A tax collection system where the tax liability by the recipient is paid in part of the goods/service at the time of making payment to the supplier is known as Tax Deduction at Source or TDS.
TDS ensures that the GST amount is shared by both the supplier and recipient for certain transactions. Hence, TDS provides regular cash flow to the Government, introduces checks and balances, prevents tax evasion, and increases the tax base. Similar to TDS under Income Tax Act, GST also has provisions for TDS.
GST TDS Applicability in India
While making GST payments under GST, regular taxpayers are not required to deduct TDS. Only the following taxpayers are allowed to comply with GST TDS provisions:

As per the latest notice, dated 13th Sept 2018, the below entitles will also need to deduct TDS:
- A board or authority /any other body set up by Parliament/ State Legislature/by Government, with 51% equity owned by the Government.
- Under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, a society established by any state or central Government or a local authority registered.
- Public sector undertakings.
Who are Deductor and Deductee?

GST TDS Rate
From the payment made to the supplier of taxable products/services, TDS is expected to be deducted at 2% if the supply value exceeds Rs.2.5 Lakhs under the contract. From 1st Oct 2018, the terms of TDS on GST shall apply. The following shall be excluded to determine the value of the contract.
- GST Central
- GST Integrated
- GST Union Territory
- Cess
- GST State
Under GST, the TDS rate is 2%, which means the deductor has to deduct TDS at 2% on the payment made/credited to the deductee for the taxable goods or services or both.
Under GST, cases when TDS is deducted
Threshold Limit for Deduction of TDS Under GST
If the supply value under a contract exceeds Rs.2,50,000, the TDS under GST has to be deducted. The TDS value of deduction will be considered, excluding the SGST, CGST, UTGST, IGST, and Cess under GST.
Hence, the TDS is deductable when only a contract/single purchase order exceeds Rs.2,50,000/-. In simple words, no TDS will be attracted of the value for the supply of goods and services or both, under the contract is up to Rs.2,50,000/-. Below is the explanation with an example,

