What if you could reduce manufacturing costs without compromising on product quality? The answer lies in mastering your BOM (Bill of Materials) cost analysis—a critical yet often overlooked step in achieving profitability and efficiency in manufacturing operations. Whether you're producing electronics, consumer goods, or industrial equipment, the real cost of your product starts long before it hits the production line.
Every item, screw, material, or process listed in a BOM contributes to your final cost—and if not properly analyzed, even minor inefficiencies can escalate into significant financial losses. That’s why manufacturers today are prioritizing BOM cost management as a strategic move rather than a simple bookkeeping task. With the increasing complexity of supply chains and volatile raw material prices, a real-time, data-driven approach to BOM costing is more important than ever.
This is where smart tools like Deskera MRP come into play. Deskera’s Material Requirements Planning (MRP) module helps manufacturers streamline their production planning, manage real-time inventory costs, and accurately forecast material needs. Its intuitive interface, automated BOM generation, and AI-powered assistant “David” enable businesses to detect inefficiencies, prevent overstocking, and gain full visibility into manufacturing costs—all in one platform.
In this blog, we’ll explore the key components of BOM cost analysis, common challenges faced by manufacturers, and proven strategies to reduce expenses without sacrificing performance. Whether you're a plant manager or a supply chain leader, this guide will help you make smarter cost decisions and build a more resilient manufacturing operation.
What is BOM Cost Analysis?
BOM cost analysis is the process of evaluating and calculating the total cost of all components, materials, sub-assemblies, labor, and overhead listed in a Bill of Materials (BOM) for a product. This analysis helps manufacturers understand how much it truly costs to produce an item—from raw materials to the finished product.
Key Elements Included in BOM Cost Analysis:
- Direct Material Costs: The cost of raw materials, parts, and components required for production.
- Labor Costs: Wages paid for the labor directly involved in assembling or manufacturing the product.
- Overhead Costs: Indirect costs such as equipment depreciation, utilities, and factory maintenance.
- Packaging and Logistics: Shipping materials, taxes, and delivery charges that contribute to the product's final cost.
By performing a BOM cost analysis, companies can:
- Identify cost drivers in the production process.
- Compare supplier pricing and sourcing options.
- Optimize production planning to reduce waste and overstocking.
- Forecast profits and set competitive pricing strategies.
In short, BOM cost analysis enables better decision-making and improved cost control throughout the product lifecycle.
Why BOM Cost Analysis Is Crucial for Modern Manufacturing
BOM cost analysis is not just an accounting task—it’s a strategic function that influences everything from production planning to profitability. Accurately analyzing the costs within your Bill of Materials helps you build a solid financial foundation for each product you manufacture.
Here’s how BOM cost analysis makes a measurable difference across the organization:
1. Budgeting and Financial Planning
Precise BOM cost analysis enables accurate budgeting by giving full visibility into how much each component and process costs. Without this, manufacturers risk underestimating material expenses or overcommitting financial resources.
When BOM data is clear and reliable, finance teams can forecast cash flow needs, allocate budgets more effectively, and avoid production halts due to funding gaps or resource shortages.
2. Improving Profit Margins
Your BOM directly affects your cost of goods sold (COGS)—and in turn, your profit margins. If your BOM cost is inaccurately low, you might price products below break-even points.
If it’s too high due to inefficiencies or outdated sourcing, you may lose out to competitors. BOM cost analysis empowers you to optimize each line item, seek cost-effective alternatives, and set pricing that ensures sustainable profits.
3. Smarter Supplier Negotiations
A detailed and well-maintained BOM allows procurement teams to approach negotiations with confidence. When you understand exactly how much you’re spending on each part—and know the market rates—you’re in a strong position to ask for discounts, bulk purchase terms, or switch to better vendors. Strategic sourcing decisions like these can drive down long-term costs significantly.
4. Enhancing Production Efficiency
By identifying the true cost of materials and processes, manufacturers can optimize procurement schedules and inventory levels. This reduces both over-purchasing (which leads to excess inventory and tied-up capital) and under-stocking (which causes production delays and missed delivery timelines). BOM cost analysis ensures smoother production cycles and leaner operations.
