As a small business owner, do you come across many payroll taxes? One such significant tax is FUTA. The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) is a finance tax paid by employers on worker compensation. The expense is 6.0% on the first $7,000 a worker earns; any profit past $7,000 is not taxed.

The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) is a part of regulation that enforces a payroll tax on any business with workers. The income it produces is apportioned to state unemployment insurance agencies and used to subsidize unemployment benefits for individuals who are unemployed.
Following are the topics we shall cover:
- What is FUTA?
- Reporting FUTA
- Who is Exempt from FUTA tax?
- How Often Do You Pay FUTA Tax?
- Credit Reduction State
- State Unemployment Taxes (SUTA) vs. FUTA
- Difference between FUTA and FICA
What is FUTA?
FUTA is a government regulation that raises revenue to manage unemployment insurance and occupation service programs in each state. The FUTA was passed in 1939. As coordinated by the Act, businesses are expected to pay yearly or quarterly government unemployment taxes; they make up a piece of what is ordinarily known as payroll charges.
Practically speaking, the genuine rate paid is typically 0.6%. FUTA expects that employers add to the federal unemployment pool which covers workers who fit the bill for unemployment benefits. Assuming that you have at least one worker who works nearly 20 weeks out of the year or have paid workers basically $1,500 in any quarter, you are liable for paying FUTA taxes.
Key pointers to remember about FUTA:
There is no FUTA tax for independently employed people. In this manner, assuming you are a partner, there is no FUTA on your distributive portion of partnership benefits. Assuming you draw in self-employed entities in your business, you don't pay FUTA on payments to them.
FUTA is a tax that businesses pay to the federal government. Workers don't settle any FUTA charge or have anything deducted from their checks. The tax applies just to the first $7,000 of wages to every worker (other than the compensation that is excluded from FUTA). This wage limit has been in effect since 1983, yet could be changed by Congress later on.
FUTA Tax:
Numerous businesses are obliged to pay both a particular Federal and a state unemployment tax. This tax reserve, as the IRS (Internal Revenue Service) notices, is then allotted to pay unemployment remuneration to workers who have lost their jobs, except if dismissal came about because of unfortunate misconduct.
While various states may have their own guidelines in regards to unemployment benefits, now and again they come up short on satisfactory assets to cover unemployment remuneration. If a state needs to acquire money from the Federal government, the FUTA tax fund can supply monetary help for unemployment benefits.
Any business that has paid $1,500 or more in compensation during any calendar quarter, should pay FUTA tax on the first $7,000 of wages for every worker each year. Anything past this edge, be that as it may, is non-taxable. In contrast to charges under FICA (or the Federal Insurance Contributions Acts), the business pays this tax rather than the worker.
Any businesses that have recruited at least one or more workers for a minimum part of a day, for at least 20 weeks in a single year, should settle FUTA tax.
Calculating FUTA Tax:
FUTA Tax per worker= (Taxable Wage Base Limit) x (FUTA Tax Rate)
With the Taxable Wage Base Limit at $7,000,
FUTA Tax per worker= $7,000 x 6% (0.06) = $420
Consider a business having 10 workers. We should perceive how to work out the FUTA tax.
