In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing industry, the ability to adapt and stay ahead of the curve is paramount for success. With technological advancements, shifting customer demands, and increasing global competition, manufacturers face unprecedented challenges in production planning. However, with the right strategies in place, they can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and efficiency.
According to a recent survey, 78% of manufacturing companies consider changing customer demands as the most significant factor impacting their production planning processes.
Furthermore, 62% of respondents stated that technological advancements have greatly influenced their manufacturing operations. These statistics clearly highlight the need for manufacturers to embrace new strategies to navigate the changing landscape.
Successful production planning requires a holistic approach that considers various aspects of the manufacturing process, including forecasting, agility, technology adoption, supply chain collaboration, continuous improvement, and human capital development. By implementing these production planning strategies effectively, manufacturers can optimize their operations, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge.

We will discuss the importance of accurate forecasting and demand planning, the benefits of implementing agile production systems, the role of technology in enhancing production planning, the significance of supply chain collaboration and integration, the value of continuous improvement and optimization, and the importance of developing a skilled workforce.
Join us as we unravel the key strategies that will empower manufacturing companies to thrive amidst the changing manufacturing landscape and achieve efficient and effective production planning.
- Significance of Production Planning in Manufacturing
- Challenges and Changes in the Manufacturing Landscape
- Strategies for Successful Production Planning in a Changing Manufacturing Landscape
- Understanding the Changing Manufacturing Landscape
- Effective Forecasting and Demand Planning
- Implementing Agile Production Systems
- Embracing Technology for Enhanced Production Planning
- Supply Chain Collaboration and Integration
- Continuous Improvement and Optimization
- Human Capital Development and Training
- Conclusion
- How can Manufacturers stay competitive in the evolving industry?
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Significance Of Production Planning In Manufacturing
Production planning plays a crucial role in the manufacturing industry as it encompasses the strategic and operational processes necessary to optimize production activities.
Here are some key reasons why production planning is significant:
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Effective production planning ensures optimal utilization of resources such as materials, equipment, and labor. By carefully scheduling and coordinating production activities, manufacturers can minimize waste, reduce downtime, and maximize productivity, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved profitability.
- Meeting Customer Demand: Production planning enables manufacturers to align their production capabilities with customer demand. By accurately forecasting demand, manufacturers can ensure that the right products are available in the right quantities at the right time. This helps in avoiding stockouts, minimizing lead times, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Cost Control: Production planning allows manufacturers to control costs by streamlining production processes and identifying areas for efficiency improvement. By optimizing production schedules, reducing setup times, and minimizing inventory levels, manufacturers can lower production costs, increase operational efficiency, and maintain competitive pricing.
- Inventory Management: Effective production planning helps in managing inventory levels and minimizing holding costs. By synchronizing production with demand, manufacturers can avoid overstocking or understocking situations, leading to optimized inventory levels, reduced carrying costs, and improved cash flow.
- Quality Control: Production planning plays a crucial role in maintaining product quality. By establishing quality control measures and integrating them into production processes, manufacturers can ensure consistency, reliability, and adherence to quality standards. This helps in minimizing defects, reducing rework, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: In a dynamic manufacturing landscape, production planning enables manufacturers to adapt to changes quickly. By incorporating flexibility into production schedules, manufacturers can respond to unexpected events, such as supply chain disruptions or fluctuating customer demand, with minimal disruption to operations.
In summary, production planning is significant in manufacturing as it optimizes resource utilization, meets customer demand, controls costs, manages inventory, ensures quality, and provides the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances.
By implementing effective production planning strategies, manufacturers can enhance operational efficiency, profitability, and competitiveness in the industry.
Challenges And Changes In The Manufacturing Landscape
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing significant changes and facing various challenges. These factors impact how manufacturers operate and necessitate adaptation and strategic planning. Let's explore some of the key challenges and changes in the manufacturing landscape:
- Technological Advancements: Rapid advancements in technology, such as automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence, are transforming the manufacturing industry. While these technologies offer opportunities for increased efficiency and productivity, they also require manufacturers to invest in new equipment, retrain employees, and adapt their processes to leverage the benefits effectively.
- Globalization and Supply Chain Complexity: Globalization has opened up new markets and expanded opportunities for manufacturers. However, it has also increased supply chain complexity. Manufacturers now face challenges in managing global suppliers, dealing with trade regulations and tariffs, and mitigating risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
- Evolving Customer Demands: Customer expectations and preferences are continually evolving, driven by factors like changing demographics, technological advancements, and sustainability concerns. Manufacturers must stay attuned to these shifting demands and be agile in adapting their products, processes, and supply chains to meet customer expectations.
- Sustainability and Environmental Considerations: Increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility is reshaping the manufacturing landscape. Manufacturers are under pressure to reduce their environmental footprint, adopt sustainable practices, and meet regulatory requirements. This necessitates investing in eco-friendly technologies, implementing energy-efficient processes, and adopting circular economy principles.
- Workforce Skills Gap: The manufacturing industry is facing a skills gap, with a shortage of qualified workers who possess the necessary technical skills and knowledge. Rapid technological advancements require a highly skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining complex machinery and leveraging new technologies.
- Changing Regulations and Compliance: Manufacturers must navigate a complex web of regulations and compliance standards, both at the local and global levels. Compliance with quality standards, safety regulations, data protection laws, and industry-specific regulations adds complexity to manufacturing operations and requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation.
- Market Volatility and Uncertainty: Economic volatility, market fluctuations, and geopolitical factors contribute to uncertainty in the manufacturing landscape. Manufacturers must be prepared to adjust production levels, manage inventory, and adapt their strategies in response to changing market conditions.
Adapting to these challenges and changes requires manufacturers to embrace innovation, invest in technology, foster a culture of continuous improvement, enhance supply chain visibility and resilience, and prioritize workforce development.
By proactively addressing these challenges, manufacturers can position themselves for success in the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape.
Strategies For Successful Production Planning In A Changing Manufacturing Landscape
In today's rapidly changing manufacturing landscape, successful production planning is essential for manufacturers to stay competitive and achieve operational excellence. Here are key strategies to navigate the challenges and embrace opportunities in this dynamic environment:
- Embrace Advanced Technologies: Incorporate cutting-edge technologies like automation, robotics, Internet of Things (IoT), and data analytics into production planning processes. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient utilization of resources, resulting in improved productivity, reduced costs, and enhanced quality.
- Agile Production Systems: Implement agile production systems such as lean manufacturing and Just-in-Time (JIT) principles. These systems promote flexibility, waste reduction, and efficient use of resources. By adopting these methodologies, manufacturers can quickly respond to changing customer demands, reduce lead times, and optimize production flow.
- Demand Forecasting and Collaboration: Accurate demand forecasting is critical for effective production planning. Collaborate closely with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams to gather market insights, customer feedback, and sales data. This collaboration helps in aligning production plans with demand fluctuations, minimizing stockouts, and avoiding overproduction.
- Supply Chain Integration: Foster strong partnerships and integrate supply chain processes. Collaborate closely with suppliers, distributors, and logistics providers to streamline material flows, reduce lead times, and enhance supply chain visibility. Integration enables better coordination, mitigates risks, and improves overall production planning effectiveness.
- Continuous Improvement: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and lean thinking. Encourage employees to identify bottlenecks, suggest process improvements, and implement problem-solving methodologies like Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM). Regularly evaluate and optimize production processes to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leverage data analytics and advanced planning tools to make informed decisions. Utilize historical data, real-time information, and predictive analytics to optimize production schedules, inventory levels, and resource allocation. Data-driven insights enable proactive decision-making and enhance production planning accuracy.
- Workforce Development: Invest in employee training and skill development programs. Equip your workforce with the necessary technical skills, cross-functional knowledge, and adaptability to thrive in a changing manufacturing landscape. Encourage continuous learning and empower employees to contribute ideas for process improvement.
- Risk Management and Business Continuity Planning: Identify potential risks and develop robust contingency plans. Anticipate supply chain disruptions, natural disasters, or market volatility, and establish backup strategies to ensure business continuity. Regularly review and update risk management plans to mitigate potential disruptions to production planning.
By adopting these strategies, manufacturers can optimize production planning, enhance operational efficiency, meet customer demands effectively, and adapt to the changing manufacturing landscape. Embrace innovation, leverage technology, collaborate with stakeholders, and prioritize continuous improvement to stay competitive in this dynamic industry.
