In a world where businesses are under constant pressure to operate faster, smarter, and with greater accuracy, ERP automation has become one of the most critical priorities for 2025. Organizations can no longer rely on manual processes or fragmented systems when customers expect instant responses and markets shift overnight. This urgency is reflected in the rapid expansion of the ERP landscape itself. The global ERP software market is projected to grow at a CAGR of roughly 8.4% to 10.5% between 2022 and 2028, and some forecasts estimate the market will reach $117.09 billion by 2030—a clear sign of how central ERP has become to modern operations.
A major driver of this growth is the accelerated adoption of cloud-based solutions. As companies demand greater accessibility, real-time visibility, and scalable workflows, cloud ERP continues to dominate. In fact, cloud-based ERP solutions are expected to represent over 70% of the enterprise ERP market by 2025, with a steady growth trajectory of around 10.2% CAGR. This shift isn’t just about technology preference—it’s about enabling automation, integration, and intelligent decision-making at a speed on-premise systems simply cannot match.
As we move into 2025, ERP automation is evolving far beyond basic workflow triggers. Businesses today want predictive systems, AI-powered insights, and autonomous processes that eliminate repetitive work, reduce risk, and unlock new levels of efficiency. Whether it’s automated financial postings, real-time inventory adjustments, or intelligent demand forecasts, automation is now the backbone of future-ready operations. Companies that adopt these capabilities early aren’t just improving productivity—they’re building a competitive advantage that compounds over time.
This is where Deskera ERP stands out as a modern, automation-first platform designed for growing businesses. With features such as AI-powered insights, automated accounting entries, smart inventory control, demand forecasting, and mobile-first approvals, Deskera helps organizations streamline their workflows with ease. Its built-in AI assistant, David, further enhances productivity by simplifying tasks, answering queries, and offering real-time suggestions. By combining powerful automation with a user-friendly interface, Deskera gives businesses the agility and intelligence they need to thrive in 2025 and beyond.
What Is ERP Automation?
ERP automation refers to the use of advanced technologies—such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and the Internet of Things (IoT)—to streamline and accelerate the processes that run through an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. Instead of relying on humans to manually enter data, validate information, trigger workflows, or move tasks from one department to another, automated ERP systems perform these actions independently and consistently.
A helpful way to understand ERP automation is to imagine an ERP system evolving from a manual, instruction-dependent tool into an intelligent, self-operating platform. Traditional ERPs store and categorize data; automated ERPs interpret information, learn from patterns, and make predictive decisions. By integrating AI and ML, the system can forecast demand, detect anomalies, recommend actions, and continuously optimize workflows—much like a trained professional who improves with every cycle of experience.
At the core of this transformation is the ERP’s centralized database, shared across departments such as finance, procurement, inventory, HR, and manufacturing. When this shared data is combined with automation and IoT inputs, the ERP can instantly update records, trigger alerts, synchronize transactions, and maintain real-time accuracy across the business. Tasks like order processing, invoicing, compliance checks, inventory updates, and financial closings can be completed without human intervention, reducing errors and freeing teams to focus on strategic work.
Modern ERP automation goes beyond speeding up routine tasks. It provides predictive insights, continuous visibility, and intelligent decision support. A fully automated ERP environment ensures faster operations, improved compliance, higher productivity, and seamless collaboration across teams. It transforms disconnected manual processes into an integrated digital ecosystem—enabling organizations to scale efficiently, improve accuracy, and operate with the agility required in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Traditional ERP vs. Automated ERP
As businesses evolve toward faster, more intelligent, and data-driven operations, the gap between traditional ERP systems and modern automated ERPs becomes increasingly clear.
While traditional ERPs provide a centralized system for managing core business functions, automated ERPs extend far beyond basic data processing—leveraging AI, cloud technologies, and machine learning to deliver speed, accuracy, and predictive intelligence.
Below is a clear comparison highlighting how the two differ across key dimensions.
1. Human Intervention
Traditional ERP: Relies heavily on manual data entry, user-driven workflow approvals, and routine administrative tasks. Employees must frequently check records, update information, and move processes forward, which increases workload and the risk of human error.