FUTA Tax Rate = 6% (0.06)
Number of workers= 10
FUTA Tax per worker = $7,000 x 6% (0.06) = $420
The FUTA charge for the business will be $4,200. [($7,000 x 10) x $0.06]
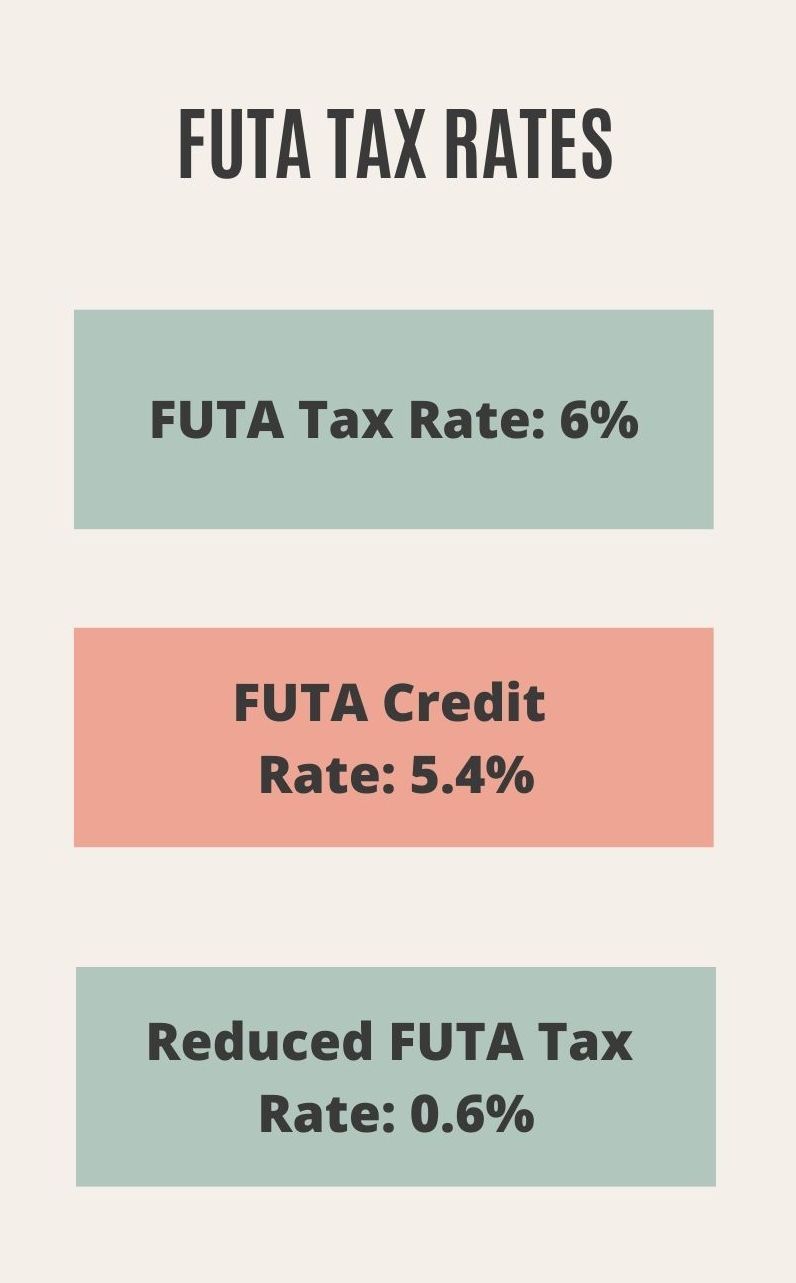
FUTA tax rate:
The fundamental rate of FUTA charge is 6%. Be that as it may, organizations that pay state unemployment insurance can get a government tax reduction of up to 5.4%. This can bring the current FUTA tax rate down to as low as 0.6%. Applied to the first $7,000 of every worker's wages just, this likens to simply $42 per worker.
The tax applies to the first $7,000 you paid to every worker as wages during the year. The $7,000 is frequently alluded to as the government or FUTA wage base. Your state wage base might be different in light of the particular state's rules.
This credit rate may not be reachable in the event that a state has not wrapped up reimbursing the Federal government in the wake of borrowing from the FUTA tax fund to cover unemployment benefits. In the event that a state fails reimbursement of a Federal loan following two successive years, it becomes known as a 'credit reduction state'.
By and large, assuming you paid wages subject to state unemployment tax, you might get a credit of up to 5.4% of FUTA taxable wages when you document your Form 940. Assuming you're qualified for the maximum 5.4% credit, the FUTA tax rate after the credit is 0.6%.
For the most part, you're qualified for the maximum credit assuming you settled upon your state unemployment taxes completely, on time, and the state is not determined to be a credit reduction state.
FUTA Tax Credit:
The maximum FUTA tax reduction is 5.4%. Assuming the business is qualified for the maximum credit, it implies that the tax rate will be just 0.6% i.e: 6% short 5.4%.
The uplifting news is, assuming you pay SUTA (State Unemployment Tax Act) on time, you are qualified for a FUTA tax break.
Payments are expected quarterly. In the tax world, it's normal to have quarterly expense cutoff times. Similar applies for FUTA with deadlines of April 30th, July 31st, October 31st, and January 31st. Ensure you pay on time or, in all likelihood you could face a penalty somewhere in the range of 2% and 15%. implies that the tax rate will be just 0.6% i.e: 6% short 5.4%.
