structured process for reviewing and updating revenue recognition policies.
This process should involve collaboration among finance, legal, and other relevant teams. It is important to allocate sufficient time and resources to conduct thorough reviews and communicate policy updates effectively.
By regularly reviewing and updating revenue recognition policies, organizations can ensure compliance, adapt to changing business environments, enhance consistency, and improve internal controls.
This best practice supports accurate financial reporting, transparency, and informed decision-making for stakeholders.
Perform Internal Controls and Independent Reviews
Performing internal controls and independent reviews is indeed a crucial best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability: Internal controls and independent reviews are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of revenue recognition. These practices help identify and mitigate risks associated with revenue recognition errors, misstatements, or fraudulent activities. By implementing effective internal controls and conducting independent reviews, organizations can increase confidence in the accuracy of their financial statements and revenue recognition processes.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Internal controls and independent reviews help organizations comply with regulatory requirements and accounting standards related to revenue recognition. By establishing control activities that align with industry best practices and conducting independent reviews, organizations demonstrate their commitment to meeting regulatory obligations and maintaining financial transparency.
- Mitigating Risk of Errors and Fraud: Revenue recognition involves various complexities and judgments. Effective internal controls and independent reviews help mitigate the risk of errors and fraud in the revenue recognition process. Through segregation of duties, approval workflows, reconciliations, and periodic reviews, organizations can detect and prevent potential errors or fraudulent activities that could impact revenue recognition.
- Assessing and Enhancing Control Environment: Performing internal controls and independent reviews provides an opportunity to assess the overall control environment related to revenue recognition. Organizations can evaluate the design and effectiveness of their control activities, identify any control gaps or weaknesses, and implement necessary improvements. Regular monitoring and evaluation of internal controls help maintain a robust control environment.
- Independent Validation of Revenue Recognition: Independent reviews provide an objective assessment of an organization's revenue recognition practices. External auditors or internal audit teams can conduct independent reviews to evaluate the appropriateness and effectiveness of revenue recognition policies and procedures. This independent validation enhances confidence in the accuracy and reliability of revenue recognition practices.
- Identification of Areas for Improvement: Internal controls and independent reviews can help identify areas for improvement in the revenue recognition process. They provide valuable insights into potential weaknesses, inefficiencies, or gaps in control activities. By addressing these identified areas, organizations can enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and reliability of their revenue recognition practices.
- Documentation and Reporting: Performing internal controls and independent reviews involves documenting the control activities, reviewing findings, and remediation actions are taken. Proper documentation supports transparency, provides evidence of compliance with regulations, and facilitates communication with external stakeholders. Additionally, reporting the results of independent reviews to management and the audit committee helps to drive accountability and facilitate decision-making.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should establish a framework for internal controls and independent reviews specific to revenue recognition. This includes defining control activities, assigning responsibilities, conducting periodic reviews, and engaging independent auditors or internal audit teams.
Regular training and communication with relevant stakeholders are also important to ensure understanding and compliance with control procedures.
By performing internal controls and independent reviews, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance compliance, and improve the accuracy and reliability of revenue recognition. These practices promote transparency, accountability, and confidence in financial reporting for stakeholders.
Provide Ongoing Education and Training
Providing ongoing education and training is indeed a critical best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Awareness of Revenue Recognition Standards: Revenue recognition standards, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), are complex and subject to updates. Ongoing education and training ensure that finance and accounting teams stay informed about the latest standards, interpretations, and guidance related to revenue recognition. This awareness helps prevent misunderstandings and promotes accurate and consistent application of the standards.
- Understanding Organizational Policies and Procedures: Each organization may have its specific revenue recognition policies and procedures tailored to its business model and industry. Ongoing education and training ensure that employees understand these policies and procedures, including the criteria for revenue recognition, documentation requirements, and internal controls. This understanding helps maintain consistency and compliance across the organization.
