What’s slowing down your production line—people, machines, or processes? If you’re not sure, you’re not alone. Many manufacturers face hidden inefficiencies that quietly impact output and profitability. From frequent downtime to manual workflows and siloed data, these issues limit productivity across the shop floor—whether you're running a small factory or managing multiple large-scale facilities.
In today’s highly competitive manufacturing landscape, maximizing work productivity is essential for staying agile and profitable. Boosting productivity doesn’t just mean working harder—it means working smarter. With the right strategies in place, manufacturers can streamline operations, reduce waste, improve quality, and enhance decision-making across all levels of production.
That’s where Deskera MRP comes in. Built to support manufacturing operations of all sizes—from small businesses to large-scale enterprises—Deskera MRP offers powerful features for production planning, work order management, inventory control, procurement, and more. With real-time visibility, automation, mobile access, and AI-powered insights, Deskera helps manufacturers optimize workflows, reduce delays, and drive continuous improvement across their operations.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through 10 proven strategies to maximize work productivity in your manufacturing operations. These are practical, scalable techniques that apply across industries and plant sizes—designed to help you boost efficiency, empower your workforce, and improve output without compromising on quality.
What Is Work Productivity?
Work productivity refers to the amount of useful output produced by an individual, team, or system within a given period, using a defined set of inputs like time, labor, materials, and equipment. In manufacturing, it’s typically measured by how efficiently workers, machines, and processes convert raw materials into finished goods.
High work productivity means more products are made with fewer resources, less waste, and minimal downtime. It’s not just about speed—it’s about optimizing efficiency, accuracy, and consistency across the production line. Whether you’re tracking units per labor hour, cycle times, or equipment effectiveness, improving productivity directly contributes to lower costs, higher margins, and better competitiveness.
For manufacturers, work productivity is a critical performance metric that influences everything from delivery timelines to customer satisfaction. By identifying inefficiencies and applying targeted improvements, companies can boost productivity without adding extra labor or capital investment.
Tools like Deskera MRP make it easier to monitor and enhance work productivity. By integrating production planning, inventory, and real-time reporting into one platform, Deskera helps manufacturers gain full visibility into operations, reduce delays, and improve overall shop floor performance.
Key Components of Work Productivity in Manufacturing
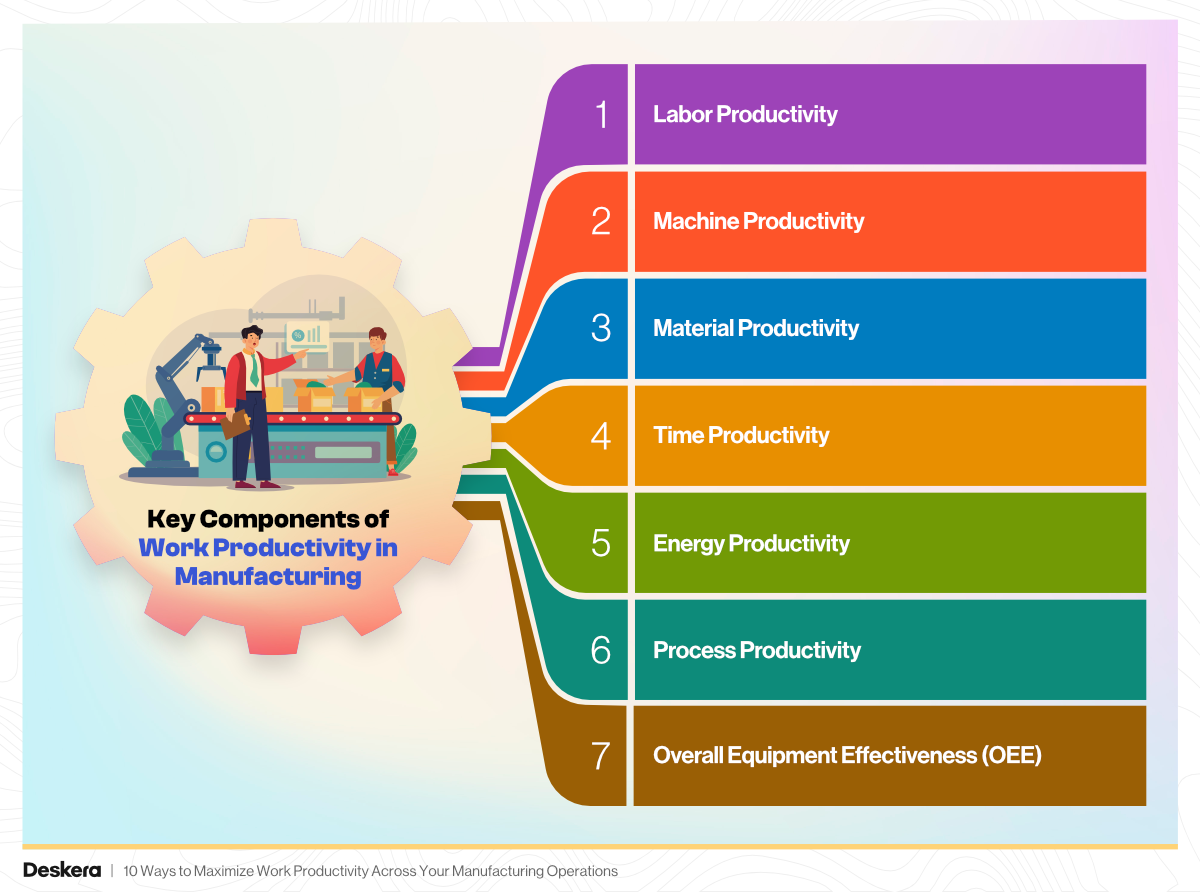
Work productivity in manufacturing is influenced by several interrelated components that together determine how efficiently a facility operates. These components help managers analyze performance, identify bottlenecks, and implement targeted improvements. Here are the most critical ones:
1. Labor Productivity
