From manufacturing plants optimizing production schedules to service industries streamlining client tasks, the orchestration of work orders can spell the difference between success and stagnation.
Delving into the intricate economics of work order processes reveals a realm of significance that resonates far beyond mere administrative tasks.
According to recent industry surveys, businesses with streamlined work order procedures report an average of 25% reduction in operational costs and a notable 20% increase in overall productivity. These statistics underscore the critical role of work orders as economic drivers, not just task directives.
This exploration embarks on a journey to demystify the economic underpinnings of work order processes, transcending their apparent simplicity. By understanding how optimized work orders minimize delays, curtail excess resource allocation, and empower informed decision-making, executives can leverage this knowledge to foster growth.

From examining the synergy between technology and work order efficiency to foreseeing future trends, we illuminate a path towards harnessing the latent economic potential that work order processes hold.
In essence, the economics of work orders cease to be an operational footnote; they emerge as a strategic playbook for visionary executives navigating the complexities of today's business landscape.
- Importance Of Work Order Processes In Business Operations
- Significance Of Understanding The Economics Behind Work Order Processes
- Fundamentals of Work Order Processes
- Efficiency and Productivity
- Cost Management
- Impact on Decision Making
- Technology and Automation
- Challenges and Mitigation
- Continuous Improvement
- Future Trends
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Importance Of Work Order Processes In Business Operations
Work order processes play a pivotal role in the seamless functioning of business operations. They serve as structured roadmaps, guiding tasks, resources, and timelines to ensure efficient execution and optimal resource utilization.
The importance of work order processes in business operations can be understood through several key aspects:
- Efficiency and Accountability: Work orders define the scope, objectives, and steps required for a task. This clarity reduces ambiguity, minimizing errors and rework. With assigned responsibilities and timelines, accountability is enhanced, ensuring tasks are completed on schedule.
- Resource Allocation: Work orders allocate resources such as labor, materials, and equipment based on predefined requirements. This prevents resource overages or shortages, resulting in cost savings and improved productivity.
- Cost Management: Well-structured work orders allow accurate estimation of costs associated with tasks. This enables businesses to budget effectively, control expenses, and identify potential areas for cost reduction.
- Productivity Enhancement: Clear instructions and streamlined workflows provided by work orders lead to faster task completion. This heightened productivity translates to increased output and revenue generation.
- Data-Driven Insights: Work order processes generate valuable data that can be analyzed to identify trends, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. These insights empower executives to make informed decisions and implement strategic changes.
- Effective Communication: Work orders facilitate transparent communication between different departments or teams involved in a task. This minimizes miscommunication, fosters collaboration, and ensures a cohesive approach towards achieving goals.
- Customer Satisfaction: In service-oriented industries, work order processes help ensure that customer requests are addressed promptly and accurately. This contributes to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Compliance and Regulation: For industries subject to regulatory standards, work order processes ensure tasks are carried out in compliance with legal requirements and industry regulations.
- Continual Improvement: By analyzing work order data, businesses can identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. This promotes a culture of continuous enhancement, leading to refined processes and higher overall performance.
Understanding and optimizing work order processes can significantly contribute to a company's bottom line and competitive advantage in today's fast-paced and demanding business landscape.
Significance Of Understanding The Economics Behind Work Order Processes
Understanding the economics behind work order processes holds immense significance for businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive and dynamic market. This understanding goes beyond the surface-level execution of tasks; it delves into the financial intricacies that influence a company's profitability, efficiency, and strategic decision-making.
The following points emphasize the significance of grasping the economics behind work order processes:
Cost Control: Work order processes are intricately linked to costs, including labor, materials, and overhead. By comprehending these cost drivers, businesses can implement strategies to optimize resource allocation, reduce wastage, and improve cost-efficiency.
Resource Utilization: Efficient work order processes ensure that resources are allocated judiciously. A deep understanding of the economics helps in avoiding over-allocation, underutilization, and unnecessary expenses, ultimately leading to higher returns on investments.
Profitability Enhancement: The economics of work order processes directly impact a company's profit margins. Streamlining workflows, reducing operational delays, and controlling costs can significantly contribute to improved profitability.
Strategic Planning: Business leaders armed with insights into work order economics are better equipped to make informed decisions. They can strategically allocate resources, set realistic timelines, and prioritize tasks based on their economic impact.
Performance Metrics: Metrics such as Return on Investment (ROI), Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), and Gross Margin can be directly influenced by the efficiency of work order processes. Understanding these metrics enables executives to monitor performance and implement corrective measures.
Competitive Advantage: In a global marketplace, where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are paramount, a firm grasp of work order economics can provide a competitive edge. Businesses that optimize their processes can offer better pricing, quicker turnaround times, and improved quality.
Risk Mitigation: Economic insights enable businesses to identify potential bottlenecks, risks, and vulnerabilities within work order processes. This proactive approach allows for the implementation of risk mitigation strategies to safeguard profitability.
Continuous Improvement: Understanding work order economics fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By analyzing data, identifying inefficiencies, and making targeted changes, companies can evolve and adapt to changing market demands.
Customer Satisfaction: Efficient work order processes often result in quicker delivery of products or services, leading to heightened customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal patrons and brand advocates.
