Are you someone who wants to open a new shop or establishment in the State of Haryana? Do you want to make sure that you comply with all the statutory requirements for the same?
If your answer to both of these questions is yes, then you are on the right page. This article will be your complete guide by covering all the important details of the Haryana Shops Commercial Establishments Act.

The Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules are applicable to all the shops and commercial establishments in the areas as notified by the Government of Haryana. This Act was enacted with the main purpose of protecting the rights of employees while providing regulations of payment of wages, terms of service, work hours, rest intervals, and so on.
To be your complete guide to the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, this article will cover the following topics:
- Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
- Important Definitions in the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
- Registration under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
- Exemptions under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
- Employment Conditions for Young People
- Hours of Employment
- Intervals for Rest or Meals
- Opening and Closing Hours
- Employees’ Off Day in a Week
- Close Day for the Employees
- Holidays for the Employees
- Leave for the Employees
- Wages for Close Days and During Leave Period
- Wage Period and Deductions from Wages
- Realization of Compensation
- Penalties Imposed on Employers
- Prohibition of Employment of Children
- Conditions of Employment of Women
- Notice of Removal
- Notice by Employee
- Records to be Showcased and Maintained by the Employers
- Enforcement and Appointment of Inspectors
- Forms for Compliances
- How Can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
Enacted with the main purpose of protecting the rights of employees, the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules follow the Punjab Shops And Commercial Establishments Act of 1958. This Act is applicable to all the shops, and commercial establishments based in the areas notified accordingly by the Government of Haryana.
In order to protect the employees of the shops and commercial establishments, this Act provides regulations for the following:
- Payment of wages
- Terms of service
- Working hours
- Rest intervals
- Over-time work
- Opening and closing hours
- Closed days
- Holidays
- Leaves
- Maternity leave and benefits
- Working conditions
- Rules of employment of children
- Records maintenance of the employees
And so on. Be it inter-state migrant workers, or intra-state migrant workers, or even the local workers, this Act aims to protect the vulnerable workers when there are no other overarching acts to ensure that.
Important Definitions in the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
The important definitions in the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules are:
- Commercial Establishment: It refers to any premises wherein any trade, business, or profession is carried on for-profit and includes journalistic or printing establishment and premises in which business of banking, insurance, stocks and shares, brokerage or produce exchange is carried on or which is used as a restaurant, hotel, boarding, or eating-house, cinema, theater, or other places of public entertainment or any other place which the Government may declare, through a notification in the Official Gazette to be a commercial establishment for the purposes of this Act.
- Establishment: It refers to a shop or a commercial establishment.
- Shop: It means any premises where any business or trade is carried on or where services are rendered to customers and includes store-rooms, offices, godowns, sale depots, or warehouses, whether in the same premises or otherwise, used in connection with such trade or business, but does not include a commercial establishment or a shop attached to a factory where the persons employed in the shop are allowed the benefits provided for the workers under the Factories Act.
- Employee: An employee refers to a person who is wholly or principally employed in, or in connection with, an establishment, whether working on permanent, periodical, contract, or piece-rate wages or on a commission basis, even though he receives no reward for his labor, but does not include a member of the employer’s family.
- Government: Here, Government means the Government of Haryana.
- Register of Establishment: It means a register that is maintained for the registration of establishments under this Act.
- Registration Certificate: It refers to the certificate that will show the registration of an establishment.
Note: “As per the provisions of this Act, any employment in the service of the employer of an establishment upon any work, whether within the establishment or outside it, but which relates to, or is connected with, or is ancillary to the business carried on at the establishment, shall be deemed to be about the business of the establishment.”
Registration under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
It is mandatory that within a period of thirty days, establishments that exist in the areas where the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules is applicable or where this Act is extended (the date on which the Act comes into force or the date on which the Act is extended, as the applicable case may be), the new establishments in such areas (the date on which the establishment commences its work will be considered), will have to send to the prescribed authority concerned, a statement in the prescribed form, accompanied by such fees as may be prescribed.
The form should contain:
- The name of the employer and the manager (if any)
- Postal address of the establishment
- The name (if any) of the establishment
- Number of persons employed in the establishment
And other such particulars as may be prescribed to you through this Act.
After the concerned authorities receive your statement and the prescribed fees, and if they are satisfied by the correctness of your statement, then they will register your establishment in the register of establishments in such a manner as may be prescribed.
