NAM estimates that the manufacturing sector in the United States made an astounding $2.33 trillion contribution to the GDP of the nation, highlighting the industry's significance as an engine of economic prosperity.
The value-added output of the industry, according to the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, was almost $2.1 trillion. These numbers highlight the enormous impact that manufacturing has on the national economy.
In tandem with this economic prominence, the adoption of multi-channel sales strategies has emerged as a game-changing approach for manufacturers aiming to streamline operations and maximize revenue streams.

Manufacturers, whether large corporations or small enterprises operate in a complex ecosystem where production intricacies must harmonize with consumer demands. Recent trends indicate a significant shift in how products are marketed and sold, with digital platforms and online marketplaces becoming increasingly influential.
Against this backdrop, recent studies have illuminated the transformative power of multi-channel sales management in driving manufacturing efficiency.
This article delves into the realm of multi-channel sales management as a catalyst for enhanced manufacturing efficiency. We will navigate through its nuances, benefits, and challenges.
As the manufacturing sector continues to navigate an era of unprecedented change, understanding the role of multi-channel sales management becomes paramount in unlocking streamlined processes, heightened profitability, and a competitive edge in the market.
Here is all that we shall discover in this post:
- Streamlining Manufacturing With Multi-Channel Sales
- Efficiency Unleashed: Multi-Channel Manufacturing
- Revolutionizing Manufacturing via Multi-Channel
- From Factory to Customer: Sales Efficiency
- Synergizing Production and Sales Channels
- Dynamics of Multi-Channel Efficiency
- Strategies for Multi-Channel Manufacturing Success
- New Paradigm: Multi-Channel Integration
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
Streamlining Manufacturing With Multi-Channel Sales
Manufacturers are continually looking for ways to improve their operational efficiency and broaden their market reach in today's quickly changing business environment. The use of multi-channel sales tactics is one such tactic that has become very popular.
This approach involves selling products through various distribution channels, including online marketplaces, brick-and-mortar stores, social media platforms, and more. By embracing multi-channel sales, manufacturers can streamline their manufacturing processes, optimize resource allocation, and achieve greater customer engagement.
The Evolution of Sales Channels
Traditionally, businesses relied on a single sales channel, often a physical storefront, to connect with customers and drive revenue. However, as technology advanced and consumer behavior shifted, the concept of multi-channel sales emerged.
Multi-channel sales refer to the practice of offering products or services through multiple sales channels, which may include physical stores, e-commerce websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, third-party marketplaces, and more.
The rise of the internet and digital technologies has dramatically altered consumer expectations and purchasing habits. Today's consumers demand convenience, accessibility, and seamless experiences across various touchpoints. As a result, businesses have been compelled to adopt multi-channel sales strategies to remain relevant and competitive in an increasingly interconnected world.
The Multi-Channel Sales Landscape
- Diversification of Sales Channels: Manufacturers are no longer limited to traditional sales avenues. Multi-channel sales enable them to tap into a diverse range of platforms, such as e-commerce websites, third-party marketplaces (Amazon, eBay), social media storefronts, and physical retail stores. This diversification reduces dependency on a single channel and enhances resilience against market fluctuations.
- Market Reach Expansion: By engaging with consumers across multiple channels, manufacturers can access a broader audience. Online channels provide global exposure, while offline channels maintain a local presence, allowing manufacturers to target a wider demographic.
Streamlining Manufacturing Processes
- Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management: Multi-channel sales generate a wealth of data, aiding in accurate demand forecasting. Manufacturers can leverage this information to optimize inventory levels, reducing excess stock and minimizing stockouts. This data-driven approach enhances production efficiency and resource allocation.
- Production Synchronization: Multi-channel sales enable manufacturers to align production cycles with demand patterns across different channels. This synchronization minimizes idle production capacities and reduces the need for rush orders or excessive downtime.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment: Manufacturers can optimize order fulfillment by strategically locating warehouses and distribution centers. This localization reduces shipping costs and delivery times, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Customer Engagement
- Personalized Customer Experience: Multi-channel sales allow manufacturers to gather insights from various touchpoints, enabling the creation of personalized customer experiences. Tailored marketing messages and recommendations foster customer loyalty and drive repeat business.
- Omnichannel Support: Customers expect seamless interactions across all channels. Manufacturers can provide omnichannel support, enabling customers to purchase, inquire, and seek assistance effortlessly, thereby boosting satisfaction and loyalty.
Efficiency Unleashed: Multi-Channel Manufacturing
As technology continues to advance, manufacturers are embracing new strategies to optimize their operations. One such strategy that has gained traction is Multi-Channel Manufacturing (MCM). MCM is a revolutionary approach that allows manufacturers to leverage multiple channels simultaneously, resulting in streamlined processes, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experiences.
This section delves into the concept of Multi-Channel Manufacturing, its benefits, challenges, and its potential impact on the manufacturing industry.
Understanding Multi-Channel Manufacturing: Multi-Channel Manufacturing refers to the practice of utilizing multiple distribution and sales channels to produce and deliver products. Traditionally, manufacturers relied on a single channel to reach consumers, often limiting their market reach and responsiveness.