Informed Investment: When planning technology upgrades or process enhancements, a thorough understanding of the economics helps in evaluating potential returns on investments and justifying expenditures.
In essence, understanding the economics behind work order processes transforms these seemingly mundane tasks into critical components of business strategy. It empowers executives to make well-informed decisions that not only enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness but also contribute to the overall success and longevity of the organization.
Fundamentals of Work Order Processes
At the heart of every smoothly functioning business operation lies a fundamental tool that guides tasks, allocates resources, and orchestrates timelines: the work order process. This section delves into the foundational principles that underpin effective work order processes. By exploring the core elements that constitute a work order and understanding its purpose, we embark on a journey to uncover the essential building blocks that enable organizations to translate plans into actions with precision and efficiency.
Just as a blueprint shapes the construction of a building, a well-structured work order process lays the groundwork for the successful execution of tasks, ensuring that the right resources are allocated at the right time to achieve optimal outcomes.
Through this exploration, we gain insight into how these fundamental processes serve as the backbone of operational excellence, enabling businesses to navigate the complexities of modern business environments with confidence and finesse.
A. Definition and purpose of work orders
A work order is a foundational document that serves as a compass for various business activities, guiding the execution of tasks, resource allocation, and time management. It is a structured directive that communicates specific instructions, objectives, and expectations related to a particular task or project within an organization.
The primary purpose of work orders is to streamline and formalize the process of assigning, tracking, and completing tasks or projects. They provide a clear and standardized framework for communication between different teams, departments, or individuals involved in a task.
Work orders serve as a bridge between strategic planning and operational execution, ensuring that the organization's goals are translated into actionable steps.
Work orders carry several essential functions:
- Task Clarity: Work orders provide detailed descriptions of the tasks to be performed, ensuring that everyone involved understands the scope and requirements. This clarity minimizes misunderstandings and reduces the potential for errors.
- Resource Allocation: Work orders specify the necessary resources, including labor, materials, equipment, and tools, required to complete the task. This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and without excess or shortage.
- Time Management: Work orders include deadlines and timelines for task completion. These timeframes help prioritize tasks, prevent delays, and ensure that projects progress according to schedule.
- Documentation: Work orders create a documented record of tasks, facilitating accountability and future reference. This documentation is valuable for tracking progress, analyzing performance, and improving processes over time.
- Communication: Work orders serve as a means of communication between different stakeholders. They provide a consistent format for conveying instructions, expectations, and updates, fostering effective collaboration.
- Measurement and Evaluation: Work orders enable the measurement of task completion against predefined criteria. This evaluation allows for performance assessment and identification of areas for improvement.
B. Key components of a work order
The effectiveness of a work order lies in its structure and comprehensiveness. Key components work together to provide a clear and comprehensive overview of the task at hand. These components ensure that everyone involved in the process understands the scope, requirements, and expectations.
The primary components of a work order include:
- Task Description: This section outlines the nature of the task to be completed. It provides detailed information about the task's purpose, objectives, and any specific instructions or requirements.
- Task Priority: Work orders often indicate the priority level of the task. This helps teams understand the relative importance of the task and allocate resources accordingly.
- Resource Allocation: This component specifies the resources needed to complete the task. It includes details about the personnel involved, required materials, equipment, and tools. Clear resource allocation prevents unnecessary delays and ensures efficient task execution.
- Timeline and Deadlines: Work orders include specific start and end dates for the task, as well as any intermediate deadlines. These timeframes help teams manage their schedules, prioritize tasks, and maintain project timelines.
- Location or Area: For tasks that require physical presence or specific locations, the work order should indicate where the task needs to be performed. This is particularly relevant for maintenance, repair, and installation tasks.
- Supervision and Approval: Work orders might require approval from supervisors or managers before the task can commence. Clearly stating the necessary approvals ensures that tasks align with organizational protocols.
- Safety Guidelines: If the task involves potentially hazardous activities, this section outlines safety protocols and precautions that need to be followed to ensure the well-being of personnel and the organization.
- Contact Information: This section provides contact details for key personnel involved in the task. It enables effective communication in case of clarifications, updates, or issues that may arise during task execution.
- Attachments: Work orders can include relevant documents, diagrams, or specifications that provide additional context and details related to the task.
- Progress Tracking: Some work orders include sections for tracking the progress of the task. This can include checkboxes or fields indicating different stages of completion.
- Notes and Comments: A space for additional notes or comments allows for any relevant information that doesn't fit within the structured components of the work order.
Efficiency and Productivity
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, efficiency and productivity stand as cornerstones of success. Within this context, the significance of work order processes emerges as a catalyst for optimizing these critical factors. This section delves into the symbiotic relationship between work order efficiency and overall productivity, highlighting how streamlined processes not only enhance task completion but also reverberate through the entire operational framework.
Streamlined work order processes exert a profound impact on operational efficiency, fundamentally reshaping the way tasks are executed and resources are managed. When work orders are optimized and structured for efficiency, several significant benefits emerge:
Reduced Delays: Clear task descriptions, well-defined timelines, and precise resource allocation minimize the chances of bottlenecks and delays. Work orders ensure that everyone involved understands their responsibilities and the sequence of tasks, facilitating smooth task progression.
