Globally, only 9% of all plastic waste ever produced has been recycled, with 12% incinerated and the remaining 79% ending up in landfills or the natural environment. (Source: National Geographic, 2020)
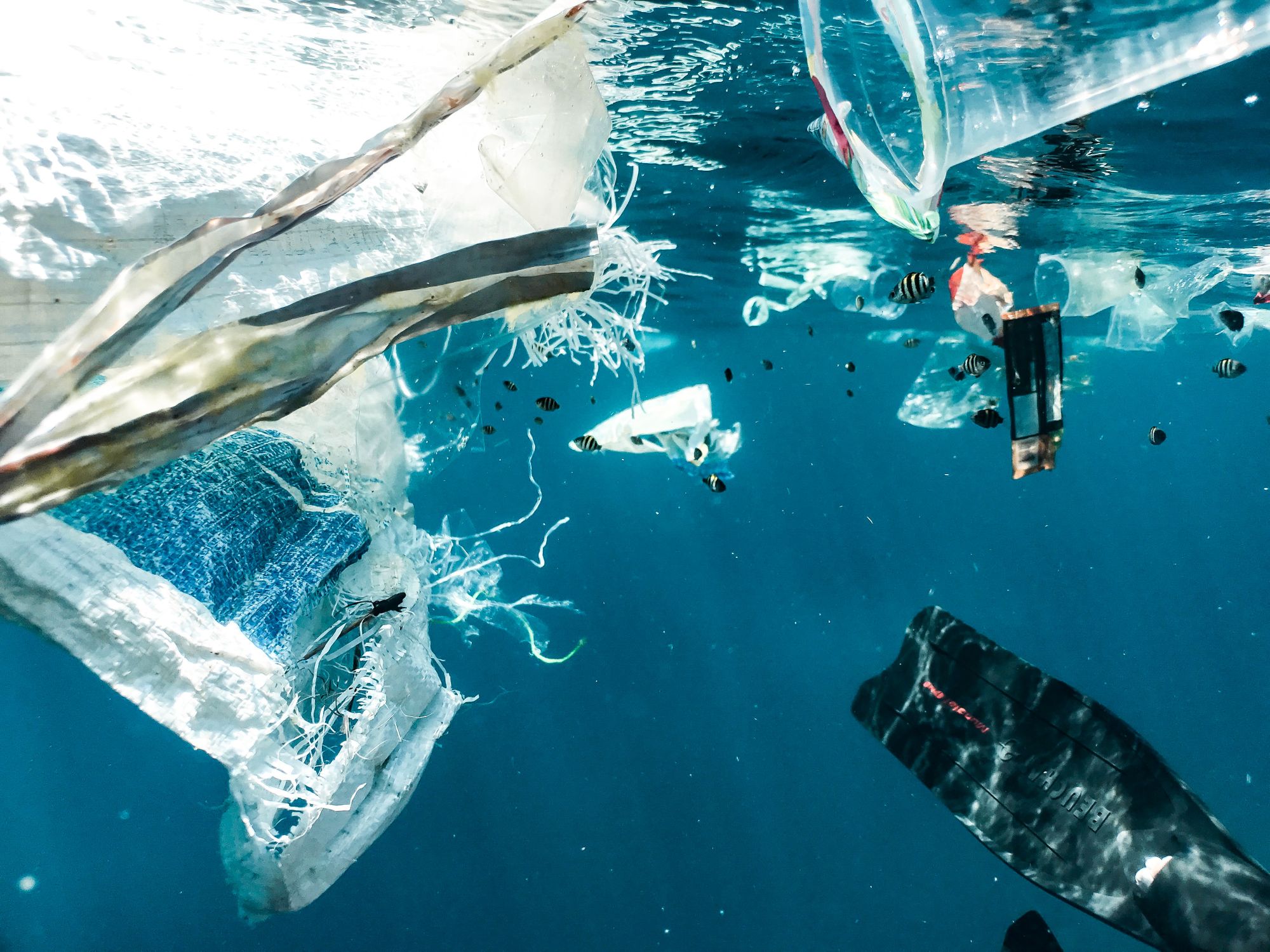
Plastic pollution is estimated to cost $13 billion annually in environmental damage to marine ecosystems, and this cost is projected to increase to $139 billion by 2050 if current trends continue. (Source: World Economic Forum, 2020)
Microplastics, tiny plastic particles less than 5mm in size, have been found in 90% of all bottled water and in 83% of all tap water samples tested globally. (Source: Orb Media, 2018)

Plastic packaging waste generated in the United States in 2018 totaled 14.5 million tons, and only 3.14 million tons (21.5%) of that was recycled. (Source: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2021)
Lastly, the plastic production industry is projected to increase by 40% over the next decade, leading to an additional 1.8 trillion plastic items produced each year by 2030. (Source: The Guardian, 2020)
Plastic is an incredibly versatile and widely used material that has revolutionized industries ranging from packaging and construction to electronics and transportation. However, the increasing use of plastic has also led to a growing environmental concern due to its negative impact on ecosystems, wildlife, and human health.
