With the relentless growth of e-commerce and the ever-increasing demands of tech-savvy consumers, manufacturers are facing unprecedented challenges in meeting customer expectations. Embracing a multi-channel order management strategy has emerged as the key to survival and success in this competitive market.
According to recent industry reports, over 70% of consumers expect a seamless shopping experience across various channels, including online marketplaces, social media, and brick-and-mortar stores. Shockingly, only 39% of manufacturers have fully implemented a multi-channel order management system to cater to these demands. This discrepancy highlights a significant gap in the industry's readiness to adapt to the changing consumer landscape.
In this article, we will delve into the transformative potential of multi-channel order management for manufacturers. We will explore its benefits, the technologies driving its implementation, and the challenges that must be addressed.

Moreover, we will present compelling case studies and insights from successful adopters. Join us as we uncover the future of manufacturing, where embracing multi-channel order management is not just an option but a necessity for sustainable growth and customer satisfaction.
- Overview of the Manufacturing Industry
- The Changing Landscape of Manufacturing
- Understanding Multi-Channel Order Management
- Key Technologies Enabling Multi-Channel Order Management
- Advantages and Opportunities for Manufacturers
- Challenges and Risks in Implementing Multi-Channel Order Management
- Best Practices for Successful Implementation
- The Future Outlook of Multi-Channel Order Management
- Conclusion
- How can Deskera Help You?
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Overview of the Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry, often regarded as the backbone of economic development, plays a crucial role in shaping the modern world. From producing consumer goods to industrial equipment, manufacturing is the driving force behind global supply chains.
It encompasses a vast array of sectors, ranging from automotive and electronics to pharmaceuticals and textiles. As a significant contributor to employment and GDP, the manufacturing sector's health is a key indicator of a nation's economic strength.
Over the years, the manufacturing industry has witnessed significant advancements, with cutting-edge technologies revolutionizing production processes. Automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, and data analytics have paved the way for increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved quality control.
However, alongside these opportunities come challenges, such as the need to adapt to changing consumer preferences, supply chain disruptions, and environmental sustainability.
In this section, we will provide an insightful overview of the manufacturing industry, exploring its historical significance, current state, and future prospects. Understanding the broader context of manufacturing is essential to appreciate the significance of embracing multi-channel order management as a strategic move towards staying competitive and resilient in an ever-changing market.
Importance of order management in manufacturing
Order management is of paramount importance in the manufacturing industry as it serves as the backbone of the entire production and supply chain process. It involves the end-to-end management of customer orders, from the initial placement to fulfillment and delivery.
Here are some key reasons why order management is crucial in manufacturing:
Customer Satisfaction: Efficient order management ensures timely and accurate order fulfillment, leading to increased customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates, driving long-term business growth.
Inventory Control: Effective order management helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels. Manufacturers can avoid stockouts and overstock situations, reducing carrying costs and wastage while ensuring products are readily available for customers.
Supply Chain Efficiency: A well-integrated order management system streamlines communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. This enhances supply chain visibility, coordination, and agility, allowing for quicker responses to demand fluctuations and reducing lead times.
Cost Optimization: By optimizing order processing, manufacturers can minimize operational costs associated with manual errors, redundant processes, and order delays. Efficient order management can also lead to better negotiation power with suppliers and improved pricing strategies.
Real-Time Insights: Modern order management systems provide real-time data and analytics on sales trends, customer behavior, and inventory levels. These insights enable manufacturers to make informed decisions, anticipate market changes, and adapt production strategies accordingly.
Compliance and Accuracy: In industries with strict regulations, such as pharmaceuticals and aerospace, order management ensures compliance with quality standards, certifications, and traceability requirements. Accuracy in order processing reduces the risk of errors and potential legal or financial repercussions.
Multi-Channel Integration: As manufacturing increasingly embraces multi-channel sales (e.g., online platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, and distributors), order management becomes critical for seamless integration across various channels, providing a unified customer experience.
Scalability and Adaptability: A robust order management system can accommodate business growth and changing market demands. Manufacturers can easily scale their operations and adapt to new sales channels or emerging technologies.
In conclusion, order management is not just a logistical function but a strategic asset that impacts customer satisfaction, supply chain efficiency, cost management, and overall competitiveness in the dynamic manufacturing industry. Embracing efficient and integrated order management solutions is imperative for manufacturers seeking sustainable success in a highly competitive market.
Transition to multi-channel order management
The transition to multi-channel order management is a natural response to the changing landscape of consumer behavior and the increasing prominence of digital commerce. Traditionally, manufacturers relied on a single-channel approach, often limited to brick-and-mortar stores or direct sales to distributors.
However, the rise of e-commerce, social media platforms, and online marketplaces has transformed the way consumers interact with brands and make purchase decisions.
The transition to multi-channel order management involves several key steps:
Understanding Customer Behavior: Manufacturers need to study their target audience to identify preferred channels and touchpoints. This includes understanding which platforms customers use for research, comparison, and purchase.
Integrating Sales Channels: To enable seamless order management, manufacturers must integrate various sales channels into a centralized system. This integration allows for real-time inventory updates, order processing, and synchronized product information across all platforms.
Implementing Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based order management systems provide the flexibility and scalability necessary to manage multiple sales channels effectively. Cloud solutions enable manufacturers to access data from anywhere, facilitate collaboration, and respond quickly to market changes.
Enhancing Customer Experience: Multi-channel order management is all about creating a consistent and delightful customer experience across all touchpoints. Manufacturers should focus on providing seamless navigation, personalized recommendations, and efficient order fulfillment to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Investing in Technology: Adopting new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, helps manufacturers gain valuable insights into customer behavior, demand patterns, and inventory management. These technologies also enable predictive analysis to forecast demand accurately.
Training and Empowering Employees: Employees need to be well-trained in utilizing multi-channel order management systems effectively. Providing adequate training and support ensures smooth implementation and utilization of new technologies.
Collaborating with Partners: In multi-channel order management, collaboration with suppliers, distributors, and logistics partners becomes crucial. Manufacturers must establish strong partnerships and ensure streamlined communication to optimize the entire supply chain.
Continuous Improvement: The transition to multi-channel order management is an ongoing process. Manufacturers should regularly analyze performance metrics, gather customer feedback, and identify areas for improvement to stay competitive and meet evolving customer demands.
Ultimately, the transition to multi-channel order management is about adapting to the preferences of modern consumers and harnessing the power of digital technologies to create a seamless, connected, and customer-centric buying experience. By embracing this transformation, manufacturers can unlock new opportunities for growth, expand their market reach, and solidify their position in the competitive global marketplace.
The Changing Landscape of Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by evolving consumer expectations and the relentless advancement of digital technologies. As consumers become increasingly tech-savvy and demand seamless shopping experiences, manufacturers must adapt to the changing landscape to remain competitive.
Moreover, the rapid rise of e-commerce and the prevalence of multi-channel sales have disrupted traditional manufacturing processes, challenging the efficacy of conventional order management systems.
In this section, we will explore the dynamic shifts in the manufacturing landscape, shedding light on the impact of these changes on the industry. From the revolutionizing effect of e-commerce on consumer behavior to the hurdles faced by manufacturers with traditional order management, we will dissect the forces shaping the future of manufacturing.
Understanding these changes is crucial to recognizing the need for embracing multi-channel order management as a strategic imperative in meeting customer demands and securing a thriving position in the fast-paced and competitive market. Let us embark on this journey to comprehend the changing face of manufacturing and the opportunities it presents for growth and innovation.
A. Evolving consumer expectations
Modern consumers seek more than just products; they demand seamless, personalized, and engaging experiences throughout their buying journey. Several key factors contribute to the evolving consumer expectations:
Personalization: Consumers expect tailored product recommendations and personalized shopping experiences. They prefer brands that understand their preferences, purchase history, and individual needs.
Convenience: With the proliferation of e-commerce, consumers now demand convenience in every aspect of their shopping experience. They expect hassle-free ordering, fast delivery, and easy returns.
Omni-Channel Access: Consumers want the freedom to interact with brands across multiple channels seamlessly. They may start their research on social media, make comparisons on e-commerce platforms, and finalize their purchase in a physical store.
Transparency and Sustainability: Modern consumers value transparency in business practices and the sourcing of products. They are increasingly conscious of environmental and social impact, preferring brands that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices.
