What if manufacturers could produce only what customers need, exactly when they need it, without excess inventory or wasted resources? This is the promise of on-demand manufacturing—a model that is reshaping the way businesses approach production. Unlike traditional mass production, on-demand manufacturing emphasizes flexibility, customization, and efficiency, aligning perfectly with today’s fast-paced and customer-driven markets.
The numbers speak for themselves: the global on-demand manufacturing service market is projected to reach $16.68 billion by 2031, growing at a remarkable CAGR of 15.16%. This growth highlights how businesses across industries—from automotive to healthcare—are adopting agile production models to stay competitive. As companies strive to reduce costs, minimize waste, and deliver personalized products, on-demand manufacturing stands out as a strategic solution.
However, making the shift requires more than just new equipment or technology—it requires a complete rethink of processes. Companies must embrace advanced digital tools, data-driven insights, and real-time collaboration with suppliers and customers. By doing so, they can overcome challenges like supply chain complexity, quality control in small batches, and high dependence on accurate forecasting.
This is where platforms like Deskera MRP make a difference. With features like demand forecasting, production planning, real-time inventory tracking, and seamless integration across departments, Deskera MRP empowers manufacturers to run leaner and more responsive operations. Its built-in AI assistant, David, further enhances decision-making by analyzing data and providing actionable insights—making it easier for businesses to embrace the on-demand model and achieve long-term growth.
What is On-Demand Manufacturing?
On-demand manufacturing, also known as manufacturing on demand, custom manufacturing, or cloud manufacturing, is a production model in which goods are manufactured only when required and in the exact quantities needed. Unlike traditional manufacturing—which relies on producing large volumes in advance and storing them as inventory—this approach aligns production directly with real customer orders, eliminating excess stock and reducing waste.
Historically, this model was difficult to achieve due to limitations in technology and supply chain coordination. Today, however, advancements in digital manufacturing systems, automation, and real-time data analytics have made it possible for manufacturers to efficiently respond to customer requests as they come in. This creates a more agile and demand-driven production process.
When executed effectively, on-demand manufacturing can deliver several benefits, including improved cash flow, resource utilization, and customer satisfaction. It minimizes the risks of overproduction while offering flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions. Conversely, if poorly implemented, it can lead to production delays and missed opportunities, especially in industries where speed and reliability are critical.
At its core, on-demand manufacturing is about responsiveness and flexibility. By integrating digital workflows, manufacturers can quickly process customer specifications, generate real-time pricing, plan material requirements, and initiate production without the need for large-scale pre-production runs. This shift from forecast-driven to demand-driven production marks a significant evolution in the way modern businesses approach manufacturing.
On-Demand Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing
The key difference between on-demand manufacturing and traditional manufacturing lies in how production is planned and executed.
- Traditional Manufacturing relies on large-scale production runs based on forecasts. Companies produce goods in bulk, store them in warehouses, and then distribute them as demand arises. While this method benefits from economies of scale, it also creates challenges such as high inventory costs, overproduction risks, and limited flexibility to adapt to changing customer needs.
- On-Demand Manufacturing, on the other hand, is an order-driven model. Products are manufactured only after a confirmed request, eliminating the need to stockpile finished goods. This reduces storage costs, minimizes waste, and allows for greater customization and responsiveness. However, it requires robust digital systems and agile supply chains to ensure timely delivery.
Key Differences at a Glance
In essence, while traditional manufacturing prioritizes volume and efficiency, on-demand manufacturing emphasizes agility, customization, and waste reduction. For businesses navigating unpredictable markets, the on-demand model provides a more sustainable and customer-centric approach.
On-Demand Manufacturing vs. Just-in-Time Manufacturing
While on-demand manufacturing (ODM) and just-in-time manufacturing (JIT) are often mentioned together, they are distinct approaches with unique goals and processes. Both aim to reduce waste and improve efficiency, but they operate differently in practice.
- Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT) focuses on producing goods exactly when needed for the production line or customer delivery. It relies on precise forecasting, close supplier coordination, and lean inventory practices to minimize storage costs. The idea is to receive materials “just in time” for production, reducing excess stock of raw materials and components.
- On-Demand Manufacturing (ODM), in contrast, is initiated only after a customer order is placed. Instead of producing in anticipation of demand, production begins once the demand is confirmed. This allows for greater product customization, reduced risk of unsold inventory, and the flexibility to meet unique customer requirements.
Key Differences at a Glance
In summary, JIT optimizes the timing of production inputs, ensuring manufacturers don’t hold excess raw materials, while on-demand manufacturing optimizes the output side, ensuring finished goods are only created when there is actual demand.
Many modern businesses integrate both approaches—using JIT for materials management and on-demand for finished product flexibility—to achieve the best of both worlds.