Understanding The Changing Manufacturing Landscape
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving customer demands, globalization, and sustainability concerns. To thrive in this dynamic landscape, manufacturers must develop a deep understanding of the changes and challenges they face. By embracing this understanding, they can proactively adapt their strategies and operations to stay competitive and achieve success.
In this section, we will explore the key factors shaping the changing manufacturing landscape. We will delve into the impact of technological advancements, such as automation and artificial intelligence, and their implications for production processes. Additionally, we will examine the evolving expectations and preferences of customers, and how manufacturers must respond to meet their changing demands.
Furthermore, we will discuss the implications of globalization on supply chain management, including the challenges of navigating global markets, managing complex supplier networks, and mitigating risks associated with international trade. We will also explore the increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations, and how manufacturers can integrate eco-friendly practices into their operations.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these transformative forces, manufacturers can position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities and address the challenges that come with change. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of the changing manufacturing landscape and uncover strategies for success in this dynamic industry.
Factors driving change in the manufacturing industry
The manufacturing industry is undergoing significant changes driven by several key factors. These factors are reshaping how manufacturers operate and compelling them to adapt to stay competitive. Let's explore some of the primary drivers of change in the manufacturing industry:
- Technological Advancements: Rapid advancements in technology, such as automation, robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), are revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape. These technologies improve efficiency, enhance productivity, enable real-time data collection and analysis, and facilitate seamless connectivity across various stages of the production process.
- Globalization and Market Expansion: Globalization has opened up new markets and opportunities for manufacturers. Increased connectivity and reduced trade barriers have enabled manufacturers to access global supply chains, reach international customers, and expand their operations worldwide. However, globalization also presents challenges related to managing global supply chains, navigating diverse regulatory environments, and addressing geopolitical risks.
- Evolving Customer Demands: Customers' expectations and preferences are continually evolving. They seek personalized products, shorter lead times, enhanced customization options, and sustainable and ethically produced goods. Manufacturers must stay attuned to these changing demands and be agile in adapting their processes, technologies, and business models to meet customer expectations.
- Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: Growing awareness of environmental sustainability has influenced the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers are under pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, adopt eco-friendly practices, and embrace circular economy principles. This includes using renewable energy sources, minimizing waste and emissions, and optimizing resource consumption throughout the production lifecycle.
- Data Analytics and Connectivity: The rise of big data and analytics is transforming the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers are leveraging data to gain actionable insights, optimize production processes, and make data-driven decisions. Connectivity between machines, systems, and stakeholders enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and supply chain visibility, leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
- Skills and Workforce Transformation: Technological advancements and changing industry requirements demand a skilled and adaptable workforce. Manufacturers need employees with a blend of technical expertise, digital literacy, problem-solving capabilities, and adaptability to work in an increasingly automated and connected environment. Upskilling and reskilling programs are crucial for nurturing a workforce that can leverage new technologies and drive innovation.
Understanding these driving factors is essential for manufacturers to navigate the evolving landscape successfully. By embracing technology, adapting to globalization, aligning with customer demands, prioritizing sustainability, leveraging data analytics, and investing in workforce development, manufacturers can position themselves for success in the changing manufacturing industry.
Highlight the impact of these changes on production planning
The changes in the manufacturing industry have a significant impact on production planning. Let's explore how each factor influences production planning strategies:
- Technological Advancements: The adoption of advanced technologies, such as automation, robotics, and AI, transforms production planning. It enables real-time monitoring of machines and processes, predictive maintenance, and optimization of production schedules. Manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved resource allocation through integration of technology into production planning.
- Globalization and Market Expansion: Globalization introduces complexities to production planning due to extended supply chains, diverse regulatory environments, and varying customer demands in different regions. Manufacturers need to account for lead times, transportation logistics, and inventory management across multiple locations. Global market expansion also requires adapting production plans to cater to specific market demands and preferences.
- Evolving Customer Demands: Changing customer expectations necessitate flexibility in production planning. Manufacturers must align their plans with customized product variations, shorter lead times, and increased product personalization. Agile production planning processes are crucial to meet the dynamic demands of customers and provide a competitive edge.
- Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: Environmental considerations impact production planning as manufacturers strive to reduce their environmental footprint. Planning must incorporate sustainable practices, such as optimizing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and implementing eco-friendly materials. This involves evaluating the environmental impact of each production step and incorporating sustainability goals into the planning process.
- Data Analytics and Connectivity: The availability of data and connectivity influences production planning through data-driven decision-making. Real-time data on machine performance, inventory levels, and customer demands can optimize production schedules, inventory management, and resource allocation. Connectivity allows seamless integration of suppliers and customers into the planning process, enhancing collaboration and responsiveness.
- Skills and Workforce Transformation: The changing manufacturing landscape demands a skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining advanced technologies. Production planning must consider workforce training and development initiatives to ensure employees possess the necessary skills for efficient utilization of technology. Workforce planning becomes crucial to address the skills gap and maintain a competent workforce in the face of technological advancements.
In summary, the changes in the manufacturing industry necessitate a shift in production planning strategies. Manufacturers need to embrace technology, adapt to global markets, align with evolving customer demands, integrate sustainability practices, leverage data analytics, and invest in workforce development.
By incorporating these factors into production planning, manufacturers can optimize operations, enhance efficiency, meet customer expectations, and stay competitive in the evolving manufacturing landscape.
Emphasize the need for adaptability and flexibility in response to the evolving manufacturing landscape
In the face of the evolving manufacturing landscape, adaptability and flexibility have become paramount for manufacturers. The rapid pace of technological advancements, changing customer demands, and global market dynamics require a nimble and responsive approach to remain competitive. Here's why adaptability and flexibility are essential in this context:
- Meeting Changing Customer Demands: Customer preferences are evolving at an unprecedented pace. Manufacturers must be adaptable to quickly adjust their production plans and processes to cater to customized products, shorter lead times, and shifting market trends. Flexibility in production planning enables manufacturers to align with changing customer demands and deliver products that meet or exceed expectations.
- Embracing Technological Advancements: Technology continues to transform the manufacturing landscape. Manufacturers must embrace new technologies, such as automation, AI, and IoT, to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Adaptability is crucial to integrate these technologies into production planning, enabling manufacturers to leverage their benefits and stay ahead of the competition.
- Managing Global Market Dynamics: Globalization has expanded opportunities for manufacturers but also brings complexities. Adapting to diverse regulatory environments, varying customer preferences in different markets, and fluctuations in supply chain dynamics requires flexibility. Manufacturers must be able to adjust their production plans, distribution channels, and sourcing strategies to effectively navigate the global market and seize opportunities.
- Dealing with Uncertainty and Disruptions: The manufacturing industry is susceptible to various uncertainties, such as supply chain disruptions, market volatility, and unforeseen events. Being adaptable allows manufacturers to respond swiftly to disruptions, adjust production plans, and identify alternative sourcing options. Flexibility in production planning enables agile responses to unexpected challenges, ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of disruptions.
- Driving Continuous Improvement: Adaptability and flexibility foster a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. By embracing change, manufacturers can identify opportunities for process optimization, cost reduction, and innovation. Flexibility in production planning allows for experimentation, testing new approaches, and implementing process enhancements, leading to increased efficiency and competitiveness.
- Seizing Emerging Opportunities: The evolving manufacturing landscape presents new opportunities for growth and expansion. Manufacturers need to be adaptable to identify and capitalize on these opportunities. Flexibility in production planning enables manufacturers to pivot their strategies, develop new product lines, enter new markets, or forge strategic partnerships to leverage emerging trends and unlock business potential.
By emphasizing adaptability and flexibility in production planning, manufacturers can proactively respond to the ever-changing manufacturing landscape. This approach allows them to stay agile, align with customer expectations, embrace technological advancements, navigate global market dynamics, and seize opportunities for growth.
In a world of constant transformation, adaptability and flexibility are key differentiators that drive success in the manufacturing industry.
Effective Forecasting and Demand Planning
In the dynamic and rapidly changing manufacturing landscape, accurate forecasting and demand planning have become crucial for manufacturers to optimize their production processes, inventory management, and overall supply chain operations. Understanding customer demands, predicting market trends, and aligning production capabilities with expected demand are vital for achieving operational efficiency and maintaining a competitive edge.
In this section, we will delve into the realm of effective forecasting and demand planning strategies. We will explore the importance of accurate demand forecasting and how it enables manufacturers to anticipate customer needs, optimize inventory levels, and reduce costs. Additionally, we will discuss the various methods and tools available for forecasting, including statistical models, data analytics, and market research.
