DRC-03 is a form that is filed by a taxpayer for paying tax under the GST law. Sometimes, the GST liability does not get recorded while filing GST returns. Later on, such errors can come to your notice and you may want to correct them. Now, there are two methods to rectify these errors. You can either notice the error and voluntarily correct it or you get a Show Cause Notice (SCN) for the same under Section 73 and 74 of the CGST Act.

Section 73-This rules deals with the tax that is underpaid or unpaid without any fraudulent intention or invocation.
Section 74-This rule deals with the tax that is unpaid or underpaid with some fraudulent intention or invocation.
Applicability for Paying Tax in Form DRC-03
Let’s take a look at some of the causes for making payments under DRC-03.
Audit/Reconciliation Statement
During the audit for the financial year, if the GST auditor finds out any case of short payment of tax or excess claim of the input tax credit, the taxpayer must make voluntary payment through form DRC-03. This payment consists of taxes, interest, and penalties. The GST Auditor is required to report this in GSTR-9C.
Investigation & Others
During the investigation of the taxpayer, if it is found that the taxpayer had defaulted incorrect payment of taxes, then he may have to voluntarily make payment through form DRC-03.
Annual Return
Before filing the annual returns, the taxpayer should conduct reconciliation for the entire year. During such reconciliation, a mismatch of any short payment of taxes, interest, or penalties due to non-reporting or under-reporting of taxable supplies can be discovered. In such scenarios, taxpayers are required to pay the tax differences in cash and get it reported by filing DRC-03.
Demand or in response to show cause notice
In response to a show-cause notice, the taxpayer can pay the tax demanded along with interest using form DRC-03, but within 30 days of the date of the issue mentioned in the show-cause notice.
There are two scenarios where SCN comes to the picture i.e., Section 73 and Section 74.
Section 73 – deals with cases where tax is not paid or underpaid without any intention of fraud.
Section 74 – deals with cases where tax is not paid or underpaid with intention of fraud
Liability Mismatch
Liability mismatch occurs when there is a mismatch between GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B sales data of taxpayers. This option has been added in February 2021.
If the tax authorities have sent notice for differences, then the taxpayer is liable to make the payment through DRC-03 or reply by justifying the reasons.
ITC Mismatch
If there is a mismatch between GSTR-2A/2B and GSTR-3B, after the extra 5% credit allowed as per CGST rule 36 (4), it refers to ITC mismatch. If more purchases are shown, then it may lead to reduced tax payment. The tax authority can send a notice in such kind of mismatch situations. If the taxpayer agrees to this, then he is required to pay the amount in GST DRC 3 by justifying a reason for the same. This option was also added in February 2021.
Important Point to Note: You need to make all the payments either from input tax credit available in the electronic credit ledger or cash balance available in the electronic cash ledger. However, in case of interest and penalties, ITC utilization is not available, you have to compulsorily pay only cash in such cases.
Prerequisites before filing DRC-03
To make a voluntary payment of tax, Form DRC-03 is used. The payment can be made if either of the following conditions is met:
- Before show cause notice (SCN) gets issued
- Within 30 days of issuance of SCN, in case SCN is already issued
What is the Procedure to file DRC?
Let’s take a look at some of the steps to file DRC-03:
Step 1-The foremost step is to login into the GST portal using your login ID and password. Then you need to choose ‘User Services’ under the ‘Services’ tab. Then you need to click on ‘My Applications’.
Step 2- The next step is to choose from three cases under which a taxpayer makes payment:
Case 1-No payment has been made and no Payment Reference Number (PRN) has been generated
Step a. In this case, you need to select the Application type as ‘Intimation of Voluntary Payment-DRC-03’ and then click on ‘New Application.’
Step b. As a taxpayer, you will have to select from any of the two options:
Voluntary payment: In this case, you will see the date of payment without giving you the option to edit it. This application can be saved at any stage during the filing process for up to 15 days. After this, the draft will be deleted from the database. The saved application can be viewed after clicking on ‘My Saved Applications’ under the ‘User Services’ tab.