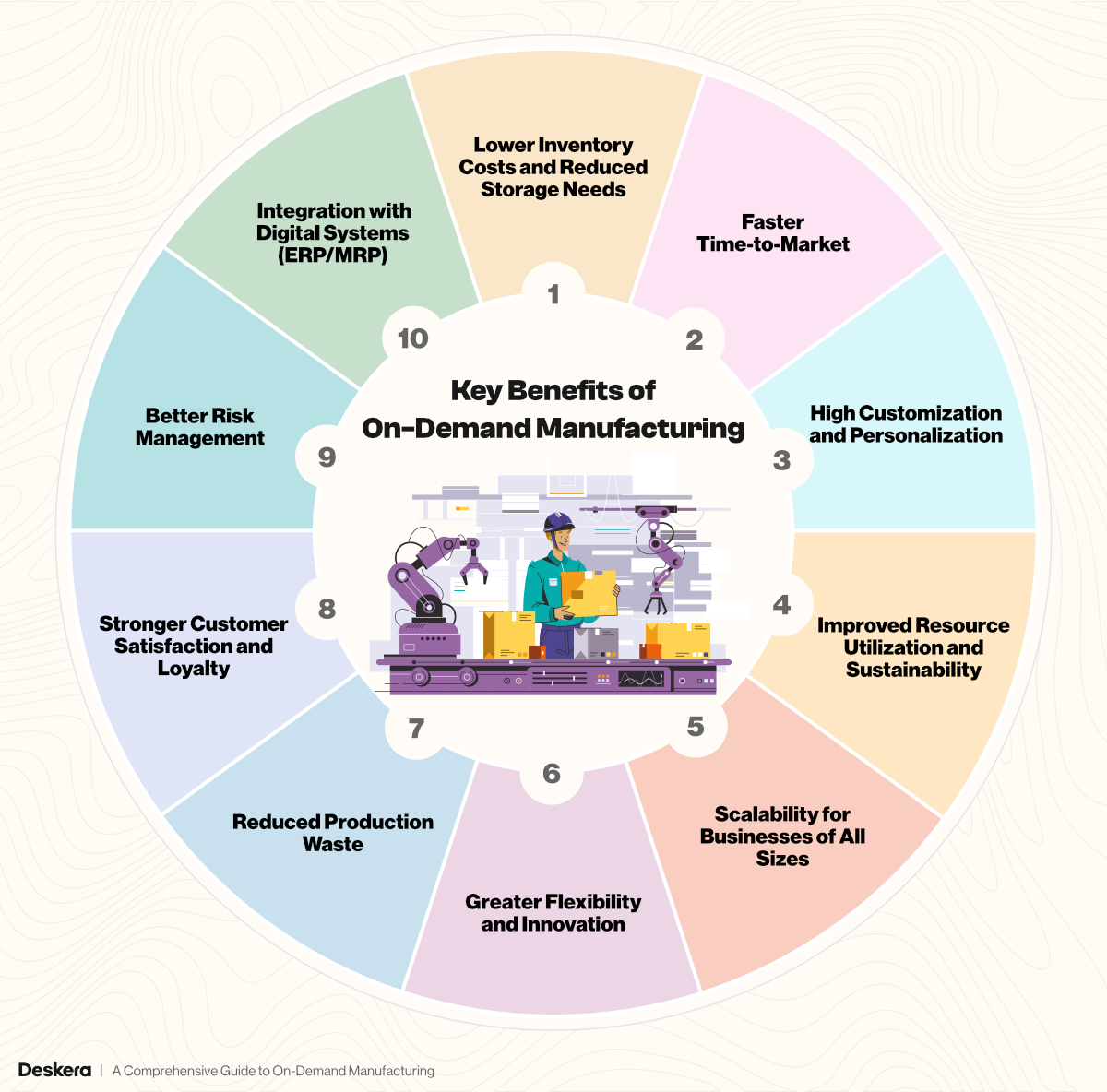
Key Benefits of On-Demand Manufacturing
On-demand manufacturing is more than just a production strategy—it’s a complete shift in how businesses align manufacturing with customer demand.
By integrating manufacturing processes with enterprise systems like ERP and leveraging digital tools, companies can achieve greater agility, sustainability, and profitability. Below are some of the most significant benefits:
1. Lower Inventory Costs and Reduced Storage Needs
One of the most immediate benefits of on-demand manufacturing is the elimination of excess inventory. Since products are only created after an order is confirmed, manufacturers don’t need to maintain large warehouses or stockpiles of finished goods.
This not only cuts down on storage costs but also reduces the financial risk associated with unsold inventory. Real-time tracking systems further enhance efficiency, helping businesses streamline production and avoid bottlenecks in the fulfillment process.
2. Faster Time-to-Market
On-demand manufacturing shortens production cycles by tapping into digital workflows and agile equipment. Companies can move quickly from design to finished product, enabling them to respond rapidly to shifting customer needs or market trends.
This speed is especially valuable in competitive industries where being first to market can create a decisive advantage. By accelerating product development and minimizing delays, businesses improve their cash flow and increase customer satisfaction.
3. High Customization and Personalization
Unlike traditional manufacturing, which focuses on standardized production, on-demand manufacturing thrives on customization. Customers can personalize products during the ordering process, and manufacturers can deliver goods tailored to those specifications.
This high level of flexibility fosters stronger customer engagement and loyalty while differentiating brands in crowded markets. Digital systems make it easy to manage these variations without compromising efficiency.
4. Improved Resource Utilization and Sustainability
On-demand manufacturing minimizes waste by producing only what is required. Advanced technologies, such as CNC machining and additive manufacturing, optimize raw material use while repurposing or recycling scrap where possible.
This not only reduces environmental impact but also aligns with consumer expectations for sustainable practices. A recent PwC survey found that customers are willing to pay nearly 10% more for sustainably produced goods, highlighting how sustainability is becoming a competitive advantage.
5. Scalability for Businesses of All Sizes
Whether it’s a small startup producing low-volume custom runs or a large enterprise adapting to fluctuating demand, on-demand manufacturing is inherently scalable.