Automated ERP: Integrates AI, ML, and smart workflows to minimize human involvement. Routine tasks like order processing, invoice updates, stock adjustments, and financial postings run autonomously, allowing teams to focus on strategic work instead of repetitive actions.
2. Data Storage
Traditional ERP: Often deployed on-premise, storing data locally. This setup can create vulnerabilities due to limited cybersecurity measures, outdated hardware, and higher risks during system failures.
Automated ERP: Uses secure cloud-based infrastructure with professionally managed storage, real-time backups, and multi-layered security protocols. This ensures higher uptime, better accessibility, and stronger protection against cyber threats.
3. Cost Efficiency
Traditional ERP: Typically requires costly server maintenance, manual upgrades, dedicated IT staff, and ongoing hardware investments. These expenses increase with scale and can limit agility.
Automated ERP: Operates largely on a more affordable SaaS model, eliminating hardware costs and minimizing maintenance expenses. Built-in automation reduces labor-intensive tasks, improving overall cost efficiency across operations.
4. System Updates
Traditional ERP: Requires manual installations and technical intervention every time an update or security patch is needed. This often leads to downtime, version gaps, and performance inconsistencies.
Automated ERP: AI- and ML-enabled systems automatically manage updates, apply security patches, and optimize performance in the background—ensuring uninterrupted productivity and seamless scalability.
5. Process Intelligence
Traditional ERP: Provides structured workflows but lacks real-time predictive insights. Users must analyze data manually to detect issues or make decisions.
Automated ERP: Delivers built-in analytics, predictive modeling, and automated insights. The system can identify bottlenecks, forecast future scenarios, and recommend actions without manual analysis.
6. Flexibility and Scalability
Traditional ERP: Scaling requires expensive infrastructure changes and tends to be rigid, making it difficult to adapt quickly to market changes or growing business needs.
Automated ERP: Easily scales with business growth thanks to cloud architecture, modular features, and pre-configured automation templates. Companies can expand usage without disruption.
7. Integration Capabilities
Traditional ERP: Often struggles with integrating external systems and may require custom development or third-party tools to sync data.
Automated ERP: Supports real-time API-driven integrations with CRM, eCommerce, supply chain platforms, finance tools, and more—ensuring seamless data flow across the digital ecosystem.
How ERP Automation Works
ERP automation transforms traditional, manually driven processes into intelligent, self-running workflows that help businesses operate faster, more accurately, and with far fewer errors. By combining technologies like AI, ML, RPA, OCR, APIs, and cloud integrations, automated ERPs act as smart systems that execute tasks, analyze data, and make decisions with minimal human involvement.
Here’s a clear, step-by-step breakdown of how ERP automation works.
1. Identifying Repetitive and Rule-Based Tasks
The process begins by pinpointing tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, and follow predictable rules—such as data entry, invoice processing, inventory updates, workflow approvals, PO creation, and report generation. These are the areas where automation delivers the biggest impact by saving hours of manual work.
2. Setting Automation Rules and Workflows
Once the tasks are identified, businesses create automation rules that specify when and how certain actions should happen automatically. Examples include:
- Auto-generating a purchase order when stock drops below a threshold
- Auto-sending reminders for overdue invoices
- Auto-routing documents to the right approver based on amount or department
These workflows ensure consistency and eliminate the need for human checks at every step.
3. Integrating Automation Tools with the ERP System
Automation tools—whether built into the ERP or connected via APIs—are integrated directly with the system. This gives them the ability to read data, trigger workflows, update records, and execute tasks in real time. Seamless integration ensures the ERP becomes the central nervous system for automated operations.
4. Data Collection and Processing
Automation tools pull data from multiple sources such as:
- Transaction logs
- IoT devices
- Sales portals
- Supplier systems
- Payment gateways
Once collected, the data is cleaned, validated, and processed based on predefined rules. For example, new sales entries can be automatically captured, posted to accounts, and reflected immediately in inventory records—no manual input required.
