Businesses today are constantly looking for ways to improve efficiency and reduce costs. One of the most important areas where manufacturers can save time and money is in the procurement process.
The procurement process is the set of activities involved in acquiring goods and services from suppliers. It can be a complex and time-consuming process, involving many different steps, such as creating purchase orders, requesting quotes, and approving orders.
Manual procurement processes are prone to errors and inefficiencies. They can also be slow and time-consuming, which can lead to delays in production.
Procurement automation is the use of technology to streamline and automate the procurement process. By automating tasks such as creating purchase orders, requesting quotes, and approving orders, procurement automation can save manufacturers time, money, and errors.
According to a study by Aberdeen Research, companies that have implemented procurement automation have seen a 25% reduction in procurement costs and a 15% reduction in procurement cycle time.
Here are some other interesting stats about procurement automation:
- 78% of manufacturers believe that procurement automation is essential for improving efficiency.
- 62% of manufacturers have implemented some form of procurement automation.
- The average return on investment (ROI) for procurement automation is 220%.
- The most common tasks that are automated in procurement are purchase order creation, supplier selection, and invoice processing.

Procurement automation is a powerful tool that can help manufacturers improve efficiency and reduce costs. If you are looking to improve your manufacturing operations, procurement automation is a great place to start.
- Definition of Procurement and Purchase Orders
- The Importance of Procurement Efficiency In Manufacturing
- The Challenges of Manual Procurement Processes
- Benefits of Procurement Automation
- Types of Procurement Automation Solutions
- How to Implement Procurement Automation
- Impact of Procurement Automation on the Bottom Line
- Impact of Procurement Automation on the Bottom Line
- Future of Procurement Automation
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
- Related Articles
Definition of Procurement and Purchase Orders
Procurement refers to the process of acquiring goods, services, or works from external sources for an organization's needs. It involves various activities such as sourcing suppliers, negotiating contracts, selecting vendors, and managing the overall supply chain to ensure that the organization receives the necessary resources at the right time, in the right quantity, and at the right cost.
Effective procurement aims to optimize the balance between quality, cost, and delivery, while also considering factors such as supplier relationships, risk management, and sustainability.
Purchase Order (PO): A Purchase Order (PO) is a legally binding document issued by a buyer to a supplier indicating the details of a transaction for goods or services. It serves as an official request to the supplier to provide the specified products or services at agreed-upon terms, such as quantity, price, delivery date, and payment terms. A purchase order typically includes:
- PO Number: A unique identifier for tracking and reference purposes.
- Supplier Information: Name, address, contact details of the supplier.
- Buyer Information: Name, address, contact details of the buyer.
- Item Details: Description, quantity, unit price, and total price of each item.
- Delivery Date: The date by which the goods or services are expected to be delivered.
- Payment Terms: Details about how and when the payment will be made to the supplier.
- Shipping and Billing Addresses: Addresses where the goods will be delivered and where the invoice should be sent.
- Terms and Conditions: Any additional terms, conditions, or instructions related to the purchase.
Once a supplier receives a purchase order, they acknowledge it and initiate the process of fulfilling the order. A purchase order acts as a contract between the buyer and the supplier, protecting both parties' interests by establishing clear expectations and obligations. It also helps prevent disputes and ensures proper record-keeping of transactions.
The Importance of Procurement Efficiency In Manufacturing
Procurement efficiency plays a crucial role in the manufacturing industry for several reasons:
Cost Savings: Efficient procurement helps manufacturers secure the best prices for raw materials, components, and services. By negotiating favorable terms and sourcing from reliable suppliers, manufacturers can reduce their procurement costs, which directly impacts their overall production costs and competitiveness in the market.
Supply Chain Stability: Timely and reliable procurement ensures a steady flow of materials and components needed for production. This stability minimizes production disruptions due to shortages, enabling manufacturers to meet customer demands and maintain consistent product quality.
Inventory Management: Efficient procurement allows manufacturers to maintain optimal inventory levels. Excess inventory ties up capital and storage space, while insufficient inventory can lead to production delays. By procuring the right quantities at the right time, manufacturers can balance their inventory needs effectively.
Quality Assurance: Proper procurement processes include supplier evaluation and quality checks. By sourcing from reputable suppliers, manufacturers can ensure the consistent quality of materials and components, reducing the risk of defects and production issues.
Innovation and Product Development: Efficient procurement enables manufacturers to access new technologies and materials that can enhance their products or streamline their processes. Collaborating closely with innovative suppliers can lead to product improvements and differentiation in the market.
