As businesses expand their reach across various sales channels – from traditional brick-and-mortar stores to online marketplaces and beyond – the need to seamlessly synchronize order processing and manufacturing operations becomes evident.
This article explores how the integration of multi-channel order management systems with manufacturing processes holds the potential to revolutionize efficiency in production.
By fostering real-time inventory visibility, enhancing demand forecasting accuracy, and enabling adaptable production scheduling, manufacturers can not only meet the diverse demands of their customers but also optimize resource utilization.

Through a comprehensive analysis of benefits, challenges, and future implications, this article underscores the strategic importance of embracing multi-channel integration as a means to drive manufacturing efficiency in an increasingly interconnected business landscape.
Here is all that we shall discover in this post:
- Brief Overview of Multi-Channel Order Management
- Importance of Manufacturing Efficiency in Today's Competitive Market
- Understanding Multi-Channel Order Management
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Key Concepts and Indicators
- The Integration of Multi-Channel Order Management with Manufacturing
- Impact on Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
- Enhancing Production Scheduling and Resource Allocation
- Challenges and Considerations
- Future Trends and Implications
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Brief Overview of Multi-Channel Order Management
Multi-channel order management refers to the strategic approach of efficiently handling customer orders from various sales channels, such as online marketplaces, retail stores, social media platforms, and direct websites.
In today's dynamic business environment, where consumers interact with brands through diverse touchpoints, businesses need to seamlessly manage and fulfill orders across these channels. Multi-channel order management involves the integration of technology, processes, and systems to ensure a consistent and streamlined customer experience.
This process involves centralizing order data from different channels, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, automating order processing, and coordinating production and fulfillment activities. The aim is to optimize the entire order-to-delivery process while minimizing errors, reducing costs, and meeting customer expectations for fast and accurate delivery.
Multi-channel order management systems facilitate better communication between sales, production, and fulfillment teams, allowing them to collaborate effectively and respond to fluctuations in demand.
Ultimately, this approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also has a direct impact on manufacturing efficiency by enabling informed decision-making, efficient resource allocation, and adaptable production scheduling.
Importance of Manufacturing Efficiency in Today's Competitive Market
Manufacturing efficiency holds a paramount role in today's fiercely competitive market environment. As businesses strive to meet ever-evolving customer demands, control costs, and maintain sustainable growth, the efficacy of their manufacturing processes becomes a crucial determinant of success.
Several reasons highlight the significance of manufacturing efficiency:
- Cost Reduction: Efficient manufacturing processes minimize waste, reduce production time, and optimize resource utilization. This directly translates into lower operational costs, allowing businesses to offer competitive prices without compromising quality.
- Agility and Responsiveness: Rapid changes in consumer preferences and market trends require manufacturers to swiftly adapt. Efficient processes enable quicker product development, production, and delivery, giving companies the agility to respond to shifts in demand.
- Quality Assurance: Efficient manufacturing processes are often associated with consistent quality outcomes. When production is streamlined and standardized, the likelihood of defects and errors decreases, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Market Penetration: Efficient manufacturing allows companies to scale their operations more effectively. As they expand to new markets or launch new products, they can do so with confidence, knowing that their processes can handle increased demand.
- Innovation: By reducing the time and resources spent on routine tasks, manufacturing efficiency frees up capacity for innovation. This empowers businesses to invest in research and development, fostering the creation of new products and technologies.
- Resource Conservation: Sustainable manufacturing practices are becoming increasingly important in the modern business landscape. Efficient processes minimize resource consumption, contributing to environmental stewardship and meeting the expectations of socially responsible consumers.
- Competitive Advantage: In a market where consumers demand fast delivery, customization, and consistent quality, manufacturers who can meet these expectations efficiently gain a competitive edge. Efficiency allows them to offer superior products and services at a compelling value proposition.
- Profitability: Manufacturing efficiency directly impacts a company's bottom line. When resources are optimized, waste is minimized, and production is streamlined, profits increase due to higher output and reduced operational costs.
In essence, manufacturing efficiency is not just about producing more; it's about producing smarter. In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and global connectivity, businesses that excel in manufacturing efficiency are better positioned to thrive and outpace their competitors in the race for market dominance.
Understanding Multi-Channel Order Management
Multi-channel order management is a comprehensive approach that businesses adopt to seamlessly handle and fulfill customer orders across various sales channels. These channels encompass a diverse array, including online platforms, physical stores, social media, marketplaces, and more.
The core goal of multi-channel order management is to provide customers with a consistent and satisfactory experience while optimizing operational efficiency.
Key components of multi-channel order management include:
Centralized Order Processing: Orders from different sales channels are consolidated into a single system. This centralization enables businesses to manage orders more efficiently, minimizing the risk of errors and improving order accuracy.
Real-time Inventory Visibility: A pivotal element in multi-channel order management is maintaining accurate and up-to-date information about inventory levels. This visibility ensures that customers can place orders confidently, knowing that products are available, and helps manufacturers plan production and replenishment accurately.
Automated Order Fulfillment: Automation plays a critical role in multi-channel order management. Automated processes for order confirmation, invoicing, picking, packing, and shipping enhance speed and accuracy while reducing the need for manual intervention.
Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication between various departments, such as sales, manufacturing, and fulfillment, is vital. Multi-channel order management systems facilitate cross-functional collaboration, ensuring that each department is aligned with the others.
Flexible Order Routing: Multi-channel order management allows businesses to determine the most efficient route for order fulfillment. For instance, an order could be fulfilled from the nearest warehouse, store, or distribution center, minimizing shipping costs and delivery times.
Customer Insights: Through multi-channel order management, businesses can gather valuable data on customer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns. This information aids in refining marketing strategies and product offerings.
Customer Experience: Customers expect a consistent experience, regardless of the channel they use to interact with a business. Multi-channel order management ensures that customers receive the same level of service and product quality across all touchpoints.
Scalability: As businesses grow and expand into new markets or sales channels, a well-implemented multi-channel order management system can accommodate increased demand while maintaining operational efficiency.