Instant Gratification: The era of instant gratification has shaped consumer behavior, with expectations for immediate responses to inquiries, real-time updates on orders, and quick resolutions to issues.
Reviews and Recommendations: Online reviews, ratings, and influencer recommendations hold substantial sway over consumer decisions. Positive reviews can boost brand credibility, while negative feedback can be detrimental to reputation.
Seamless Customer Service: Consumers expect exceptional customer service, accessible through various channels, such as live chat, social media, and phone support.
Product Quality and Innovation: High-quality products that embrace innovation and cutting-edge technology capture the attention of consumers who seek enhanced functionality and value.
For manufacturers, meeting these evolving consumer expectations requires a fundamental shift in their approach to order management. Traditional systems may struggle to cope with the demands of real-time updates, personalized experiences, and multi-channel interactions.
Embracing multi-channel order management becomes essential to ensure customer satisfaction, loyalty, and continued growth in an increasingly customer-centric marketplace. By understanding and adapting to these changing expectations, manufacturers can position themselves as customer favorites and thrive in an ever-evolving landscape.
B. Rise of e-commerce and its impact on manufacturing
The rise of e-commerce has revolutionized the retail landscape, profoundly impacting the manufacturing industry. E-commerce, facilitated by the internet and digital technologies, has changed the way consumers shop and interact with brands. This shift has far-reaching implications for manufacturers, influencing various aspects of their operations:
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Sales: E-commerce platforms enable manufacturers to bypass traditional retail channels and sell directly to consumers. This D2C approach provides manufacturers with greater control over branding, pricing, and customer relationships.
Global Reach and Market Expansion: E-commerce eliminates geographical barriers, allowing manufacturers to reach a global audience without the need for physical storefronts. This opens up new markets and opportunities for expansion.
Real-Time Market Insights: Online sales platforms generate a wealth of data on customer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns. Manufacturers can leverage this data for market research, product development, and targeted marketing strategies.
Customization and Personalization: E-commerce platforms facilitate personalized shopping experiences through data-driven recommendations and customization options. Manufacturers can offer products tailored to individual customer preferences, fostering brand loyalty.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management: The digital nature of e-commerce allows manufacturers to gather real-time data on product demand. This data can be used to optimize inventory management, reducing overstock and stockouts.
Shorter Product Lifecycles: E-commerce accelerates product lifecycles as trends and consumer preferences change rapidly. Manufacturers must stay agile and responsive to keep up with these shifts.
Fulfillment and Logistics: E-commerce necessitates efficient order fulfillment and delivery mechanisms. Manufacturers need to establish robust logistics networks to meet customer expectations for fast and reliable shipping.
Customer Service and Reviews: E-commerce platforms provide customers with the opportunity to leave reviews and feedback. Positive reviews can boost a manufacturer's reputation, while negative feedback requires prompt and effective customer service.
Competition and Price Transparency: E-commerce fosters intense competition as consumers can easily compare prices and products across different brands. Manufacturers must remain competitive and ensure pricing strategies align with market expectations.
Channel Integration: To capitalize on the e-commerce boom, manufacturers often sell their products through multiple online channels. Integrating these channels into a unified order management system is essential for streamlined operations.
In response to the rise of e-commerce, manufacturers must adapt their order management processes to cater to the demands of online sales and meet the expectations of digitally savvy consumers.
Embracing multi-channel order management enables manufacturers to leverage the opportunities presented by e-commerce, expand their market reach, and remain competitive in the ever-evolving landscape of modern retail.
C. Challenges with traditional order management systems
Traditional order management systems, which were designed for a single-channel sales approach, face numerous challenges in the rapidly evolving business landscape. As the manufacturing industry embraces e-commerce and multi-channel sales, these challenges become more pronounced and can impede a manufacturer's ability to meet customer expectations and remain competitive.
Some of the key challenges with traditional order management systems include:
Lack of Integration: Traditional systems are often isolated, operating independently from other business processes and systems. This lack of integration hinders real-time visibility and coordination across different sales channels, leading to potential discrepancies in inventory levels and order fulfillment.
Manual Processes: Many traditional order management systems rely heavily on manual data entry and processing. This approach is time-consuming and prone to human errors, resulting in delayed order processing and dissatisfied customers.
Inefficient Inventory Management: Traditional systems may struggle to provide accurate and real-time inventory data, leading to overstocking or stockouts. This inefficiency can result in increased carrying costs, missed sales opportunities, and customer dissatisfaction.
Limited Customer Insights: Traditional systems often lack sophisticated analytics capabilities, making it challenging to gain actionable insights into customer behavior and preferences. This limitation hinders personalized marketing and customer retention efforts.
Scalability Issues: As manufacturers expand their business and embrace multi-channel sales, traditional systems may struggle to scale effectively. The inability to handle increased order volumes and complex processes can hinder growth.
Inconsistent Customer Experience: With limited integration, traditional systems may not provide a unified customer experience across different sales channels. Customers may encounter discrepancies in product information, pricing, and order status, leading to confusion and frustration.
Reactive Approach: Traditional order management systems may not offer real-time visibility into order statuses, which can lead to a reactive approach in addressing issues and resolving customer inquiries. Proactive customer service becomes challenging without real-time insights.
High Maintenance Costs: Outdated legacy systems may require significant maintenance and customization to adapt to the changing business environment. This can result in higher operational costs and slower response times to market demands.
Compliance and Security Concerns: In industries with strict regulations, such as healthcare or aerospace, traditional systems may struggle to meet compliance and data security requirements, leading to potential legal and reputational risks.
Understanding Multi-Channel Order Management
In the era of interconnected commerce and diverse consumer touchpoints, understanding multi-channel order management has become paramount for manufacturers seeking to thrive in the modern market.
Traditional order management systems are no longer sufficient to meet the demands of tech-savvy customers who expect seamless shopping experiences across various channels. Multi-channel order management, an integrated and holistic approach, offers a solution to bridge the gap between online and offline sales channels.
In this section, we will delve into the concept of multi-channel order management, exploring its definition, key components, and the benefits it brings to manufacturers. By grasping the intricacies of this transformative approach, manufacturers can unlock new avenues for growth, enhance customer satisfaction, and stay agile in an ever-evolving business landscape.
A. Key concepts
The key concepts of multi-channel order management revolve around creating a seamless and unified approach to handling customer orders across various sales channels. It involves integrating different channels, processes, and data to deliver a consistent customer experience and optimize operational efficiency.
Here are the essential key concepts of multi-channel order management:
Sales Channel Integration: Multi-channel order management involves the integration of various sales channels, such as e-commerce websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, and third-party marketplaces. This integration allows for a centralized view of inventory, order statuses, and customer information, regardless of where the sale originated.
Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Multi-channel order management relies on real-time inventory updates to ensure accurate product availability across all sales channels. Having a comprehensive view of inventory levels helps prevent stockouts, overstocking, and backorders.
Order Orchestration: Order orchestration involves managing the entire order fulfillment process, from order placement to delivery. It includes routing orders to the appropriate fulfillment center, tracking order status, and coordinating multiple steps in the supply chain.
Omnichannel Customer Experience: Multi-channel order management aims to provide a consistent and seamless customer experience regardless of the sales channel used. Customers should receive the same level of service, product information, and pricing, promoting brand loyalty and customer satisfaction.
Centralized Data Management: A central database or order management system stores and manages all customer, product, and order data. This centralized approach ensures data consistency and eliminates data silos, enabling better decision-making and analytics.
Customer Engagement and Communication: Multi-channel order management involves proactive customer engagement and communication throughout the order process. Customers should receive order updates, shipping notifications, and personalized messages at different touchpoints.
Scalability and Flexibility: The multi-channel order management system must be scalable to handle increased order volumes and accommodate future growth. Additionally, it should be flexible enough to adapt to changing market demands and new sales channels.
Automation and Efficiency: Automation plays a vital role in multi-channel order management, automating repetitive tasks, order processing, and inventory updates. This streamlines operations, reduces manual errors, and improves overall efficiency.
Analytics and Insights: Multi-channel order management generates valuable data and insights on customer behavior, sales trends, and inventory performance. Leveraging analytics helps manufacturers make data-driven decisions to enhance their strategies.
By understanding and embracing these key concepts, manufacturers can leverage the power of multi-channel order management to optimize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and unlock new growth opportunities in today's dynamic and customer-centric market.