The production and disposal of plastic waste can cause pollution and greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to climate change. Additionally, plastic waste can accumulate in landfills and oceans, leading to a host of ecological problems.
Addressing these critical issues and challenges of plastic manufacturing requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals to reduce plastic use, increase recycling rates, and promote sustainable production practices.
Innovative solutions such as biodegradable plastics, recycled plastics, plant-based plastics, chemical recycling, upcycling, and smart plastics are emerging as promising ways to combat these challenges and create a more sustainable future.
This article will be your guide for critical issues and challenges of plastic manufacturing and cover the following topics:
- Plastic Manufacturing: Critical Issues and Challenges
- What are the Strategies for Combating Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing?
- What are Some of the Most Promising Innovations that will Help Combat Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing?
- FAQs related to Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing
- How can Deskera Help with Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Plastic Manufacturing: Critical Issues and Challenges
There are several critical issues and challenges in plastic manufacturing, including:
Environmental Impact
Environmental impact is a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing for several reasons:
- Resource Depletion: Plastic manufacturing requires significant amounts of natural resources such as crude oil, natural gas, and water. The extraction and processing of these resources can have negative environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Consumption: Plastic manufacturing is energy-intensive, requiring large amounts of electricity and other forms of energy. This leads to increased greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to climate change.
- Pollution: The production and disposal of plastic products can result in pollution of the air, water, and soil. Plastic waste can also harm wildlife and ecosystems, as well as contribute to the buildup of non-biodegradable waste in landfills and the ocean.
- Health Hazards: Plastic manufacturing can also pose health hazards to workers who are exposed to toxic chemicals during the production process.
- End-of-Life Management: The disposal of plastic products at the end of their useful life is a major challenge, as plastic waste can take hundreds of years to decompose. This contributes to the proliferation of plastic waste in landfills, oceans, and other natural environments, which has a range of negative environmental and health impacts.
Overall, the environmental impact of plastic manufacturing is a critical issue and challenge that must be addressed through sustainable production practices, waste reduction and recycling, and other measures.
Health Concerns
Health concerns are a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing due to the potential exposure of workers to hazardous chemicals and toxins during the production process. Some of the ways in which health concerns can arise in plastic manufacturing include:
- Exposure to Chemicals: Plastic manufacturing involves the use of a variety of chemicals, including solvents, resins, and plasticizers, which can be harmful if workers are exposed to them without proper protective measures. Prolonged exposure to these chemicals can cause respiratory problems, skin irritations, and other health issues.
- Air Quality: The production of plastic products can lead to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants, which can negatively affect the health of workers and nearby residents. Exposure to high levels of these pollutants can cause respiratory problems, headaches, and other health issues.
- Noise Pollution: Plastic manufacturing often involves the use of heavy machinery, which can generate high levels of noise. Prolonged exposure to this noise can lead to hearing loss and other hearing-related problems.