In a competitive market where customer satisfaction and operational effectiveness are paramount, multi-channel order management bridges the gap between customer expectations and manufacturing capabilities.
By integrating different sales channels and optimizing order processing and fulfillment, businesses can achieve streamlined operations, reduced costs, and improved customer loyalty, ultimately contributing to their long-term success
Manufacturing Efficiency: Key Concepts and Indicators
In the realm of modern manufacturing, efficiency stands as a cornerstone of success, dictating a company's ability to thrive in a rapidly evolving market. This section delves into the vital domain of manufacturing efficiency, elucidating its core concepts and pivotal indicators that serve as benchmarks for operational excellence.
As businesses strive to maximize output while minimizing resources and costs, understanding the fundamental principles of manufacturing efficiency becomes not only a strategic advantage but an imperative. By examining the key elements that define efficiency within manufacturing processes and delving into the metrics that gauge its prowess, we uncover a nuanced landscape where optimization and innovation intersect.
From streamlined production workflows to optimized resource utilization, the ensuing exploration sheds light on the intricate interplay between efficient manufacturing practices and a company's ability to remain competitive, adaptable, and sustainably profitable in an ever-demanding global market.
A. Definition of manufacturing efficiency
Manufacturing efficiency refers to the systematic utilization of resources and processes to produce goods or services with the highest possible output and quality while minimizing waste, costs, and time. It represents the optimization of every aspect of the production cycle, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery.
Manufacturing efficiency is characterized by the ability to achieve desired outcomes while conserving energy, reducing environmental impact, and maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction.
Efficiency in manufacturing involves streamlining operations, eliminating bottlenecks, and adopting best practices to ensure that each step in the production process contributes to the overall effectiveness of the entire operation. This encompasses factors such as production speed, utilization of machinery, reduction of defects, and the synchronization of production schedules with demand forecasts.
Manufacturing efficiency does not solely focus on output volume; it emphasizes producing more value with fewer inputs. Companies that prioritize manufacturing efficiency not only enhance their competitiveness but also contribute to sustainability goals and customer expectations for high-quality products delivered promptly.
B. Importance of efficiency in reducing costs and improving competitiveness
Efficiency stands as a linchpin in the manufacturing landscape, exerting a profound impact on a company's bottom line and its ability to remain competitive in a global marketplace.
The role of efficiency extends far beyond mere operational optimization; it becomes a pivotal driver in reducing costs and elevating competitiveness in the following ways:
- Cost Reduction: Efficient manufacturing processes minimize waste, unnecessary steps, and resource consumption. This directly translates into lower production costs, enabling companies to offer products at more competitive prices without sacrificing quality. Cost reductions extend to areas such as labor, energy consumption, and raw materials.
- Enhanced Productivity: Streamlined workflows and processes increase productivity by ensuring that each step contributes meaningfully to the end goal. This leads to higher output within the same time frame, amplifying a company's capacity to meet market demands efficiently.
- Reduced Lead Times: Efficient manufacturing reduces production lead times, allowing companies to respond quickly to market fluctuations and changing consumer preferences. This agility positions them to capitalize on emerging trends and seize business opportunities swiftly.
- Improved Quality: Efficiency often goes hand in hand with quality improvements. By optimizing processes and minimizing errors, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of consistency and precision, resulting in fewer defects and customer returns.
- Innovation and Investment: Efficient operations free up resources that can be redirected towards research, development, and innovation. This paves the way for the creation of new products, technologies, and processes, fostering long-term growth and competitiveness.
- Global Competitiveness: In an interconnected global marketplace, companies that can produce goods efficiently gain a competitive edge. Cost-effective manufacturing allows businesses to remain competitive both domestically and internationally.
- Adaptation to Industry Trends: Efficiency enables manufacturers to adapt to evolving industry trends, such as sustainable practices and digital transformation. Businesses that optimize their operations for efficiency are better equipped to embrace change and stay relevant.
- Sustainable Practices: Efficient manufacturing often aligns with sustainable practices by minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and optimizing resource utilization. This not only benefits the environment but also resonates with environmentally conscious consumers.
As market dynamics continue to evolve and competition intensifies, manufacturers that prioritize efficiency are positioned to thrive by meeting customer demands effectively, innovating for the future, and contributing to a sustainable business model
C. Key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring manufacturing efficiency
Measuring manufacturing efficiency requires a comprehensive set of quantifiable metrics that provide insights into various facets of production. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as invaluable tools for assessing the effectiveness of manufacturing processes and identifying areas for improvement.
The following KPIs offer a holistic view of manufacturing efficiency:
- Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE): OEE is a composite metric that gauges the utilization, performance, and quality of equipment on the production floor. It factors in equipment availability, production speed, and product quality to provide a comprehensive assessment of manufacturing efficiency.
- Cycle Time: Cycle time measures the time it takes to complete one production cycle from start to finish. Reducing cycle time enhances production throughput and responsiveness to customer demands.
- First Pass Yield (FPY): FPY calculates the proportion of products that pass quality checks on the first attempt. A high FPY indicates efficient manufacturing processes with minimal rework or defects.
- Downtime: Downtime measures the duration during which production is halted due to equipment breakdowns, maintenance, or other issues. Reducing downtime improves resource utilization and overall productivity.
- Labor Efficiency Ratio (LER): LER assesses the ratio of actual labor hours worked to the standard labor hours required for a given task. This KPI highlights labor efficiency and helps optimize workforce utilization.
- Inventory Turnover: Inventory turnover measures how quickly raw materials or finished goods are used or sold within a specific period. High inventory turnover indicates efficient production and reduced holding costs.
- Setup Time: Setup time measures the duration required to prepare a machine or production line for a new task. Reducing setup time enhances flexibility and allows for more frequent production changeovers.
- Scrap and Rework Rates: These KPIs quantify the amount of defective products that need to be scrapped or reworked. Lower scrap and rework rates reflect efficient manufacturing processes and higher product quality.