Improved Task Clarity: Streamlined work orders provide concise instructions and expectations, eliminating confusion and the need for constant clarifications. This clarity accelerates decision-making and task execution.
Enhanced Resource Utilization: Efficient work orders allocate resources based on actual requirements. This prevents over-allocation of resources, such as excessive labor or materials, and reduces wastage, leading to cost savings.
Optimized Workflows: Well-structured work orders outline the sequence of tasks and their dependencies, allowing for the identification of potential workflow inefficiencies. This optimization minimizes redundant steps and ensures tasks are carried out in the most logical and efficient order.
Minimized Rework: Clear instructions in streamlined work orders result in fewer errors and misunderstandings. This reduction in mistakes leads to a decrease in rework and revisions, saving time, resources, and costs.
Faster Task Completion: Efficient work orders eliminate ambiguity and procedural confusion, enabling teams to work swiftly and effectively. This acceleration translates to faster task completion and overall project advancement.
Proactive Issue Resolution: Streamlined work orders often include contingency plans or guidelines for potential challenges. This proactive approach enables teams to address issues promptly, minimizing disruptions and further enhancing efficiency.
Consistent Standards: Standardized work order processes ensure uniformity in task execution across the organization. This consistency reduces variability and ensures a high level of quality in outcomes.
Data-Driven Insights: Efficient work order processes generate data that can be analyzed to identify areas for improvement. Insights from historical data enable businesses to refine processes continually and enhance efficiency.
B. Impact of Streamlined Work Order Processes on Productivity:
The impact of streamlined work order processes extends beyond efficiency, directly influencing overall productivity:
- Higher Output: Efficient work orders enable teams to complete tasks faster and with fewer obstacles. This increased pace translates to higher task and project completion rates, driving overall productivity.
- Resource Maximization: Optimal resource allocation facilitated by streamlined work orders ensures that resources are channeled towards tasks that contribute most to the organization's goals. This maximization of resource utility enhances overall productivity.
- Task Prioritization: Well-structured work orders often include task priorities. This prioritization ensures that critical tasks receive appropriate attention, resulting in the efficient allocation of time and resources.
- Time Savings: Minimized delays, reduced errors, and faster task completion collectively save valuable time. This time efficiency allows teams to take on more tasks or allocate time to strategic initiatives.
- Cumulative Effects: As tasks are completed efficiently, the positive effects accumulate, creating a ripple effect throughout the organization. This leads to increased throughput, better project management, and ultimately higher productivity levels.
Cost Management
In the intricate dance of business operations, where every action incurs costs, the role of effective cost management cannot be overstated. This section delves into the critical nexus between work order processes and cost management, revealing how astutely managed work orders can shape the financial landscape of an organization.
A. Cost elements in work order processes
Work order processes are intimately entwined with the financial fabric of a business, involving various cost elements that impact the organization's profitability and budgetary control. These cost elements represent the economic underpinnings of executing tasks and projects efficiently. The three primary cost elements within work order processes are:
1. Labor Costs: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with the workforce involved in executing tasks outlined in work orders. This includes direct labor, such as wages and salaries of employees performing the tasks, as well as indirect labor costs related to supervisory roles or support functions.
Efficient work order processes that provide clear task descriptions, allocate appropriate personnel, and set realistic timelines contribute to optimal labor cost management. Streamlined processes reduce idle time, prevent duplication of efforts, and ensure that labor resources are used efficiently.
2. Material Costs: Material costs comprise expenditures tied to the physical resources required to complete tasks outlined in work orders. These resources can range from raw materials to components and consumables. Effective work order processes ensure accurate specification of required materials, preventing over-purchasing or stockpiling of excess inventory. By minimizing material waste and ensuring timely procurement, businesses can control material costs and enhance overall cost-effectiveness.
3. Overhead Expenses: Overhead expenses include indirect costs necessary for the operation of the business but not directly tied to specific tasks. This encompasses expenses like utilities, rent, administrative salaries, and maintenance. While not tied to a single work order, these costs are distributed across various tasks and projects. Efficient work order processes indirectly impact overhead expenses by contributing to streamlined operations. By reducing delays and errors, overhead costs associated with prolonged project durations or rework can be minimized, ultimately leading to cost savings.
B. Importance of accurate cost estimation in work orders
Accurate cost estimation within work orders is a linchpin of effective financial management and strategic decision-making. This component is not just about projecting expenses; it's a pivotal factor that influences budgeting, resource allocation, profitability assessment, and overall business viability.
The importance of accurate cost estimation within work orders is underscored by several critical reasons:
- Informed Decision-Making: Accurate cost estimates enable informed decision-making at both tactical and strategic levels. Businesses can assess the financial feasibility of projects, allocate resources intelligently, and determine the potential return on investment (ROI).
- Budgetary Control: Work orders serve as the foundation for creating budgets. Accurate cost estimation ensures that budgets are realistic and aligned with the actual financial requirements of tasks. This prevents cost overruns and enhances financial predictability.
- Resource Allocation: Accurate cost estimation aids in optimal resource allocation. When costs are well-estimated, resources can be allocated proportionally, preventing underutilization or overextension of personnel and materials.
