Effective production planning plays a pivotal role in the success of manufacturing operations. In today's competitive business landscape, where companies strive to optimize productivity, reduce manufacturing costs, and meet customer demands, an efficient production planning process has become more critical than ever.
By strategically aligning resources, capacity, and schedules, manufacturers can achieve streamlined operations, improved efficiency, and ultimately, enhanced profitability.
According to a survey conducted by the Manufacturing Institute, inadequate production planning is one of the primary reasons for supply chain disruptions, leading to increased costs and delayed deliveries. In fact, the survey revealed that 74% of manufacturers experienced at least one supply chain disruption in the past year, with 39% directly attributing it to poor production planning.
Additionally, a study by the Aberdeen Group found that companies with effective production planning processes achieved a 20% increase in production output and a 30% reduction in inventory holding costs compared to their counterparts with less efficient planning systems.
Furthermore, market dynamics and customer expectations are continually evolving. Manufacturers face the challenge of meeting fluctuating demand patterns, managing complex supply chains, and adapting to rapid technological advancements. Effective production planning serves as the foundation for addressing these challenges and navigating the ever-changing manufacturing landscape.

In this article, we will explore the key elements of effective production planning, the benefits it brings to manufacturing organizations, the challenges faced, and how to overcome them. Through real-world case studies and industry insights, we will shed light on the critical role of production planning in driving manufacturing success.
Here is what we cover on this page:
- Definition of Production Planning
- Importance of Production Planning in Manufacturing
- Key Elements of Effective Production Planning
- Demand Forecasting and Analysis
- Capacity Planning and Optimization
- Inventory Management
- Scheduling and sequencing
- Benefits of Effective Production Planning
- Challenges in Production Planning and How to Overcome Them
- Uncertain Demand and Market Fluctuations
- Complex Supply Chain Dynamics
- Rapid Technological Advancements
- Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Production Planning Strategies
- 10 Recommendations for Successful Production Planning
- Conclusion
- Future of Production Planning in an Evolving Manufacturing Landscape
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Definition of Production Planning
Production planning is the process of strategically and systematically determining the most efficient and effective way to utilize resources, facilities, and personnel to meet production goals and satisfy customer demand. It involves a series of activities that encompass forecasting demand, determining production requirements, scheduling tasks, allocating resources, and coordinating various stages of the production process.
At its core, production planning aims to optimize the allocation of available resources, such as raw materials, labor, machinery, and time, to ensure smooth and cost-effective production operations. It takes into account factors such as production capacity, lead times, inventory levels, and market demand to create a comprehensive plan that guides the entire manufacturing process.
Production planning involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer forecasts to estimate future demand. This information is used to determine the quantity and timing of production runs, as well as the necessary resources and schedules to meet those demands. The planning process also considers factors like production sequencing, quality control measures, and the coordination of various departments or teams involved in the production process.
By effectively aligning production plans with organizational goals, production planning helps manufacturing companies optimize their operations, minimize costs, reduce lead times, improve productivity, and ultimately deliver high-quality products to customers in a timely manner.
Importance of Production Planning in Manufacturing
Production planning plays a vital role in the success of manufacturing operations. It is essential for several reasons:
- Optimal Resource Utilization: Effective production planning ensures that resources such as raw materials, equipment, and labor are efficiently allocated. By analyzing production requirements and available resources, manufacturers can avoid underutilization or overutilization, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
- Meeting Customer Demand: Production planning helps manufacturers align their production capabilities with customer demand. By accurately forecasting demand patterns and planning production accordingly, companies can avoid stockouts, minimize lead times, and fulfill customer orders in a timely manner, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Cost Reduction: Production planning enables manufacturers to identify and eliminate inefficiencies in the production process. By streamlining workflows, optimizing inventory levels, and minimizing waste, companies can reduce costs associated with excess inventory, downtime, overproduction, and material shortages.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Well-planned production processes lead to increased efficiency and productivity. By establishing optimized production schedules, coordinating tasks, and ensuring smooth workflow transitions, manufacturers can minimize bottlenecks, eliminate idle time, and maximize the utilization of resources.
- Effective Decision Making: Production planning provides a framework for making informed decisions regarding production strategies, resource allocation, and capacity management. With a clear understanding of production requirements and constraints, manufacturers can make data-driven decisions that align with their overall business objectives.
- Adaptability to Market Changes: In a dynamic business environment, production planning enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to market fluctuations and changing customer demands. By regularly reviewing and adjusting production plans, companies can adapt to market trends, optimize production capacity, and maintain a competitive edge.
Overall, effective production planning is crucial for manufacturing success as it drives operational efficiency, cost reduction, customer satisfaction, and agility in a rapidly evolving marketplace. By implementing robust production planning processes, manufacturers can optimize their operations and achieve long-term sustainability and growth.
Overview of the article's purpose
The purpose of this article is to emphasize the critical role of effective production planning in achieving manufacturing success. It aims to highlight the importance of production planning in optimizing resources, meeting customer demand, reducing costs, improving efficiency, and making informed decisions.
The article will delve into the key elements of production planning, including demand forecasting and analysis, capacity planning, inventory management, and scheduling. It will explain how each of these elements contributes to the overall effectiveness of production planning and their impact on manufacturing operations.
Furthermore, the article will discuss the benefits of effective production planning, such as improved productivity, cost reduction, enhanced customer satisfaction, and better decision-making. It will provide evidence through relevant statistics and case studies to demonstrate the tangible advantages that organizations can achieve by implementing efficient production planning strategies.
Additionally, the article will address the challenges faced in production planning, such as uncertain demand, complex supply chain dynamics, and technological advancements. It will offer insights and recommendations on how to overcome these challenges, emphasizing the importance of adaptability and embracing digitalization and automation.
Overall, the article seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of why effective production planning is critical to manufacturing success. It aims to equip readers with valuable knowledge, practical insights, and real-world examples that will help them optimize their production planning processes and drive positive outcomes for their manufacturing operations.
Key Elements of Effective Production Planning
To ensure manufacturing success, several key elements form the foundation of effective production planning. These elements encompass various aspects of the planning process, including demand forecasting, capacity planning and optimization, inventory management, and scheduling and sequencing.
By focusing on these essential components, manufacturers can strategically align resources, streamline operations, and meet customer demands efficiently.
In this section, we will delve into each of these key elements, exploring their significance and providing insights on how they contribute to the overall effectiveness of production planning.
By understanding and implementing these elements effectively, manufacturers can lay the groundwork for successful production planning that drives operational excellence and facilitates business growth.
Here are the key elements of an effective production planning:
- Demand forecasting and analysis
- Capacity planning and optimization
- Inventory management
- Scheduling and sequencing
Let’s learn in detail about these in the forthcoming sections.
Demand Forecasting and Analysis
Accurate demand forecasting and analysis form a critical pillar of effective production planning in manufacturing. Understanding customer demand patterns and market dynamics is essential for aligning production resources and schedules to meet anticipated demand.
In this section, we will delve into the importance of demand forecasting and analysis, exploring techniques and methodologies that enable manufacturers to make informed predictions about future demand. By leveraging market research, historical data, and advanced analytics, manufacturers can gain valuable insights that inform production plans, minimize inventory costs, and ensure timely product availability.
Effective demand forecasting and analysis empower manufacturers to proactively respond to market fluctuations, optimize production levels, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction.
Through a comprehensive examination of this key element, this section aims to provide practical guidance and best practices for incorporating demand forecasting and analysis into production planning strategies, thereby driving manufacturing success.
Understanding customer demand patterns
Understanding customer demand patterns involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer behavior to gain insights into the preferences, buying patterns, and expectations of consumers. It is a critical aspect of effective production planning as it enables manufacturers to align their production capabilities with the anticipated demand, minimizing the risk of underproduction or overproduction.
By studying historical sales data and customer purchasing patterns, manufacturers can identify seasonal trends, cyclical fluctuations, and other demand patterns that influence their products' popularity and sales volumes. This analysis helps in accurately forecasting future demand and adjusting production plans accordingly.
Moreover, market trends and consumer preferences continually evolve, influenced by factors such as changing demographics, technological advancements, and economic conditions. By staying abreast of these trends through market research and analysis, manufacturers can anticipate shifts in customer demand and proactively adjust their production plans to meet evolving needs.