Lead Time Reduction: Effective procurement strategies can lead to shorter lead times for raw materials and components. This agility is crucial for responding quickly to changes in market demand or unexpected disruptions.
Risk Management: Diversification of suppliers and proactive risk assessment are key components of efficient procurement. This helps manufacturers mitigate the impact of supply chain disruptions, such as geopolitical issues, natural disasters, or supplier bankruptcies.
Compliance and Sustainability: Procurement efficiency involves considering factors beyond cost, such as ethical sourcing and environmental sustainability. Manufacturers that prioritize these aspects can improve their reputation, meet regulatory requirements, and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Resource Optimization: Efficient procurement involves optimizing the use of resources, including time and labor, by automating processes, using technology, and streamlining workflows. This results in reduced administrative burden and increased operational efficiency.
Financial Planning and Forecasting: Accurate procurement processes provide manufacturers with a clear understanding of their expenses, helping them plan budgets, allocate resources, and forecast future production needs more effectively.
In summary, procurement efficiency in manufacturing has a cascading effect on various aspects of the business, from cost control and production stability to innovation and sustainability. Manufacturers that prioritize efficient procurement practices are better positioned to remain competitive, adapt to market changes, and deliver high-quality products to their customers.
The Challenges of Manual Procurement Processes
Manual procurement processes can introduce several challenges for organizations, leading to inefficiencies, errors, and increased operational costs. Some of the common challenges associated with manual procurement processes include:
- Human Error: Manual data entry and processing are prone to human errors, such as typos, incorrect calculations, and misinterpretation of information. These errors can lead to incorrect orders, inaccurate financial records, and production delays.
- Lack of Visibility: Manual processes often lack real-time visibility into procurement activities, making it difficult to track the status of orders, monitor inventory levels, and identify potential issues in a timely manner.
- Inefficient Communication: Manual processes rely on paper-based communication or emails, which can lead to delays in approvals, misunderstandings, and difficulty in tracking communication history.
- Slow Processing Times: Manual procurement processes involve physical handling of documents, leading to slower processing times for purchase orders, approvals, and supplier interactions. This can result in delays in receiving essential materials.
- Difficulty in Auditing: Auditing and tracking procurement activities become challenging when records are maintained manually. Ensuring compliance with regulations and internal policies becomes more cumbersome and time-consuming.
- Limited Supplier Collaboration: Manual processes hinder effective collaboration with suppliers. Lack of timely communication can lead to misunderstandings, delayed deliveries, and missed opportunities for negotiation.
- Higher Costs: Manual procurement processes require more resources in terms of labor, paper, printing, and storage. Additionally, errors and inefficiencies can lead to higher operational costs and potential financial losses.
- Lack of Data Insights: Manual processes generate limited data and make it harder to analyze procurement trends, identify cost-saving opportunities, and make informed strategic decisions.
- Scalability Issues: As organizations grow, manual procurement processes become increasingly challenging to manage. The complexities of handling a larger volume of transactions and suppliers can overwhelm manual workflows.
- Reduced Agility: Manual processes are less adaptable to changes in market conditions, customer demands, and supplier relationships. This lack of agility can hinder an organization's ability to respond effectively to evolving business needs.
- Security Risks: Paper-based processes can be more susceptible to security breaches, loss of sensitive information, and unauthorized access.
- Lack of Integration: Manual processes often lack integration with other systems, such as accounting, inventory management, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This results in data silos and manual data transfer between systems.
- Sustainability Concerns: Manual procurement processes contribute to excessive paper usage, leading to environmental concerns and higher operational costs for paper supplies and storage.
To address these challenges, many organizations are adopting digital procurement solutions and technologies, such as procurement software, electronic procurement platforms, and e-procurement systems. These technologies streamline and automate procurement workflows, enhance visibility, improve accuracy, and enable organizations to make data-driven decisions for more effective procurement management.
Benefits of Procurement Automation
The integration of automation into procurement processes brings forth a multitude of advantages that significantly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and strategic decision-making.
By replacing manual tasks with streamlined digital workflows, organizations can unlock a range of benefits that extend from cost savings and improved vendor relationships to enhanced data analysis and better compliance management. In this section, we delve into the compelling benefits of procurement automation and explore how it revolutionizes traditional procurement practices.
1. Speed Up the Purchase Order Process: Procurement automation accelerates the purchase order (PO) process by eliminating manual bottlenecks. Automated workflows ensure that purchase requests are routed swiftly for approval, and generated POs are instantly transmitted to suppliers.