Payment against SCN: You need to enter the SCN number manually and select the date of issue and make the payment in 30 days.
Step c. Now select the Section under which payment is being made. Choose the financial year and then select ‘from date’ and ‘to date’ of the overall tax period.
Step d. Now you need to enter the payment details including interest and penalty. Additional details can be provided by the taxpayer by clicking on ‘Add’. Then click on ‘Proceed to Pay’.
Step e. Now the Voluntary payment page will appear which is further divided into 3 sections:
- Liability Details: In this table, liabilities are displayed.
- Cash Ledger Balance: In this table, you will find the cash balance available on a particular date. The value of cash to be paid from the available balance has to be entered against outstanding liabilities.
- Credit Ledger balance: Here, you can see the amount available as credit of purchases and expenses. ITC available as on date can be seen in this table. The value of the liability to be paid through ITC has to be entered and then click on Set-Off.
Step f. You will see a confirmation message appearing on the screen showing the cash and ITC balance getting used for doing the payment. Then, click on ‘Ok’, a PRN will get generated and a successful payment message will appear.
Note: If PRN is not available, then you need to click on the ‘Electronic Liability Register’ under Services>Ledgers>Electronic Liability Register.
Step g. If you want to look at the draft DRC-03, then you need to click on the ‘Preview’ button on the page-‘Intimation of payment made voluntarily or against SCN’.
Step h. You need to provide reasons if any, in the field provided. Thereafter, choose a file in the attachments section and upload it. Once this is done, click on the verification checkbox and then select the ‘Authorised Signatory’ and enter the ‘Place’.
Step i. Next, click on ‘File’. You will get two options:
File with DSC: You need to browse the certificate and then click on the button ‘sign’.
File with EVC: You will receive an OTP to your registered mobile number and email ID. On validation of OTP, you will get a success message along with ARN.
Case 2: PNR is generated but is unutilized and the taxpayer has come for payment within 30 minutes of PNR generation
Step a. You need to follow the same steps just as in Case 1 until you reach the page ‘Intimation of payment made voluntarily or against the SCN page’.
Step b. Under the option ‘Have you made payment?’ Select ‘Yes’ and enter the PRN.
Step c. You will see a link, known as ‘Get payment details’. Once you click on it, details will be auto-populated based on the payment that was made.
Step d. Next, click on ‘Preview’ to look at the draft DRC-03 GST and then you need to follow the same steps to apply just as in the Case 1.
Case 3: PNR is generated but is unutilized and the taxpayer has come for payment after 30 minutes of PNR generation
Step a. You need to follow the same steps as in Case 1 until you reach on ‘Intimation of payment made voluntarily or against the SCN page’.
Step b. Under the option ‘Have you made payment?’, select YES and enter the PRN.
Step c. You will see a link, known as ‘Get payment details’. Once you click on it, you need to enter the details as they will not be auto-populated as in Case 2. The reason for this is that the time limit of 30 minutes will be passed. Once this is done, the details will be verified and then the intimation form will be accepted or rejected accordingly.
Step d. To look at the DRC-03 draft, you need to click on the ‘Preview’ button and follow the same steps as mentioned in Case 1.
Note: With respect to Case 2 and Case 3, if the PRN is already utilized, an error message will appear asking you to enter the unutilized PRN.
Where to Report cash payments in GST returns?
Cash payments in GST returns are reflected in the Electronic Ledger:
Monthly Return in GSTR-3B
Basically, an electronic ledger is kind of an e-wallet. All payments made in cash/bank can be showcased in this ledger. A taxpayer needs to utilize his ITC balance to pay off his tax liabilities. In case, where the balance is less than the liabilities, the difference needs to be paid in cash.
Annual Return in GSTR-9
If you have any tax liabilities that have not been paid in GSTR-3B, then they have to be paid in GSTR-9. The balance that is available in the electronic cash ledger can be utilized to pay off liabilities. If you find that the available cash balance is lesser than the liabilities, then a challan will have to be issued in order to make additional payments in cash.