5. Strategic Cost Optimization
Analyzing BOM costs regularly helps manufacturers pinpoint areas for cost reduction—whether through alternative materials, design simplifications, or supplier changes. It’s a proactive way to improve product profitability without compromising quality. Over time, this leads to better pricing strategies and stronger competitiveness in the market.
6. Competitive Pricing and Market Strategy
Understanding your BOM cost helps set prices that are both profitable and competitive. It also allows you to adapt quickly to market fluctuations—such as raw material price hikes—by recalculating production costs and adjusting pricing accordingly. This agility is key to surviving and thriving in fast-changing industries.
7. Risk Mitigation and Business Resilience
A granular view of BOM costs reveals potential risks like cost volatility, supplier dependency, and component obsolescence. By identifying high-cost or high-risk components early, businesses can build contingency plans, negotiate long-term pricing, or qualify secondary vendors—minimizing the risk of disruptions and unexpected expenses.
8. Better Alignment with Business Objectives
Effective BOM management ensures that cost-saving measures align with broader business goals like sustainability, quality, and innovation. Instead of cutting corners, companies can achieve smarter savings—balancing cost efficiency with long-term strategic outcomes.
9. Driving Continuous Improvement
The best manufacturers use BOM cost analysis not as a one-time exercise but as part of a continuous improvement process. Regular reviews help identify inefficiencies, track supplier performance, and spot trends that may lead to further cost savings or design improvements.
In summary, BOM cost analysis is a critical tool for cost control, risk management, and strategic growth. It not only guides day-to-day operations but also shapes long-term success by enabling informed decision-making across engineering, procurement, and finance teams.
Key Factors That Influence BOM Cost
Accurately calculating the Bill of Materials (BOM) cost is vital for manufacturers aiming to maintain healthy profit margins, set competitive prices, and ensure efficient resource allocation.
BOM cost goes far beyond just listing components—it encapsulates a range of dynamic and interrelated factors, from material procurement to labor inputs and inventory management.
Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the critical elements that influence BOM cost and how each can impact your production economics.
1. Cost of Raw Materials and Base Manufacturing Inputs
This includes all primary materials directly used in creating the product—such as metals, plastics, textiles, or chemicals. These costs fluctuate due to global commodity prices, material quality, supplier contracts, and availability. A rise in raw material costs can quickly inflate overall BOM costs, especially in material-heavy products.
2. Pricing of Purchased and Outsourced Components
These are pre-manufactured or off-the-shelf components sourced from third-party vendors, such as microchips, motors, resistors, or specialized modules. Their cost depends on unit pricing, order quantities, supplier reliability, lead times, and technological obsolescence, all of which can influence BOM totals significantly.
3. Labor Costs Across All Manufacturing Stages
Labor costs include both direct labor (assembly line workers, machine operators) and indirect labor (quality inspectors, supervisors, engineers). Costs vary depending on workforce skill levels, regional wage rates, union requirements, and the complexity of tasks involved in manufacturing each unit.
4. Allocation of Fixed and Variable Overhead Expenses
Overhead includes non-material, non-labor costs like rent, electricity, insurance, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. These costs are typically allocated across all production units and must be tracked accurately to avoid underestimating true BOM cost.
5. Manufacturing Process Complexity and Production Efficiency
The chosen production methods can greatly affect cost. Automated, high-speed processes often reduce per-unit cost over time but require large capital investments. Manual or semi-automated processes may be cheaper initially but slower and more prone to errors, leading to waste or rework.
6. Logistics, Shipping, and Handling Expenditures
When components are sourced internationally or from multiple vendors, the BOM must include all logistics costs such as shipping fees, customs duties, warehouse storage, insurance, and internal handling. Delays or disruptions in the supply chain can also result in added expenses.
7. Currency Exchange Rate Volatility
If you source materials or components globally, fluctuating exchange rates can unpredictably increase your BOM cost. Even small changes in currency rates can have a significant impact on high-volume or high-value material purchases.
8. Inventory Carrying and Storage Costs
Inventory costs account for warehousing, inventory tracking, capital tied up in stock, and the risk of damage, obsolescence, or shrinkage. A just-in-time (JIT) inventory model can reduce these costs but requires strong supply chain coordination.
9. Supplier Lead Times, Reliability, and Contract Terms
Unpredictable lead times or supplier inconsistencies can force last-minute purchases or expedited shipping, which drive up costs. Long-term supplier relationships with favorable pricing and dependable deliveries can help keep BOM costs stable.