- Capacity Utilization: Capacity utilization measures the extent to which manufacturing facilities are being used to their full potential. Higher utilization indicates efficient resource allocation.
- Lead Time: Lead time measures the time taken for an order to move through the production process, from order placement to delivery. Reducing lead time enhances responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
- Energy Consumption per Unit: This KPI evaluates the energy efficiency of manufacturing processes by measuring energy consumption per unit of production. Lower energy consumption per unit signifies sustainable and efficient operations.
- Return on Assets (ROA): ROA assesses the efficiency of asset utilization by measuring the ratio of net income to total assets. A higher ROA indicates better efficiency in converting assets into profits.
The Integration of Multi-Channel Order Management with Manufacturing
In an era defined by interconnected commerce and dynamic customer expectations, the convergence of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes has emerged as a pivotal strategy for businesses seeking to optimize their operations.
This section delves into the transformative power of integrating multi-channel order management systems with manufacturing, illuminating how this synergy revolutionizes the way companies produce, fulfill, and deliver products.
A. Benefits of integrating order management systems with manufacturing processes
The integration of order management systems with manufacturing processes heralds a transformative paradigm shift that yields a multitude of advantages for businesses operating in today's complex marketplace. This symbiotic relationship between sales channels and production brings forth a range of benefits that span from operational efficiency to elevated customer satisfaction.
Some of the key benefits include:
- Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Integration provides a holistic view of inventory levels across all sales channels. This real-time insight empowers manufacturers to align production with actual demand, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
- Optimized Production Planning: Seamless integration enables manufacturers to adjust production schedules based on current orders and inventory data. This adaptability leads to efficient resource allocation and reduced production bottlenecks.
- Streamlined Communication: By connecting order management systems with production departments, communication becomes more cohesive. Sales, production, and fulfillment teams can collaborate effectively, leading to fewer errors and smoother workflows.
- Faster Order Fulfillment: Integration expedites order processing, enabling swift and accurate fulfillment. This speed enhances customer satisfaction and enables companies to meet tight delivery deadlines.
- Reduced Lead Times: Integration shortens the time between order placement and product delivery. This efficiency addresses consumer expectations for prompt order processing and delivery, contributing to enhanced brand reputation.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: The seamless flow of information allows businesses to provide customers with accurate updates on order status and delivery times. This transparency contributes to a positive customer experience.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Integration minimizes wastage by aligning production with demand. Resources such as raw materials, labor, and machinery are utilized optimally, reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Accurate Demand Forecasting: Aggregated data from various sales channels aids in more accurate demand forecasting. This foresight empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions about production volumes and schedules.
- Customization and Personalization: Integration facilitates the efficient handling of customized orders. Manufacturers can tailor products to individual customer preferences without compromising production efficiency.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The integration generates valuable data insights that inform strategic decisions. Manufacturers can identify trends, assess performance, and refine strategies for sustained growth.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that integrate order management systems with manufacturing processes gain a competitive edge. They can respond swiftly to market changes and fulfill customer demands with agility.
- Operational Scalability: As businesses expand to new markets or sales channels, integration accommodates increased complexity without compromising operational efficiency.
In summary, the integration of order management systems with manufacturing processes transcends transactional convenience to revolutionize the very foundation of production. The benefits extend beyond enhancing internal operations; they ripple outward, resonating with satisfied customers and bolstering a business's standing in a demanding and competitive market landscape
B. Real-time inventory visibility and its impact on production planning
Real-time inventory visibility, facilitated by the integration of order management systems with manufacturing processes, emerges as a cornerstone of operational excellence, fundamentally reshaping the way production planning is conceived and executed.
This facet of integration ushers in a host of advantages that profoundly influence production efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Demand-Driven Production: Real-time inventory data provides manufacturers with accurate insights into the actual demand for products. This demand-driven approach minimizes the risk of overproduction and ensures that production aligns precisely with customer orders.
- Reduced Overstocking and Stockouts: With up-to-the-minute visibility into inventory levels across all sales channels, manufacturers can strategically balance stock levels. This reduces the likelihood of costly overstock situations while mitigating the detrimental impact of stockouts.
- Enhanced Production Efficiency: The availability of real-time inventory information allows manufacturers to fine-tune production schedules. This minimizes idle time, optimizes resource utilization, and streamlines production workflows for maximum efficiency.
- Minimized Lead Times: The accuracy of inventory data aids in predicting lead times more effectively. Manufacturers can communicate more accurate delivery estimates to customers, improving transparency and building trust.
- Improved Production Forecasting: Real-time inventory visibility provides valuable historical data on sales trends and product demand. This data-driven forecasting enhances manufacturers' ability to anticipate future demand and adjust production plans accordingly.
- Effective Resource Allocation: Integration empowers manufacturers to allocate resources, such as raw materials and labor, based on actual demand. This ensures that resources are used efficiently and prevents unnecessary expenditures.
- Just-In-Time Manufacturing: Real-time inventory data supports a just-in-time manufacturing approach, where products are produced only when orders are received. This lean methodology reduces waste, storage costs, and excess inventory.
- Customization and Personalization: With instant access to inventory levels, manufacturers can accommodate customized orders without disrupting production schedules. This flexibility enhances the ability to deliver tailored products to customers.
- Agility in Production Planning: Market dynamics can change rapidly. Real-time inventory visibility allows manufacturers to swiftly adjust production plans to capitalize on emerging trends or respond to unforeseen shifts in demand.
- Cost Savings: Accurate inventory information prevents overproduction, minimizing storage costs and waste. It also reduces the need for rush production or expedited shipping, contributing to overall cost savings.
In essence, real-time inventory visibility's integration with production planning orchestrates a harmonious symphony of operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and waste reduction. This dynamic interplay empowers manufacturers to synchronize their production efforts with actual market demand, cultivating a more responsive, adaptable, and profitable manufacturing environment
C. Streamlined communication between sales, production, and fulfillment departments
The integration of order management systems with manufacturing processes fosters a seamless and interconnected ecosystem where effective communication between sales, production, and fulfillment departments emerges as a pivotal advantage.