- Bid Proposals: In industries involving contracts and bids, accurate cost estimation is crucial for competitive bidding. An accurately estimated cost ensures that bids are not only competitive but also cover all expenses, safeguarding profitability.
- Profitability Analysis: Accurate cost estimates enable accurate profitability analysis post-task completion. This analysis helps businesses understand the actual costs incurred against projected costs, allowing for adjustments and improvements in future estimations.
- Contract Management: Accurate cost estimates provide a basis for negotiating contracts, pricing services, and agreeing on payment terms. Precise estimation ensures that contracts are fair to both parties and protect the organization's financial interests.
- Risk Management: Inaccurate cost estimates can lead to unforeseen financial challenges during task execution. Accurate estimations facilitate better risk assessment and mitigation planning, safeguarding against financial surprises.
- Client Relationships: In service-oriented industries, accurate cost estimates build trust with clients. Clients appreciate transparency in pricing, and precise estimates prevent disputes or dissatisfaction arising from unexpected costs.
- Project Viability: Accurate cost estimation helps evaluate the viability of potential projects or initiatives. Businesses can assess whether the projected revenue justifies the estimated expenses and make informed go/no-go decisions.
C. Cost control strategies through optimized work order management
Optimized work order management serves as a powerful tool for controlling costs within an organization. By implementing effective strategies, businesses can proactively manage expenses, prevent financial leakage, and enhance overall profitability.
Here are two critical cost control strategies achieved through optimized work order management:
1. Preventing Scope Creep: Scope creep refers to the gradual expansion of a project's objectives, tasks, or requirements beyond the initial agreement. This expansion often leads to increased costs, extended timelines, and resource overuse. Preventing scope creep is a paramount concern in cost control. Optimized work order management addresses scope creep through:
- Clear Task Definitions: Detailed task descriptions and objectives in work orders leave little room for ambiguity. When expectations are explicitly outlined, it becomes easier to identify any deviations from the original scope.
- Change Management: Work order processes can include formal change request procedures. Any modifications to the scope should be documented, reviewed, and approved before implementation. This ensures that changes are assessed for their impact on costs and timelines.
- Stakeholder Communication: Effective communication with stakeholders, including clients and team members, helps manage expectations. Regular updates and transparent discussions can help prevent scope creep by addressing any changes early.
2. Minimizing Rework and Revisions: Rework and revisions can significantly inflate costs and undermine productivity. Optimized work order management minimizes these by:
- Comprehensive Task Descriptions: Well-detailed work orders leave no room for interpretation, reducing the chances of incorrect execution and subsequent rework.
- Regular Feedback Loops: Establishing feedback loops during task execution allows for intermediate reviews, reducing the likelihood of costly errors going unnoticed until completion.
- Quality Control Checks: Implementing quality control checks at key milestones helps catch errors before they propagate, minimizing the need for extensive revisions or rework.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing data from historical work orders can identify patterns of rework or revisions. Insights from these analyses can guide process improvements to mitigate such occurrences in the future.
Impact on Decision Making
This section delves into a pivotal facet of work order processes: their profound influence on decision-making. By exploring how work order processes yield invaluable data-driven insights, inform strategic planning, and empower executives to make informed choices, we embark on a journey that unveils the intricate interplay between operational efficiency and visionary decision-making.
In a world where the quality of decisions shapes the destiny of businesses, understanding the far-reaching impact of work order processes on decision-making emerges as a navigational compass for driving growth, innovation, and sustainable success.
A. Data-driven insights from work order processes
Work order processes generate a wealth of data that, when harnessed effectively, can provide valuable insights into operational efficiency, resource utilization, and overall performance. These data-driven insights allow businesses to make informed decisions and refine their processes.
Here's how work order data contributes to data-driven insights:
- Performance Analysis: Analyzing completed work orders provides insights into task completion times, resource allocation, and overall productivity. Patterns and trends emerge, revealing areas of excellence and potential bottlenecks.
- Resource Optimization: By analyzing resource utilization patterns, organizations can identify overused or underused resources. This insight informs decisions on reallocating resources for maximum efficiency.
- Process Bottlenecks: Data from work orders highlights recurring delays or inefficiencies in workflows. Identifying these bottlenecks enables businesses to address them strategically, streamlining processes and reducing costs.
- Quality Assessment: Work order data can shed light on the frequency of rework or revisions. This insight helps in pinpointing quality issues and implementing corrective actions.
- Predictive Maintenance: For maintenance tasks, historical work order data can be used to predict when equipment or assets are likely to require maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing operational continuity.
B. Utilizing Historical Work Order Data for Strategic Planning:
Historical work order data holds a treasure trove of information that can guide strategic planning and future decision-making. This data provides a foundation for informed actions and long-term vision:
- Resource Allocation: Historical data helps organizations allocate resources based on past demand, avoiding under or over-allocation that can impact costs and productivity.
- Budgeting: Accurate historical data aids in creating realistic budgets for future projects, ensuring that financial resources are allocated appropriately.
- Trend Analysis: By analyzing historical data, organizations can identify trends in task completion times, costs, and other variables. This trend analysis informs strategies for enhancing efficiency and cost control.