10. Regulatory Compliance and Quality Control Measures
Costs related to certifications, testing, product validation, and quality assurance also contribute to BOM. Defective components or non-compliant materials can result in rework, recalls, or fines—all of which inflate total production costs.
Common Challenges in BOM Cost Management
Managing the cost of a Bill of Materials (BOM) is more complex than simply tracking material prices. It involves overseeing a web of suppliers, labor resources, operational costs, and ever-changing market conditions. For manufacturers, even a slight miscalculation or oversight can result in reduced margins, delayed production, or supply chain disruptions.
Below are the most common challenges faced in BOM cost management and their implications on business operations.
1. Inaccurate or Incomplete BOM Data
A poorly defined BOM—missing part numbers, quantities, or supplier details—can lead to cost miscalculations, procurement errors, and production delays. Without accurate and up-to-date data, cost forecasting becomes unreliable and inventory planning suffers.
2. Volatility in Raw Material Prices
Material costs are influenced by global supply and demand, geopolitical factors, and seasonal fluctuations. Sudden spikes in raw material prices can significantly alter your total BOM cost, especially in industries heavily reliant on commodities like metals or plastics.
3. Inconsistent Supplier Pricing and Terms
Different vendors may offer varying prices, lead times, or payment terms for the same components. Without a consistent supplier management strategy, costs can spiral due to missed bulk discounts, rush orders, or last-minute sourcing from secondary vendors.
4. Currency Fluctuations in International Sourcing
Global sourcing exposes manufacturers to exchange rate risks. Fluctuations in currency can alter the landed cost of imported materials, making budget control difficult and impacting the overall BOM cost unpredictably.
5. Hidden Overhead and Indirect Costs
Many organizations fail to factor in indirect costs—like tooling, machine maintenance, utilities, or facility management—accurately into their BOM. These hidden costs can accumulate and skew the true cost of production if not allocated correctly.
6. Poor Change Management and Version Control
Product designs often evolve, but failure to properly track BOM revisions can lead to using outdated components or incorrect cost estimates. A lack of version control creates confusion across teams and inflates costs due to errors or rework.
7. Manual Processes and Lack of Automation
Relying on spreadsheets or disconnected systems increases the risk of human error, duplicate entries, and miscommunication between teams. Without automation, it's difficult to maintain real-time visibility into BOM cost changes and their impact on production.
8. Complex Product Configurations and Customizations
Highly customizable products or complex assemblies with many variations can make BOM cost management a logistical challenge. Each variation may require a different combination of parts, increasing the difficulty of tracking costs accurately.
9. Inventory Misalignment and Overstocking
Poor inventory management can result in overstocking high-cost items or running short on essential components, leading to emergency orders or production delays—both of which inflate BOM-related costs unnecessarily.
10. Lack of Integration Between Engineering, Procurement, and Finance
When engineering teams design products without input from procurement or finance, BOM decisions may overlook cost implications. Disconnected departments often lead to inefficiencies, incompatible sourcing strategies, and inflated production costs.
Strategies for Effective BOM Cost Analysis
Accurately analyzing the cost of your Bill of Materials (BOM) is essential for maintaining profitability, ensuring cost control, and making informed manufacturing decisions.
From understanding material and labor costs to leveraging digital platforms and real-time data, a strategic approach can transform BOM cost management into a competitive advantage.
Below are proven strategies and best practices to enhance your BOM cost analysis.
1. Digitize Your BOMs for Better Visibility and Control
Moving away from spreadsheets and adopting digital BOM management tools is the foundation for efficient cost analysis. Platforms like Deskera MRP or Part Analytics provide centralized, version-controlled BOMs that allow for easy updates, configurable alerts, and data-backed decision-making.
2. Gather and Maintain Accurate Data on All Components
Start by compiling a complete and up-to-date list of all components, including raw materials, assemblies, and subassemblies. Ensure that the unit cost and quantity for each part is accurate, reflecting current supplier quotes, volume discounts, or price breaks. Regular updates are essential as supplier pricing and sourcing options evolve.
3. Calculate Direct Material Costs with Precision
Multiply the unit cost of each component by its quantity to calculate direct material costs. Summing these gives you the core BOM cost baseline. Complex product designs or rare materials should be assessed carefully, as they often drive up raw material costs disproportionately.
