Did you ever wonder if anyone is keeping record of the accidents which happen in a factory? According to Tamil Nadu Factories Act, Every employer is expected to maintain a Register of Accidents in a specific format.
In this article we will dive deep into Form-26 Register of Accidents. Following are the topics covered:
Tamil Nadu Factories Rules, 1950
The Factories Act is a part of social legislation that was created to protect worker welfare, health, and safety on the job. The Tamil Nadu Factories Rules, 1950, are the rules that the State of Tamil Nadu has developed in accordance with the Act.
Compliance
- Form 1 - Application for permission to construct, extend or take into use any building as a factory
- Form 25-B - Service Card
- Form 26 - Register of Accidents
- Form 10 - Overtime muster roll for exempted workers
- Form 2 - Application for registration and grant or renewal of license for the year
- Form 3 - Register of Factories
- Form 3-A - Notice of change of Manager
- Form 4 - Registration and License to work a factory
- Form 11 - Notice of Periods of work for adult workers and children
- Form 18-B - Report of further details of accident
- Form 5 - Certificate of fitness
- Form 12 - Register of adult workers
- Form 21 - Half Yearly Return
- Form 6 - Humidity Register
- Form 7 - Record of lime-washing, painting, etc
- Form 14 - Register for young person workers
- Form 22 - Combined Annual Return
- Form 8 - Report of examination of pressure vessel or plant
- Form 15 - Register of leave with wages
- Form 25 - Muster Roll
- Form 8-A - Report of examination of water-sealed gas-holder
- Form 17 - Health Register
- Form 9 - Register of Compensatory holidays
- Form 18 - Report of Accident
- Form 25-A - Muster Roll of Adult Workers
Applicability
The Act is applicable to all factories, including those owned and operated by the State and the Federal Government, in locations where:
• Ten or more workers are engaged using power;
• At least 20 people are employed without the usage of electricity.
• Less than 10 employees, if the State Government is notified of the action.
Amendments to the Tamil Nadu Factories Rules, 1950
The Governor of Tamil Nadu hereby amends the Tamil Nadu Factories Rules, 1950 in accordance with the authority granted by Section 112 of the Factories Act, 1948 (Central Act LXIII of 1948), the draught of which was earlier published in accordance with Section 115 of the aforementioned Act:
In the said Rules,-
(1) In rule 86, for the expression "column (3) of Form No. 12", the expression "column (6) of Form No. 12" shall be substituted;
(2) In rule 88, in sub-rule (2), for the expression "fifteen paise", the expression "five rupees" shall be substituted;
(3) for rule 103, the following rule shall be substituted, namely:-.
Maintenance of Muster Roll and Registers
(1) Every factory's manager is required to keep a muster roll of every worker working there on Form No. 25, and entries must be made at the start of each work session.
(2) The Manager shall maintain the muster roll for a period of three years following the last entry and shall make it easily available for inspection by the inspector at all times during working hours or when any work is being done in the factory.
(3) The muster roll and Register of Compensatory Holidays in Form No. 25, along with the Register of Adult Workers and Young Persons in Form No. 12, Register of Leave with Wages in Form No. 15, and Register of Adult Workers and Young Persons in Form No. 12 shall be deemed to serve the purposes of the Registers and Muster Roll specified hereunder, namely: -
(i) The Tamil Nadu Contract Labor (Regulation and Abolition) Rules, 1975's Form XXVI for the registration of contract labor employment, Form XXVII for the registration of wages, and Form XXIX for the registration of advances, deductions for damage or loss, and fines;
(ii) Register of Workmen Employed by Contractor in Form XIII in accordance with Rule 49, Muster Roll Register in Form XVII in accordance with Sub-Rule (2), Clause (a), Register of Wages in Form XVIII in accordance with Sub-Rule (2), Clause (a), Register of Deductions for Damage or Loss in Form XIX in accordance with Sub-Rule (2), Clause (c), Register of Fines in Form XX in accordance with clause (c) of sub-rule (2) of Rule 52, Register of Advances in Form XXI as per clause (c) of sub-rule (2) of rule 52 and Register of Overtime in Form XXII as per clause (d) of sub-rule (2) of Rule 52 of the Inter-State Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Service) (Tamil Nadu) Rules, 1983;
(iii) The Tamil Nadu Payment of Wages Rules, 1937 list the following: Register of Fines in Form I as per Rule 3, Register of Deductions for Damage or Loss Caused to the Employer by the Negligence or Default of the Employees in Form II as per Rule 4, and Register of Advances made to Employees in Form III as per Rule 17.