Smaller companies benefit from reduced upfront costs and the ability to test new ideas without massive investments, while larger manufacturers can quickly adjust production volumes without worrying about excess stock.
This scalability allows businesses of any size to innovate more freely and adapt to changing markets with confidence.
6. Greater Flexibility and Innovation
On-demand production empowers businesses to quickly pivot in response to shifting market conditions or consumer preferences. Because production isn’t tied to rigid mass-production runs, companies can experiment with designs, materials, and product variations without significant risk. This flexibility encourages innovation, enabling rapid prototyping, faster testing, and quicker rollout of new products.
7. Reduced Production Waste
Advanced equipment used in on-demand manufacturing is highly precise, allowing for exact cuts, tailored assemblies, and minimal material waste. Any unavoidable scrap from technologies such as 3D printing can often be recycled or repurposed. This focus on reducing waste not only lowers costs but also supports sustainability goals.
8. Stronger Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
When customers receive exactly what they want—whether it’s a personalized product, a faster delivery, or sustainably produced goods—they are more likely to stay loyal to a brand. On-demand manufacturing directly enhances customer experience by combining speed, customization, and quality, building long-term trust.
9. Better Risk Management
Traditional manufacturing often involves the risk of overproduction, product obsolescence, or massive losses if demand shifts suddenly. On-demand manufacturing reduces these risks by producing only in response to confirmed demand. This agile approach ensures manufacturers are not left with unsold stock or outdated products.
10. Integration with Digital Systems (ERP/MRP)
When paired with enterprise resource planning (ERP) or material requirements planning (MRP) systems, on-demand manufacturing becomes even more powerful.
Businesses can synchronize production schedules with order data, optimize resource allocation, and track performance in real time. This level of integration ensures efficiency across procurement, manufacturing, and fulfillment while keeping operations lean.
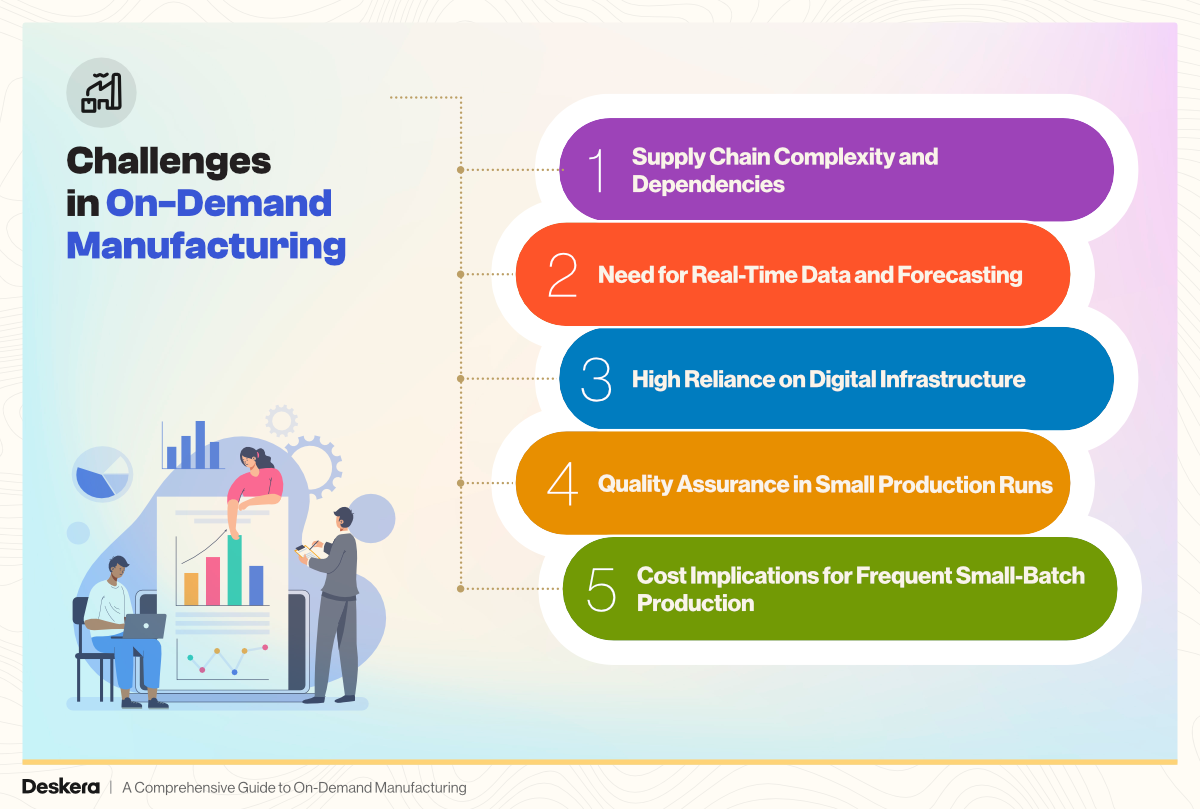
Challenges in On-Demand Manufacturing
While on-demand manufacturing offers clear advantages in flexibility, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, it also introduces unique challenges. Producing goods only when orders are placed requires precision, agility, and a robust digital ecosystem.
Below are some of the most pressing challenges businesses face when adopting this model:
1. Supply Chain Complexity and Dependencies
Unlike traditional manufacturing, which relies on bulk purchasing and stockpiling, on-demand production depends on real-time coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics partners.
Any disruption—whether due to material shortages, shipping delays, or geopolitical events—can halt production and cause missed deadlines.
