The global market size of the pulp and paper industry was valued at US $368.10 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach US $368.10 billion by 2026. (Source: Grand View Research)
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, the total global area of forest land has decreased by 178 million hectares between 1990 and 2020 due in part to deforestation for purposes such as paper production. (Source: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations)
The United States was the world's second-largest producer of paper and cardboard in 2019, with a production volume of approximately 72.8 million metric tons. (Source: Statista)
In 2020, China was the world's largest producer of paper and cardboard, with a production volume of approximately 115 million metric tons. (Source: Statista)

Despite the advent of digital technology, paper is still widely utilized every day for a variety of functions. In fact, more than 400 million metric tonnes of paper and cardboard are produced worldwide each year. The most common type of paper is packing paper and board, whose demand has risen recently as a result of the explosion in online shopping.
The process of paper production involves harvesting trees, processing the wood pulp, and then converting it into a finished paper product. While paper production has contributed significantly to economic growth and development, it also has environmental impacts, such as deforestation and carbon emissions.
As a result, the industry has made efforts to become more sustainable, by implementing practices such as using recycled materials and reducing water and energy consumption during production.
This highlights the importance of unpacking the basics of paper production to be able to have a complete understanding of the same. This article will help you with the same by covering the following topics:
- Overview of the Paper Production Process
- Step-by-Step Guide to Paper Production Process
- Importance of Paper Production
- Factors Affecting the Paper Production
- What are the Determinants of Texture and Thickness of Paper in Paper Production?
- Different Types of Paper
- Sustainability in Paper Production
- Challenges in Paper Production
- Importance of Quality Control in Paper Production
- Importance of Understanding Paper Production for a Sustainable Future
- Safety Precautions that Should be Considered During Paper Production
- FAQs related to Paper Production
- How can Deskera Help You with Paper Production?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Overview of the Paper Production Process
The paper production process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation of raw materials: The raw materials used in papermaking include wood chips, recycled paper, and agricultural residues. These materials are sorted, cleaned, and processed to remove impurities and improve their quality.
- Pulping: The prepared raw materials are then subjected to pulping, which involves the separation of fibers from the other components. This is done through mechanical or chemical means.
- Screening and cleaning: After pulping, the pulp is screened to remove large impurities like rocks and sticks. It is then cleaned to remove smaller particles like sand and dirt.
- Bleaching (optional): Depending on the desired end-product, the pulp may be bleached to remove any remaining impurities and lighten its color.
- Papermaking: The cleaned and screened pulp is mixed with water and chemicals to form a slurry, which is then fed onto a paper machine. The paper machine consists of several sections, each designed to perform a specific function, such as forming, pressing, drying, and calendaring.
- Finishing: Once the paper is dried, it may undergo additional processing to achieve specific properties like smoothness, gloss, or printability. This can include coating, sizing, or calendaring.
- Winding and cutting: The finished paper is wound onto large rolls, which are then cut into smaller rolls or sheets based on customer specifications.
- Packaging and distribution: The final step involves packaging the paper and distributing it to customers, which can include printers, publishers, or other industries that use paper as a raw material.
Step-by-Step Guide to Paper Production Process
The process of paper production can vary depending on the type of paper being produced and the specific techniques used by the manufacturer. However, the basic steps involved in most paper production processes are as follows:
Preparation of Raw Materials
The preparation of raw materials is a crucial step in the paper production process, as it can impact the quality and characteristics of the final paper product. The raw materials used in paper manufacturing can vary depending on the type of paper being produced and the availability of resources.
Here are some common raw materials used in paper production and how they are prepared:
- Wood chips: Wood chips are one of the most common raw materials used in paper manufacturing. The wood chips are typically harvested from trees and then processed to remove bark, leaves, and other impurities. The wood chips are then sorted by size and quality, with larger chips typically used for making pulp and smaller chips used for producing paperboard or packaging materials.
- Sawdust: Sawdust is another common raw material used in paper manufacturing, particularly for producing lower-quality paper products. Sawdust is created when the wood is cut or milled, and it can be collected and processed to remove impurities before being used in the papermaking process.
- Recycled paper: Recycled paper is an increasingly popular raw material for paper manufacturing, as it is more environmentally friendly and cost-effective than using new wood fibers. The recycled paper is typically collected and sorted by type, with different grades of paper being used for different types of products. The paper is then processed to remove any inks, coatings, or other impurities before being pulped and turned into new paper products.
- Other fibers: In addition to wood chips, sawdust, and recycled paper, other fibers can be used as raw materials in paper manufacturing, including cotton, hemp, and flax. These fibers are typically processed and cleaned to remove any impurities before being pulped and turned into paper.