(iv) The Minimum Wages (Tamil Nadu) Rules, 1953, include the following: Register of Fines in Form I as per sub-rule (4) of Rule 21, Register of Deductions for Damage or Loss Caused to the Employer by the Negligence or Default of the Employed Person in Form II as per sub-rule (4) of Rule 21, Overtime Register for Workers in Form IV as per sub-rule (2) of Rule 26, Muster Roll in Form V as per sub-rule (5) of of rule 27 and Register of Employees in Form XI as per sub-rule (6) of rule 27 of the Minimum Wages (Tamil Nadu) Rules, 1953;
(v) Tamil Nadu Maternity Benefit Rules, 1967, Rule 3, Sub-rule (1), Muster Roll in Form A;
(vi) Tamil Nadu Industrial Establishments (National, Festival and Special Holidays) Rules, 1959, Rule 7, Sub-rule (1), Register of National, Festival and Special Holidays in Form VI;
(vii) Tamil Nadu Industrial Establishments (Conferment of Permanent Status to Workmen) Rules, 1981, sub-rule (1), "Register of Workmen in Form I";
(viii) Tamil Nadu Payment of Subsistence Allowance Rules, 1981, Rule 3: Register of Employees Placed Under Suspension in Form No. 1;
(ix) Register of Wages in Form B, Register of Fines and Unpaid
Form-26 Register of Accidents
Every employer is required to keep a Form 26 - Register of Accidents in the format specified.
The Tamil Nadu Factories Rules
FORM 26
(Prescribed under Rule 104)
Register of Accidents
Name and address of the factory___________________________________________________
Calendar year _____________________Registration number of the factory_______________
Health and Welfare
Prohibition of employment of young persons in certain process
(1) No young person under the age of 18 may work in any of the following activities:
(a) the use of an asbestos spray to apply the material; or
(b) the dismantling of asbestos lagging for removal; or
(c) cleaning of asbestos-containing sacks or other containers; or
(d) the use of portable power saws to cut through asbestos-containing materials; or
(2) the cleaning, scaling, or scurfing of boilers, combustion chambers, or smoke boxes, where his employment exposes him to dust that is of a type and quantity that is likely to be harmful or repulsive to others who operate in those environments.
Restriction in the use of lead
(i) Lead paint may not be sprayed on any portion of a ship or vessel's interior while painting.
(ii) Wherever lead sheathing work is done to create cold storage chambers in ships, effective exhaust systems with portable extractors should be supplied to keep lead fumes out of the small areas.
Provision of stretchers, ambulances and ambulance rooms, etc.
(i) In every shipyard, there must be
(a) at least two numbers of suitably constructed sling stretchers or other similar appliances for lifting injured people;
(b) at least two numbers of carrying or wheel stretchers; and at least two numbers of sling stretchers; all of these must be available and kept in stock.
(c) at least two sets of appropriate breathing equipment and oxygen, and the stretchers, appliances, and equipment so provided must be kept in good condition.
(ii) A responsible person or persons must always be on hand at every shipyard during working hours with the authority to call for an ambulance or other form of transportation in the event of an accident or illness. In every shipyard, reputable copies of a notice identifying that individual, or as the case may be, these persons, must be posted in conspicuous locations.
(iii) In every shipyard, excluding a dry dock that is available for hire:
(a) where the average number of employees exceeds 500; or
(b) A properly constructed ambulance room with at least the equipment listed in rule 64 of the Tamil Nadu Factories Rules, 1950, must be provided and kept in good order and clean condition in any workplace where the average number of people employed exceeds 100 and the workplace is more than ten miles from a hospital.