5. AI-Driven Decision-Making
Modern ERP automation goes beyond basic rule-based automation. AI and ML analyze data patterns to make proactive decisions. For example:
- Predicting stockouts and triggering reorders
- Suggesting optimal suppliers
- Forecasting future cash flow
- Identifying anomalies in invoices or payments
This intelligence helps businesses act faster, reduce risks, and optimize operations.
6. Notifications, Alerts, and Automated Reporting
ERP automation ensures stakeholders stay informed without manually checking dashboards. For instance:
- When a payment is received, financial records update automatically
- Alerts trigger when inventory hits critical levels
- Dashboards refresh with up-to-the-minute insights
This keeps teams aligned and accelerates decision-making across departments.
7. Error Handling and Exception Management
Even automated systems encounter unexpected scenarios—missing data, mismatched invoices, or rule conflicts. ERP automation includes built-in exception handling where:
- Errors are flagged instantly
- The system pauses the workflow
- Human intervention is requested only when necessary
This minimizes disruptions while maintaining accuracy and control.
8. Continuous Improvement and Optimization
ERP automation is iterative, not static. Over time, businesses refine workflows, add new rules, and adjust processes as needs evolve. AI further improves performance by learning from historical data and adapting rules for better outcomes.
9. Scalability for Growing Business Needs
As data volume increases and workflows become more complex, automation scales effortlessly. Cloud-based systems can handle more transactions, users, integrations, and processes—without adding IT overhead or operational strain.
10. Maintaining Security and Compliance
Security is at the core of ERP automation. Automated systems enforce:
- Role-based access controls
- Audit trails
- Automated compliance checks
- Secure cloud storage practices
This ensures data remains protected while meeting industry-specific regulations such as GST, SOX, HIPAA, or GDPR.
Why ERP Automation Matters More Than Ever in 2025
As businesses step into 2025, speed, accuracy, and adaptability have become non-negotiable. Markets shift overnight, customers expect instant fulfillment, and operational complexity continues to rise.
Traditional ERP systems—while still valuable—can no longer keep pace with these accelerated demands when they rely heavily on manual input and static workflows. ERP automation fills this gap, empowering organizations to operate with intelligence, precision, and real-time responsiveness.
Below are the key reasons ERP automation is now essential rather than optional.
1. Rising Operational Complexity Across Industries
Global supply chains, multi-channel sales, remote workforces, and tighter compliance requirements have made operations more intricate than ever. ERP automation helps businesses manage this growing complexity by streamlining workflows, synchronizing cross-departmental data, and reducing manual coordination. Automated approvals, alerts, and workflows keep operations flowing even in high-pressure, multi-team environments.
2. Demand for Faster, Data-Driven Decision-Making
In 2025, organizations need insights instantly—not after hours of spreadsheet cleanup or manual reporting. Automated ERPs provide real-time, accurate data without human intervention. AI- and ML-powered analytics offer predictive suggestions, identify bottlenecks, and highlight risks before they escalate. This shift enables leaders to make confident, data-driven decisions at the speed the market requires.
3. Shorter Customer and Market Cycles
Customers now expect quicker deliveries, seamless digital experiences, and transparent order tracking. Competitive markets also reset faster, forcing businesses to adapt frequently. ERP automation accelerates everything—from order processing to inventory updates to fulfillment—ensuring businesses respond promptly to customer needs and shifting demand patterns. Automated workflows improve service levels and minimize delays.
4. Escalating Pressure to Reduce Costs and Increase Efficiency
Economic uncertainty and rising operational expenses are pushing businesses to optimize every resource. Automation minimizes manual tasks, lowers labor-intensive workloads, and reduces costly errors. It eliminates redundant processes, ensures consistency, and drives leaner operations. In 2025’s climate, this efficiency is not just beneficial—it directly impacts profitability and competitiveness.
5. The Shift Toward Cloud and AI-First Business Models
As cloud ERP adoption surpasses on-premise systems, automation becomes far easier to deploy and scale. Cloud-native ERPs embed AI, RPA, and integration capabilities that allow businesses to automate deeper and faster than older systems ever could. This shift empowers organizations to modernize their processes without heavy IT infrastructure investments, making automation accessible to companies of every size.
