A recent survey of manufacturing professionals produced interesting insights. The survey found that over 60% of respondents used a combination of both push and pull systems in their operations.
The push-pull system of manufacturing management is a powerful strategy. It proves excellent for improving the efficiency and accuracy of the production process. The system is based on the principles of Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing. It is a production system that delivers raw materials and components close to production time.
The push-pull system balances the production process. This is done by providing the right amount of materials and components to the right place at the right time. It ensures that materials are available when needed and used efficiently.
With ERP.AI, manufacturers can further enhance push-pull systems by using AI-driven demand forecasting, real-time inventory visibility, and production analytics, enabling faster, data-backed decisions and minimizing delays or overstock.
The push-pull system allows manufacturers to maximize their resources and optimize production. It also allows for more accurate forecasting and planning of production runs. This eventually helps to reduce waste and improve quality.
Additionally, the push-pull system can be used to coordinate multiple product lines. This allows for better coordination and integration of activities. The push-pull system is an effective method for improving the efficiency and accuracy of the production process.
In this post, we shall provide more details about the push and pull manufacturing:
What is a Push System?
A push system in manufacturing indicates that a corporation creates things based on a demand projection. This is also known as make-to-stock manufacturing. It is commonly used to produce commodities with a low likelihood of unanticipated demand changes. This is commonly seen in the food sector, pharmaceuticals sector, and so on.
Therefore, based on historical data, a push system begins production to anticipate future demand. Goods are "pushed" through the supply chain in this approach. It considers demand forecasts that initiate manufacturing. Simultaneously, it oversees the delivery of finished goods to distributors or retailers. These retailers will then sell the products and wait for customers to make the purchase.
We can summarize the mechanism through the following points:
- Push systems involve the production of items in response to actual customer demand.
- The production process is not planned in advance.
- Rather, production is triggered by the actual receipt of customer orders.
- This method of production requires a high degree of flexibility. It rapidly switches production between different items.
What is a Pull System?
The pull system is a lean manufacturing technique. This method produces goods based on actual demand rather than expectations. Companies in this type of operation only store as much inventory. They create only as much as is required to respond to existing customer orders.
In a pull system, commodities are thus "pulled" through the supply chain. This is done after a client order initiates a series of events in which the required amount of products are manufactured. After that, the raw materials utilized in their manufacture are replenished.
Just-in-time manufacturing is an excellent example of a pull system. The primary concept of JIT is to schedule the process so that materials arrive at the facility precisely when production is scheduled to begin. The production is scheduled for completion exactly when the goods should be shipped to the customer.
Summarizing the pull system through the following points:
- A pull system is a production strategy in which materials and products are pulled through the production line
- The products are then supplied to the customer as they are needed.
- This is done instead of being pushed through the production line in larger batches.
- This system is also known as a just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing system.
- The goal of a pull system is to minimize waste and increase efficiency.
Push System Examples
Let’s look at some examples of the push system:
- Food Business: Push manufacturing systems are commonly used in the food and restaurant sector. The businesses understand that the customers would not wait for too long. They must create a surplus inventory, which is food in this case. This way, they can ensure customer satisfaction.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Push manufacturing helps the pharma sector by providing the necessary inventory to meet customer demand. Medicines and medical supplies need to be in additional quantity. The demand must be met adequately. Therefore, the push system is an ideal system for pharma manufacturing.

Pull System Examples
Let’s look at some examples of the pull system:
- Kanban: Kanban is a pull system in manufacturing that uses visual signals to indicate the need for materials or components. This system uses cards, bins, or other visual signals to indicate when something needs to be replenished.
- Just-in-Time (JIT): JIT is a pull system in manufacturing that involves producing only what is needed when it is needed. It is a production system designed to reduce inventory and increase efficiency.
- Production Leveling: Production leveling is a pull system that involves balancing the production of multiple products. This way it ensures that all products are produced at the same rate. This system is designed to reduce inventory and improve efficiency.
