Is your business unknowingly losing money despite steady sales? Revenue loss often hides behind everyday inefficiencies — from inaccurate inventory records and delayed invoicing to poor demand forecasting and manual errors. For many organizations, these leaks go unnoticed until they start impacting cash flow and profitability. In today’s competitive market, even small inefficiencies can create a ripple effect that erodes margins and hinders growth.
Statistics show that 42% of businesses experience some form of revenue leakage, with typical losses ranging from 1% to over 10% of annual revenue, depending on the cause and industry. These figures highlight a critical truth — preventing revenue loss isn’t just about boosting sales but about improving visibility, accuracy, and operational control across the organization. Without the right systems in place, businesses risk losing revenue through billing errors, missed renewals, inefficient processes, and mismanaged data.
This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come in. By integrating key business functions such as finance, sales, inventory, and production into a unified platform, ERP systems provide the transparency and automation needed to plug these revenue gaps. They help businesses monitor financial performance in real-time, detect inconsistencies early, and make informed decisions that safeguard profitability.
Modern solutions like Deskera ERP take this a step further by combining automation, AI-driven insights, and user-friendly dashboards to streamline every aspect of operations. With features for real-time accounting, inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and mobile accessibility, Deskera ERP empowers businesses to reduce errors, enhance decision-making, and maintain tighter control over revenue flow. In essence, it transforms how companies identify, prevent, and recover from potential revenue losses — ensuring sustainable growth in a dynamic business environment.
What Are Revenue Losses?
Revenue loss refers to the money your business should have earned but didn’t — the gap between your potential revenue and your actual revenue. It represents missed opportunities, inefficiencies, or errors that prevent income from reaching your accounts. While every business faces expenses as part of its operations, revenue loss is different because it reflects unrealized income rather than planned spending.
Revenue loss can occur for many reasons. Some are internal and controllable, such as poor pricing strategies, delayed invoicing, inaccurate billing, or slow follow-up on leads. Others are external and uncontrollable, including economic downturns, supply chain disruptions, or changing market conditions. Even small lapses — like inventory mismatches or data entry errors — can accumulate over time and have a significant impact on overall profitability.
Unlike direct costs, which are recorded and budgeted, revenue losses are often hidden and harder to detect. They quietly affect cash flow, reduce margins, and make it more difficult to forecast financial performance accurately. When left unchecked, consistent revenue leakage can compromise a company’s stability and long-term growth potential.
Understanding where and why revenue loss occurs is the first step toward preventing it. Once businesses can pinpoint the sources — whether operational inefficiencies, system gaps, or external pressures — they can take proactive measures to close those leaks. This is where modern ERP systems play a pivotal role, offering the visibility, automation, and analytics needed to track, analyze, and protect every stream of revenue.
Revenue Losses vs. Capital Losses
Revenue Losses vs. Expenses
Revenue Losses vs. Profit Margin
Common Causes of Revenue Loss in Businesses
Understanding the causes of revenue loss is essential for maintaining financial stability and long-term growth. Revenue loss can stem from both internal sources — factors within your business that you can control — and external sources, which are often outside your influence but still impact your bottom line. Identifying the specific cause helps you respond effectively and implement the right strategies to minimize losses.
Operational Inefficiencies
When business processes are slow, outdated, or poorly coordinated, opportunities slip away. Delays in production, missed sales handoffs, inefficient supply chain management, and manual errors can all lead to lost revenue. Even small inefficiencies across departments compound over time, reducing productivity and profit margins. Streamlining workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and using ERP systems can significantly reduce these losses.
Pricing Errors and Discounting Issues
Setting prices too low, misjudging market demand, or offering excessive discounts can eat into profits. Inaccurate margin calculations or inconsistent pricing strategies across sales channels often result in revenue leakage. Businesses should implement centralized pricing controls and use ERP tools to monitor profitability and prevent misaligned discounting practices.