Must-Know ERP Automation Trends Shaping 2025
As ERP systems evolve into intelligent, autonomous business platforms, 2025 marks a turning point where automation is no longer just an add-on—it becomes the backbone of digital operations. AI, machine learning, and real-time integrations are transforming how businesses plan, produce, sell, and serve.
Below are the most impactful ERP automation trends businesses need to watch and adopt to stay competitive.
1. AI-Driven Predictive Workflows Become the New Standard
AI and machine learning are shifting ERP systems from reactive to predictive. Instead of waiting for users to initiate tasks, automated workflows now anticipate needs—whether it’s predicting stockouts, recommending reorder quantities, highlighting late deliveries, or forecasting cash flow risks. This level of foresight reduces disruptions and enables smarter planning.
2. Hyper-Automation Across Core Business Functions
Hyper-automation links multiple automated processes across departments, removing the inefficiencies of siloed workflows. In 2025, businesses are automating end-to-end sequences such as sales-to-fulfillment, procure-to-pay, and quote-to-cash. This ensures process continuity, eliminates repetitive tasks, and boosts overall operational velocity.
3. Intelligent Process Mining for Continuous Optimization
Process mining tools integrated within ERPs analyze real-time operational data to uncover bottlenecks, deviations, and inefficiencies. Rather than guessing where delays occur, businesses now rely on automated insights that map actual process behavior. This trend empowers leaders to redesign workflows based on evidence, not assumptions.
4. No-Code/Low-Code Automation for Business Users
2025 is seeing a rise in “citizen developers”—non-technical users who build workflows using drag-and-drop automation tools. No-code/low-code capabilities within ERPs help organizations launch automated rules, alerts, and forms without IT intervention. This democratizes automation and accelerates innovation across teams.
5. Conversational ERP Assistants and Autonomous Agents
AI agents like Deskera’s David are transforming user interaction with ERP systems. These assistants can fetch reports, create transactions, answer operational questions, and trigger automated workflows through simple chat prompts. They reduce learning curves, improve adoption, and enable employees to work more efficiently.
6. Real-Time Integrations Across Digital Ecosystems
Businesses increasingly rely on multiple SaaS tools—CRM, eCommerce, payment gateways, shipping platforms, and manufacturing systems. Modern ERPs use API-driven automation and iPaaS integrations to ensure real-time data sync. Automated updates eliminate data gaps, speed up cross-functional processes, and maintain accuracy across platforms.
7. Autonomous Inventory and Supply Chain Automation
IoT devices, smart sensors, and AI algorithms now enable ERPs to automate inventory counting, replenishment, vendor selection suggestions, and logistics planning. Real-time data helps systems predict shortages, optimize reorder points, and prevent stockouts—all without constant human oversight.
8. Automated Reporting and AI-Generated Insights
Manual reporting is being replaced by automated dashboards, KPI alerts, and AI-generated summaries. ERPs now provide instant insights on performance, cash flow, production delays, sales trends, and operational bottlenecks. These automated insights help leaders act quickly and confidently.
Benefits of ERP Automation
As business operations grow more complex and data-driven, manual processes can no longer keep up with rising demands for speed, accuracy, and real-time visibility. ERP automation bridges this gap by transforming traditional workflows into intelligent, self-running systems that reduce effort, eliminate errors, and improve overall performance. From finance and inventory to compliance and analytics, automated ERP capabilities help organizations operate with greater efficiency, scalability, and strategic clarity.
Below are the most impactful benefits businesses can unlock through ERP automation:
1. Streamlined Workflows and Faster Operations
ERP automation accelerates operations by removing manual steps from everyday processes such as approvals, reconciliations, and purchase workflows. Automated triggers ensure tasks move seamlessly through each stage without delays, reducing bottlenecks and human dependency. This improves process consistency, shortens cycle times, and enables teams to work faster and with greater accuracy.
2. Centralized and Integrated Data Across the Organization
Automated ERP systems unify data from finance, inventory, HR, CRM, and supply chain into a single platform. This eliminates data duplication and discrepancies caused by siloed systems. With synchronized, real-time information available to all teams, businesses can maintain consistency, improve collaboration, and make better decisions supported by accurate, unified insights.