- Knowledge of Industry-Specific Considerations: Different industries may have unique revenue recognition considerations and practices. Ongoing education and training provide an opportunity to educate employees on industry-specific revenue recognition challenges, practices, and emerging trends. This knowledge enables employees to apply the relevant guidance appropriately and address industry-specific complexities in revenue recognition.
- Skill Development and Technical Competence: Revenue recognition requires a combination of technical knowledge, analytical skills, and judgment. Ongoing education and training help develop and enhance these skills among finance and accounting professionals. Training programs can focus on topics such as contract review, identification of performance obligations, allocation of the transaction price, and revenue recognition over time. By investing in skill development, organizations can ensure their staff possesses the necessary expertise to accurately apply revenue recognition principles.
- Continuous Improvement and Knowledge Sharing: Ongoing education and training foster a culture of continuous improvement and knowledge sharing within the organization. Regular training sessions, workshops, or webinars provide a platform for employees to discuss challenges, share insights, and learn from each other's experiences. This collaborative environment promotes best practices and enhances the overall competency of the finance and accounting teams involved in revenue recognition.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness: Well-trained employees are more likely to understand the importance of compliance with revenue recognition standards and internal controls. Ongoing education and training create awareness of the implications of non-compliance and the potential impact on financial reporting. This knowledge helps ensure that employees adhere to established policies, follow proper procedures, and maintain audit readiness throughout the revenue recognition process.
- Documentation and Communication: Education and training initiatives should be well-documented, including training materials, manuals, and resources. Proper documentation supports consistency and provides a reference for employees to reinforce their knowledge and address questions or concerns. Additionally, effective communication channels should be established to disseminate updates, clarify policies, and address any queries related to revenue recognition.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should develop a comprehensive training program that covers both foundational revenue recognition concepts and updates on emerging issues.
Training sessions can be conducted through a variety of formats, such as in-person training, e-learning modules, workshops, or guest speaker sessions.
It is important to tailor the training to the specific roles and responsibilities of employees involved in revenue recognition.
By providing ongoing education and training, organizations can enhance the knowledge, skills, and competence of their employees in revenue recognition.
This best practice promotes the accurate application of accounting standards, and compliance with policies, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
Ultimately, it supports the organization in achieving reliable and transparent financial reporting.
Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes and Industry Guidance
Staying updated with regulatory changes and industry guidance is indeed a crucial best practice for revenue recognition. Here's why it is important and how it can be implemented effectively:
- Compliance with Evolving Standards: Revenue recognition standards and regulations, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), are subject to updates and revisions. Staying updated with these changes ensures compliance with the latest requirements and guidelines. It helps organizations avoid non-compliance issues, potential penalties, and reputational risks.
- Accurate and Consistent Application: Regulatory changes and industry guidance often provide clarifications and interpretations on revenue recognition principles. By staying updated, organizations can ensure accurate and consistent application of revenue recognition standards. It helps prevent misinterpretation or outdated practices that may result in errors or inconsistencies in financial reporting.
- Incorporating Industry-Specific Considerations: Different industries may have unique revenue recognition considerations and practices. Staying updated with industry-specific guidance allows organizations to incorporate relevant industry-specific considerations into their revenue recognition processes. This helps ensure that revenue recognition practices align with the specific requirements and dynamics of the industry, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of financial reporting.
- Proactive Response to Regulatory Changes: Being aware of regulatory changes in advance allows organizations to proactively assess the potential impact on their revenue recognition processes. By staying updated, organizations can evaluate the necessary adjustments to their policies, procedures, and internal controls to align with the new requirements. Proactive response helps ensure a smooth transition and timely compliance with updated regulations.
- Industry Benchmarking and Best Practices: Industry guidance often includes best practices and benchmarks for revenue recognition. Staying updated with industry guidance allows organizations to benchmark their revenue recognition practices against industry peers and adopt best practices. This helps drive continuous improvement, enhance the quality of financial reporting, and align with industry norms and expectations.