- Repetitive Motion Injuries: Workers in plastic manufacturing may also be at risk for repetitive motion injuries, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, due to the repetitive nature of some tasks in the production process.
Overall, the health concerns associated with plastic manufacturing require careful monitoring and management to ensure the safety and well-being of workers. This can include the use of protective equipment, proper ventilation systems, and ergonomic work practices, as well as ongoing monitoring of air quality and other environmental factors.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions are a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing due to the complex and global nature of the industry. The production of plastic products involves a wide range of inputs, including raw materials, energy, and labor, which are often sourced from different parts of the world.
As a result, disruptions in any part of the supply chain can have a significant impact on the production and availability of plastic products. Some of the ways in which supply chain disruptions can affect plastic manufacturing include:
- Raw Material Shortages: The production of plastic products relies heavily on the availability of raw materials such as crude oil and natural gas. Disruptions in the supply of these materials, such as due to geopolitical tensions or natural disasters, can lead to shortages and increased manufacturing costs for manufacturers.
- Transportation Disruptions: The transportation of raw materials, finished products, and other inputs is a critical part of the plastic manufacturing supply chain. Disruptions to transportation systems, such as due to strikes, natural disasters, or border closures, can lead to delays and increased operating costs for manufacturers.
- Labor Disruptions: The plastic manufacturing industry relies heavily on labor, both skilled and unskilled. Disruptions to labor, such as due to strikes or other labor disputes, can impact the production of plastic products and lead to increased costs for manufacturers.
- Regulatory Changes: The plastic manufacturing industry is subject to a wide range of regulations related to environmental and health concerns. Changes in these regulations, such as new restrictions on the use of certain chemicals, can impact the production and availability of plastic products.
Overall, supply chain disruptions are a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing that require careful management and planning to ensure the availability and affordability of plastic products. This can involve diversifying supply chains, investing in alternative materials and production methods, and developing contingency plans for disruptions.
Cost Pressures
Cost pressures are a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing for several reasons. Some of the ways in which cost pressures can affect plastic manufacturing include:
- Raw Material Costs: The cost of raw materials such as crude oil and natural gas, which are used to produce plastic products, can be volatile and subject to fluctuation due to a range of economic and geopolitical factors. This can impact the cost of production for plastic manufacturers and their ability to maintain profitability.
- Energy Costs: Plastic manufacturing is an energy-intensive process requiring significant amounts of electricity and other forms of energy. The cost of energy can vary based on a range of factors, including supply and demand, weather patterns, and regulatory changes, and can impact the cost of production for plastic manufacturers.
- Labor Costs: The plastic manufacturing industry requires skilled and unskilled labor, and the cost of labor can vary based on a range of factors, including geographic location, labor market conditions, and regulatory requirements. Rising labor costs can impact the cost of production for plastic manufacturers and their ability to maintain profitability.
- Competition: The plastic manufacturing industry is highly competitive, and companies must continually innovate and invest in new technologies and processes to stay ahead. This can create cost pressures for manufacturers as they invest in research and development and compete on price with other companies in the industry.
Overall, cost pressures are a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing that require careful management and planning to ensure the sustainability and profitability of the industry. This can involve strategies such as investing in new technologies and processes to reduce costs, diversifying supply chains to mitigate price volatility, and identifying new markets and product lines to generate revenue.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are both a critical issue and a challenge in plastic manufacturing. While advancements in technology can help improve the efficiency, quality, and sustainability of plastic manufacturing, they can also create challenges for manufacturers who must keep up with rapidly evolving technologies to remain competitive in the industry.
Some of the ways in which technological advancements can affect plastic manufacturing include the following:
- Automation: Advances in automation technology have the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and quality of plastic manufacturing processes, as well as reduce costs associated with labor. However, the adoption of automation can also require significant investment in new equipment and training for workers.
- Digitalization: Digitalization and the use of data analytics can help improve process control and reduce waste in plastic manufacturing. However, the implementation of digitalization technologies can require significant investments in hardware, software, and personnel training.