This measures the output generated per worker or per labor hour. It reflects how efficiently human resources are being utilized in the production process.
Formula: Labor Productivity = Total Output / Total Labor Hours
2. Machine Productivity
This refers to how effectively machines or equipment are used to produce goods. It's measured in terms of output per machine hour and is essential for understanding the ROI of capital-intensive assets.
3. Material Productivity
This evaluates how efficiently raw materials are converted into finished products, with minimal waste. High material productivity means less scrap, fewer defects, and better resource utilization.
4. Time Productivity
This assesses how well time is used during production. It includes minimizing idle time, delays, and non-value-adding activities like waiting for materials or maintenance.
5. Energy Productivity
An increasingly important component, especially in energy-intensive industries. It measures output per unit of energy consumed, encouraging sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing.
6. Process Productivity
This focuses on the efficiency of workflows and production processes themselves. Lean manufacturing practices, automation, and streamlined workflows contribute directly to improved process productivity.
7. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
While not a single component, OEE is a composite metric that evaluates equipment productivity through three factors: Availability, Performance, and Quality. It provides a holistic view of machine and process effectiveness.
Together, these components give manufacturers a complete picture of their operational productivity. Tools like Deskera MRP help track these components in real time, offering insights into labor utilization, machine efficiency, and material consumption—enabling better decisions, faster improvements, and increased profitability.
What Do Manufacturers Consider When Evaluating Work Productivity?
For manufacturers, work productivity goes beyond just measuring output. It’s about understanding the broader factors that influence how effectively people, machines, and systems work together to achieve production goals.
Here’s what manufacturers typically consider when evaluating and improving work productivity:
1. Alignment with Production Goals
Manufacturers assess whether productivity levels support overall business objectives—such as meeting delivery deadlines, maintaining consistent quality, and achieving cost targets. Productivity isn’t just about speed; it’s about producing the right quantity at the right time.
2. Process Efficiency and Flow
Evaluating how smoothly materials, tasks, and information move through the production process is crucial. Bottlenecks, redundant steps, or manual handoffs can slow down productivity—even if labor or machine utilization seems high.
3. Workforce Capability and Engagement
Productivity is directly impacted by how skilled, motivated, and well-supported the workforce is. Manufacturers consider factors like training, role clarity, employee morale, and incentives when analyzing output levels.
4. Technology and Automation Readiness
Adopting the right tools and systems is a strategic decision. Manufacturers look at whether their current tech stack—MRP systems, machines, or digital tools—is enabling productivity or creating silos and inefficiencies.