To overcome this, businesses need agile supply chains, diverse vendor relationships, and advanced supply chain management systems that provide real-time visibility and predictive analytics.
2. Need for Real-Time Data and Forecasting
On-demand manufacturing thrives on accurate and timely data. Without robust forecasting tools, companies risk misjudging demand or failing to plan material procurement effectively. Real-time analytics allow manufacturers to anticipate customer needs, monitor order flows, and optimize resource allocation.
Integrating ERP or MRP systems can ensure that every stage—from order capture to fulfillment—is informed by live data, reducing inefficiencies and improving responsiveness.
3. High Reliance on Digital Infrastructure
The on-demand model is powered by automation, cloud platforms, and digital workflows. However, this reliance creates vulnerability: system outages, cybersecurity threats, or poor integration between tools can derail operations.
Businesses must invest in secure, scalable digital infrastructure, supported by regular updates and cybersecurity measures, to ensure uninterrupted production. In addition, seamless integration of production planning, procurement, and logistics systems is critical for maintaining efficiency.
4. Quality Assurance in Small Production Runs
Ensuring consistent quality across custom or small-batch orders can be more challenging than in mass production. Frequent equipment adjustments and diverse specifications increase the risk of errors or defects.
To mitigate this, manufacturers should implement robust quality control measures, automated testing protocols, and continuous monitoring. Investing in advanced equipment capable of fast recalibration also reduces variability and ensures high standards are maintained across every unit produced.
5. Cost Implications for Frequent Small-Batch Production
While on-demand manufacturing reduces inventory costs, it can increase per-unit expenses. Smaller production runs often mean higher procurement costs (due to lack of bulk discounts) and greater overhead allocation per product. Additionally, frequent machine adjustments can slow production and raise utility and labor costs.
Businesses can address these challenges by streamlining production workflows, adopting automation to reduce setup times, and optimizing procurement through smarter inventory management and supplier collaboration.
Strategies to Overcome On-Demand Manufacturing Challenges
While on-demand manufacturing comes with notable hurdles, businesses can mitigate these challenges through smart planning, technology adoption, and process optimization. Here are some practical strategies:
1. Managing Supply Chain Complexity and Dependencies
- Diversify supplier base: Relying on multiple vendors reduces the risk of disruption.
- Leverage digital supply chain platforms: Tools with real-time visibility help track supplier performance and shipment progress.
- Adopt flexible procurement models: Establish agreements with suppliers for smaller, frequent shipments without excessive costs.
2. Enhancing Real-Time Data and Forecasting
- Integrate ERP and AI-driven analytics: These systems forecast demand more accurately and help optimize production schedules.
- Use predictive maintenance: Ensures machines are ready for sudden production changes.
- Build data-sharing partnerships: Collaborate with suppliers and logistics providers for seamless information exchange.
3. Strengthening Digital Infrastructure
- Invest in cloud-based manufacturing systems: Enables scalability and remote access to production data.
- Enhance cybersecurity protocols: Protects sensitive product and order information.
- Automate workflows: Reduces human errors and speeds up order-to-production cycles.
4. Ensuring Quality in Small-Batch Production
- Adopt modular production systems: Streamlined setups allow faster adaptation without compromising quality.