MCM, however, combines various channels such as direct-to-consumer (DTC), wholesale, retail, e-commerce, and even partnerships with third-party sellers. By diversifying their channels, manufacturers can better meet the dynamic demands of the market and consumer preferences.
Benefits of Multi-Channel Manufacturing:
- Enhanced Market Reach: By expanding across multiple channels, manufacturers can access a wider audience and tap into new markets, both geographically and demographically. This diversification reduces the risk associated with relying on a single market.
- Improved Customer Experience: MCM enables manufacturers to meet customers on their preferred platforms, whether it's in physical stores, online marketplaces, or social media. This personalized approach enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased Flexibility: Manufacturers can adapt to market fluctuations and trends more effectively through MCM. They can quickly adjust production and distribution based on real-time data from various channels, minimizing excess inventory and reducing costs.
- Data-Driven Insights: Multi-Channel Manufacturing generates a wealth of data from different sources. Analyzing this data provides valuable insights into customer behavior, allowing manufacturers to make informed decisions about product development, pricing, and marketing strategies.
- Competitive Advantage: Adopting MCM gives manufacturers a competitive edge by allowing them to offer a seamless and integrated shopping experience. This can differentiate them from competitors who rely solely on traditional manufacturing approaches.
Challenges of Multi-Channel Manufacturing:
- Complex Logistics: Operating across multiple channels introduces logistical challenges, including inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipping coordination. Manufacturers must invest in efficient systems to manage these complexities.
- Integration Efforts: Different channels often require unique technologies and processes. Integrating these systems and ensuring seamless communication between them can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Brand Consistency: Maintaining a consistent brand identity and customer experience across diverse channels can be tricky. Manufacturers must ensure that their messaging, branding, and product quality remain uniform.
- Resource Allocation: Implementing MCM demands additional resources for technology, personnel, and training. Manufacturers must carefully allocate resources to ensure the success of each channel.
- Data Security and Privacy: Handling data from various sources necessitates stringent measures to ensure data security and comply with privacy regulations.
Maximizing Output With Multi-Channel Sales
While the benefits of multi-channel sales are clear, successful implementation requires a well-thought-out and strategic approach. Here are key steps to consider:
Know Your Audience
Before expanding into multiple sales channels, it's crucial to understand your target audience. Different channels attract different demographics, and tailoring your approach to each segment is essential. Conduct market research to identify where your customers spend their time and how they prefer to shop.
Seamless Integration
Ensure that your various sales channels are seamlessly integrated. Customers should experience a consistent brand identity, pricing, and product information, regardless of the channel they choose. A unified experience helps build trust and enhances the customer journey.
Optimize for Mobile
Given the increasing use of smartphones and mobile devices for online shopping, it's essential to optimize your sales channels for mobile responsiveness. A mobile-friendly experience improves accessibility and encourages conversions.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Leverage data analytics to monitor the performance of each sales channel. Track metrics such as conversion rates, customer engagement, and sales volume to identify which channels are most effective. Use this information to allocate resources and refine your strategy over time.
Customer Support and Engagement
Provide consistent and responsive customer support across all channels. Utilize social media, chatbots, and other communication tools to engage with customers and address their inquiries promptly. A positive interaction can significantly impact customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Cross-Promotion and Marketing
Use cross-channel promotions and marketing campaigns to drive traffic and sales across various platforms. For example, you can offer exclusive discounts to customers who visit your physical store after making an online purchase, or vice versa.
Experimentation and Adaptation
The business landscape is constantly changing, and consumer preferences evolve. Be prepared to experiment with new channels and adapt your strategy based on market trends and customer feedback. Flexibility is key to long-term success.
Revolutionizing Manufacturing via Multi-Channel
Multi-channel manufacturing emerged as a response to these shifting dynamics. This approach integrates various sales channels, production methods, and customer touchpoints to create a cohesive and adaptable manufacturing ecosystem.
It recognizes that modern consumers engage with brands through multiple avenues, including e-commerce platforms, social media, physical stores, and more. As a result, manufacturers are leveraging this concept to create a seamless, customer-centric, and technologically advanced manufacturing process.
The Key Elements of Multi-Channel Manufacturing
Diverse Sales Channels
The cornerstone of multi-channel manufacturing is the integration of diverse sales channels. This includes traditional retail outlets, e-commerce platforms, mobile applications, and third-party marketplaces.
By offering products through multiple channels, manufacturers can tap into various consumer segments and meet them where they prefer to shop. This approach not only enhances market reach but also provides a competitive edge in an increasingly saturated marketplace.
Smart Manufacturing Technologies
Multi-channel manufacturing thrives on the backbone of smart manufacturing technologies. Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, and real-time data analytics enable manufacturers to monitor production processes, identify bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation.
By collecting and analyzing data from different stages of production, manufacturers can make informed decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure product quality.
Supply Chain Integration
An essential aspect of multi-channel manufacturing is the integration of the supply chain. Manufacturers collaborate closely with suppliers, distributors, and logistics partners to ensure a seamless flow of materials and finished products across various channels.
Supply chain integration reduces lead times, minimizes stockouts, and enhances overall responsiveness to changing market demands.