The room must only be used for rest and treatment, and it must be under the supervision of someone who is sufficiently qualified and accessible during working hours. All accidents and illnesses that are treated in the room must also be documented.
Restrictions In the employment of young persons
(i) No young person shall be employed in connection with the operations in a shipyard on a stage from which, or in any part of a ship where, he is liable to fall a distance of more than 2 m. or into water where there is a risk of drowning, until he has been employed in a shipyard or shipyards for at least six months.
(ii) Any young person under the age of sixteen must be supervised by an experienced worker when working in shipyard activities.
Safety supervisions
A person skilled in the work of such yards shall be appointed and employed solely to exercise general supervision of the observance of this rule and to promote the safe conduct of the work generally in every shipyard, other than a dry deck available for hire, where the number of workers regularly or occasionally exceeds 500.
Safety Committee
(1) In every factory
(a) when there are typically 250 or more employees employed; or
(b) which conducts any procedure or activity listed as hazardous under Section 87 of the Act; or
(c) which conducts hazardous processes as described in Section 2 of the Act; a Safety Committee shall be present.
(2) The members of the Safety Committee's management delegation shall include
(a) A senior person who, given his or her position within the company, can effectively contribute to the Committee's operation shall serve as Chairman;
(b) Whenever possible, a Safety Officer and a Factory Medical Officer, with the Safety Officer serving as the Committee's Secretary in this instance;
(c) a representative from each of the departments of production, maintenance, and purchases.
(3) The number of workers' representatives on this committee must match the number of management representatives voted by the workers.
(4) The Committee will be in place for three years.
(5) As often as necessary, but at least once every quarter, the safety committee must convene. The meeting's minutes must be kept and made available to the Inspector upon request.
(6) The Safety Committee has the right to receive adequate and pertinent information about
(a) Potential risks to workers' health and safety that could arise at work.
(b) Information on accidents, as well as information gathered by monitoring the working environment and the health of employees exposed to potentially harmful substances in the context of the factory
As long as the Committee agrees to utilize the information in a private manner and only to offer recommendations on how to enhance worker safety, health, and working conditions.
(7) The Safety Committee's duties and responsibilities shall include
(a) helping and collaborating with management to accomplish the goals and objectives stated in the occupier's health and safety policy
(b) addressing all issues relating to health, safety, and the environment and finding workable solutions to issues that arise;
(c) promoting worker safety awareness;
(d) carrying out educational, training, and promotional initiatives;
(e) discussing reports on safety, environmental, and occupational health surveys, safely audits, risk assessment, emergency and disaster management plans, and execution of the reports' recommendations;
(f) conducting health and safety audits and identifying accident causes;
(g) investigating any complaint regarding the potential of an impending threat to the workers' safety and health and advising remedial action; and
(h) examining how its proposals have been put into practice.
(8) Where the functions referred to in sub-rule (7) cannot be properly carried out by the Safety Committee due to the size of the factory or for any other cause, it may establish sub-committees as may be required to help it.
Review of the information furnished to workers
(1) The information provided under regulations 62-D and 62-H to the workers and the Chief Inspector must be reviewed by the Occupier once each calendar year and modified, if necessary.
(2) The information provided must be evaluated and amended as needed in the event of any process, operation, or work method changes, the introduction of a new substance in the processor, or the occurrence of a significant accident.
Ambulance Van
(1) A properly designed ambulance van staffed by a full-time Driver/Mechanic and a Helper with first-aid training shall be provided and kept in excellent working order in any factory that engages in "hazardous process" for the transportation of serious cases of accidents or illness.
The ambulance van must only be used for the purposes specified here and is typically stationed at or close to the Occupational Health Center. However, factories employing fewer than 200 workers may make arrangements to quickly obtain such a facility from a nearby hospital or other locations in the event of an emergency.