They will then issue in a prescribed form a registration certificate to you- the employer. If at any time, the inspector ensuring the execution of the provisions of this Act demands that the registration certificate be shown to him, you, as an employer, will have to.
After every three years, the registration certificate shall have to be renewed. However, a grace time of thirty days will be allowed for the renewal of the certificate after the payment of a prescribed fee.
Remember, it would be your responsibility as an employer to notify the prescribed authority if there have been any changes in respect of any information contained in your statement in the prescribed form within seven days from the date on which the change took place. If the authorities are satisfied with its correctness, then they would make the same changes in the register of establishments and, if necessary, even amend your registration certificate.
Similarly, if you shut down your establishment, then you are liable to inform the prescribed authorities the same in writing within ten days of you closing your establishment. Once the concerned authority is satisfied with the correctness of such information, they will remove the name of your establishment from the register of establishments and even cancel your registration certificate.
Note: If you fail to comply with the provisions of this section, or there is any contravention, then on conviction, you would be liable to pay your applicable fine, which might extend to include your prescribed registration or renewal fee, as the case may be.
Exemptions under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules
The exemptions under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules are:
- Offices of or under the Central or State Government (except commercial undertakings), the Reserve Bank of India, any railway administration, or any local authority
- Any railway service, water transport service, air service, tramway, postal, telegraph, or telephone service, any system of public conservancy or sanitation, or any industry, business, or undertaking that supplies power, light, or water to the public
- Railway dining cars
- Offices of lawyers
- Any person employed in the business of any establishment mentioned above
- Any person whose hours of employment are regulated by or under the Factories Act 1948, except the provisions of sub-section (3), (4), and (5) of Section 7 of this Act insofar as they relate to employment in a factory
- Any person whose work is inherently intermittent
- Establishment of stamp vendors and petition writers
Note: The Government, through a notification, may declare that any class of establishments or persons specified therein to not be exempted from the operation of such provisions of this Act as may be specified in the notification.
Employment Conditions for Young People
The conditions for employment of young people under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Acts and Rules are:
- For each young person employed in the business of an establishment, their total number of working hours should exceed thirty hours in any one week or five hours in any one day, exclusive of intervals for meals and rest.
- A young person employed in the business of an establishment shall not be employed continuously for more than three hours without an interval of at least half an hour for a meal or rest.
- With respect to the employment of young persons employed in the business of establishments or any class of them, the Government might prescribe further conditions, including conditions regarding the daily period of employment of those persons (if it finds such a condition to be necessary). No individual shall then be employed without fulfilling these conditions.
- If you, as an employer, fail to comply with the provisions of this section of this Act or there is any contravention, then on conviction, you would be liable to pay the due fines.
- Where, in proceedings for an offense under this section, the person in respect of whom the offense was committed was a young person, and he appears to the court to have been at the date of the commission of the offense a young person, he or she shall, for the purposes of this Act, be presumed at that date to have been a young person unless the contrary is proved.
Hours of Employment
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Acts and Rules, the hours of employment are:
- Subject to the provisions of this Act, no person shall be employed about the business of an establishment for more than nine hours in any one day or forty-eight hours in a week.
- During seasonal or exceptional pressure of work, an employee may be allowed to work for more hours than the working hours specified above. However, the total number of overtime hours worked by any employee should not exceed fifty in a quarter. Additionally, for the overtime working hours, he or she should be paid remuneration at twice the rate of his normal wages calculated by the hour.
- On any day or in any week, you should not employ about the business of the establishment, any person who has been previously employed on that day or in that week in another establishment or a factory for a longer period than shall, together with the time during which he has been previously employed on that day or in that week in such other establishment or factory, exceed the number of hours permitted by this Act (sub-section 3).
- If there are any proceedings launched against you because you contravened with the provisions of the sub-section 3, then you will have to defend yourself by proving that you did not know and could not, with reasonable diligence, ascertain that the person was previously employed by the employer of the other establishment or factory.
- No person is allowed to work about the business of an establishment or two or more establishments or an establishment and a factory in excess of the period during which he was lawfully employed under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Acts and Rules.
Intervals for Rest or Meals
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Acts and Rules, no employee, except a watchman, chowkidar, or a guard, be allowed to work continuously in an establishment for more than five hours before he gets an interval for rest for at least half an hour.