Product or Service Quality Problems
Revenue loss often arises when products or services fail to meet customer expectations. Poor quality leads to higher return rates, warranty claims, and negative reviews — all of which damage reputation and reduce repeat business. Maintaining quality control standards and tracking customer feedback are crucial for minimizing such losses.
Billing and Contract Errors
Incorrect invoicing, missed renewal dates, and overlooked contract terms are common yet costly mistakes. In subscription-based models, even one missed renewal can translate into thousands in lost revenue. Automating billing and contract management through ERP systems helps ensure accuracy, timely renewals, and consistent cash flow.
Market or Economic Downturns
External factors such as recessions, fluctuating interest rates, or shifts in consumer demand can reduce overall revenue. While these conditions are beyond a business’s control, maintaining financial agility, diversifying offerings, and using real-time data forecasting can help cushion the impact during market downturns.
Fraud or Data Breaches
Unauthorized transactions, cyberattacks, and payment fraud can cause direct monetary loss and long-term reputational harm. Small, unnoticed fraudulent activities often accumulate into significant revenue erosion. Strengthening cybersecurity measures and regularly auditing financial systems are essential steps toward preventing such losses.
Customer Churn
Losing existing customers — whether due to poor service, competitive alternatives, or failed payments — is one of the most significant contributors to revenue loss. High churn not only affects current income but also eliminates future recurring revenue opportunities. Proactive engagement, loyalty programs, and strong customer support can help retain clients and stabilize revenue streams.
Regulatory or Compliance Issues
Noncompliance with legal or contractual requirements can lead to fines, penalties, or even suspension of business operations. For instance, failing to meet industry standards or contract terms may force companies to offer discounts or pay compensations. Implementing compliance tracking tools within ERP systems ensures adherence to regulations and minimizes financial risks.
Poor Customer Engagement
Weak customer relationships often translate to missed upsell opportunities, lower renewal rates, and reduced referrals. When customers don’t feel connected to your brand — due to slow follow-up, lack of communication, or poor onboarding — they’re more likely to disengage. Consistent communication, personalized experiences, and nurturing programs can significantly improve engagement and protect long-term revenue.
By identifying these internal and external factors early, businesses can take targeted actions to prevent financial leakage. Modern ERP systems like Deskera ERP play a key role here — offering automation, real-time monitoring, and data insights that help detect revenue risks before they escalate into major losses.
How to Calculate Revenue Loss
Calculating revenue loss is an essential step toward understanding where and how your business is losing money. The formula itself is simple — the challenge lies in accurately estimating what your expected revenue should have been based on realistic performance data, not assumptions.
The Basic Formula
Revenue Loss = Expected Revenue - Actual Revenue
This formula helps you identify the gap between the income you anticipated and what you actually earned. However, determining “expected revenue” requires careful consideration of factors like historical sales data, seasonality, customer behavior, and market trends.
Defining Expected Revenue
“Expected revenue” varies by business model:
- For subscription-based businesses (like SaaS): Expected revenue is typically your Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) assuming all customers renew and no potential sales are lost.
- For retail or eCommerce businesses: Expected revenue might come from projected sales based on historical demand, seasonal trends, or average foot traffic data.
- For B2B sales teams: Expected revenue may include both closed-won deals and forecasted opportunities from the sales pipeline.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a SaaS company scenario:
Starting MRR: $200,000
Lost revenue due to churned subscriptions: $15,000
New revenue from additional sales: $5,000
Expected Revenue = 200,000 + 5,000 = 205,000
Actual Revenue = 190,000
Revenue Loss = 205,000 - 190,000 = 15,000
So, the company’s revenue loss for the month is $15,000.
Accurately Tracking Revenue Loss
While this example is straightforward, a complete calculation involves combining billing data, CRM forecasts, and customer retention metrics to capture both realized and missed revenue opportunities.
To get a true picture, track the following:
- Churn rate: Percentage of customers lost over a period.