Understanding customer demand patterns also involves gathering feedback from customers, monitoring social media, conducting surveys, and engaging in direct communication to gain insights into their expectations and preferences. This customer-centric approach allows manufacturers to tailor their production plans, product offerings, and marketing strategies to align with customer demands effectively.
By understanding customer demand patterns, manufacturers can optimize production levels, reduce the risk of inventory obsolescence, minimize stockouts, and improve overall operational efficiency. Additionally, aligning production with customer demand enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring products are available when and where customers need them.
Ultimately, by investing in understanding customer demand patterns, manufacturers can make more accurate forecasts, plan production resources effectively, and position themselves competitively in the market.
Utilizing market research and data analysis
Utilizing market research and data analysis is a crucial aspect of effective production planning in manufacturing. Market research involves gathering and analyzing information about the market, industry trends, competitors, and customer preferences to make informed decisions regarding production planning.
Market research provides valuable insights into the target market, including customer demographics, buying behaviors, and preferences. It helps manufacturers understand the competitive landscape, identify emerging trends, and anticipate changes in demand. By studying market research reports, conducting surveys, and analyzing customer feedback, manufacturers can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics and make data-driven decisions.
Data analysis plays a significant role in extracting meaningful information from the vast amount of data available. By employing various analytical techniques, such as statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and data visualization, manufacturers can uncover patterns, correlations, and trends in the data. This analysis aids in identifying demand patterns, forecasting future demand, and making accurate production plans.
Through market research and data analysis, manufacturers can gather insights on factors such as consumer preferences, seasonal fluctuations, geographic variations, and emerging market segments. This information helps them align their production plans with market demand, optimize resource allocation, and adjust production levels to meet customer expectations.
Furthermore, market research and data analysis enable manufacturers to identify new market opportunities, develop targeted marketing strategies, and make informed decisions about product development and innovation. By understanding market trends and customer needs, manufacturers can tailor their offerings to stay ahead of the competition and meet evolving consumer demands.
Overall, utilizing market research and data analysis in production planning empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions, optimize production resources, and effectively respond to market dynamics. It enhances their ability to meet customer demands, improve operational efficiency, and achieve manufacturing success.
Capacity Planning and Optimization
Capacity planning and optimization are integral components of effective production planning in manufacturing. Ensuring that production capacity aligns with demand is crucial for maximizing operational efficiency, minimizing costs, and meeting customer expectations.
In this section, we will explore the significance of capacity planning and optimization, delving into strategies and techniques that enable manufacturers to assess and manage their production capabilities.
By analyzing existing resources, evaluating production capacity, and implementing optimization measures, manufacturers can strike a balance between supply and demand, avoid bottlenecks, and optimize resource utilization.
This section aims to provide insights and practical guidance on capacity planning and optimization, highlighting their importance in achieving manufacturing success and enabling companies to effectively respond to market fluctuations and changing customer needs.
Evaluating existing resources and capabilities
Evaluating existing resources and capabilities is a critical step in capacity planning and optimization within production planning. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the available resources, including machinery, equipment, labor, facilities, and technology, to determine their capacity and capabilities.
By evaluating existing resources, manufacturers can gain a clear understanding of their production capacity and limitations. This assessment involves gathering data on the capacity of each resource, such as the maximum output it can generate within a given timeframe, its efficiency, and any constraints or bottlenecks associated with it. It also includes considering factors such as maintenance schedules, downtime, and resource availability.
Additionally, evaluating capabilities involves assessing the skill sets and expertise of the workforce. Understanding the knowledge, experience, and training levels of employees is crucial in determining the capacity and efficiency of the labor force. This evaluation helps identify any skill gaps or training needs that may impact production capacity.
Furthermore, the evaluation encompasses an analysis of the overall production process, including the flow of materials, workstations, and production sequences. It involves examining the efficiency of the workflow, identifying potential areas for improvement, and optimizing the production layout for smoother operations.
By conducting a thorough evaluation of existing resources and capabilities, manufacturers can determine their production capacity and identify any constraints or inefficiencies that may hinder optimal performance. This assessment provides a foundation for making informed decisions regarding production planning, such as determining feasible production volumes, identifying potential production bottlenecks, and allocating resources effectively.
Ultimately, evaluating existing resources and capabilities allows manufacturers to optimize their production capacity, align it with customer demand, and make strategic decisions that maximize operational efficiency and profitability. It enables them to identify opportunities for improvement, address constraints, and enhance their overall production planning process.
Balancing production capacity with demand
Balancing production capacity with demand is a crucial aspect of effective production planning. It involves ensuring that the available production resources and capabilities align with the anticipated customer demand.
To achieve this balance, manufacturers need to accurately forecast and analyze customer demand patterns. By understanding the demand fluctuations, seasonal trends, and market dynamics, manufacturers can estimate the quantity and timing of products needed to fulfill customer orders.
Once the demand is forecasted, it is compared with the production capacity. Manufacturers evaluate their existing resources, including machinery, labor, and facilities, to determine if they have the necessary capacity to meet the anticipated demand. This assessment takes into account factors such as production rates, cycle times, and overall efficiency.
In cases where the demand exceeds the production capacity, manufacturers may need to explore options to increase capacity, such as investing in additional equipment, expanding facilities, or outsourcing certain production processes. On the other hand, if the production capacity exceeds the demand, manufacturers can explore strategies to optimize resource utilization, such as adjusting production schedules, improving workflow efficiency, or diversifying product offerings.
Balancing production capacity with demand is crucial to avoid underproduction or overproduction. Underproduction can result in stockouts, missed sales opportunities, and dissatisfied customers. Overproduction, on the other hand, leads to excess inventory, increased carrying costs, and potential waste.
By striking the right balance between production capacity and demand, manufacturers can optimize their operations, minimize costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. It enables them to meet customer expectations by ensuring timely product availability while avoiding unnecessary expenses associated with excess inventory or production bottlenecks.
Continuous monitoring and adjustment of production plans based on demand fluctuations are necessary to maintain the balance between capacity and demand. This flexibility allows manufacturers to respond swiftly to changes in the market, customer preferences, and unforeseen events, thereby maintaining a competitive edge in the industry.
Overall, balancing production capacity with demand is a critical element of effective production planning. It enables manufacturers to optimize resource utilization, minimize costs, and meet customer demands efficiently, leading to improved operational efficiency and overall manufacturing success.
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is a pivotal component of successful production planning in manufacturing. Maintaining the right balance of inventory levels is essential for ensuring smooth operations, minimizing costs, and meeting customer demands.
In this section, we will delve into the significance of inventory management, exploring strategies and best practices that enable manufacturers to optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and enhance overall efficiency. By implementing robust inventory management techniques, manufacturers can mitigate the risks of stockouts and overstocking, improve order fulfillment rates, and streamline the production process.
This section aims to provide insights and practical guidance on inventory management, highlighting its critical role in achieving manufacturing success and delivering exceptional customer satisfaction.
Minimizing excess inventory and associated costs
Minimizing excess inventory and associated costs is a key objective of effective inventory management in manufacturing. Excess inventory refers to inventory levels that surpass the immediate demand or the desired stock levels. It can result from overproduction, inaccurate demand forecasting, poor inventory control, or inefficient production planning.
Managing excess inventory is crucial because it incurs several costs for manufacturers. First, carrying costs include expenses such as warehousing, storage, insurance, depreciation, and obsolescence. Excess inventory ties up valuable capital that could be invested elsewhere in the business, limiting cash flow and hindering financial flexibility.
Second, excess inventory can lead to increased risk of obsolescence. Products that stay in inventory for an extended period may become outdated, resulting in potential write-offs or markdowns to clear the inventory.
Furthermore, excess inventory impacts production efficiency. It consumes valuable storage space, which could be utilized for more critical purposes, and it can lead to logistical challenges in managing and organizing inventory. It also adds complexity to the production process, requiring additional resources for handling and managing the excess stock.
To minimize excess inventory and associated costs, manufacturers employ various strategies:
- Accurate demand forecasting: Implementing robust demand forecasting techniques enables manufacturers to anticipate customer demand accurately and adjust production levels accordingly, reducing the risk of overproduction.
- Lean production principles: Embracing lean manufacturing principles, such as just-in-time (JIT) production and kanban systems, helps synchronize production with demand, minimizing the need for excess inventory.
- Inventory optimization: Utilizing inventory optimization tools and techniques, such as economic order quantity (EOQ) and safety stock analysis, helps determine optimal inventory levels based on demand variability, lead times, and desired service levels.