Personalization and Customization
Consumer preferences for personalized products and experiences have driven the adoption of customization in multi-channel manufacturing. Advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing and computer numerical control (CNC) machining enable manufacturers to produce customized products on demand.
This level of personalization not only increases customer satisfaction but also reduces waste and excess inventory.
Real-time Communication
Multi-channel manufacturing relies on real-time communication with customers, suppliers, and partners. Manufacturers leverage digital platforms, social media, and mobile apps to engage with consumers, gather feedback, and address inquiries promptly.
This direct interaction fosters brand loyalty, enhances customer trust, and facilitates agile responses to market trends.
Agile Production Processes
Traditional manufacturing often involves long lead times and inflexible production processes. Multi-channel manufacturing emphasizes agility by enabling rapid adjustments to production based on real-time market feedback and demand fluctuations.
Manufacturers can quickly scale production up or down, introduce new product variations, and respond to changing customer preferences.
The Transformative Impact on Manufacturing
The integration of multi-channel strategies into manufacturing brings forth a host of transformative impacts that redefine industry norms and elevate overall performance.
Efficiency and Resource Optimization
Multi-channel manufacturing optimizes resource allocation through data-driven insights. Manufacturers can identify inefficiencies in production, logistics, and inventory management, leading to reduced waste and cost savings.
Predictive analytics enable better demand forecasting, ensuring that production aligns with market needs, thus minimizing overproduction and underutilization of resources.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Central to multi-channel manufacturing is a heightened focus on delivering exceptional customer experiences. Manufacturers can interact directly with customers, gather feedback, and tailor products to individual preferences.
This customer-centric approach cultivates brand loyalty, increases customer retention rates, and generates positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Speed to Market
Multi-channel manufacturing accelerates the speed to market for new products and innovations. By leveraging real-time data and agile production processes, manufacturers can swiftly respond to emerging trends and introduce new products that resonate with consumer demands.
This agility provides a competitive advantage by capitalizing on market opportunities more rapidly than traditional manufacturing models.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
The integration of multi-channel strategies contributes to sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Customized and on-demand manufacturing minimizes excess inventory, reducing the need for storage and transportation.
Additionally, optimized production processes lower energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with the growing demand for environmentally responsible practices.
Global Reach
Multi-channel manufacturing transcends geographical boundaries, enabling manufacturers to reach global markets with ease.
E-commerce platforms and digital marketing strategies facilitate international sales, allowing companies to tap into diverse consumer bases and explore new growth opportunities.
From Factory to Customer: Sales Efficiency
The journey from factory to customer involves a complex web of processes, each contributing to the overall sales performance. As consumer expectations rise and technology continues to reshape the way business is conducted, optimizing the entire sales process has become essential.
The Sales Journey Unveiled
The sales journey encompasses a series of interconnected steps that extend from the factory where products are manufactured to the moment they reach the customer's hands. This journey can be divided into several key stages:
Manufacturing and Production:
The sales journey begins at the factory where products are conceived, designed, and manufactured. Streamlining production processes, minimizing waste, and ensuring product quality are crucial factors that influence sales efficiency downstream.
Distribution and Logistics:
Efficient distribution and logistics play a vital role in getting products from the factory to various sales channels. Effective supply chain management, inventory optimization, and strategic partnerships with logistics providers contribute to timely and cost-effective delivery.
Sales and Marketing:
Sales and marketing teams work together to create awareness, generate leads, and convert prospects into customers. Leveraging data-driven insights, targeted marketing campaigns, and effective sales strategies can optimize this stage and increase conversion rates.
Order Processing:
Once a customer places an order, seamless order processing is essential. Automation of order fulfillment, accurate inventory management, and real-time tracking contribute to a positive customer experience and improved sales efficiency.
Customer Engagement and Support:
Providing exceptional customer service before and after the sale enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. Prompt responses to inquiries, personalized interactions, and effective issue resolution contribute to a positive overall experience.
Delivery and Post-Purchase Experience:
The final stage involves delivering the product to the customer and ensuring their satisfaction. Efficient last-mile delivery, easy returns processes, and gathering feedback contribute to a smooth post-purchase experience.
Strategies for Enhancing Sales Efficiency
To maximize sales efficiency and optimize the journey from factory to customer, businesses can implement a range of strategies:
Data-Driven Decision Making:
Leverage data analytics to gain insights into customer preferences, buying patterns, and market trends. This information informs production quantities, inventory management, marketing strategies, and customer engagement efforts.
Process Automation:
Implement automation technologies to streamline repetitive tasks, such as order processing and inventory management. Automation reduces manual errors, accelerates processes, and allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
Real-Time Visibility:
Utilize technology to provide real-time visibility into the supply chain, inventory levels, and order status. This transparency ensures that all stakeholders have accurate information, enabling better decision-making and improved coordination.
Omni-Channel Integration:
Integrate various sales channels, including e-commerce platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, and third-party marketplaces, to provide customers with a seamless shopping experience. Centralized data and inventory management prevent overselling and underselling.