This streamlined communication not only bridges organizational silos but also amplifies operational efficiency, customer experience, and overall business success.
- Accurate Order Transmission: Integration enables sales orders to be transmitted directly to production and fulfillment teams, reducing the risk of errors that can occur during manual data entry.
- Real-Time Updates: Sales teams gain instant visibility into production progress and inventory availability, enabling them to provide accurate and timely updates to customers regarding order status and delivery.
- Coordination of Resources: Seamless communication ensures that production teams are well-informed about incoming orders. This facilitates better resource allocation, enabling efficient planning for materials, labor, and equipment.
- Responsive Demand Management: Sales teams can provide real-time feedback to production based on changing customer demands or trends. This agility allows for prompt adjustments in production plans.
- Early Issue Identification: Improved communication allows potential issues to be identified early in the process. Production teams can address concerns related to materials, design, or feasibility before they escalate.
- Order Prioritization: Clear communication between departments enables the prioritization of urgent orders or special requests, ensuring that critical customer needs are met promptly.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment: Production and fulfillment teams receive accurate and detailed information about customer orders, resulting in more efficient and accurate order processing and shipping.
- Reduced Lead Times: Communication among departments reduces delays caused by miscommunication or misunderstandings. This accelerates the entire order fulfillment process.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Customers benefit from a unified experience where accurate information about orders is consistently relayed across departments. This improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Collaborative Problem-Solving: When issues arise, cross-departmental communication facilitates collaborative problem-solving. Sales, production, and fulfillment teams can work together to find solutions swiftly.
- Continuous Improvement: Open communication channels encourage feedback loops. Departments can share insights on challenges and successes, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Employee Morale: Streamlined communication minimizes frustration stemming from miscommunication or confusion. This contributes to improved employee morale and a more harmonious work environment.
In essence, the integration of order management systems with manufacturing processes transcends technology to create a coherent and collaborative operational framework. The synchronized communication between sales, production, and fulfillment departments amplifies efficiency, reduces errors, and positions businesses to provide a seamless and satisfying customer experience, cementing their reputation as responsive and customer-centric enterprises.
Impact on Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
In the intricate dance of modern commerce, where consumer preferences and market dynamics continuously evolve, the integration of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes holds the potential to orchestrate a symphony of precision: one that harmonizes demand forecasting and inventory management.
This section delves into the profound impact of this integration on these critical aspects of business operations.
A. Improved accuracy in demand forecasting through multi-channel data aggregation
The integration of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes heralds a new era of demand forecasting accuracy, where the aggregation of data from diverse sales channels becomes a driving force behind informed decision-making. This synergy transcends traditional forecasting methods, offering businesses a dynamic perspective into consumer behavior and market trends.
The benefits of this integration are manifold:
- Holistic Data Insights: Multi-channel data aggregation enables businesses to capture a comprehensive view of customer behavior across various touchpoints. This holistic perspective leads to a more accurate understanding of consumer preferences and buying patterns.
- Enhanced Granularity: By amalgamating data from different sales channels, businesses can analyze demand trends at a granular level. This enables them to identify nuances that might be missed when examining individual channels in isolation.
- Real-Time Analysis: The integration allows for real-time data analysis, enabling businesses to detect shifts in demand patterns as they occur. This agility empowers manufacturers to adjust production plans promptly.
- Seasonal and Regional Variations: Multi-channel data aggregation illuminates seasonal and regional variations in demand. This insight helps manufacturers tailor production and inventory strategies to specific market segments.
- Product Performance Insights: Businesses can analyze the performance of individual products across different channels. This knowledge informs decisions about inventory levels, production schedules, and marketing strategies.
- Forecast Refinement: The integration facilitates the continuous refinement of demand forecasts. Businesses can incorporate real-time data, leading to more accurate predictions and reduced instances of understocking or overstocking.
- New Product Launches: Multi-channel data aggregation aids in launching new products by identifying potential demand and gauging customer interest before full-scale production.
- Reduced Bullwhip Effect: The integration minimizes the bullwhip effect—a phenomenon where small fluctuations in demand lead to amplified variations in supply chain orders. Accurate demand forecasting mitigates this issue.
- Supplier Collaboration: Reliable demand forecasts enable better communication with suppliers. Manufacturers can provide suppliers with accurate information, fostering more efficient procurement processes.
- Risk Mitigation: Improved forecasting reduces the risk of carrying excess inventory or experiencing stockouts, resulting in cost savings and enhanced customer satisfaction.
In essence, the integration of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes serves as a catalyst for demand forecasting precision.
B. Efficient inventory management with real-time insights from different sales channels
The convergence of multi-channel order management and manufacturing processes ushers in a new era of inventory management, where real-time insights harvested from diverse sales channels redefine how businesses optimize their inventory levels. This integration empowers companies with the agility to anticipate market fluctuations, mitigate risks, and respond proactively to evolving customer demands.
The benefits of this symbiotic relationship are multifaceted:
- Accurate Demand Projections: Real-time insights from various sales channels provide a more accurate picture of customer demand. This enables manufacturers to adjust inventory levels in accordance with current buying patterns.
- Reduced Holding Costs: With precise demand projections, businesses can maintain leaner inventory levels. This minimizes holding costs associated with excess stock, contributing to cost savings.
- Minimized Stockouts: The integration ensures that businesses can identify and respond to low inventory levels promptly. This reduces the risk of stockouts and enhances customer satisfaction by meeting demand consistently.
- Optimized Replenishment: Real-time insights enable businesses to optimize the timing of replenishment orders. Manufacturers can place orders for raw materials or finished goods just in time to meet actual demand.
- Dynamic Safety Stock Management: Businesses can dynamically adjust safety stock levels based on real-time demand data. This prevents excessive safety stock and optimizes resource allocation.
- Seasonal and Trend Analysis: Real-time insights allow for the identification of seasonal and trend-based demand patterns. Businesses can adjust inventory strategies to align with anticipated changes in consumer behavior.