(2) The following equipment is suggested for the ambulance:
(a) General: A wheeled stretcher with folding and adjusting devices, with the stretcher's head being able to be inclined upward; Equipment for a fixed suction unit and a fixed oxygen supply cushion with a case; blankets, towels, emesis bags, bedpans, and linens Bathroom: Glass:
(b) Safety equipment includes flashlights, floodlights, and flares with a 30-minute lifespan. — Insulated gauntlets; dry powder fire extinguishers;
(c) Emergency Medical Supplies
(i) Resuscitation - Portable oxygen and suction units, as well as airways, mouth guards, and operated artificial ventilation devices, are also available. I.V. fluids with administration unit, a short spine board, a cup for measuring blood pressure, and a stethoscope;
(ii) Long and short padded boards for immobilization; Splints for wire ladders: Triangle shackle —boards with long and short spines;
(iii) Gauze pads, 4 x 4, universal dressing, 10 x 36, a roll of aluminum foil, and soft roller bandages are all examples of dressings. 6 x 5" yards, 3" rolls of adhesive tape, bandage sheets, safety pins, and a burn sheet;
(iv) Ipecac syrup, pre-packaged activated charcoal, a kit for snake bites, and water are all examples of poisoning treatments.
(v) Emergency Medicines -As per requirement (under the advice of Medical Officer only)
Personal Accident Insurance
Every factory where the manufacture of matches or fireworks is carried out requires the occupier to prepare a report detailing the insurance coverage for the employees employed, in such a factory in Form No. 41, and send it to the chief inspector once every six months via the deputy chief inspector of factories with jurisdiction over the area where the factory is located.
Notification of accidents
(1) When any of the accidents or dangerous occurrences listed in the Schedule take place in a factory, the factory management must immediately notify the inspector and chief inspector by phone, special messenger, or telegram: As long as notice is also made to the following parties in the event of any accident or harmful occurrence listed in sub-item(a) of Items 1 and 2 of the Schedule:
(a) the Sub-Divisional Officer or District Magistrate; and (b) the Officer-in-Charge of the Police Station with local jurisdiction Provided further that in respect of any accident specified in item to the Schedule, notice as aforesaid shall also be sent to the next relative of the injured or deceased person.
(2) The management of the factory must confirm the notice issued in accordance with sub-rule (1) by providing the aforementioned authorities, within 12 hours of the accident, a separate written report for each person killed or injured in the approved Form No. 18.
(3) The management of the factory must confirm the notice provided under rule (1) in regards to a dangerous event indicated in paragraph 2 of the schedule by sending a written report in the required format to the aforementioned authorities within 12 hours of the dangerous occurrence.
(4) When an accident occurs in a factory that results in a physical injury that prevents the person from working for 48 hours after the accident, the manager of the factory is required to send the inspector, within 24 hours of the expiration of the 48-hour period following the accident, a separate report of the accident regarding each person injured, in the prescribed Form No. 18: With the caveat that the Chief Inspector of Factories is free to accept a report in any other form as long as he is satisfied that it has all the details listed in Form No. 18 above.
(5) When an injured person returns to work in a factory without becoming disabled before 21 days have passed since the accident, the factory manager must provide the inspector a written report detailing the circumstances within 7 days of the injured person's return to work.
(a) the factory's registration number;
b) the accident's pertinent serial running number for the calendar year and calendar year as stated against item 2 in the report in Form No. 18;
(c) the name of the wounded party;
(d) the accident's date;
(e) the date of return to work ; and
(f) the number of days the person injured was away from work. These reports can also be provided in handy bundles for several accidents at once within the allotted time.
(6) The Manager of the Factory shall send to the Inspector a written report in the prescribed Form No. 18-B within 28 days of the accident's occurrence and follow it up as necessary in cases where the injured person does not return to work in the factory before the expiration of 21 days after the accident, with or without disablement, and in cases where the injured person returns to work in the factory after sustaining compensable disablement as a result of the accident.
Within seven days of his name being removed from the factory's Muster Roll, the Manager of the plant must also submit to the Inspector the full circumstances of the case if the injured individual does not return to work on his own initiative or in any other way. It is the Manager of the Factory's responsibility to gather the pertinent information for the purposes of this regulation and to report it to the Inspector in accordance with the authorized procedures, even if the injured party were to be covered by the Employees' State Insurance Scheme.