Additionally, an employee’s daily period of work, inclusive of his interval for rest, be fixed and spread in such a manner that it is not for more than twelve hours in a day.
Opening and Closing Hours
The Government will be fixing the opening and closing hours of all classes of establishments through a notification. However, different opening and closing hours may be fixed for different classes of establishments and for different areas, provided that the Government permits an establishment attached to a factory to observe such opening and closing hours as directed by the Government.
Employees’ Off Day in a Week
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, no employee shall be required to work on:
- A close day, in any establishment which is required to observe a close day.
- One day in a week, in any other establishment.
- Before the opening hours of their establishment and after the closing hours of their establishment.
Note: A watchman may be allowed or required to work on an off day under this section if he is allowed another off day in the week.
Close Day for the Employees
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, every establishment must remain closed on every Sunday unless provided otherwise by the provisions of this Act. In case your establishment is attached to a factory, then you can substitute the close day of your establishment to correspond with the close day of the factory in the same manner and subject to the same conditions as are laid down on this behalf in the Factories Act, 1948.
Further on, the Government may also fix any other day to be the close day for the establishments through a notification. This would be applicable to every class of establishments for the whole of the State, or a part thereof, as mentioned in the notification by the Government.
You may, however, open your establishment on a close day if such a day happens to coincide with a festival and if the employees who work for you on that day are paid remuneration at double the rate of their normal wages calculated by the hour.
Note: You can change the working hours and period of interval once in a quarter of the year. However, you will have to do so after giving due intimation at least fifteen days before the change will be taking place in the prescribed form to the prescribed authority.
Holidays for the Employees
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, each of your employees will be allowed:
- A holiday with wages on the Independence Day, Republic Day, and Mahatma Gandhi’s Birthday
- Other than these three days, they would also be allowed five other holidays with wages in a year. These should be in connection with such festivals as the Government may declare from time to time by the notification.
Note: If you require your employee or employees to work on these holidays, then they should be paid remuneration at the double the rate of their normal wages calculated by the hour.
Leave for the Employees
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, the provisions for leaves for the employees are:
- For each employee who has been in your establishment’s employment for not less than twenty days in a year will be entitled to one day’s earned leave for every such twenty days. If, however, your employee is a young person, then he or she will be entitled to one day’s earned leave for every fifteen days of employment during the year.
- If you discharge or dismiss your employee from his or her services during the course of the year, then he or she will be entitled to leave with wages or wage in lieu of unused leave at the rates laid down in the clause.
- While calculating the leaves of your employees as per the provisions of this section of this Act, a fraction of half a day or more shall be treated as one day’s leave, and a fraction of less than half a day shall be ignored.
- If your employee does not in one year take all of the leaves given to him, then any leave not taken by him will be added to the leaves that he can take in the succeeding year. However, as per the specific agreement between you and your employee, the total number of leaves that can be carried forward to a succeeding year cannot exceed forty if the employee is a young person and thirty in other cases. If there is any award, contract of service, or agreement that provides for a longer leave with wages or weekly holidays than those provided under this section, then your employees will be entitled to only such longer leave or weekly holidays as the case may be.
- When your employee applies for his or her leave, it must be granted within fifteen days of the application unless you have a valid reason for not doing so, which must be communicated to them in writing. However, if any such leaves are refused, your employees can apply for them again, and if they do, they will be allowed during the year.
- Notwithstanding anything contained in the previously discussed sub-section, every employee in your establishment must be given paid seven days of casual leave and paid seven days of sick leave in a year.
Note: When calculating the period of employment of your employee, the period during which he or she was on leave, as well as the off days in a week, will be included. Also, the unused leave of your employee will not be taken into account in computing the period of any notice required to be given before their dismissal, removal, or discharge.
Wages for Close Days and During Leave Period
As per the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Acts and Rules, the provisions for wages for close days and during leave periods are:
- For every employee who has been employed in your establishment for a period of fifteen days or more shall receive for every off day in a week (as referred to earlier in the section- Employees’ Off Day in a Week) wages at the rate of not less than the average daily wages earned by him or her for the days on which he or she worked during the week immediately preceding every such off day.
- For each leave allowed to him (under the provisions of the section discussed previously- Leave for the Employees), your employee should be paid at the rate equal to the daily average of his total full-time earnings for the days on which he worked during the month immediately preceding his leave. This would be exclusive of any bonus or overtime but inclusive of dearness allowances and the cash equivalent of the advantage accruing through the concessional sale to the employee of food grains and other articles.