The employers can claim this maximum credit of 5.4% assuming that they fulfill both the circumstances beneath:
- Settled upon state unemployment taxes on time completely
- Not working under the state that has any outstanding government unemployment insurance loans
A business that fits the bill for the full tax credit will have a duty pace of 0.6%. This results in the minimum amount of FUTA tax of $42 per worker.
Workers don't pay FUTA. There are some payroll taxes that workers add to, similar to Social Security and Medicare taxes however FUTA is one that the sole responsibility falls on the business.
While these are a portion of the top things you ought to understand about FUTA, on the off chance that you're eager for more data, here are six additional tips to take care of you.
Since calculating finance taxes can be confounding and overpowering, going to an online payroll provider can help. Alongside Social Security, Medicare, and other finance taxes, a finance service for entrepreneurs can likewise assist with overseeing FUTA and guarantee that you're staying consistent.
Reporting FUTA
Despite the fact that there is a yearly reporting for FUTA (clarified next), the tax should be deposited at least quarterly assuming it is more than $500 per quarter. All the more explicitly, in the event that FUTA tax liability is more than $500 for the year, you should deposit something like one quarterly installment.
Assuming FUTA tax liability is $500 or less in a quarter, convey it forward to the following quarter and keep on doing as such until your total FUTA tax liability is more than $500. By then, you should deposit your FUTA tax for the quarter.
How to report FUTA?
FUTA tax should be accounted for utilizing Form 940, or the Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment Tax Return. This should be finished assuming that the accompanying measures are met:
- An organization has paid an employee(s) $1,500 or more in any quarter of the current or earlier year.
- An organization has recruited 1+ workers for any part of a day in 20+ long stretches of the current or earlier year.
Form 940 should be filed by January 31st of the particular year. For the 2021 fiscal year, for instance, the form ought to be completed by January 31st, 2022. Deposits are made through the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS). In the event that you don't surpass the $500 edge, you can pay the tax when you record your yearly FUTA government form.
The IRS commands managers to report the FUTA tax on Form 940, Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment Tax Return. The form is utilized to answer to the IRS the FUTA taxes kept for the year the payments made each quarter. Form 940 is expected by January 31 consistently. On the off chance that you possess deposited FUTA taxes on time for all quarters, you might file the form by February 10.
The tax is accounted for on Form 940, Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return. The return should be documented if:
- You paid wages of $1,500 or more to workers in any calendar quarter during the current or earlier year.
- You have at least one worker for a minimum part of a day in any 20 distinct weeks in the current or earlier year.
- Extraordinary guidelines apply to employers of agricultural laborers. They are in the Instructions to Form 943.
- Returns can be sent or e-filed (the IRS has a list of approved suppliers here). On the off chance that you don't know how to ascertain, file, or meet your FUTA commitments, a tax expert can help.
The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA), with state unemployment systems, accommodates payments of unemployment remuneration to laborers who have lost their positions.
Most employers pay both a Federal and a state unemployment tax. For a list of state unemployment tax offices, visit the U.S. Division of Labor's Contacts for State UI Tax Information and Assistance. Just the employer pays FUTA tax; it isn't deducted from the worker's wages.
Who should file?
There are three tests used to decide if you should pay FUTA tax: an overall test, agricultural employers, and household employers test.
Assuming that a business was sold or moved during the year, every business that meets one of the circumstances above should record Form 940. In any case, do exclude any wages paid by the predecessor business on your Form 940 except if you're a successor employer.
Who is Exempt from FUTA tax?
Any organization that pays under $1,500 to a representative for every quarter doesn't have to settle FUTA tax. Moreover, as indicated by the IRS, any organization that is absolved from income tax under section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code is additionally excluded from FUTA charge.
Compensation that a business pays to their spouse, a child younger than 21, or guardians doesn't consider FUTA compensation. Besides, payments, for example, fringe benefits, group term life insurance benefits, and manager contributions to worker retirement accounts are excluded from the tax calculation for the federal unemployment tax.
How Often Do You Pay FUTA Tax?
How frequently FUTA tax should be paid relies upon the number of workers you have, and this will decide the amount you owe. FUTA tax is, by and large, are paid quarterly. Assuming that an organization's FUTA tax adds up to more than $500 for the year, they should make somewhere around one quarterly payment.