3. Higher Data Accuracy and Fewer Manual Errors
Manual data entry is one of the biggest sources of business mistakes. ERP automation drastically reduces these errors by enforcing validation rules, automating entries, and cross-checking information across modules. The result is highly accurate financial, inventory, and operational data, minimizing costly rework, compliance risks, and decision-making errors.
4. Real-Time Reporting, Analytics, and Decision Intelligence
Automated ERPs provide instant access to dashboards and KPIs without manual compilation. Real-time analytics highlight performance trends, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement. Predictive insights generated by AI help forecast demand, optimize resources, and support data-driven decisions, enabling leadership teams to act quickly and stay ahead of market fluctuations.
5. Improved Inventory Control and Supply Chain Efficiency
ERP automation enhances inventory accuracy through real-time tracking, automated reordering, and intelligent stock optimization. Businesses can reduce excess inventory, prevent stockouts, and improve demand planning. These capabilities create a more responsive supply chain, reduce carrying costs, and ensure products are available exactly when customers need them.
6. Cost Savings Through Reduced Manual Effort
By automating labor-intensive tasks such as invoicing, reconciliation, data entry, and reporting, companies can operate efficiently with smaller teams. Reduced manual intervention also lowers error-related costs and process delays. Over time, the savings accumulate across labor, inventory, and operational expenses, significantly improving overall financial performance and profitability.
7. Improved Employee Productivity and Reduced Workload
Automation frees employees from repetitive, time-consuming tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic work such as customer service, process innovation, and analysis. With streamlined approvals and automated task routing, teams spend less time on administrative work and more time contributing to growth initiatives, increasing engagement and overall productivity.
8. Strengthened Compliance, Auditability, and Data Security
Automated ERPs enforce standardized workflows that ensure compliance with internal policies and regulatory requirements. Built-in audit trails track every change, approval, and transaction, supporting transparency and accountability. Automated security controls protect sensitive data, reduce compliance risks, and help businesses stay aligned with evolving industry and legal standards.
9. Scalability, Agility, and Business Growth Enablement
ERP automation supports rapid business growth by eliminating manual bottlenecks and ensuring processes scale effortlessly. Whether increasing transaction volumes, expanding product lines, or entering new markets, automated workflows adapt without requiring proportional increases in manpower. This agility allows companies to respond quickly to market shifts and scale sustainably.
10. Reduced Environmental Impact and a Smaller Carbon Footprint
By replacing paper-intensive workflows with digital processes, automated ERPs significantly reduce paper consumption and waste. Companies save on printing, storage, and manual documentation costs while operating more sustainably. Digital approvals, e-invoicing, and online reporting all contribute to a greener, more environmentally responsible business model.
Key Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While ERP automation unlocks significant benefits, many organizations encounter roadblocks during implementation. These challenges often stem from outdated processes, low data maturity, or resistance to technological change.
Understanding these barriers—and preparing for them—ensures a smoother transition, better adoption, and faster ROI from your automation investment.
1. Legacy Systems and Poor Integration Capabilities
Many businesses rely on outdated systems that cannot easily integrate with modern automation tools. These legacy environments create data silos, slow down workflows, and limit automation potential.
How to overcome it: Adopt an integration-first strategy using APIs, middleware, and cloud-ready tools. Standardize data formats, modernize critical systems gradually, and choose an ERP platform that supports low-code/no-code automation and plug-and-play integrations.
2. Low-Quality or Inconsistent Data
Automation is only as good as the data it uses. Inaccurate, duplicate, or outdated data leads to incorrect outputs, failed workflows, and poor decision-making.
How to overcome it: Implement data governance, conduct thorough data cleaning before automation, and establish validation rules. Use automated data checks, master data management (MDM), and AI-powered cleansing tools to maintain accuracy.
3. Resistance to Change Among Employees
Employees may fear automation will replace jobs, alter routines, or disrupt established processes. This resistance slows adoption and reduces the effectiveness of automation initiatives.
How to overcome it: Invest in transparent communication, change management, and role-based training. Emphasize that automation reduces repetitive work—not jobs—and highlights the new skills, opportunities, and high-value work employees will gain.