- For each employee who has been allowed a leave of at least five days in case of a young person and four days in case of others, they should be paid the wages due for the period of leave allowed, before his or her leave begins, and if demanded so by them.
Wage Period and Deductions from Wages
As per the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, the provisions in regards to the wage period are:
- As a person who is responsible for the payment of wages to your employees, you are obligated to fix a period during which these wages will become payable.
- None of your wage periods for your employees should exceed a period of one month.
- You are obligated to ensure that your employees are paid before the expiry of the seventh date from the date on which the payment of wages became due.
- In case of the termination of the employment of your employee, either by you or by someone on behalf of you, then you are liable to pay the wages earned by your employee as well as the remuneration in lieu of the unused period of due leave before the expiry of the second working day after the date of the termination of their employment. This is also applicable in cases where your employee quits on or before the next payday.
As per the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, the provisions in regards to the deductions from wages are:
- You have to pay the wages to your employees without any deductions, except those that are authorized by or under the Payment of Wages Act, 1936. If this is applicable, then the deduction would be made to the extent that it is applicable to your employee, and in such a manner, to such an extent, and subject to such conditions as are specified in the Payment of Wages Act 1936.
Realization of Compensation
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, if a judicial magistrate is satisfied that your employees have not been paid their due wages, then you will be directed to pay the due wages, along with compensation that cannot exceed eight times the amount of wages withheld.
Thus, for the purposes of the recovery of the due wages, the amount of wages withheld and the compensation payable with them will be considered as a fine imposed under this Act, in addition to the penalty (as covered in the section- Penalties Imposed on Employers) that would be imposed and realized.
Penalties Imposed on Employers
Subject to the provision of the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Acts and Rules, whoever contravenes any of the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder, and no penalty has been provided for such contravention in this Act, then once convicted, would become liable to pay a fine not exceeding hundred rupees for the first offense, and three hundred rupees for every subsequent offense.
Note: The fine for the subsequent offenses within the same year should not be less than one hundred rupees in any case.
Power to Compound Offenses
Notwithstanding anything contained in this Act or the rules covered within, if the compounding authority is notified by the Government in the Official Gazette, then he or she will compound the offense committed under this Act and its rules.
This means that in such cases, the compounding authority will discharge you (here, an offender) by recovering a sum of money not less than fifty percent of the maximum amount of fine prescribed under this Act or in the rules framed thereunder.
However, if your violations are related to the registration of shops and commercial establishments, then the compounding authority will recover the prescribed fee in addition to the full amount of the fine. Remember, no offense of the same nature will be compoundable if it is committed more than twice in a year.
If you want to appeal against the order of the compounding authority, then you will have to do it within thirty days from the date of the order of the compounding authority. You will have to appeal before the appellate authority as will be notified by the Government. The decisions of the appellate authority will be final and binding.
Note: No appeal shall be maintainable unless you have deposited the amount of the fine with the said authority.
Unless you are given a notice in writing, which informs you of the grounds on which you are being penalized, no penalty can be imposed on you.
Note: The compounding and appellate authority will have all the powers of a civil court under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908. This means that while exercising powers under that Act, they will be able to:
- Summon and enforce the attendance of witnesses
- Require the discovery and production of any document.
- Requisition any public record or copy thereof from any office or court.
- Receive evidence on affidavit
- Issue commissions for the examination of documents or witnesses.
Note: No prosecution, suit, or other legal proceedings can be undertaken against any public servant or any other person in the service of the State or Central Government, acting under the direction of any such public servant, for anything in good faith done or intended to be done in pursuance of the provisions of this Act or of any rule made thereunder.
Cognizance of Offenses
Remember, no court will take cognizance of any offense punishable under this Act or any rules made thereunder, or of the abetment of or attempt to commit such an offense, save on a complaint made by the concerned employee or by an officer who is authorized to do so in writing by the Government.
Prohibition of Employment of Children
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, children who have not completed 14 years of age cannot be employed in any establishment.
Conditions of Employment of Women
As per the provisions of the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules,
- No women shall be required or permitted to work, whether as an employee or otherwise, in any establishment during the night. This is applicable to all establishments unless an establishment is engaged in the treatment and care of the sick, the destitute, the infirm, or the mentally unfit.
