Have you ever wondered why some manufacturers are thriving while others are struggling to keep up? The difference often comes down to how quickly they embrace change—especially in the form of manufacturing automation. In an era where speed, precision, and adaptability determine success, relying solely on manual processes is no longer enough. Manufacturers that adopt automation are not just keeping pace; they are setting the pace.
The modern industrial era is defined by rapid technological advancements, global competition, and ever-changing customer demands. Small, medium, and large enterprises alike are under constant pressure to produce more, reduce costs, and deliver faster without compromising quality. Automation has emerged as the most effective way to achieve this, enabling manufacturers to optimize workflows, improve accuracy, and unlock higher profitability.
From robotics and AI to IoT-enabled machines, manufacturing automation is transforming production floors into smart, data-driven ecosystems. It’s no longer just about replacing human labor—it’s about empowering teams to work smarter, ensuring consistent quality, and adapting to market demands in real time. Whether you operate a small workshop or a large-scale manufacturing plant, automation levels the playing field by offering scalable, high-impact solutions.
This is where Deskera MRP comes in. Designed for manufacturers of all sizes, Deskera MRP combines powerful automation with easy-to-use features for production planning, demand forecasting, inventory control, and real-time reporting. Its AI-powered assistant, David, helps streamline decision-making and minimize downtime, while mobile accessibility ensures you can manage operations from anywhere. With Deskera MRP, businesses can seamlessly integrate manufacturing automation into their daily processes, paving the way for greater efficiency and sustainable growth.
What is Manufacturing Automation?
Manufacturing automation is the use of software, machines, robotics, and other advanced technologies to produce, assemble, and package goods with minimal or no human intervention.
By streamlining repetitive and precision-driven processes, automation enables manufacturers to operate more efficiently, reduce errors, improve safety, and lower production costs—all while increasing output. Beyond simply replacing manual labor, automation allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks such as oversight, innovation, and strategic decision-making.
Modern manufacturing automation covers a wide spectrum of tools and systems, including computer-controlled machinery, robotic arms, autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs), automated assembly lines, and AI-driven quality inspection systems.
For instance, robots can handle intricate assembly tasks, perform dangerous operations in hazardous environments, or synthesize chemicals in precise laboratory conditions. Sensors and vision systems allow for automated real-time quality control, while ERP software consolidates operational data to provide better visibility and informed decision-making.
As manufacturing becomes increasingly data-driven, automation is not just a way to cut costs—it’s a pathway to competitiveness, scalability, and innovation. According to an EY survey, 97% of industrial manufacturing CEOs see digital technology as a key driver for growth and efficiency in the near term.
With the continued advancement of AI, IoT, and robotics, manufacturing automation will play an even greater role in shaping the future of production across industries and business sizes.
Deskera MRP helps manufacturers harness the power of automation by streamlining production planning, optimizing inventory control, and enabling real-time tracking of operations.
Its AI-powered assistant, David, provides predictive insights for demand forecasting and preventive maintenance, while mobile accessibility ensures you can manage manufacturing workflows from anywhere. By integrating Deskera MRP into their operations, businesses can simplify complex processes, reduce downtime, and unlock the full benefits of manufacturing automation.
Types of Manufacturing Automation
Manufacturing automation is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Depending on the nature of production, the variety of products, and the level of flexibility required, manufacturers can choose from different types of automation systems. The three primary types are fixed automation, programmable automation, and flexible automation.
1. Fixed Automation
Fixed automation—also known as hard automation—is designed for high-volume production of a single product or a narrow product range. In this setup, the sequence of operations is predefined and remains unchanged.
Equipment, such as automated assembly lines, transfer machines, and chemical processing systems, is specifically built for the task and offers high production rates with minimal human intervention.
- Best for: Mass production of standardized products.
- Advantages: High efficiency, low unit cost, and consistent quality.
- Limitations: Low flexibility—making changes requires significant downtime and cost.
2. Programmable Automation
Programmable automation is ideal for batch production where product designs change periodically. Here, the production equipment can be reprogrammed or reconfigured to produce different items, although retooling can take time.