- Capacity Planning: Understanding historical resource utilization helps in planning for future capacity needs. This is especially crucial in industries with fluctuating demand.
- Risk Assessment: Historical data can reveal past challenges and issues faced during task execution. This insight helps in identifying potential risks in upcoming projects and developing mitigation strategies.
C. Case Studies Showcasing How Work Order Economics Influenced Decisions:
Real-world case studies exemplify how work order economics directly impact decision-making and organizational outcomes:
- Cost-Effective Expansion: A manufacturing company analyzed historical work order data to identify peak production periods. This insight guided their decision to expand production capacity, ensuring resources were utilized optimally.
- Optimal Workforce Allocation: A service organization examined past work orders to determine staffing requirements during different seasons. This data-driven approach enabled them to allocate workforce efficiently, avoiding overstaffing or understaffing.
- Vendor Negotiations: Using historical work order data, a construction firm negotiated favorable terms with suppliers by demonstrating the quantity of materials required over time. This data-driven negotiation strategy led to cost savings.
- Predictive Maintenance: An energy company utilized historical work order data to predict maintenance needs for power generation equipment. This proactive approach reduced downtime and operational disruptions.
Technology and Automation
In the digital age, where innovation propels industries forward, the convergence of technology and business operations has become a defining hallmark. This section delves into a transformative dimension of work order processes: the integration of technology and automation.
By exploring how cutting-edge solutions reshape traditional workflows, enhance accuracy, and unlock unprecedented efficiency, we embark on a journey that underscores the synergy between human ingenuity and technological prowess.
In a landscape where businesses seek to harness the full potential of automation, understanding the dynamic interplay between work order processes and technology becomes paramount, as it paves the way for operational excellence and a future shaped by seamless precision.
A. Role of technology in modern work order processes
Technology has emerged as a catalyst for revolutionizing work order processes, propelling them beyond traditional paper-based systems into the realm of efficiency, accuracy, and real-time collaboration. The role of technology in modern work order processes encompasses a spectrum of advancements that streamline operations and enhance decision-making:
1. Digital Work Orders and Real-Time Updates: Digital work orders replace manual paperwork with electronic documents accessible on various devices. This shift offers several advantages:
- Real-Time Accessibility: Digital work orders can be accessed anytime, anywhere, providing field technicians and stakeholders with up-to-date information.
- Immediate Updates: Changes, revisions, or progress updates can be made instantly, ensuring that everyone is on the same page without delays.
- Collaboration: Digital work orders enable real-time collaboration. Technicians, supervisors, and managers can communicate seamlessly, share updates, and address issues promptly.
- Data Capture: Digital work orders allow for automated data capture, reducing the likelihood of errors caused by manual data entry.
2. Automation of Routine Tasks: Automation leverages technology to handle repetitive and routine tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex activities:
- Task Assignment: Automated systems can assign tasks to appropriate personnel based on skills, availability, and workload, minimizing manual intervention.
- Notifications and Alerts: Automated notifications keep stakeholders informed about task progress, delays, or any exceptional circumstances.
- Inventory Management: Automation tracks inventory levels and triggers reorder alerts when stock is low, preventing delays due to material shortages.
- Scheduling and Routing: Automated scheduling optimizes task sequences, considering factors like location and technician availability to reduce travel time and improve efficiency.
- Data Analysis: Automation processes work order data to generate insights, helping organizations identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
In essence, technology empowers work order processes to transcend their conventional limitations, fostering enhanced collaboration, accuracy, and efficiency. The integration of digital work orders and automation equips businesses with tools to navigate the complexities of modern operations, enabling them to adapt, innovate, and thrive in a fast-paced digital landscape.
B. Economic benefits of technology adoption in work order management
The adoption of technology in work order management brings about a transformative impact on an organization's economic landscape. Beyond operational efficiencies, technology yields tangible economic benefits that contribute to cost savings, revenue generation, and improved financial health.
Here are two key economic benefits of technology adoption in work order management:
1. Reduced Administrative Costs: Technology streamlines administrative processes, reducing the time, effort, and resources required for manual administrative tasks. This reduction in administrative overhead translates into cost savings:
- Paperless Operations: Digital work orders eliminate the need for paper-based documentation, reducing costs associated with printing, storage, and physical filing systems.
- Automated Communication: Technology automates communication processes, minimizing the need for manual coordination and follow-up. This reduces labor costs and prevents time wastage.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Automation ensures that resources are allocated optimally, reducing the chances of overallocation and related expenses.
- Faster Decision-Making: Real-time data accessibility speeds up decision-making, preventing delays and enhancing operational efficiency.
2. Enhanced Accuracy and Data Integrity: Technology introduces precision and data integrity into work order processes, minimizing errors and reducing associated costs:
- Reduced Rework: Automated systems and digital work orders minimize errors that often lead to rework, saving time, resources, and costs associated with redoing tasks.
- Accurate Resource Allocation: Automation ensures that the right resources are allocated to tasks, preventing wastage and unnecessary expenses.
- Data-Driven Insights: Accurate and comprehensive data generated by technology enables organizations to make informed decisions, minimizing costly mistakes resulting from incomplete or incorrect information.