This speed enhances procurement responsiveness, reduces lead times, and ensures that critical materials are procured on time. By removing delays inherent in manual processes, organizations can optimize their supply chain efficiency and meet production demands more effectively.
2. Reduce Errors: Automation minimizes errors that often occur in manual data entry and processing. Digital systems validate information against predefined rules, reducing the chances of inaccuracies. Automated data transfer between systems also eliminates the risk of transcription errors.
The result is increased accuracy in order placement, reduced instances of incorrect deliveries, and improved financial record-keeping. This reduction in errors leads to better product quality, lower returns, and improved customer satisfaction.
3. Improve Visibility into Spending: Procurement automation provides real-time insights into spending patterns. Centralized data allows organizations to monitor expenditures across various categories, departments, and projects. This visibility enables better budget control, identifies potential cost-saving opportunities, and supports informed decision-making. By having a clear overview of spending trends, organizations can negotiate better terms with suppliers and implement effective cost containment strategies.
4. Free Up Procurement Staff Time for More Strategic Tasks: Automating routine procurement tasks liberates procurement teams from administrative burdens. With less time spent on manual processes, staff can focus on strategic activities such as supplier relationship management, contract negotiations, and market research. This shift enables procurement professionals to contribute more to the organization's strategic goals, innovate procurement strategies, and drive business growth.
5. Improve Supplier Relationships: Automation enhances supplier relationships by ensuring smoother communication, timely order processing, and accurate documentation. Suppliers receive orders promptly, and any changes or updates are communicated in real time.
This transparency fosters trust and collaboration, leading to improved reliability, on-time deliveries, and potential for co-innovation. Strengthened supplier relationships can result in preferential treatment, access to supplier expertise, and mutually beneficial agreements.
6. Reduce Costs: One of the most compelling benefits of procurement automation is cost reduction. By eliminating manual processes, organizations reduce labor costs, decrease operational inefficiencies, and minimize the risk of errors that can lead to additional expenses.
Automation also enables better spend visibility and cost tracking, allowing organizations to identify areas for cost optimization and negotiate more favorable terms with suppliers. These cumulative effects contribute to substantial cost savings across the procurement lifecycle.
Types of Procurement Automation Solutions
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the need to harness the power of automation to streamline and enhance their procurement processes. In this section, we explore the diverse landscape of procurement automation solutions, each tailored to address specific challenges and opportunities within the procurement lifecycle.
From e-procurement platforms to supplier management systems and beyond, these solutions are shaping a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and strategic decision-making in procurement.
Cloud-based procurement software
Cloud-based procurement software is a digital solution hosted on remote servers, accessible via the internet. It enables organizations to manage their procurement processes efficiently and collaboratively from anywhere. Such software offers features like electronic requisitions, purchase order creation, automated approvals, and supplier management.
By utilizing cloud technology, organizations can centralize procurement data, enhance collaboration among stakeholders, and gain real-time visibility into purchasing activities. Cloud-based procurement software is scalable, reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure, and often comes with regular updates to ensure compliance and security.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are comprehensive software solutions that integrate various business processes, including procurement, finance, inventory management, and more. In the context of procurement, ERP systems provide end-to-end visibility into procurement activities. They streamline purchasing, automate order processing, facilitate supplier collaboration, and offer tools for spend analysis.
ERP systems centralize data, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time insights. By connecting different departments and functions, ERP systems ensure data consistency, reduce duplication of efforts, and promote seamless communication throughout the organization
Supplier relationship management (SRM) software
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) software is designed to optimize interactions and collaboration with suppliers. SRM solutions enable organizations to manage supplier information, performance, contracts, and negotiations. These systems facilitate strategic sourcing, supplier evaluation, and performance measurement. SRM software helps organizations build stronger supplier relationships.
This is achieved by providing a unified platform for communication, reducing administrative tasks, and ensuring compliance with supplier agreements. The goal is to align supplier capabilities with organizational needs, reduce risks, and maximize the value derived from supplier partnerships.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves using software robots or "bots" to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. In procurement, RPA can be employed to automate tasks like data entry, invoice processing, order placement, and data validation. By mimicking human interactions with software applications, RPA accelerates processes, reduces errors, and frees up human resources for more strategic activities.
RPA can integrate with existing systems, enabling organizations to automate specific tasks without undergoing extensive IT infrastructure changes. It's particularly valuable in scenarios where legacy systems need to interact with modern software or data sources.