- Engaging with Professional Networks and Associations: Participating in professional networks and associations related to accounting and finance can provide valuable resources and updates on regulatory changes and industry guidance. Organizations can leverage these networks to access industry-specific insights, attend conferences or webinars, and engage in discussions with peers and experts. Active engagement in professional networks facilitates ongoing learning and staying updated with the latest developments.
- Internal Communication and Training: Establishing effective communication channels within the organization is essential to disseminate regulatory changes and industry guidance related to revenue recognition. This can include regular internal newsletters, email updates, or dedicated training sessions. By ensuring that relevant stakeholders, including finance, accounting, and legal teams, are aware of the changes, organizations can promote a consistent understanding and application of updated revenue recognition requirements.
To implement this best practice effectively, organizations should establish a process for monitoring regulatory changes and industry guidance. This can involve assigning responsibility to a dedicated team or individual to track updates, conduct research, and disseminate relevant information to the appropriate stakeholders.
Utilizing reputable sources, such as regulatory bodies, professional organizations, and industry publications, can help ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information gathered.
By staying updated with regulatory changes and industry guidance, organizations can maintain compliance, enhance the accuracy of revenue recognition, and align their practices with evolving standards and industry expectations.
This best practice supports transparent financial reporting, mitigates risks, and promotes sound decision-making for stakeholders.
FAQs related to Revenue Recognition in the Digital Age
- How do emerging technologies impact revenue recognition?
Emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and IoT improve the accuracy, efficiency, and transparency of revenue recognition by automating processes, enhancing data analysis, and enabling real-time tracking of revenue-related information.
- What are multi-element arrangements, and how do they affect revenue recognition?
Multi-element arrangements involve bundled products or services. Determining revenue allocation among different elements requires careful analysis, including fair value assessments and standalone selling price considerations.
- How do subscription-based models impact revenue recognition?
Subscription-based models often require revenue recognition to be spread over the subscription period rather than recognized upfront. This reflects the ongoing value delivered to customers throughout their subscriptions.
- What are some best practices for revenue recognition in the digital age?
Best practices include leveraging advanced technologies for automation and data analysis, collaborating between finance, operations, and technology teams, and adhering to industry guidelines and accounting standards.
- What are some examples of advanced technologies used in revenue recognition?
Examples include AI-powered analytics tools, blockchain-based smart contracts for transparent revenue tracking, and IoT devices for real-time data collection.
- How do businesses ensure compliance with accounting standards in revenue recognition?
Businesses ensure compliance by following industry guidelines and accounting standards, such as IFRS 15 and ASC 606, which provide specific rules and requirements for revenue recognition.
- How can emerging technologies help businesses improve revenue recognition accuracy?
Emerging technologies automate processes, reduce human error, and enable real-time data analysis, leading to more accurate revenue recognition and financial reporting.
- What challenges do businesses face in revenue recognition in the digital age?
Challenges include complex revenue models, determining the fair value of bundled products or services, tracking revenue from subscription-based models, and adapting to evolving accounting standards.
- What role does collaboration play in revenue recognition?
Collaboration between finance, operations, and technology teams is essential to ensure accurate revenue recognition, as it requires input from various stakeholders and expertise across different areas.
- How can businesses adapt their revenue recognition practices to accommodate emerging technologies?
Businesses can adapt by investing in technology infrastructure, training employees on new tools and processes, and continuously updating their revenue recognition practices to align with emerging technologies.
- What benefits do businesses gain from implementing best practices in revenue recognition?
Implementing best practices improves data accuracy, enhances efficiency, ensures compliance, enables timely financial reporting, and provides stakeholders with transparent and reliable revenue information.
- Are there any specific considerations for revenue recognition in e-commerce platforms?
Yes, e-commerce platforms often deal with digital goods, multi-element arrangements, and complex customer interactions. Revenue recognition must account for these factors, considering fair value and customer engagement.
- How can businesses utilize data analytics in revenue recognition?