B. Integration of sales channels and order processing
The integration of sales channels and order processing lies at the core of multi-channel order management. It involves connecting various sales channels, such as e-commerce platforms, physical stores, social media, and third-party marketplaces, into a unified system for seamless order processing and fulfillment. This integration enables manufacturers to provide a consistent customer experience across all channels and efficiently manage the entire order journey.
Here's how the integration process works:
Centralized Order Management System: At the heart of multi-channel order management is a centralized order management system (OMS) or an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. This system acts as a hub that consolidates and manages all incoming orders from different sales channels.
Real-Time Inventory Sync: The OMS or ERP system connects with inventory management systems to maintain real-time visibility of product availability. When an order is placed through any channel, the inventory is instantly updated, preventing overselling and stockouts.
Omnichannel Customer Experience: Integration ensures that customers receive a consistent experience across all channels. For instance, a customer can start browsing products on a mobile app and later complete the purchase on the website or at a physical store, with the order details seamlessly transferred between channels.
Order Routing and Fulfillment: The centralized system routes orders to the most suitable fulfillment center based on inventory levels, shipping options, and customer locations. This optimizes the order fulfillment process and reduces delivery time.
Automated Order Processing: Automation plays a crucial role in multi-channel order management, automating order processing tasks such as invoicing, payment processing, and shipping label generation. This saves time and reduces errors in manual data entry.
Shipping and Logistics Integration: The order management system integrates with shipping carriers and logistics providers, allowing for real-time tracking and shipping updates. This provides customers with accurate delivery estimates and enhances transparency.
Customer Communication: Integration enables automated order status updates and shipping notifications to be sent to customers through various communication channels like email or SMS. This proactive communication keeps customers informed and reduces inquiries.
Data Synchronization: The integrated system ensures that customer and product data remain consistent across all channels. Any changes or updates made to customer information or product details are reflected universally.
Analytics and Reporting: Integrated order processing generates valuable data and insights that can be used to analyze sales performance, customer behavior, and channel effectiveness. This data-driven approach enables manufacturers to make informed decisions and optimize their strategies.
By integrating sales channels and order processing, manufacturers can optimize their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve greater efficiency and agility in meeting the demands of the modern multi-channel marketplace. This holistic approach to order management empowers manufacturers to stay competitive, scale their business, and build strong customer relationships across various touchpoints.
C. Benefits of adopting multi-channel order management
Adopting multi-channel order management offers numerous benefits that can significantly impact a manufacturer's operations, customer satisfaction, and overall business growth. As modern consumers increasingly interact with brands through multiple channels, embracing a cohesive and integrated approach to order management becomes crucial. Here are the key benefits of adopting multi-channel order management:
Enhanced Customer Experience: Multi-channel order management ensures a consistent and seamless customer experience across all sales channels. Customers can access the same product information, pricing, and promotions, regardless of where they make their purchase. This consistency fosters trust and brand loyalty.
Improved Inventory Management: Real-time inventory visibility across all sales channels prevents stockouts and overstock situations. Manufacturers can optimize inventory levels and distribution, reducing carrying costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
Agile Order Fulfillment: Multi-channel order management enables efficient order routing and fulfillment. Orders are automatically directed to the most appropriate fulfillment center, ensuring quick and accurate order processing.
Personalization and Targeted Marketing: By centralizing customer data, manufacturers can gain insights into customer preferences and behavior. This information enables personalized marketing campaigns and product recommendations, increasing the likelihood of repeat purchases.
Operational Efficiency: Automation of order processing tasks reduces manual errors and streamlines workflows. This leads to improved operational efficiency, reduced processing times, and lower administrative costs.
Expanded Market Reach: Multi-channel order management allows manufacturers to reach customers on various sales channels, including e-commerce platforms, social media, and third-party marketplaces. This expansion broadens the potential customer base and increases brand exposure.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Integrated order management systems provide valuable data and analytics on sales performance, customer behavior, and channel effectiveness. Manufacturers can use this data to make informed decisions, optimize strategies, and identify growth opportunities.
Flexibility and Scalability: Multi-channel order management systems are designed to be flexible and scalable, allowing manufacturers to adapt to changing market demands and handle increased order volumes as the business grows.
Efficient Customer Service: With centralized order information, customer service teams can respond promptly to customer inquiries and provide accurate order status updates. This proactive approach to customer service enhances customer satisfaction.
Competitive Advantage: Embracing multi-channel order management positions manufacturers ahead of competitors still reliant on traditional systems. It enables them to meet the expectations of modern consumers who value convenience and a seamless shopping experience.
Key Technologies Enabling Multi-Channel Order Management
From cloud-based solutions to advanced data analytics, the right technologies empower manufacturers to stay ahead of the curve and thrive in a multi-channel marketplace.
In this section, we will explore the key technologies that underpin the effectiveness of multi-channel order management. From automating order processing to providing real-time insights, these technologies hold the potential to transform the way manufacturers handle customer orders and streamline their supply chains.
A. Cloud-based order management systems
Cloud-based order management systems have emerged as a game-changer for manufacturers seeking to embrace multi-channel order management. Unlike traditional on-premise solutions, cloud-based systems operate on remote servers accessible through the internet.
These systems offer numerous advantages that enhance efficiency, scalability, and flexibility in managing customer orders across various sales channels.
Here are the key benefits of cloud-based order management systems:
Real-Time Accessibility: Cloud-based systems enable real-time access to order data from anywhere, empowering manufacturers and their teams to monitor and manage orders on-the-go. This accessibility is particularly valuable for businesses with multiple locations or remote teams.
Seamless Integration: Cloud-based systems facilitate seamless integration with other business applications, such as inventory management, CRM, and accounting software. This integration streamlines data flow and ensures consistency across different departments.
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based solutions are highly scalable, allowing manufacturers to expand their operations and handle increased order volumes without investing in costly hardware upgrades. This scalability is particularly advantageous for growing businesses.
Automatic Updates: Cloud-based order management systems receive regular updates and improvements from the provider. This ensures that the manufacturer always has access to the latest features and functionalities without the need for manual upgrades.
Data Security: Reputable cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures, protecting sensitive customer and order data from potential breaches and cyber threats. Manufacturers can have confidence in the security of their data.
Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based solutions eliminate the need for physical infrastructure and maintenance costs associated with on-premise systems. Manufacturers can enjoy a pay-as-you-go model, reducing upfront expenses and optimizing their IT budget.
Collaboration and Centralization: Cloud-based systems facilitate collaboration among teams, enabling seamless communication and access to real-time order information. This centralization ensures that all stakeholders have visibility into the order process.
Rapid Deployment: Implementing a cloud-based order management system is faster compared to traditional systems, which may require extensive installation and configuration. This quick deployment allows manufacturers to start benefiting from the system promptly.
Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers often have redundant data centers, ensuring high availability and data recovery in case of system failures or natural disasters. This enhances the reliability and continuity of operations.
Analytics and Insights: Cloud-based systems typically come with advanced data analytics and reporting tools, providing manufacturers with valuable insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and inventory management. This data-driven approach enables better decision-making and strategic planning.
B. Inventory management and tracking solutions
Inventory management and tracking solutions are essential components of multi-channel order management, enabling manufacturers to efficiently monitor, control, and optimize their inventory across various sales channels. These advanced technologies offer a range of benefits that contribute to smoother operations, improved customer satisfaction, and cost savings.
Here are the key advantages of adopting inventory management and tracking solutions in multi-channel order management:
Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Inventory management solutions provide real-time visibility into stock levels across all sales channels. This prevents stockouts and overstocking, ensuring that products are available when and where customers want to make a purchase.
Inventory Optimization: By analyzing demand patterns and historical data, inventory management systems help manufacturers optimize their inventory levels. This reduces carrying costs while ensuring adequate stock to meet customer demand.
Centralized Inventory Control: With a centralized inventory management system, manufacturers can manage inventory from a single platform. This simplifies coordination and reduces the risk of errors caused by managing multiple systems.
Demand Forecasting: Inventory management solutions use data analytics to forecast future demand for products. This enables manufacturers to plan production and replenishment strategies proactively, reducing lead times and inventory holding costs.
Order Synchronization: Inventory management systems are integrated with order processing systems, allowing for automatic order synchronization. This ensures that the available stock is accurately reflected in the order fulfillment process.