5. Flexibility and Scalability
Can the production environment adapt to changes in demand, custom orders, or supply disruptions? Manufacturers consider how adaptable their operations are, since rigid systems can slow productivity under pressure.
6. Quality and Rework Rates
High productivity means little if it's accompanied by poor quality or frequent rework. Manufacturers evaluate how well processes support quality output with minimal errors or material waste.
By considering these strategic factors, manufacturers can gain a deeper understanding of what drives or hinders productivity. Platforms like Deskera MRP help unify these insights by offering real-time data, workflow visibility, and automation—making it easier to make informed, productivity-driven decisions at every level of manufacturing.
Why Work Productivity Matters in Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, productivity is more than a metric—it’s a fundamental driver of success. Improving work productivity means achieving greater output with the same or fewer resources. It’s what enables manufacturers to meet deadlines, reduce costs, and improve product quality—all while remaining competitive in an evolving market.
Whether you're managing a small factory or overseeing operations across global plants, focusing on productivity leads to measurable business advantages. The benefits extend beyond the shop floor and directly impact profitability, customer satisfaction, and operational agility.
Here’s why maximizing productivity should be a top priority in your manufacturing operations:
- Increased Output: Higher productivity allows you to produce more units in less time, helping meet growing customer demand without needing additional resources.
- Lower Operational Costs: Efficient workflows, reduced downtime, and optimized labor help cut unnecessary expenses and improve profit margins.
- Better Resource Utilization: By making the most of your workforce, equipment, and materials, you reduce waste and minimize underused assets.
- Improved Quality: Streamlined processes often lead to fewer errors and defects, enhancing product quality and reducing rework costs.
- Shorter Lead Times: When productivity improves, so does your ability to fulfill orders faster—giving you a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced markets.
- Higher Employee Morale: Efficient operations reduce frustration on the shop floor, boost job satisfaction, and encourage workers to perform at their best.
- Greater Scalability: Productivity improvements help your business scale operations more effectively, without being held back by inefficiencies.
In a modern manufacturing environment where digital tools and real-time data are reshaping how factories run, improving work productivity isn’t optional—it’s essential for long-term growth and sustainability.
