Day offs provide much-needed relief from the hectic workdays. Every company offers a set number of leaves to its employees. Besides the holidays and days off, employees are entitled to a certain number of leaves each year. The Shops and Establishments Act specifies three types of leave: Privilege leave, Sick leave, and Casual leave.
Each state defines its own rules and the number of leaves differs from one state to the other. Thus, the number of leaves an employee receives will vary depending on the state where the establishment is based.
An establishment's leave policy should be in line with the leave provisions of its state's Shops and Establishment Act. Its leave policy has to be equally beneficial to the employees as prescribed by the state’s Shops and Establishments Act.
While the overall structure of providing leaves is the same across the states, there may be minor changes in the leave provision of every state. Keeping a record of the leaves is imperative for every employer and therefore, the employers in AP need to fill out Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of leave.
Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave is a form that all enterprises under the APSE Act must maintain to track the leaves their employees have taken for a given duration.

The primary points described in the article are:
- What is a Leave Register?
- Andhra Pradesh Shops and Establishments Rules (APSE), 1990
- What is the Shops and Establishment Act?
- Objectives of Shops and Establishment Act
- Documents for Registration under the Shops and Establishments Act
- Who Maintains the Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave?
- Particulars of the Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave and Format
- How many leaves is Employee Entitled to as per APSE, 1990?
- Other Holidays
- Important Definitions
- Casual leave
- Sick Leave
- Privilege Leaves
- Maternity Leaves
- Normal Working hours
- Overtime Hours
- Interval
- Rate of Overtime Wages
What is a Leave Register?
A Leave register is a book of records that maintains information pertaining to the leaves and attendance of the employees. The employers maintain and preserve the leave registers with the details and particulars of the leave.
Leave registers are also used to keep records of leave transactions and encashment of leaves in case the leaves are with wages (paid leaves). The purpose of maintaining a leave register is to keep a track of the leaves of all employees for the given year.
Every organization allows its employees a fixed number of leaves and the shops and other commercial establishments in Andhra Pradesh comply with the APSE Act, 1988 and APSE Rules, 1990.
Andhra Pradesh Shops and Establishments Rules (APSE), 1990
The Andhra Pradesh Shops & Establishments Act, 1988 is the basis of the formation of the Andhra Pradesh Shops and Establishments Rules, 1990. The rules in the document are set and fixed by the Governor of Andhra Pradesh and they came into effect on 1st November 1991.
The rules give directions to the shops and establishments that seek registration under the Act. The APSE Act, 1988 and the rules, 1990 must be implemented by all the shops and establishments in Andhra Pradesh. This part of the article helps us understand the outline of the APSE Act, 1988 which lays down the guidelines for the specified fields below.
Let’s take a look:
- Registration of establishments
- Shops
- Establishments other than the shops
- Employment of women, children, and young persons
- Health and safety
- Leave and holidays with wages and insurance scheme for employees
- Wages, conditions for termination of services along with appeals
- Appointment, powers, and duties of the authority
- Appointment, powers, and duties of the chief inspector
- Penalties for offenses
What is the Shops and Establishment Act?
Every state in India has promulgated the Shops and Establishments Act. The Act intends to govern the various elements pertaining to the workers in an establishment. The document includes guidelines for wage payment, working hours, intervals and rest time, holidays, opening and closing hours, overtime work and wages, conditions of the employment. It also gives directions and regulates the various types of leaves: casual leaves, annual leaves, and sick leaves.
Every state has its laws and regulations regarding the Shops and Establishment Act. As the Act falls under the state's legislation, the state government must design the rules. These rules, therefore, vary from state to state with the basic framework remaining the same. Thus, the companies looking to establish themselves and begin their operations must abide by the rules set by the Act in their respective state.
The categories of establishments that come under the Shops and Establishment Act are:
- All shops
- hotels
- restaurants
- theatres and movie halls
- any place of public amusement or
- establishment and other commercial establishments
All such establishments and outlets must register under the Act.