- Regulatory Compliance: Accurate record-keeping facilitated by technology ensures compliance with regulations, avoiding potential fines and legal expenses.
Challenges and Mitigation
In the labyrinthine realm of work order processes, where efficiency and accuracy reign supreme, challenges are inevitable companions. This section delves into a comprehensive exploration of the obstacles that can hinder the smooth execution of work order processes.
By examining these challenges through a critical lens and unveiling strategies to mitigate them, we embark on a journey to decipher the delicate art of navigating complexity.
In a world where success is measured by the ability to overcome hurdles, understanding the intricacies of challenges within work order processes empowers organizations to fortify their operational foundations and stride confidently toward optimal outcomes.
A. Common challenges in work order processes
Work order processes, while integral to operational success, are not immune to challenges that can impede efficiency and effectiveness. Recognizing and addressing these challenges is essential for maintaining smooth operations. Here are some common challenges faced in work order processes:
1. Communication Gaps: Effective communication is paramount for successful work order execution. Communication gaps can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and errors. These gaps may occur between different teams, departments, or even within the same team. They can result from unclear instructions, lack of updates, or miscommunication channels.
2. Unclear Task Descriptions: Unclear or ambiguous task descriptions can lead to confusion, inefficiencies, and subpar outcomes. If work orders lack detailed instructions or specific requirements, individuals tasked with execution may struggle to understand what's expected of them. This can lead to errors, rework, and delays.
3. Inefficient Resource Allocation: Allocating resources haphazardly can lead to resource shortages or oversupply, resulting in wasted time and money. Poor resource allocation can be caused by insufficient planning, inadequate data analysis, or the absence of visibility into resource availability.
Now, let's delve deeper into the challenges:
1. Communication Gaps: Effective communication is the bedrock of successful work order processes. When communication breaks down, the consequences can be far-reaching:
- Delayed Execution: Miscommunications can lead to delays as individuals wait for clarification or make assumptions about tasks.
- Errors and Rework: Lack of clear communication can result in tasks being executed incorrectly, leading to rework and additional costs.
- Missed Deadlines: If updates or changes to work orders are not communicated promptly, deadlines may be missed.
To mitigate communication gaps, organizations should establish clear communication protocols, use collaborative tools, and encourage open dialogue among teams. Regular status updates and clear channels of communication can prevent misunderstandings and ensure everyone is on the same page.
2. Unclear Task Descriptions: Unclear task descriptions can result in confusion and suboptimal outcomes:
- Productivity Loss: Employees spend time seeking clarification or attempting to decipher ambiguous instructions.
- Quality Issues: Unclear instructions can lead to tasks being executed incorrectly, affecting the quality of work.
- Wasted Resources: Incorrectly executed tasks may need to be redone, wasting time, labor, and materials.
To address this challenge, work orders should include detailed and specific task descriptions. Providing context, objectives, and expected outcomes helps ensure that everyone involved understands the scope and requirements of the task.
3. Inefficient Resource Allocation: Inefficient resource allocation can lead to wasted resources and increased costs:
- Excess Inventory: Overestimating material requirements can lead to excess inventory, tying up capital and storage space.
- Underutilization of Labor: Poor planning may result in labor resources being idle or not utilized optimally.
- Missed Opportunities: Inefficient resource allocation can lead to missed opportunities for cost savings and productivity gains.
Efficient resource allocation requires a thorough analysis of historical data, real-time demand, and capacity. Utilizing technology, such as predictive analytics and resource management software, can help organizations make data-driven decisions and optimize resource allocation for each task.
B. Strategies to overcome challenges and improve economic outcomes
While challenges in work order processes are inevitable, organizations can proactively employ strategies to overcome these hurdles and achieve improved economic outcomes. By implementing these strategies, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and elevate overall performance.
Here are three key strategies:
1. Clear Communication Channels: Effective communication is the linchpin of successful work order processes. To overcome communication gaps:
- Regular Updates: Establish a practice of providing regular updates on work order progress, changes, and developments. This ensures that all stakeholders are informed and aligned.
- Digital Collaboration Tools: Utilize digital platforms and collaboration tools to facilitate real-time communication, enabling teams to exchange information, seek clarification, and address concerns promptly.
- Centralized Communication: Designate a central communication hub for work orders. This hub can serve as a repository for all communications, ensuring that information is easily accessible and not scattered across various channels.
2. Standardized Work Order Templates: Standardized work order templates contribute to clearer task descriptions and improved task execution:
- Consistent Format: Utilize standardized templates that outline key components of a work order consistently. This format ensures that essential information is included in every work order.
- Detailed Instructions: Standardized templates should include detailed task descriptions, objectives, requirements, and any specific instructions. This clarity eliminates ambiguity and minimizes errors.
- Customization: While maintaining consistency, allow for customization of templates to accommodate unique requirements for different tasks.
3. Cross-Functional Collaboration: Collaboration across different departments and teams fosters a holistic approach to work order processes:
- Interdepartmental Coordination: Encourage collaboration between departments involved in different stages of work order execution. This alignment ensures smooth transitions and reduces delays.