- Knowingly, no employer of any establishment shall employ a woman, and neither shall any woman get employed in any establishment during six weeks following the day of her confinement or miscarriage.
- If it finds fit, the Government may also prescribe further conditions for the employment of women in your establishment. These conditions might be related to the daily period of employment, leave, and other such matters. You are obliged to make sure that you are not employing any woman without meeting these conditions.
Maternity Benefits
As per the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, the provisions related to maternity benefits are:
- If your woman employee has been continuously employed by you in a particular establishment of yours or in your other establishments for a period of at least six months preceding the date of her delivery, then she will be entitled to receive a payment of maternity benefit from her employer, and as prescribed by the Government for every day during the six weeks immediately preceding and including the day of her delivery, and for each day of the six weeks following her delivery.
- The manner in which you will be required to pay the maternity benefit may also be prescribed by the Government.
Note: If on any day during the six weeks preceding her delivery, she attends work and receives payment for the same, then the above-mentioned provision for the payment will not be applicable for that day.
Notice of Removal
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, the provisions for notice of removal are:
- You cannot remove any employee from service unless you have given one month’s prior notice or pay in lieu thereof has been given to him or her.
- However, if you are removing an employee due to their misconduct, which has been established on record as well, then you are not obligated to give one-month prior notice or pay in lieu thereof.
- You are obligated to give one month’s prior notice or pay in lieu thereof only if that particular employee has been working continuously for you for a period of at least three months.
- If any contravention to the provisions of this Act has been observed, and if the Judicial Magistrate is satisfied that you have removed an employee without a reasonable cause, then the Judicial Magistrate, with reasons recorded in writing, award compensation to that particular employee equivalent to two months salary. However, such a claim of contravention must be made by your employee within six months from the date of his removal.
Note: The amount that will be payable to your employee as compensation under this section of this Act will be in addition to the fine payable (As discussed in Penalties Imposed on Employers). Additionally, none of your employees who have already been awarded compensation under this section shall be entitled to bring a civil suit in respect of the same claim.
Notice by Employee
As per the provisions of the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules,
- No employee, who has been in your service continuously for a period of three months, can terminate their employment unless he has given you notice thirty days prior or pay in lieu thereof.
- If the previously mentioned provision is contravened by the employee, then you can forfeit that employee’s unpaid wages for a period not exceeding thirty days.
Records to be Showcased and Maintained by the Employers
As per the provisions of the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishment Act and Rules,
- You will be required to exhibit a notice in your establishment in the prescribed format, which mentions the close day, the working hours, and the period of interval of employed persons, if any, and such other particulars as may be prescribed.
- You will be required to keep a record in the prescribed format and manner of the working hours, rest intervals, leaves availed by your employees, and overtime working hours of your employees, which will have to be entered separately in the record.
- You will have to maintain a register dedicated to marking the attendance of your employees within one hour of the start of their duty. In the case of overtime, each entry dedicated to it should mention the time at which overtime has commenced, as well as the time at which it has ended.
- For all your employees who have completed three continuous months in your establishment, you will need to keep their photograph. If your employee fails to supply such a photograph within fifteen days of the completion of such service, then his or her failure to do so should be recorded by you under his or her signature.
- As prescribed, you will have to maintain such other records and registers and display such other notices for the purposes of this Act.
- If you have contravened any of the provisions of this section of this Act, then on conviction, you will be liable to a fine not exceeding five rupees for every day on which the contravention continues or occurs.
- If you, with an intent to deceive makes, or causes or allows to be made in any such register, record, or notice as aforesaid an entry which is to your knowledge false in any material particular, or you willfully omit or causes or allowed to be omitted from any such register, record, or notice, an entry that is required to be made therein, on conviction, you would become liable to imprisonment for a term not more than three months, or to a fine that will not be less than twenty-five rupees, and can extend to two hundred rupees, or both.
Inspection of Registers and Calling for Information
Under the provision of the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules,
- It is your duty as an employer to make available for inspection of such officer, as may be prescribed, all accounts or other records required to be kept for the purposes of this Act and to give such officer any other information in connection therewith as may be required.
- If you contravene this provision of this section of this Act, or if you willfully obstruct the inspecting authority in the exercise of the powers under this Act, or if you conceal or prevent any employee of your establishment from appearing before or being examined by the authority, then on conviction, you would be liable to a fine which is at least of twenty-five rupees and may extend to two hundred rupees as well.