4. Incorporate Labor Costs Based on Skill and Efficiency
Identify the labor hours required for each production step and apply appropriate hourly rates based on worker roles (e.g., skilled, semi-skilled). Consider workforce efficiency—quicker, well-trained staff can reduce overall production time and cost. This labor cost should then be integrated into the overall BOM calculation.
5. Allocate Overhead, Handling, and Indirect Costs
To get a full picture of the BOM cost, factor in indirect expenses such as utilities, equipment depreciation, facility maintenance, and quality control. Additionally, include logistics-related costs like shipping, customs duties, and warehousing—especially for imported components or globally distributed operations.
6. Factor in Currency Fluctuations and Inflation Projections
When sourcing internationally, apply exchange rate buffers to account for currency risks. It's also important to build inflationary trends into cost forecasts to ensure future pricing remains realistic and profitable over the product lifecycle.
7. Add a Profit Margin Strategically
Once the total production cost is calculated, add a realistic profit margin aligned with your business goals and market conditions. This ensures not only sustainable operations but also competitiveness in your pricing strategy.
8. Leverage Real-Time Market and Supplier Data
Use software that integrates real-time market data to stay updated on price trends, availability, and regulatory impacts. This allows you to proactively manage risks, compare supplier performance, and negotiate better deals with reliable vendors.
9. Involve Cross-Functional Teams in Cost Estimation
Collaborate closely with procurement, finance, and engineering during the BOM analysis stage. Engineering input ensures accurate material specifications, while procurement offers insight into supplier pricing and contractual terms—leading to more grounded and actionable cost estimates.
10. Perform BOM Cost Risk and Sensitivity Analysis
Identify high-cost, volatile, or long-lead-time components within the BOM. Perform “what-if” scenarios to understand the financial impact of price spikes, supplier changes, or volume fluctuations. This helps build cost resilience and prioritize strategic sourcing decisions.
11. Monitor Actual Costs vs. Forecasts and Iterate
Compare actual material and production costs from the shop floor with the BOM estimates. Use these insights to fine-tune your cost models, adjust forecasts, and improve accuracy over time. This closed-loop feedback system leads to better financial planning and cost accountability.
12. Identify and Act on Cost Reduction Opportunities
Analyze BOM structures to find opportunities for cost optimization—such as using alternate materials, consolidating parts, redesigning for manufacturability, or switching to lower-cost suppliers. These changes can significantly reduce your overall production expense without compromising quality.
13. Integrate BOM Data with ERP/MRP Systems
Link your BOM cost data directly to enterprise systems like Deskera ERP or MRP for seamless coordination between inventory, procurement, and production planning. This integration enables automated updates, real-time costing, and smoother decision-making across departments.
How to Overcome Common BOM Cost Calculation Challenges
Managing the cost of a Bill of Materials (BOM) is inherently complex—especially in today's global, fast-paced manufacturing environment.
Factors such as supplier disruptions, data inconsistencies, and price volatility can all distort cost projections and hurt profitability. However, with the right processes, tools, and foresight, these challenges can be effectively addressed.
Here’s how to overcome the most common BOM cost calculation hurdles:
1. Mitigating Raw Material Price Volatility
Challenge: Fluctuating prices of metals, plastics, and electronic components can disrupt budgeting and cost forecasts.
Solution:
- Negotiate long-term contracts with fixed pricing for frequently used materials.
- Maintain a multi-supplier sourcing strategy to increase bargaining power and price stability.
- Use cost buffering and predictive analytics to model inflation trends and material price spikes.
2. Reducing Supplier Delays and Associated Costs
Challenge: Delays in part delivery can result in increased labor downtime, expedited shipping fees, and missed deadlines.
Solution:
- Build relationships with high-performance suppliers and review their delivery metrics regularly.
- Qualify secondary/backup vendors for critical components to maintain production continuity.
- Use supplier scorecards and implement incentives/penalties for lead-time compliance.
3. Ensuring Accurate and Up-to-Date BOM Data
Challenge: Outdated or inconsistent BOM data leads to miscalculations, procurement errors, and inventory mismatches.
Solution:
- Centralize BOM data using cloud-based BOM management systems with version control.
- Integrate BOM data with ERP and MRP systems for seamless real-time updates across departments.