4. High Initial Costs and Unclear ROI
Automation can require upfront investment in software, integration, data cleanup, and training. Without a clear ROI or phased roadmap, organizations may hesitate or underinvest.
How to overcome it: Start with high-impact, low-complexity processes such as AP automation, order processing, or inventory sync. Track time savings, error reduction, and cost benefits. Present a clear ROI blueprint to justify phased expansion.
5. Over-automation and Process Misalignment
Some companies automate broken or inefficient processes, leading to even more complications. Automating everything at once often results in complexity and workflow failures.
How to overcome it: Optimize processes before automating them. Use process mapping, value-stream analysis, and stakeholder workshops to simplify workflows. Prioritize automation based on feasibility, business value, and user impact.
6. Scalability Limitations as the Business Grows
Automation built without scalability in mind can struggle as data volumes, transactions, or process complexity increase.
How to overcome it: Choose cloud-native ERP solutions with elastic scaling, modular automation, and flexible workflow design. Regularly review performance, update rules, and ensure your architecture supports future expansion.
7. Security and Compliance Risks
Automation increases system interconnectivity, which can expose sensitive data if not properly secured. Non-compliant workflows may also introduce regulatory risks.
How to overcome it: Implement role-based access controls, encryption, automated audit trails, and compliance workflows. Conduct regular security assessments and ensure automation rules align with industry standards such as GDPR, SOC 2, PCI-DSS, or tax regulations.
8. Lack of Skilled Workforce to Manage Automation
Automation requires technical understanding, rule configuration, and ongoing optimization. Many companies lack trained staff to maintain these systems.
How to overcome it: Upskill employees through continuous training, certifications, and hands-on workshops. Select automation tools with intuitive, no-code interfaces and strong vendor support to minimize dependency on specialized IT teams.
Implementation Roadmap: How to Adopt ERP Automation in 2025
Adopting ERP automation in 2025 requires more than adding new tools—it demands a structured, strategic, and outcome-driven roadmap. With evolving technologies like AI, hyper-automation, and API-first ERP solutions, businesses must approach implementation with clarity, alignment, and scalability in mind.
Below is a step-by-step roadmap that ensures smooth adoption, rapid value realization, and long-term success.
1. Assess Current Processes and Identify Automation Opportunities
Start by mapping all workflows across finance, operations, supply chain, and HR. Identify repetitive, manual, and error-prone tasks—such as invoice routing, stock updates, or data entry—that consume time but add little strategic value. Prioritizing these processes helps create a clear automation pipeline.
2. Define Goals, KPIs, and Expected ROI
Before choosing tools, outline what automation should achieve: faster closing cycles, reduced errors, better inventory accuracy, or improved compliance. Set measurable KPIs like processing time, cost per transaction, cycle time reduction, or accuracy improvement. A strong ROI case builds stakeholder confidence.
3. Select the Right ERP Platform and Automation Tools
Choose an ERP that supports AI, RPA, workflows, APIs, and low-code customization. Ensure the platform integrates easily with automation tools for AP, approvals, reporting, demand planning, or CRM. Evaluate vendor scalability, security, mobile accessibility, and support.
4. Clean, Standardize, and Prepare Your Data
Data readiness is a critical step. Conduct data cleaning, remove duplicates, fix inconsistencies, and standardize naming conventions. Establish master data management practices so automation can run reliably without producing incorrect outcomes.
5. Design Automation Workflows and Rules
Build automation rules for approvals, notifications, triggers, and system actions. Map input conditions (e.g., inventory level drops), workflow logic (e.g., auto-create PO), and output actions (e.g., notify purchasing). Involve finance, operations, and warehouse teams to ensure real-world accuracy.
6. Integrate Automation Tools with Your ERP
Use APIs, connectors, and middleware to sync your ERP with third-party tools. Ensure real-time data flow between modules such as accounting, inventory, CRM, procurement, and manufacturing. Test integrations for reliability, latency, and error handling.
7. Run Pilot Projects and Test Extensively
Begin with a small, high-impact use case—such as AP automation, order sync, or automated reporting. Test end-to-end processes, validate rules, and monitor system behavior. Fix bugs, refine workflows, and gather user feedback before scaling.