- Minimized Obsolescence: Accurate demand insights reduce the risk of carrying obsolete inventory. Manufacturers can avoid producing excess quantities of products that might become outdated.
- Reduced Supply Chain Disruptions: The integration enables businesses to detect potential supply chain disruptions early by monitoring inventory levels across various sales channels.
- Smoother Production Schedules: Efficient inventory management based on real-time insights leads to smoother production schedules. Manufacturers can avoid sudden spikes or dips in production requirements.
- Enhanced Financial Performance: Optimized inventory management leads to better cash flow management and improved return on investment by minimizing tied-up capital in excess inventory.
In essence, the fusion of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes reshapes inventory management from a reactive process into a proactive and strategic endeavor
Enhancing Production Scheduling and Resource Allocation
In the intricate choreography of modern manufacturing, where precision and efficiency are paramount, the integration of multi-channel order management with production processes emerges as a conductor of symphonic harmony.
This section delves into the transformative power of this integration, focusing on how it elevates the domains of production scheduling and resource allocation to new heights of efficiency.
As we delve into the intricacies of this interplay, a narrative unfolds where real-time insights from multi-channel order data infuse agility into production schedules, while optimized resource allocation orchestrates a symphony of operational excellence.
Through a deeper exploration of these intricacies, we unravel a landscape where manufacturing evolves beyond tradition, guided by data-driven strategies and adaptive methodologies.
A. Adaptive production scheduling based on fluctuating multi-channel demand
The integration of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes ushers in a paradigm shift in production scheduling, where the ebb and flow of multi-channel demand becomes the heartbeat guiding operational efficiency. This integration introduces the concept of adaptive production scheduling, a dynamic approach that responds to real-time demand fluctuations across various sales channels.
The benefits of this approach are far-reaching and transformative:
- Real-Time Demand Responsiveness: Adaptive production scheduling enables manufacturers to respond promptly to changes in demand across different sales channels. This agility ensures that production aligns closely with current customer requirements.
- Minimized Overproduction: By synchronizing production with actual demand, manufacturers can avoid overproduction, which can lead to excess inventory and associated costs.
- Reduced Underproduction: The integration allows manufacturers to prevent underproduction scenarios by quickly ramping up production when demand spikes, mitigating the risk of stockouts.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Adaptive scheduling optimizes resource allocation by allocating labor, machinery, and materials as needed. This reduces inefficiencies stemming from over- or underutilization of resources.
- Faster Time-to-Market: The integration facilitates quicker time-to-market for products by accelerating production based on real-time demand insights, ensuring that products reach customers when they're in demand.
- Dynamic Lead Time Adjustments: Adaptive production scheduling enables manufacturers to adjust lead times based on current production capacity and demand levels, providing accurate delivery estimates to customers.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: The ability to swiftly adapt production to changing customer demands enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely order fulfillment.
- Optimized Inventory Levels: Adaptive scheduling prevents excessive inventory buildup by producing what is needed, when it's needed. This streamlines inventory management and minimizes holding costs.
- Enhanced Forecast Accuracy: Real-time demand data informs forecast accuracy. Manufacturers can fine-tune their forecasting models based on current sales trends, leading to more precise predictions.
- Lean Production Practices: Adaptive scheduling aligns with lean manufacturing principles by minimizing waste and optimizing production processes to meet customer needs effectively.
In essence, adaptive production scheduling brings manufacturing into a new era of responsiveness and efficiency. By leveraging real-time data from multi-channel sales channels, businesses can optimize production in sync with actual customer demand. This integration transforms production from a rigid endeavor into an agile and dynamic process, positioning manufacturers to stay competitive, minimize costs, and consistently deliver what customers want, when they want it
B. Optimized resource allocation considering diverse order requirements
The integration of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes ushers in a transformative approach to resource allocation, where the complexities of diverse order requirements are met with a symphony of efficiency and precision. This integration redefines how manufacturers allocate resources across different sales channels and order types, ultimately resulting in streamlined operations and enhanced customer satisfaction.
The benefits of this optimized resource allocation are profound:
- Tailored Production Plans: Integration enables manufacturers to allocate resources according to specific order requirements. Different products, quantities, and customizations are factored into production plans, ensuring efficient utilization of resources.
- Reduced Changeover Times: By allocating resources strategically, manufacturers can minimize the need for frequent production line changeovers. This reduces downtime and accelerates production efficiency.
- Flexibility for Custom Orders: Manufacturers can allocate resources for custom or personalized orders without disrupting the overall production flow. This agility caters to diverse customer preferences.
- Optimal Material Utilization: With insight into different order types, resource allocation ensures that materials are used optimally. Wastage is minimized, leading to cost savings and sustainability benefits.
- Balanced Workloads: Integration enables even distribution of workload across production lines and workstations. This prevents bottlenecks and ensures smooth production processes.
- Adaptive Workforce Planning: Manufacturers can allocate labor resources based on the types of orders in the pipeline. This prevents labor shortages during peak demand periods.
- Efficient Machine Utilization: Resource allocation considers the production requirements of different order types. This maximizes the utilization of machinery, reducing idle time and operational costs.
- Improved Lead Times: Optimized resource allocation leads to more accurate lead time estimates. This enhances transparency and enables better communication with customers regarding order delivery.
- Cost Reduction: Strategic resource allocation minimizes inefficiencies, leading to cost reductions across labor, materials, and energy consumption.
- Customer-Centric Operations: By allocating resources according to diverse order requirements, manufacturers enhance their ability to fulfill customer needs accurately and promptly, elevating customer satisfaction.
In essence, optimized resource allocation fueled by the integration of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes fosters a harmonious balance between operational efficiency and customer-centricity.
This approach acknowledges the diverse demands of today's market landscape, allowing manufacturers to cater to a wide array of order requirements while ensuring optimal use of resources. As a result, businesses can operate with agility, minimize waste, and meet customer expectations with precision
Challenges and Considerations
As businesses embark on the transformative journey of integrating multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes, it is imperative to recognize that this dynamic synergy does not come without its share of challenges and complexities. This section delves into the intricate landscape of challenges and considerations that manufacturers must navigate while pursuing this integration.