Overall, the preparation of raw materials is an important step in the paper production process, as it can impact the quality, strength, and other characteristics of the final product. Manufacturers must carefully select and prepare their raw materials to ensure that they can create high-quality paper products that meet the needs of their customers.
Pulping
Pulping is a crucial step in the paper production process that involves breaking down the raw materials, such as wood chips or recycled paper, into a pulp that can be used to create new paper products. The pulping process can be accomplished through mechanical or chemical means, and the choice of method can impact the quality and characteristics of the final paper product.
Mechanical pulping:
Mechanical pulping is a process that involves grinding or refining raw materials, such as wood chips, to create a pulp. The mechanical pulping process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The raw materials are prepared by removing impurities, such as bark or dirt, and reducing them to a size that can be processed by the refining equipment.
- Grinding: The raw materials are then ground or crushed using a series of mechanical grinders or refiners. This process breaks down the fibers in the raw materials and produces a pulp that is suitable for papermaking.
- Screening: The pulp is then screened to remove any remaining impurities, such as knots or dirt, and to ensure that the pulp has a uniform consistency.
Chemical pulping:
Chemical pulping is a process that involves cooking the raw materials in a chemical solution to break down the fibers and create a pulp. The chemical pulping process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The raw materials are prepared by removing impurities and reducing them to a size that can be processed by the pulping equipment.
- Cooking: The raw materials are then cooked in a chemical solution, such as sodium hydroxide or sulfurous acid, to break down the fibers and create a pulp.
- Washing: The pulp is then washed to remove any remaining chemicals or impurities.
Overall, the pulping process is a critical step in paper manufacturing, as it creates the pulp that is used to create new paper products. By carefully selecting the pulping method and optimizing the process parameters, manufacturers can produce a high-quality pulp that meets the specific requirements of their customers.
Screening and Cleaning
After pulping, the next step in the paper production process is screening and cleaning. Screening and cleaning are essential processes that help to remove impurities, such as dirt, debris, and ink, from the pulp.
These impurities can affect the quality of the final paper product, so it's important to remove them before proceeding with the papermaking process. Here's an overview of how screening and cleaning are typically carried out in paper manufacturing:
Screening:
Screening is a process that involves passing the pulp through a series of screens or filters to remove any large impurities. The screens are typically made of metal or plastic and have small holes or slots that allow the pulp to pass through while trapping larger impurities.
The screening process can be accomplished in one or more stages, depending on the quality of the pulp and the requirements of the final paper product. In some cases, the screens are washed or sprayed with water to remove any remaining impurities.
Cleaning:
Cleaning is a process that involves removing smaller impurities from the pulp using a series of cleaning devices. The cleaning devices can include centrifugal cleaners, which use centrifugal force to remove heavy contaminants such as sand and grit, and flotation cells, which use air bubbles to lift and remove lighter contaminants such as ink and wax.
The cleaning process can also include a process called deinking, which is used to remove ink and other coatings from the pulp. Deinking is typically accomplished by washing the pulp with a series of chemicals and then using flotation cells to lift and remove the ink particles.
Overall, screening and cleaning are essential processes in paper manufacturing that help to ensure the quality and purity of the pulp. By carefully screening and cleaning the pulp, manufacturers can produce high-quality paper products that meet the specific requirements of their customers.
Refining
Refining is a key step in the paper production process that involves mechanically treating the pulp to improve its quality and physical properties. The refining process can help to increase the strength, density, and smoothness of the paper, as well as improve its printability and other characteristics.
The refining process typically involves passing the pulp through a series of refining machines, which use pressure and friction to break down the fibers and make them more flexible and uniform. The refining machines can be classified into two categories:
- Conical refiners: Conical refiners are the most commonly used type of refiner and are typically used for mechanical pulp. They consist of a rotating cone and a stationary bed plate. The pulp is fed into the narrow end of the cone, and as it moves towards the wider end, it is subjected to increasing pressure and friction, which breaks down the fibers.
- Double disc refiners: Double disc refiners are typically used for chemical pulp and recycled pulp. They consist of two parallel discs that rotate in opposite directions. The pulp is fed between the discs, which apply pressure and friction to the pulp and break down the fibers.
In addition to improving the quality of the pulp, the refining process can also affect the final paper product in several ways. For example, the degree of refining can impact the paper's strength, porosity, and smoothness. It can also affect the paper's printability and ink absorption properties.
Overall, refining is an important step in the paper production process that can significantly impact the quality and characteristics of the final paper product. By carefully controlling the refining process and selecting the appropriate refining machines, manufacturers can produce paper products that meet the specific requirements of their customers.