Personalization and Customer Insights:
Employ personalization techniques to tailor marketing messages and product recommendations to individual customers. Utilize customer insights to anticipate needs, offer relevant promotions, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Collaborative Partnerships:
Forge strong partnerships with suppliers, distributors, and logistics providers to ensure a smooth flow of products. Collaborative relationships contribute to reliable inventory replenishment, efficient order fulfillment, and timely delivery.
Synergizing Production and Sales Channels
In the traditional business model, production and sales were often treated as distinct and separate functions. However, the modern business landscape demands a more integrated and holistic approach.
The convergence of production and sales channels involves aligning these functions to work harmoniously towards common goals. This integration creates a virtuous cycle where production informs sales and sales influence production, resulting in a cycle of continuous improvement and growth.
Real-World Examples
Zara - Fast Fashion:
Zara, a renowned fast-fashion retailer, exemplifies the synergy between production and sales channels. The company's agile production processes allow it to respond rapidly to emerging fashion trends.
Zara's sales data is closely monitored, and this information influences production decisions. The result is a quick and efficient cycle that ensures the right products are available in stores at the right time.
Tesla - Demand-Driven Production:
Tesla's approach to production is tightly integrated with demand signals. The company leverages real-time data from its sales channels to adjust production schedules and allocate resources accordingly. This synergy allows Tesla to minimize excess inventory and tailor production to meet customer demand.
Amazon - Dynamic Fulfillment:
Amazon's fulfillment centers are a prime example of the synergy between production and sales. By leveraging advanced technologies and real-time data, Amazon optimizes its inventory management, order processing, and delivery processes.
The result is a seamless experience for customers, with products readily available and rapidly delivered.
Future Considerations
As businesses continue to evolve, the synergy between production and sales channels remains a cornerstone of success. Looking ahead, several considerations will shape this dynamic relationship:
- Technology Advancements: Continued advancements in data analytics, AI, and automation will further facilitate seamless integration and real-time collaboration between production and sales.
- Personalization: The trend toward personalized products and experiences will drive the need for production processes that can accommodate customization on a large scale.
- Sustainability: Synergy between production and sales can play a pivotal role in promoting sustainability by reducing waste, optimizing resource allocation, and aligning production with actual demand.
- Global Supply Chain Challenges: Navigating global supply chain disruptions will require agile production and sales strategies that can adapt to changing circumstances.
In a world where speed, agility, and customer-centricity are paramount, the synergy between production and sales channels provides a competitive advantage. Businesses that master this integration stand poised to not only optimize their operations but also create exceptional customer experiences and unlock untapped revenue potential.
The blueprint for success lies in fostering collaboration, embracing data-driven insights, and aligning both production and sales functions toward a common vision of growth and prosperity.
Evolution of Sales in Manufacturing
The evolution of sales in manufacturing has undergone significant changes over the years, driven by technological advancements, market dynamics, and shifts in consumer behavior. Here's an overview of the key stages in the evolution of sales in manufacturing:
Traditional Sales Approach (Pre-Industrial Revolution): Before the Industrial Revolution, manufacturing was largely artisanal and localized. Sales were conducted through direct interactions between producers and customers, often in local markets or through commissioned agents.
The focus was on building relationships and delivering personalized products to meet individual needs.
Industrial Revolution and Mass Production (Late 18th to 19th Century): The Industrial Revolution marked a transformative shift in manufacturing, enabling mass production and standardization of goods. Sales efforts began to involve broader distribution channels, such as wholesalers and retailers.
The advent of sales teams and representatives emerged to reach a wider customer base.
Emergence of Marketing and Advertising (Late 19th to Early 20th Century): With increased competition and the rise of consumerism, manufacturers began to adopt marketing and advertising strategies to promote their products.
Print media, such as newspapers and magazines, played a crucial role in reaching larger audiences. Sales messages started to focus on product features and benefits.
Direct Sales and Personal Selling (Mid to Late 20th Century): The mid-20th century saw the rise of direct sales and personal selling approaches. Salespeople developed strong relationships with clients, often engaging in door-to-door sales or face-to-face interactions.
This approach emphasized consultative selling, understanding customer needs, and providing tailored solutions.
Telemarketing and Cold Calling (Late 20th Century): As telecommunications technology advanced, telemarketing and cold calling gained popularity. Sales teams could reach potential customers over the phone, allowing for more efficient lead generation and customer outreach.
This method enabled manufacturers to expand their reach beyond local markets.
Digital Transformation and E-commerce (Late 20th Century to Present): The digital age brought about a profound shift in sales for manufacturing. E-commerce platforms emerged, enabling manufacturers to sell directly to customers online.
This eliminated intermediaries, increased market accessibility, and facilitated personalized shopping experiences. Manufacturers also began using digital marketing techniques, such as social media and search engine optimization, to enhance their online presence.
Data-Driven Sales and CRM (21st Century): Manufacturing companies embraced data-driven sales strategies with the adoption of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems.
These tools allow for better tracking of customer interactions, preferences, and purchasing behaviors. Data analytics empowered manufacturers to personalize sales approaches and predict customer needs.