- Supplier collaboration: Collaborating closely with suppliers can help ensure timely and accurate delivery of materials, reducing the need for excessive inventory buffers.
- Efficient production scheduling: Implementing effective production scheduling techniques helps minimize production bottlenecks and idle time, ensuring a more efficient use of resources and reducing the need for excess inventory.
By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can minimize excess inventory, reduce carrying costs, enhance cash flow, and improve overall operational efficiency. This approach allows for a lean and agile inventory management system that is responsive to customer demand while optimizing resources and costs.
Implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems
Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system is a widely recognized approach to inventory management in manufacturing. JIT aims to minimize inventory levels by synchronizing production with customer demand, ensuring that materials and components arrive precisely when needed for production.
The key principle of JIT is to produce and deliver products "just in time" to meet customer orders, eliminating the need for excessive inventory buffers. This approach offers several benefits for manufacturers:
- Reduced inventory costs: JIT inventory systems minimize the need for large inventory holdings, resulting in lower carrying costs such as storage, insurance, and obsolescence. Manufacturers can free up capital that would otherwise be tied up in inventory and invest it in other areas of the business.
- Improved cash flow: With reduced inventory levels, manufacturers can optimize cash flow as they spend less on purchasing and holding inventory. This provides financial flexibility to allocate resources to other critical areas, such as research and development or marketing initiatives.
- Enhanced production efficiency: JIT promotes smooth production flow by ensuring that materials and components arrive precisely when needed. This reduces the risk of production bottlenecks, minimizes idle time, and improves overall production efficiency.
- Quality control and waste reduction: JIT emphasizes quality control throughout the production process. By minimizing inventory, manufacturers can quickly identify and address quality issues, resulting in lower rework, scrap, and waste.
- Faster response to market changes: JIT enables manufacturers to respond rapidly to changing customer demands and market fluctuations. With reduced inventory levels, manufacturers can quickly adjust production volumes and product offerings, allowing them to be more agile and responsive in meeting customer needs.
Implementing a JIT inventory system requires effective coordination with suppliers, accurate demand forecasting, and efficient production scheduling. It involves establishing strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring reliable and timely deliveries, and closely monitoring inventory levels to maintain the right balance between production and customer demand.
While JIT offers numerous advantages, it also comes with challenges. It requires a high level of operational efficiency, effective communication across the supply chain, and careful risk management to avoid disruptions in the supply of materials. However, when implemented successfully, JIT can lead to significant improvements in inventory management, cost reduction, and overall manufacturing performance.
Scheduling and Sequencing
Scheduling and sequencing play a critical role in effective production planning in manufacturing. Properly organizing and sequencing production activities ensures optimal resource utilization, efficient workflow, and timely delivery of products.
In this section, we will explore the significance of scheduling and sequencing, examining the key principles and techniques that manufacturers employ to optimize production schedules.
By strategically planning and sequencing production tasks, manufacturers can minimize idle time, reduce production bottlenecks, and enhance overall operational efficiency. This section aims to provide insights and practical guidance on scheduling and sequencing, emphasizing their crucial role in achieving manufacturing success and meeting customer expectations.
Optimizing production schedules for efficiency
Optimizing production schedules for efficiency is a key objective in production planning for manufacturing. An optimized production schedule ensures that resources, including labor, machinery, and materials, are utilized effectively to meet production targets and minimize waste and idle time. By streamlining the production process, manufacturers can achieve higher productivity, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
To optimize production schedules, several factors need to be considered:
- Demand forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting serves as a foundation for effective production scheduling. By understanding customer demand patterns, manufacturers can align production schedules to meet anticipated demand, avoiding overproduction or underproduction.
- Production capacity assessment: Evaluating the available production capacity is crucial for optimizing production schedules. Manufacturers need to consider the capacity of machinery, equipment, and labor to ensure that production volumes can be achieved within the given timeframes.
- Resource allocation: Efficient resource allocation is vital in production scheduling. It involves assigning the right resources to the right tasks at the right time. By considering factors such as skill levels, equipment availability, and production dependencies, manufacturers can ensure a smooth workflow and minimize delays.
- Sequencing and prioritization: Proper sequencing and prioritization of production tasks are essential for efficient production schedules. Tasks should be sequenced logically, considering factors such as task dependencies, production lead times, and setup times. Prioritizing critical tasks and balancing workload across the production floor helps avoid bottlenecks and maintain a steady production flow.
- Real-time monitoring and adjustment: Continuous monitoring of production progress allows for timely identification of potential delays or bottlenecks. Real-time data and feedback from the production floor enable manufacturers to make necessary adjustments to the schedule, allocate additional resources, or resequence tasks to maintain efficiency.
- Lean manufacturing principles: Adopting lean manufacturing principles, such as minimizing setup times, reducing waste, and implementing just-in-time (JIT) practices, can significantly improve production scheduling efficiency. These principles help eliminate non-value-added activities and focus on producing goods in response to actual customer demand.
Optimizing production schedules requires a balance between maximizing production efficiency and meeting customer demands. It requires collaboration among various departments, including production, operations, and sales, to align objectives and ensure synchronization across the supply chain.
By optimizing production schedules for efficiency, manufacturers can achieve higher productivity, reduce lead times, minimize costs, and improve overall operational performance. This results in improved customer satisfaction, increased competitiveness, and enhanced manufacturing success.
Prioritizing tasks and minimizing downtime
Prioritizing tasks and minimizing downtime are critical aspects of efficient production planning in manufacturing. By effectively prioritizing tasks and minimizing downtime, manufacturers can optimize resource utilization, reduce idle time, and maximize productivity. This section will explore the importance of task prioritization and downtime reduction in production planning, as well as strategies and techniques to achieve these objectives.
Prioritizing tasks involves determining the order and importance of production activities based on various factors, such as customer demand, production dependencies, criticality, and resource availability. By assigning priorities to tasks, manufacturers can ensure that critical and time-sensitive activities are completed on time, minimizing delays and bottlenecks in the production process.
Furthermore, minimizing downtime is crucial for maintaining continuous production flow and maximizing resource utilization. Downtime refers to periods when machinery, equipment, or resources are not actively engaged in productive activities. It can occur due to maintenance, setup, changeovers, breakdowns, or other unplanned events. By minimizing downtime, manufacturers can maximize production capacity and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
To prioritize tasks and minimize downtime, manufacturers can employ several strategies:
- Task sequencing: Proper sequencing of tasks ensures a logical and efficient flow of production activities. By carefully arranging tasks based on dependencies, setup times, and equipment availability, manufacturers can minimize idle time and optimize resource utilization.
- Maintenance planning: Implementing proactive maintenance schedules helps reduce unexpected breakdowns and equipment downtime. Regular maintenance and inspections prevent unplanned interruptions and extend the lifespan of machinery.
- Quick changeovers: Streamlining changeover procedures between different product runs or setups can significantly reduce downtime. By implementing efficient changeover techniques, such as Single Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED), manufacturers can minimize the time required to switch between different production configurations.
- Predictive maintenance and condition monitoring: Utilizing predictive maintenance techniques, such as vibration analysis and sensor-based monitoring, allows manufacturers to detect potential equipment failures before they occur. By proactively addressing issues, unplanned downtime can be minimized.
- Employee training and empowerment: Well-trained and empowered employees can identify and resolve issues efficiently, minimizing downtime. Providing training on equipment operation, troubleshooting, and problem-solving empowers employees to address minor issues and keep production running smoothly.
- Real-time monitoring and analytics: Leveraging real-time data and analytics provides insights into production performance and helps identify bottlenecks or areas of improvement. By monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyzing production data, manufacturers can make data-driven decisions to optimize production schedules and reduce downtime.
By prioritizing tasks and minimizing downtime, manufacturers can enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. It enables them to meet customer demands promptly, minimize production bottlenecks, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Benefits of Effective Production Planning
Effective production planning offers a multitude of benefits for manufacturers, enabling them to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and achieve manufacturing success. This section explores the significant advantages that result from implementing robust production planning strategies.
By understanding and harnessing these benefits, manufacturers can enhance their competitive edge, meet customer demands effectively, and drive overall business growth. From cost savings and resource optimization to improved customer satisfaction and agility, the benefits of effective production planning are diverse and impactful.
This section aims to shed light on these advantages, emphasizing the importance of adopting comprehensive production planning approaches for sustainable manufacturing success.