By addressing these potential hurdles with foresight and strategic planning, businesses can ensure a smoother transition and fully harness the benefits of this powerful convergence.
From technology adoption to organizational alignment, the exploration that follows sheds light on the intricacies that define the path to successful integration and the pivotal role of effective management in overcoming obstacles.
A. Technical challenges in integrating multi-channel order data with manufacturing systems
The integration of multi-channel order data with manufacturing systems presents a spectrum of technical challenges that require careful consideration and strategic solutions. As businesses strive to achieve seamless connectivity between diverse sales channels and production processes, several complexities emerge:
- Data Compatibility: Different sales channels and manufacturing systems may use disparate data formats and structures. Ensuring compatibility and smooth data exchange requires careful data mapping and transformation.
- Data Volume and Velocity: Multi-channel order data can be vast and dynamic, leading to challenges in processing and managing high data volumes and rapid changes in data velocity.
- Real-Time Data Synchronization: Achieving real-time data synchronization across various systems demands robust integration tools and technologies capable of maintaining accurate and up-to-date information.
- Data Security and Privacy: Integrating systems involves sharing sensitive customer and order information. Implementing robust security measures to safeguard data privacy and prevent breaches is crucial.
- System Interoperability: Integrating diverse systems, such as order management, inventory management, and production planning, necessitates seamless interoperability, which can be complex to achieve.
- API Complexity: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are pivotal for data exchange. Integrating APIs from various sources requires comprehensive knowledge of their intricacies.
- Legacy Systems: Existing legacy systems may not be inherently compatible with modern integration technologies. Migrating data and processes from legacy systems can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, the integrated system should be able to scale to accommodate increased data volumes and new sales channels without sacrificing performance.
- Customization Challenges: Customized business processes or unique sales channel requirements may complicate integration efforts, requiring tailor-made solutions.
- Resource Allocation: Integrating systems may require significant IT resources and expertise, including skilled developers, infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance.
- Testing and Validation: Ensuring the integration works as intended requires rigorous testing and validation to identify and rectify any data inconsistencies or errors.
- Cost Considerations: Integrating systems involves investments in technology, resources, and ongoing maintenance, necessitating careful budgeting and cost analysis.
While technical challenges in integrating multi-channel order data with manufacturing systems are undeniably complex, they are not insurmountable. Addressing these challenges with a well-defined strategy, the right technology partners, and a commitment to ongoing improvement can lead to a successful integration that unlocks operational efficiency and customer-centric benefits
B. Data security and privacy concerns when sharing sensitive order information
The integration of multi-channel order data with manufacturing systems introduces a critical dimension of data security and privacy concerns. As businesses interconnect various sales channels and manufacturing processes, safeguarding sensitive order information becomes paramount.
Several key data security and privacy challenges arise:
- Data Breach Risk: Sharing order information across systems increases the risk of data breaches. Unauthorized access to customer data can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
- Customer Privacy: Multi-channel order data often includes personally identifiable information (PII) of customers. Ensuring the privacy of this information is vital to maintain customer trust.
- Compliance Regulations: Businesses must adhere to data protection regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). Integrating systems while complying with these regulations requires careful attention.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implementing robust authentication and authorization mechanisms is essential to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Encryption: Data should be encrypted during transmission and storage to protect it from interception and unauthorized viewing.
- Data Masking: Masking or anonymizing sensitive data in non-production environments minimizes the exposure of confidential information during testing and development.
- Vendor Security: If third-party vendors are involved in the integration process, ensuring their security practices align with your data protection standards is crucial.
- Audit Trails: Tracking data access and changes through audit trails aids in identifying any unauthorized activities and facilitates accountability.
- Data Retention: Clear policies on data retention and disposal ensure that sensitive order information is not retained longer than necessary.
- Employee Training: Employees handling integrated systems must be trained in data security best practices to prevent unintentional data exposure.
- Data Minimization: Minimizing the sharing of sensitive data and using anonymized data whenever possible can reduce the risk of exposure.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring and auditing of integrated systems can help detect and address security vulnerabilities promptly.
Addressing these data security and privacy concerns requires a multi-faceted approach, involving robust encryption, access controls, comprehensive policies, and ongoing vigilance. Businesses must strike a balance between data sharing for operational efficiency and protecting sensitive customer information.
By adopting a proactive stance on data security and privacy, manufacturers can instill confidence in customers, meet regulatory requirements, and mitigate potential risks associated with integrating multi-channel order data.
C. Staff training and change management for a seamless transition to multi-channel integration
The integration of multi-channel order management with manufacturing processes introduces not only technical complexities but also the need for effective staff training and change management. This integration reshapes workflows and operational paradigms, necessitating a comprehensive approach to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits.
Key considerations in staff training and change management include:
- Awareness and Education: Provide clear communication to employees about the integration's purpose, benefits, and how it aligns with the company's strategic goals. This creates a shared understanding and buy-in from the start.
- Customized Training Plans: Develop tailored training programs based on employees' roles and responsibilities. Different departments may require different levels of training to effectively use the integrated systems.
- Technology Familiarization: Ensure employees are comfortable with the technology and tools involved in the integration. Conduct training sessions that cover navigation, data entry, and troubleshooting.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration among teams that will be affected by the integration. This helps break down silos and fosters a sense of unity in navigating the change.
- Change Champions: Identify change champions within the organization who can advocate for the integration, provide guidance, and address concerns from their respective departments.
- Open Communication: Maintain open channels of communication to address questions, concerns, and feedback from employees. Regular updates on the integration's progress can help manage expectations.
- Hands-On Training: Incorporate hands-on training sessions that allow employees to interact with the integrated systems in a controlled environment, fostering practical understanding.
- Scenario-Based Training: Provide training that simulates real-world scenarios employees may encounter during daily operations. This prepares them to handle different situations effectively.