Examples include CNC (computer numerical control) machines and industrial robots that can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks.
- Best for: Medium-volume production with product variety.
- Advantages: Greater flexibility than fixed automation, ability to switch between product designs.
- Limitations: Changeovers can be time-consuming, making it less efficient for very small batches.
3. Flexible Automation
Flexible automation—sometimes called soft automation—takes adaptability to the next level. Systems are designed to switch between different products automatically, with minimal downtime. This is achieved using advanced robotics, sensors, and computer systems that adjust operations on the fly.
Flexible automation is common in industries that need to respond quickly to customer demands and market changes.
- Best for: Low to medium-volume production with frequent product changes.
- Advantages: High adaptability, minimal changeover time, supports customization.
- Limitations: Higher initial investment and complexity in setup.
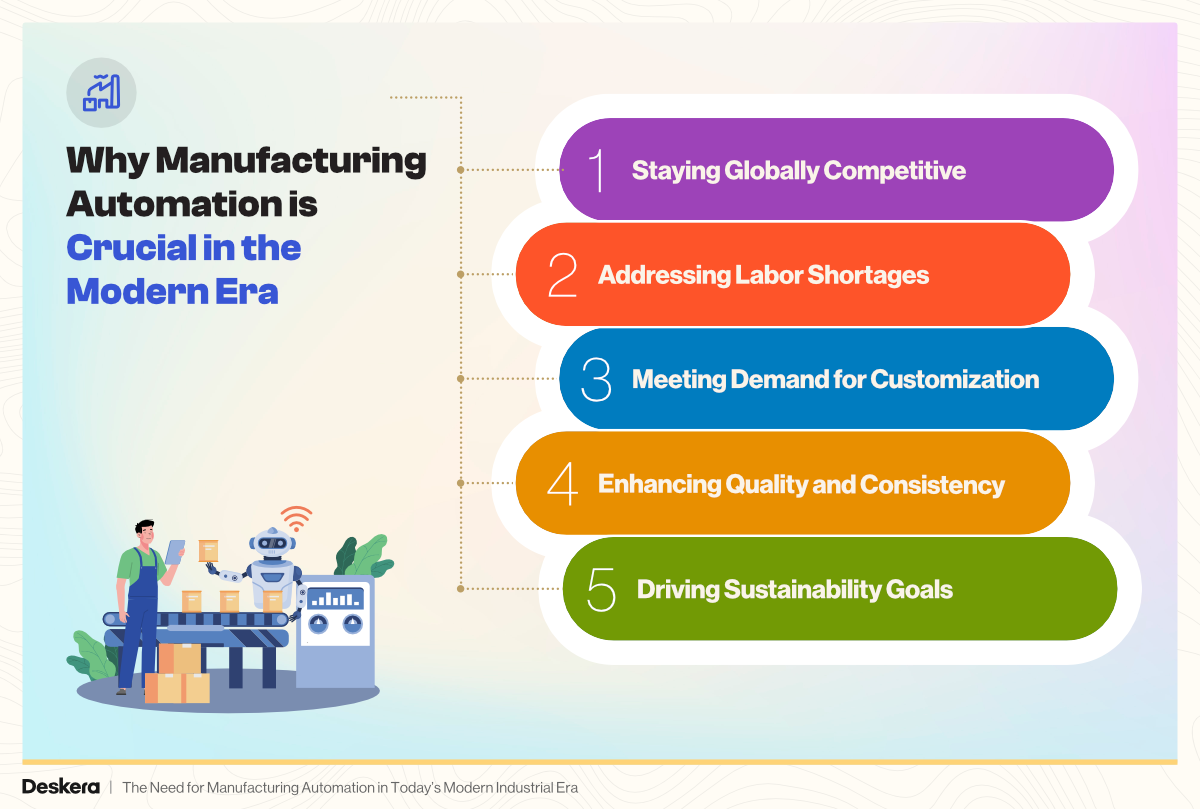
Why Manufacturing Automation is Crucial in the Modern Era
The modern industrial era is defined by rapid technological change, globalized competition, and evolving customer expectations. In such an environment, manufacturers—regardless of size—must operate faster, smarter, and more cost-effectively to remain competitive.