10 Proven Strategies to Maximize Work Productivity in Manufacturing
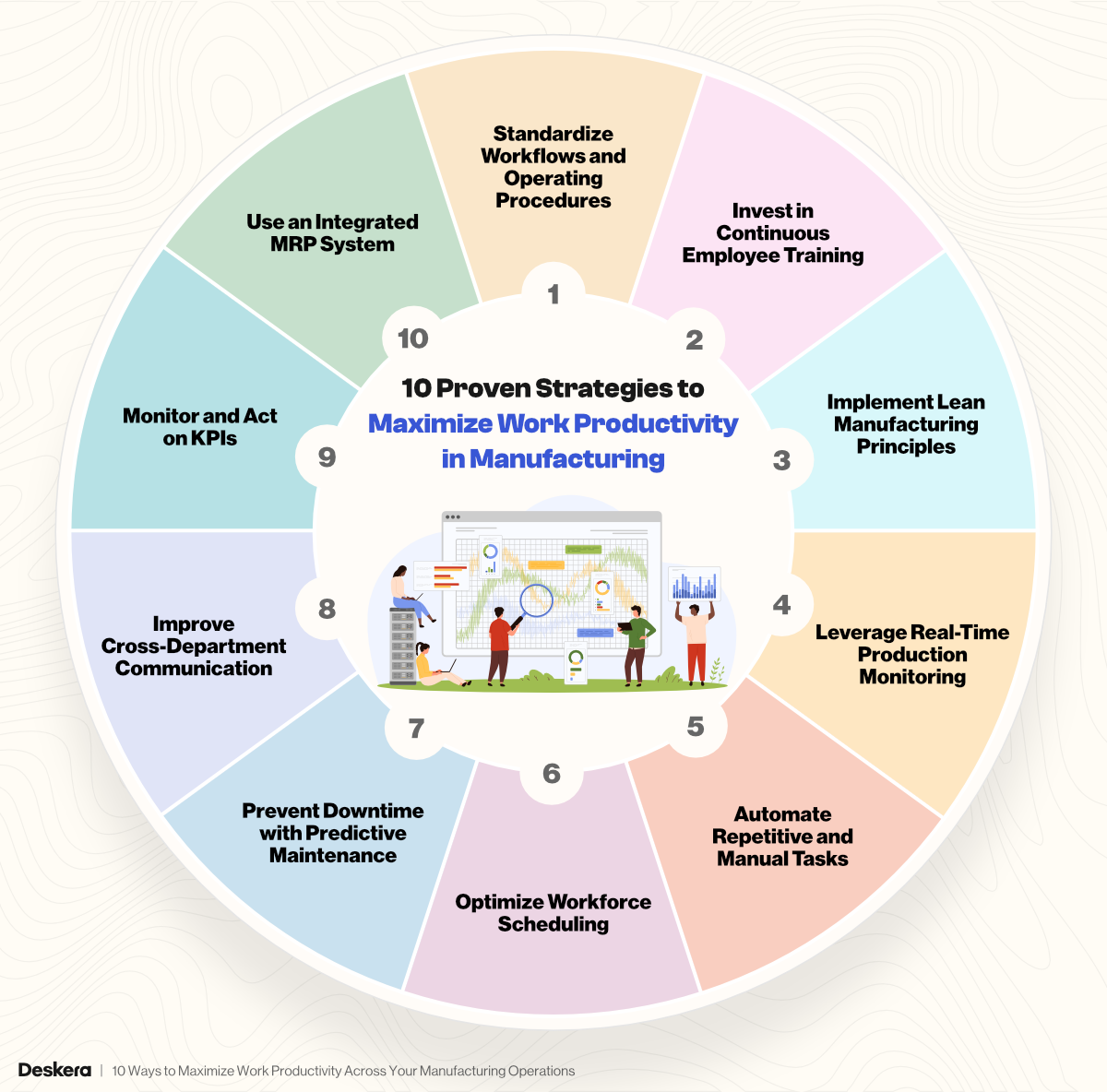
Improving work productivity in manufacturing isn’t about working harder—it’s about working smarter. By aligning people, processes, and technology, manufacturers can unlock greater efficiency, reduce waste, and boost output without compromising on quality.
Here are 10 practical strategies to help you do just that:
1. Standardize Workflows and Operating Procedures
Standardized workflows form the foundation of an efficient manufacturing operation. When every employee follows consistent procedures, it reduces confusion, minimizes variation, and improves product quality.
Clear documentation of SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) ensures that tasks are performed uniformly regardless of shift or operator. This also simplifies training and accelerates onboarding for new workers.
Standardization supports process audits and continuous improvement efforts by providing a baseline for measurement. Manufacturers that invest in documenting and enforcing workflows often see improved cycle times, lower error rates, and smoother handoffs between departments—critical elements for scaling productivity across the shop floor.
2. Invest in Continuous Employee Training
Your workforce is one of the most valuable assets for improving productivity. Continuous training empowers employees to work more efficiently, adapt to new technologies, and follow safety protocols with confidence. In manufacturing environments, even small knowledge gaps can result in costly errors, downtime, or equipment damage.
By offering skill development programs—such as equipment certification, process updates, and digital literacy—manufacturers can boost workforce agility and morale. Trained employees also tend to take more initiative and contribute to process improvements. When combined with clear career progression, ongoing training enhances both employee retention and shop floor productivity.
3. Implement Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean manufacturing is centered around one core idea: eliminate waste in all its forms. This includes wasted time, motion, materials, inventory, and overproduction. Applying Lean tools like 5S (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), Value Stream Mapping, and Kaizen (continuous improvement) enables manufacturers to identify inefficiencies and streamline operations.
For example, reorganizing workspaces to reduce unnecessary movement or using JIT (Just-in-Time) inventory can significantly improve workflow efficiency. Lean also encourages a culture of accountability and problem-solving, empowering employees to find and eliminate bottlenecks. When practiced consistently, Lean methodologies lead to better resource utilization and increased output with fewer inputs.