Demand Notices
You can use both ITC and cash balance to make payment of demand notices. An additional challan needs to be issued in order to pay the remaining liabilities. You need to remember that interest and penalty can be paid only in cash. A proper officer will be issuing an acknowledgement in Form DRC-04 with respect to the payment made in Form DRC-03. He will conclude the proceedings by issuing an order in Form DRC-05.
What happens after filing DRC-03?
Once you file DRC-03, the status will get changed to “Pending for approval by Tax officer”.
The tax officer allocates an acknowledgement to the taxpayer within the form GST DRC-04 (Acknowledgement of Acceptance of voluntary payment).
A taxpayer will find no restriction on making another payment on a voluntary basis, while the acknowledgement by the tax officer is still pending.
Frequently Asked Questions on DRC-03
When can a taxpayer pay tax voluntarily under GST?
Voluntary tax payment can be done before the notice gets issued under Sections 73 or 74 of the CGST Act, 2017, or within 30 days of issuance of SCN. He /She cannot make voluntary payment after thirty days of the issuance of SCN.
What are the prerequisites to make voluntary tax payments?
Take a look at the prerequisites for making voluntary payment:
(a) Before the issue of SCN, the voluntary payment of tax is made-
SCN defining the tax must not be issued.
(b) Where the voluntary tax payment is done after the issuance of SCN or statement-
The time limit of 30 days must not have passed since the issuance of SCN.
Can you make partial payments against a liability?
No, the taxpayer is not allowed to make partial payments against a liability raised in the show-cause notice. Even the GST portal does not allow partial payments.
Are you allowed to save the application for intimation of voluntary payment?
Yes, you can save the application for intimating voluntary payment in DRC-03 at any stage of the filing process for a maximum of fifteen days. If you fail to file it within that stipulated time, then the saved draft will be deleted from the GST database.
If you want to view the saved application, you need to go to ‘Services’ > click on ‘User Services’ > option called ‘My Saved Applications’.
What will happen once the DRC-03 form is filed on the GST portal?
When you file the form DRC-03, then all the three ledgers- Electronic Liability Ledger, Electronic Cash Ledger, and Electronic Credit Ledger will get updated, i.e., respective debit and credit entries will be passed and PRN will get generated.
What to do in case there is no sufficient balance in the cash ledger to make voluntary payment in DRC-03 against a liability raised in an SCN?
All you need to do is use the “Create Challan” option available on the voluntary payment screen in order to deposit the amount in Electronic Cash Ledger. Once you click the “Create Challan” button, you will be redirected to a screen in the Payment module.
On the ‘Create Challan’ page, the amount gets auto-populated in the challan. This amount is calculated based on the extra cash required after evaluating the tax liabilities.
How can Deskera help you in your business?
Deskera is an all-in-one software through which you can combine accounting, financial management, inventory management and many more such features using Deskera Books.
While the taxation regimes followed by most countries tend to be intimidating and nerve-wracking, the key to understanding them is by starting to understand each of their nitty-gritty. In the case of GST in India, this involves understanding the Forms GSTR-1, GSTR-2A, GSTR-2B, GSTR-3B, the difference between GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C, reverse charge mechanism under GST and many more such details.