Sales Automation and AI (Present and Future): In recent years, sales automation and artificial intelligence (AI) have been transforming manufacturing sales. AI-driven tools can analyze vast amounts of data, predict market trends, optimize pricing strategies, and even assist in lead qualification. Chatbots and virtual assistants provide real-time customer support and assistance throughout the sales process.
Overall, the evolution of sales in manufacturing has shifted from localized, relationship-based approaches to global, technology-driven strategies that leverage data, automation, and AI to optimize customer engagement and increase sales effectiveness.
Dynamics of Multi-Channel Efficiency
The dynamics of multi-channel efficiency refer to how effectively a business manages and optimizes its various sales and distribution channels to maximize customer reach, sales, and overall performance.
Multi-channel efficiency involves coordinating and integrating different channels, both online and offline, to provide a seamless and satisfying customer experience while achieving business objectives. Here are some key dynamics to consider:
- Channel Diversification: Businesses often utilize multiple sales channels, such as physical stores, e-commerce websites, social media platforms, marketplaces, and more. The dynamics involve selecting the right mix of channels based on target audience preferences, product characteristics, and market trends.
- Channel Integration: Successful multi-channel efficiency requires integrating different channels to ensure a consistent and unified customer experience. This includes aligning branding, messaging, pricing, and promotions across all channels.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Understanding the customer journey is crucial. Mapping out how customers interact with various channels during their buying process helps identify touchpoints and potential areas for improvement.
- Data Sharing and Analysis: Efficient multi-channel strategies involve collecting and analyzing data from different channels to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns. This data-driven approach enables businesses to tailor their strategies and offerings to customer needs.
- Inventory Management: Proper inventory management across multiple channels is essential to avoid stockouts or overstock situations. Inventory should be synchronized to provide a seamless shopping experience, whether customers are buying online or in-store.
- Personalization: Leveraging customer data and analytics allows businesses to personalize marketing messages and product recommendations across different channels. Personalization enhances customer engagement and increases the likelihood of sales.
- Omnichannel Experience: Creating an omnichannel experience involves enabling customers to switch seamlessly between channels. For instance, a customer might browse products online, visit a physical store to see items in person, and then complete the purchase online. Ensuring a smooth transition between these channels is a key dynamic.
- Technology and Automation: Utilizing technology and automation tools, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software, inventory management systems, and marketing automation, helps streamline operations and improve multi-channel efficiency.
- Channel-Specific Strategies: Each channel may require a different approach. For example, social media might focus on engagement and brand-building, while e-commerce platforms emphasize product details and conversion optimization. Tailoring strategies to each channel's strengths is important.
- Feedback and Adaptation: Regularly gather feedback from customers and monitor channel performance. Be willing to adapt and make changes based on customer preferences and market trends.
- Training and Skill Development: Sales and customer service teams should be trained to effectively manage interactions across different channels. This includes understanding the nuances of each channel and providing consistent service.
- Channel Performance Metrics: Define and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) for each channel, such as conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and customer satisfaction scores. This data helps evaluate the effectiveness of each channel and make informed decisions.
In summary, the dynamics of multi-channel efficiency involve a holistic approach to sales and distribution, focusing on seamless integration, data-driven decision-making, customer-centricity, and effective management of various channels to drive business growth and enhance customer satisfaction.
Multi-Channel Performance Metrics
Businesses are now presented with an array of marketing channels, each catering to a specific demographic and offering unique engagement opportunities. Analyzing the performance of these channels individually might not provide a holistic view of the overall marketing strategy.
Multi-channel performance metrics bridge this gap by offering a comprehensive perspective on how different channels interact and contribute to the overall business objectives.
Types of Multi-Channel Performance Metrics:
Conversion Rate: The conversion rate indicates the proportion of users who took a desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up, out of the total number of visitors to a channel. It can be calculated using the formula:
Conversion Rate = (Number of Conversions / Total Visitors) * 100
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC measures the cost incurred to acquire a single customer from a specific channel. It considers various expenses, including marketing spend and operational costs. The formula for calculating CAC is:
CAC = (Total Marketing Costs + Total Operational Costs) / Number of Acquired Customers
Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS): ROAS assesses the effectiveness of advertising campaigns by comparing the revenue generated from the campaigns to the cost of running them. The formula is:
ROAS = (Revenue from Advertising / Cost of Advertising)
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): CLTV calculates the total revenue a customer generates over their entire engagement with a business. It is a crucial metric for evaluating the long-term profitability of a marketing channel. The formula is:
CLTV = Average Purchase Value * Average Purchase Frequency * Customer Lifespan
Attribution Models: Attribution models assign credit for conversions to various touchpoints in a customer's journey. Popular models include First-Touch, Last-Touch, Linear, Time Decay, and U-Shaped, each offering a different perspective on the impact of different channels.
Calculation Methods and Formulas:
Multi-Channel Attribution: Determining the contribution of each channel to conversions involves complex attribution models. For example, the Linear Attribution model divides credit equally among all touchpoints. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Linear Attribution = 1 / Total Touchpoints
Cross-Channel Analysis: Analyzing the interactions between channels can be achieved through various methods like Venn diagrams or cross-channel matrices. These tools visually represent the overlap and complementarity of different channels in terms of audience reach and conversion.