4. Leverage Real-Time Production Monitoring
Real-time production monitoring gives manufacturers instant visibility into what's happening on the shop floor. Instead of relying on end-of-day reports or spreadsheets, teams can track cycle times, downtime, throughput, and machine status live. This enables immediate response to performance issues or delays, reducing unplanned downtime and preventing minor problems from becoming major disruptions.
Digital dashboards and IoT-enabled machines play a vital role in making this data accessible and actionable. Managers can analyze trends, identify root causes, and optimize processes quickly. Real-time monitoring supports proactive decision-making, helping manufacturers keep productivity on track and operations aligned with production goals.
5. Automate Repetitive and Manual Tasks
Automation is one of the most effective ways to boost work productivity in manufacturing. By automating repetitive or time-consuming tasks—like material handling, quality inspections, data entry, or report generation—manufacturers free up human labor for higher-value work. Automation reduces human error, accelerates cycle times, and ensures consistency in output.
Depending on scale and complexity, automation can range from simple conveyor systems to fully integrated robotics and AI-driven quality control. Even partial automation can make a big difference in reducing operational friction. Long-term, automation helps manufacturers scale more efficiently and compete in fast-moving markets where time and precision are everything.
6. Optimize Workforce Scheduling
Strategic workforce scheduling ensures the right people are in the right place at the right time. Poor scheduling leads to underutilized labor, missed production targets, and worker fatigue. On the other hand, optimized scheduling balances workloads, reduces idle time, and prevents overstaffing.
With digital scheduling tools, manufacturers can align labor with real-time production demands, forecast staffing needs during peak periods, and manage multi-shift operations more effectively.
Factors like skills, shift preferences, machine availability, and maintenance windows can all be accounted for. A well-planned schedule improves productivity while supporting employee satisfaction and operational predictability—both vital for long-term success.
7. Prevent Downtime with Predictive Maintenance
Downtime is one of the biggest killers of productivity in manufacturing. Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and machine learning to forecast equipment failures before they happen. This proactive approach allows maintenance teams to schedule service during planned downtime instead of reacting to unexpected breakdowns.
Predictive tools monitor vibrations, temperature, run time, and other indicators that signal wear and tear. With fewer interruptions and extended equipment life, manufacturers can maintain consistent production output.
When combined with a centralized system like Deskera MRP, predictive maintenance strategies ensure maintenance planning is aligned with production goals, minimizing disruption and maximizing uptime.
8. Improve Cross-Department Communication
Miscommunication between departments—such as production, procurement, and logistics—can lead to delays, material shortages, and duplicated efforts. Improving communication ensures everyone is on the same page regarding schedules, inventory levels, and production priorities. This can be achieved through centralized platforms, ERP systems, and automated alerts that provide real-time updates.
Holding regular cross-functional meetings or using digital collaboration tools also helps identify issues early. When communication flows smoothly, teams respond faster to disruptions, coordinate more efficiently, and maintain operational continuity. Ultimately, strong interdepartmental collaboration creates a more agile manufacturing environment, where decisions are faster and productivity remains high.
9. Monitor and Act on KPIs
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for managing and improving productivity. Common manufacturing KPIs include Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), yield, scrap rate, downtime, and labor efficiency. By setting targets and consistently monitoring performance, manufacturers can quickly spot trends, diagnose issues, and measure the impact of improvement efforts.
Data-driven decision-making leads to better resource allocation and continuous process refinement. Visual dashboards and automated reporting tools make it easier to keep teams informed and accountable. When KPIs are aligned with business goals, they provide a roadmap for operational excellence and a framework for sustainable productivity growth.
10. Use an Integrated MRP System
An integrated MRP (Material Requirements Planning) system like Deskera MRP is a game-changer for manufacturers aiming to maximize productivity. It connects all essential functions—inventory, production planning, procurement, and order management—into one centralized platform. With real-time data, automation, and intelligent forecasting, manufacturers can reduce stockouts, plan work orders efficiently, and avoid bottlenecks.
Deskera MRP also offers mobile accessibility and AI-powered insights, allowing managers to make informed decisions on the go. By unifying workflows and reducing manual coordination, MRP systems help manufacturers operate more efficiently, scale faster, and stay competitive in a fast-changing global market.