Improved productivity and efficiency
Improved productivity and efficiency are among the key benefits of effective production planning in manufacturing. When production processes are carefully planned and optimized, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of productivity and operational efficiency, leading to several advantages.
- Optimal resource utilization: Effective production planning ensures that resources, including labor, machinery, and materials, are utilized optimally. By streamlining workflows, reducing downtime, and minimizing idle time, manufacturers can maximize the productivity of their resources and minimize waste.
- Streamlined processes: Through production planning, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, eliminate unnecessary steps, and streamline processes. This leads to smoother operations, reduced lead times, and improved overall efficiency. Streamlined processes also result in fewer errors, rework, and waste, leading to cost savings and increased productivity.
- Enhanced capacity utilization: By aligning production schedules with demand forecasts, manufacturers can optimize their production capacity. This means producing the right quantity of products at the right time, avoiding underutilization or overutilization of resources. Maximizing capacity utilization helps manufacturers achieve higher output levels without compromising on quality or incurring unnecessary costs.
- Reduced cycle times: Effective production planning enables manufacturers to identify opportunities for reducing cycle times, which is the time it takes to complete a production cycle. By analyzing and optimizing each step of the production process, manufacturers can identify and eliminate inefficiencies, ultimately reducing cycle times and increasing throughput.
- Efficient inventory management: Production planning helps manufacturers maintain optimal inventory levels, avoiding excess inventory or stockouts. By aligning production schedules with demand forecasts, manufacturers can produce the right amount of products at the right time, minimizing inventory holding costs and reducing the risk of obsolescence.
- Continuous improvement: Effective production planning involves monitoring and analyzing production data, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to enhance productivity and efficiency. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, manufacturers can continually refine their production processes, leading to incremental gains in productivity over time.
Improved productivity and efficiency contribute to cost savings, increased output, and enhanced competitiveness. Manufacturers can achieve higher production volumes, deliver products more quickly, and respond effectively to customer demands. By optimizing resource utilization, reducing waste, and streamlining processes, manufacturers can achieve higher profitability and create a strong foundation for sustained growth and success.
Cost reduction and optimized resource allocation
Cost reduction and optimized resource allocation are significant benefits that result from effective production planning in manufacturing. By implementing comprehensive production planning strategies, manufacturers can identify cost-saving opportunities, streamline operations, and allocate resources efficiently. This section explores the advantages of cost reduction and optimized resource allocation in production planning.
- Reduced operational costs: Effective production planning helps identify and eliminate inefficiencies, waste, and redundancies in the production process. By streamlining workflows, optimizing production schedules, and minimizing downtime, manufacturers can reduce costs associated with labor, energy consumption, raw materials, and overhead expenses.
- Improved inventory management: Production planning allows manufacturers to maintain optimal inventory levels, avoiding excessive inventory holdings. By aligning production schedules with demand forecasts, manufacturers can produce the right quantity of products at the right time, minimizing carrying costs, storage expenses, and the risk of inventory obsolescence.
- Minimized production downtime: Through effective production planning, manufacturers can reduce downtime by optimizing machine setup, changeover times, and maintenance schedules. By minimizing interruptions and maximizing machine availability, manufacturers can optimize production capacity and reduce costs associated with idle time and lost production opportunities.
- Efficient resource allocation: Production planning facilitates the efficient allocation of resources, including labor, machinery, and materials. By carefully assessing resource availability and demand requirements, manufacturers can allocate resources effectively, avoiding overutilization or underutilization. This leads to improved resource efficiency, reduced costs, and increased overall productivity.
- Elimination of overproduction: Overproduction is a common waste in manufacturing that leads to unnecessary costs. By aligning production schedules with accurate demand forecasts, manufacturers can avoid overproduction, reduce excess inventory, and associated holding costs. This ensures resources are utilized efficiently, minimizing waste and optimizing cost-effectiveness.
- Supplier relationship management: Effective production planning enables manufacturers to establish strong relationships with suppliers. By accurately communicating production requirements and schedules, manufacturers can improve collaboration and negotiate favorable terms, such as bulk discounts or reduced lead times. This helps optimize procurement costs and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
By reducing operational costs and optimizing resource allocation, manufacturers can achieve higher profitability, improve financial performance, and remain competitive in the market. These benefits enable manufacturers to allocate resources strategically, invest in growth opportunities, and enhance their ability to respond to market fluctuations and changing customer demands.
Effective production planning serves as a catalyst for cost reduction, resource optimization, and sustainable manufacturing success.
Enhanced customer satisfaction and on-time delivery
Enhanced customer satisfaction and on-time delivery are crucial outcomes of effective production planning in manufacturing. By aligning production processes with customer demands and implementing robust planning strategies, manufacturers can ensure that products are delivered promptly and meet customer expectations.
This section explores the advantages of enhanced customer satisfaction and on-time delivery resulting from effective production planning.
- Meeting customer demands: Effective production planning enables manufacturers to align production schedules with accurate demand forecasts. By understanding customer requirements and preferences, manufacturers can produce the right quantity of products, avoiding stockouts or excess inventory. This leads to improved customer satisfaction as customers receive their desired products in a timely manner.
- On-time delivery: Timely delivery is a critical factor in customer satisfaction. Production planning helps manufacturers optimize production schedules, allocate resources efficiently, and minimize production lead times. By adhering to planned schedules and streamlining operations, manufacturers can increase their ability to deliver products on time, meeting customer expectations and building trust.
- Improved product quality: Effective production planning emphasizes quality control throughout the production process. By implementing quality assurance measures and monitoring production parameters, manufacturers can ensure that products meet or exceed customer expectations in terms of quality and performance. Consistently delivering high-quality products enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduced lead times: Production planning enables manufacturers to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and reduce cycle times. By streamlining processes, manufacturers can reduce lead times, from order placement to product delivery. This agility in production allows manufacturers to respond quickly to customer demands and provide shorter lead times, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Flexibility and responsiveness: Effective production planning enables manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing customer demands and market dynamics. By having a well-structured production plan, manufacturers can adjust production volumes, prioritize orders, and introduce new products or variants efficiently. This flexibility and responsiveness contribute to customer satisfaction by ensuring that manufacturers can meet evolving customer needs promptly.
- Proactive communication: Production planning involves effective communication with customers regarding order status, delivery timelines, and any potential delays. By keeping customers informed and maintaining open lines of communication, manufacturers can manage customer expectations and address any concerns promptly. Proactive communication builds trust and enhances customer satisfaction.
Enhanced customer satisfaction and on-time delivery result in repeat business, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and customer loyalty. By consistently meeting customer expectations, manufacturers can build strong relationships with their customers, gain a competitive advantage, and position themselves as reliable partners in the market.
Effective production planning plays a pivotal role in ensuring customer satisfaction and timely product delivery, contributing to long-term business success.
Better decision-making and risk mitigation
Better decision-making and risk mitigation are significant benefits that arise from effective production planning in manufacturing. By gathering and analyzing relevant data, implementing comprehensive planning strategies, and considering potential risks, manufacturers can make informed decisions and minimize uncertainties.
This section explores the advantages of better decision-making and risk mitigation resulting from effective production planning.
- Data-driven decision-making: Production planning involves collecting and analyzing data related to production processes, resource utilization, demand patterns, and market trends. By leveraging this data, manufacturers can make informed decisions regarding production volumes, resource allocation, scheduling, and inventory management. Data-driven decision-making reduces guesswork and enables manufacturers to optimize operations and achieve better outcomes.
- Improved forecasting accuracy: Production planning requires accurate demand forecasting, which involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer insights. By utilizing advanced forecasting techniques and models, manufacturers can improve the accuracy of demand forecasts. This helps in aligning production capacities and resources accordingly, reducing the risk of underproduction or overproduction.
- Risk identification and mitigation: Effective production planning involves assessing and mitigating various risks that can impact manufacturing operations. These risks can include supply chain disruptions, equipment breakdowns, raw material shortages, or changes in customer demand. By proactively identifying risks and implementing contingency plans, manufacturers can minimize the impact of potential disruptions and ensure business continuity.
- Scenario analysis and optimization: Production planning allows manufacturers to conduct scenario analysis, evaluating different production scenarios and their potential outcomes. By modeling various scenarios, manufacturers can assess the impact of different factors, such as changes in demand, resource availability, or production constraints. This enables them to optimize production plans, identify potential bottlenecks, and make informed decisions to mitigate risks and maximize efficiency.