8. Train Employees and Build Change Readiness
Successful automation depends on user adoption. Offer hands-on training, role-based sessions, and interactive demos. Highlight the benefits—reduced workload, fewer errors, and easier reporting—to overcome resistance and build enthusiasm.
9. Roll Out Automation in Phases
Use a phased rollout strategy:
- Phase 1: Automate simple, repetitive tasks.
- Phase 2: Automate cross-departmental workflows.
- Phase 3: Introduce AI-based forecasting, analytics, and optimization.
This phased approach minimizes disruption and ensures stable progress.
10. Monitor, Optimize, and Scale Continuously
Automation is not a one-time project. Track KPIs, monitor workflow performance, review bottlenecks, and gather user insights. Continuously refine automation logic and expand automation into new areas such as inventory forecasting, quality control, or multi-entity reporting.
11. Ensure Security, Compliance, and Governance
Embed audit trails, access controls, and automated compliance workflows. Conduct periodic security assessments to protect data and prevent unauthorized changes. As regulations evolve, update automation rules to maintain audit readiness.
How Can Deskera ERP Help You?
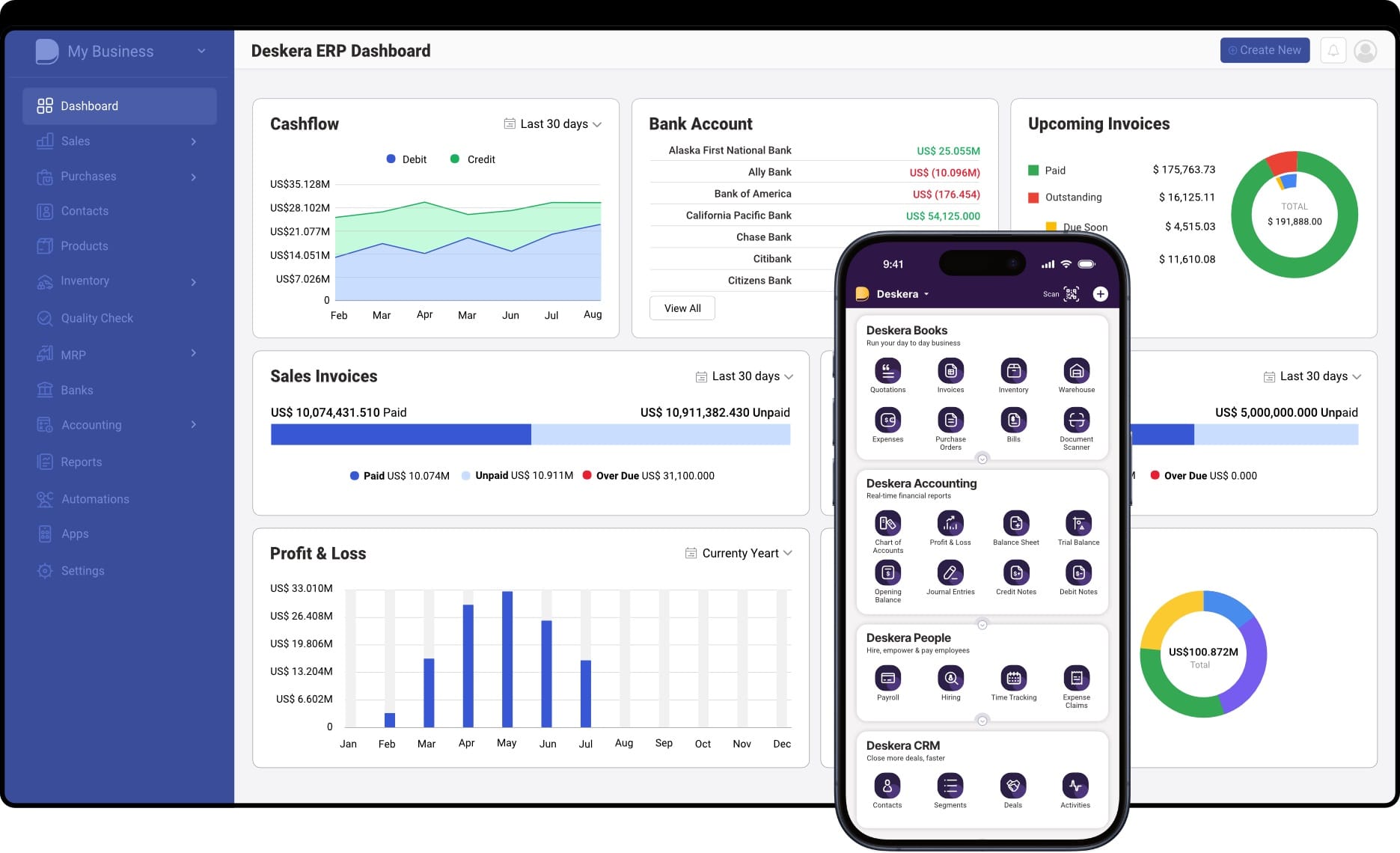
Deskera ERP empowers businesses to adopt ERP automation seamlessly by bringing together AI-driven intelligence, cloud-native architecture, and user-friendly workflows. Designed for growing companies, it simplifies complex operations, reduces manual effort, and accelerates decision-making through real-time insights.
1. AI-Powered Process Automation
Deskera automates repetitive tasks such as purchase approvals, invoice matching, stock updates, and financial reconciliations. With AI-driven recommendations and automated workflows, businesses can reduce human error, speed up operations, and ensure consistent process execution across departments.
2. Real-Time Visibility Across All Business Functions
The platform offers unified dashboards that display real-time data from inventory, sales, finance, and production. Leaders gain instant clarity on KPIs, allowing them to make informed decisions, identify issues early, and optimize performance without switching between multiple systems.
3. Cloud-Based Scalability and Flexibility
Deskera’s cloud-first design enables teams to access data anytime, anywhere. It eliminates infrastructure costs, enhances security, and allows organizations to scale effortlessly. Whether you’re expanding product lines or entering new markets, Deskera adapts to your operational needs.