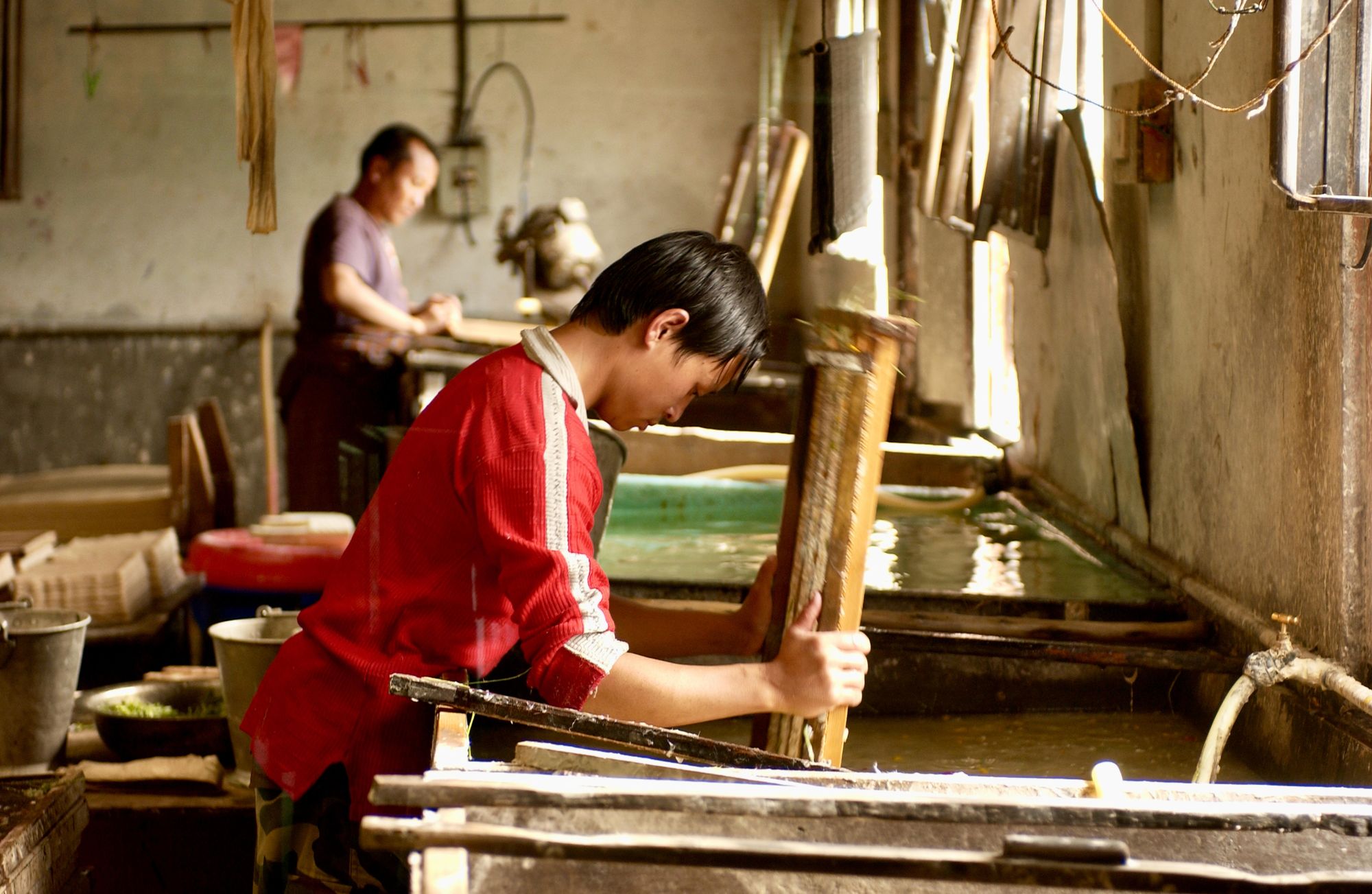
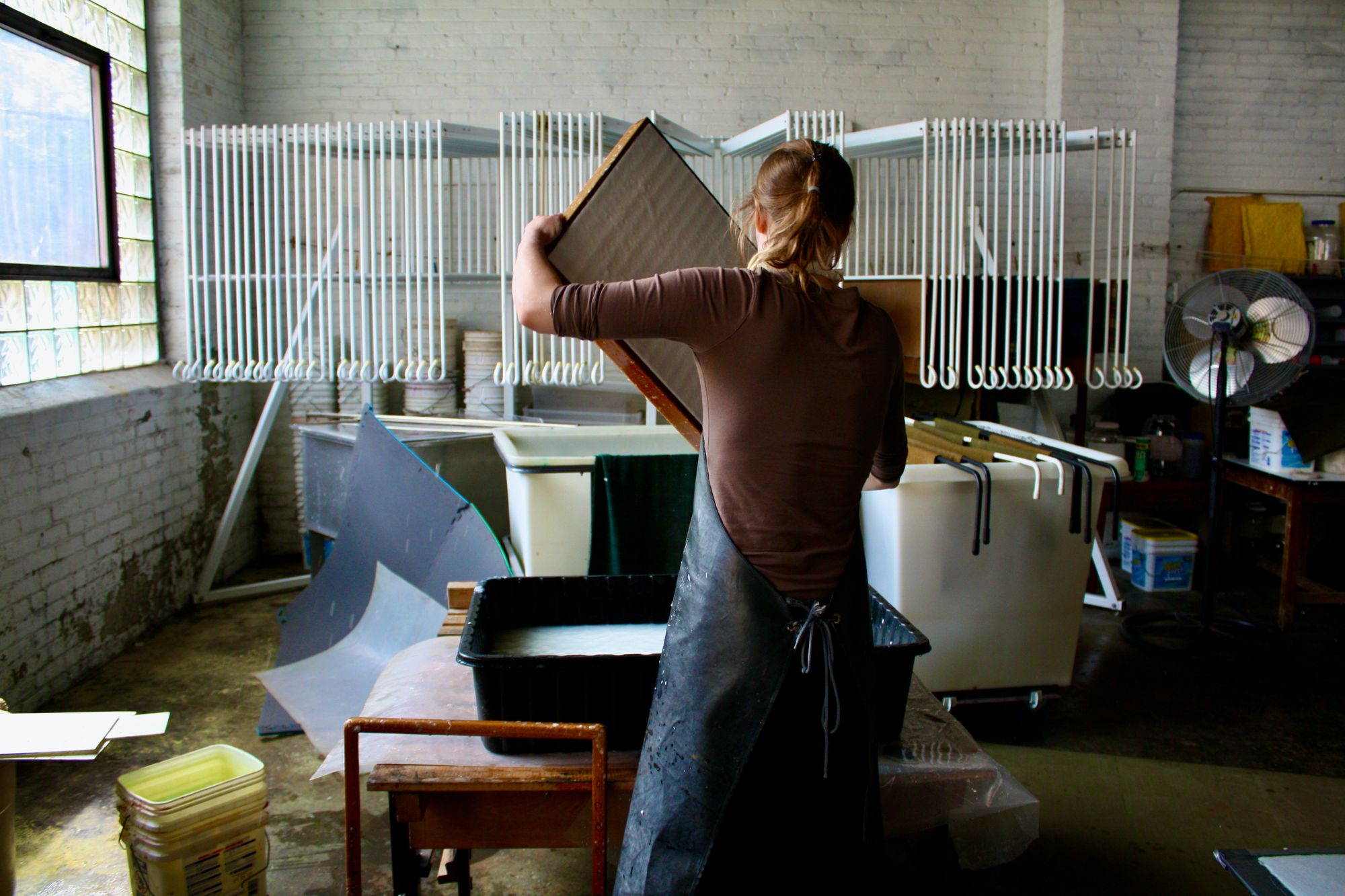
Papermaking
Papermaking is a crucial step in the paper production process. It involves the transformation of pulp, which is a mixture of fibers and water, into a flat, continuous sheet of paper.
The papermaking process consists of several stages, including sheet formation, pressing, and drying. During sheet formation, the pulp slurry is spread evenly onto a moving mesh screen, and the water is drained away, leaving a mat of fibers on the screen. The mat is then pressed to remove excess water, and finally, the paper is dried through the application of heat and/or airflow.
The quality of the paper produced depends on many factors, including the quality of the pulp, the composition of the fiber mixture, and the processing conditions. Modern papermaking technology allows for the production of a wide range of paper products, from newsprint and cardboard to high-quality printing paper and specialty papers such as tissue and paperboard.
Overall, papermaking is a critical step in the paper production process, and advancements in papermaking technology have played a significant role in the growth and development of the global paper industry.
Drying
Drying is an essential step in the paper production process. After the paper has been formed and pressed, it still contains a significant amount of moisture. The purpose of the drying stage is to remove the remaining moisture from the paper, resulting in a final product that is flat, dry, and ready for use.
The drying stage is typically accomplished through the use of a series of heated rollers. As the paper moves through the rollers, the heat evaporates the remaining water, and the paper becomes increasingly dry. The speed and temperature of the rollers must be carefully controlled to ensure that the paper dries evenly and does not become overheated or scorched.