Furthermore, we will highlight the significance of demand planning in synchronizing production schedules, procurement activities, and logistics operations. We will discuss the role of collaborative planning, sales and operations planning (S&OP), and demand-driven supply chains in aligning production capabilities with anticipated demand. Effective demand planning ensures the right products are produced at the right time, in the right quantities, and delivered to the right locations.
By focusing on effective forecasting and demand planning, manufacturers can mitigate risks associated with inaccurate forecasts, reduce stockouts or excess inventory, enhance customer satisfaction, and optimize resource utilization. Join us as we explore the strategies, methodologies, and best practices for achieving effective forecasting and demand planning in the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape.
Significance of accurate forecasting in production planning
Accurate forecasting plays a crucial role in production planning and is a key driver of operational success in the manufacturing industry. Here are some significant reasons why accurate forecasting is essential:
- Optimal Resource Allocation: Accurate forecasting helps manufacturers allocate their resources effectively. By predicting future demand, manufacturers can plan their production schedules, raw material procurement, and workforce utilization accordingly. This enables them to avoid overproduction or underproduction scenarios, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing waste.
- Inventory Management: Forecasting accuracy directly impacts inventory management. With accurate demand forecasts, manufacturers can maintain optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand without incurring excessive carrying costs. By aligning production output with anticipated demand, manufacturers can reduce inventory holding costs, minimize stockouts, and avoid obsolete inventory.
- Cost Reduction: Accurate forecasting helps manufacturers identify cost-saving opportunities. By understanding demand patterns and market trends, manufacturers can optimize their production processes, negotiate better pricing with suppliers, and streamline their supply chain operations. This leads to cost efficiencies and improved profitability.
- Customer Satisfaction: Meeting customer demand and delivering products on time are critical for customer satisfaction. Accurate forecasting enables manufacturers to anticipate customer needs and plan production accordingly. This helps in fulfilling orders promptly, minimizing delivery delays, and enhancing customer satisfaction levels. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat customers and advocates for the brand.
- Production Efficiency: Accurate forecasting contributes to production efficiency by eliminating bottlenecks and reducing idle time. Manufacturers can plan their production schedules based on anticipated demand, ensuring optimal machine utilization and minimizing downtime. This leads to improved production efficiency, reduced lead times, and increased overall operational productivity.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Accurate forecasting provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making. Manufacturers can assess market trends, identify growth opportunities, and make informed decisions about capacity expansion, product diversification, or market entry. Reliable forecasts empower manufacturers to stay ahead of the competition and adapt their strategies to changing market dynamics.
In summary, accurate forecasting is of utmost significance in production planning. It enables manufacturers to optimize resource allocation, manage inventory effectively, reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, improve production efficiency, and make informed strategic decisions.
By leveraging reliable forecasting techniques, manufacturers can navigate the challenges of a dynamic manufacturing landscape and achieve operational excellence.
Methods and tools for demand forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of production planning, enabling manufacturers to anticipate customer needs and align their operations accordingly. Here are some commonly used methods and tools for demand forecasting:
- Historical Data Analysis: One of the fundamental approaches to demand forecasting is analyzing historical sales data. By examining past trends, seasonality, and patterns, manufacturers can make informed predictions about future demand. Statistical techniques like moving averages, exponential smoothing, and trend analysis can help identify patterns and forecast future demand based on historical data.
- Market Research and Surveys: Conducting market research and customer surveys can provide valuable insights into consumer preferences, purchasing behavior, and upcoming trends. This qualitative approach helps manufacturers understand customer expectations, new product demands, and changes in market dynamics. Market research firms, focus groups, and online surveys are commonly employed tools in this process.
- Collaborative Planning: Collaborative planning involves collaborating with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders in the supply chain to gather information and improve demand forecasting accuracy. By sharing sales data, market insights, and demand forecasts, manufacturers can gain a holistic view of the market and align production plans with customer requirements.
- Time Series Analysis: Time series analysis uses historical data to forecast future demand based on patterns, seasonality, and trends. Techniques such as autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), seasonal decomposition of time series (STL), and Box-Jenkins models are commonly used for time series analysis. These methods consider historical data points and project future demand based on mathematical algorithms.
- Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning: With the advent of advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can leverage predictive analytics tools to improve demand forecasting accuracy. These tools can analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and generate forecasts based on complex algorithms. Machine learning models can learn from historical data and adapt to changing market dynamics, enabling more accurate predictions.
- Demand Planning Software: Specialized demand planning software, often integrated with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, provides advanced forecasting capabilities. These tools use a combination of statistical algorithms, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to generate accurate demand forecasts. They can also incorporate real-time data, market insights, and external factors like economic indicators or weather conditions to enhance forecasting accuracy.
- Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP): S&OP is a collaborative process that aligns sales forecasts, production plans, inventory management, and financial goals. It involves cross-functional coordination and integration of demand, supply, and financial plans. S&OP enables manufacturers to optimize production capacity, manage inventory levels, and synchronize activities across the supply chain.
By employing these methods and utilizing advanced tools, manufacturers can enhance their demand forecasting capabilities, improve production planning accuracy, optimize inventory management, and respond effectively to changing market dynamics.
A combination of historical data analysis, market research, collaboration, advanced analytics, and specialized software empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions and optimize their operations for success in a dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Importance of collaborating with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams for demand planning
Collaboration among sales, marketing, and supply chain teams is of paramount importance for effective demand planning in manufacturing. Here are some key reasons highlighting the significance of such collaboration:
- Accurate Demand Insights: Sales and marketing teams are at the forefront of interacting with customers and understanding their needs. By collaborating with these teams, supply chain professionals can gain valuable insights into customer preferences, market trends, and upcoming product demands. This information plays a critical role in accurately forecasting demand and aligning production plans accordingly.
- Enhanced Forecast Accuracy: Collaborating with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams allows for the integration of multiple perspectives and expertise. Sales teams can provide input based on their market interactions and customer feedback, while marketing teams can contribute insights on promotional activities and campaign impact. By incorporating these inputs into the demand planning process, manufacturers can achieve higher forecast accuracy and reduce the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
- Alignment of Objectives: Effective demand planning requires the alignment of objectives across different functions within an organization. Collaborating with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams helps establish a shared understanding of business goals and objectives. This alignment ensures that demand plans are developed in accordance with sales targets, marketing strategies, and supply chain capabilities, resulting in cohesive and synchronized operations.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Collaboration facilitates better resource utilization across the organization. When sales, marketing, and supply chain teams work together, they can collectively assess demand patterns, production capabilities, and inventory levels. This enables more efficient resource allocation, ensuring that production capacities, raw material procurement, and logistics operations are optimized to meet anticipated demand. Efficient resource utilization leads to cost savings, improved operational efficiency, and better customer service.
- Proactive Issue Resolution: Collaboration fosters proactive issue identification and resolution. By working closely with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams, potential bottlenecks, supply constraints, or market fluctuations can be identified in advance. This allows for proactive planning and corrective measures to mitigate risks and maintain smooth operations. Early collaboration enables cross-functional teams to address challenges collectively, resulting in more effective and timely solutions.
- Agility in Response to Change: In today's dynamic manufacturing landscape, the ability to respond quickly to changing market conditions is crucial. Collaborating with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams ensures that organizations are agile and responsive to market shifts, customer demands, or unforeseen disruptions. The collective expertise of these teams enables manufacturers to adapt production plans, adjust inventory levels, and optimize supply chain operations in real-time.
In summary, collaborating with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams is vital for successful demand planning in manufacturing. It enables accurate demand insights, enhances forecast accuracy, aligns objectives, optimizes resource utilization, facilitates proactive issue resolution, and fosters agility in response to change.
By leveraging the collective knowledge and expertise of these teams, manufacturers can achieve effective demand planning, streamline operations, and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape.
Implementing Agile Production Systems
In today's rapidly changing manufacturing landscape, companies are increasingly recognizing the need for agile production systems to stay competitive and meet evolving customer demands. Agile production systems enable manufacturers to adapt quickly to market shifts, optimize operations, and improve overall efficiency.
This section will explore the implementation of agile production systems and highlight their benefits for manufacturers. From embracing lean principles to leveraging advanced technologies, we will delve into strategies and best practices that empower organizations to foster flexibility, responsiveness, and continuous improvement in their production processes.
By embracing agility, manufacturers can enhance their ability to navigate uncertainties, capitalize on opportunities, and drive success in the dynamic manufacturing industry.