Enforcement and Appointment of Inspectors
As per the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules,
- Through a notification, the Government may appoint such persons or class of persons that it finds fit to be inspecting officers for the purposes of this Act within such local limits as it may respectively assign to them.
- Subject to the rules made by the Government on this behalf, the inspecting officer within the local limits for which he or she is appointed,
- Enter at all reasonable times and with such assistants, if any, being persons in the service of Government or of any local authority as he thinks fit, any place which is or which he has reasons to believe to be an establishment.
- Make such examination of the premises and of any prescribed records, registers, and notices, and take on the spot or otherwise evidence of any persons as he or she may deem necessary for carrying out the purposes of this Act. This, however, is applicable only as long as no one is required to answer any question or give any evidence tending to incriminate him.
Note: Every inspection officer appointed under this section will be considered to be a public servant within the meaning of Section 21 of the Indian Penal Code.
Forms for Compliances
Under the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules, the forms for compliance are:
Form A: Intimation of Working Hours and Intervals
INTIMATION UNDER SECTION 10(1)(1) OF THE PUNJAB SHOPS AND COMMERCIAL ESTABLISHMENT ACT 1959
(Rule 3 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishment rules 1958)
To
The Inspector of Shops and Commercial
Establishment Circle___________
I hereby furnish the following information, which is correct to the best of my knowledge.
The working hours and the periods of interval of the persons employed in my establishment are fixed below shall take effect from dated___________
|
Name of the employee and father’s or husband’s name |
Working Hours |
Interval for Rest |
||||
|
From |
To |
From |
To |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
||
|
1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
Young Persons |
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
6. |
Other Persons |
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
7. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
8. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
9. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
10. |
|
|
|
|
|
(Sd.)_________________
Name and Percentage of employer
with full address
Form B: Display of Notices
NOTICE TO BE EXHIBITED UNDERSECTION 20(1) OF THE SHOPSAND COMMERCIAL ESTABLISHMENT ACT 1958
(Rule 4 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishments Rules 1958)
1. Close day if any Year
2. Opening hours of the Establishment Closing hours of the Establishment
3. Name and parentage of the Employer
4. Name of the Manager if any,
5. Name of the Establishment
6. Name of Business
7. Full address
8.
|
Name of the employee and father’s name
or husband’s name |
Working Hours |
Interval of Rest |
Weekly off day |
|||
|
From |
To |
From |
To |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
1. |
Young Persons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Other Persons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. Date of declaration__________________
10. Inspections by authorities________________________
Signature of the employer (Name and full Address)
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
Form C: Register of Employees
REGISTER OF EMPLOYEES
(Rules 5 of Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishments Rules 1958)
Name of Establishment Year and Month Name of employee Father’s/Husbands name
Age Nature of work whether employed on daily monthly contract or piece-rate.
Date of appointment__________________
|
Supervisor |
Interval for Rest and Meals |
Overtime |
Leave |
Signature of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date |
Fr om |
To tal |
Fro m |
Tot al |
Tot al wor kers |
Fro m |
To |
Total |
Re mun erat ion due |
Ded ucti on |
Dat e of appl icati on |
Dat e of gra nt |
Re mar ks |
Em ploy er |
Em plo ye e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Total hours of overtime employment during the month_____________________
2. Leave availed during the month______________________
Note. – If an employee has worked with previous employer the hours worked with him may be shown in the Remarks column.