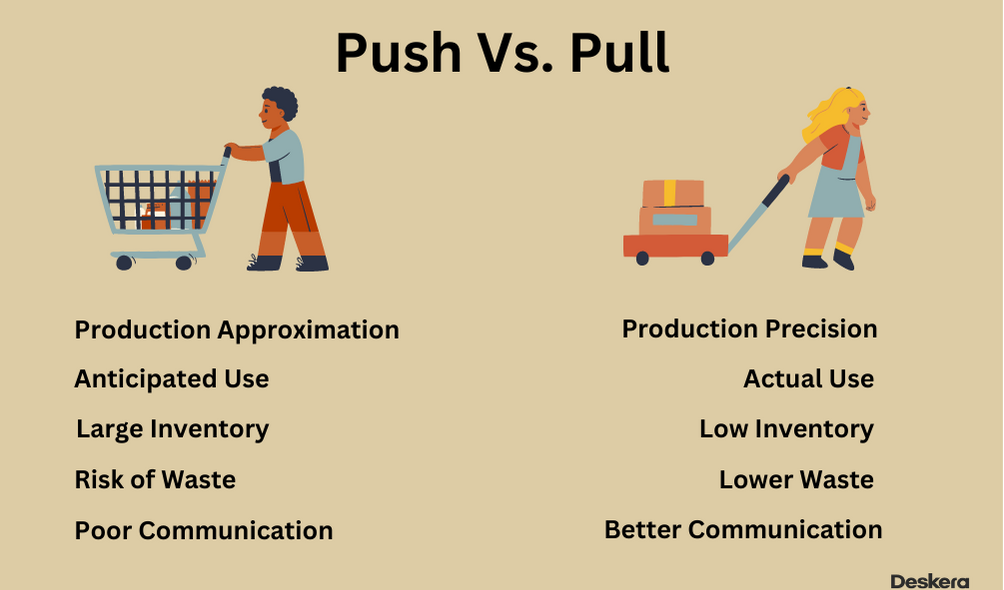
Push System vs. Pull System
A push system is a type of inventory control system in which businesses predict consumer demand. Then they push products to distributors and retailers in anticipation of consumer purchases.
In contrast, a pull system is an inventory control system in which businesses respond to consumer demand. They pull products from suppliers only when consumer demand is detected. The main difference between a push system and a pull system is the way in which inventory is managed.
The following table sums up the primary differences between push and pull systems:
A push system requires businesses to accurately predict consumer demand. On the other hand, a pull system requires businesses to respond to consumer demand as it arises.
In a push system, businesses stock up on inventory in anticipation of consumer demand. This can lead to excess inventory and wasted resources. Conversely, businesses only stock up on inventory in a pull system when consumer demand is detected. This can lead to shortages if demand is higher than expected.
Overall, businesses must carefully consider their inventory control strategy. They must also determine whether a push or pull system is more appropriate for their organization.
Let’s also analyze the areas that must be considered before opting for a push, pull, or hybrid system:
- WIP Inventory
- Consider Inventory Costs
- Product Availability
- Effect on Businesses that offer product customizations
We shall understand these aspects in depth in the oncoming sections.
Consider WIP Inventory
One of the key differences between push and pull systems is the amount of WIP inventory allowed. There are no signals returning to the manufacturing floor in a push system. Therefore, there is no clear limit on WIP inventory. However, the system regulates the quantity of WIP in a pull system.
For a pull system, the WIP limit is reached when no products can be sold or consumed. This is to say that there is no signal to trigger another replenishment. That means at least one unit of product in WIP must be finished and sold before another replenishment signal may be issued.
Consider Inventory Costs
The push method relies on projections to determine production volume. Also, forecasts may not be accurate all the time. Thus, unsold items may take up inventory management resources and storage space.
So, in this case, the unsold goods may become obsolete. Inventory expenses would be more than necessary in this case.
Now, in a pull system, the manufacturer only produces what the clients have bought. Therefore, inventory is kept to a bare minimum at all times. The finished goods are supplied to clients on time. The raw material inventories are replaced as needed.