- Support Resources: Offer readily accessible resources, such as user guides, FAQs, and helpdesk support, to assist employees as they navigate the integrated systems.
- Continuous Learning: Integration technologies and processes may evolve over time. Establish a culture of continuous learning to keep employees updated and adaptable.
- Feedback Incorporation: Actively gather feedback from employees about their experiences with the integration. Incorporate this feedback into ongoing training and improvement efforts.
- Celebrating Wins: Celebrate successes achieved through the integration, acknowledging the efforts of employees and teams who contribute to the transition.
Effective staff training and change management not only facilitate a smooth transition to multi-channel integration but also empower employees to embrace the change and contribute to its success.
Future Trends and Implications
As businesses navigate the dynamic landscape of multi-channel order management integration with manufacturing processes, it is essential to cast a forward-looking gaze toward the future trends and implications that will shape this evolving synergy.
This section explores the horizon of possibilities, considering how emerging technologies, shifting consumer behaviors, and industry dynamics will influence the trajectory of this integration.
From the integration of AI and IoT to the unfolding potential of sustainable manufacturing practices, the exploration that follows delves into the transformative forces that will redefine how businesses manufacture, fulfill, and satisfy customer demands in the years to come.
A. Role of emerging technologies like AI and IoT in further enhancing multi-channel integration
The future of multi-channel integration with manufacturing processes is intricately intertwined with the rapid evolution of emerging technologies, notably Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). These transformative forces hold the potential to elevate the integration to new heights of sophistication and efficiency.
Here's how AI and IoT are poised to enhance this synergy:
- AI-Driven Demand Forecasting: AI-powered algorithms can analyze multi-channel data streams to provide more accurate and granular demand forecasts. This precision enables manufacturers to anticipate customer needs with unprecedented accuracy, optimizing production and inventory strategies.
- Predictive Maintenance through IoT: IoT sensors embedded in manufacturing equipment can monitor performance in real-time. AI algorithms can predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted production.
- Personalized Customer Insights: AI can analyze multi-channel customer interactions to glean insights into preferences, behaviors, and trends. These insights guide personalized marketing strategies and product offerings.
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: IoT-enabled tracking devices offer real-time visibility into inventory levels across different channels and locations. This information enhances inventory management and prevents stockouts or overstocking.
- Adaptive Production Optimization: AI can analyze multi-channel data to optimize production schedules dynamically. IoT sensors can provide real-time updates on machine performance, enabling adjustments for maximum efficiency.
- Intelligent Order Routing: AI algorithms can intelligently route orders to the most suitable manufacturing facilities based on factors like capacity, proximity, and expertise.
- Supply Chain Visibility: IoT sensors and AI analytics offer end-to-end visibility across the supply chain. This transparency enables businesses to address bottlenecks and disruptions proactively.
- Enhanced Customer Service: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer inquiries across multiple channels, offering real-time responses and improving customer experience.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: AI and IoT can optimize energy usage, resource allocation, and waste reduction, aligning with sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Continuous Improvement: AI can analyze multi-channel data to identify trends and areas for improvement, enabling businesses to refine processes and strategies continually.
As AI and IoT technologies mature, their convergence with multi-channel integration promises a future where manufacturing becomes even more agile, customer-centric, and efficient.
B. Anticipated shifts in customer expectations and how they'll impact manufacturing efficiency
The evolution of customer expectations is a driving force that shapes the future landscape of manufacturing efficiency. As consumers' preferences and demands continue to evolve, businesses must adapt their strategies to meet these changing dynamics.
Several anticipated shifts in customer expectations are poised to impact manufacturing efficiency:
- Demand for Personalization: Customers increasingly expect personalized products and experiences. Manufacturing processes will need to accommodate customization without sacrificing efficiency, potentially through advanced manufacturing technologies like 3D printing.
- Shorter Lead Times: With the rise of fast shipping and instant gratification, customers expect shorter lead times. Manufacturers will need to optimize production schedules and supply chains to fulfill orders quickly and efficiently.
- Transparency and Sustainability: Customers are demanding transparency in sourcing and sustainable practices. Manufacturing efficiency will involve adopting eco-friendly materials and processes, along with providing clear information about product origins.
- Omnichannel Experience: Customers expect a seamless experience across various sales channels. Manufacturing efficiency will require integration between sales channels, enabling consistent order processing and fulfillment.
- Real-Time Updates: Customers expect real-time updates on order status and delivery. Manufacturing systems must provide accurate and timely information to meet these expectations.
- Responsive Communication: Customers value responsive communication. Manufacturers will need streamlined communication channels to address inquiries, changes, or concerns promptly.
- Quality and Consistency: While speed is important, customers also demand high-quality products. Balancing speed and quality in manufacturing processes will be crucial.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Environmentally conscious consumers prefer sustainable packaging. Manufacturing efficiency will involve optimizing packaging materials and designs to reduce waste.
- Flexible Return and Exchange Policies: Customers expect hassle-free return and exchange processes. Efficient reverse logistics systems will be necessary to manage returns while minimizing disruptions.
- Value-Added Services: Beyond the product itself, customers appreciate value-added services like installation, maintenance, or post-purchase support. Manufacturing processes may need to accommodate these additional services seamlessly.
As these shifts in customer expectations reshape the manufacturing landscape, businesses that proactively align their processes and strategies will thrive. By embracing these changes, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, elevate customer satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace
C. Potential for predictive analytics to optimize production and order fulfillment
The realm of manufacturing efficiency is poised for a groundbreaking transformation through the potential of predictive analytics. This cutting-edge technology holds the promise of revolutionizing production and order fulfillment by harnessing the power of data-driven insights.
Here's how predictive analytics can optimize manufacturing processes:
- Demand Forecasting Precision: Predictive analytics leverages historical data, market trends, and external factors to generate highly accurate demand forecasts. Manufacturers can align production with actual demand, reducing waste and optimizing resource allocation.
- Inventory Management: By analyzing data patterns, predictive analytics can anticipate inventory needs. This ensures optimal stock levels, minimizes overstocking or stockouts, and reduces carrying costs.