- Renewal rate: Percentage of customers who continue subscriptions.
- Pipeline conversion rate: Ratio of deals won vs. deals forecasted.
- Average deal size: Helps quantify the impact of missed deals.
- Lost deal count: Tracks potential opportunities that didn’t close.
Using ERP systems like Deskera ERP, which integrates financial, sales, and CRM data, helps automate this tracking. With real-time dashboards and AI-driven analytics, businesses can monitor fluctuations, detect early signs of revenue leakage, and adjust strategies before losses accumulate.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Using unrealistic targets that exaggerate revenue loss figures.
- Failing to differentiate one-time losses (like a canceled order) from recurring losses (like ongoing churn).
- Ignoring indirect losses, such as delayed deal closures or missed upsell opportunities.
By grounding your calculations in accurate data and integrating systems for transparency, you can move from merely identifying losses to actively preventing them.
The Business Impact of Revenue Loss
Revenue loss doesn’t just reduce your top-line income—it can destabilize your entire organization. Its effects cascade across financial, strategic, operational, and reputational dimensions, ultimately threatening long-term sustainability if not addressed promptly.
How ERP Systems Help Prevent Revenue Loss
Revenue loss can creep into a business in multiple ways—missed billings, manual errors, inefficient operations, delayed payments, or even poor inventory decisions.
ERP systems act as a safeguard against such leakages by integrating all core business functions—finance, operations, sales, inventory, and procurement—within a single, unified platform.
This real-time visibility and process automation help companies close performance gaps, strengthen controls, and keep every dollar accounted for.
1. Financial and Administrative Controls
ERPs play a vital role in establishing financial discipline and control across the organization.
- Prevent undercharging and missed billing: Automated invoicing ensures that all client work, hours, and project deliverables are billed accurately and on time. No revenue slips through the cracks.
- Improve financial visibility: Centralized financial dashboards offer complete transparency into budgets, transactions, and expenses—helping identify revenue leaks from fraud, non-compliance, or inaccurate reporting.
- Enforce credit and payment discipline: ERP systems streamline credit policy enforcement and dunning processes to ensure timely collections, reducing overdue payments and bad debt risk.
- Reduce manual errors: Automated payroll, expense recording, and order processing reduce costly human errors that lead to mispayments or unbilled transactions.
- Support audit readiness: With standardized processes and real-time data logs, ERP systems simplify internal audits and ensure full compliance with accounting standards and tax laws.
2. Operational Efficiency
ERP systems digitize and streamline everyday operations—plugging leakages caused by inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or resource wastage.
- Optimize inventory management: Real-time tracking prevents both overstocking and stockouts, ensuring that capital isn’t tied up unnecessarily and sales aren’t lost due to unavailable stock.
- Streamline procurement: Automated purchase requisitions and supplier tracking reduce unplanned purchases and improve negotiation leverage with vendors.
- Enhance production planning: Historical data and sales forecasts help align production with demand, minimizing waste and avoiding lost revenue from over- or under-production.
- Standardize workflows: Digitized SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) ensure consistency, improve coordination, and eliminate delays in approvals or process handovers.
- Avoid project and delivery delays: ERP-enabled scheduling tools prevent missed deadlines and help manage resources efficiently—ensuring customer satisfaction and repeat business.
3. Data and Decision-Making
Access to accurate, real-time data is crucial for preventing losses caused by poor decision-making.
- Provide real-time visibility: A single source of truth across departments enables leaders to detect potential leakages early—whether in billing, procurement, or customer payments.
- Enable data-driven decisions: ERP dashboards and reporting tools give management actionable insights into KPIs, sales performance, and expense trends—allowing quick course correction.
- Integrate systems across departments: By connecting finance, operations, and CRM data, ERPs eliminate data silos that often lead to errors, missed opportunities, or duplicate efforts.
- Support predictive analytics: Forecasting tools within ERP help anticipate demand shifts, budget shortfalls, or cost overruns—reducing the risk of unexpected losses.