- Resource optimization and cost control: Effective production planning helps manufacturers optimize resource allocation, including labor, machinery, and materials. By strategically allocating resources based on demand forecasts, production capacities, and cost considerations, manufacturers can optimize operational efficiency and control costs. This ensures that resources are utilized effectively, minimizing waste and unnecessary expenses.
- Continuous improvement and adaptation: Production planning promotes a culture of continuous improvement by monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluating production outcomes. By analyzing data and performance metrics, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, implement process enhancements, and adapt production plans accordingly. Continuous improvement drives better decision-making by incorporating lessons learned and evolving to meet changing market conditions.
Better decision-making and risk mitigation enable manufacturers to navigate uncertainties, optimize operations, and drive sustainable growth. By making informed decisions based on accurate data and considering potential risks, manufacturers can enhance operational efficiency, control costs, and improve overall business performance.
Effective production planning serves as a foundation for proactive decision-making and risk mitigation, providing manufacturers with a competitive advantage in the dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Challenges in Production Planning and How to Overcome Them
Production planning in manufacturing is a complex process that involves numerous variables and considerations. Despite its importance, there are various challenges that manufacturers encounter when implementing effective production planning strategies.
This section explores the common challenges faced in production planning and provides insights into how these challenges can be overcome. By understanding and addressing these challenges, manufacturers can enhance their production planning processes and achieve greater efficiency and success.
Let’s list down the challenges before we study about them further in detail:
- Uncertain demand and market fluctuations
- Complex supply chain dynamics
- Rapid technological advancements
Uncertain Demand and Market Fluctuations
Uncertain demand and market fluctuations pose significant challenges for manufacturers in their production planning efforts. The dynamic nature of markets, changing consumer preferences, and unpredictable external factors can make demand forecasting and production scheduling complex.
This section explores the challenges associated with uncertain demand and market fluctuations and discusses strategies to overcome them. By proactively addressing these challenges, manufacturers can navigate market uncertainties, optimize production plans, and maintain a competitive edge in the ever-changing business landscape.
Utilizing forecasting techniques and scenario planning
Utilizing forecasting techniques and scenario planning is a crucial approach for manufacturers to tackle the challenges of uncertain demand and market fluctuations in production planning. These strategies enable manufacturers to make informed decisions based on anticipated demand scenarios and potential market changes.
Here is an explanation of how forecasting techniques and scenario planning can be utilized:
- Forecasting techniques: Manufacturers can employ various forecasting techniques to estimate future demand accurately. These techniques may include statistical models, trend analysis, market research, historical data analysis, and customer insights. By analyzing past data and considering market trends, manufacturers can develop forecasts that serve as a basis for production planning. These forecasts provide valuable insights into expected demand levels, seasonal variations, and potential growth opportunities.
- Scenario planning: Scenario planning involves creating different hypothetical situations or scenarios to evaluate potential outcomes and their impacts on production planning. Manufacturers can consider various scenarios such as changes in customer demand, economic conditions, competitor actions, and supply chain disruptions. By modeling these scenarios, manufacturers can assess their potential effects on production capacities, resource requirements, and inventory levels. This helps in developing contingency plans and adapting production strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
- Collaborative demand planning: Engaging in collaborative demand planning with key stakeholders, such as sales teams, marketing departments, and customers, can provide valuable insights into market dynamics and demand fluctuations. By incorporating multiple perspectives and expertise, manufacturers can gain a comprehensive understanding of market trends, customer preferences, and upcoming events that may impact demand. Collaborative demand planning fosters better communication, alignment, and accuracy in forecasting, enabling more effective production planning.
- Real-time data analysis: Manufacturers can leverage real-time data and analytics tools to monitor market trends, customer behavior, and demand patterns. By continuously analyzing data from various sources, such as point-of-sale systems, customer feedback, social media, and industry reports, manufacturers can identify emerging trends, demand fluctuations, and market opportunities. Real-time data analysis provides manufacturers with up-to-date information to adjust production plans, respond to changes promptly, and make informed decisions based on the most recent market insights.
By utilizing forecasting techniques and scenario planning, manufacturers can navigate the challenges posed by uncertain demand and market fluctuations. These strategies provide manufacturers with valuable insights into anticipated demand levels, enable proactive decision-making, and help optimize production plans accordingly.
With accurate forecasts, proactive scenario planning, and real-time data analysis, manufacturers can adapt to market dynamics, minimize risks, and seize opportunities to enhance their production planning effectiveness.
Establishing flexible production systems
Establishing flexible production systems is a key approach for manufacturers to address the challenges in production planning posed by uncertain demand and market fluctuations. Flexibility in production systems allows manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing conditions, optimize resource utilization, and meet varying customer demands.
Here is an explanation of how establishing flexible production systems can help overcome these challenges:
- Modular production processes: Implementing modular production processes enables manufacturers to configure and reconfigure production lines quickly based on changing product requirements and demand patterns. By designing production systems with modular components and interchangeable modules, manufacturers can efficiently adjust production capacities and mix to respond to shifts in demand. This flexibility ensures that resources are utilized optimally and enables rapid changes in production setups to meet evolving customer needs.
- Cross-training and multi-skilled workforce: Developing a cross-trained and multi-skilled workforce allows manufacturers to have versatile employees who can perform multiple tasks and operate different machinery. This flexibility in workforce skills enables manufacturers to reallocate labor resources based on changing production needs. When demand fluctuates or specific skills are in high demand, manufacturers can shift employees to different tasks or production lines to ensure smooth operations and maintain productivity levels.
- Agile production planning and scheduling: Implementing agile production planning and scheduling practices helps manufacturers respond quickly to changes in demand or market conditions. This approach involves shorter planning horizons, frequent review of production schedules, and the ability to make adjustments in real-time. Agile production planning allows manufacturers to allocate resources dynamically, optimize production sequences, and make rapid decisions to accommodate fluctuating demand patterns.
- Collaboration with suppliers: Building strong partnerships and collaboration with suppliers is crucial for establishing flexible production systems. Manufacturers can work closely with their suppliers to ensure timely delivery of raw materials, components, and parts. Collaborative relationships enable manufacturers to access additional resources or adjust supply chain processes swiftly when demand patterns change. This collaboration helps mitigate supply chain disruptions, maintain a steady flow of materials, and enhance overall production flexibility.
- Investment in technology and automation: Leveraging advanced technologies and automation systems enables manufacturers to achieve higher levels of flexibility in production. Robotics, advanced control systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) integration can facilitate rapid reconfiguration of production lines, efficient resource allocation, and real-time monitoring of production processes. Automation reduces dependency on manual labor and enables manufacturers to scale production up or down as needed, improving responsiveness to changes in demand.
By establishing flexible production systems, manufacturers can effectively address the challenges posed by uncertain demand and market fluctuations. Flexibility allows for efficient resource utilization, quicker response times, and the ability to adapt production capacities and processes to match varying customer requirements.
Manufacturers with flexible production systems are better positioned to navigate market uncertainties, optimize production planning, and maintain a competitive edge in the dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Complex Supply Chain Dynamics
Complex supply chain dynamics present significant challenges for manufacturers in their production planning processes. Global sourcing, multiple suppliers, lead time variability, and supply chain disruptions can create uncertainties and complexities that impact production schedules and resource allocation.
This section delves into the challenges associated with complex supply chain dynamics and explores strategies to overcome them.
By addressing these challenges, manufacturers can enhance supply chain visibility, improve coordination, and optimize production planning to ensure a smooth flow of materials and minimize disruptions.
Collaborating with suppliers and partners
Collaborating with suppliers and partners is a crucial aspect of production planning that helps manufacturers optimize their operations, streamline supply chains, and enhance overall efficiency.
This section focuses on the importance of collaboration with suppliers and partners in production planning and explores the benefits it brings. By fostering strong relationships, sharing information, and working together, manufacturers can improve supply chain visibility, mitigate risks, and achieve mutual success.
- Enhanced supply chain visibility: Collaborating with suppliers and partners allows manufacturers to gain better visibility into the entire supply chain network. By sharing information on inventory levels, production capacities, and demand forecasts, manufacturers can optimize production planning based on accurate and up-to-date data. Increased visibility helps identify potential bottlenecks, address supply chain disruptions proactively, and ensure timely delivery of materials.