Hence, the WIP is kept to a minimum. However, reduced inventory implies less space and labor wasted on keeping and managing the items. This lowers inventory costs.
Product Availability
A push system aims at providing a service level that ensures product availability. While a pull system responds to consumer orders, a push system anticipates them. It ensures that customers receive the needed quantity of merchandise at the earliest.
This becomes crucial in market segments where lead times influence client decision-making processes.
So, companies must consider the importance of product availability for their business.
Product Customization
Product customization in push-pull is the process of adapting a product to a customer's specific needs. This involves designing a product to meet requirements such as size, shape, color, and other specifications. The customization process includes a combination of design and manufacturing processes. This way, it creates a unique product that meets the customer’s requirements.
Companies offering customization must incorporate characteristics from a pull system into their manufacturing. Otherwise, companies would have to build several distinct types into stock. This will complicate their manufacturing processes and increase their inventory. Eventually, it will imply more expenses for the business.
Therefore, manufacturers of customizable goods can keep their inventory to a minimum with a pull system. A hybrid version of the two systems can be successfully applied in the situation of mass customization. The hybrid version is also known as the push-pull system.
How does Product Customization affect Manufacturers?
Product customization can have a major impact on push-pull manufacturers. It allows manufacturers to respond quickly to customer demands. They can then customize their product offerings to meet those needs. It also increases the efficiency of production. The manufacturers can now produce goods tailored to the customer's specific requirements. Product customization can also increase customer loyalty and satisfaction. Customers feel like their needs are being met on an individual basis.
Finally, product customization can lead to increased sales and profits for manufacturers. Customers are more likely to purchase customized products for increased value and satisfaction.
Push-Pull System
Hybrid push-pull manufacturing is a system where components are pushed down the production line based on a predetermined schedule. However, when the demand for a product increases, the production system can switch to a pull system which is based on customer orders or demand.
In a pull system, components are only produced when needed. Thus, allowing the production system to quickly and efficiently respond to changes in customer demand.
Push and pull systems can complement each other, delivering benefits from both. Manufacturers utilize demand forecasting to calculate the number of items used as base inventory in this situation. However, client orders drive further production.
Benefits of Using a Hybrid Push-Pull System
Let’s go through the benefits of using a hybrid Push-Pull System:
- Increased Efficiency: A hybrid push-pull system allows for greater efficiency as it takes advantage of both push and pull strategies. This means that the system can be used to better manage inventory levels. It also manages production and delivery operations.
- Better Customer Service: Customers can benefit from faster response times by utilizing a hybrid push-pull system. They can also avail increased stock availability. This allows for a better customer experience and greater customer satisfaction.
- Reduced Costs: A hybrid push-pull system can help to reduce costs associated with storage, transportation, and inventory management. By reducing costs, businesses can increase their margins and profits.
- Improved Supply Chain Management: A hybrid push-pull system can help to improve supply chain management. It does so by allowing for better forecasting, planning, and coordination. This can help to reduce lead times and improve stock availability.
- Increased Visibility: A hybrid push-pull system can provide increased visibility into the supply chain and enable better decision-making. This can help businesses to improve their operations and increase efficiency.
Push, Pull, and MRP
MRP is strongly related to push-pull manufacturing. This is because it helps to plan when a product should be released into the market or "pushed" into the supply chain. MRP can also help determine when components or raw materials should be "pulled" from the supply chain as demand for a product increases. MRP also helps coordinate the production and delivery timing of a product.
The classic material requirements planning is also called MRP I. It can be thought of as a push system that follows a master production schedule based on projections. Today's manufacturing resource planning system is called MRP II. It can also be thought of as a complement to pull systems.
Modern MRP systems may monitor material availability. They may also schedule both production and purchases as soon as a client order is received. This is because the data integration ability of modern cloud-based software systems establishes the foundation for real-time administration of all elements of the organization.
The system tracks stock item consumption, production activity, and work-in-progress inventories. The visual indications of a Kanban system are thus simply converted into digital signals. Thus, the software controls the flow of information.