Multi-Warehouse Management: For manufacturers with multiple warehouses or distribution centers, inventory management solutions enable efficient allocation and movement of inventory, optimizing logistics and reducing shipping costs.
Backorder Management: When a product is temporarily out of stock, inventory management systems can manage backorders effectively, providing customers with visibility into order status and estimated delivery dates.
Returns and Exchanges: Inventory tracking solutions assist in managing returns and exchanges, streamlining the process and reducing the time between receipt of returned items and their availability for resale.
Fraud Detection: Some advanced inventory management solutions include fraud detection mechanisms to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions, safeguarding both inventory and revenue.
Data-Driven Insights: Inventory management systems generate valuable data and insights on inventory performance, sales trends, and product demand. Manufacturers can use this information to make informed decisions and optimize their inventory strategies.
C. Warehouse automation and robotics
Warehouse automation and robotics are transformative technologies that have revolutionized the manufacturing and logistics industries. In the context of multi-channel order management, these advancements play a critical role in streamlining operations, increasing efficiency, and meeting the demands of modern consumers.
Here are the key benefits of adopting warehouse automation and robotics in multi-channel order management:
Improved Order Fulfillment: Warehouse automation and robotics enable faster and more accurate order picking, packing, and shipping. Automated systems can process a higher volume of orders in less time, reducing order processing lead times and ensuring on-time deliveries.
Enhanced Inventory Management: Automated systems can monitor inventory levels in real-time and manage stock movements efficiently. This minimizes the risk of stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory levels for better cost control.
Reduced Labor Costs: By automating repetitive tasks, warehouse automation and robotics reduce the reliance on manual labor, leading to cost savings and increased productivity. This allows human workers to focus on more strategic tasks that require critical thinking and decision-making.
Increased Warehouse Capacity: Robotic systems can utilize vertical space more effectively and operate in narrow aisles, allowing for higher storage density and increased warehouse capacity without the need for expanding physical space.
Order Accuracy and Quality Control: Automation reduces the risk of human errors in order processing, ensuring a higher level of order accuracy and minimizing returns or customer complaints.
24/7 Operation: Automated systems can operate around the clock, enabling continuous order processing and fulfillment. This enhances responsiveness to customer demands and reduces order processing times.
Scalability and Flexibility: Warehouse automation and robotics systems are designed to be easily scalable to accommodate increasing order volumes and changing business needs. They can adapt to new product lines and sales channels efficiently.
Safer Working Environment: Automated systems can handle hazardous or heavy materials, reducing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries for human workers.
Data-Driven Insights: Warehouse automation generates valuable data and analytics on warehouse performance, order fulfillment rates, and resource utilization. Manufacturers can leverage this information to make data-driven decisions and optimize warehouse operations.
Competitive Advantage: Embracing warehouse automation and robotics gives manufacturers a competitive edge by enabling them to provide faster order processing, shorter delivery times, and higher order accuracy compared to competitors still reliant on manual processes.
D. Data analytics and AI-driven insights
Data analytics and AI-driven insights have emerged as powerful tools for manufacturers in the realm of multi-channel order management. Leveraging the vast amounts of data generated through various sales channels, these technologies offer valuable insights into customer behavior, demand patterns, and operational performance. Here are the key advantages of adopting data analytics and AI-driven insights in multi-channel order management:
Customer Segmentation and Personalization: Data analytics allow manufacturers to segment their customer base based on demographics, preferences, and buying behavior. AI-driven insights enable personalized marketing strategies and product recommendations, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization: By analyzing historical sales data and external factors, AI-driven demand forecasting helps manufacturers predict future demand accurately. This data-driven approach optimizes inventory levels, reducing carrying costs and avoiding stockouts.
Real-Time Order Tracking: AI-powered tracking systems provide real-time visibility into the status of orders in transit, enabling proactive communication with customers and reducing inquiries about delivery updates.
Predictive Maintenance: AI-driven analytics can be used to monitor equipment and warehouse systems, predicting maintenance needs and preventing unexpected downtime. This enhances warehouse efficiency and reduces operational disruptions.
Fraud Detection and Risk Management: Data analytics and AI algorithms can identify potential fraudulent transactions or unusual patterns, mitigating the risk of financial losses and enhancing security measures.
Supply Chain Optimization: AI-driven insights help manufacturers optimize their supply chain by identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement. This results in streamlined operations and reduced lead times.
Price Optimization: Data analytics can analyze market trends, competitor pricing, and customer behavior to determine optimal pricing strategies that maximize profits while remaining competitive.
A/B Testing and Performance Evaluation: Manufacturers can conduct A/B testing using data analytics to assess the effectiveness of different marketing strategies or sales channels. This data-driven approach ensures continuous improvement and innovation.
Proactive Customer Service: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer inquiries, provide personalized recommendations, and resolve common issues, offering 24/7 customer support and improving response times.
Strategic Decision Making: Data analytics and AI-driven insights empower manufacturers to make informed and strategic decisions based on data rather than intuition. This data-driven decision-making approach enhances overall business performance.
Advantages and Opportunities for Manufacturers
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, adopting multi-channel order management and embracing advanced technologies offers manufacturers a plethora of advantages and opportunities. From enhancing customer satisfaction to optimizing operational efficiency, this section explores the key benefits that arise from integrating sales channels, leveraging data-driven insights, and automating warehouse processes.
By seizing these opportunities, manufacturers can position themselves at the forefront of the industry, navigate the complexities of a multi-channel marketplace, and drive sustainable growth in today's customer-centric and competitive environment. Let's explore the exciting advantages and opportunities that lie ahead for manufacturers on the path to multi-channel order management success.
A. Enhanced customer experience and satisfaction
Enhancing customer experience and satisfaction is one of the most significant advantages of adopting multi-channel order management for manufacturers. In today's competitive marketplace, where consumers have numerous choices and high expectations, providing a seamless and personalized experience is crucial for building strong customer relationships and fostering brand loyalty.
Multi-channel order management enables manufacturers to deliver an exceptional customer experience in the following ways:
Consistent Brand Experience: With integrated sales channels, customers receive a consistent brand experience regardless of where they interact with the manufacturer. This unified approach builds brand trust and recognition.
Personalization: Multi-channel order management allows manufacturers to collect and analyze customer data from different touchpoints. This information enables personalized product recommendations, offers, and marketing messages, creating a more relevant and engaging shopping experience.
Quick and Accurate Order Fulfillment: Automation and real-time inventory tracking ensure faster and error-free order processing. Customers receive timely updates on order status and benefit from prompt deliveries, contributing to overall satisfaction.
Seamless Shopping Across Channels: Customers can switch between online and offline sales channels without any disruptions in their shopping journey. For example, they can start browsing products online and complete the purchase at a physical store or vice versa.
Efficient Returns and Exchanges: Multi-channel order management streamlines the returns and exchange process, making it easier for customers to manage post-purchase issues. A smooth return experience boosts confidence and satisfaction.
24/7 Customer Support: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can provide round-the-clock customer support, addressing inquiries and resolving issues promptly, even outside business hours.
Customer Feedback and Insights: Multi-channel order management systems capture customer feedback and preferences, allowing manufacturers to gather insights for continuous improvement and product innovation.
Loyalty Programs and Rewards: Manufacturers can implement loyalty programs that reward customers for their repeat business. These programs incentivize customer loyalty and encourage repeat purchases.
Seamless Integration of Marketing Campaigns: Multi-channel order management ensures that marketing campaigns and promotions are seamlessly integrated across all sales channels, increasing their effectiveness and impact.
Word-of-Mouth and Referrals: Satisfied customers are more likely to share positive experiences with others and recommend the brand to their network, contributing to organic growth and brand advocacy.
By prioritizing enhanced customer experience and satisfaction through multi-channel order management, manufacturers can differentiate themselves in the market, attract new customers, and retain existing ones. A delighted and loyal customer base serves as a solid foundation for sustained success and growth in the highly competitive manufacturing landscape.
B. Improved inventory and supply chain management
Improved inventory and supply chain management are significant advantages of adopting multi-channel order management for manufacturers. The integration of sales channels and data-driven insights allows manufacturers to optimize inventory levels, reduce carrying costs, and streamline supply chain operations.