- Implement rigorous quality checks: Use digital twin technology and IoT sensors for real-time inspection.
- Train workforce on flexibility: Skilled workers who can handle variations ensure consistency.
5. Controlling Costs in Frequent Small-Batch Production
- Optimize setup times with automation: Reduces downtime between product runs.
- Adopt lean manufacturing practices: Minimizes waste and maximizes efficiency.
- Use demand forecasting to negotiate better rates: Even with small batches, accurate predictions can strengthen supplier negotiations.
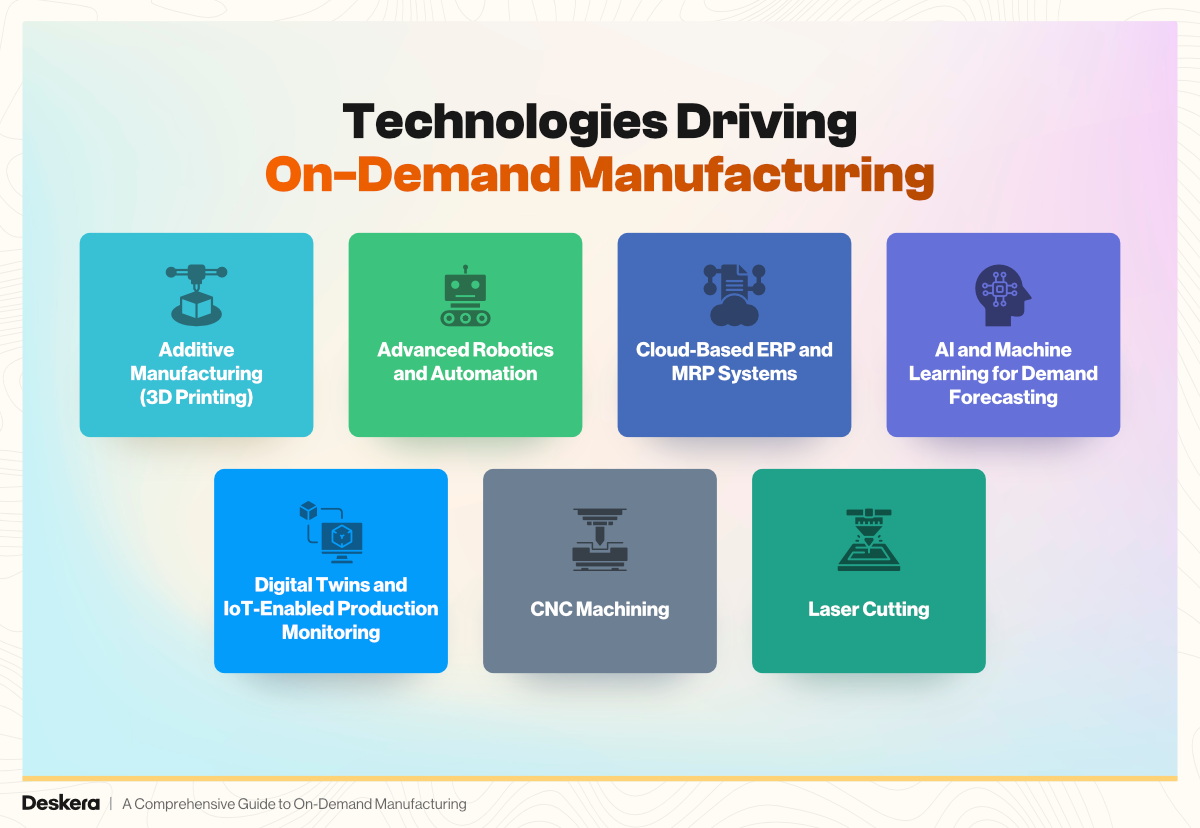
Technologies Driving On-Demand Manufacturing
On-demand manufacturing relies heavily on advanced technologies that make production more flexible, efficient, and scalable. These technologies enable businesses to quickly adapt to customer requirements, reduce waste, and streamline operations, all while maintaining product quality.
Below are some of the key technologies transforming the on-demand manufacturing model:
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, involves layering materials such as plastics, metals, or ceramics to create precise components.
It is particularly valuable for producing prototypes, complex geometries, or customized parts in short lead times. Manufacturers benefit from reduced material waste, faster design iterations, and lower tooling costs.
Advanced Robotics and Automation
Automation enhances nearly every step of on-demand manufacturing—from processing customer schematics to adjusting production machinery in real time.
Robotics systems can perform repetitive, labor-intensive, or hazardous tasks, improving productivity and workplace safety. Automated calibration and robotic handling also help manufacturers switch between custom orders with minimal downtime.
Cloud-Based ERP and MRP Systems
Cloud platforms integrate operations across order intake, production, inventory, quality control, and shipping. These systems provide real-time visibility and allow manufacturers to scale operations as demand fluctuates.
With cloud-based ERP and MRP tools like Deskera MRP, businesses can centralize processes, optimize resources, and seamlessly integrate emerging technologies such as IoT and AI.
AI and Machine Learning for Demand Forecasting
AI-driven algorithms strengthen production planning and supply chain forecasting. By analyzing customer preferences, historical data, and market trends, AI helps businesses predict demand more accurately.
Machine learning also powers real-time quality checks using computer vision, ensuring higher product standards and reducing rework or recalls.
Digital Twins and IoT-Enabled Production Monitoring
Digital twins create virtual models of machinery or production systems, enabling manufacturers to test processes, monitor performance, and predict failures.
Combined with IoT sensors, they deliver real-time insights into equipment health, production efficiency, and material usage. This improves predictive maintenance and minimizes downtime.
CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining uses programmed software to guide machinery in cutting, drilling, milling, or shaping raw materials into precise components.
It offers high accuracy, repeatability, and scalability, making it ideal for producing custom parts on demand. CNC machines can operate continuously with minimal human supervision, increasing productivity while enhancing workplace safety by automating hazardous tasks.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology enables manufacturers to cut, engrave, or shape materials such as metal, plastic, or wood with exceptional precision. Its programmability and accuracy make it perfect for highly customized or intricate designs required in small-batch, on-demand orders. Laser cutting also reduces waste, shortens lead times, and improves design flexibility compared to traditional methods.