- Materials Science: Advances in materials science have led to the development of new and improved plastics that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly. However, the development and adoption of these new materials can be costly and require significant research and development investment.
- Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, have the potential to significantly transform plastic manufacturing by enabling the production of complex geometries and reducing waste. However, the adoption of additive manufacturing can require significant investments in new equipment and training for workers.
Overall, technological advancements are a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing that require careful management and planning to ensure that manufacturers can keep pace with the latest developments in the industry while maintaining profitability and sustainability. This can involve strategies such as investing in research and development, partnerships with technology providers, and ongoing training for workers.
Government Regulations
Government regulation is a critical issue and challenge in plastic manufacturing, as it can affect the production, use, and disposal of plastic materials. Some examples of government regulations that impact the plastic manufacturing industry include:
- Bans on single-use plastics: Many countries and municipalities have implemented bans on single-use plastics, such as straws, cutlery, and bags. These bans can reduce the amount of plastic waste generated, but can also impact the demand for plastic products and the profitability of plastic manufacturing companies.
- Extended producer responsibility (EPR): EPR policies require manufacturers to take responsibility for the end-of-life disposal of their products. In the case of plastic manufacturing, this can mean implementing recycling programs or paying for the cost of waste management. EPR policies can incentivize companies to design more sustainable products, but can also increase costs and regulatory burdens.
- Recycling and waste management standards: Governments may set standards for the collection, sorting, and processing of plastic waste, which can impact the viability of plastic recycling programs. Regulations on landfill disposal or incineration of plastic waste can also impact the waste management options available to plastic manufacturers.
- Chemical safety regulations: Governments may regulate the use of certain chemicals in plastic production, such as bisphenol A (BPA) or phthalates, due to health and safety concerns. Compliance with these regulations can require changes to manufacturing processes and materials, which can impact costs and production efficiency.
- Trade agreements and tariffs: International trade agreements and tariffs can impact the supply and demand for plastic materials, as well as the competitiveness of plastic manufacturing companies. For example, tariffs on plastic imports may increase the cost of raw materials for domestic manufacturers, while export restrictions on plastic waste can impact the availability of recycled materials.
What are the Strategies for Combating Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing?
Combating Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of plastic manufacturing is a critical issue that needs to be addressed to ensure the sustainability of our planet. Some of the strategies that can be employed to combat the environmental impact of plastic manufacturing include:
- Reduce plastic usage: One of the simplest ways to combat the challenges of plastic manufacturing is to reduce the amount of plastic used in various products. This can be achieved by encouraging the use of alternative materials or by designing products that require less plastic.
- Use of renewable energy sources: The use of renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power can help reduce the environmental impact of plastic manufacturing by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Design for recyclability: Designing plastic products that are easily recyclable can help reduce the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills and oceans. This can be achieved by using materials that are easier to recycle and avoiding the use of complex combinations of materials that are difficult to separate.
- Use of biodegradable plastics: Biodegradable plastics break down more easily than traditional plastics and are less harmful to the environment. The use of biodegradable plastics can help reduce the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills and oceans.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): EPR is a strategy that requires manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire life cycle of their products. This includes designing products that are more easily recyclable or biodegradable, as well as taking steps to reduce the environmental impact of the manufacturing process.
- Recycling: Recycling plastic helps to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and can also help conserve natural resources. Governments and organizations can promote and invest in recycling infrastructure to make recycling more accessible and efficient.
- Education and awareness: Educating consumers about the environmental impact of plastic and the benefits of reducing, reusing, and recycling can help change behavior and reduce plastic waste. Governments and organizations can launch public awareness campaigns to increase understanding and promote sustainable practices.
- Government regulations: Governments can implement regulations that limit the use of certain types of plastics or incentivize the use of more sustainable materials. This can help drive innovation and promote more sustainable practices in the industry.