- Enhance supply chain visibility: Integration with suppliers and logistics partners helps businesses manage disruptions and maintain revenue continuity.
4. Compliance and Risk Management
Revenue loss isn’t always due to operational inefficiency—non-compliance with legal or financial regulations can also lead to heavy penalties. ERP systems reduce these risks by automating compliance-related processes.
- Automated tax and reporting compliance: ERP ensures timely and accurate filing of tax returns and regulatory reports.
- Maintain audit trails: Every financial transaction is recorded and traceable, enabling quick response to audit or compliance queries.
- Enforce policy adherence: From credit approvals to procurement limits, ERP systems enforce pre-defined policies to minimize the risk of unauthorized spending or fraud.
- Mitigate financial risks: With better control over cash flow, credit, and asset management, ERP systems safeguard against liquidity crises or unplanned expenditures.
5. Integrated Data Management
Centralized data management ensures that all business functions operate from one consistent data source—preventing duplication, errors, and inconsistencies that could result in financial losses.
- Consolidate data from all departments: ERP systems unify accounting, inventory, HR, and sales data, ensuring consistency across reports.
- Identify leakage points quickly: Unified visibility helps detect issues such as unpaid invoices, lost purchase orders, or inventory discrepancies before they escalate.
- Improve interdepartmental coordination: Shared data fosters collaboration and faster decision-making, preventing miscommunication-based losses.
6. Performance Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Sustainable profitability depends on monitoring key metrics and improving continuously—something ERP systems enable with powerful analytics.
- Define and track KPIs: Businesses can set measurable performance indicators across finance, production, sales, and inventory.
- Benchmark performance: Regular comparison of KPIs against historical data helps pinpoint underperforming areas.
- Automated reporting: Detailed financial and operational reports help leaders act on insights rather than assumptions.
- Support continuous improvement: With regular performance reviews, ERP systems help organizations adopt corrective actions to boost efficiency and reduce waste.
7. Optimizing Inventory and Procurement Processes
Since inventory and procurement can make up to 60% of expenses for many manufacturers, ERP systems help optimize these high-cost areas.
- Demand planning and MRP: ERP tools use historical and real-time data to plan material requirements accurately, preventing both stockouts and overstocking.
- Aggregate purchase orders: Consolidating purchase requests from multiple departments improves supplier negotiations and bulk pricing.
- Track supplier performance: Monitoring lead times, pricing, and delivery reliability ensures value for every purchase.
- Reduce obsolescence and waste: Smart inventory tracking avoids losses from expired, damaged, or unsellable stock.
8. Strengthening Customer and Revenue Management
Customer satisfaction directly influences revenue. ERP systems ensure that customers receive accurate billing, timely orders, and reliable service.
- Integrate CRM and ERP data: This ensures seamless coordination between sales, service, and finance.
- Improve order accuracy: Automated order management minimizes cancellations and refunds.
- Track customer payments and renewals: ERP alerts teams to upcoming renewals or overdue invoices, reducing churn and missed revenue.
9. Digitizing and Streamlining Business Operations
By moving manual, disconnected workflows into a digital ecosystem, ERP systems increase visibility, reduce process lag, and cut unnecessary costs.
- Eliminate paper-based inefficiencies: Electronic records save time and reduce administrative overhead.
- Enable workflow automation: Tasks like purchase approvals, expense reporting, and payment processing become faster and error-free.
- Facilitate remote monitoring: Cloud ERP systems give leaders real-time oversight of financial and operational performance, ensuring continuity and control even across distributed teams.
10. Improving Financial Discipline and Liquidity
Financial discipline is the foundation of sustained revenue performance.
- Department-level budgeting: ERP systems let companies allocate and monitor budgets by department, preventing overspending.
- Enforce approval hierarchies: Built-in authorization workflows ensure spending aligns with policies.