How To Implement Procurement Automation
Implementing procurement automation involves a structured approach to ensure a smooth transition and effective utilization of technology. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Assess Your Current Procurement Processes: Begin by thoroughly evaluating your existing procurement processes. Identify pain points, bottlenecks, and areas that require improvement. This assessment provides a clear understanding of where automation can bring the most significant benefits.
Identify the Areas Where Automation Can Be Most Beneficial: Based on the assessment, pinpoint specific tasks and processes that can be streamlined through automation. Consider processes such as purchase requisitions, approvals, purchase order generation, supplier communication, invoice processing, and spend analysis. Focus on areas that have a high volume of transactions or are error-prone.
Select the Right Procurement Automation Solution: Research and select a procurement automation solution that aligns with your organization's needs. Look for features that address your identified pain points and offer scalability for future growth. Consider cloud-based solutions for flexibility and accessibility. Evaluate the solution's integration capabilities with your existing systems, user-friendliness, and potential for customization.
Implement the Solution and Train Your Staff: Engage with your chosen solution provider to implement the system. This includes configuring the software according to your processes, data migration, and integration with other systems if necessary. Simultaneously, provide comprehensive training to your staff. Ensure they understand how to use the new software effectively and efficiently.
Test and Refine: Before full deployment, conduct thorough testing to identify any glitches, issues, or gaps in the automation process. Adjust the solution as needed to ensure it aligns perfectly with your organization's requirements.
Rollout and Monitor: Launch the procurement automation solution gradually, starting with a pilot phase if possible. Monitor its performance closely to address any unforeseen challenges or adjustments needed. Gather feedback from users and incorporate their suggestions for continuous improvement.
Ensure Data Security and Compliance: As you automate procurement processes, ensure that sensitive data is securely managed and compliant with relevant regulations. Implement appropriate access controls and encryption methods to safeguard confidential information.
Continuous Improvement: Procurement automation is not a one-time project; it's an ongoing effort. Regularly review the performance of the solution and its impact on your procurement processes. Identify opportunities for optimization and enhancement, and adapt the solution to changing business needs.
In essence, successful procurement automation involves careful planning, choosing the right tools, aligning technology with process improvements, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
These steps collectively ensure a well-structured approach to implementing procurement automation, leading to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved overall procurement management.
Impact of Procurement Automation on the Bottom Line
Procurement automation has a substantial impact on an organization's bottom line by driving significant cost reductions and improving operational efficiency. Here's how procurement automation positively affects the bottom line:
Reduced Costs: Procurement automation directly contributes to cost savings by streamlining processes, minimizing errors, and optimizing resource allocation:
- Operational Efficiency: Automation eliminates manual tasks and reduces the need for paper-based processes, leading to lower labor costs and increased operational efficiency.
- Error Reduction: Automation reduces the risk of human errors in data entry, calculations, and order processing. This minimizes costly mistakes, such as over-ordering, incorrect pricing, and duplicate payments.
- Supplier Negotiations: Automation provides data-driven insights that empower organizations during supplier negotiations. Organizations can leverage spend analytics to negotiate better terms, discounts, and pricing with suppliers.
- Spend Management: Automation tools offer real-time visibility into spending patterns, enabling organizations to identify areas of excessive spending, enforce budget controls, and optimize procurement decisions.
- Invoice Processing: Automated invoice processing ensures accurate and timely payments, avoiding penalties and interest charges associated with late payments.
Improved Efficiency: Procurement automation enhances operational efficiency through streamlined workflows and quicker decision-making:
- Faster Procurement Cycle: Automated processes reduce cycle times for requisition approvals, purchase order generation, and supplier communication. This accelerates procurement processes, allowing organizations to respond faster to market demands.
- Real-time Visibility: Automation provides real-time insights into procurement activities, supplier performance, and spending trends. This visibility enables better decision-making and proactive issue resolution.
- Resource Allocation: By automating routine tasks, procurement teams can allocate their time and expertise to more strategic initiatives, such as supplier relationship management, strategic sourcing, and innovation.
- Consistency and Compliance: Automation ensures that procurement processes follow standardized procedures and compliance protocols. This consistency minimizes the risk of regulatory violations, audits, and associated financial penalties.
Overall, the impact of procurement automation on the bottom line is multi-faceted. It reduces costs associated with errors, inefficiencies, and suboptimal supplier relationships, while simultaneously boosting efficiency through streamlined workflows and data-driven decision-making. These benefits collectively contribute to enhanced profitability, improved financial performance, and a competitive advantage in the market.