- Maintenance Optimization: Predictive analytics can predict equipment maintenance needs based on data patterns, preventing unexpected breakdowns and minimizing production downtime.
- Quality Control Enhancement: Analyzing data from production processes allows predictive analytics to identify potential quality issues before they occur, improving product quality and reducing defects.
- Lead Time Prediction: Predictive analytics can estimate lead times by considering historical production data, potential delays, and other variables. This enhances communication with customers regarding order delivery.
- Resource Allocation Efficiency: By analyzing production data, predictive analytics can optimize resource allocation, ensuring the right resources are available at the right time for efficient production.
- Supplier Performance Forecasting: Predictive analytics can assess supplier performance based on historical data, helping manufacturers anticipate potential supply chain disruptions and take proactive measures.
- Order Prioritization: Through predictive analytics, manufacturers can prioritize orders based on various factors, such as customer importance, production capacity, and delivery deadlines.
- Scenario Planning: Predictive analytics can simulate different scenarios to assess the impact of changes in production processes, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: Data analysis through predictive analytics identifies areas for improvement in manufacturing processes, facilitating ongoing refinement for optimal efficiency.
As manufacturers embrace predictive analytics, they embark on a journey of data-driven decision-making that goes beyond intuition and assumptions.
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of modern manufacturing, the integration of multi-channel order management with production processes emerges as a transformative force that redefines efficiency, agility, and customer-centricity. As we conclude our exploration into the impact of this integration, we recognize the profound implications it holds for the manufacturing landscape.
Amid the technical challenges and change management considerations, we've discerned a pathway that leads to operational excellence. The integration not only optimizes production scheduling and inventory management but also nurtures collaborative communication and responsive manufacturing.
As we peer into the future, we envision the infusion of emerging technologies like AI and IoT, the recalibration of customer expectations, and the transformative potential of predictive analytics. These forces shape a manufacturing landscape that is not only efficient but also adaptable to the dynamic demands of the modern consumer.
In this evolving paradigm, businesses that master the art of multi-channel integration and manufacturing efficiency position themselves as pioneers. They become orchestral conductors harmonizing data, technology, and strategy to deliver exceptional products and experiences to their customers. This integration becomes the cornerstone of competitiveness, resilience, and growth.
As the final note of this exploration resounds, we invite businesses to embrace this integration as a symphony of possibilities. Through effective strategy, diligent execution, and an unwavering commitment to customer satisfaction, manufacturers can navigate the challenges, seize the opportunities, and create a harmonious blend of multi-channel order management and manufacturing efficiency that resonates with success.
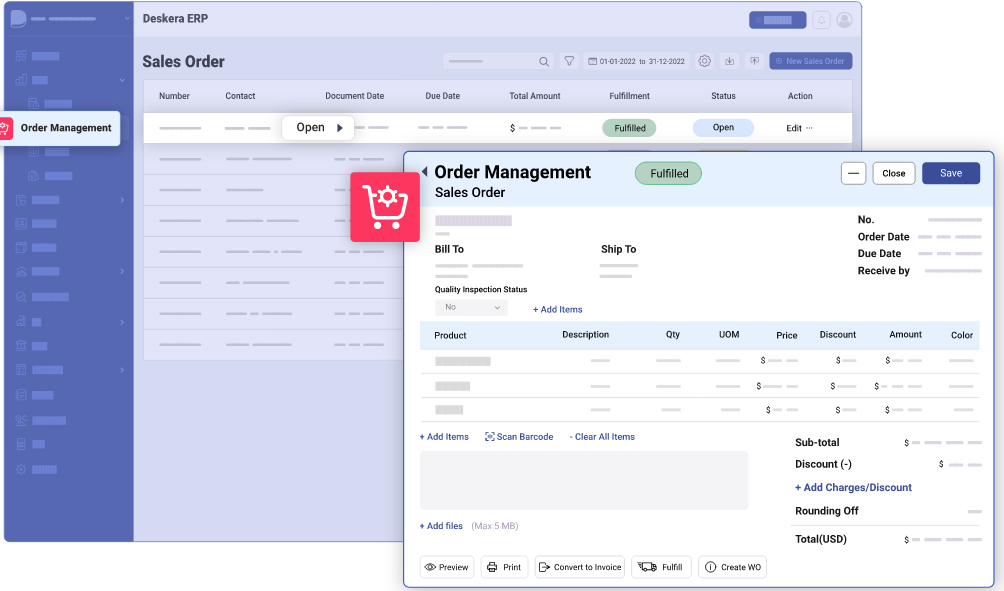
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- Operational Symphony: Integration orchestrates an operational symphony where multi-channel order data harmonizes with manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency, agility, and customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturing Efficiency's Vitality: Manufacturing efficiency is pivotal in today's competitive landscape, driving cost savings, customer satisfaction, and overall business success.
- Multi-Channel Complexity: Understanding multi-channel order management's complexity is essential, encompassing diverse sales channels, customer preferences, and real-time data aggregation.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Data's central role in decision-making is undeniable. Leveraging multi-channel data empowers businesses to anticipate demand, adjust production, and optimize inventory levels.
- Integration Benefits: Integrating order management with manufacturing processes offers real-time inventory visibility, streamlined communication, and improved demand forecasting accuracy.
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Manufacturing efficiency translates to cost reduction through minimized waste, lean practices, and optimized resource allocation.
- KPIs for Measurement: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like OEE, cycle time, and lead time offer quantifiable ways to measure manufacturing efficiency and drive continuous improvement.
- Seamless Integration: The integration's benefits extend to production scheduling, resource allocation, and adaptable workflows, fostering operational agility.
- Change Management and Training: Effectively managing staff training and change is crucial to ensure a seamless transition and embrace the integration's potential.
- Future-Proofing: Embracing emerging technologies like AI and IoT, anticipating shifts in customer expectations, and harnessing predictive analytics will shape the future of manufacturing efficiency and multi-channel integration.
Related Articles