Different types of paper may require different drying conditions. For example, high-quality printing paper may require a slower, gentler drying process to prevent damage to the fibers and maintain a smooth surface. On the other hand, newsprint and other lower-quality papers may be dried at a higher temperature and faster rate to improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
In addition to heated rollers, other drying methods, such as air drying and infrared drying, may also be used in certain paper manufacturing processes. Overall, the drying stage is critical to the production of high-quality paper products, and modern papermaking technology has allowed for significant improvements in the efficiency and effectiveness of the drying process.
Finishing
Finishing is the final step in the paper production process, and it involves several different operations to prepare the paper for its intended use. Finishing can include cutting, coating, embossing, and other treatments to enhance the appearance and functionality of the paper product.
One of the most common finishing operations is cutting, which involves cutting large rolls of paper into smaller, more manageable sizes for distribution and sale. Cutting may be done using automated machinery or by hand, depending on the specific requirements of the product.
The coating is another common finishing operation, which involves applying a thin layer of material to the surface of the paper to improve its appearance or performance. For example, the coating can be used to add a glossy or matte finish, to make the paper more water-resistant, or to enhance its printability.
Embossing is a finishing technique that involves creating a raised pattern or design on the surface of the paper. This can add a decorative element to the paper product and can also be used for branding or identification purposes.
Other finishing operations may include perforating, laminating, or folding the paper, depending on the specific requirements of the product. The goal of finishing is to create a final paper product that is visually appealing, functional, and meets the specific needs of its intended use.
Overall, the finishing stage is critical to the success of the paper product, as it can significantly impact its appearance, performance, and marketability. Modern papermaking technology has allowed for a wide range of finishing options, and advancements in finishing techniques continue to drive innovation in the paper industry.
Importance of Paper Production
Paper production is an essential industry that plays a significant role in modern society. Here are some reasons why paper production is important:
- Communication: Paper is the primary medium for communication in our world. It is used to print books, newspapers, magazines, letters, and much more. Without paper, we would not be able to share our ideas and thoughts with others effectively.
- Education: Paper plays a vital role in education, as it is used to create textbooks, workbooks, and other learning materials. It is also used for writing notes, assignments, and tests. A world without paper would make education more challenging and less accessible.
- Economic value: The paper industry is a significant contributor to the global economy. It provides jobs for millions of people worldwide and generates billions of dollars in revenue each year.
- Packaging: Paper is used for packaging various products, such as food, clothing, and electronics. It provides a lightweight and cost-effective solution to protect items during transport.
- Recycling: Paper is one of the most recycled materials in the world. Recycling paper reduces waste and conserves resources, making it an environmentally friendly option.
In conclusion, paper production is essential to our daily lives and has significant economic, social, and environmental benefits. It enables communication, education, and packaging, provides jobs and revenue, and is an important part of the recycling industry.
Factors Affecting the Paper Production
There are many factors that can affect the paper production process, including:
- Raw materials: The quality and composition of the raw materials used in papermaking can significantly impact the quality and characteristics of the final product. Factors such as fiber type, size, and length can all affect the strength, stiffness, and texture of the paper.
- Water quality: Water is a critical component of the papermaking process, and its quality can impact the efficiency of the process and the quality of the final product. Water that contains high levels of impurities or contaminants can lead to quality issues such as discoloration or weakened fibers.
- Chemical additives: Various chemicals are used in papermaking to improve the quality and performance of the paper, such as sizing agents, fillers, and pigments. The type and amount of chemical additives used can affect properties such as color, strength, and printability.
- Processing conditions: The conditions under which the paper is processed, such as temperature, pressure, and drying time, can all impact the quality and characteristics of the final product.
- Equipment: The quality and performance of the equipment used in papermaking can also affect the efficiency and quality of the process. Modern papermaking equipment is designed to optimize production and quality, and technological advancements have led to significant improvements in the efficiency and consistency of the process.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and air quality can also affect the paper production process. For example, high humidity can cause problems with the curling and buckling of the paper, while low humidity can lead to static and other handling issues.
Overall, the paper production process is complex and requires careful attention to many different factors to produce high-quality, consistent products. Advances in technology and process control have allowed for significant improvements in the efficiency and quality of the process while ongoing research and development continue to drive innovation in the industry.
What are the Determinants of Texture and Thickness of Paper in Paper Production?
The texture and thickness of paper in paper production can be determined by several factors, including:
- Type of pulp: Different types of pulp, such as hardwood or softwood pulp, can result in different textures and thicknesses of paper.
- Fiber length: The length of the fibers in the pulp can affect the texture of the paper. Longer fibers can create a smoother texture, while shorter fibers can create a rougher texture.
- Coatings and additives: Coatings and additives, such as clay, can be applied to the paper to achieve a specific texture or finish.
- Method of production: Different methods of production, such as the Fourdrinier machine or the cylinder machine, can produce paper with different textures and thicknesses.