Here are the key ways multi-channel order management improves inventory and supply chain management:
Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Multi-channel order management systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels across all sales channels. Manufacturers can accurately track stock levels, avoiding stockouts and overstocking.
Demand Forecasting: Data analytics and AI-driven insights enable manufacturers to forecast demand more accurately. This allows for better inventory planning and reduces the risk of inventory imbalances.
Inventory Optimization: By analyzing customer behavior and sales data, multi-channel order management systems help optimize inventory levels. This ensures that the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantities.
Centralized Inventory Control: Multi-channel order management centralizes inventory data, enabling manufacturers to manage and monitor inventory from a single platform. This streamlines coordination and reduces the risk of data discrepancies.
Efficient Order Fulfillment: With real-time inventory data and automated order processing, manufacturers can fulfill orders more efficiently, reducing lead times and improving customer satisfaction.
Supplier Collaboration: Multi-channel order management systems facilitate better communication and collaboration with suppliers. Manufacturers can share real-time inventory data and demand forecasts, enabling suppliers to plan production accordingly.
Reduced Carrying Costs: Optimized inventory levels and efficient order fulfillment contribute to reduced carrying costs. Manufacturers can minimize storage expenses and avoid excess inventory.
Inventory Turnover: Multi-channel order management helps increase inventory turnover by ensuring that products are sold and restocked at an optimal rate. This frees up working capital and improves cash flow.
Streamlined Warehousing: Warehouse automation and robotics, integrated into multi-channel order management, optimize storage space and automate inventory handling, reducing manual errors and maximizing warehouse efficiency.
Supply Chain Visibility: By integrating sales and inventory data, multi-channel order management systems provide comprehensive supply chain visibility. This enables manufacturers to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the supply chain and implement improvements.
Overall, improved inventory and supply chain management through multi-channel order management lead to cost savings, better resource allocation, and increased responsiveness to customer demands. Manufacturers can operate more efficiently, make data-driven decisions, and maintain a competitive edge in the market, ensuring sustainable growth and success in the dynamic manufacturing landscape.
C. Increased operational efficiency and cost savings
Increased operational efficiency and cost savings are key advantages that manufacturers can achieve by adopting multi-channel order management. This integrated approach streamlines processes, automates repetitive tasks, and optimizes resource utilization, leading to significant cost reductions and improved overall efficiency.
Here's how multi-channel order management drives operational efficiency and cost savings:
Streamlined Order Processing: Multi-channel order management automates order processing tasks, such as order routing, invoicing, and payment processing. This reduces manual errors, accelerates order fulfillment, and improves the overall speed of operations.
Automated Inventory Management: Real-time inventory tracking and automation in multi-channel order management systems optimize inventory levels, reducing carrying costs and minimizing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
Warehouse Automation: Incorporating robotics and automation in warehouse operations enhances efficiency by improving order picking, packing, and shipping processes. This leads to faster order fulfillment and reduced labor costs.
Reduced Labor Costs: Automation of repetitive tasks in multi-channel order management reduces the need for manual labor, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic activities. This lowers labor expenses and improves productivity.
Demand Forecasting Accuracy: AI-driven demand forecasting in multi-channel order management systems improves inventory planning, minimizing excess inventory and waste while ensuring products are available when needed.
Efficient Resource Allocation: Multi-channel order management provides insights into the performance of various sales channels and marketing campaigns. Manufacturers can allocate resources more effectively, optimizing marketing spend and maximizing returns.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Access to real-time data and analytics enables manufacturers to make informed decisions based on customer behavior, sales trends, and operational performance. This data-driven approach minimizes guesswork and reduces the risk of costly errors.
Efficient Supplier Collaboration: By sharing real-time inventory data and demand forecasts with suppliers, multi-channel order management enhances supplier collaboration. This leads to better negotiation opportunities and reduced procurement costs.
Improved Customer Service: Efficient order processing, accurate inventory management, and real-time order updates contribute to superior customer service. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers, reducing customer acquisition costs.
Cost-Effective Returns Management: Multi-channel order management streamlines the returns process, reducing the costs associated with product returns and exchanges.
Overall, the increased operational efficiency and cost savings achieved through multi-channel order management directly impact the bottom line for manufacturers. By optimizing processes, leveraging data insights, and embracing automation, manufacturers can run their operations more efficiently, allocate resources strategically, and achieve sustainable growth in today's competitive marketplace.
D. Expansion into new markets and sales channels
Expansion into new markets and sales channels is a significant opportunity that multi-channel order management presents to manufacturers. With the integration of diverse sales channels and advanced technologies, manufacturers can reach new customer segments and expand their market presence.
Here are the key ways multi-channel order management facilitates expansion into new markets and sales channels:
Multi-Channel Reach: Multi-channel order management enables manufacturers to sell their products through various channels, such as e-commerce platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, social media, and third-party marketplaces. This broader reach exposes the brand to a larger audience and potential customers.
Global Market Access: With the ability to integrate with international sales channels and efficient order processing, multi-channel order management allows manufacturers to enter global markets without significant infrastructure investments.
Targeted Marketing: Data-driven insights and customer segmentation capabilities in multi-channel order management help manufacturers identify new market opportunities and tailor marketing strategies to specific customer segments.
Strategic Partnerships: Multi-channel order management opens the door for strategic partnerships with other businesses and marketplaces. Manufacturers can collaborate with retailers, distributors, or online platforms to expand their sales reach.
Launching New Product Lines: Multi-channel order management facilitates the introduction of new product lines in different sales channels, allowing manufacturers to test market demand and respond to customer feedback.
Geographical Expansion: With real-time inventory tracking and efficient order fulfillment, manufacturers can expand their geographical footprint and serve customers in new regions without geographical limitations.
Omnichannel Experience: Offering a seamless omnichannel experience attracts customers who prefer to interact with the brand across multiple channels. This cohesive approach enhances customer loyalty and supports market expansion.
Competitive Advantage: Manufacturers embracing multi-channel order management gain a competitive advantage over competitors who may still rely on traditional sales approaches. This modern approach can attract customers looking for convenience and a consistent experience.
Data-Driven Market Analysis: The data analytics capabilities of multi-channel order management provide valuable insights into market trends and customer preferences, aiding manufacturers in making informed decisions about expansion strategies.
Scalability: Multi-channel order management systems are designed to be scalable, allowing manufacturers to accommodate increased order volumes and new sales channels as the business grows.
Challenges and Risks in Implementing Multi-Channel Order Management
While multi-channel order management offers numerous advantages, its successful implementation comes with its fair share of challenges and risks for manufacturers. Integrating diverse sales channels, adopting new technologies, and managing complex data sets can present hurdles that need to be carefully navigated. In this section, we will explore the key challenges and risks that manufacturers may encounter when implementing multi-channel order management.
By understanding and addressing these obstacles proactively, manufacturers can mitigate risks, optimize their strategies, and ensure a smooth and successful transition to a multi-channel order management system. Join us as we delve into the complexities and potential pitfalls that lie on the path to unlocking the full potential of multi-channel order management for manufacturers.
A. Integration complexities
Integration complexities are one of the primary challenges manufacturers face when implementing multi-channel order management. Integrating various sales channels, back-end systems, and data sources into a cohesive and unified platform requires careful planning, technical expertise, and seamless coordination.
Here are the key integration complexities manufacturers may encounter:
Diverse Sales Channels: Manufacturers often have multiple sales channels, such as e-commerce websites, mobile apps, physical stores, and third-party marketplaces. Integrating these channels to ensure consistent and real-time data flow can be complex.
Legacy Systems: Some manufacturers may have legacy systems that are not easily compatible with modern order management solutions. Integrating these systems with new technologies can require additional efforts and investments.
Data Synchronization: Ensuring that data from different sales channels and back-end systems remains consistent and up-to-date is a critical challenge. Mismatched or outdated data can lead to errors and customer dissatisfaction.
Scalability: As the business grows and additional sales channels are added, the order management system must be scalable to handle increased order volumes and data flow.
Customization: Each manufacturer's business processes and requirements may differ. Customizing the order management system to align with specific needs can add complexity to the integration process.
API Integration: Integrating with third-party platforms and applications through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) requires understanding their functionalities and data structures. Compatibility issues may arise during API integration.
Real-Time Updates: For efficient multi-channel order management, real-time data updates are essential. Ensuring that inventory levels, product information, and order statuses are consistently updated across all channels can be challenging.
Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing and quality assurance are necessary to identify and resolve integration issues before the system goes live. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Training and Adoption: Ensuring that employees are adequately trained to use the new multi-channel order management system is crucial for successful adoption. Change management and training efforts may be needed to onboard staff effectively.
Data Security: Integrating multiple systems introduces data security risks. Manufacturers must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive customer and business data.
Addressing these integration complexities requires careful planning, collaboration with technology partners, and a deep understanding of the manufacturer's specific requirements.
B. Data security and privacy concerns
With the integration of various sales channels and the collection of customer data, ensuring the protection and privacy of sensitive information becomes paramount. Here are the key data security and privacy concerns manufacturers may encounter:
Customer Data Protection: Multi-channel order management involves collecting and storing customer data, including personal information and payment details. Manufacturers must implement robust security measures to safeguard this sensitive data from unauthorized access or data breaches.
Compliance with Regulations: Different regions and countries have stringent data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with these regulations to avoid legal consequences.
Third-Party Vulnerabilities: Integrating with third-party platforms, payment gateways, and logistics providers can introduce additional security risks. Manufacturers need to assess the security practices of these external partners and ensure they meet industry standards.
Cybersecurity Threats: With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, manufacturers must be vigilant against potential cyberattacks, such as ransomware, phishing, and DDoS attacks.
Insider Threats: Data security risks also arise from within the organization. Manufacturers need to implement access controls and monitor employee activities to mitigate insider threats.
Data Encryption: Protecting data both at rest and in transit is crucial. Data encryption ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access to the data, they cannot decipher sensitive information.
Data Breach Response Plan: Having a robust data breach response plan is essential to minimize the impact of potential breaches. Manufacturers must be prepared to take immediate action to protect customer data and inform affected individuals if a breach occurs.
Vendor Security: When using third-party service providers for hosting or managing the order management system, manufacturers must verify that these vendors have stringent security protocols in place.
Data Retention and Deletion: Multi-channel order management systems may store customer data for extended periods. Manufacturers must have clear data retention and deletion policies in compliance with data protection regulations.
Transparency and Customer Consent: Manufacturers should be transparent with customers about the data they collect, how it will be used, and obtain explicit consent for data processing activities.
Addressing data security and privacy concerns requires a comprehensive approach that includes robust security measures, employee training, regular audits, and compliance with relevant regulations.
C. Training and upskilling the workforce
The adoption of new technologies, integration of diverse sales channels, and implementation of automated processes require employees to acquire new skills and adapt to the changing business landscape. Here are the key challenges and considerations related to training and upskilling the workforce:
Technical Competency: Employees need to gain proficiency in using the multi-channel order management system and associated technologies. This includes understanding how to navigate the system, process orders, and leverage data analytics tools.
Change Management: Introducing new processes and technologies can lead to resistance and apprehension among the workforce. Effective change management strategies are needed to address concerns and encourage acceptance of the changes.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Multi-channel order management often involves collaboration between different departments, such as sales, marketing, inventory, and customer service. Training programs should foster teamwork and promote effective communication.
Continuous Learning: The technology landscape is constantly evolving, and manufacturers must promote a culture of continuous learning to keep employees updated on the latest developments and best practices in multi-channel order management.
Customized Training Programs: Tailoring training programs to the specific needs of each department and employee role ensures that the workforce gains relevant skills for their responsibilities.
Integration with Existing Knowledge: Employees may have existing knowledge of certain processes or systems. Training programs should integrate this knowledge and build upon it to ease the learning curve.
Training Metrics and Evaluation: Manufacturers should establish training metrics to assess the effectiveness of the training programs. Regular evaluation allows identifying areas for improvement and gauging the impact of upskilling efforts.
Upskilling for Data Analytics: With data-driven decision-making becoming essential, employees need to develop data analysis skills to interpret and utilize insights from the multi-channel order management system.
Support and Coaching: Providing ongoing support and coaching to employees during the implementation phase and beyond helps reinforce their learning and ensures the successful adoption of new skills.
Upskilling Leadership: Managers and leaders play a crucial role in driving the success of multi-channel order management. Upskilling leadership in areas such as data-driven decision-making and change management enhances the overall implementation process.
D. Managing channel conflicts and pricing strategies
Managing channel conflicts and pricing strategies is another significant challenge that manufacturers face when implementing multi-channel order management. With different sales channels often catering to different customer segments or geographical markets, conflicts can arise in areas such as pricing, product availability, and promotions. Here are the key considerations manufacturers should address:
Price Consistency: Maintaining consistent pricing across all sales channels is essential to avoid customer confusion and conflicts. Manufacturers must establish clear pricing policies that are consistently applied across online and offline channels.
Channel Partner Relations: In multi-channel order management, manufacturers often work with various channel partners, such as distributors and retailers. Ensuring clear communication and mutually beneficial agreements with these partners is crucial to avoid conflicts.
Competing with Retailers: Manufacturers with direct-to-consumer channels may face challenges when competing with their own retail partners. Careful pricing and promotional strategies are necessary to strike a balance and prevent channel conflicts.
Market Segmentation: Different sales channels may cater to distinct customer segments with varying price sensitivities. Manufacturers should develop pricing strategies that align with each channel's target market.
Price Discrimination: Offering different prices to different customers based on their location or purchasing behavior can lead to customer dissatisfaction and legal issues. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Transparent Pricing Policies: Transparent pricing policies build trust with customers and reduce the likelihood of conflicts. Manufacturers should clearly communicate pricing and discount structures across all channels.
Monitoring Online Resellers: For manufacturers selling through third-party marketplaces, monitoring and enforcing minimum advertised price (MAP) policies can help prevent price undercutting and maintain brand value.
Dynamic Pricing: Utilizing dynamic pricing algorithms requires careful consideration to avoid price wars and maintain profitability.
Data-Driven Pricing: Leveraging data analytics to set prices based on market demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior requires continuous monitoring and adjustment.
Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Manufacturers should have clear conflict resolution mechanisms in place to address disputes between channel partners or customers, ensuring a fair and timely resolution.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
To successfully implement multi-channel order management, manufacturers need to adopt a strategic and well-executed approach. In this section, we will explore the best practices that can guide manufacturers through the complexities of integrating diverse sales channels, leveraging advanced technologies, and optimizing operational efficiency.
From effective planning and training to data security and customer-centric strategies, these best practices pave the way for a seamless and successful transition to multi-channel order management. Join us as we delve into the key principles that will empower manufacturers to unlock the full potential of multi-channel order management, drive growth, and thrive in today's dynamic and customer-focused manufacturing landscape.
A. Conducting a comprehensive assessment of existing systems
Conducting a comprehensive assessment of existing systems is a critical first step in the successful implementation of multi-channel order management for manufacturers. Before integrating new technologies and sales channels, manufacturers must thoroughly understand their current processes, infrastructure, and data flow. Here are the key aspects to consider during the assessment:
Current Order Management System: Evaluate the capabilities and limitations of the existing order management system, including its ability to handle multiple sales channels, data synchronization, and real-time updates.
Sales Channels and Touchpoints: Identify all current sales channels, including e-commerce platforms, physical stores, marketplaces, and any other touchpoints where customers interact with the brand.
Data Integration: Assess how data is currently integrated across various systems and sales channels. Identify potential data silos and inconsistencies that may hinder efficient multi-channel operations.
Inventory Management: Evaluate the current inventory management processes, including how inventory is tracked, replenished, and managed across different locations and sales channels.
Customer Data Handling: Analyze how customer data is collected, stored, and used. Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations and assess the security measures in place to protect customer information.
Order Processing Efficiency: Review the efficiency and speed of the existing order processing system. Identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Staff Skillsets: Assess the current skillsets of employees involved in order management. Determine if additional training or upskilling is required to handle multi-channel operations.
Technology Compatibility: Determine if the existing systems can seamlessly integrate with new technologies, such as cloud-based order management or analytics tools.
Vendor Evaluation: If third-party vendors are involved in the order management process, evaluate their performance and capabilities to ensure they align with the multi-channel strategy.
Customer Experience: Gather feedback from customers to understand pain points and areas where the current order management system can be enhanced to improve the overall customer experience.