- Efficient inventory management: Effective collaboration with suppliers and partners enables manufacturers to optimize inventory management. By sharing demand forecasts and production plans, manufacturers can align their inventory levels with anticipated requirements, reducing excess inventory and minimizing stockouts. Timely communication with suppliers helps coordinate material deliveries, ensuring that raw materials and components are available when needed, avoiding production delays.
- Coordinated production scheduling: Collaboration facilitates coordinated production scheduling between manufacturers and suppliers. By sharing production capacities, lead times, and constraints, manufacturers can align their production schedules with supplier capabilities. This synchronization minimizes idle time, reduces production cycle times, and improves overall operational efficiency. Coordinated scheduling also helps prevent overburdening suppliers and enables efficient resource allocation.
- Risk mitigation: Collaborating with suppliers and partners strengthens risk mitigation efforts. By sharing insights into potential risks, such as supply chain disruptions, changes in market conditions, or regulatory challenges, manufacturers can collectively develop contingency plans. This proactive approach enables quick responses to unforeseen circumstances, ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of disruptions on production planning.
- Innovation and continuous improvement: Collaboration fosters innovation and continuous improvement in production planning. Manufacturers can engage suppliers and partners in joint problem-solving, sharing ideas, and exploring opportunities for process optimization and cost reduction. By leveraging the expertise and insights of suppliers and partners, manufacturers can identify innovative solutions, implement best practices, and drive continuous improvement in production planning processes.
- Supplier relationship development: Collaborating with suppliers and partners strengthens relationships and builds long-term partnerships based on trust and mutual understanding. Strong relationships lead to better communication, transparency, and mutual support. Manufacturers can work closely with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, explore cost-saving opportunities, and access new technologies or resources that can enhance production planning effectiveness.
By collaborating with suppliers and partners, manufacturers can tap into a network of expertise, resources, and support to optimize production planning. Effective collaboration improves supply chain visibility, enables efficient inventory management, facilitates coordinated scheduling, mitigates risks, fosters innovation, and strengthens relationships.
Ultimately, this collaborative approach contributes to streamlined operations, reduced costs, and improved overall performance for manufacturers and their partners alike.
Implementing robust communication and information systems
Implementing robust communication and information systems is crucial for manufacturers in their production planning efforts. Effective communication and information exchange are essential for seamless coordination, timely decision-making, and efficient resource allocation.
This section explores the significance of robust communication and information systems in production planning and the benefits they bring. By establishing reliable communication channels and leveraging advanced information systems, manufacturers can enhance collaboration, improve data accuracy, and optimize production planning processes.
- Real-time information sharing: Robust communication systems enable real-time sharing of critical information among different stakeholders involved in production planning. Manufacturers can communicate production forecasts, demand changes, and resource requirements instantly, ensuring that all parties have access to the most up-to-date information. Real-time information sharing improves coordination, enables faster response times, and reduces miscommunication or delays.
- Streamlined collaboration: Effective communication systems facilitate seamless collaboration among various teams involved in production planning, such as sales, production, procurement, and logistics. By providing a platform for clear and efficient communication, manufacturers can ensure that all relevant parties are aligned, understand their roles and responsibilities, and work together towards common goals. Streamlined collaboration leads to better decision-making, improved efficiency, and optimized production plans.
- Centralized data management: Robust information systems allow manufacturers to centralize and manage production-related data in a structured manner. By utilizing dedicated software or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, manufacturers can capture and store data related to demand forecasts, inventory levels, production capacities, and resource utilization. Centralized data management ensures data accuracy, facilitates data analysis, and enables informed decision-making based on reliable and consistent information.
- Enhanced data analysis and insights: Advanced information systems provide manufacturers with powerful tools for data analysis and generating meaningful insights. By leveraging data analytics techniques, manufacturers can analyze historical production data, market trends, and customer behavior to identify patterns, forecast demand more accurately, and optimize production planning strategies. Enhanced data analysis helps in identifying opportunities for improvement, optimizing resource allocation, and mitigating risks.
- Automation and integration: Robust communication and information systems often involve automation and integration of various processes and systems. Automated data capture, real-time updates, and seamless integration between different software applications enable manufacturers to streamline production planning workflows. This automation reduces manual errors, enhances data accuracy, and improves overall efficiency in the production planning process.
- Performance tracking and monitoring: Effective communication and information systems enable manufacturers to track and monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) related to production planning. By collecting and analyzing data on production outputs, resource utilization, lead times, and inventory levels, manufacturers can evaluate the effectiveness of their production planning strategies and make data-driven improvements. Performance tracking facilitates continuous improvement and helps manufacturers adapt their plans to changing market dynamics.
By implementing robust communication and information systems, manufacturers can streamline communication channels, improve data accuracy, and optimize production planning processes. Effective communication and information exchange enable seamless collaboration, enhance decision-making, and promote efficient resource allocation.
With reliable communication and advanced information systems in place, manufacturers can achieve better coordination, improved efficiency, and enhanced productivity in their production planning efforts.
Rapid Technological Advancements
Rapid technological advancements have revolutionized the manufacturing industry, presenting both opportunities and challenges in production planning.
As new technologies emerge and existing ones evolve, manufacturers need to adapt their production planning processes to leverage the benefits and stay competitive. This section explores the impact of rapid technological advancements on production planning and discusses strategies to harness the potential of these technologies.
By embracing innovative solutions, manufacturers can optimize their production planning, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing.
Embracing digitization and automation
Embracing digitization and automation is a critical response to the rapid technological advancements in production planning. Digitization involves the transformation of manual and paper-based processes into digital systems, while automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention.
By leveraging digitization and automation, manufacturers can streamline their production planning processes, enhance efficiency, and unlock various benefits. Here is an explanation of how embracing digitization and automation can revolutionize production planning:
- Streamlined data management: Digitization allows manufacturers to digitize and centralize their data, eliminating the need for manual record-keeping and paper-based systems. This enables easy access to production-related information, such as demand forecasts, inventory levels, and production schedules, in a centralized digital platform. Streamlined data management enhances data accuracy, reduces errors, and facilitates real-time updates, enabling better decision-making and improved production planning.
- Improved communication and collaboration: Digitization facilitates seamless communication and collaboration among different stakeholders involved in production planning. With digital platforms and tools, manufacturers can share information, exchange updates, and collaborate in real-time. This enhances coordination, reduces miscommunication, and enables effective collaboration across teams, departments, and even geographically dispersed locations. Improved communication and collaboration ensure that everyone has access to the same information, promoting alignment and synergy in production planning efforts.
- Enhanced demand forecasting: Digitization and automation enable manufacturers to gather and analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, such as sales data, customer feedback, and market trends. Advanced analytics tools can process this data and generate accurate demand forecasts, taking into account historical patterns, seasonal variations, and emerging trends. Enhanced demand forecasting empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions in production planning, optimize resource allocation, and align production capacities with anticipated demand.
- Efficient inventory management: Digitization and automation support efficient inventory management by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and streamlining inventory tracking processes. With automated systems, manufacturers can track inventory movements, monitor stock levels, and implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory strategies. This improves inventory accuracy, reduces excess inventory, minimizes stockouts, and optimizes working capital utilization.
- Optimized production scheduling: Automation plays a crucial role in optimizing production scheduling. By leveraging advanced software and algorithms, manufacturers can automate production scheduling processes, taking into account factors such as production capacities, resource availability, and order priorities. Automated production scheduling enables efficient resource utilization, reduces idle time, minimizes changeover times, and improves overall production efficiency.
- Data-driven decision-making: Digitization and automation provide manufacturers with access to real-time data and analytics, enabling data-driven decision-making in production planning. Manufacturers can leverage data visualization tools, performance dashboards, and predictive analytics to gain insights into production performance, identify bottlenecks, and make proactive decisions to optimize production processes. Data-driven decision-making enhances agility, reduces reliance on intuition, and improves the overall effectiveness of production planning strategies.
By embracing digitization and automation, manufacturers can revolutionize their production planning processes. Streamlined data management, improved communication, enhanced demand forecasting, efficient inventory management, and optimized production scheduling.
Training and upskilling the workforce
Training and upskilling the workforce is a vital aspect of addressing the impact of rapid technological advancements on production planning. As new technologies and automation systems are implemented, it becomes essential for manufacturers to ensure that their workforce has the necessary skills to operate, maintain, and optimize these technologies.
This section focuses on the significance of training and upskilling the workforce in production planning and discusses the benefits it brings. By investing in employee development, manufacturers can empower their workforce, enhance productivity, and effectively navigate the evolving manufacturing landscape.