- Calendering: Calendering is a process in which the paper is passed through rollers to compress and smooth it, which can affect the texture and thickness of the paper.
- Drying method: The drying method used in paper production, such as air drying or using heated rollers, can also affect the texture and thickness of the paper.
Overall, a combination of these factors can contribute to the final texture and thickness of paper in paper production.
Different Types of Paper
There are many different types of paper available, each with its own characteristics and uses. Here are some of the most common types of papers:
- Bond paper: This is a high-quality paper typically used for letterheads, stationery, and documents. It is smooth, strong, and has a weight of 16-20 pounds.
- Copy paper: This is a basic paper used for everyday printing and copying. It is lightweight, has a weight of 20 pounds, and is available in various sizes.
- Glossy paper: This is a type of coated paper with a shiny finish. It is often used for printing photographs, marketing materials, and brochures.
- Newsprint paper: This is a low-cost, lightweight paper used for printing newspapers and other publications. It has a weight of 30-35 pounds and is not as durable as other types of paper.
- Art paper: This is a high-quality paper used for printing artwork, photographs, and other images. It has a weight of 50-70 pounds and comes in various finishes, such as matte, glossy, and satin.
- Cardstock paper: This is heavy-duty paper used for making cards, invitations, and other crafts. It has a weight of 65-110 pounds and is available in a variety of colors and textures.
- Tissue paper: This is a lightweight, delicate paper used for gift wrapping, decorations, and crafts. It is available in many colors and designs.
- Carbonless paper: This is a specialty paper used for making duplicate and triplicate copies of documents. It is often used for invoices, receipts, and other business forms.
In conclusion, there are many different types of paper available, each with its unique characteristics and uses. Bond paper, copy paper, glossy paper, newsprint paper, art paper, cardstock paper, tissue paper, and carbonless paper are just a few examples of the types of paper available.
Sustainability in Paper Production
Sustainability is an important consideration in the paper production industry, as it involves balancing economic, environmental, and social factors to ensure that resources are used efficiently and responsibly. Here are some ways in which paper manufacturers are working towards greater sustainability:
- Sustainable sourcing: Many paper manufacturers are working to ensure that the raw materials used in papermaking come from sustainable sources. This can involve certification programs such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC), which ensure that forests are managed in an environmentally and socially responsible manner.
- Energy efficiency: Paper production is a highly energy-intensive process, and many manufacturers are working to improve energy efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This can involve measures such as using renewable energy sources, optimizing equipment and processes to reduce energy use, and implementing energy management systems.
- Water conservation: Water is a critical resource in paper manufacturing, and many manufacturers are implementing strategies to reduce water use and improve water efficiency. This can involve measures such as recycling water, implementing closed-loop systems, and optimizing processes to reduce water use.
- Waste reduction: Many paper manufacturers are working to reduce waste and increase recycling rates. This can involve measures such as reducing the amount of waste generated during production, reusing and recycling materials, and implementing closed-loop systems to reduce waste.
- Product innovation: Paper manufacturers are also working to develop new products and processes that are more sustainable. This can involve using alternative raw materials, developing new products with improved environmental properties, and implementing new technologies that reduce the environmental impact of the paper production process.
- Responsible Disposal: The responsible disposal of paper products, such as recycling or composting, can help reduce waste and promote sustainability.
- Product Design: Designing paper products that are durable, reusable, or made from recycled materials can help reduce the environmental impact of the paper industry.
- Certification: Certification programs, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), can help ensure that paper products are sourced from responsibly managed forests and produced using sustainable practices.
Overall, sustainability is an ongoing challenge for the paper production industry, but many manufacturers are making significant strides toward greater sustainability in paper production by implementing strategies that reduce environmental impact, conserve resources, and promote responsible practices.
Challenges in Paper Production
Paper production faces several challenges that can affect its sustainability and efficiency. Some of these challenges in paper production are:
- Deforestation: The primary raw material for paper production is wood fiber, and deforestation can have a significant impact on the environment. The loss of forest cover can lead to soil erosion, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- Energy Consumption: The paper production process requires a significant amount of energy, mainly in the form of electricity and heat. This can lead to high energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
- Water Use: The paper production process also requires a large amount of water, and this can have an impact on water availability, quality, and ecosystems. Wastewater from the paper production process can also be contaminated with chemicals and pollutants, affecting the environment.
- Waste Management: The paper production process generates waste, including sludge, bark, and other residues. Proper disposal or recycling of these wastes can be a challenge, and inappropriate disposal can lead to environmental pollution.
- Product Quality: The paper industry must maintain high-quality standards to meet customer demands. This can be a challenge due to variations in raw materials, production processes, and product specifications.