Data analytics can help businesses identify revenue patterns, customer behavior, and trends. This data can be used to improve revenue recognition models, pricing strategies, and decision-making processes.
- Is it necessary for businesses to update their revenue recognition practices regularly?
Yes, it is crucial for businesses to stay updated on emerging technologies, industry guidelines, and accounting standards, and to continuously assess and adapt their revenue recognition practices to ensure accuracy and compliance in the dynamic digital age.
How can Deskera Help You with Revenue Recognition?
Deskera ERP is a cloud-based software platform that offers various solutions to assist businesses in managing their operations, including revenue recognition.

Here are some ways Deskera can help with revenue recognition:
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Deskera is designed to comply with accounting standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15. The software helps businesses adhere to the guidelines outlined in these standards, ensuring accurate revenue recognition and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Comprehensive Revenue Management: Deskera offers features to manage the entire revenue lifecycle, from sales orders and contracts to invoicing and revenue recognition. Businesses can track revenue generation, monitor contract performance, and ensure revenue is recognized appropriately based on the specific terms and conditions outlined in the contracts.
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics: Deskera provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities that enable businesses to gain insights into their revenue recognition processes. Users can generate customizable reports, analyze revenue trends, identify potential issues, and make data-driven decisions to optimize revenue recognition and improve financial performance.
- Audit Trail and Documentation: Deskera facilitates documentation and record-keeping related to revenue recognition. It maintains an audit trail of revenue recognition activities, contract changes, and supporting documentation, ensuring transparency and providing evidence for compliance purposes or audits.
- Collaboration and Workflow Management: Deskera enables collaboration among team members involved in revenue recognition. It provides workflow management features to streamline communication, track progress, and ensure timely completion of revenue recognition tasks.
Key Takeaways
Revenue recognition in the digital age refers to the process of accounting for and reporting revenue in the context of evolving business models and the adoption of emerging technologies.
Some of the key emerging technologies for revenue recognition in the digital age are:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies can automate data analysis, identify patterns, and detect anomalies in revenue-related data. These technologies can help in identifying revenue recognition issues, assessing contract terms, and providing predictive analytics for accurate revenue forecasting. They can also automate routine tasks, such as data entry and reconciliation, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA involves the use of software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks. In revenue recognition, RPA can streamline processes such as data extraction from contracts, validation of contract terms, calculation of revenue recognition schedules, and generation of financial reports. RPA can significantly reduce the time and effort required for manual tasks, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology provides a decentralized and transparent ledger that can be utilized for revenue recognition purposes. Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate revenue recognition based on predefined rules and conditions. These smart contracts can ensure accurate and tamper-proof recording of revenue transactions, enabling real-time visibility and auditability.
- Data Analytics and Visualization: Advanced data analytics and visualization tools can help analyze large volumes of revenue-related data to identify trends, patterns, and outliers. These insights can assist in revenue recognition decision-making, contract analysis, and revenue forecasting. Interactive visualizations can present complex revenue data in a user-friendly manner, facilitating better understanding and interpretation.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing platforms offer scalable and secure infrastructure for revenue recognition processes. Cloud-based solutions enable easy access, storage, and processing of revenue data from multiple sources. They also facilitate collaboration among teams involved in revenue recognition and provide the flexibility to adapt to changing business needs.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices and sensors generate vast amounts of data, which can be leveraged for revenue recognition. For example, in the case of usage-based pricing models, IoT data can provide real-time information about customer usage and consumption, enabling accurate revenue recognition based on actual usage patterns.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP technology can interpret and analyze unstructured textual data, such as contracts, invoices, and customer communications, for revenue recognition purposes. NLP algorithms can extract relevant information, identify contract terms, and assess performance obligations, contributing to accurate and efficient revenue recognition.
- Advanced Visualization and Reporting Tools: Advanced visualization and reporting tools help present revenue recognition data in a visually appealing and insightful manner. These tools enable stakeholders to understand revenue trends, performance metrics, and key insights at a glance, facilitating informed decision-making and effective communication of revenue-related information.