Marketing Mix Modeling: This statistical analysis helps allocate resources to different channels optimally. It involves regression analysis to identify relationships between marketing spend and business outcomes. The formula can be:
Sales = β₀ + β₁ * (Marketing Spend on Channel 1) + β₂ * (Marketing Spend on Channel 2) + ... + ε
Real-World Applications:
Budget Allocation: Multi-channel performance metrics assist in allocating marketing budgets effectively. Channels with higher ROI can receive more investment, leading to optimal resource allocation.
Channel Optimization: By analyzing metrics like conversion rates, businesses can identify underperforming channels and optimize them for better results.
Customer Insights: Understanding multi-channel behavior provides insights into customer preferences and helps tailor marketing strategies accordingly.
Campaign Evaluation: ROAS and CLTV metrics help evaluate the success of marketing campaigns, ensuring efficient resource utilization.
Strategies for Multi-Channel Manufacturing Success
The rise of digital technology, changing consumer behaviors, and global competition have necessitated the adoption of multi-channel strategies for manufacturing success. This section explores the strategies for achieving multi-channel manufacturing success.
- Integrated Technology Infrastructure:
Implementing a robust technology infrastructure is a cornerstone of multi-channel manufacturing success. An integrated system that connects different channels, inventory management, order processing, and customer data is essential.
This ensures real-time visibility, efficient inventory management, and consistent customer information across all touchpoints.
- Customer-Centric Approach:
Manufacturing companies must prioritize understanding their customers' preferences and behaviors across various channels. This data-driven approach enables them to tailor their offerings, marketing messages, and user experiences to align with customer expectations.
- Channel Alignment and Consistency:
Maintaining a consistent brand presence and customer experience across all channels is crucial. This includes uniform product information, pricing, promotions, and messaging. Inconsistencies can lead to confusion and erode customer trust.
- Omni-Channel Fulfillment:
Offering flexible fulfillment options, such as buying online and pick up in-store (BOPIS), or ship from the store, provides customers with convenience and choice. Manufacturers need to optimize their supply chain and inventory management to support these options seamlessly.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:
Manufacturing companies should leverage data analytics to gain insights into channel performance, customer behavior, and market trends. This data-driven approach helps in refining strategies, optimizing resource allocation, and identifying growth opportunities.
- E-Commerce Integration:
Establishing a strong online presence through e-commerce platforms enables manufacturers to directly engage with customers and capture a larger share of the market. Seamless integration between e-commerce and other channels is critical for providing a unified customer experience.
- Partner Collaboration:
Collaboration with distributors, retailers, and other partners is essential for successful multi-channel manufacturing. Joint planning, shared data, and coordinated marketing efforts can create a synergistic effect and enhance the overall customer experience.
Connecting Shop Floor to Market via Multi-Channel
Connecting the shop floor to the market via a multi-channel approach involves integrating various communication and sales channels to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and improve overall business efficiency.
This approach can help your business reach customers across different touchpoints and provide a seamless shopping experience. Here's a breakdown of the steps and considerations involved:
- Channel Selection: Identify the relevant communication and sales channels that align with your business goals and target audience. Examples of channels include physical retail stores, e-commerce websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, marketplaces (e.g., Amazon, eBay), and more.
- Integration: Implement robust systems and technologies to integrate your shop floor operations with your chosen sales channels. This may involve setting up APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or utilizing e-commerce platforms that facilitate data synchronization and real-time updates between your inventory, sales, and other systems.
- Inventory Management: Ensure accurate and real-time tracking of inventory levels across all channels. This prevents overselling, reduces the risk of stockouts, and provides customers with up-to-date product availability information.
- Order Fulfillment: Establish efficient order fulfillment processes that can handle orders from different channels. This may involve optimizing warehouse operations, packaging, and shipping to ensure timely and accurate deliveries.
- Unified Customer Experience: Create a consistent and unified customer experience across all channels. Customers should be able to seamlessly transition between online and offline interactions without encountering discrepancies or confusion.
- Data Analytics: Utilize data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns across different channels. This information can guide your marketing strategies, product offerings, and channel optimization efforts.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Implement a CRM system to manage customer interactions, track communication history, and personalize marketing messages based on customer preferences gathered from various channels.
- Marketing and Promotions: Coordinate marketing efforts across channels to ensure consistent messaging and branding. Use targeted promotions and campaigns to drive traffic from one channel to another (e.g., offering online discounts to in-store shoppers).
- Customer Support: Provide seamless customer support across all channels, allowing customers to reach out for assistance through their preferred communication method. This could involve live chat, email, phone support, or social media.
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Collect feedback from customers across all channels to identify areas for improvement. Regularly analyze your multi-channel strategy's performance and make necessary adjustments to enhance the customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Mobile Integration: Given the growing importance of mobile devices, ensure that your multi-channel approach includes mobile-friendly interfaces and apps to cater to customers who prefer shopping and interacting via smartphones and tablets.
By successfully connecting your shop floor to the market via a multi-channel approach, you can expand your reach, provide a more convenient shopping experience, and position your business for growth in a rapidly evolving retail landscape.