- Adaptability to technological changes: Rapid technological advancements require a workforce that is adaptable and capable of embracing new technologies. By providing training and upskilling opportunities, manufacturers equip their employees with the knowledge and skills needed to operate and utilize advanced production planning systems effectively. This adaptability helps manufacturers keep pace with evolving technologies, enhance operational efficiency, and remain competitive in the industry.
- Efficient utilization of technology: Training and upskilling the workforce in production planning enables employees to fully leverage the capabilities of technological solutions. When employees are trained on how to use automation tools, data analytics platforms, and production planning software, they can optimize their use, resulting in improved productivity, streamlined processes, and enhanced decision-making. Well-trained employees are more likely to identify opportunities for process improvement and utilize technology effectively to achieve production goals.
- Improved problem-solving and decision-making: Training and upskilling programs equip employees with problem-solving and analytical skills necessary for effective production planning. By providing employees with a comprehensive understanding of production processes, data analysis techniques, and decision-making frameworks, manufacturers empower their workforce to identify and address production challenges. Skilled employees are more equipped to analyze data, interpret trends, and make informed decisions that optimize production planning strategies.
- Enhanced productivity and efficiency: Training and upskilling the workforce contribute to increased productivity and efficiency in production planning. Employees who have a deep understanding of production processes, best practices, and advanced technologies can perform their tasks more efficiently, minimize errors, and maximize output. Skilled employees are also better equipped to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and implement continuous improvement initiatives, leading to enhanced productivity and cost savings.
- Employee engagement and retention: Providing training and upskilling opportunities demonstrates a commitment to employee development and growth, which boosts employee engagement and retention. Employees who receive training and have the opportunity to enhance their skills are more likely to feel valued, motivated, and invested in their work. This fosters a positive work environment and reduces turnover, leading to a more stable and knowledgeable workforce in production planning.
- Agile response to industry changes: By investing in the training and upskilling of the workforce, manufacturers build a workforce that is adaptable and capable of responding to industry changes and emerging trends. Skilled employees can quickly adapt to new technologies, implement process improvements, and adjust production plans to meet changing customer demands or market conditions. This agility enables manufacturers to stay ahead of the competition, seize new opportunities, and effectively navigate dynamic manufacturing landscapes.
Training and upskilling the workforce in production planning is a strategic investment that yields significant benefits for manufacturers. It equips employees with the necessary skills to embrace technological advancements, enhances problem-solving and decision-making capabilities, improves productivity and efficiency, boosts employee engagement, and enables agile responses to industry changes.
By prioritizing workforce development, manufacturers ensure that their production planning processes remain optimized and their workforce remains a valuable asset in an evolving manufacturing environment.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Production Planning Strategies
Case studies provide valuable insights into real-world examples of successful implementation of production planning strategies. In this section, we delve into several case studies that highlight companies that have effectively implemented production planning strategies to achieve significant improvements in their manufacturing processes.
These case studies demonstrate the practical application of production planning principles and showcase the benefits that can be realized through effective implementation.
By examining these success stories, manufacturers can gain inspiration and valuable lessons to inform their own production planning strategies.
Tesla: Streamlining production processes and reducing lead times
One notable example of a company that has successfully implemented production planning strategies to streamline production processes and reduce lead times is Tesla Inc. Tesla, an electric vehicle and clean energy company, has revolutionized the automotive industry with its innovative approach to manufacturing.
The company's commitment to efficient production planning has been instrumental in its ability to deliver electric vehicles in a timely manner and meet the increasing demand for its products.
Tesla's production planning strategies involve a combination of advanced automation, data analytics, and lean manufacturing principles. The company utilizes robotic assembly lines and advanced manufacturing technologies to optimize production efficiency and reduce manual labor. By automating repetitive tasks and leveraging sophisticated robotics, Tesla has significantly minimized production cycle times and improved overall productivity.
In addition to automation, Tesla employs advanced data analytics to enhance production planning. The company collects and analyzes real-time data on various aspects of its manufacturing processes, such as production rates, quality metrics, and supply chain performance. This data-driven approach allows Tesla to identify bottlenecks, optimize production schedules, and make informed decisions to improve overall efficiency.
Furthermore, Tesla follows lean manufacturing principles, which focus on eliminating waste, optimizing resources, and continuously improving processes. The company employs just-in-time inventory management techniques to minimize excess inventory and reduce lead times. By maintaining lean inventories and aligning production with customer demand, Tesla can rapidly respond to market fluctuations and deliver vehicles in a more efficient manner.
As a result of their streamlined production processes and focus on reducing lead times, Tesla has been able to scale its production volumes significantly. Despite the challenges associated with manufacturing electric vehicles at a large scale, Tesla has successfully increased its production output and reduced the time it takes to deliver vehicles to customers.
The case of Tesla highlights the importance of production planning in streamlining processes and reducing lead times. By leveraging automation, data analytics, and lean manufacturing principles, companies can optimize production efficiency, improve productivity, and meet customer demand in a timely manner. Tesla's success serves as an inspiration for other manufacturers seeking to streamline their production processes and achieve similar improvements in their operations.
Walmart: Implementing real-time data analytics for accurate demand forecasting
One example of a company that has successfully implemented real-time data analytics for accurate demand forecasting is Walmart. Walmart, the world's largest retailer, utilizes advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time. By leveraging their vast network of stores and online platforms, Walmart collects data on customer purchases, inventory levels, and market trends.
Walmart's demand forecasting system incorporates real-time data from various sources, including point-of-sale transactions, online sales, and external data such as weather patterns and social media sentiment. By continuously analyzing this data using advanced analytics techniques, Walmart can accurately predict customer demand at a granular level and adjust its inventory levels and production plans accordingly.
The real-time nature of Walmart's data analytics allows them to respond quickly to changes in customer preferences and market conditions. For example, during seasonal peaks or promotional events, Walmart can quickly identify trends, adjust pricing strategies, and optimize inventory allocation to meet the surge in demand effectively.
Walmart's implementation of real-time data analytics for demand forecasting has provided several benefits, including improved inventory management, reduced stockouts, and enhanced customer satisfaction. By accurately predicting demand, Walmart can ensure that products are available when customers need them, minimizing the risk of lost sales due to insufficient stock or overstocking.
Additionally, Walmart's real-time data analytics enables the company to identify demand patterns, trends, and customer preferences. This information helps Walmart optimize its product assortment, improve marketing strategies, and make data-driven decisions to enhance customer experience and drive sales.
Overall, Walmart's successful implementation of real-time data analytics for accurate demand forecasting exemplifies the importance of leveraging advanced analytics capabilities in driving effective production planning.
By harnessing real-time data, companies can optimize inventory levels, respond quickly to market changes, and deliver the right products at the right time, leading to improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Toyota: Adopting lean manufacturing principles for efficient production planning
One example of a company that has successfully adopted lean manufacturing principles for efficient production planning is Toyota. Toyota, a renowned automotive manufacturer, is widely recognized for its implementation of the Toyota Production System (TPS), which is rooted in lean manufacturing principles.
Toyota's production planning strategies focus on waste reduction, continuous improvement, and efficient resource utilization. The company emphasizes eliminating activities that do not add value to the production process, such as overproduction, excess inventory, and unnecessary transportation.
By implementing lean manufacturing principles, Toyota has achieved significant improvements in production efficiency and cost reduction. The company has adopted practices such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory management, where parts and components are delivered precisely when needed in the production process, minimizing inventory carrying costs and reducing waste.
Toyota also emphasizes the concept of kaizen, which refers to continuous improvement. This involves empowering employees at all levels to identify and suggest improvements to production processes, leading to ongoing enhancements in efficiency and quality.
The adoption of lean manufacturing principles has allowed Toyota to achieve remarkable results, including shorter lead times, reduced production costs, improved quality, and increased customer satisfaction. By eliminating waste, optimizing workflows, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, Toyota has established itself as a leader in efficient production planning.
Furthermore, Toyota's success with lean manufacturing principles has extended beyond its own operations. The company has shared its production planning practices with suppliers, encouraging them to adopt similar lean principles. This collaborative approach ensures a streamlined supply chain and synchronized production processes, leading to improved overall efficiency and customer responsiveness.