- Shared Insights: Create forums or meetings where teams can share insights, challenges, and best practices related to work order processes. This promotes learning and continuous improvement.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops that allow individuals involved in different stages of work order processes to provide input. This iterative approach enhances the overall quality of work orders and outcomes.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement, also known as Kaizen, is a philosophy and methodology that focuses on incremental and ongoing enhancements to processes, products, or services. It involves identifying areas for improvement, making changes, and consistently seeking ways to optimize performance.
Continuous improvement is a dynamic approach that encourages organizations to evolve, adapt, and excel over time, fostering a culture of innovation, efficiency, and excellence.
A. Implementing a Culture of Continuous Improvement:
Creating a culture of continuous improvement is essential for sustaining growth and innovation within an organization:
- Leadership Buy-In: Leadership support is crucial. When leaders endorse and actively participate in continuous improvement initiatives, it sends a clear message about its importance.
- Employee Engagement: Involve employees at all levels in identifying improvement opportunities. Employees on the frontline often possess valuable insights into daily operations and challenges.
- Training and Education: Provide training in continuous improvement methodologies to equip employees with the skills needed to identify inefficiencies and contribute to solutions.
- Open Communication: Encourage open dialogue where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and suggestions for improvement without fear of criticism.
B. Measuring Success through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics that help organizations track their progress and measure the success of continuous improvement efforts:
- Relevance: Choose KPIs that align with the organization's goals and areas of focus for improvement.
- Data-Driven: KPIs should be based on accurate and reliable data. Regularly collect and analyze data to assess performance.
- Actionable: KPIs should provide actionable insights. They should help identify trends, highlight areas for improvement, and guide decision-making.
- Benchmarking: Compare KPIs against industry standards or past performance to gauge improvement over time.
C. Feedback Loops and Adapting Work Order Processes based on Outcomes:
Feedback loops play a crucial role in continuous improvement by allowing organizations to adapt work order processes based on outcomes:
- Gather Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from employees, stakeholders, and customers involved in work order processes.
- Review Outcomes: Analyze outcomes, including successes and failures. Identify areas where processes can be enhanced or refined.
- Adaptation: Use feedback and outcome analysis to make necessary adjustments to work order processes. This might involve revising templates, workflows, or resource allocation.
- Iterative Approach: Continuous improvement is an ongoing cycle. Continuously gather feedback, review outcomes, and adapt processes based on new insights.
Incorporating these principles of continuous improvement fosters an organizational environment that thrives on innovation, collaboration, and the pursuit of excellence. By embracing change and consistently seeking ways to enhance work order processes, organizations position themselves to remain competitive, agile, and attuned to the evolving needs of their industry and customers.
Future Trends
Future trends in work order processes reflect the evolving landscape of technology, industry demands, and organizational priorities. These trends shape how businesses manage tasks, allocate resources, and drive efficiency in an increasingly interconnected and data-driven world.
A. Anticipated Developments in Work Order Processes:
The future of work order processes is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and real-time decision-making. Here are two anticipated developments:
1. AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionize how organizations approach maintenance tasks. Predictive maintenance, powered by AI algorithms, leverages historical data and real-time sensor information to predict when equipment or assets require maintenance before failure occurs. This trend offers several benefits:
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance helps prevent unplanned downtime by addressing maintenance needs proactively, saving time and costs associated with emergency repairs.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: By accurately predicting maintenance requirements, organizations can allocate resources precisely when needed, preventing overallocation or underutilization.
- Enhanced Cost Efficiency: AI-driven predictive maintenance reduces maintenance costs by addressing issues before they escalate into major problems, thus avoiding costly repairs.
2. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) for Real-Time Monitoring: The Internet of Things (IoT) involves connecting devices and assets to the internet to gather and exchange data. In work order processes, IoT integration enables real-time monitoring of equipment, assets, and tasks. This integration yields benefits such as:
- Real-Time Updates: IoT devices provide continuous data streams, enabling real-time updates on task progress, equipment status, and environmental conditions.
- Automated Alerts: IoT-enabled sensors can trigger automated alerts when predefined thresholds are exceeded, notifying relevant stakeholders of potential issues.
- Data-Driven Insights: The data collected from IoT devices offers valuable insights into equipment performance, usage patterns, and potential areas for improvement.
- Proactive Decision-Making: Real-time data from IoT devices empowers organizations to make proactive decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and address emerging challenges promptly.
These anticipated developments signify a shift toward proactive and data-driven work order processes. AI-driven predictive maintenance and IoT integration exemplify how organizations are leveraging technology to optimize operations, minimize downtime, and enhance overall efficiency.
B. Economic implications of future trends on work order management
The anticipated future trends in work order management, driven by technological advancements, hold profound economic implications that can reshape the financial landscape of organizations. These trends are not only transformative in terms of operational efficiency but also have far-reaching effects on costs, revenue generation, and overall economic outcomes.