Objectives of Shops and Establishment Act
The Act aims at securing the rights of both employers and employees. The Shop and Establishment Act regulates payment of wages, and other terms of services which include the following:
- wages for holidays
- leave policy
- work conditions
- overtime work
- the interval for meals and rest
- prohibition for employment of children
- employment of young persons or women
- maternity leave and benefits thereof
- opening and closing hours
- closed days
- weekly holiday
- dismissal
- fire safety and precautions
- accidents
- record-keeping, and so on
Who Maintains the Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave?
Maintaining the register of leaves is a statutory requirement. Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave is a form that the employers of all establishments in Andhra Pradesh must fill out with the required details. They must maintain a leave register to keep a record of the leave granted to employees through the year in his establishment.
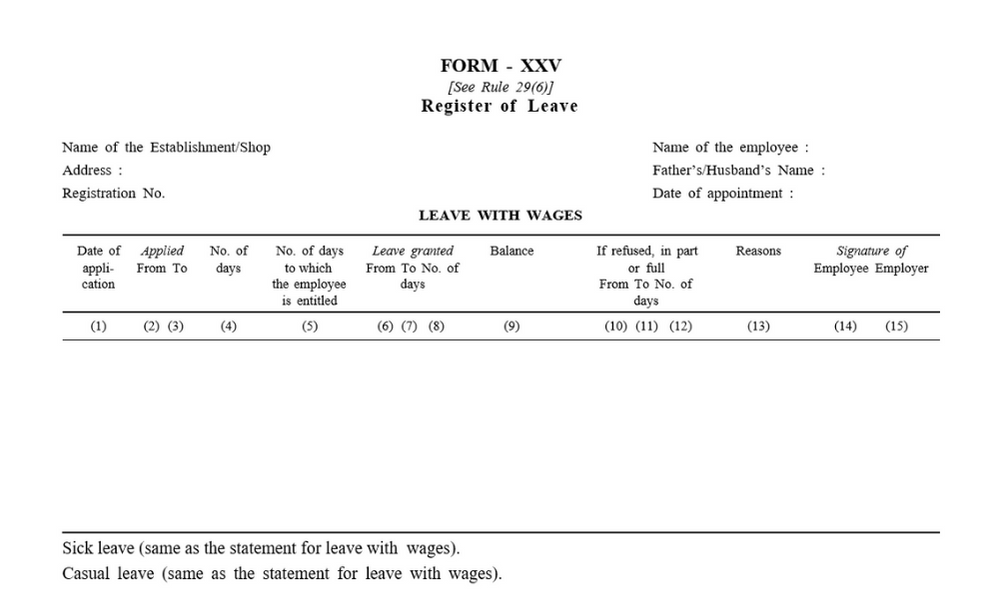
Particulars of the Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave and Format
The format of the Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave needs the employers to fill out the following details:
- Name of the Establishment or Shop
- Address of the establishment
- Registration number
- Name of the employee
- Father’s or Husband’s name
- Date of Appointment
- Date of Application
- Applied From
- Applied to
- Number of days
- Number of days to which the employee is entitled
- Leave granted from
- To
- Number of Days
- Reasons
- Signature of the employee
- Signature of the employer
How many Leaves is Employee Entitled to?
Based on the prescriptions of the AP Shops and Establishment Act, 1988, the employees shall be eligible to avail of leaves in the mentioned scenarios:
- An employee who has served for 240 days in a year shall receive 15 days of leave with wages if such leave with wages has been accumulated up to 60 days:
i) In addition, any continuous period of service before the date on which this Act applies to that establishment shall also be included,
ii) A worker's leave accumulated prior to the date on which this Act becomes effective is unaffected,
iii) Additionally, every employee of any shop or establishment may encash their leave with wages for a period of eight days per year
- The employee must notify the employer in writing about the leave plan at least 7 full working days prior to the date they intend to take the leave, provided a maximum of three installments may be taken in one 12-month period
- An employee whose leave of 5 or more days has been approved can receive their wages in full for the duration of the leave, if they have requested for it
- If an employee who has served for a period of 240 days continuously for 12 months is eligible to receive encashment of 8 days of leave with wages during the subsequent span of 12 months.