In conclusion, Toyota's successful adoption of lean manufacturing principles exemplifies the significance of efficient production planning. By embracing waste reduction, continuous improvement, and collaborative approaches, companies can optimize production processes, minimize costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Toyota's example serves as a valuable benchmark for other manufacturers seeking to implement lean manufacturing principles in their production planning strategies.
10 Recommendations for Successful Production Planning
To ensure successful production planning, here are some key recommendations:
- Invest in Advanced Technologies: Embrace technology solutions that support production planning, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, manufacturing execution systems (MES), and data analytics tools. These technologies provide real-time insights, automate processes, and enhance decision-making.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Foster strong relationships with suppliers, partners, and internal teams involved in the production process. Effective collaboration improves coordination, reduces lead times, and enhances overall efficiency.
- Implement Continuous Improvement: Adopt a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are encouraged to identify and implement process enhancements. Emphasize lean manufacturing principles, kaizen, and regular performance evaluations to drive efficiency gains.
- Foster Data-Driven Decision-Making: Leverage real-time data analytics to inform production planning decisions. Collect and analyze relevant data on demand patterns, customer preferences, inventory levels, and production performance to make informed choices and anticipate future requirements.
- Embrace Flexibility: In today's dynamic market, it's crucial to build flexibility into production planning. Be prepared to adjust production schedules, inventory levels, and resource allocation in response to changing market conditions, customer demands, and unforeseen disruptions.
- Optimize Supply Chain Collaboration: Strengthen collaboration and communication with suppliers and partners. Implement strategies like vendor-managed inventory (VMI) or collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment (CPFR) to enhance supply chain efficiency and responsiveness.
- Train and Develop Employees: Invest in training programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of employees involved in production planning. Equip them with the necessary tools and expertise to effectively analyze data, use technology, and make informed decisions.
- Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish and monitor KPIs that align with production planning goals, such as on-time delivery, inventory turnover, production cycle time, and customer satisfaction. Regularly assess performance and take corrective actions as needed.
- Regularly Review and Update Plans: Production planning is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update plans based on changing market dynamics, customer feedback, and internal performance evaluations. Continuously seek opportunities for improvement and adaptation.
- Seek Industry Best Practices: Stay updated with industry trends and best practices in production planning. Attend conferences, participate in industry networks, and collaborate with industry experts to learn from their experiences and gain insights into emerging strategies.
Future of Production Planning in an Evolving Manufacturing Landscape
As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, the future of production planning holds immense potential for driving efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. Embracing this future requires a proactive approach and a willingness to adapt to changing technologies and market dynamics.
Here are a few key considerations for shaping the future of production planning:
- Embrace Industry 4.0 Technologies: Leverage emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and predictive analytics to enhance production planning capabilities. These technologies enable real-time data integration, autonomous decision-making, predictive maintenance, and dynamic production scheduling.
- Focus on Data-driven Insights: Utilize big data analytics and real-time data streams to gain valuable insights into customer preferences, market trends, and production performance. Harness the power of predictive analytics to forecast demand accurately, optimize inventory levels, and identify potential bottlenecks in advance.
- Enable Smart Manufacturing: Adopt smart manufacturing principles and digital twins to create a virtual representation of the production process. This enables manufacturers to simulate scenarios, test different strategies, and optimize production planning outcomes before implementation.
- Foster Collaboration and Connectivity: Establish interconnected networks and collaborative platforms that facilitate seamless communication and information sharing among suppliers, partners, and customers. This enables agile response to market changes, promotes supply chain transparency, and enhances overall coordination.
- Emphasize Sustainability and Resilience: Incorporate sustainability practices into production planning, such as energy-efficient processes, waste reduction, and responsible sourcing. Additionally, develop resilient production plans that can withstand disruptions, natural disasters, and global supply chain challenges.
- Embrace Agile Production Models: Implement agile production models, such as lean and flexible manufacturing, to respond quickly to changing customer demands and market trends. This involves modular production systems, flexible workforce arrangements, and rapid reconfiguration of production lines.
- Invest in Talent and Skills Development: Focus on upskilling and reskilling the workforce to meet the demands of an evolving manufacturing landscape. Train employees in data analytics, digital technologies, and cross-functional collaboration to drive innovation and adaptability.
In conclusion, the future of production planning in manufacturing is poised to be highly dynamic and technologically advanced. By embracing emerging technologies, leveraging data-driven insights, fostering collaboration, and adopting sustainable and agile practices, manufacturers can position themselves for success in an ever-evolving industry.
Embracing this future of production planning is not only crucial for staying competitive but also for driving innovation, improving operational efficiency, and delivering customer-centric solutions. Now is the time to envision the possibilities and seize the opportunities that lie ahead.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective production planning is undeniably critical to manufacturing success. It serves as the backbone of efficient operations, enabling manufacturers to optimize resources, meet customer demands, and achieve their business objectives.
By considering the key elements of production planning, such as demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, scheduling, and sequencing, companies can unlock numerous benefits that contribute to their overall success.
First and foremost, effective production planning leads to improved productivity and efficiency. It allows manufacturers to streamline their processes, eliminate bottlenecks, and maximize the utilization of resources. This, in turn, results in higher output, reduced lead times, and increased profitability.
Furthermore, effective production planning brings about cost reduction and optimized resource allocation. By accurately forecasting demand, aligning production capacity, and implementing just-in-time inventory systems, manufacturers can minimize excess inventory, reduce storage costs, and optimize their use of materials and labor.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
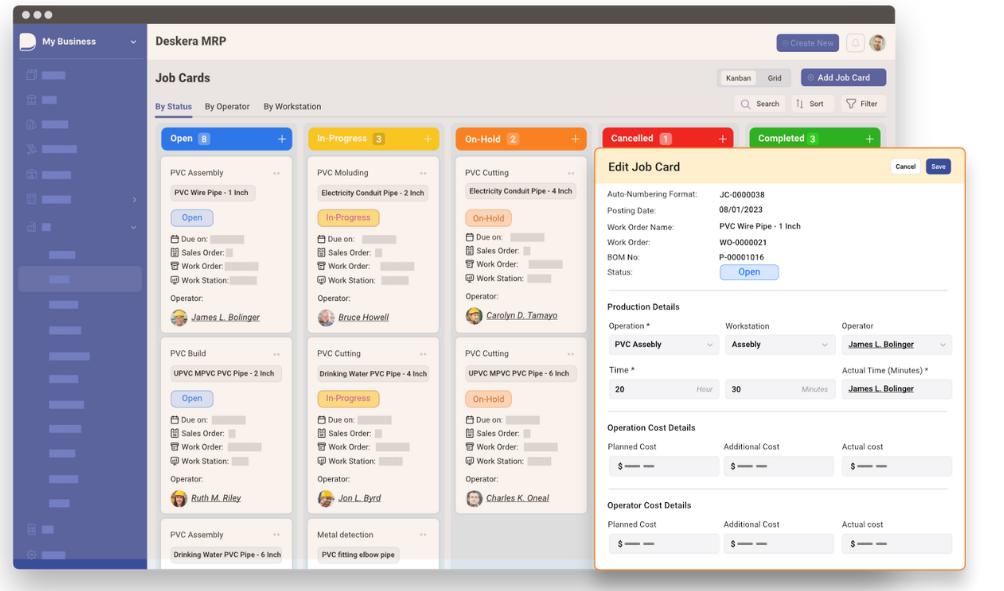
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- Effective production planning is essential for optimizing resources, maximizing productivity, and achieving manufacturing success.
- Accurate demand forecasting and analysis help manufacturers understand customer preferences and align production accordingly.
- Utilizing market research and data analysis allows manufacturers to make informed decisions and anticipate market trends.
- Evaluating existing resources and capabilities ensures that production capacity aligns with demand, avoiding over or underutilization.
- Balancing production capacity with demand is crucial to avoid stockouts or excessive inventory levels, leading to improved customer satisfaction and cost efficiency.
- Inventory management plays a vital role in minimizing excess inventory and associated costs, optimizing working capital, and reducing storage expenses.
- Implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems enables manufacturers to maintain lean inventory levels and respond quickly to fluctuating demand.
- Scheduling and sequencing production activities optimally reduces lead times, minimizes downtime, and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Effective production planning results in improved productivity, efficiency, and cost reduction through streamlined processes and resource optimization.
- Benefits of effective production planning include enhanced customer satisfaction, on-time delivery, better decision-making, and risk mitigation, leading to a competitive advantage in the market.
Related Articles