New Paradigm: Multi-Channel Integration
The concept of "Multi-Channel Integration" represents a new paradigm in the business landscape, focusing on the seamless convergence of various sales and communication channels to create a unified and enhanced customer experience.
This approach goes beyond mere coordination of channels and emphasizes deep integration to provide customers with a consistent and interconnected journey across different touchpoints. Here's an exploration of this new paradigm and its implications:
Definition of Multi-Channel Integration: Multi-Channel Integration refers to the strategic alignment and synchronization of diverse sales and communication channels within a business, aimed at delivering a harmonious and holistic customer experience. It involves breaking down silos between different channels to enable data sharing, process automation, and real-time interactions.
Key Components and Features:
- Data Synergy: Multi-Channel Integration involves a robust data infrastructure that enables seamless sharing of customer information, purchase history, preferences, and interactions across channels. This empowers businesses to personalize experiences and anticipate customer needs.
- Omnichannel Consistency: Unlike traditional multi-channel approaches, Multi-Channel Integration strives for true omnichannel consistency. This means customers can start an interaction on one channel and seamlessly continue it on another without any disruption.
- Real-time Communication: Integration allows for real-time communication between channels, enabling instant updates on inventory, order status, promotions, and customer inquiries. This responsiveness enhances customer trust and satisfaction.
- Process Automation: Multi-Channel Integration leverages automation to streamline processes like inventory management, order fulfillment, and customer support. This reduces manual efforts, minimizes errors, and increases operational efficiency.
- Unified Customer Profiles: Every customer interaction contributes to a unified customer profile, capturing insights from different channels. This comprehensive view helps businesses understand customer behavior and tailor offerings accordingly.
- Cross-Channel Analytics: Integrated data analytics provide a holistic view of channel performance, customer journey mapping, and sales trends. These insights guide informed decision-making and future strategies.
- Agile Adaptation: Multi-Channel Integration supports agile adaptation to market changes. Businesses can quickly launch campaigns, promotions, or new channels, responding to evolving customer preferences.
- Enhanced Customer Support: Integrated channels allow customer support agents to access complete customer histories, enabling them to provide more personalized and effective assistance.
- Technology Stack: Implementing Multi-Channel Integration requires a robust technology stack, including APIs, CRM systems, marketing automation tools, e-commerce platforms, and analytics solutions.
Benefits and Impacts:
- Superior Customer Experience: Multi-Channel Integration prioritizes customer-centricity, leading to higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and increased repeat business.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Streamlined processes and automation lead to reduced operational costs, minimized redundancies, and optimized resource allocation.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that master Multi-Channel Integration gain a competitive edge by delivering unparalleled convenience and engagement to customers.
- Innovative Marketing: Integrated channels enable innovative marketing strategies, such as using one channel to promote another or launching cross-channel campaigns.
- Real-time Insights: Data-driven decision-making becomes more effective with real-time insights, fostering agility and responsiveness.
- Brand Cohesion: Customers perceive a consistent brand image and messaging across all interactions, reinforcing brand identity.
- Global Reach: Multi-Channel Integration facilitates global expansion by tailoring offerings to specific markets while maintaining a cohesive customer experience.
- Future-Proofing: The integration approach ensures businesses can adapt to emerging channels and technologies, future-proofing their operations.
Efficient Manufacturing Meets Multi-Channel Mastery
The convergence of efficient manufacturing practices with multi-channel mastery presents a compelling opportunity for businesses to optimize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and achieve competitive advantage.
This integration combines streamlined manufacturing processes with a comprehensive approach to sales and customer engagement. Here's how efficient manufacturing can synergize with multi-channel mastery:
- Demand-Driven Manufacturing: Efficient manufacturing starts with accurate demand forecasting. Multi-channel mastery provides insights into customer preferences and buying behaviors across different sales channels, enabling manufacturers to align production with actual demand.
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Applying lean principles to manufacturing processes helps minimize waste, reduce lead times, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Multi-channel mastery complements this by providing data to fine-tune production schedules based on real-time sales data.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory: Multi-channel integration enables real-time inventory tracking across various sales channels. This information can be leveraged to implement JIT inventory strategies, reducing carrying costs and optimizing stock levels.
- Supply Chain Collaboration: Efficient manufacturing requires collaboration with suppliers to ensure timely deliveries of raw materials. Multi-channel mastery can enhance communication and collaboration across the supply chain by sharing sales data and demand forecasts.
- Personalized Product Offerings: Manufacturing efficiency can be leveraged to produce personalized and customized products. Multi-channel mastery enables businesses to offer these tailored products across different channels, catering to diverse customer preferences.
- Agile Manufacturing: Efficient manufacturing systems allow for agile production adjustments. Multi-channel mastery complements this agility by providing real-time data on changing customer demands, allowing manufacturers to pivot quickly.
- Integrated Production and Sales Data: Integrating manufacturing and sales data from various channels provides a comprehensive overview of product performance, helping manufacturers refine their offerings based on customer preferences.
- Global Reach and Localization: Efficient manufacturing can adapt products for different markets. Multi-channel mastery takes this further by facilitating the distribution of localized products through global sales channels.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Combining manufacturing efficiency with multi-channel mastery creates a customer-centric approach. Products are produced efficiently while being tailored to meet customer needs and preferences.