Future Of Procurement Automation
The future of procurement automation is marked by continued technological advancements, deeper integration of AI and analytics, and a focus on strategic value creation. Here are some key trends that shape the future of procurement automation:
1. Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play an increasingly critical role in procurement automation. AI-powered systems will assist in predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and supplier performance evaluation. These technologies will enable organizations to make more accurate decisions based on data-driven insights, optimizing procurement strategies and resource allocation.
2. Intelligent Process Automation: Intelligent process automation, which combines robotic process automation (RPA) with AI, will lead to more sophisticated and adaptable automation solutions. These systems will not only automate repetitive tasks but also handle more complex processes that require decision-making, cognitive understanding, and adaptability.
3. Cognitive Procurement: Cognitive procurement involves AI systems that can understand and process unstructured data, such as contracts, emails, and social media feeds. This capability enables organizations to gain deeper insights into supplier sentiment, market trends, and regulatory changes, facilitating more informed procurement decisions.
4. Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology will enhance transparency and traceability in procurement processes. It will provide a secure and tamper-proof record of transactions, ensuring the authenticity of supplier information, certifications, and compliance records.
5. Supplier Ecosystem Collaboration: Procurement automation will extend beyond the organization's boundaries to collaborate seamlessly with suppliers. Supplier portals, digital marketplaces, and integrated communication channels will enable real-time collaboration, enhancing supplier relationships, and facilitating more efficient order processing.
6. Sustainability Integration: Automation will enable organizations to incorporate sustainability considerations into their procurement decisions more effectively. AI-driven tools can assess suppliers' environmental and social practices, helping organizations make ethical and sustainable sourcing choices.
7. Data-Driven Insights for Strategic Decision-Making: Procurement automation will increasingly provide advanced analytics and visualization tools, allowing organizations to identify trends, patterns, and opportunities within their procurement data. This will empower strategic decision-makers to optimize procurement strategies and drive competitive advantage.
8. Personalized Procurement: Automation will enable organizations to tailor procurement processes to individual user preferences. This personalization will improve user adoption, increase efficiency, and create a more intuitive procurement experience.
9. Continuous Improvement through Cognitive Learning: Systems will continuously learn from historical data and user interactions to refine processes, predict future needs, and proactively identify areas for improvement. This self-learning capability will drive ongoing optimization in procurement operations.
10. Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures: As procurement processes become more digitized, cybersecurity will become paramount. Automation solutions will incorporate advanced security measures to protect sensitive procurement data and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
In summary, the future of procurement automation lies in leveraging cutting-edge technologies to drive strategic value, enhance decision-making, and create a more efficient and collaborative procurement ecosystem. Organizations that embrace these trends will be better positioned to navigate complex supply chain landscapes and achieve sustained growth and success.
Conclusion
In a dynamic and ever-evolving business landscape, the adoption of procurement automation emerges as a transformative force with far-reaching implications. The journey from manual processes to digital sophistication signifies not just a technological shift, but a strategic leap towards operational excellence and strategic empowerment.
Procurement automation has proven its mettle by reshaping traditional practices and redefining the role of procurement within organizations. From swift purchase order processing to real-time spend analytics, its impact on the bottom line is profound.
The reduction in costs, derived from minimized errors and optimized supplier relationships, directly contributes to increased profitability. Improved efficiency, achieved through streamlined workflows and data-driven decision-making, translates into better resource allocation and quicker response to market dynamics.
Yet, the story of procurement automation transcends financial benefits alone. It speaks to a future where AI, machine learning, and intelligent automation orchestrate a symphony of efficiency, sustainability, and collaboration. Supplier ecosystems become seamlessly integrated, sustainability principles are engrained in processes, and predictive insights guide strategic direction. Procurement emerges as a nexus of innovation, strategic agility, and ethical responsibility.
As we embrace this future, it's crucial to acknowledge that procurement automation isn't just about replacing manual tasks; it's about liberating human potential. By automating routine activities, professionals can elevate their roles, focusing on strategic relationships, innovation, and data-driven decision-making. The synergy between human ingenuity and technological prowess paves the way for procurement's reimagined role within organizations.
In conclusion, procurement automation isn't merely a technological transition; it's a paradigm shift that propels businesses into a realm of heightened efficiency, competitive edge, and sustainable growth. By embracing this transformative journey, organizations embark on a trajectory where procurement is not just a functional process, but a strategic catalyst for innovation and success in the years to come.
How Can Deskera Help You?