Definition of agile production systems and their benefits
Agile production systems refer to manufacturing processes and systems designed to quickly adapt and respond to changing market conditions, customer demands, and internal factors. These systems emphasize flexibility, speed, and responsiveness, enabling manufacturers to efficiently produce a variety of products in smaller batches while maintaining high-quality standards. Agile production systems typically involve the adoption of lean principles, the use of advanced technologies, and the implementation of cross-functional collaboration.
Benefits of Agile Production Systems:
Increased Flexibility: Agile production systems enable manufacturers to respond rapidly to changes in customer demand, market trends, and product variations. By embracing flexibility in production processes, manufacturers can easily introduce new product lines, modify existing products, and adjust production volumes to meet shifting market needs.
Faster Time to Market: Agile production systems reduce lead times and accelerate the time to market for new products. The ability to quickly adapt and reconfigure production processes allows manufacturers to respond swiftly to market opportunities, reducing the time between product conceptualization and launch.
Improved Responsiveness: Agile production systems enhance responsiveness to customer needs and market fluctuations. Manufacturers can quickly adjust production schedules, prioritize urgent orders, and align their operations with customer requirements. This responsiveness leads to higher customer satisfaction, improved customer retention, and increased market competitiveness.
Cost Efficiency: Agile production systems promote cost efficiency by minimizing waste, optimizing resource utilization, and reducing inventory levels. By adopting lean principles, such as just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing and waste reduction techniques, manufacturers can eliminate unnecessary production steps, reduce excess inventory, and lower overall operational costs.
Enhanced Quality Control: Agile production systems emphasize continuous improvement and quality control throughout the production process. By implementing rigorous quality management practices, manufacturers can identify and address defects or issues promptly, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Agile production systems encourage collaboration and communication among different departments and teams within the organization. This cross-functional collaboration enables better coordination, knowledge sharing, and the efficient utilization of resources, leading to improved production efficiency and overall operational effectiveness.
Innovation and Adaptability: Agile production systems foster a culture of innovation and adaptability within manufacturing organizations. By embracing new technologies, exploring process improvements, and encouraging employee creativity, manufacturers can stay ahead of market trends, identify opportunities for innovation, and continuously adapt their production systems to remain competitive.
In summary, agile production systems offer numerous benefits to manufacturers, including increased flexibility, faster time to market, improved responsiveness, cost efficiency, enhanced quality control, cross-functional collaboration, and a focus on innovation.
By implementing these systems, manufacturers can navigate the challenges of the changing manufacturing landscape, seize opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth in a dynamic and competitive market environment.
Lean manufacturing principles and their role in agility
Lean manufacturing principles play a crucial role in enabling agility within production systems. These principles, rooted in the Toyota Production System, aim to eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and create value for customers. Here are some key lean manufacturing principles and their role in promoting agility:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Production: JIT production focuses on producing and delivering products at the precise time they are needed, minimizing inventory and reducing lead times. By implementing JIT, manufacturers can quickly respond to changes in customer demand, reduce storage costs, and improve overall production efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Kaizen emphasizes the philosophy of continuous improvement, encouraging employees at all levels to identify and address inefficiencies in the production process. Through ongoing small-scale improvements, manufacturers can optimize workflows, eliminate bottlenecks, and enhance agility by adapting processes to changing requirements.
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): Value stream mapping is a visual representation of the entire production process, from raw material acquisition to product delivery. This tool helps identify non-value-added activities and bottlenecks, enabling manufacturers to streamline processes, eliminate waste, and improve the flow of materials and information.
- Standardized Work: Standardized work establishes consistent processes, procedures, and work instructions for each task within the production system. By setting clear standards, manufacturers can ensure efficient operations, minimize errors, and provide a foundation for continuous improvement and agility.
- Pull Production System: The pull production system focuses on producing items based on actual customer demand, rather than pushing products through the production process based on forecasts. This principle enables manufacturers to adjust production levels based on real-time demand signals, avoiding overproduction and reducing inventory holding costs.
- Visual Management: Visual management uses visual cues, such as color coding, signage, and charts, to enhance communication, improve workflow, and facilitate problem-solving. By making information readily accessible and visible, manufacturers can enhance transparency, promote collaboration, and enable quick decision-making, contributing to overall agility.
- Employee Empowerment: Lean manufacturing principles emphasize the importance of empowering employees and encouraging their involvement in process improvement initiatives. By fostering a culture of employee engagement and ownership, manufacturers can tap into the collective knowledge and creativity of their workforce, driving continuous improvement and adaptability.
These lean manufacturing principles collectively contribute to the agility of production systems by reducing waste, increasing efficiency, promoting employee engagement, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
By embracing these principles, manufacturers can enhance their ability to respond to changing market demands, optimize operations, and stay competitive in the dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Strategies for implementing agile production systems
Strategies for implementing agile production systems involve various methodologies and approaches that enable manufacturers to enhance their agility. Here are three prominent strategies commonly used:
Kanban
Kanban is a visual workflow management system that helps manufacturers optimize production processes, manage inventory levels, and improve overall efficiency. It involves using visual cards or digital systems to signal the need for replenishing materials or initiating production.
Kanban enables just-in-time inventory management, reduces waste, and facilitates smooth production flow. By implementing Kanban, manufacturers can respond quickly to changes in demand, minimize inventory holding costs, and improve production lead times.
Just-in-Time (JIT)
Just-in-Time (JIT) is a production strategy that aims to produce and deliver products precisely when they are needed, eliminating excess inventory and waste. JIT focuses on minimizing inventory holding costs, reducing lead times, and maintaining production flexibility.
By implementing JIT, manufacturers can improve production efficiency, reduce the risk of obsolete inventory, and enhance responsiveness to customer demand. JIT requires effective coordination and collaboration with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of materials and components.
Quick Response Manufacturing (QRM)
Quick Response Manufacturing (QRM) is a production strategy designed to reduce lead times and improve responsiveness by streamlining internal processes and decision-making. QRM emphasizes the concept of time as a competitive advantage. It involves creating dedicated cells or cells within cells (QRCs) that are self-contained and focus on specific products or customer groups.
QRM promotes cross-functional collaboration, simplifies decision-making, and allows for quick adjustments to production schedules based on changing customer requirements. By implementing QRM, manufacturers can achieve shorter lead times, faster response to market changes, and improved customer satisfaction.
These strategies, including Kanban, JIT, and QRM, provide manufacturers with effective approaches to implement agile production systems. By adopting these methodologies, manufacturers can enhance their ability to respond to changing customer demands, optimize resource utilization, reduce waste, and improve overall operational efficiency.
It is important for manufacturers to carefully assess their specific production requirements and choose the most suitable strategy or combination of strategies to achieve their agility goals.
Embracing Technology for Enhanced Production Planning
In the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape, technology plays a pivotal role in driving innovation, optimizing processes, and enabling agility. This section explores the significance of embracing technology for enhanced production planning.
From advanced planning and scheduling (APS) systems to the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), we delve into the transformative capabilities of technology in streamlining production operations, improving efficiency, and fostering proactive decision-making.
By harnessing the power of digital solutions, manufacturers can overcome challenges, adapt to changing market dynamics, and achieve higher levels of productivity and competitiveness. Join us as we explore the cutting-edge technologies that are revolutionizing production planning and discover the benefits they offer in navigating the complexities of today's manufacturing environment.
Role of technology in modern production planning
Technology plays a crucial role in modern production planning, offering advanced tools and systems that enable manufacturers to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and drive competitiveness. Here are key roles that technology plays in modern production planning:
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Systems: APS systems leverage sophisticated algorithms and data analysis to generate optimized production plans, considering factors such as demand forecasts, inventory levels, resource availability, and production constraints. These systems enable manufacturers to create realistic production schedules, reduce lead times, and improve resource utilization.
Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT connects machines, devices, and sensors in the manufacturing environment, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis. By integrating IoT devices into production planning, manufacturers gain access to valuable insights, such as equipment performance, maintenance needs, and supply chain visibility. This enables proactive decision-making, predictive maintenance, and improved production efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies have the ability to analyze large volumes of data and identify patterns, trends, and correlations. In production planning, AI can help optimize production processes, forecast demand more accurately, identify potential bottlenecks, and automate repetitive tasks. Machine learning algorithms can continuously learn from data, improving decision-making and enabling adaptive production planning.
Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems, allowing manufacturers to simulate and analyze production processes before implementation. By creating digital representations of production lines, manufacturers can optimize layouts, test different scenarios, and identify potential issues, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing provides a scalable and flexible platform for storing and accessing production data, facilitating collaboration and data sharing across departments and locations. Manufacturers can leverage cloud-based production planning systems to centralize information, enable real-time collaboration, and ensure data integrity and security.
Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation technologies streamline production processes, reduce manual labor, and enhance productivity. From robotic arms on assembly lines to automated material handling systems, these technologies enable faster and more accurate production, freeing up human resources for more complex tasks.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: Data analytics and business intelligence tools help manufacturers make data-driven decisions by providing insights into key performance indicators, production trends, and customer preferences. By analyzing data, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, optimize production workflows, and make strategic decisions to enhance overall performance.
In summary, technology plays a transformative role in modern production planning, enabling manufacturers to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and adapt to the demands of the changing manufacturing landscape.
By harnessing the power of advanced planning and scheduling systems, IoT, AI, digital twins, cloud computing, robotics, and data analytics, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of productivity, agility, and competitiveness in today's complex manufacturing environment.
Exploring technologies such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) systems
This section will help us analyze some of the latest and cuting-edge technologies that assist in production.
Exploring Technologies for Enhanced Production Planning:
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES):
MES is a comprehensive software solution that bridges the gap between planning and execution on the shop floor. It provides real-time visibility into production processes, capturing data on machine performance, labor utilization, and material usage. MES enables manufacturers to monitor production activities, track quality metrics, and ensure compliance with standards and regulations.
By integrating MES with production planning, manufacturers can streamline operations, enhance traceability, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):
ERP systems serve as a central hub for managing various aspects of a manufacturing enterprise, including finance, inventory, procurement, and production. In the context of production planning, ERP systems provide a unified platform to coordinate resources, track orders, and manage material requirements.
By integrating production planning with ERP, manufacturers can align production schedules with resource availability, optimize inventory levels, and improve coordination between different departments.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Systems:
APS systems leverage advanced algorithms and optimization techniques to generate accurate production plans, considering various constraints and objectives.
These systems incorporate factors such as demand forecasts, production capacity, material availability, and lead times to create optimized schedules. APS systems enable manufacturers to simulate different scenarios, perform "what-if" analysis, and make informed decisions to maximize efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Internet of Things (IoT) in Production Planning:
The IoT enables the connectivity of machines, sensors, and devices within the manufacturing environment, facilitating data collection and analysis. By integrating IoT devices into production planning, manufacturers can access real-time data on equipment performance, energy consumption, and production metrics. This data can be used to monitor production processes, identify bottlenecks, optimize maintenance schedules, and make data-driven decisions to improve production efficiency.
Digital Twin Technology:
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing manufacturers to simulate and optimize production processes. By creating a digital twin of a production line, manufacturers can analyze and test different scenarios, optimize layouts, and identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Digital twins enable manufacturers to make data-driven decisions, reduce risks, and optimize production planning for better performance.
By embracing technologies such as MES, ERP, APS systems, IoT, and digital twins, manufacturers can enhance production planning, optimize resource utilization, improve efficiency, and respond quickly to market changes. These technologies enable better visibility, data-driven decision-making, and automation, ultimately leading to improved productivity and competitiveness in the modern manufacturing landscape.
Benefits and considerations when adopting technology for production planning
This section will explore the benefits and considerations when adopting technology for production planning.
Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Technology streamlines production planning processes, automates tasks, and improves overall efficiency. It enables real-time data analysis, accurate forecasting, and optimized scheduling, leading to reduced lead times, minimized waste, and enhanced productivity.
- Improved Accuracy: Technology-driven systems provide accurate data analysis and forecasting, reducing errors and improving the accuracy of production planning. This helps in meeting customer demands, optimizing inventory levels, and avoiding costly overstock or stockouts.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Technology facilitates collaboration among different teams involved in production planning, such as sales, marketing, supply chain, and production. Shared platforms and real-time data accessibility enable better communication, coordination, and alignment of goals, resulting in improved decision-making and overall operational efficiency.
- Better Decision-Making: Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities provided by technology enable manufacturers to make informed decisions based on real-time data insights. With accurate and timely information, manufacturers can adjust production plans, allocate resources effectively, and respond quickly to changing market dynamics.
- Increased Flexibility and Agility: Technology enables manufacturers to adapt to changing customer demands, market conditions, and production constraints more effectively. With real-time visibility into production processes, manufacturers can make proactive adjustments, optimize production schedules, and maintain a high level of agility in a dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Considerations:
- Implementation and Integration: Adopting new technologies for production planning requires careful planning, implementation, and integration with existing systems. Manufacturers should consider the cost, resources, and potential disruptions during the adoption phase.
- Data Security and Privacy: As technology involves collecting, storing, and analyzing data, manufacturers must prioritize data security and privacy. Robust cybersecurity measures, data encryption, and compliance with relevant regulations are essential to safeguard sensitive information.
- Training and Skill Development: Embracing technology often requires employees to acquire new skills and knowledge. Providing adequate training and support is crucial to ensure smooth adoption and maximize the benefits of technology in production planning.
- Scalability and Upgrades: Manufacturers should consider the scalability of the chosen technology solution and its ability to accommodate future growth. Additionally, regular upgrades and system maintenance may be necessary to keep up with evolving industry standards and technological advancements.
- Cultural Change and Resistance: Introducing new technologies may require a cultural shift within the organization. Employees may need to adapt to new processes, embrace change, and overcome resistance to fully leverage the benefits of technology in production planning.
By carefully considering the benefits and considerations, manufacturers can adopt technology for production planning in a strategic and effective manner. With proper planning, implementation, and support, technology-driven production planning can enhance efficiency, accuracy, collaboration, decision-making, and overall operational performance in the manufacturing industry.
Supply Chain Collaboration and Integration
In today's complex and interconnected manufacturing landscape, effective supply chain collaboration and integration have become critical for successful production planning. Collaborating closely with suppliers, distributors, and other key partners allows manufacturers to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and respond quickly to market demands.
This section explores the significance of supply chain collaboration and integration in production planning and highlights the benefits it brings to manufacturers. By establishing strong partnerships and integrating supply chain processes, manufacturers can enhance visibility, optimize inventory management, reduce lead times, and ultimately achieve a competitive advantage in the dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Importance of collaboration with suppliers and partners in the supply chain
In today's globalized and interconnected business environment, collaboration with suppliers and partners in the supply chain has become increasingly important for manufacturers. The success of production planning relies heavily on effective communication, coordination, and cooperation throughout the entire supply chain.
Here are key reasons why collaboration with suppliers and partners is crucial:
Enhanced Visibility and Transparency: Collaborating with suppliers and partners provides manufacturers with better visibility into the entire supply chain. Sharing information on inventory levels, production schedules, and demand forecasts enables all stakeholders to make more informed decisions, identify potential bottlenecks, and proactively address issues. This increased transparency leads to improved coordination, reduced lead times, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Optimal Inventory Management: Collaboration helps in aligning inventory levels with demand fluctuations. By sharing real-time data and forecasts, manufacturers can work closely with suppliers to optimize inventory levels and prevent stockouts or excess inventory. This leads to improved cash flow, reduced carrying costs, and minimized waste throughout the supply chain.
Improved Quality and Responsiveness: Collaboration fosters closer relationships between manufacturers and suppliers, enabling a deeper understanding of quality requirements and specifications. Suppliers can provide valuable input on materials, components, and processes, leading to improved product quality. Additionally, effective collaboration allows for faster response times to changes in customer demand, enabling manufacturers to meet evolving market needs promptly.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency: Collaborative efforts with suppliers and partners can lead to cost savings and operational efficiencies. By sharing best practices, exploring joint improvement initiatives, and conducting joint value engineering, manufacturers can identify areas of waste, streamline processes, and drive down costs. This collaboration also facilitates the identification of alternative suppliers, fostering healthy competition and reducing dependence on single sources.
Innovation and Continuous Improvement: Collaborating with suppliers and partners encourages the exchange of ideas, knowledge, and expertise. This creates an environment of innovation and continuous improvement throughout the supply chain. Suppliers can contribute insights on emerging technologies, market trends, and industry best practices, enabling manufacturers to stay competitive and drive innovation in their production planning strategies.
In conclusion, collaboration with suppliers and partners is vital for effective production planning in the modern manufacturing landscape. By fostering strong relationships, sharing information, and working together towards common goals, manufacturers can achieve greater visibility, optimize inventory management, improve quality and responsiveness, reduce costs, and foster innovation.