4. Integrated Inventory, Accounting, and MRP Modules
Deskera ERP brings all core business functions under one platform—inventory management, accounting, MRP, sales, purchase, and HR. This reduces system fragmentation, improves data accuracy, and ensures a smooth end-to-end experience across the supply chain.
5. Advanced Forecasting and Demand Planning
With built-in forecasting tools, businesses can predict sales, plan production, and optimize stock levels. Automated insights help reduce overstocking, minimize stockouts, and improve working capital efficiency.
6. Mobile Accessibility for On-the-Go Management
With Deskera’s mobile app, leaders can approve requests, monitor operations, and track financials in real time from any device. This improves responsiveness and ensures uninterrupted workflows across teams.
7. Easy Implementation and User-Friendly Interface
Deskera minimizes the complexity of ERP adoption with intuitive navigation, pre-built templates, and guided onboarding. Teams can get up to speed quickly, reducing the learning curve and ensuring faster value realization.
Key Takeaways
- ERP automation has become essential for improving accuracy, reducing operational costs, and enabling faster decision-making in an increasingly data-driven and competitive business environment.
- AI-driven workflows, cloud adoption, predictive analytics, and intelligent integrations define the future of ERP, offering businesses greater speed, agility, and resilience.
- Automated ERP systems outperform traditional models by reducing manual effort, lowering maintenance costs, and enabling real-time, cloud-powered updates that enhance efficiency and scalability.
- ERP automation helps companies eliminate repetitive tasks, improve process consistency, strengthen data accuracy, and boost productivity across every department.
- Challenges such as integration complexities, change resistance, data migration, and skill gaps can be mitigated with strong planning, stakeholder alignment, and phased implementation.
- A structured roadmap—covering assessment, system selection, data preparation, rollout planning, training, and continuous optimization—is essential for successful ERP automation adoption.
- Deskera ERP simplifies automation with AI-powered workflows, real-time visibility, cloud scalability, integrated modules, and an easy-to-use interface that accelerates digital transformation for modern businesses.
Related Articles