Manufacturing automation has emerged as the key enabler of this transformation, allowing businesses to boost productivity, improve quality, and adapt to market shifts with agility.
1. Staying Globally Competitive
Manufacturers today compete not only with local businesses but with global players operating at scale. Automation helps level the playing field by increasing throughput, reducing operational costs, and enabling just-in-time production. Companies that adopt automation can meet tight deadlines, deliver consistent quality, and maintain competitive pricing.
2. Addressing Labor Shortages
Many industries are facing a shortage of skilled labor, making it challenging to meet production demands. Automation bridges this gap by taking over repetitive, hazardous, or labor-intensive tasks. This not only ensures uninterrupted production but also frees skilled workers to focus on higher-value roles such as process optimization and quality control.
3. Meeting Demand for Customization
Customers increasingly expect personalized products delivered quickly. Flexible automation systems allow manufacturers to switch between product designs with minimal downtime, enabling mass customization without sacrificing efficiency.
4. Enhancing Quality and Consistency
Human error can lead to defects, rework, and wastage. Automated systems deliver precise, repeatable results that maintain quality standards across every production run. Advanced sensors and AI-driven inspections detect defects in real time, preventing costly errors from reaching the customer.
5. Driving Sustainability Goals
Sustainability is no longer optional—regulatory requirements and consumer expectations demand it. Automation optimizes resource usage, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes waste, making it easier for manufacturers to meet sustainability targets while improving profitability.
In short, manufacturing automation is not just a technology upgrade—it’s a strategic necessity. Companies that embrace it gain the agility, resilience, and efficiency needed to thrive in today’s competitive industrial era.
Benefits of Manufacturing Automation for Different Business Sizes
While the core advantages of automation—efficiency, cost savings, and quality improvement—apply across all manufacturers, the way these benefits are realized often depends on business size. Whether you run a small workshop or a global manufacturing enterprise, automation can transform your operations in unique ways.
Small Businesses
For small manufacturers, resources are often limited, and every investment must deliver a clear, measurable return. Automation helps these businesses compete with larger players by:
- Lower operational costs – Automated equipment and software complete tasks more quickly and accurately, reducing labor costs and material waste. With shorter ROI timelines—sometimes as little as 1–3 years—automation becomes a viable growth strategy.
- Improved efficiency without a large workforce – Automated systems can work 24/7 without breaks, enabling higher output without the need for a big team.
- Access to scalable solutions – Cloud-based tools and modular automation systems can grow alongside the business, allowing for gradual adoption without overwhelming resources.
Medium-Sized Manufacturers
Mid-sized manufacturers often face the challenge of balancing product variety with production efficiency. Automation offers the following advantages:
- Streamlined production lines – Automated processes reduce bottlenecks, enhance consistency, and shorten production cycles.
- Better inventory control – IoT-enabled sensors and ERP integration provide real-time stock visibility, reducing overstock and stockouts.
- Faster time-to-market – Flexible automation allows for quicker changeovers between products, enabling faster responses to shifting customer demands.
Large Enterprises
For large-scale manufacturers, the focus is often on optimizing complex, multi-site operations and maintaining global competitiveness. Automation delivers high-impact benefits such as:
- Full integration with ERP/MES systems – Consolidated data from production, inventory, and supply chain operations improves visibility and coordination across locations.
- Predictive maintenance and AI-driven decision-making – Sensors and analytics anticipate machine failures before they happen, minimizing downtime and maximizing output.
- Global supply chain visibility – Real-time data collection across production sites supports better forecasting, resource allocation, and risk management.
Across all business sizes, automation also boosts workplace safety, improves product quality, reduces waste, and provides actionable insights through real-time data collection.
By enabling manufacturers to meet demand with greater speed and reliability, automation not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction—helping businesses strengthen their market position over the long term.