Form D: Register of Wages of Employees
REGISTER OF WAGES OF EMPLOYEES
(Rule 5 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishments Rules 1958)
Name of employee and Father’s name or Husband’s name Month Year Wages Fixed______________________________
|
Arrears |
Wages |
Deductio |
Advances |
Payment |
Signatu |
Signature |
Stamp |
REMARK |
|
from last |
due |
ns as |
made on |
s made |
re of |
of |
|
S |
|
month |
|
shown in |
(date) |
|
employ |
employer |
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
ee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wages |
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
earned |
balance |
|||||||
|
during |
carried |
|||||||
|
the |
over |
|||||||
|
month |
|
|||||||
|
Ordinary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overtime |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stamp |
|
Form E: Register of Deductions
Form E - REGISTER OF DEDUCTIONS
(Rules 5 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishment Rules 1958)
Name of the establishment Year Acts and omissions approved by the authorities_________________
|
Serial No. |
Name of employee |
Parentage |
Wage |
Wages Payable |
Amount deducted |
Fault for which
deductions made |
Date of deduction |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Whether employee showed cause against deductions |
Amount of deduction and purpose for
which utilised |
Date of utilisation |
Balance with the
employer |
Signature of employee |
Signature of employer |
REMARKS |
|
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form F: Statement for Registration of Establishments
STATEMENT FOR REGISTRATION OF ESTABLISHMENT UNDER SECTION 13 OF THE PUNJAB SHOPS AND COMMERCIAL ESTABLISHMENTS ACT, 1958
(Rule 13 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishments Rules, 1958)
To
The Inspector of Shops and Commercial Establishment Circle
I hereby submit this statement for the Registration / renewal of my establishment for the year The information furnished hereunder is correct to the best of my knowledge.
1. Name and parentage of employer__________________
2. Name of Manager,if any___________________
3. Name of the establishment___________________
4. Full Postal address of the establishment____________________
5. Nature of Business________________________
6. No. of employees if any:
Young Persons Other Persons________________________
7. No. and date of previous registration certificate surrendered______________
8. Date___________________
Signature of employer___________________
(To be filled in by the authority)
R. No. The establishment mentioned above is hereby registered till 21st March,19
Inspector,
Shops and Commercial Establishments.
Circle
Form G: Form of Change of Information
Form G - FORM OF CHANGE IN RESPECT OF INFORMATION CONTAINED IN STATEMENT REQUIRED BY SUB-SECTION 13 OF THE PUNJAB SHOPS AND COMMERCIAL ESTABLISHMENTS ACT, 1958
(Rule 13 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial establishments rules, 1958)
To
The Inspector of Shops and Commercial Establishment Circle
I hereby notify that the following change has with effect from (date) taken place in respect of the information relating to the establishment as supplied by me in my statement dated .
My registration certificate number is_________________________
Date________________
(Here mention the change)
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Dated____________________
(Signature of the employer) __________________
Note. -- The change is required under sub-section (4) of Section 13 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1958, to be notified by the employer within seven days after the change has taken place.
Form H: Registration of Establishment
REGISTRATION OF ESTABLISHMENT REQUIRED UNDER SECTION 13(2)(1)OF THE PUNJAB SHOPS AND COMMERCIAL ESTABLISHMENT ACT, 1958
(Rule 13 of the Punjab Shops and Commercial Establishments Rules 1958)
Name of the Circle
Name of Town________________
|
Registration |
|
Number of employees |
|
||||||||
|
Serial No. |
No. |
Date |
Name of the employer |
Name and address
of establish ment |
Young persons |
Other perso
ns |
Tot al |
Date of rene wal
1959 -60 |
Date of renew
al 1960- 61 |
Date of renew
al 1961- 62 |
Remar ks |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How Can Deskera Help You?
Deskera People is your HR dedicated cloud-based software that will let you select your own payroll schedules based on the different groups of employees or contractors and their different pay schedules like weekly, semi-monthly, monthly, and more. This will thus let you all handle all industry-specific pay frequencies.