- Assign BOM ownership to specific roles or teams to enforce accountability for data accuracy.
4. Managing Complexity in Multi-Level BOMs
Challenge: Multi-tiered BOMs with many subassemblies increase the likelihood of missed cost roll-ups or oversight.
Solution:
- Use BOM software that supports multi-level hierarchies and automatic cost roll-ups.
- Visualize and audit BOM structures regularly to ensure accuracy at every level.
- Create modular BOM templates for complex assemblies to simplify cost tracking and updates.
5. Handling Frequent Design and Engineering Changes
Challenge: BOMs become outdated when product designs are updated but not reflected promptly in cost models.
Solution:
- Implement a formal engineering change order (ECO) process that triggers immediate BOM updates.
- Use cross-functional collaboration tools to keep engineering, procurement, and finance aligned.
- Set automated alerts for BOM changes, ensuring cost revisions are reflected in real-time.
6. Reducing Manual Errors Through Automation
Challenge: Manual entry and spreadsheet-based BOMs are error-prone and hard to scale.
Solution:
- Replace spreadsheets with specialized BOM software or integrated ERP/MRP platforms (e.g., Deskera MRP).
- Automate cost calculations, inventory tracking, and supplier data syncing.
- Use digital audit trails to trace changes and prevent unauthorized updates.
7. Addressing External Market and Financial Fluctuations
Challenge: Exchange rates, inflation, and global market shifts can unpredictably impact component costs.
Solution:
- Incorporate currency risk buffers and use hedging strategies for international transactions.
- Regularly benchmark prices using market intelligence tools.
- Forecast BOM costs with scenario modeling to understand the impact of different market conditions.
8. Enhancing Collaboration Across Departments
Challenge: Disconnected teams often work in silos, leading to misaligned data and duplicated efforts.
Solution:
- Establish collaborative workflows that involve engineering, procurement, and finance in BOM reviews.
- Conduct regular cross-functional BOM audits to catch discrepancies early.
- Use shared dashboards and alerts to notify all stakeholders of cost-impacting changes.
By addressing these challenges systematically, manufacturers can strengthen their BOM cost analysis process, reduce waste, improve profitability, and gain greater resilience in a volatile production landscape.
Significant Cost Reduction Strategies to Optimize Your BOM Costs
Bill of Materials (BOM) cost optimization isn't just about cutting costs—it's about identifying smart savings opportunities while maintaining the integrity and performance of the final product.
To remain competitive in today's volatile manufacturing landscape, businesses must employ proactive and strategic approaches.
Below are some of the most effective BOM cost reduction strategies:
1. Apply Value Engineering for Smarter Design Choices
What it means: Value engineering is the structured evaluation of BOM components and processes to find alternatives that reduce costs without compromising quality or functionality.
How to implement:
- Substitute expensive materials with more cost-effective, performance-equivalent options.
- Re-engineer non-essential features that inflate costs but add minimal customer value.
- Collaborate with R&D to ensure cost-effective design from the start.
2. Strengthen Supplier Collaboration
What it means: Engaging suppliers as strategic partners can unlock better pricing models and ensure more predictable costs.
How to implement:
- Negotiate volume discounts or long-term pricing contracts.
- Evaluate supplier performance regularly to identify better pricing, quality, or lead times.
- Explore dual sourcing to improve negotiation leverage and cost control.
3. Streamline Process Efficiency
What it means: Inefficiencies in manufacturing processes directly impact BOM costs through wasted materials, time, and labor.
How to implement:
- Adopt lean manufacturing principles to eliminate non-value-adding tasks.
- Integrate automation in repetitive or precision-critical areas to boost consistency and reduce manual errors.
- Use time-and-motion studies to find opportunities for labor optimization.
4. Perform Regular Cost Analysis and Forecasting
What it means: Continuously monitoring and analyzing BOM cost trends helps manufacturers adjust before small issues become costly problems.
How to implement:
- Track material cost trends, currency shifts, and market fluctuations.
- Use cost modeling tools to simulate various sourcing or design scenarios.
- Revisit BOM cost assumptions quarterly or when major market events occur.
5. Implement Design Standardization
What it means: Using common components across product lines simplifies sourcing and reduces overall costs.
How to implement:
- Create a preferred parts list shared across engineering and procurement.
- Limit customization unless it's critical to performance or customer satisfaction.