Assuming FUTA tax liability is $500 or less for a quarter, the sum ought to be extended into the following quarter until the cumulative liability is more than $500.Organizations that never surpass the $500 figure for the year can pay FUTA tax in their yearly tax return.
Credit Reduction State
This is a state that hasn't reimbursed money it acquired from the national government to pay unemployment benefits. The Department of Labor runs the advance program and decides the credit reduction states every year.
Assuming a business pays compensation that is dependent upon the unemployment tax laws of a credit reduction state, the credit a business might get for state unemployment tax paid is diminished, bringing about a more noteworthy measure of government unemployment tax due while recording its Form 940 and including the Schedule A (Form 940), Multi-State Employer and Credit Reduction Information.
You should utilize Schedule A (Form 940) assuming you paid wages to workers in more than one state or on the other hand assuming you paid wages in any state that is liable to credit reduction.
State Unemployment Taxes (SUTA) vs. FUTA
Many states gather an extra unemployment tax from businesses, known as the state unemployment tax (SUTA). These reach from 2% to 5% of a worker's wages.
Paying SUTA taxes can diminish the weight of FUTA charges. Managers can assume a tax acknowledgment of up to 5.4% of available pay on the off chance that they cover state unemployment taxes and on time. This sum is deducted from how many workers government unemployment taxes are owed.
A business that meets all requirements for the most noteworthy credit will have a net tax rate of 0.6% (determined as 6% short 5.4%). Along these lines, the base amount a business can pay in FUTA tax is $42 per worker. Nonetheless, organizations that are absolved from state unemployment taxes don't fit the bill for the FUTA credit.
Difference between FUTA and FICA
FUTA, which is for unemployment benefits for workers, ought to be recognized from FICA, which is a different tax paid by the two employers and workers to give Social Security and Medicare benefits. The FICA charge is 6.2 percent on taxable remuneration up to a proper sum yearly (e.g., $137,700 in 2020) for the Social Security segment and 1.45 percent of taxable pay for the Medicare segment (with next as far as possible).
A similar amount is paid by the business and the worker. For instance, in the event that a worker acquires $50,000, the business' FICA charge is $3,825 (6.2% of $50,000 + 1.45% of $50,000). The worker pays the equivalent $3,825, which is kept from their wages.
How Deskera Can help You?
Deskera People helps digitize and automate HR processes like hiring, payroll,leave, attendance, expenses, and more.
Deskera People is a cloud-based software which will help to create and assign custom pay components to an employee in light of your requirements. Deskera People will distinguish those components assigned to the employee and naturally compute the wages taking in the specific conditions which can be designed in each component like pre and post-tax deductions.
Conclusion
FUTA, or the Federal Unemployment Tax Act, is an arrangement intended to assist states with paying unemployment benefits to those whose work contracts have been fired. However, this is just applicable on the off chance that specialists have not been excused for absurd wrongdoing.
There are a few inquiries encompassing compliance matters and the different obligations of the business with respect to FUTA tax. On the off chance that you're an entrepreneur and have staff, regardless of whether you just utilize a couple of laborers, it's significant to comprehend FUTA, including its present rates, how regularly it ought to be paid, and who may be excluded.
Key takeaways:
- The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) made a program to assist states with paying for unemployment benefits for laborers who have been fired (other than for unfortunate misconduct).
Assuming that you pay wages of $1,500 or more to workers, you should pay this tax every year. This tax is notwithstanding any state unemployment insurance you might owe.
- Businesses who likewise pay their state unemployment insurance can get a government tax reduction of up to 5.4%, coming about in a successful FUTA tax rate of 0.6%.
- The funds in the record are utilized for unemployment remuneration installments to laborers who have lost their positions. Albeit how much the FUTA finance charge depends on workers' wages, it is imposed on businesses, not their workers. At the end of the day, it isn't deducted from a laborer's wages.
- In the event that a state has not reimbursed acquiring from the national government to cover its unemployment benefits obligation, it very well might be a "credit reduction state."
This implies how much the credit for state unemployment tax is diminished and the FUTA rate is really expanded. The designation of credit reduction states is made by the Department of Labor.
Related Articles