Combating Health Concerns
Plastic manufacturing can pose health concerns for workers who are exposed to chemicals and toxins during the manufacturing process. Some strategies that can be employed to combat the health concerns of plastic manufacturing include:
- Occupational safety measures: Employers can implement occupational safety measures to protect workers from exposure to harmful chemicals and toxins. This can include providing protective gear, improving ventilation systems, and implementing safety protocols.
- Alternative materials: The use of alternative materials that are less harmful to health, such as natural fibers, can help reduce the health risks associated with plastic manufacturing.
- Safer chemical alternatives: Manufacturers can substitute harmful chemicals used in plastic manufacturing with safer alternatives. This can help reduce the risk of exposure to harmful chemicals and toxins.
- Monitoring and testing: Regular monitoring and testing of the air quality and levels of exposure to harmful chemicals can help identify potential health risks and allow for timely intervention.
- Education and awareness: Educating workers about the health risks associated with plastic manufacturing and promoting good hygiene practices can help prevent exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Government regulations: Governments can implement regulations that limit the use of certain chemicals in plastic manufacturing and require manufacturers to implement safety measures to protect workers. These regulations can help improve the safety and health of workers in the industry.
- Research and development: Continued research and development of safer materials and manufacturing processes can help reduce the health risks associated with plastic manufacturing. Manufacturers can invest in research and development to create safer alternatives to harmful materials and chemicals.
Combating Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions in plastic manufacturing can occur due to various factors such as natural disasters, trade disputes, and pandemics. Some strategies that can be employed to combat the issue of supply chain disruptions in plastic manufacturing include:
- Diversification of suppliers: Manufacturers can reduce their reliance on a single supplier by diversifying their supplier base. This can help reduce the impact of supply chain disruptions caused by the failure of a single supplier.
- Resilient supply chains: Manufacturers can develop resilient supply chains that can quickly adapt to changing circumstances. This can include contingency planning, such as maintaining safety stocks, having backup suppliers, and developing alternative transport routes.
- Collaboration and partnerships: Collaboration and partnerships between manufacturers, suppliers, and logistics providers can help increase the resilience of supply chains. Sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise can help reduce the impact of supply chain disruptions.
- Technology and automation: The use of technology and automation can help reduce the dependence on human labor and increase the efficiency and resilience of supply chains. This can include the use of artificial intelligence, robotics, and automation of processes.
- Government support: Governments can provide support to manufacturers and suppliers by providing incentives and assistance to diversify their supplier base, invest in technology and automation, and develop more resilient supply chains.
- Sustainability and circular economy: Implementing sustainable practices and transitioning to a circular economy can help reduce the reliance on virgin plastics and reduce the impact of supply chain disruptions caused by fluctuations in the availability of raw materials.
- Risk management: Implementing effective risk management strategies can help manufacturers identify potential risks in the supply chain and take proactive measures to minimize their impact. This can include conducting risk assessments and implementing risk mitigation plans.
Combating Cost Pressures
Cost pressures in plastic manufacturing can occur due to various factors, such as fluctuations in the cost of raw materials, energy prices, and labor costs. Some strategies that can be employed to combat the issue of cost pressures of plastic manufacturing include:
- Resource efficiency: Improving resource efficiency can help reduce the cost of plastic manufacturing by minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and increasing productivity. This can be achieved through the use of more efficient equipment, processes, and technology. This will lead to increased net revenue and net profit ratio.
- Alternative materials: The use of alternative materials that are cheaper than traditional plastics can help reduce the cost of plastic manufacturing. This can include the use of recycled materials, bioplastics, and natural fibers.
- Process innovation: Innovation in manufacturing processes can help reduce the cost of plastic manufacturing by increasing efficiency, reducing waste, and improving product quality. This can include the use of automation, robotics, and new manufacturing techniques. All of this will lead to improved business metrics and higher returns on investment.
- Supply chain optimization: Optimizing the supply chain can help reduce the cost of plastic manufacturing by minimizing transportation costs, reducing lead times, and improving inventory management. This can include the use of just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing and lean manufacturing principles.