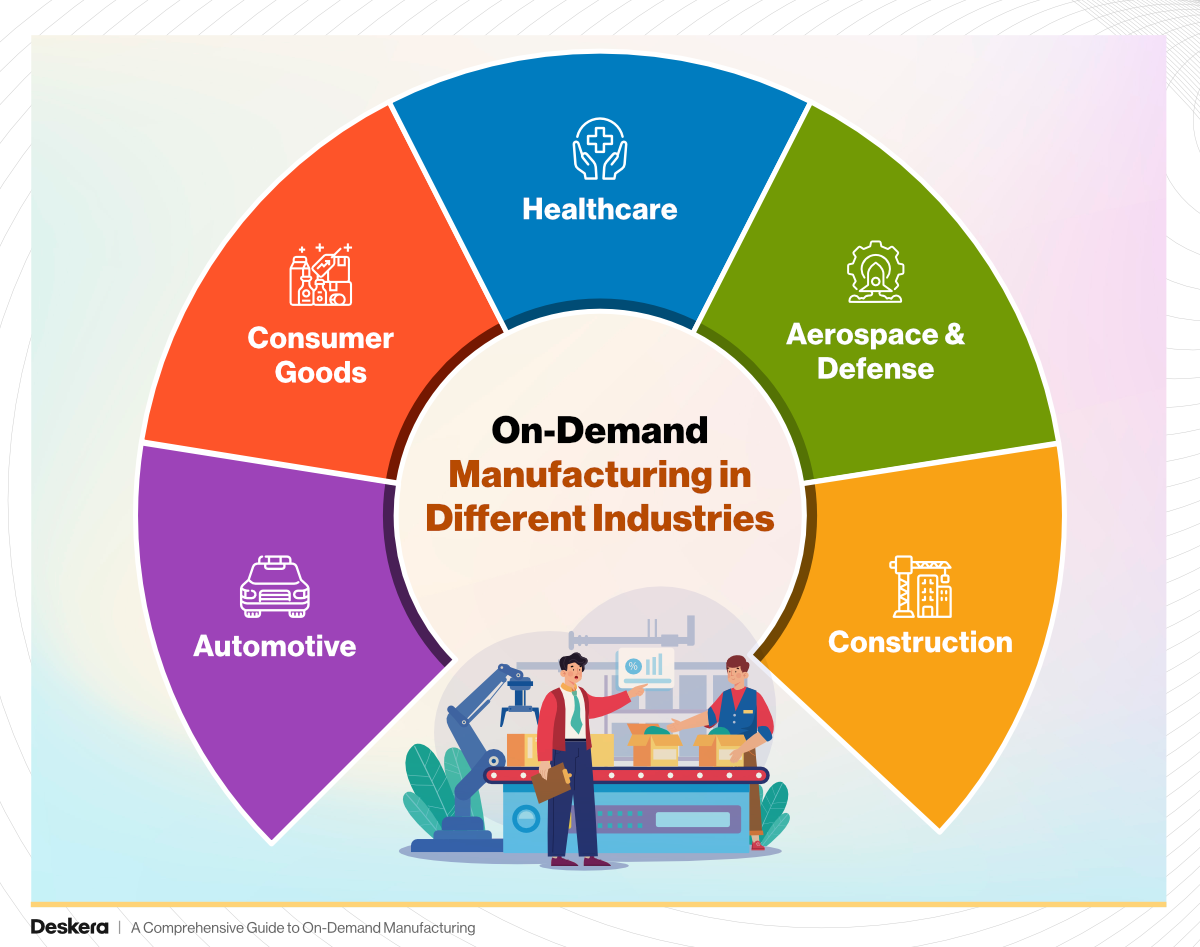
On-Demand Manufacturing in Different Industries
On-demand manufacturing has diverse applications across industries, as nearly anything can be produced to order. Each sector has its own unique priorities—speed, precision, customization, or cost efficiency—and therefore adopts different on-demand production methods such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting.
Let’s explore how some major industries leverage this manufacturing model:
1. Automotive
The automotive industry has embraced on-demand manufacturing to improve flexibility and reduce inventory costs. Instead of producing and storing thousands of spare parts, manufacturers now create them as needed using 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting.
- Customized parts and spares: Car makers and aftermarket companies can deliver highly customized accessories or performance upgrades without mass-producing them.
- Faster adaptation to regulations: On-demand methods allow rapid updates of vehicle components to comply with evolving safety standards.
- Reduced inventory burden: Automakers save significantly by manufacturing low-volume parts only when required.
2. Consumer Goods
Consumer goods, especially fashion, footwear, and electronics, are experiencing a shift toward personalization and sustainability. With rising demand for unique and eco-friendly products, on-demand manufacturing provides the perfect solution.
- Personalized products: Clothing brands can create limited runs of trendy styles, while footwear companies offer custom-fitted shoes for individual buyers.
- Sustainability: Producing only what is ordered reduces waste and excess stock, aligning with eco-conscious consumer preferences.
- Rapid prototyping: Electronics companies can quickly launch and test new designs without committing to large-scale production.
3. Healthcare
Healthcare is one of the biggest beneficiaries of on-demand manufacturing due to its need for custom, patient-specific solutions.
- Custom medical devices: Techniques like 3D printing produce personalized prosthetics, implants, and hearing aids tailored to each patient.
- Faster innovation: Rapid prototyping shortens the time required to test and refine new medical devices.
- Precision and complexity: High-accuracy methods such as CNC machining ensure critical components meet stringent quality standards.
4. Aerospace & Defense
The aerospace and defense industry requires lightweight, high-performance components with extreme precision. On-demand production provides unmatched advantages here.
- Low-volume, high-complexity parts: CNC machining and additive manufacturing create intricate structures with optimized weight-to-strength ratios.
- Remote production: On-demand manufacturing can even produce parts directly at remote locations or in space, minimizing reliance on long supply chains.
- Customization and safety: Engineers design parts with specialized geometric features to meet unique mission requirements.
5. Construction
Though less common than in other industries, construction is steadily adopting on-demand manufacturing for customized building components and tools.
- Tailored designs: Laser cutting and injection molding produce construction parts that match exact project dimensions.
- Onsite fabrication: Portable 3D printers allow components to be created directly at the site, drastically reducing turnaround times.
- Reduced waste and costs: By producing only what’s needed, construction companies save resources and minimize excess material usage.
How to Implement On-Demand Manufacturing in Your Business
Transitioning to on-demand manufacturing requires more than just adopting new technologies—it demands a mindset shift, process optimization, and the right infrastructure.
Here are key steps to successfully implement on-demand manufacturing in your business:
1. Assess Business Needs and Market Demand
- Start by analyzing which products or components would benefit most from on-demand production.
- Identify high-variability, low-volume items or products that require frequent customization.
- Conduct market research to understand customer demand trends, so you can match supply precisely with requirements.