By conducting a comprehensive assessment of existing systems, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, develop a clear understanding of their current capabilities, and make informed decisions on how to proceed with the implementation of multi-channel order management. This assessment serves as a foundation for developing a well-aligned strategy that maximizes the benefits of multi-channel order management and addresses any potential challenges.
B. Selecting the right multi-channel order management solution
Selecting the right multi-channel order management solution is a pivotal decision for manufacturers. The chosen solution will form the backbone of the entire multi-channel operation, impacting efficiency, customer experience, and business growth.
Here are the key factors to consider when selecting the right multi-channel order management solution:
Scalability: Ensure that the chosen solution can scale with the growth of the business and handle increasing order volumes and data flow.
Integration Capabilities: The solution should seamlessly integrate with existing systems, sales channels, and third-party applications to facilitate smooth data flow and process automation.
Centralized Control: Look for a solution that provides centralized control over inventory management, order processing, and customer data across all sales channels.
Real-Time Updates: Real-time data synchronization and updates are critical for accurate inventory tracking, order status, and customer information.
User-Friendly Interface: A user-friendly interface simplifies the onboarding process and reduces the learning curve for employees using the new system.
Customization and Flexibility: The solution should be customizable to align with the specific needs and processes of the manufacturing business.
Data Security and Compliance: Prioritize solutions that have robust data security measures in place to protect sensitive customer information and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
Analytics and Reporting: Look for a solution that provides comprehensive analytics and reporting capabilities to gain insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and operational performance.
Customer Support: Evaluate the level of customer support and training offered by the solution provider to ensure a smooth implementation and ongoing assistance.
Cost-Effectiveness: Consider the total cost of ownership, including implementation, maintenance, and any additional fees, to ensure the solution is cost-effective for the business.
Vendor Reputation: Research the reputation and track record of the solution provider in the industry to ensure reliability and credibility.
Customer References: Seek feedback from existing customers of the solution provider to understand their experiences and satisfaction with the system.
By carefully evaluating these factors, manufacturers can identify the multi-channel order management solution that best aligns with their business requirements and strategic goals. Making the right choice will set the foundation for a successful multi-channel operation, empowering the manufacturing business to thrive in the dynamic and customer-centric market.
C. Collaborating with partners and suppliers
In a multi-channel environment, manufacturers often work with various stakeholders, including distributors, retailers, logistics providers, and technology partners. Effective collaboration ensures a seamless flow of information, products, and services across the supply chain. Here are the key considerations for successful collaboration:
Clear Communication: Establish open and transparent communication channels with partners and suppliers to foster understanding, alignment, and efficient problem-solving.
Shared Objectives: Ensure that all parties involved in the multi-channel order management process share common objectives and goals. Aligning interests helps maintain a unified focus on customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Data Sharing: Collaborate on data sharing to provide partners with real-time visibility into inventory levels, order statuses, and customer insights. This shared information enables better decision-making and proactive response to market demands.
Technology Integration: Integrate systems and processes with partners to streamline data exchange and automate order processing, reducing manual errors and processing delays.
Consistent Policies: Establish consistent pricing, discounting, and promotion policies across all partners to avoid conflicts and maintain a consistent customer experience.
Performance Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the performance of partners and suppliers to ensure they meet agreed-upon standards and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Joint Marketing Efforts: Collaborate with partners on joint marketing campaigns and promotions to drive customer engagement and brand visibility across multiple channels.
Vendor Training: Offer training and support to partners and suppliers on using the multi-channel order management system effectively. This ensures a smooth and efficient collaboration.
Performance Incentives: Implement performance-based incentives to motivate partners and suppliers to excel in meeting shared objectives.
Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by sharing feedback and best practices among all stakeholders. This fosters innovation and optimization throughout the supply chain.
Collaborating effectively with partners and suppliers in a multi-channel order management ecosystem empowers manufacturers to deliver a seamless and customer-centric experience. By fostering strong relationships and efficient processes, manufacturers can optimize their supply chain, expand market reach, and gain a competitive advantage in the dynamic and evolving marketplace.
D. Aligning sales, marketing, and customer service teams
Aligning sales, marketing, and customer service teams is crucial for the successful implementation of multi-channel order management. In a multi-channel environment, these teams play interconnected roles in delivering a consistent and exceptional customer experience. Here are the key strategies for achieving alignment:
Shared Goals and Objectives: Establish shared goals and objectives that align the efforts of sales, marketing, and customer service teams towards a unified vision of customer satisfaction and business growth.
Cross-Functional Communication: Facilitate regular communication and collaboration between teams to share insights, coordinate efforts, and address customer needs seamlessly.
Customer Journey Mapping: Map the customer journey across various sales channels to understand touchpoints and pain points. Use this information to align sales, marketing, and customer service strategies to create a cohesive and seamless customer experience.
Data Sharing: Ensure that teams have access to shared customer data and insights to gain a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences, behavior, and interactions with the brand.
Integrated Marketing Campaigns: Align marketing campaigns with sales initiatives to promote consistent messaging and offers across all channels, driving customer engagement and sales conversions.
Service-Oriented Mindset: Instill a service-oriented mindset across all teams, emphasizing the importance of meeting customer needs and exceeding expectations.
Cross-Training and Collaboration: Encourage cross-training and collaboration between teams to foster mutual understanding and empathy for each other's roles and challenges.
Feedback Loop: Implement a feedback loop to capture insights and feedback from sales and customer service teams to inform marketing strategies and product improvements.
Performance Metrics: Define common performance metrics and KPIs that measure the impact of joint efforts and collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
Technology Integration: Utilize technology solutions that integrate customer data, marketing automation, and customer service tools to streamline processes and enhance collaboration.
The Future Outlook of Multi-Channel Order Management
The future outlook of multi-channel order management holds immense promise for manufacturers, as they navigate an ever-evolving landscape of customer expectations and technological advancements. In this section, we explore the emerging trends and innovations that are reshaping the multi-channel order management landscape.
From leveraging cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain to embracing hyper-personalization and sustainability, manufacturers are poised to revolutionize how they manage orders across diverse sales channels.
A. Trends shaping the future of manufacturing and order management
The future of manufacturing and order management is being shaped by a range of transformative trends that are redefining the industry. Manufacturers are embracing new technologies, adapting to changing customer expectations, and prioritizing sustainability to stay competitive in the global market.
Here are the key trends that are shaping the future of multi-channel order management:
Advanced Technologies: Manufacturers are leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, optimize supply chain operations, and enhance the overall order management process.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT-enabled devices and sensors are being utilized to monitor inventory levels, track shipments, and optimize warehouse operations in real-time, ensuring efficient order fulfillment.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chain management by providing transparency, traceability, and enhanced security. Manufacturers are adopting blockchain to create immutable records of product origin and distribution.
Hyper-Personalization: Customers now expect personalized experiences across all sales channels. Manufacturers are leveraging customer data and AI-driven insights to deliver hyper-personalized product recommendations, pricing, and promotions.
Omnichannel Experience: Manufacturers are focusing on providing a seamless omnichannel experience, where customers can switch between online and offline channels seamlessly, with consistent branding and customer service.
Sustainable Practices: Eco-conscious consumers are demanding environmentally sustainable products and practices. Manufacturers are integrating sustainable sourcing, production, and distribution methods into their order management processes.
Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation are transforming warehouse operations, enabling faster order processing, accurate picking, and efficient inventory management.
Voice Commerce: Voice-activated assistants and smart speakers are becoming popular shopping tools. Manufacturers are adapting their order management systems to accommodate voice-based ordering and customer support.
3D Printing and Customization: Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, allows for on-demand production and customization of products. Manufacturers are integrating 3D printing capabilities into their order management systems to meet customer demands for personalized products.
Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics is being used to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and prevent supply chain disruptions, leading to more efficient order management.
These trends are reshaping the manufacturing and order management landscape, providing manufacturers with opportunities to enhance customer experiences, optimize operations, and drive sustainable growth.
B. Predictions for the next 5-10 years
Over the next 5-10 years, the future of multi-channel order management is set to undergo remarkable transformations, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. Here are some predictions for the next decade:
Seamless Integration of AI and ML: Artificial intelligence and machine learning will be deeply integrated into multi-channel order management systems. AI-driven algorithms will enable better demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and personalized customer experiences.