- Enhance working capital management: Real-time cash flow tracking helps businesses maintain healthy liquidity and avoid shortfalls.
How Deskera ERP Helps Safeguard Business Revenue
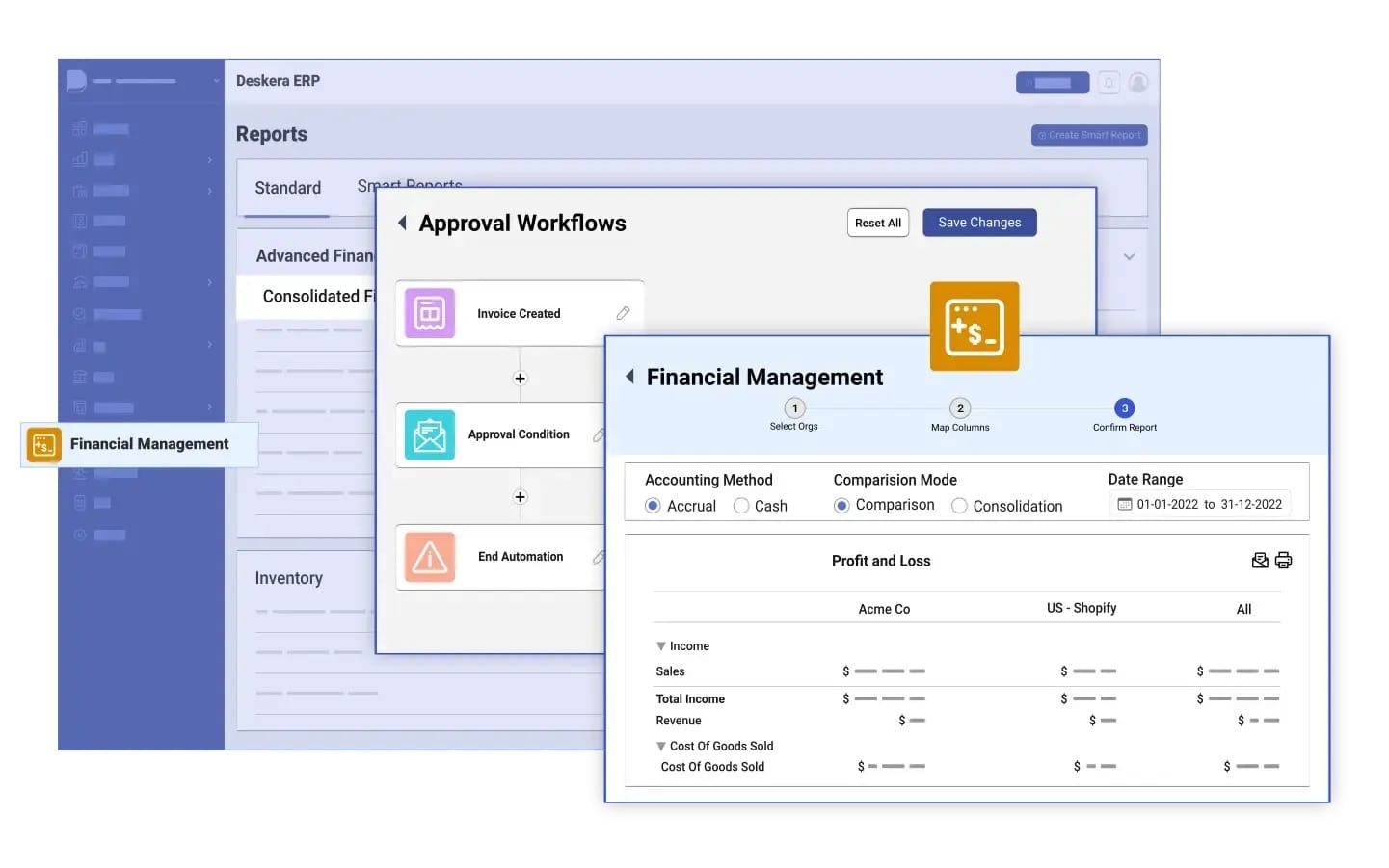
Deskera ERP offers an all-in-one platform designed to integrate finance, operations, sales, inventory, and reporting—helping businesses proactively detect and prevent revenue leakages. With automation, AI-powered insights, and real-time data visibility, it enables organizations to operate with precision, efficiency, and confidence. Here’s how Deskera ERP safeguards your revenue at every stage of business operations.