Deskera ERP and MRP systems help you to keep your business units organized. The system's primary functions are as follows:
- Keep track of your raw materials and final items inventories
- Control production schedules and routings
- Keep a bill of materials
- Produce thorough reports
- Make your own dashboards
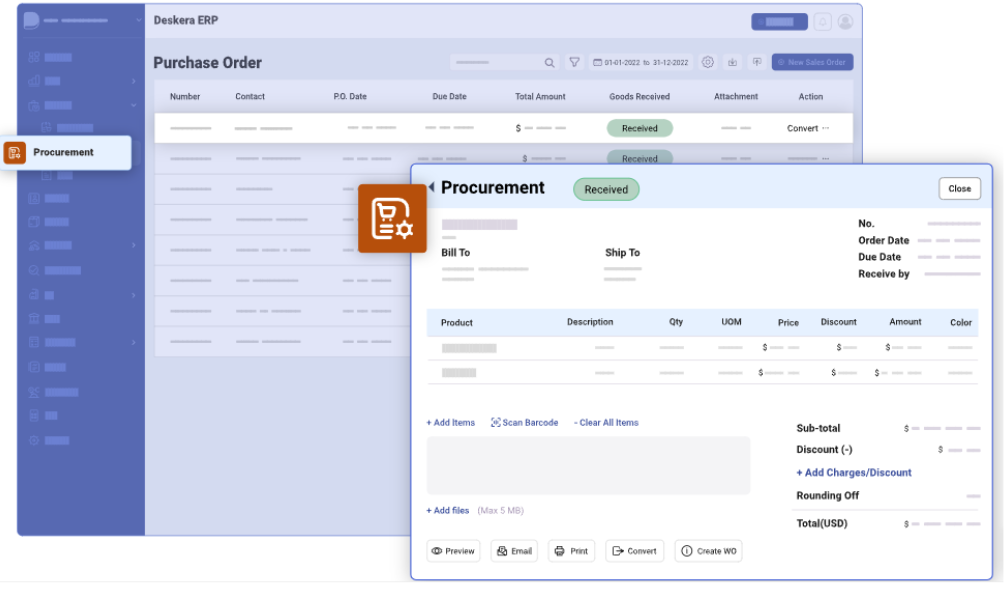
Here are some ways Deskera ERP's Procurement functionality can assist you:
- Create Requisitions and RFQs
- Generate Vendor Quotations
- Set up Vendor Scorecards
- Manage Preferred Suppliers
- Scan Purchase Invoices
- Create Purchase Orders
Deskera Books enables you to manage your accounts and finances more effectively. Maintain sound accounting practices by automating accounting operations such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing.
Deskera CRM is a strong solution that manages your sales and assists you in closing agreements quickly. It not only allows you to do critical duties such as lead generation via email, but it also provides you with a comprehensive view of your sales funnel.
Deskera People is a simple tool for taking control of your human resource management functions. The technology not only speeds up payroll processing but also allows you to manage all other activities such as overtime, benefits, bonuses, training programs, and much more.
Key Takeaways
- Efficiency at its Core: Procurement automation streamlines workflows, reducing manual tasks, and accelerating processes for enhanced efficiency across the procurement lifecycle.
- Cost Savings: Automation minimizes errors, optimizes supplier relationships, and improves spend management, resulting in substantial cost reductions and improved financial performance.
- Strategic Focus: Automation liberates procurement professionals from mundane tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives like supplier relationship management and innovation.
- Real-Time Insights: Automation provides real-time visibility into spending, supplier performance, and market trends, empowering data-driven decision-making.
- Supplier Collaboration: Automation extends collaboration with suppliers through digital portals, enabling better communication, faster order processing, and improved relationships.
- Risk Mitigation: Automated systems enhance compliance with regulations and contractual agreements, reducing the risk of penalties and legal disputes.
- AI-Powered Analytics: The integration of AI and analytics enables predictive insights, demand forecasting, and smarter supplier negotiations, adding strategic value.
- Sustainability Integration: Automation facilitates ethical and sustainable sourcing decisions by assessing suppliers' environmental and social practices.
- Continuous Improvement: Automation systems learn from historical data, enabling continuous process optimization and adaptation to changing business needs.
- Human-Centric Transformation: Procurement automation isn't just about technology; it's about empowering professionals to excel in strategic thinking, innovation, and relationship management.
These takeaways underscore the transformative impact of procurement automation, positioning organizations for efficiency, strategic growth, and sustained success.
Related Articles