i) the employer must pay the amount of the encashed leaves within a week since the date of application of encashment
- During the first twelve months of continuous service and during the next twelve months of service, every employee shall also receive:
i) leave with wages for up to twelve days on account of sickness or injury,
ii) casual leave with wages for a period not exceeding twelve days or for any other reason
- Every employee who has worked for at least 6 months for the same employer will also be entitled to a special casual leave of no more than six days, following the completion of a vasectomy or tubectomy operation, provided they produce a certificate from the doctor who performed the operation
- If an employee entitled to leave under subsection(1) is discharged by his employer before he has been granted the leave, or if the employer refuses the leave, or if he quits before the leave has been granted, his employer must make him a payment for the leave under this Act
- When a sick or injured employee is allowed a discharge by his employer, the employer must pay him the amount payable under this Act for the period of leave he was entitled to upon discharge together with the amount, if any, payable to him under subsection (3)
- An employee of a hostel of a school or college or of an establishment that is maintained to provide accommodation for pupils may enjoy the privileges referred to in sub-sections (1) to (8). However, there will be a reduction proportional to the period for which he had served continuously in the previous year, or his period of continuous employment in the current year, and applying all the references to the leave periods in sub-sections (1) and (5)
Other Holidays
Apart from the leaves and leave conditions discussed in the previous section, we shall also learn about the other holidays the employees receive. Here they are:
- All employees are entitled to 9 holidays in a year, the notifications of which will be displayed in advance by the Government of India
- These include 26th January - Republic Day
- 1st May - May Day
- 15th August - Independence Day
- 2nd October - Gandhi Jayanti
- 1st November - Andhra Pradesh Formation Day
- Besides, these dates, a Chief Inspector may notify other days as holidays with wages to employees after assessing an emergency situation prevailing in the state
- However, employees working at restaurants, theatres, or any such place of public entertainment may have to work on specific holidays declared under sub-section 1 and 2, on the condition that they will be allotted compensatory leaves
- Such compensatory leaves must not exceed 7 in a year;
- Also, if an employee works on a compensatory holiday will receive additional wages from the employer
- Subsection 1 will not be applicable in a case where the employer provides more holidays than the holidays notified by the government. Such employer must share the list of allowed holidays with wages which include 5 holidays mentioned in subsection 1 with the Inspector and Chief Inspector
- Wages during holidays and leaves: All employees shall receive the same rate of the daily average wages for the days they worked in the previous month excluding any earning for overtime work. This point is applicable for the leaves allowed under subsections 1 and 5 of Section 30 or Section 31
- Provision for extending the period of leave allowed under Section 30: Irrespective of the points mentioned in Section 30, the government may notify an increment in the number of leaves allowed under subsection 1. It may also inform a change in the maximum number of days that may be accumulated under that sub-section
Important Definitions
Here are some more important definitions within the scope of the Shops and Establishments Act, 1988.
Casual Leave
Casual leaves are when an employee remains absent from work due to unforeseen events or personal emergencies. They could be absent for a day or two, however, the number of casual leaves vary from state to state. For Andhra Pradesh, the employees are entitled to receive up to 12 casual leaves during their first year (duration of 12 months) and continued service.
Casual leaves are meant for absence for short durations only. In circumstances where the employee requires an extended period of casual leaves, they must request permission from the employer. In general, casual leaves cannot be encashed and cannot be carried forward.
Sick Leave
The employees can apply for sick leave when they are unwell or due to sickness. Like casual leaves, the number of sick leaves allowed varies from one state to another. For Andhra Pradhesh the permitted sick leaves are allowed up to 12 in their first year (duration of 12 months) and continued service. Employees can carry the sick leaves forward to the next year in some states. However, APSE Rules do not allow carrying forward sick leaves.