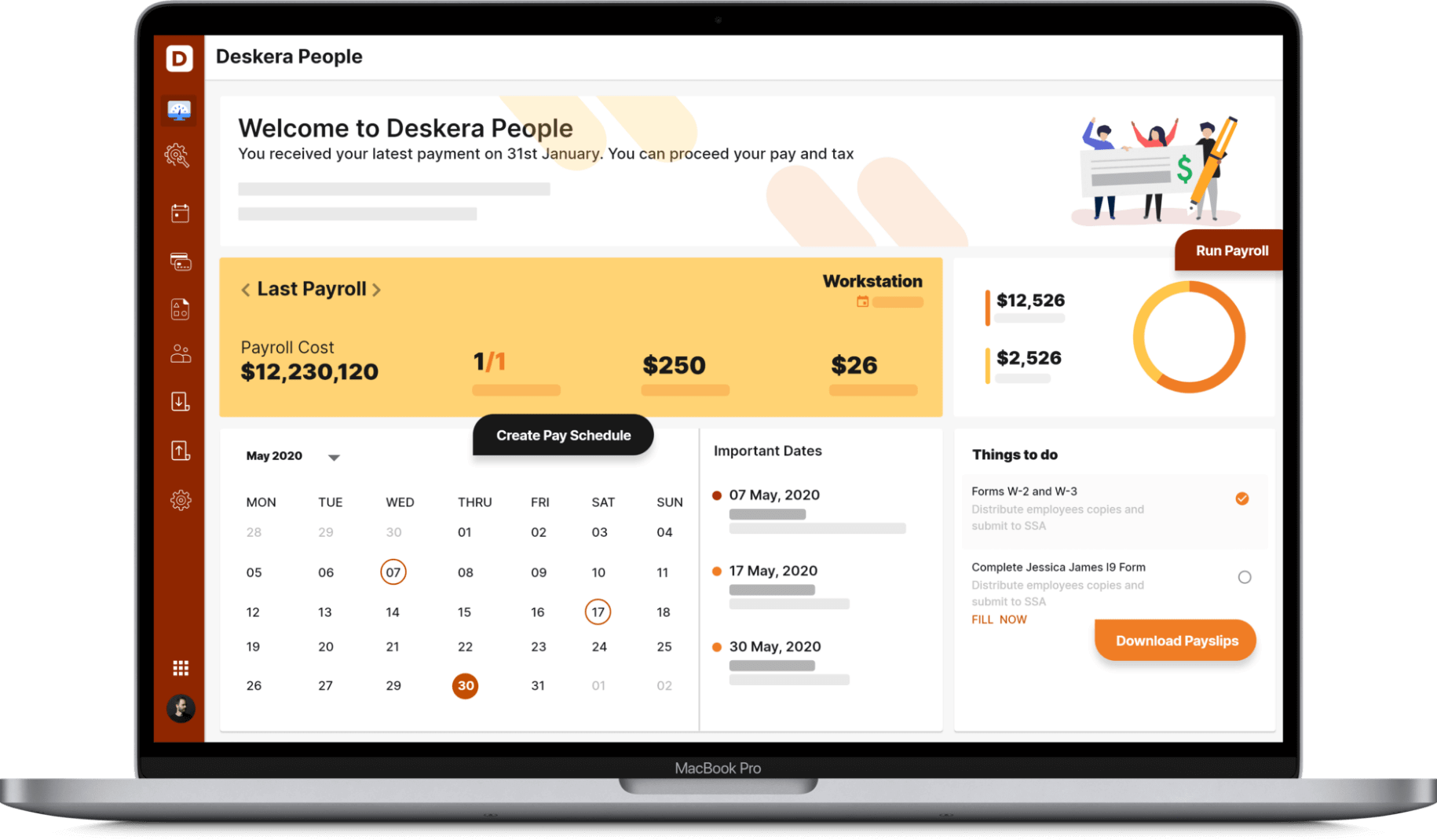
Additionally, you will also be able to set up a custom pay package with custom components like employee bonuses, overtime remuneration, voluntary deductions, etc. These will be automatically identified by Deskera People, and thereafter each of your employees’ wages will be calculated accordingly.
In fact, through Deskera People Direct Deposit Service, you would be able to send your employees’ salary directly to their bank accounts as soon as their payroll is processed.
Lastly, through Deskera People, you would also be able to maintain detailed records of each of your employees, including their personal details as well. All of this will help you in complying with the provisions of the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules.
Key Takeaways
Enacted with the main purpose of protecting the rights of the employees, the Haryana Shops and Commercial Establishments Act and Rules are applicable to all the shops and commercial establishments in the areas that are notified by the Government of Haryana. This Act follows the Punjab Shops And Commercial Establishments Act of 1958.
Starting from the number of working hours, payment of wages and overtime wages, rest hours, leaves, close days, holidays, rules for employment of children, conditions for employment of women, maternity leave and benefit, rules regarding notice period for dismissal of employees, and many such factors, this Act covers it all, including inspectors, registration of the establishment, registers to be maintained and penalties in cases of non-compliance.
On November 21, 2018, the Government of Haryana exempted all commercial establishments and establishments from requiring periodic renewal of their registration certificates with immediate effect.
To keep up with all such changes, filling out all the forms required to be compliant, maintaining the register of your employees in one place, and basically ensuring that you are fulfilling all statutory requirements, Deskera People would be your best assistant.
Related Articles