Unified Commerce Platforms: Manufacturers will adopt unified commerce platforms that consolidate all sales channels into a single, centralized system. This approach will provide real-time data synchronization and enable seamless customer experiences across channels.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Shopping: Virtual and augmented reality technologies will revolutionize the way customers shop. Manufacturers will offer immersive shopping experiences, allowing customers to visualize products in their homes before purchase.
Drone Delivery: Drone technology will play a significant role in order fulfillment, especially for quick and efficient delivery of products to customers' doorsteps, especially in urban areas.
Sustainability as a Differentiator: Sustainability will become a key differentiator in the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers that prioritize eco-friendly practices and transparent supply chains will gain a competitive edge.
Hyper-Localized Marketing: AI-powered analytics will enable hyper-localized marketing strategies, targeting customers with personalized offers based on their location, preferences, and purchase history.
Voice Commerce Dominance: Voice commerce will become a mainstream shopping method, with a significant portion of orders being placed through voice-activated devices and virtual assistants.
Emphasis on Last-Mile Delivery: The focus on optimizing last-mile delivery will intensify, with manufacturers exploring innovative solutions like delivery robots and autonomous vehicles.
Customer-Centric Service: Customer service will be highly customer-centric, with AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants handling routine inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on complex customer issues.
Integration of Sustainability Metrics: Manufacturers will integrate sustainability metrics into their order management systems, allowing customers to make environmentally conscious choices during the purchasing process.
Supply Chain Resilience: After experiencing disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic, manufacturers will invest in building resilient supply chains to mitigate future risks and disruptions.
On-Demand Manufacturing: On-demand manufacturing, enabled by 3D printing and other additive manufacturing technologies, will become more common, reducing lead times and waste.
These predictions indicate a future where manufacturers leverage advanced technologies to deliver superior customer experiences, prioritize sustainability, and optimize supply chain efficiency. The multi-channel order management landscape will continue to evolve rapidly, and the manufacturers that embrace these trends will be best positioned to thrive in the ever-changing market.
C. Recommendations for manufacturers to stay competitive
To stay competitive in the rapidly evolving multi-channel order management landscape, manufacturers should adopt strategic approaches that prioritize innovation, customer-centricity, and operational efficiency. Here are some key recommendations:
Embrace Digital Transformation: Invest in digital technologies like AI, ML, and IoT to streamline order management, optimize inventory, and enhance customer experiences.
Implement Unified Commerce Platforms: Adopt unified commerce platforms that integrate all sales channels, enabling seamless data synchronization and consistent customer experiences.
Personalize Customer Experiences: Leverage customer data and AI-driven insights to deliver hyper-personalized offers, recommendations, and pricing across all channels.
Prioritize Sustainability: Embrace sustainable practices in sourcing, production, and distribution to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly products and transparent supply chains.
Optimize Last-Mile Delivery: Focus on last-mile delivery optimization, utilizing technology like drones and autonomous vehicles to expedite delivery and enhance customer satisfaction.
Invest in Customer Service: Enhance customer service by deploying AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to handle routine inquiries, freeing human agents for more complex issues.
Collaborate with Partners: Foster strong relationships with partners and suppliers to ensure smooth data exchange and efficient collaboration across the supply chain.
Monitor Emerging Trends: Stay informed about emerging trends and innovations in the industry to proactively adapt to changing customer preferences and market dynamics.
Empower Workforce: Invest in employee training and upskilling to ensure the workforce is equipped to leverage new technologies and adapt to evolving customer needs.
Data Security and Privacy: Prioritize data security and compliance with data privacy regulations to build customer trust and protect sensitive information.
Enable Omnichannel Experiences: Focus on providing a seamless omnichannel experience, allowing customers to interact with the brand across multiple touchpoints seamlessly.
Monitor Customer Feedback: Regularly gather customer feedback to identify pain points and areas for improvement in the order management process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of manufacturing lies in embracing multi-channel order management, a transformative approach that leverages advanced technologies, customer-centric strategies, and sustainable practices. The manufacturing industry is evolving rapidly, driven by changing customer behaviors, emerging technologies, and the imperative of sustainability. Manufacturers that successfully navigate this dynamic landscape will gain a competitive edge and thrive in the global market.
By conducting comprehensive assessments of existing systems, selecting the right multi-channel order management solution, and collaborating effectively with partners and suppliers, manufacturers can lay a strong foundation for successful implementation. Aligning sales, marketing, and customer service teams will create a cohesive approach, delivering a seamless and personalized customer experience across diverse sales channels.
Looking ahead, emerging trends like AI-driven insights, blockchain transparency, and hyper-personalization will reshape the multi-channel order management landscape. Sustainability will be a key differentiator, and manufacturers that prioritize eco-friendly practices will resonate with increasingly conscious consumers. Voice commerce, drone delivery, and 3D printing will revolutionize the order fulfillment process.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
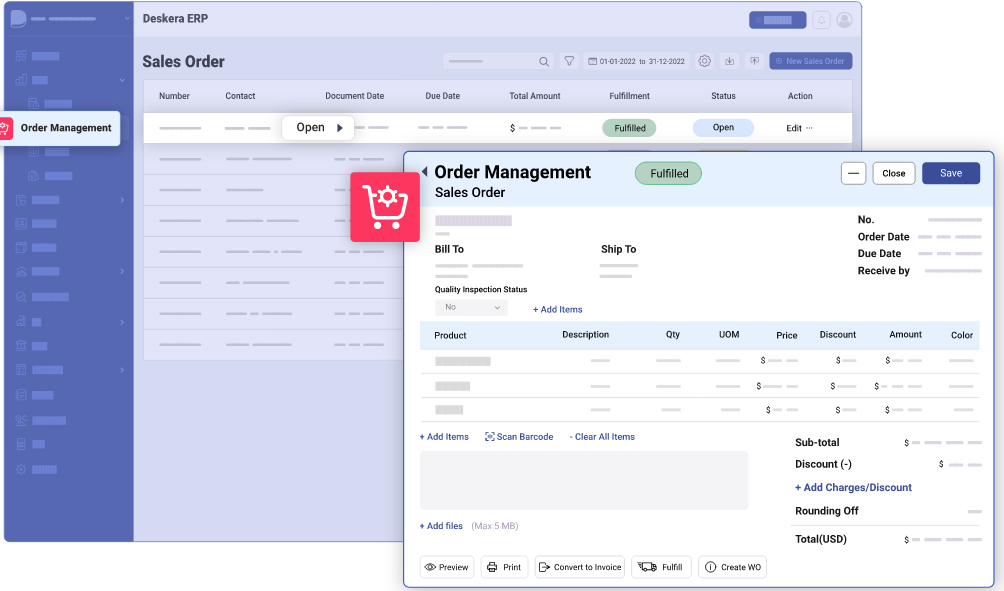
Deskera's integrated financial planning tools enable investors to better plan and track their investments. It can assist investors in making faster and more accurate decisions.
Deskera Books allows you to better manage your accounts and finances. Maintain good accounting practices by automating tasks like billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a powerful solution that manages your sales and helps you close deals quickly. It not only enables you to perform critical tasks like lead generation via email, but it also gives you a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a straightforward tool for centralizing your human resource management functions.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-channel order management is a critical strategy for manufacturers to meet the demands of modern consumers and remain competitive in the market.
- Comprehensive assessment of existing systems is essential before implementing multi-channel order management, allowing manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and alignment with business objectives.
- The right multi-channel order management solution should be scalable, integrative, and capable of providing real-time updates for efficient operations.
- Collaboration with partners and suppliers is crucial for a smooth and seamless supply chain, ensuring a unified customer experience across all sales channels.
- Aligning sales, marketing, and customer service teams fosters a customer-centric approach, driving higher customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
- Advanced technologies such as AI, ML, and IoT play a pivotal role in optimizing order management, inventory control, and personalized customer experiences.
- Sustainability is a key differentiator for manufacturers, as eco-conscious consumers prioritize transparent and eco-friendly products and practices.
- Manufacturers need to adapt to emerging trends like voice commerce, blockchain transparency, and hyper-personalization to stay ahead in the dynamic multi-channel order management landscape.
- Prioritizing data security and customer privacy is essential to build trust with consumers and protect sensitive information.
- Embracing digital transformation, investing in employee upskilling, and monitoring customer feedback are crucial steps for manufacturers to thrive in the evolving multi-channel order management ecosystem.
Related Articles