- Design with modular assemblies to reuse subcomponents across SKUs.
6. Use Technology-Driven Cost Optimization Tools
What it means: Digital tools can provide visibility into BOM costs, suggest optimization opportunities, and reduce human error.
How to implement:
- Deploy ERP and BOM management software (like Deskera MRP) for real-time cost tracking and integration.
- Use AI-based procurement tools to optimize supplier selection and material sourcing.
- Set up automated alerts for cost variances or supplier price changes.
7. Audit Inventory and Reduce Excess Stock
What it means: Overstocking ties up capital and increases storage costs, indirectly driving up BOM-related expenses.
How to implement:
- Align BOMs with just-in-time inventory practices.
- Review historical demand data to reduce over-purchasing.
- Use ABC analysis to prioritize high-cost or high-impact components.
8. Encourage Cross-Functional Cost Ownership
What it means: Getting input from engineering, procurement, and finance helps uncover hidden cost-saving opportunities.
How to implement:
- Host regular cross-functional reviews of top-cost components in the BOM.
- Develop shared KPIs for cost savings tied to design, sourcing, and operations.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement through team incentives.
By embedding these strategies into daily operations, manufacturers can significantly reduce their BOM costs without sacrificing performance, quality, or customer satisfaction. Continuous analysis, smart design decisions, and strategic supplier engagement form the foundation of long-term BOM cost optimization.
How Deskera MRP Helps Streamline and Optimize BOM Cost Management
Managing Bill of Materials (BOM) costs requires real-time insights, centralized control, and the ability to adapt quickly to changes in design, supply, or pricing. Deskera MRP offers a powerful, integrated platform that helps manufacturers overcome BOM cost calculation challenges and implement effective cost optimization strategies. Here’s how:
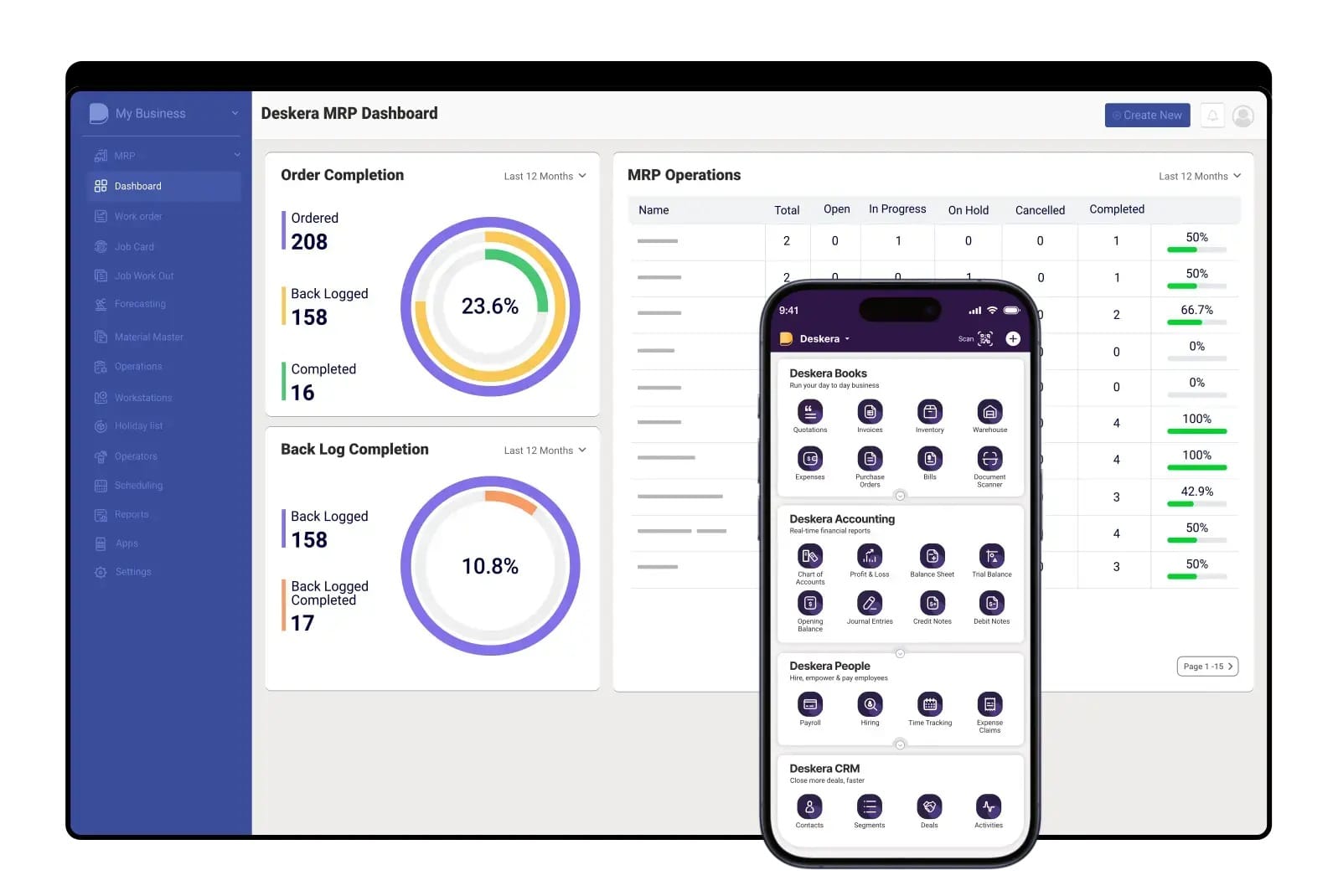
1. Centralized BOM Management with Real-Time Updates
Deskera MRP allows you to create and manage single- and multi-level BOMs with complete visibility. Any changes in design, components, or costs are automatically updated across all linked processes, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring accurate cost roll-ups.
2. Integrated Cost Tracking and Roll-Up Features
The system offers automated cost roll-ups, allowing you to track component costs across sub-assemblies and finished products. You can easily monitor total material, labor, and overhead costs—enabling informed pricing decisions and profit margin analysis.
3. Smart Procurement and Supplier Management