2. Invest in the Right Technology
- Leverage tools such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting to enable rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
- Adopt manufacturing software or ERP solutions to streamline order processing, material planning, and scheduling.
- Explore AI-driven forecasting to anticipate customer requirements and avoid overproduction.
3. Build a Flexible Supply Chain
- Partner with suppliers that can deliver raw materials or components quickly and in smaller quantities.
- Consider digital supply networks that allow you to collaborate in real time with vendors and distributors.
- Reduce reliance on bulk ordering by integrating just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices.
4. Create a Scalable Production Model
- Start small with pilot projects to test the efficiency of on-demand workflows.
- Standardize production processes so they can be scaled up or down as needed.
- Use modular manufacturing setups to switch easily between product types.
5. Leverage Data and Automation
- Implement IoT-enabled devices to track production and machine performance.
- Use real-time data analytics to optimize production scheduling and material usage.
- Automate repetitive tasks (quality checks, order tracking, invoicing) for faster response times.
6. Focus on Quality and Customization
- Incorporate strict quality control measures, especially since on-demand items are often highly customized.
- Offer customers design input options (such as digital configurators) to improve satisfaction and reduce error rates.
- Align with industry compliance and safety standards to maintain trust.
7. Train Your Workforce
- Equip employees with skills to operate advanced machinery like CNC systems, 3D printers, and laser cutters.
- Provide training in digital tools, design software, and data interpretation.
- Encourage a culture of adaptability and innovation.
8. Monitor, Measure, and Improve
- Track KPIs such as lead time reduction, inventory turnover, waste reduction, and customer satisfaction.
- Use feedback loops to refine processes and technologies.
- Continuously evaluate ROI and expand on-demand practices to new product lines.
The Future of On-Demand Manufacturing
The trajectory of on-demand manufacturing points toward an increasingly agile, personalized, and sustainable future. As technologies evolve and consumer expectations shift, the manufacturing landscape is being reshaped in several transformative ways:
1. Microfactories and Localized Production Hubs
The rise of microfactories is enabling localized, low-impact production. These compact, automated facilities operate without harmful chemicals or excessive waste and can adapt swiftly to demand changes. They’re emerging as sustainable and flexible alternatives to traditional mass-production hubs.
2. AI-Powered, Smart, and Agile Manufacturing
Artificial Intelligence is driving a shift toward “rapid-agile” manufacturing, where customer orders trigger localized production that completes within mere days—minimizing waste and aligning product creation directly with demand. In sectors like fashion, AI enables demand forecasting, workflow optimization, and near-real-time responsiveness to trends.
3. Immersive Customization Through VR/AR
Virtual and augmented reality are expected to play a growing role in creating seamless customization experiences. Imagine trying on clothes or visualizing furniture in your space through immersive digital tools before placing an on-demand order—enhancing confidence and satisfaction.
4. Smarter, Transparent Supply Chains
The integration of IoT, blockchain, and advanced analytics promises supply chains that are more transparent, efficient, and responsive. This interconnected ecosystem will enable real-time adjustments and better risk management.
5. Hyper-Personalization at Scale
Mass customization is set to become mainstream, powered by AI-driven design tools that tailor products to individual preferences—without sacrificing production speed or efficiency.
6. Sustainability as a Core Driver
As consumers increasingly prioritize ethically produced goods, on-demand manufacturing’s waste-reducing, lean model positions it as a natural champion of sustainability. The reduction in overproduction aligns well with environmental goals across sectors.
7. Smart Factories and Cyber-Physical Integration
The future factory will be cyber-manufacturing enabled—with digital twins, IoT sensors, and AI harmonizing systems to predict maintenance needs, optimize performance, and automate decision-making.
8. Next-Gen Additive Manufacturing
3D printing is advancing rapidly: printers are becoming faster, more precise, and compatible with diverse materials. Industries like aerospace, watches, and automotive are already embracing these innovations to create lightweight, complex components on demand.
9. On-Field and On-Demand in Critical Sectors
The military is exploring portable, field-deployable 3D printing and AI systems—like mobile additive manufacturing pods—to manufacture critical parts in situ, minimizing logistical vulnerabilities.
How Can Deskera MRP Help You?