A collaborative supply chain approach ultimately enhances the overall competitiveness and success of manufacturers in today's dynamic business environment.
Strategies for fostering collaboration and integrating supply chain processes
Strategies for Fostering Collaboration and Integrating Supply Chain Processes:
- Clear Communication Channels: Establish clear and open lines of communication with suppliers and partners. Regularly share information, forecasts, and performance metrics to ensure all stakeholders are on the same page. Utilize communication tools such as collaborative platforms, email, and video conferencing to facilitate effective communication.
- Shared Goals and Objectives: Align goals and objectives with suppliers and partners to create a shared vision. Develop mutually beneficial relationships that prioritize long-term collaboration and success. Encourage open discussions and joint problem-solving to foster a collaborative mindset across the supply chain.
- Collaborative Planning and Forecasting: Engage suppliers and partners in the planning and forecasting process. Seek their input and insights to improve accuracy and alignment with market demands. Collaborative planning tools and software can facilitate real-time data sharing, collaborative demand forecasting, and joint decision-making.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Implement effective supplier relationship management practices. Establish performance metrics, conduct regular performance reviews, and provide constructive feedback to build stronger relationships. Recognize and reward suppliers for their contributions to encourage ongoing collaboration.
- Information Sharing and Technology Integration: Utilize technology solutions to facilitate seamless information sharing and integration. Implement supply chain management systems and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software to streamline processes and enable real-time data visibility. Explore the use of cloud-based platforms for secure and accessible data sharing among all supply chain partners.
- Joint Improvement Initiatives: Collaborate with suppliers and partners on continuous improvement initiatives. Encourage idea sharing, process optimization, and cost reduction efforts. Conduct joint workshops, value engineering sessions, and cross-functional team meetings to identify areas of improvement and drive innovation.
- Supplier Development Programs: Invest in supplier development programs to enhance capabilities and foster long-term partnerships. Provide training, resources, and support to help suppliers improve their performance and meet quality and delivery requirements. Encourage knowledge sharing and facilitate collaboration in areas such as product development and supply chain optimization.
- Performance Measurement and Feedback: Establish clear performance metrics and regularly monitor and evaluate supplier performance. Provide timely and constructive feedback to address any issues or gaps. Collaboratively identify improvement opportunities and work together to implement corrective actions.
- Risk Management and Contingency Planning: Collaborate with suppliers to identify potential risks and develop contingency plans. Assess supplier capabilities, vulnerabilities, and capacity for resilience. Implement risk mitigation strategies and develop alternative sourcing options to ensure continuity of supply.
- Continuous Evaluation and Adaptation: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of collaboration efforts and supply chain integration. Seek feedback from suppliers and partners and make adjustments as needed. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement, innovation, and adaptation to meet evolving market demands.
By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can foster collaboration and effectively integrate supply chain processes. Collaboration across the supply chain leads to improved visibility, optimized inventory management, enhanced quality and responsiveness, cost reductions, and innovation.
Embracing a collaborative approach ultimately strengthens the overall supply chain and contributes to the success of production planning in the changing manufacturing landscape.
Benefits of integrated supply chain systems in improving production planning effectiveness
Let’s take a look at the benefits of integrated supply chain systems in improving production planning effectiveness.
- Enhanced Visibility: Integrated supply chain systems provide real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, including inventory levels, production status, and demand forecasts. This visibility allows for better decision-making, proactive identification of bottlenecks, and improved coordination among all stakeholders.
- Streamlined Communication: Integrated systems facilitate seamless communication and information sharing between different departments and supply chain partners. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces communication gaps, and ensures accurate and timely exchange of information, leading to improved collaboration and coordination.
- Efficient Inventory Management: Integrated systems enable better inventory management by providing accurate and up-to-date information on stock levels, demand patterns, and lead times. This helps optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, minimize stockouts, and avoid overstocking, leading to improved cash flow and cost savings.
- Demand Planning and Forecasting: Integrated supply chain systems integrate data from various sources, such as sales, marketing, and production, allowing for more accurate demand planning and forecasting. This improves the accuracy of production plans, reduces the risk of stockouts or excess inventory, and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Optimized Production Scheduling: Integrated systems enable better synchronization of production schedules with demand forecasts, inventory levels, and resource availability. This leads to more efficient production planning, reduced lead times, improved on-time delivery performance, and increased productivity.
- Effective Order Fulfillment: Integrated supply chain systems enable seamless order processing and fulfillment by automating workflows and providing real-time updates on order status. This results in faster order processing, improved order accuracy, and enhanced customer service.
- Improved Supplier Collaboration: Integrated systems facilitate closer collaboration with suppliers by sharing information on demand forecasts, inventory levels, and production schedules. This improves supplier performance, reduces lead times, and enhances overall supply chain efficiency.
- Data-driven Decision-making: Integrated supply chain systems provide access to comprehensive and accurate data, empowering decision-makers to make informed choices. By leveraging data analytics and reporting capabilities, manufacturers can identify trends, analyze performance metrics, and make data-driven decisions to optimize production planning strategies.
- Agility and Adaptability: Integrated systems enable quick response to changes in demand, supply, or market conditions. Manufacturers can easily adjust production plans, reassign resources, and collaborate with suppliers to meet changing customer needs and market dynamics.
- Continuous Improvement: Integrated supply chain systems facilitate continuous improvement initiatives by providing data for performance measurement, identifying areas for optimization, and supporting process refinement. This leads to ongoing enhancements in production planning effectiveness and overall supply chain performance.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization
In today's rapidly changing manufacturing landscape, continuous improvement and optimization are crucial for staying competitive and maximizing operational efficiency.
This section explores the importance of ongoing improvement initiatives in production planning and highlights strategies to optimize processes, reduce waste, and enhance overall performance.
By embracing a culture of continuous improvement, manufacturers can adapt to evolving market demands, minimize costs, and deliver high-quality products with increased efficiency.
Concept of continuous improvement in production planning
Continuous improvement in production planning is a systematic approach aimed at enhancing processes, reducing waste, and maximizing efficiency in manufacturing operations. It involves constantly evaluating existing practices, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to drive continuous growth and optimization.
The concept of continuous improvement revolves around the belief that even the most effective processes can be further refined and optimized over time. It requires a proactive mindset, where every individual within the organization is encouraged to contribute ideas and participate in problem-solving activities.
In production planning, continuous improvement focuses on streamlining workflows, eliminating bottlenecks, and improving resource utilization. It involves analyzing data, monitoring key performance indicators, and identifying opportunities for enhancement. Through techniques like lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen, companies can systematically identify waste, reduce variability, and enhance productivity.
Continuous improvement in production planning offers several benefits, including increased operational efficiency, reduced costs, improved quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and better responsiveness to market changes. It enables manufacturers to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving industry by consistently refining processes, adopting new technologies, and implementing best practices.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations create an environment where innovation is valued, employees are engaged, and the pursuit of excellence becomes a shared responsibility.
This proactive approach allows for ongoing optimization of production planning, ensuring that companies can adapt to market demands, achieve higher levels of efficiency, and deliver products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Exploring methodologies like Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM)
In the quest for continuous improvement in production planning, methodologies such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) play a significant role. These approaches provide structured frameworks and tools to identify and eliminate process inefficiencies, reduce defects, and enhance overall quality.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at minimizing process variations and defects by systematically identifying and eliminating root causes of problems. It emphasizes the importance of measurement, analysis, and statistical techniques to drive process improvement. By implementing Six Sigma principles, organizations can achieve higher process capability, improved quality, and increased customer satisfaction.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): TQM is a holistic approach that focuses on creating a culture of quality throughout the organization. It involves continuous improvement, customer focus, and employee engagement. TQM emphasizes the importance of quality at every stage of the production process, from design to delivery. By implementing TQM principles, organizations strive to meet or exceed customer expectations, reduce waste, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Both Six Sigma and TQM provide methodologies, tools, and techniques that can be applied to production planning to drive improvements. These methodologies involve:
- Define: Clearly defining the goals, objectives, and key performance indicators for production planning.
- Measure: Collecting and analyzing relevant data to understand the current state of production processes and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze: Applying statistical analysis and other techniques to identify the root causes of issues and inefficiencies in production planning.
- Improve: Implementing changes and process enhancements to address the identified issues and optimize production planning processes.
- Control: Establishing control mechanisms and monitoring systems to sustain improvements and ensure ongoing performance.