Deskera MRP helps optimize your sourcing by tracking supplier performance, costs, and delivery timelines. You can compare vendor quotations, negotiate better pricing, and set up automated reorder points to prevent stockouts and reduce urgent procurement costs.
4. Version Control for Engineering and Design Changes
When engineering or design changes occur, Deskera ensures BOM version control so your teams are always working with the most up-to-date specifications. This minimizes material mismatches, reduces rework, and keeps BOM cost calculations accurate.
5. Real-Time Inventory and Demand Forecasting
By syncing BOMs with live inventory and production data, Deskera helps avoid over-purchasing and excess stock. Its demand forecasting tools allow you to plan better for future needs, preventing last-minute purchases at inflated prices.
6. Lean Manufacturing and Workflow Automation
Deskera supports production routing, capacity planning, and job scheduling—enabling lean workflows. With fewer delays, manual errors, or production bottlenecks, you can achieve better cost efficiency across your manufacturing process.
7. Built-in Reporting and Cost Analysis Dashboards
Deskera provides detailed costing reports and dashboards that help identify trends, cost variances, and savings opportunities. You can drill down into material or production costs for specific BOMs and make data-driven adjustments quickly.
By automating key processes, improving visibility, and integrating cost control into every stage of production, Deskera MRP empowers manufacturers to manage BOM costs proactively, optimize profitability, and scale operations with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- A solid understanding of BOM structures, including direct and indirect costs, is the foundation for accurate cost analysis and efficient product costing in manufacturing.
- BOM analysis is critical for identifying cost drivers, improving profitability, and ensuring that product design, sourcing, and production align with financial goals.
- Material costs, supplier terms, production methods, and design complexity are key drivers of BOM expenses—regularly reviewing these elements helps in controlling costs and enhancing margins.
- Solutions like negotiating stable supplier contracts, using centralized BOM systems, and maintaining up-to-date data can help mitigate the risks of cost inaccuracies and supply chain disruptions.
- Implementing process automation, integrating BOM with ERP/MRP tools, and adopting proactive change management ensures more consistent, scalable, and error-free cost control.
- Leveraging value engineering, improving production efficiency, collaborating with suppliers, and conducting continuous cost analysis enable substantial BOM savings while maintaining quality.
- Deskera MRP centralizes BOM management, automates costing, and integrates real-time data from inventory and suppliers to help manufacturers make agile, cost-effective decisions.
Related Articles