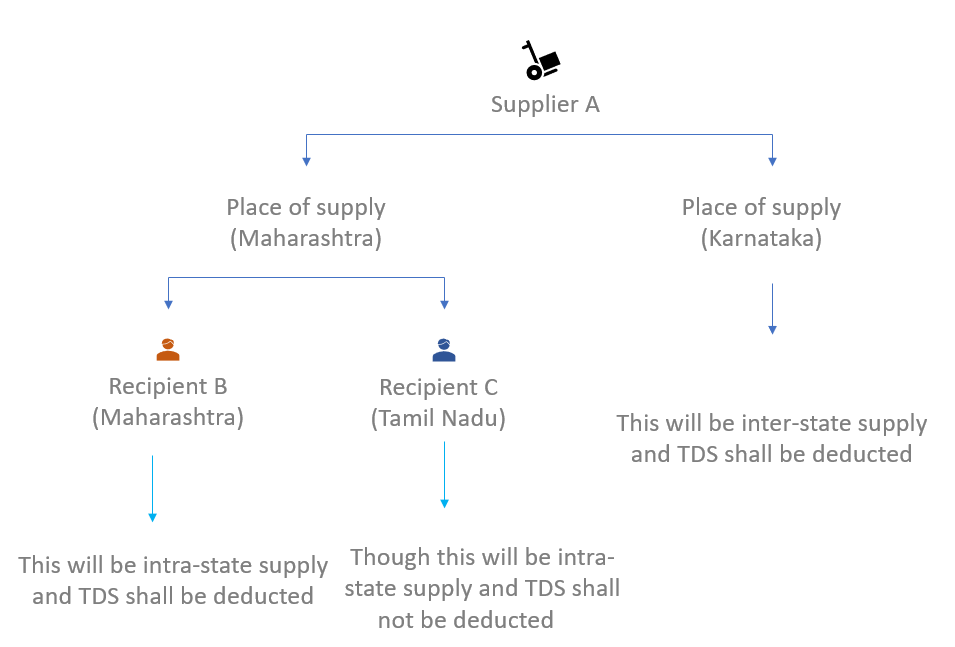
When Deduction for TDS Under GST Is Required to be Made
In the following 2 cases, the TDS is required to be deducted,
- Intra State Supply - Supplier, Recipient & Place of Supply are in the same state: This would be considered as a case of Intra-state supply CGST & SGST would be levied and TDS would be deducted.
- Inter-State Supply - Supplier, Recipient & Place of Supply are in different states: In such cases, IGST would be levied as this is a case of Inter-state supply.
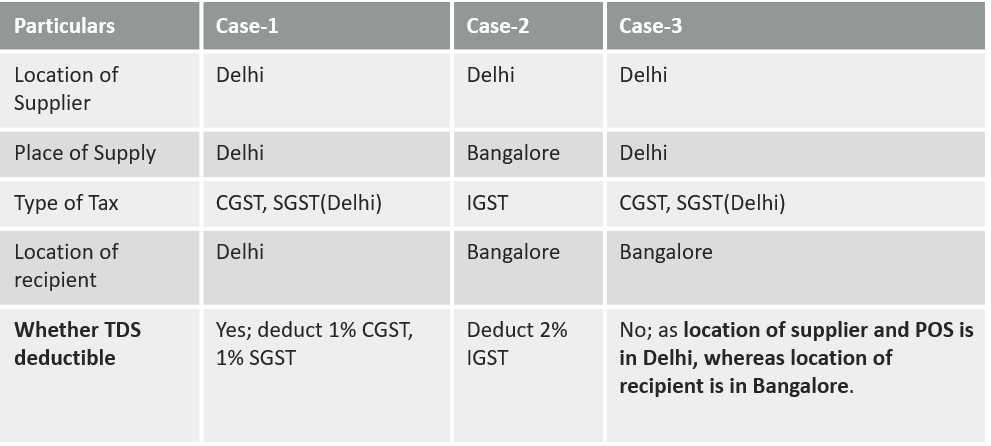
When TDS under GST Need Not Be Deducted
If the supplier's location and the place of supply are in a State/UT, which is different from the State/ UT of registration of the recipient [Proviso to section 51(1)], no TDS deduction needs to be made.
Value of supply for Deduction of TDS
For deduction of TDS base value, the supply value, i.e., Taxable Value, will be considered for TDS deduction. If the advance is paid to the supplier, incase of a transaction covered under GST TDS, it is required to be deducted on amount paid, i.e. grossing up of advance paid.
The value of supply needs to be taken as the amount excluding the tax indicated on the invoice. Thus, TDS need not to be deducted on the CGST, SGST, or IGST invoice component.
For example,
- Supplier A, supplies worth Rs.5,000 to B.
- The GST Rate is 18%.
- When B pays to A, he/she will pay Rs.5,000 (worth of Supply) + Rs.900 (GST) to A and Rs. 100 (RS. 5000*2%) as TDS to the government.
- So it can be said that TDS is not deducted on the tax element (GST) of a transaction.
Procedure for Getting Registered as Deductor
The registration application can be electronically filed for tax Deductor by just submitting a signed application in GST REG-07. In the registration application, in place of PAN, such persons will need to present their TAN. Getting a TAN issued under the income tax act is mandatory.
Following are the documents required while getting registered as Tax Deductor:
- Applicant's valid TAN.
- Applicant valid mobile number.
- Applicant valid E-mail ID.
- As required for registration, the applicant must have the prescribed documents and information on all mandatory fields.
- The place of business of the applicant must be there.
- With the valid details, there must be an authorized signatory of the applicant.
After this, the applicant's registration application will be processed further and approved by the tax officer. Then he will be issued with the registration certificate containing the number.
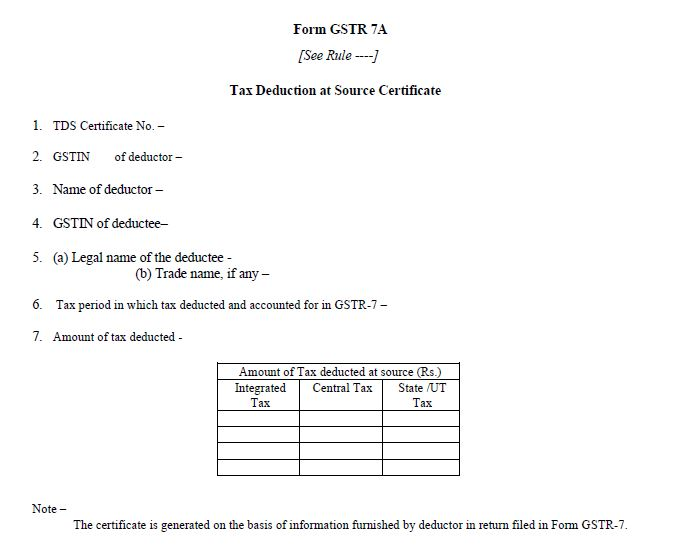
TDS Certificate to the Deductee
To all deductee's, every taxpayer is also required to issue a TDS Certificate in Form GSTR-7A, with the following details:
- the contract value,
- the deduction rate,
- the amount deducted,
- amount paid to the Government and
- such particulars as may be prescribed on this behalf
The TDS certificate needs to be issued within 5 days from the date of remittance of TDS to the Government. Failure to issue the certificate, a late fee of Rs.100 per day needs to be paid and a maximum of Rs.5000.
Certificate of TDS Format under GST
Return Filing in Respect of TDS Deducted Under GST
- The Deductor will pay the amount deducted as a tax within 10 days after the end of the month to the Government.
- GSTR 7 is the return notified by the Government for this purpose. In this return, the Total Taxable Amount, GSTN of the supplier, Amount of TDS deducted is required to be furnished. This return needs to be filed by the 10th of next month.
- If the Deductor deducts no TDS, then GSTR-7 for that month is not required to be filed. However, if any amendment in earlier deductions reflecting in the amendment tab, GSTR-7 is required to be filed.
Refund of TDS Under GST
To the Government, if any excess amount is deducted and paid, a refund needs to be claimed, as this is not the amount the Government has right on. But, if the amount deducted is already added to the electronic cash ledger of the supplier, then this added amount will not be refunded back by the Deductor. Therefore, subject to refund provisions of the act, Deductee can claim a refund of tax.
Refer the below article, to know how to apply TDS in Deskera Books?https://www.deskera.com/care/india-gst-how-to-apply-tds-in-deskera-books/
Refer to the video tutorial for, Managing TDS for India Compliance in Deskera Books
https://youtu.be/5hJhDcPjljU
Conclusion
In this article, we have understood the meaning of TDS, conditions for the application of TDS, computation of TDS, TDS Return filing, time to deposit TDS. Hope this article clears all the doubt about the TDS application under GST.
Related Articles:
- How to Register for India GST?
- How to Register for GST on the GST India Portal. A Step by Step Guide
- Complete guide to E-way Bills in India GST
- GST Calculator – Online Goods and Services Tax Calculator
- What is GSTIN?
- What is GSTN?
- Step-by-Step Guide for India GSTR Filing
- Understanding HSN Codes & SAC Codes Under India GST
- All about GST Compensation Cess
- What Is Input Credit (ITC) under GST ?
- Understanding Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) in India GST
- Special Economic Zone (SEZ) under GST
- What is TDS on Salary
- Making TDS Payments Online in India - The Complete Guide