Privilege Leave or Earned Leave
An employee gets an additional number of leaves with wages for a certain number of days that is prescribed under the Shops and Establishments Act. After 240 days of continuous service, an employee can avail of 15 privileges or earned leaves in Andhra Pradesh.
Establishments may differ from each other in the context of the number of privilege leaves they offer. Also, in Andhra Pradesh, the maximum number of privilege leaves that can be carried forward is 60.
Maternity Leave
The women employees can benefit from the prescribed rules for maternity leaves under Section 25. This type of leave will be treated as an authorized absence from duty and the employee will also receive all the maternity benefits. However, they shall not be receiving any wages for the duration of their absence.
Normal Working Hours
Normal Working hours is the number of hours the employees usually spend at the workplace. Under APSE, the normal working hours are 8 hours a day and 48 hours per week.
Overtime Hours
The number of hours an employee works apart and beyond the normal working hours is called the overtime hours. The prescribed overtime hours under APSE is 6 hours a week.
Interval
Interval is the time that acts as a break or rest time for the workers. The employees get at least 1 hour of interval for rest after a duration of 5 hours at work, as prescribed by the APSE.
Rate of Overtime Wages
The rate of wages paid for the overtime work done by an employee is called the rate of overtime wages. Under the APSE, the employees receive twice the ordinary rate of wages.
How can Deskera Help You?
As a business, you must be diligent with employee leave management. Deskera People allows you to conveniently manage leave, attendance, payroll, and other expenses. Generating pay slips for your employees is now easy as the platform also digitizes and automates HR processes.
Key Takeaways
The final takeaways from the post are:
- The Shops and Establishments Act specifies three types of leave: Privilege leave, Sick leave, and Casual leave
- An establishment's leave policy should be in line with the leave provisions of its state's Shops and Establishment Act
- Andhra Pradesh Form XXV Register of Leave is one register that all enterprises under the APSE Act must maintain
- A Leave register is a book of records that maintains information pertaining to the leaves and attendance of the employees
- The Andhra Pradesh Shops & Establishments Act, 1988 is the basis of the formation of the Andhra Pradesh Shops and Establishments Rules, 1990
- The rules give directions to the shops and establishments that seek registration under the Act. The APSE Act, 1988 and the rules, 1990 must be implemented by all the shops and establishments in Andhra Pradesh
- The Act aims at securing the rights of both employers and employees. The Shop and Establishment Act generally regulates payment of wages, and other terms of services
- Every employer must maintain a leave register - Register in Form XXV to keep a record of the leave granted to employees in his establishment
- An employee who has served for 240 days in a year shall receive 15 days of leave with wages if such leave with wages has been accumulated up to 60 days
- The employee must notify the employer in writing about the leave plan at least 7 full working days prior to the date they intend to take the leave, provided a maximum of three installments may be taken in one 12-month period
- An employee whose leave of 5 or more days has been approved can receive their wages in full for the duration of the leave, if they have requested for it
- All employees are entitled to 9 holidays in a year, the notifications of which will be displayed in advance by the Government of India
- All employees shall receive the same rate of the daily average wages for the days they worked in the previous month excluding any earnings for overtime work
- Casual leaves are when an employee remains absent from work due to unforeseen events or personal emergencies
- For Andhra Pradesh, the employees are entitled to receive up to 12 casual leaves during their first year (duration of 12 months) and continued service
- The employees can apply for sick leave when they are unwell or due to sickness
- For Andhra Pradhesh the permitted sick leaves are allowed up to 12 in their first year (duration of 12 months) and continued service
- After 240 days of continuous service, an employee can avail of 15 privileges or earned leaves in Andhra Pradesh
- The women employees can benefit from the prescribed rules for maternity leaves under Section 25
- The prescribed Overtime hours under APSE is 6 hours a week
- Under the APSE Act, the employees receive twice the ordinary rate of wages
Related Articles