By leveraging these methodologies, organizations can systematically analyze and improve production planning processes, reduce waste, enhance efficiency, and deliver products with improved quality and reliability. These approaches promote a culture of continuous improvement and empower employees to actively contribute to the optimization efforts.
It's important for organizations to carefully assess their specific needs, resources, and goals to determine which methodology, or a combination thereof, best aligns with their production planning objectives.
Implementing Six Sigma or TQM requires commitment, training, and ongoing support from management to drive successful adoption and realize the benefits of these methodologies in the production planning process.
Importance of data analysis and performance metrics for optimizing production planning processes
Data analysis and performance metrics play a crucial role in optimizing production planning processes. They provide valuable insights into the performance of various production activities, identify areas for improvement, and enable informed decision-making. Here are key reasons why data analysis and performance metrics are essential:
- Identify Inefficiencies: Data analysis allows organizations to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas of waste within production planning processes. By analyzing data on cycle times, resource utilization, and material flows, organizations can pinpoint specific areas that require optimization, leading to improved overall efficiency.
- Real-time Monitoring: Performance metrics enable real-time monitoring of production planning processes. By tracking key metrics such as production throughput, on-time delivery, and inventory levels, organizations can quickly identify deviations from desired performance and take corrective actions promptly.
- Fact-based Decision-making: Data analysis provides factual insights into production planning performance, eliminating guesswork and subjective decision-making. By utilizing accurate and reliable data, organizations can make informed decisions to optimize production processes, allocate resources effectively, and improve overall planning efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: Data analysis and performance metrics support the identification of improvement opportunities and facilitate ongoing optimization efforts. By analyzing historical and real-time data, organizations can identify patterns, trends, and areas of potential improvement, leading to a culture of continuous improvement within the production planning process.
- Resource Optimization: Data analysis helps optimize resource allocation in production planning. By analyzing data on equipment utilization, labor productivity, and material consumption, organizations can identify areas where resources are underutilized or overburdened. This allows for better resource allocation, minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
- Demand Forecasting and Planning: Data analysis supports accurate demand forecasting and planning. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and customer preferences, organizations can make more accurate demand forecasts, leading to improved production planning, reduced inventory carrying costs, and optimized resource allocation.
- Performance Evaluation: Performance metrics enable organizations to evaluate the effectiveness of production planning strategies and initiatives. By comparing actual performance against predefined targets and benchmarks, organizations can assess their progress, identify areas for further improvement, and align production planning processes with strategic goals.
In conclusion, data analysis and performance metrics are essential tools for optimizing production planning processes. They enable organizations to identify inefficiencies, make fact-based decisions, drive continuous improvement, optimize resource allocation, and align production planning with customer demands.
By leveraging data and performance metrics, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape.
Human Capital Development and Training
In the ever-changing manufacturing landscape, the role of human capital in production planning cannot be overstated. This section focuses on the importance of investing in the development and training of employees involved in production planning. It explores how organizations can empower their workforce with the necessary skills, knowledge, and expertise to navigate complex production challenges and drive continuous improvement.

By prioritizing human capital development, organizations can enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability of their production planning processes, leading to improved operational outcomes and sustained success.
Role of skilled and knowledgeable workforce in successful production planning
A skilled and knowledgeable workforce plays a pivotal role in the success of production planning. Here are key reasons why a capable workforce is essential:
- Expertise in Production Processes: Skilled employees possess in-depth knowledge and understanding of production processes, including equipment operation, material handling, and quality control. Their expertise allows them to make informed decisions, troubleshoot issues, and optimize production planning activities.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: A competent workforce can effectively allocate resources, such as labor, materials, and equipment, based on production requirements. They can assess capacity, skill sets, and availability, ensuring optimal resource utilization and minimizing production bottlenecks.
- Effective Problem-Solving: Production planning often involves addressing unforeseen challenges and issues. Skilled employees are equipped with problem-solving abilities and critical thinking skills to quickly identify root causes, develop solutions, and implement corrective actions, minimizing downtime and maintaining production efficiency.
- Adaptability to Change: The manufacturing landscape is constantly evolving, and production planning must adapt accordingly. Skilled employees are adaptable, embracing new technologies, processes, and industry trends. They can quickly learn and apply new techniques, ensuring seamless transitions during changes in production planning strategies.
- Collaboration and Communication: Successful production planning relies on effective collaboration and communication among various departments and teams. Skilled employees possess strong interpersonal skills, facilitating cross-functional collaboration, knowledge sharing, and effective communication throughout the production process.
- Continuous Improvement: A knowledgeable workforce actively contributes to the culture of continuous improvement. They are aware of industry best practices, quality standards, and emerging trends. By leveraging their expertise, organizations can identify areas for enhancement, implement process improvements, and drive continuous optimization in production planning.
- Risk Mitigation: Skilled employees are better equipped to anticipate and mitigate risks in production planning. They can identify potential bottlenecks, quality issues, or supply chain disruptions and develop contingency plans to minimize their impact. Their expertise enables proactive risk management and ensures smoother production operations.
Investing in employee training and development is crucial for cultivating a skilled and knowledgeable workforce. This can be achieved through training programs, certifications, cross-functional rotations, and continuous learning opportunities.
By equipping employees with the necessary skills and knowledge, organizations foster a workforce capable of successful production planning, enabling them to adapt to changing manufacturing landscapes, drive efficiency, and maintain a competitive edge.
Strategies for talent acquisition, training, and retention
Strategies for Talent Acquisition, Training, and Retention in Production Planning:
Targeted Recruitment: Develop a comprehensive recruitment strategy that targets individuals with relevant skills and qualifications for production planning roles. Utilize job boards, industry networks, and partnerships with educational institutions to attract talent with the desired expertise and experience.
Onboarding and Training Programs: Implement robust onboarding programs to ensure new hires quickly acclimate to the organization's production planning processes, tools, and systems. Provide comprehensive training programs that cover both technical skills and knowledge of the manufacturing industry.
Cross-Functional Training: Encourage cross-functional training and collaboration to enhance the understanding of production planning across different departments. This fosters a holistic view of the production process and promotes effective communication and problem-solving skills among employees.
Continuous Learning and Development: Establish a culture of continuous learning and professional development by offering opportunities for employees to enhance their skills and knowledge. This can include workshops, seminars, online courses, and certifications related to production planning, lean manufacturing, and supply chain management.
Mentoring and Coaching: Implement mentoring and coaching programs to provide guidance and support to employees in their professional growth. Seasoned production planning professionals can serve as mentors, offering valuable insights and advice to help employees develop their expertise and navigate complex challenges.
Competitive Compensation and Benefits: Ensure that compensation and benefits packages are competitive to attract and retain top talent in production planning. Recognize and reward exceptional performance to motivate and retain skilled employees.
Employee Engagement and Retention Initiatives: Foster a positive work environment and employee engagement by promoting teamwork, communication, and recognition. Implement initiatives such as employee feedback mechanisms, team-building activities, and employee recognition programs to enhance job satisfaction and retention.
Succession Planning: Develop a succession plan to identify and groom potential leaders in production planning. This ensures a smooth transition of knowledge and responsibilities as experienced employees retire or move into other roles within the organization.
Performance Management: Establish clear performance metrics and goals for production planning roles. Regularly assess employee performance, provide constructive feedback, and offer opportunities for growth and advancement based on merit.
Employee Well-being and Work-Life Balance: Promote employee well-being and work-life balance to support a healthy and motivated workforce. Offer flexible work arrangements, wellness programs, and initiatives that promote work-life integration.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can attract top talent, develop a skilled workforce, and retain employees with the necessary expertise in production planning. This not only ensures effective production planning but also creates a supportive and thriving work environment that drives overall operational excellence.
Need for continuous learning and development in a changing manufacturing landscape
The manufacturing industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, market demands, and global competition. In this dynamic landscape, the need for continuous learning and development among employees is paramount. Here's why continuous learning is essential:
- Adapting to Technological Advances: Technology plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, with innovations such as automation, robotics, and data analytics revolutionizing production processes. Continuous learning ensures that employees stay updated on the latest technologies and can effectively leverage them in production planning, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Embracing Industry Best Practices: Manufacturing practices and methodologies evolve over time, and it's vital for employees to stay informed about industry best practices. Continuous learning enables employees to understand and adopt new approaches, such as lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, and agile production systems, leading to streamlined processes and improved outcomes.