- Government support: Governments can provide support to manufacturers through incentives and funding programs to promote the development of more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes and to encourage the use of more sustainable materials.
- Collaboration and partnerships: Collaboration and partnerships between manufacturers, suppliers, and customers can help reduce the cost of plastic manufacturing by sharing knowledge, expertise, and resources.
- Circular economy: Transitioning to a circular economy can help reduce the cost of plastic manufacturing by promoting the reuse and recycling of materials, reducing the dependence on virgin plastics, and reducing waste. This can help create new business models and revenue streams for manufacturers.
Combating Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in plastic manufacturing can be both an opportunity and a challenge. Some strategies that can be employed to combat the issue of technological advancements in plastic manufacturing include:
- Continuous learning: Manufacturers can invest in continuous learning and training programs to keep up with the latest technological advancements in plastic manufacturing. This can include attending conferences and workshops, participating in industry associations, and collaborating with universities and research institutions.
- Innovation and research: Manufacturers can invest in research and development to develop new technologies and processes that can improve the efficiency and sustainability of plastic manufacturing.
- Collaboration and partnerships: Collaboration and partnerships with technology providers and suppliers can help manufacturers access the latest technologies and expertise and accelerate innovation in plastic manufacturing.
- Data analysis and automation: The use of data analysis and automation can help improve the efficiency and quality of plastic manufacturing processes. This can include the use of sensors, artificial intelligence, and robotics to optimize processes and reduce waste.
- Sustainability: Technological advancements in plastic manufacturing can also help promote sustainability by developing new materials and processes that reduce waste, energy consumption, and carbon emissions.
- Regulation and policy: Governments can implement regulations and policies to encourage the adoption of new technologies that promote sustainability and reduce the environmental impact of plastic manufacturing.
- Communication and transparency: Communicating with stakeholders about the benefits and challenges of technological advancements in plastic manufacturing can help build trust and support for innovation. This can include engaging with customers, suppliers, and employees to solicit feedback and ideas for improvement.
Combating Government Regulations
The following are some strategies for combating the issue of government regulations in plastic manufacturing:
- Engage with policymakers: Plastic manufacturers can engage with policymakers and regulators to better understand upcoming regulations and provide input on how regulations may impact their business. This engagement can include participating in public comment periods, attending public hearings or meetings, or meeting directly with lawmakers.
- Adopt voluntary measures: Plastic manufacturers can adopt voluntary measures to improve the sustainability of their products and reduce their environmental impact. For example, manufacturers can adopt more sustainable production processes, use recycled materials, or implement take-back programs for their products.
- Invest in research and development: Investing in research and development can help plastic manufacturers find new and innovative solutions to reduce their environmental impact and comply with regulations. This can include developing new materials, improving recycling processes, or designing more sustainable products.
- Collaborate with stakeholders: Plastic manufacturers can collaborate with other stakeholders, such as retailers, waste management companies, and NGOs, to develop solutions to environmental challenges related to plastic production and disposal. Collaboration can help manufacturers understand the perspectives and priorities of other stakeholders and develop more comprehensive solutions.
- Consider diversifying products and markets: Plastic manufacturers can consider diversifying their product offerings and expanding into new markets to reduce their reliance on specific types of plastic or regions with more stringent regulations. This diversification can also help manufacturers capture new growth opportunities and reduce their exposure to regulatory risks.
What are Some of the Most Promising Innovations that will Help Combat Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing?
Here are some promising innovations in plastic manufacturing that can help combat critical issues and challenges:
- Biodegradable plastics: Biodegradable plastics are designed to break down naturally in the environment, reducing the amount of plastic waste that accumulates in landfills and oceans.
- Recycled plastics: Recycling plastic reduces the need for virgin plastic production, conserves resources, and reduces environmental impact.
- Sustainable production practices: Sustainable production practices, such as using renewable energy sources, optimizing production processes, and reducing waste, can help reduce the environmental impact of plastic manufacturing.