Push, Pull, and ERP
Similarly, an ERP system can assist companies in manufacturing. With the various modules integrated into the system, manufacturing can be simpler.
- Supply chain management
- Inventory management
- Finance and accounts
- Customer relationship management module
These are some of the beneficial modules that businesses can utilize to enhance production. They can have clear visibility into the production process. Real-time insights shared through the common database can be advantageous, too.
To sum up, the modern ERP and MRP systems work well as business management tools in both push and pull systems. They are also greatly effective for hybrid push-pull systems.
How AI Improves Manufacturing Systems
From automating routine tasks to enabling predictive analytics, AI enhances every stage of the production cycle. It analyzes real-time data to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and reduce machine downtime through predictive maintenance. This leads to smoother operations and fewer disruptions.
AI plays a key role in this transformation by integrating AI with manufacturing workflows—allowing businesses to gain deep insights into their supply chain, automate production planning, and fine-tune resource allocation.
How can Deskera Help You?
Deskera can help manufacturers manage their push and pull systems in a number of ways. For example, Deskera’s supply chain management software lets manufacturers track material demand, production activities, and inventory levels in real-time.
This allows them to quickly determine which parts are needed and when allowing them to create a more efficient push-and-pull system.
Finally, Deskera’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) software allows manufacturers to manage their resources and processes effectively. Thus, providing an efficient way to manage the push and pull system.
Here are some ways Deskera ERP and MRP can assist you:
- Plan production schedules
- Create elaborate details
- Manage BoM or Bill of Materials
- Create a customized dashboard
Deskera ERP is a comprehensive solution for optimizing a wide range of organizational activities and monitoring supply chain operations in real-time.
Deskera Books can help you manage your finances. It is a simple cloud-based accounting and bookkeeping software that assists small businesses in managing their money. It is intended to assist small businesses in automating their bookkeeping and tracking expenses and income. You can also generate financial reports, process payroll, manage inventory, and do other things.
Deskera CRM is a sophisticated tool that may help you manage your sales and close contracts more quickly. It enables you to do critical tasks such as email lead generation and provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a cloud-based human resource management application to assist small firms in streamlining their HR operations. It includes features like staff onboarding as well as time and attendance management. Also included are leave management, payroll processing, and performance evaluations. This allows small firms to automate their HR activities and focus on other aspects of their business.
Key Takeaways
- The push-pull system of manufacturing management is a powerful strategy. It proves excellent for improving the efficiency and accuracy of the production process.
- Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of push vs. pull production is critical. It helps to comprehend the complexities of your supply chain structure and ideal stock. You can also gauge efficiencies and potential waste.
- A push-based supply chain, in theory, is based on expected and projected demand. Whereas a pull-based supply chain only produces things that are equivalent to demand. However, this explanation carries the risk of being overly simplistic. This is because the two systems are more complex when implemented in practice.
- With the right implementation of the push and pull system, companies can improve their operations. They can lower costs and create a more effective manufacturing environment.
- The push-pull system balances the production process. This is done by providing the right amount of materials and components to the right place at the right time.
- The push-pull system allows manufacturers to maximize their resources and optimize production.
- It also allows for more accurate forecasting and planning of production runs. This eventually helps to reduce waste and improve quality.
- Additionally, the push-pull system can be used to coordinate multiple product lines. This allows for better coordination and integration of activities.
- A push system in manufacturing indicates that a corporation creates things based on a demand projection. This is also known as make-to-stock manufacturing.
- The pull system is a lean manufacturing technique. This method produces goods based on actual demand rather than expectations.
- Companies in pull operation only store as much inventory. They create only as much as is required to respond to existing customer orders.
- MRP can also help determine when components or raw materials should be "pulled" from the supply chain as demand for a product increases. MRP also helps coordinate the production and delivery timing of a product.
- Similarly, an ERP system can assist companies in manufacturing. With the various modules integrated into the system, manufacturing can be simpler.
- Supply chain management and inventory management are important modules ERP offers.
- Finance and CRM module take care of other important aspects of the business.
Related Articles