Here's how these trends can impact the economics of work order management:
1. AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance: The adoption of AI-driven predictive maintenance has significant economic implications:
- Cost Savings: Predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime and emergency repairs, leading to substantial cost savings. Organizations can avoid the expenses associated with sudden equipment failures and the subsequent disruption of operations.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Resources are allocated more efficiently as maintenance tasks are scheduled based on accurate predictions. This prevents overallocation of resources and reduces unnecessary downtime.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Addressing maintenance needs proactively helps extend the lifespan of equipment and assets. This delay in replacement or major repairs leads to long-term cost savings.
2. Integration with IoT for Real-Time Monitoring: The integration of IoT for real-time monitoring carries economic implications that enhance operational effectiveness:
- Reduced Operational Costs: Real-time monitoring and automated alerts enable organizations to address issues promptly, preventing costly breakdowns and minimizing the need for costly emergency repairs.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Real-time data allows for dynamic resource allocation, ensuring that resources are utilized optimally based on current conditions and requirements.
- Enhanced Productivity: The ability to monitor equipment and tasks in real-time improves productivity as teams can react swiftly to changing conditions, minimizing delays and inefficiencies.
Conclusion
The integration of technology, data-driven insights, and a culture of continuous improvement have emerged as driving forces that shape the landscape of work order processes. Anticipated future trends, such as AI-driven predictive maintenance and IoT integration, hold promises of further economic optimization.
Challenges, once identified, are transformed into opportunities for growth through strategies like clear communication, standardized templates, and cross-functional collaboration.
In an era where data, innovation, and agility reign supreme, the economics of work order processes extend beyond mere task execution. They embody a dynamic synergy between operational acumen and financial wisdom. By mastering this synergy, organizations navigate toward higher efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainable growth.
The journey into the economics of work order processes culminates in a realization: that the intricacies of these processes are not just administrative details but a compass guiding businesses toward a prosperous future.
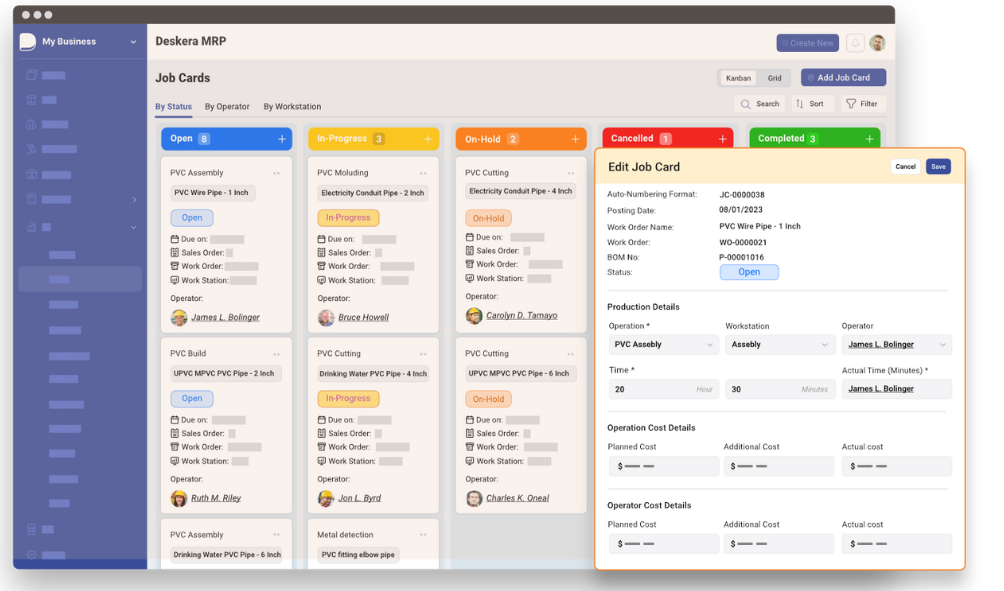
How Deskera Can Assist You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's key features of demand forecasting with Deskera include as follows:
- Establish Demand Forecasting Process
- Automate Data Collection
- Monitor Market Trends
- Analyze Historical Data
- Estimate Future Demand
- Adjust Production Levels
- Manage Supply Chain and much more!
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic Imperative: Work order processes are a strategic imperative for businesses, shaping efficiency, resource allocation, and economic success.
- Data-Driven Insights: Work order data yields invaluable insights into performance, resource utilization, and productivity, enabling informed decision-making.
- Efficiency-Productivity Nexus: Streamlined work order processes directly correlate with enhanced efficiency and overall productivity within organizations.
- Cost Elements: Accurate cost estimation within work orders encompasses labor, material, and overhead costs, forming the foundation of financial stability.
- Technology Integration: Embracing technology and automation optimizes work order management, reducing administrative costs and enhancing accuracy.
- Continuous Improvement: Fostering a culture of continuous improvement empowers organizations to adapt, innovate, and thrive amidst challenges.
- AI and IoT Influence: Future trends, like AI-driven predictive maintenance and IoT integration, promise economic optimization and operational excellence.
- Communication and Clarity: Clear communication, standardized templates, and cross-functional collaboration mitigate challenges and enhance work order processes.
- Outcome Measurement: Key performance indicators (KPIs) measure success, guiding organizations to make data-driven decisions and track improvement.
- Economic Impact: Effective work order processes positively impact an organization's bottom line, delivering cost savings, efficiency gains, and long-term financial viability.
Related Articles