- Plant-based plastics: Plant-based plastics, also known as bio-plastics, are made from renewable resources, such as corn starch, sugarcane, and vegetable oils, and are biodegradable.
- Chemical recycling: Chemical recycling breaks down plastic into its molecular components, allowing for the production of new plastic products.
- Upcycling: Upcycling is the process of transforming waste materials into new products, such as using plastic bottles to create clothing or furniture.
- Smart plastics: Smart plastics are designed with specific properties, such as self-healing, shape-memory, or conductivity, which can make them more versatile and useful in a variety of applications.
These innovations show promise in helping to combat critical issues and challenges related to plastic manufacturing, such as reducing waste, increasing sustainability, and reducing environmental impact.
FAQs related to Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing
- What are the environmental impacts of plastic manufacturing?
Plastic manufacturing contributes to environmental degradation through the release of greenhouse gases during production and disposal, water pollution, and the accumulation of plastic waste in the environment.
- What are the health impacts of plastic manufacturing?
Plastic manufacturing can expose workers to hazardous chemicals and can also result in the release of toxic substances into the environment, which can pose health risks to people living nearby.
- What are the economic impacts of plastic manufacturing?
Plastic manufacturing can provide economic benefits through job creation and the production of goods, but it can also lead to costs associated with waste management, environmental damage, and health impacts.
- What are the challenges associated with recycling plastic?
Some of the challenges associated with recycling plastic include contamination of materials, the lack of infrastructure to handle the volume of plastic waste generated, and the difficulty in recycling certain types of plastic.
- How can plastic waste be reduced?
Plastic waste can be reduced through the use of alternatives to single-use plastics, recycling and upcycling initiatives, and consumer education and behavior change.
- What are the risks associated with plastic additives?
Plastic additives can pose health risks to consumers, especially if they are ingested or come into contact with the skin. Certain additives, such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA), have been linked to hormone disruption and other health issues.
- What are the risks associated with plasticizers?
Plasticizers can pose health risks, especially to workers who are exposed to them during manufacturing. Some plasticizers have been linked to cancer and other health issues.
- How can the release of microplastics be reduced?
The release of microplastics can be reduced through the use of biodegradable plastics, improved wastewater treatment systems, and consumer education on proper disposal methods.
- What are the challenges associated with biodegradable plastics?
Some of the challenges associated with biodegradable plastics include the high cost of production, the limited availability of raw materials, and the difficulty in ensuring proper disposal and decomposition.
- What are the benefits of using recycled plastics?
Using recycled plastics can help to conserve resources, reduce waste, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. It can also help to create a market for recycled materials and support the growth of the recycling industry.
- How can plastic waste be managed in developing countries?
Plastic waste can be managed in developing countries through the implementation of waste management infrastructure, education, and awareness campaigns, and support for the informal recycling sector.
- What are the risks associated with the incineration of plastic waste?
Incineration of plastic waste can release toxic emissions into the air and contribute to climate change through the release of greenhouse gases.
- How can plastic waste be managed in coastal areas?
Plastic waste can be managed in coastal areas through beach cleanups, improved waste management infrastructure, and education and awareness campaigns targeting coastal communities.
- What are the challenges associated with the disposal of electronic waste?
Some of the challenges associated with the disposal of electronic waste include the presence of hazardous materials in electronic devices, the difficulty in recycling certain components, and the lack of infrastructure to handle the volume of electronic waste generated.
- How can the use of plastic be reduced in the food industry?
The use of plastic can be reduced in the food industry through the use of reusable containers, packaging made from biodegradable materials, and education and awareness campaigns targeted at consumers.
- How can plastic waste be managed in urban areas?
Plastic waste can be managed in urban areas through the implementation of waste management infrastructure, education, and awareness campaigns, and support for recycling initiatives.
- What are the health risks associated with plastic manufacturing?
Workers in the plastic manufacturing industry may be exposed to hazardous chemicals and fumes, which can lead to respiratory problems, skin irritations, and other health issues.