In essence, the fusion of efficient manufacturing practices with multi-channel mastery maximizes operational effectiveness and customer engagement. This integration fosters an agile, customer-focused business model that adapts to market changes, satisfies diverse customer demands, and maintains a competitive edge.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
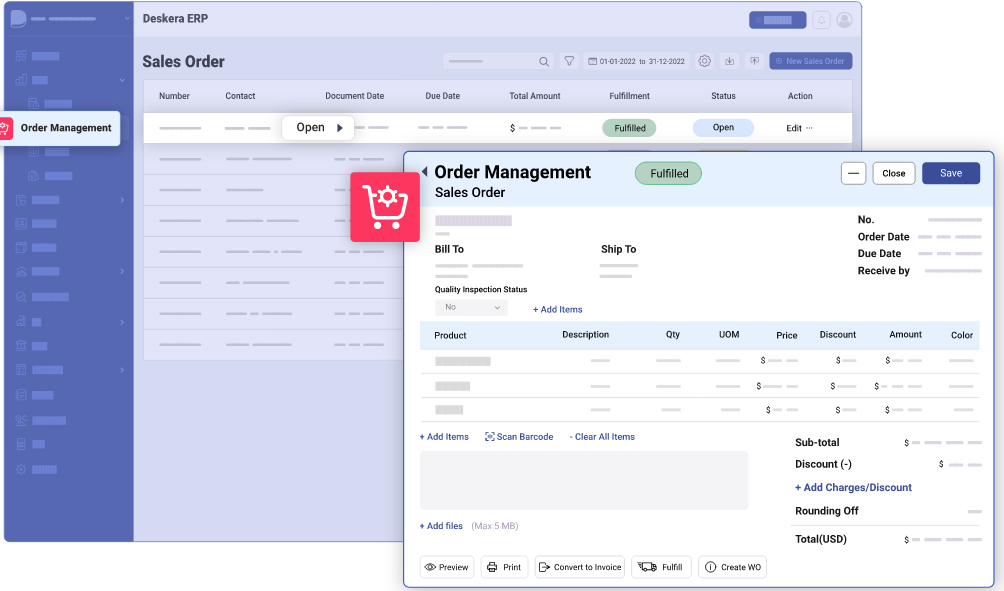
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology not only speeds up payroll processing but also allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more. This is your chance to grow your business, increase earnings, and improve the efficiency of the entire production process.
Conclusion
The integration of multi-channel sales management into manufacturing operations emerges as a formidable strategy to boost efficiency, optimize processes, and elevate overall business performance.
This article has delved into the various dimensions of multi-channel sales management, shedding light on its transformative impact and providing valuable insights for manufacturers seeking to enhance their operational excellence.
Throughout this exploration, it became evident that embracing multi-channel sales management is more than just a trend – it's a fundamental shift in how manufacturers approach their sales and distribution strategies.
The benefits of multi-channel sales management are manifold. Manufacturers can tap into a wider customer base, expand market reach, and connect with consumers through their preferred channels. This not only increases revenue streams but also cultivates stronger customer relationships and fosters brand loyalty.
Online platforms empower manufacturers to create virtual storefronts, allowing customers to shop conveniently from anywhere at any time. This dynamic shift in the purchasing landscape is a game-changer for manufacturers looking to adapt to evolving consumer behaviors.
Moreover, data-driven decision-making takes center stage in multi-channel sales management. By harnessing data and analytics, manufacturers can gain insights into customer preferences, buying patterns, and channel performance. These insights inform strategic decisions, enabling manufacturers to allocate resources effectively and tailor marketing efforts for maximum impact.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-channel sales management is a transformative strategy that can significantly enhance manufacturing efficiency by diversifying sales avenues and integrating digital platforms.
- Manufacturers can tap into a wider customer base and expand market reach by engaging with consumers through their preferred channels, leading to increased revenue streams and brand loyalty.
- Real-time inventory synchronization across channels prevents errors, stockouts, and overstocking, optimizing order fulfillment and enhancing both customer satisfaction and internal processes.
- Data and analytics-driven decision-making empower manufacturers with insights into customer preferences, buying patterns, and channel performance, facilitating effective resource allocation.
- Consistency in customer experience across all sales channels builds trust, reinforces brand identity, and contributes to a positive perception of the manufacturer.
- Challenges such as channel conflicts, inventory discrepancies, and maintaining consistent branding require careful consideration and proactive management.
- Integration of customer relationship management (CRM) systems enables personalized interactions, efficient communication, and informed decision-making, nurturing strong customer relationships.
- Social media platforms serve as powerful tools for engaging customers, sharing product information, gathering real-time feedback, and enhancing overall multi-channel sales management.
- Manufacturers must adapt to changing market dynamics and consumer preferences by embracing new technologies and strategies to drive innovation and efficiency.
- Multi-channel sales management demands strategic planning, proactive risk management, and continuous improvement efforts to address challenges and seize opportunities effectively.
Related Articles