It's important to note that the adoption and implementation of these technologies should align with business needs, industry regulations, and the availability of relevant data.
Each organization should assess its specific requirements and evaluate the potential benefits and risks associated with these technologies before implementing them in revenue recognition processes.
Additionally, some of the best practices you can adopt for revenue recognition in the digital age are:
- Understand and Apply Relevant Accounting Standards: Familiarize yourself with the applicable accounting standards, such as ASC 606 (in the United States) or IFRS 15 (globally), and ensure compliance with their principles. Understand the five-step model for revenue recognition: identify the contract, identify performance obligations, determine the transaction price, allocate the transaction price to performance obligations, and recognize revenue when performance obligations are satisfied.
- Document Contracts and Key Terms: Maintain comprehensive documentation of contracts and key terms related to revenue-generating activities. Contracts should include clear descriptions of the products or services, pricing terms, payment terms, performance obligations, and any contingencies or variable considerations. Accurate and well-documented contracts provide the basis for proper revenue recognition.
- Identify and Separate Performance Obligations: Carefully analyze contracts to identify distinct performance obligations—promises to transfer goods or services to customers. Each performance obligation should be evaluated separately to determine the appropriate timing and amount of revenue recognition. Consider factors like separability, customer acceptance criteria, and interdependency among obligations.
- Determine Transaction Price and Variable Consideration: Evaluate the transaction price, which includes fixed and variable considerations. Variable considerations, such as discounts, rebates, refunds, or performance-based payments, may require estimation. Use the most likely amount or expected value approach to determine the transaction price, considering constraints and the likelihood of additional variable consideration.
- Allocate Transaction Price: Allocate the transaction price to each identified performance obligation based on their relative standalone selling prices. When standalone selling prices are not directly observable, estimation techniques like the adjusted market assessment approach, the expected cost plus a margin approach, or the residual approach can be used. Ensure the allocation is reasonable and consistent with fair value principles.
- Recognize Revenue Over Time or at a Point in Time: Determine whether revenue should be recognized over time or at a point in time based on the transfer of control criteria. Recognize revenue over time when control is transferred over time, and use appropriate methods like output methods (e.g., surveys, milestones) or input methods (e.g., costs incurred, efforts expended) to measure progress. Recognize revenue at a point in time when control transfers at a specific moment.
- Regularly Review and Update Revenue Recognition Policies: Establish and maintain clear revenue recognition policies that align with accounting standards and industry practices. Regularly review and update these policies to reflect changes in business models, contracts, and applicable regulations. Ensure that all stakeholders are aware of and adhere to these policies consistently.
- Perform Internal Controls and Independent Reviews: Implement robust internal controls to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and integrity of revenue recognition processes. Regularly review and test these controls to identify any weaknesses or deviations. Additionally, engage independent auditors or external experts to conduct periodic reviews or audits to validate compliance with revenue recognition standards and best practices.
- Provide Ongoing Education and Training: Offer training programs to employees involved in revenue recognition, including finance, sales, legal, and IT teams. Educate them on the relevant accounting standards, company policies, and best practices. Promote a culture of awareness and understanding of revenue recognition principles throughout the organization.
- Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes and Industry Guidance: Keep abreast of changes in accounting standards, regulatory requirements, and industry-specific guidance related to revenue recognition. Stay connected with professional bodies, attend conferences, and participate in industry forums to stay informed about emerging trends, challenges, and interpretations of revenue recognition principles.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can ensure accurate, consistent, and transparent revenue recognition, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and fostering trust in financial reporting.
Overall, Deskera ERP helps businesses streamline and automate their revenue recognition processes, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, providing accurate financial reporting, and improving overall efficiency and transparency.
By leveraging Deskera's revenue recognition capabilities, businesses can reduce manual effort, mitigate risks, and optimize revenue management for improved financial performance.
Related Articles