- How can plastic manufacturers ensure the safety of their workers?
Plastic manufacturers can provide adequate training, protective gear, and safety protocols to their workers to minimize the risk of accidents and exposure to hazardous materials.
- What role do government regulations play in the plastic manufacturing industry?
Government regulations can influence the use of certain chemicals, the disposal of waste products, and the overall environmental impact of plastic manufacturing.
- How can plastic manufacturers stay competitive in a crowded market?
Plastic manufacturers can differentiate themselves by developing innovative products, improving their production processes, and offering competitive pricing.
- What is the future of plastic manufacturing?
The future of plastic manufacturing is likely to involve the increased use of biodegradable and compostable materials, as well as more sustainable production practices.
- How does the recycling of plastic impact the quality of the finished product?
The recycling of plastic can result in a lower quality product due to the degradation of the plastic during the recycling process.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using plastic in manufacturing?
The advantages of using plastic include its versatility, durability, and low cost, while the disadvantages include its negative impact on the environment and potential health risks.
- How does the plastic manufacturing process impact global warming?
The plastic manufacturing process contributes to global warming through the release of greenhouse gasses, such as carbon dioxide, during the production of plastic.
- How can plastic manufacturers improve their energy efficiency?
Plastic manufacturers can improve their energy efficiency by using renewable energy sources, optimizing their production processes, and implementing energy-saving technologies.
- How do plastic manufacturers ensure the quality of their products?
Plastic manufacturers may conduct quality control tests and inspections throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that their products meet the necessary standards.
How can Deskera Help with Critical Issues and Challenges of Plastic Manufacturing?
Deskera is a cloud-based material requirements planning (MRP) software that can assist with critical challenges and issues of plastic manufacturing in the following ways:
- Supply Chain Management: Deskera's supply chain management module can help manage complex supply chains and ensure the timely delivery of raw materials and finished products.
- Inventory Management: Deskera's inventory management module can help track inventory levels, monitor stock movement, and optimize inventory levels to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
- Production Planning and Control: Deskera's production planning and control module can help manage production schedules, optimize production processes, and ensure on-time delivery of finished products.
- Quality Control: Deskera's quality control module can help manage quality control tests and inspections throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet the necessary standards.
- Financial Management: Deskera's financial management module can help manage costs, optimize cash flow, and streamline financial reporting to improve profitability.
- Compliance Management: Deskera's compliance management module can help manage regulatory compliance, including environmental and health and safety regulations, to avoid penalties and fines.
- Reporting and Analytics: Deskera's reporting and analytics module can provide real-time insights into key performance indicators, such as production efficiency, inventory turnover, and profitability, to help make data-driven decisions and improve overall performance.
Key Takeaways
- Plastic waste is a significant environmental issue that needs to be addressed. It can have detrimental effects on wildlife, ecosystems, and human health.
- Single-use plastics, such as straws, bags, and food packaging, are major contributors to plastic waste.
- Plastic manufacturing can have a significant environmental impact, including greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and deforestation.
- Innovations in plastic manufacturing, such as biodegradable plastics, recycled plastics, sustainable production practices, plant-based plastics, chemical recycling, upcycling, and smart plastics, can help reduce the environmental impact of plastic manufacturing.
- To combat plastic waste, it's essential to reduce plastic use, increase recycling rates, and promote sustainable production practices.
- Companies can use technology solutions, such as Deskera's MRP software, to manage critical aspects of plastic manufacturing, including supply chain management, inventory management, production planning and control, quality control, financial management, compliance management, and reporting and analytics. In fact, Deskera MRP can help improve efficiency, reduce waste, ensure compliance, and improve profitability.
- Governments can implement policies, such as plastic bag bans, extended producer responsibility programs, and taxes on single-use plastics, to encourage more sustainable practices in plastic manufacturing and reduce plastic waste.
By addressing the critical challenges and issues of plastic manufacturing through a combination of innovation, technology solutions, and government policies, we can help protect the environment and promote a more sustainable future.
Related Articles