- Competitiveness: The paper industry faces intense competition from other materials, such as plastic and digital media. The industry must continue to innovate and adapt to remain competitive.
To overcome these challenges, the paper industry must implement sustainable practices, such as responsible sourcing, energy efficiency, water conservation, waste reduction and recycling, and product innovation.
Collaboration among stakeholders, including governments, producers, consumers, and civil society, is also essential to ensure the long-term sustainability of the paper industry.
Importance of Quality Control in Paper Production
Quality control is an essential aspect of paper production that ensures that the paper produced meets specific standards and requirements. Here are some of the reasons why quality control is important in paper production:
- Customer satisfaction: Paper products are used in a wide range of applications, and customers have varying requirements and expectations. Quality control ensures that the paper produced meets the customer's needs and specifications, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Consistency: Quality control helps ensure that the paper produced is consistent in terms of thickness, color, texture, and other properties. This consistency is crucial for many applications, such as printing and packaging.
- Efficiency: Quality control helps identify defects and issues early in the production process, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved profitability.
- Compliance: Quality control ensures that the paper produced meets regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as environmental regulations, safety standards, and quality management systems.
- Reputation: High-quality paper products can enhance a company's reputation and brand image. Quality control helps ensure that the paper produced is of consistent quality, leading to a positive reputation in the market.
In conclusion, quality control is crucial in paper production to ensure that the paper produced meets specific standards and requirements. It leads to higher customer satisfaction, consistency, efficiency, compliance, and reputation, which are essential for the success of paper companies in the market.
Importance of Understanding Paper Production for a Sustainable Future
Understanding paper production is essential for a sustainable future because the paper is a widely used product that has significant environmental impacts. The paper industry relies on natural resources, such as wood fibers, water, and energy, to produce paper products.
As such, understanding the environmental impacts of paper production and implementing sustainable practices is crucial to reduce the industry's negative impact on the environment.
The following are the reasons why understanding paper production is critical for a sustainable future:
- Environmental Impacts: Paper production can have negative environmental impacts, including deforestation, water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and energy consumption. Understanding these impacts is crucial to develop sustainable practices that minimize the environmental footprint of paper production.
- Resource Conservation: The paper industry relies on natural resources, such as wood fibers and water, that are finite and need to be conserved. Understanding the availability of these resources and the environmental impact of their use can help ensure their sustainable use.
- Waste Reduction: The paper industry generates a significant amount of waste, including sludge, bark, and other residues. Understanding the sources and types of waste generated and implementing sustainable practices, such as recycling and waste reduction, can help reduce the environmental impact of paper production.
- Product Innovation: Understanding paper production can also facilitate the development of innovative products and technologies that can reduce the environmental impact of paper production and meet consumer demands for sustainable products.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Understanding paper production and its environmental impacts requires collaboration among stakeholders, including governments, producers, consumers, and civil society. This collaboration can help develop sustainable policies and practices that ensure the long-term sustainability of the paper industry.
In conclusion, understanding paper production is crucial for a sustainable future. It can help reduce the environmental impact of the paper industry, conserve natural resources, reduce waste, facilitate product innovation, and promote stakeholder collaboration.
Safety Precautions that Should be Considered During Paper Production
Paper production involves many hazards, including chemical exposure, machinery hazards, and fire risks. Here are some safety precautions that should be considered during paper production:
- Personal protective equipment: Workers should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and respirators, to protect against chemical exposure and other hazards.
- Chemical handling: Workers should be trained in the safe handling and storage of chemicals used in the paper production process. Chemicals should be labeled correctly, stored in appropriate containers, and handled in well-ventilated areas.
- Machinery safety: Machinery used in paper production can pose many hazards, such as moving parts, pinch points, and entanglement hazards. Workers should receive proper training in the safe use and maintenance of machinery and should follow all safety procedures and guidelines.
- Fire prevention: Paper production involves the use of flammable materials, such as wood chips, pulp, and chemicals. Fire prevention measures, such as fire alarms, extinguishers, and sprinkler systems, should be in place and regularly tested.
- Ergonomics: Workers in the paper production industry may be exposed to ergonomic hazards, such as repetitive motions and awkward postures. Employers should provide ergonomic training and equipment to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
- Electrical safety: Electrical hazards can be present in paper mills and production areas. Workers should be trained in electrical safety, and all electrical equipment should be maintained and inspected regularly.
In conclusion, paper production involves many hazards that can cause injury or illness to workers. Personal protective equipment, chemical handling procedures, machinery safety, fire prevention, ergonomics, and electrical safety are some safety precautions that should be considered during paper production to protect workers and ensure a safe work environment.
FAQs related to Paper Production
- What are the different methods of bleaching?