1. Real-Time Financial Visibility and Control
Deskera ERP ensures that every financial transaction is tracked, recorded, and reconciled in real time.
- Accurate invoicing and billing: Automate recurring invoices and link them directly with sales and delivery data to eliminate missed billing opportunities.
- Comprehensive dashboards: Deskera’s financial dashboards consolidate revenue, expenses, and cash flow for quick, informed decision-making.
2. Automated Accounting and Error-Free Operations
Manual data entry and disconnected systems often cause hidden financial leaks. Deskera ERP automates accounting workflows—ensuring accuracy and compliance.
- Automatic journal entries and reconciliations reduce manual errors and save time.
- AI Assistant David provides smart recommendations and anomaly alerts to catch irregularities before they turn into losses.
- Integrated compliance tracking ensures your books always adhere to accounting standards and tax requirements.
3. Optimized Inventory and Procurement Management
With Deskera ERP, businesses gain complete control over inventory levels, purchases, and supplier performance—all of which directly affect profitability.
- Real-time inventory tracking: Prevent overstocking, stockouts, and wastage through automated updates and alerts.
- Material Requirement Planning (MRP): Plan production efficiently using demand forecasting, ensuring the right materials are available at the right time.
- Smart procurement tools: Combine purchase orders across departments, negotiate better terms, and avoid unnecessary purchases that drain cash flow.
4. Improved Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Deskera ERP helps businesses digitize and streamline daily operations—reducing inefficiencies that cause delays and missed opportunities.
- Automated workflows for approvals, order management, and expense tracking save time and prevent bottlenecks.
- Mobile accessibility lets teams update data, track performance, or approve transactions anytime, anywhere.
- Integrated project and resource management ensures smoother coordination, fewer delays, and consistent delivery—all contributing to revenue stability.
5. Enhanced Decision-Making with Real-Time Insights
Deskera ERP consolidates all business data into one central system, creating a single source of truth.
- Customizable dashboards and reports give decision-makers up-to-date insights into KPIs, sales, and costs.
- Data-driven forecasting helps predict revenue trends, identify potential risks, and optimize resource allocation.
- Performance monitoring tools allow leaders to set benchmarks, compare outcomes, and act swiftly to correct inefficiencies.
6. Stronger Customer and Revenue Management
Happy, engaged customers mean stable revenue. Deskera ERP ensures you maintain that relationship seamlessly.
- Integrated CRM and ERP functions link customer orders, invoices, and payments in one place.
- Automated renewal and follow-up reminders help reduce churn and missed sales opportunities.
7. Reinforced Financial Discipline and Compliance
Deskera ERP enforces financial controls and policy compliance across all departments.
- Department-wise budgeting and cost allocation help track spending accurately.
- Approval hierarchies and audit trails ensure transparency and accountability.
- Regulatory compliance automation minimizes risk of fines or penalties, keeping operations legally sound and financially secure.
8. AI-Powered Efficiency with Deskera’s Assistant – David
Deskera’s AI assistant, David, takes business automation to the next level.
- Smart alerts and recommendations: Identify unusual spending or potential revenue leaks in real time.
- Predictive insights: Suggest optimal stock levels, expense thresholds, or invoice follow-ups.
- Conversational interface: Access data or generate reports through simple chat commands, saving time and reducing dependency on manual analysis.