Key Productivity KPIs Every Manufacturer Should Track
To effectively improve work productivity, manufacturers need to monitor the right performance indicators. These key performance indicators (KPIs) help assess how efficiently labor, machinery, and materials are being utilized across the production process. By consistently tracking these metrics, decision-makers can identify bottlenecks, measure improvements, and make data-driven changes that boost overall productivity.
Here are the most essential KPIs for evaluating work productivity in manufacturing:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): OEE measures the percentage of manufacturing time that is truly productive by combining availability, performance, and quality. A higher OEE means more efficient use of machinery and minimal downtime.
- Labor Productivity: This KPI evaluates output per labor hour, helping determine how effectively your workforce contributes to production. It's useful for scheduling, training, and workforce planning.
- Throughput: Throughput refers to the number of units produced in a given time frame. Tracking this helps manufacturers assess line efficiency and identify areas for output improvement.
- Cycle Time: The time it takes to complete one production cycle. Lower cycle times typically indicate more efficient processes and faster turnaround.
- Downtime: Unplanned downtime, whether due to machine failure or labor issues, directly impacts productivity. Tracking it helps identify root causes and areas for preventive maintenance.
- Yield Rate (First Pass Yield): Measures the percentage of products manufactured correctly without needing rework. A high first-pass yield indicates efficient and accurate production.
- Capacity Utilization: This shows how much of your total production capacity is actually being used. Low utilization may indicate inefficiencies or opportunities for scaling.
Tracking these KPIs with a robust MRP system like Deskera MRP enables real-time visibility, automated reporting, and faster decision-making—making it easier to turn data into productivity gains.
How Deskera MRP Enhances Work Productivity in Manufacturing
Modern manufacturing demands more than just manual oversight and spreadsheets—it needs an integrated, intelligent system that drives efficiency at every level. That’s where Deskera MRP comes in. Designed for small, medium, and large-scale enterprises, Deskera MRP provides a comprehensive suite of tools to streamline production, optimize resources, and maximize work productivity.
Here’s how Deskera MRP supports manufacturing teams in improving productivity:
- Real-Time Production Visibility: Deskera offers real-time tracking of production schedules, work orders, and material consumption, enabling manufacturers to make faster, informed decisions and reduce delays.
- Automated Workflows: From procurement to production and inventory, Deskera automates routine processes, reducing manual errors and freeing up time for value-added tasks.
- Integrated Demand Forecasting: With built-in demand forecasting and planning tools, Deskera ensures that resources are aligned with actual market demand—minimizing overproduction and underutilization.
- Accurate Inventory Management: Avoid production stoppages with Deskera’s automated inventory tracking. The system helps maintain optimal stock levels, ensures timely replenishments, and reduces waste.
- Advanced Reporting and KPIs: Easily track productivity KPIs such as OEE, cycle time, and labor efficiency with Deskera’s real-time dashboards and reporting tools. This visibility helps drive continuous improvement.
- Mobile Accessibility: Deskera’s mobile-first platform allows managers and shop-floor workers to access critical data and updates on the go—boosting agility and responsiveness.
- Scalable and Cloud-Based: Whether you’re a growing business or a large manufacturer, Deskera adapts to your needs with scalable cloud infrastructure and robust performance.
By bringing all critical operations onto one platform, Deskera MRP empowers manufacturers to boost output, lower costs, and make smarter operational decisions—all key drivers of sustained productivity.
Key Takeaways
- Work productivity in manufacturing refers to the efficiency with which labor, machinery, and materials are converted into finished goods—it’s about doing more with the same or fewer resources.
- Manufacturers focus on output quality, machine efficiency, workforce utilization, and process consistency to determine overall productivity on the shop floor.
- Key components include labor productivity, machine productivity, material usage efficiency, and time management—all of which directly impact manufacturing performance.
- Enhancing work productivity helps reduce operational costs, improve delivery timelines, increase profitability, and support sustainable growth.
- Implementing lean manufacturing, adopting automation, streamlining workflows, training employees, and tracking KPIs are proven strategies to boost productivity.
- Metrics like Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), cycle time, throughput, labor productivity, and first-pass yield offer quantifiable insights into performance and productivity.
- Deskera MRP boosts productivity by automating workflows, offering real-time visibility, enabling demand forecasting, and providing mobile-first access for informed decision-making.
Related Articles