The different methods of bleaching include elemental chlorine-free (ECF) bleaching, chlorine-free (CF) bleaching, and totally chlorine-free (TCF) bleaching.
- What is a Fourdrinier machine?
A Fourdrinier machine is a machine that spreads the pulp evenly onto a moving mesh screen to form paper.
- What is the purpose of heated rollers in paper production?
The purpose of heated rollers is to dry the paper and achieve the desired thickness and texture.
- How is recycled paper processed?
Recycled paper is sorted and processed to remove contaminants before being turned into pulp and then paper.
- How long does the paper production process take?
The time it takes for the paper production process to be completed depends on several factors, including the type of paper being produced, the method of production, and the size of the paper mill. Generally, the process can take anywhere from a few hours to several days.
For example, the production of newsprint may take only a few hours, while the production of higher-quality paper, such as printing or writing paper, may take several days. Additionally, the recycling process may take less time since the paper has already been processed before.
- How is paper thickness determined?
Paper thickness is determined by the weight of the paper, which is measured in pounds per ream.
- How is paper texture determined?
Paper texture is determined by the type of pulp used, the method of production, and any additional coatings or additives applied to the paper.
- What is the difference between coated and uncoated paper?
Coated paper has a coating applied to it to achieve a smoother surface and better print quality, while uncoated paper has no coating and has a rougher surface.
- How is paper made waterproof?
Paper can be made waterproof by adding a waterproof coating or by using synthetic fibers instead of natural fibers.
- How is paper made fire-resistant?
Paper can be made fire-resistant by adding fire-retardant chemicals to the pulp or by applying a fire-resistant coating.
- What is the environmental impact of paper production?
Paper production can have a significant environmental impact, including deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. However, sustainable paper production practices can help to mitigate these impacts.
How can Deskera Help You with Paper Production?
Deskera MRP can help paper manufacturing companies in a variety of ways:
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Deskera's MRP software can help paper manufacturers plan their production schedules, manage inventory levels, and track raw materials and finished products. This can help paper manufacturers optimize their production processes and reduce waste.
- Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Deskera's CRM software can help paper manufacturers manage their sales pipelines, track customer interactions, and generate sales forecasts. This can help paper manufacturers improve their customer engagement and increase sales.
- Accounting and Finance Management: Deskera's accounting and finance management software, i.e., Deskera Books, can help paper manufacturers manage their financial transactions, generate financial reports, and track expenses. This can help paper manufacturers streamline their financial processes and improve their financial performance.
- Human Resource Management (HRM): Deskera People can help paper manufacturers manage their employee data, track attendance and leave, and process payroll. This can help paper manufacturers manage their workforce more efficiently and effectively.
- Business Intelligence (BI): Deskera is a BI software that can help paper manufacturers analyze their data, generate insights, and make informed business decisions. This can help paper manufacturers improve their operational efficiency and drive growth.
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, paper production is an important industry with a significant impact on the global economy and our daily lives. However, it also has environmental implications that need to be addressed to ensure a sustainable future. It is thus vital to unpack the basics of paper production.
The steps of the paper production process are as follows:
- Preparation of raw materials
- Pulping
- Screening and cleaning
- Refining
- Papermaking
- Drying
- Finishing
The importance of paper production is:
- Communication
- Education
- Economic value
- Packaging
- Recycling
The factors affecting paper production are:
- Raw materials
- Water quality
- Chemical additives
- Processing conditions
- Equipment
- Environmental factors
The determinants of texture and thickness of paper in paper production are:
- Type of pulp
- Fiber length
- Coatings and additives
- Method of production
- Calendering
- Drying method
The different types of paper are:
- Bond paper
- Copy paper
- Glossy paper
- Newsprint paper
- Art paper
- Cardstock paper
- Tissue paper
- Carbonless paper
Some of the ways in which paper manufacturers are working towards ensuring sustainability in paper production are:
- Sustainable sourcing
- Energy efficiency
- Water conservation
- Waste reduction
- Product innovation
- Responsible disposal
- Product design
- Certification
The several challenges faced in paper production are:
- Deforestation
- Energy consumption
- Water use
- Waste management
- Product quality
- Competitiveness
The importance of quality control in paper production is:
- Customer satisfaction
- Consistency
- Efficiency
- Compliance
- Regulation
The importance of understanding paper production for a sustainable future is because of the following reasons:
- Environmental impact
- Resource conservation
- Waste reduction
- Product innovation
- Stakeholder collaboration
The safety precautions that should be considered during paper production are:
- Personal protective equipment
- Chemical handling
- Machinery safety
- Fire prevention
- Ergonomics
- Electrical safety
Overall, Deskera can help paper manufacturers improve productivity, reduce costs, and ensure efficient operations by providing a unified view of the entire production process.
Related Articles