9. Scalability for Growing Businesses
As businesses grow, manual processes become prone to inefficiencies and missed revenue opportunities. Deskera ERP scales effortlessly.
- Flexible modules adapt to your industry—whether manufacturing, retail, or services.
- Cloud-based architecture ensures secure access, backups, and automatic updates without added infrastructure costs.
- Seamless integrations with CRMs, payment gateways, and e-commerce platforms help maintain revenue accuracy as your ecosystem expands.
10. Predictable Revenue Through End-to-End Integration
Deskera ERP connects every part of your business—from lead to ledger—ensuring that no financial detail gets lost in translation.
- Unified data flow: Sales, production, inventory, and finance data move seamlessly, reducing errors and duplication.
- Real-time revenue tracking: Monitor where money is earned, delayed, or lost with full transparency.
- Consistent profitability: The result is a leaner, smarter, and more resilient business that keeps revenue steady even in changing market conditions.
In essence, Deskera ERP acts as your digital safeguard—plugging revenue leaks, boosting efficiency, and building financial resilience. With automation, AI-driven insights, and real-time visibility, it ensures that every opportunity to earn, save, and grow is captured—not lost.
Key Takeaways
- Revenue loss represents the gap between what a business should have earned and what it actually earns—caused by factors like inefficiencies, poor pricing, or market fluctuations. Identifying these gaps early is the first step toward prevention.
- Revenue losses impact day-to-day operations and profitability, while capital losses relate to asset devaluation or disposal. Distinguishing between them helps businesses apply the right corrective actions.
- Revenue loss measures missed income opportunities, whereas profit margin reflects how efficiently a business turns revenue into profit. Managing both ensures sustainable financial health.
- Revenue loss stems from both internal factors—like billing errors, inefficiencies, or customer churn—and external forces such as market downturns or regulatory changes. Recognizing the root cause enables targeted interventions.
- Use the formula: Revenue Loss = Expected Revenue – Actual Revenue
- Accurate calculation depends on realistic projections, historical data, and integrated financial visibility from CRM and billing systems.
- Unchecked revenue loss affects financial stability, disrupts operations, limits strategic growth, and weakens reputation—eventually threatening long-term sustainability.
- ERP systems integrate all business processes, automate workflows, and enhance real-time data visibility to prevent missed billing, inefficiencies, and compliance errors.
- ERP systems enforce financial discipline through automated billing, credit control, and error-free accounting—ensuring every dollar is tracked and recovered.
- By streamlining procurement, production, and inventory, ERPs eliminate process delays and resource wastage that often lead to hidden losses.
- With unified data and real-time analytics, ERP systems empower leaders to make timely, data-driven decisions that reduce risk and improve profitability.
- Automated compliance features in ERP systems help businesses stay audit-ready, avoid penalties, and maintain financial integrity.
- Centralized data eliminates duplication and inconsistencies, giving businesses a single source of truth for accurate revenue tracking.
- ERP dashboards enable KPI tracking and benchmarking, helping businesses identify inefficiencies and continuously enhance profitability.
- ERP-driven demand forecasting and smart procurement minimize overstocking, wastage, and unnecessary spending—preserving cash flow.
- Integrated CRM and ERP capabilities reduce churn, ensure timely renewals, and improve customer engagement—directly safeguarding recurring revenue.
- Automated workflows and cloud-based systems cut administrative overheads, reduce delays, and improve operational agility.
- ERP systems help maintain budget control, enforce approval hierarchies, and optimize working capital—ensuring consistent liquidity and stability.
- Deskera ERP combines automation, AI insights, and real-time financial control to plug revenue leaks, optimize processes, and enhance profitability across every department.
- Deskera’s AI assistant, David, proactively detects anomalies, recommends actions, and delivers predictive insights—helping businesses prevent revenue loss before it happens.
- Through end-to-end process integration and scalable cloud infrastructure, Deskera ERP empowers businesses to maintain predictable revenue growth even in dynamic market conditions.
Related Articles