- Enhancing Skills and Competencies: Continuous learning fosters the development of new skills and competencies required in the changing manufacturing landscape. This includes skills related to data analysis, supply chain management, digitalization, and problem-solving. By acquiring these skills, employees become more versatile and capable of taking on diverse production planning challenges.
- Navigating Globalization and Market Demands: Globalization has expanded the reach of manufacturing, creating a need to understand international markets, cultural nuances, and supply chain complexities. Continuous learning equips employees with the knowledge and insights to navigate global markets and align production planning strategies with changing customer demands.
- Driving Innovation and Creativity: In an ever-evolving industry, innovation is key to staying ahead of the competition. Continuous learning encourages employees to think creatively, explore new ideas, and contribute to innovation in production planning processes. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement and drives organizational growth.
- Managing Complex Supply Chains: The modern manufacturing landscape often involves complex supply chains with multiple stakeholders and dependencies. Continuous learning helps employees understand supply chain dynamics, develop strong collaboration skills, and effectively manage supplier relationships. This enhances production planning by ensuring seamless coordination across the supply chain.
- Retaining and Attracting Talent: Continuous learning and development programs signal to employees that their growth and professional development are valued. This boosts employee morale, engagement, and job satisfaction, leading to increased retention. Additionally, organizations that prioritize continuous learning are more attractive to top talent seeking opportunities for growth and advancement.
- Future-Proofing the Workforce: The manufacturing landscape will continue to evolve, with emerging technologies and market trends shaping the industry's future. Continuous learning ensures that employees are equipped with the knowledge and skills to adapt to these changes, making the workforce more resilient and future-proof.
In summary, continuous learning and development are crucial in the changing manufacturing landscape. It enables employees to stay updated, enhance their skills, drive innovation, and effectively respond to the evolving needs of the industry.
By investing in continuous learning initiatives, organizations can cultivate a knowledgeable and agile workforce, leading to improved production planning, operational excellence, and sustainable growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of economic factors on stock market performance is undeniable. Economic indicators such as GDP, interest rates, inflation, unemployment rates, and consumer sentiment can significantly influence the behavior of stock markets. Understanding these economic factors and their relationship with the stock market is essential for investors, financial analysts, and policymakers alike.
Positive economic factors such as strong economic growth, low interest rates, stable inflation, and decreasing unemployment rates tend to have a favorable impact on stock market performance. On the other hand, negative economic factors like recessions, high interest rates, rising inflation, and increasing unemployment rates can lead to stock market downturns and volatility.
By analyzing and considering economic factors, investors can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and identify investment opportunities. Moreover, recognizing the interplay between economic factors and stock market performance allows policymakers to implement effective economic policies and regulations that support a stable and thriving stock market.
As the global economy continues to evolve, it is crucial to stay abreast of economic trends, monitor key economic indicators, and adapt investment strategies accordingly. The impact of economic factors on stock market performance is a complex and multifaceted subject, and continued research and analysis are vital for navigating the ever-changing financial landscape.
How Can Manufacturers Stay Competitive In The Evolving Industry?
Manufacturers can stay competitive in the evolving industry by adopting several key strategies:
- Embrace Technological Advancements: Manufacturers should stay updated on the latest technologies and embrace automation, artificial intelligence, IoT, and data analytics to optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and enhance product quality.
- Foster Innovation and R&D: Encourage a culture of innovation within the organization by investing in research and development activities. This includes exploring new materials, improving product designs, and finding innovative solutions to manufacturing challenges.
- Implement Lean Manufacturing Principles: Lean manufacturing principles focus on eliminating waste, improving processes, and maximizing value. By adopting lean practices, manufacturers can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and deliver products faster to meet customer demands.
- Optimize Supply Chain Management: Establish strong collaboration and integration with suppliers and partners in the supply chain. Efficient supply chain management ensures timely delivery of materials, reduces lead times, and minimizes disruptions, thereby enhancing overall competitiveness.
- Develop a Skilled Workforce: Invest in employee training and development programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of the workforce. This includes providing training on advanced technologies, process improvements, and cross-functional skills to adapt to changing industry requirements.
- Focus on Quality Control and Continuous Improvement: Implement robust quality control processes and continually strive for improvement. This involves monitoring product quality, gathering customer feedback, and implementing measures to enhance product reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Embrace Sustainable Practices: Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers should adopt environmentally friendly practices, reduce waste, and incorporate sustainable materials and processes into their operations. This not only aligns with market demands but also enhances brand reputation.
- Stay Customer-Centric: Manufacturers must understand evolving customer needs and preferences. This involves gathering customer feedback, conducting market research, and incorporating customer-centric strategies into product development, production planning, and marketing.
- Foster Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration with industry peers, research institutions, and technology providers can lead to valuable insights, shared resources, and joint innovation efforts. Collaborative partnerships can help manufacturers stay at the forefront of industry developments.
- Adapt to Regulatory and Market Changes: Manufacturers need to stay informed about regulatory changes, market trends, and emerging technologies. By anticipating and adapting to these changes, manufacturers can proactively adjust their strategies and remain competitive in the evolving industry.
By embracing these strategies, manufacturers can not only survive but also thrive in the evolving industry. Continuous improvement, innovation, adaptability, and a customer-centric approach are key to maintaining competitiveness and achieving long-term success.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
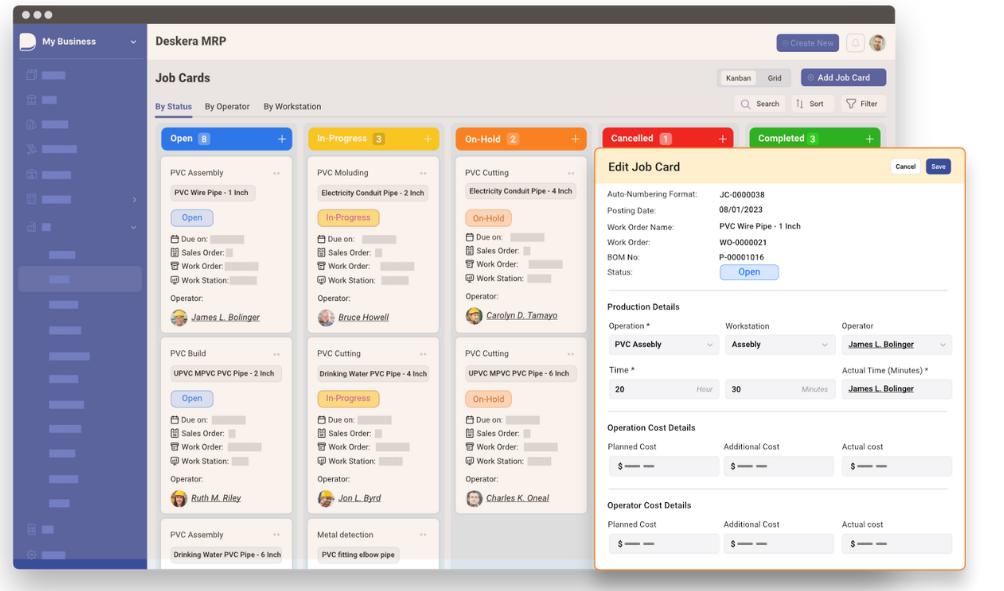
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- The manufacturing industry is undergoing significant changes due to factors such as technology advancements, globalization, and evolving customer demands.
- Effective production planning is essential in optimizing manufacturing operations, reducing costs, and meeting customer expectations.
- Adaptability and flexibility are crucial in response to the evolving manufacturing landscape, allowing manufacturers to adjust production strategies and processes accordingly.
- Accurate forecasting and demand planning are vital for aligning production with customer demand, avoiding overstock or stockouts, and optimizing inventory management.
- Agile production systems, such as Kanban, JIT, and QRM, enable manufacturers to respond quickly to changing customer demands and market dynamics, improving efficiency and reducing lead times.
- Leveraging technology, such as MES, ERP, and APS systems, streamlines production planning, enhances visibility, and enables real-time decision-making.
- Collaboration with sales, marketing, and supply chain teams is essential for effective demand planning, ensuring a holistic approach and alignment across the organization.
- Integrated supply chain systems foster collaboration with suppliers and partners, optimizing supply chain processes and improving production planning effectiveness.
- Continuous improvement methodologies, like Six Sigma and TQM, drive efficiency, quality, and waste reduction in production planning processes.
- Investing in human capital development, talent acquisition, and continuous learning promotes a skilled workforce capable of adapting to changing manufacturing landscapes and driving success.
Related Articles