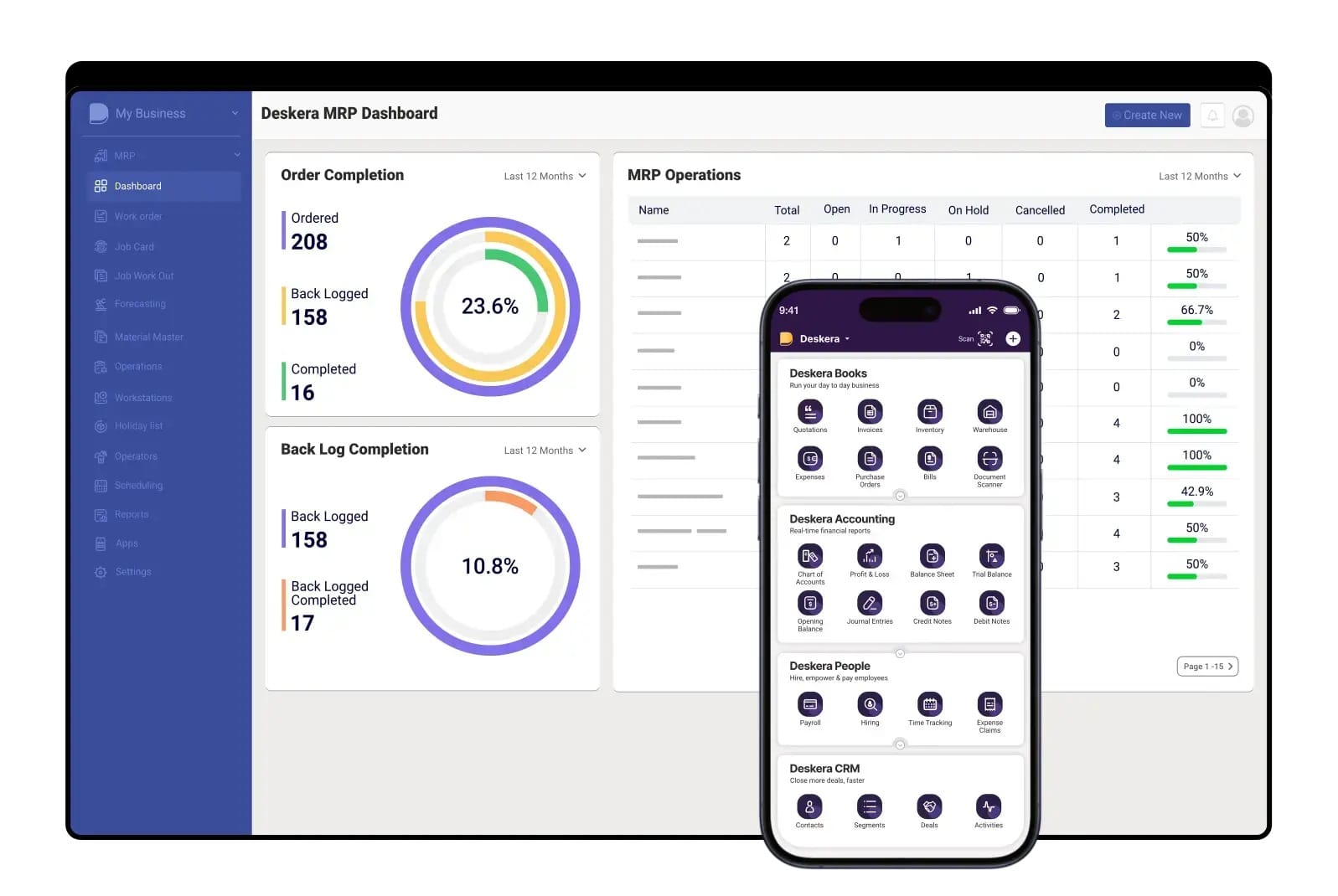
Implementing on-demand manufacturing requires precision, visibility, and seamless coordination across operations—and that’s where Deskera MRP can make a significant difference.
Deskera’s cloud-based solution enables businesses to manage production schedules, track inventory, and streamline workflows efficiently, ensuring they stay agile in a dynamic market.
With Deskera MRP, you can:
- Automate Production Planning – Create, adjust, and optimize production schedules in real-time based on demand fluctuations.
- Manage Inventory Smarter – Prevent stockouts or overstocking with automated inventory tracking and replenishment alerts.
- Enable Demand Forecasting – Leverage data-driven insights to anticipate customer needs and align resources accordingly.
- Boost Cost Efficiency – Reduce material wastage, improve resource utilization, and lower operational expenses.
- Enhance Collaboration – Give your teams a unified platform to track work orders, manage bills of materials (BOMs), and monitor production progress.
- Stay Mobile and Flexible – With Deskera’s mobile accessibility, decision-makers can oversee and control operations anytime, anywhere.
By combining these features, Deskera MRP empowers businesses to implement on-demand manufacturing strategies seamlessly, delivering faster turnaround times, improved efficiency, and higher customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaways
- On-demand manufacturing is reshaping modern production by focusing on efficiency, customization, and reduced waste. With the global market projected to hit $16.68 billion by 2031, its growth potential is undeniable.
- On-Demand Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing – Unlike traditional mass production, on-demand manufacturing emphasizes flexibility, lower inventory costs, and quicker response to customer needs.
- On-Demand Manufacturing vs. Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing – While JIT minimizes inventory by aligning production closely with demand, on-demand manufacturing offers greater scalability and customization, making it more adaptable to changing consumer preferences.
- Benefits of On-Demand Manufacturing – From reduced operational costs and faster time-to-market to better sustainability, increased customization, and risk mitigation, businesses gain significant competitive advantages.
- Challenges in On-Demand Manufacturing – Businesses may face hurdles like supply chain disruptions, high technology investment, and quality control issues, which must be strategically managed.
- Strategies to Overcome Challenges – Overcoming these obstacles requires diversifying suppliers, adopting advanced technologies, investing in staff training, and building strong quality assurance systems.
- Technologies Powering On-Demand Manufacturing – Tools like 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting are enabling rapid prototyping, precision, and high-quality production at scale.
- How to Implement On-Demand Manufacturing – Successful implementation involves assessing business needs, integrating the right technologies, streamlining workflows, and adopting robust inventory and production management systems.
- Future of On-Demand Manufacturing – The future promises integration with AI, IoT, and advanced robotics, driving greater agility, sustainability, and global adoption of on-demand models.
- How Deskera MRP Can Help – Deskera MRP supports on-demand manufacturing by automating production planning, optimizing inventory, forecasting demand, and ensuring seamless collaboration—empowering businesses to thrive in a competitive market.
Related Articles