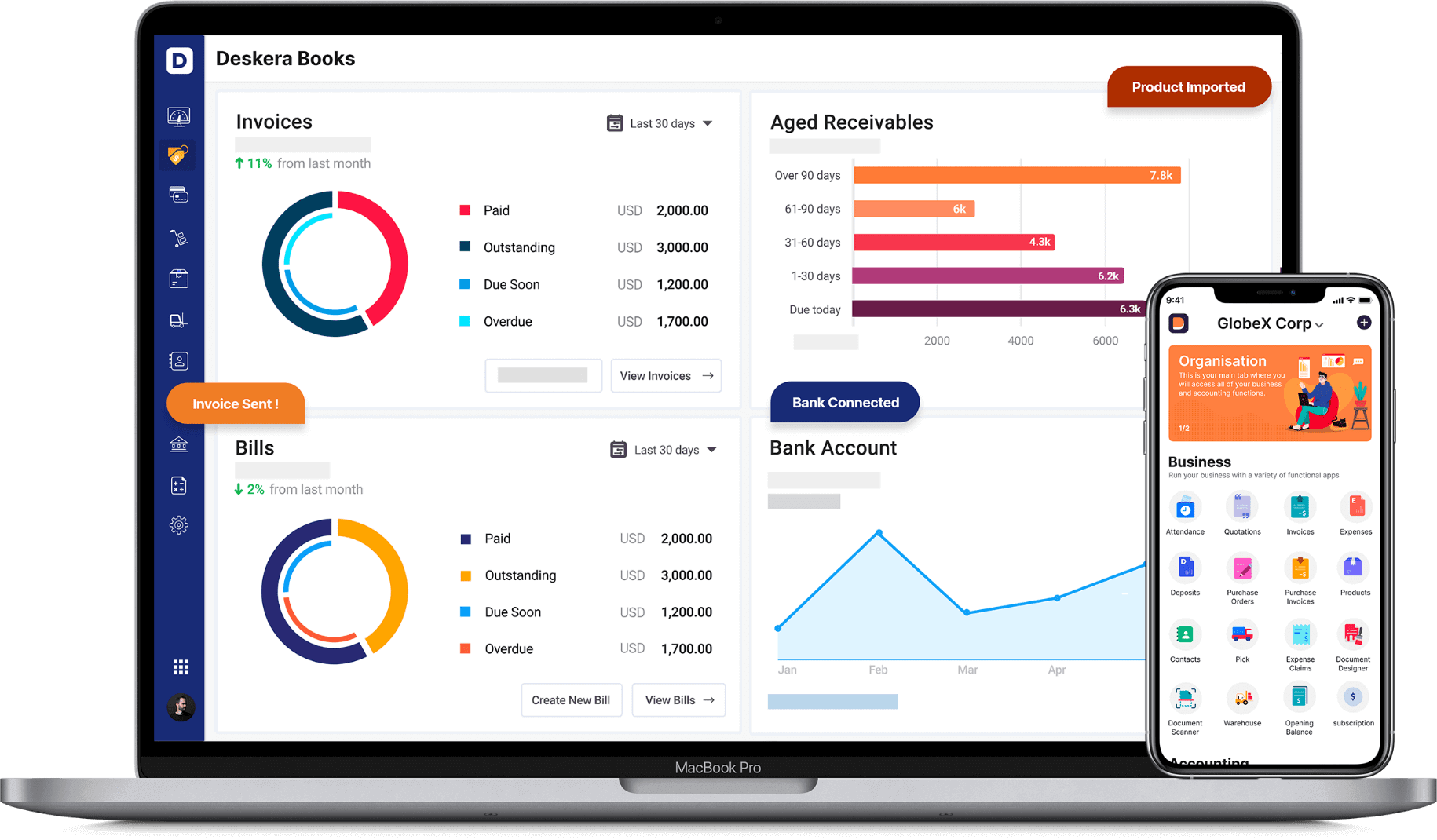
While this all seems a lot to take in, what the businesses can be relieved about is that their accounting is handled by Deskera Books. Be it tracking of financial KPIs, marketing KPIs, journal entries, financial statements, invoices, account receivables and accounts payable, Deskera Books will do it all for them- including making it easier to comply with the taxation regime of the base country.
To learn about how to manage and set up India GST in Deskera, go through this video:
Then test out our tool through the below mentioned clickable link and you will be amazed by how easy accounting has become for you.
With Deskera books, you can easily access your financial reports, create invoices, and get a real-time view of the inventory details.
Key Takeaways
- DRC-03 is a form that is filed by a taxpayer for paying tax under the GST law.
- Audit/Reconciliation Statement, investigation, annual return, Demand or in response to show cause notice, liability mismatch, ITC mismatch are some of the causes for making payments under DRC-03
- The procedure to file DRC-03 involves multiple steps
- There are some frequently asked questions related to DRC-03.
Related Articles