1. (a) An accident which causes death to any person or is of such a serious nature that it is likely to prove fatal.
(b) A serious accident that is likely to leave someone permanently disabled or losing limbs or vision.
2. The following categories are potentially risky events, regardless of whether they result in bodily injury or disability
(a) A steam supply or containment facility that was under pressure greater than atmospheric pressure bursting.
(b) The overturning of a crane, the collapse or failure of a crane, derrick, winch, hoist, or other device used in lifting or lowering people or things.
(c) A person, a room, or a place where people are working may be damaged by an explosion, fire, bursting out, leakage, or escape of any hot (molten) metal, liquid, or gas. A cotton opener may also catch fire in a room of a cotton pressing factory when it is not in use.
(d) An explosion of a receiver or container used for the storage of any gas or gases (including air), or any liquid or solid, at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure as a result of the compression of gas.
(e) any floor, gallery, roof, bridge, tunnel, chimney, wall, building, or other structure collapsing or subsiding.
(f) Centrifugal machine explosion.
How Deskera Can help You?
Deskera People provides all the employee's essential information at a glance with the employee grid. With sorting options embedded in each column of the grid, it is easier to get the information you want.
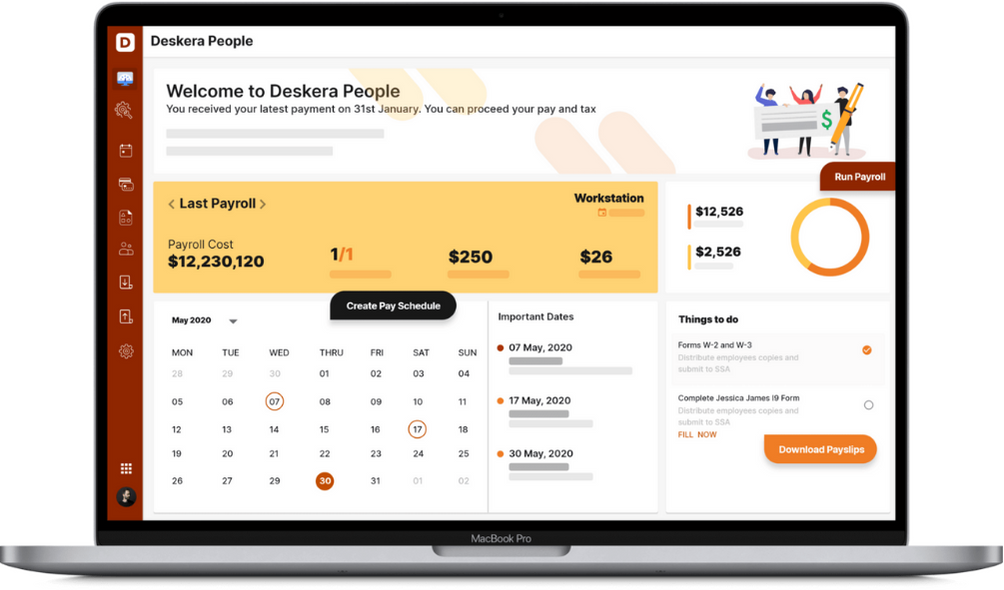
In addition to a powerful HRMS, Deskera offers integrated Accounting, CRM & HR Software for driving business growth.
To learn more about Deskera and how it works, take a look at this quick demo:
Key takeaways
- No machine, prime mover, or permanent fixture that is not depicted in the approved plans by the Chief Inspector or Deputy Chief Inspector, as the case may be shall be installed, fixed, or used in any factory except in replacement of any machine, prime mover, or permanent fixture that does not occupy more floor area than that already depicted in the approved plans.
- If possible, the wood being molded at a vertical spindle molding machine must be held in a jig or holder of such a design as to minimize the risk of injury to the worker.
- All of the areas listed in the Second Schedule to the Andhra Pradesh and Madras (Alteration of Boundaries) Act, 1959, as well as the Kanyakumari district, the Shencottah taluk of the Tirunelveli district, and the whole State of Tamil Nadu are subject to these restrictions.
Related articles