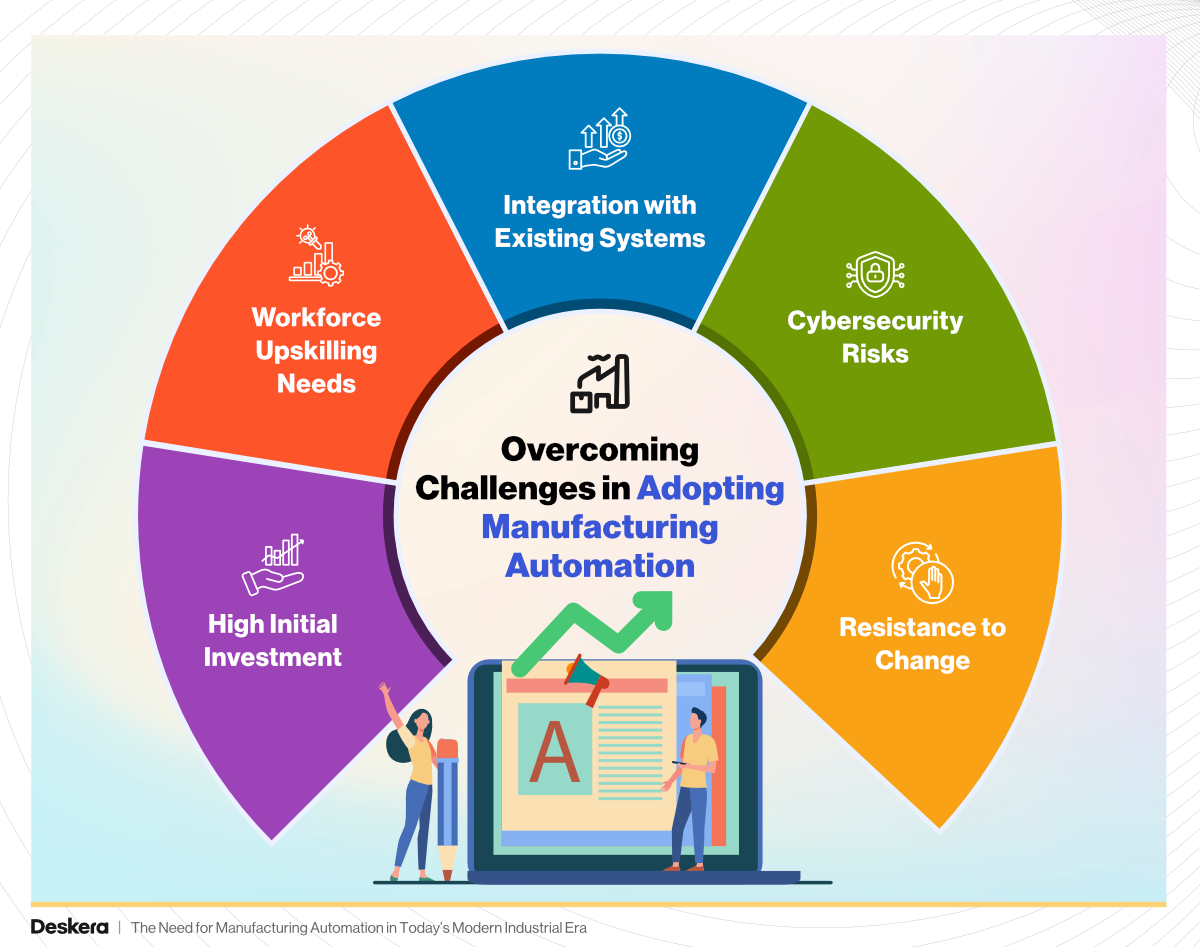
Overcoming Challenges in Adopting Manufacturing Automation
While the benefits of manufacturing automation are clear, many businesses—regardless of size—face obstacles when moving toward automated systems. From high initial costs to workforce concerns, these challenges can delay or derail automation projects if not addressed strategically. The key is to recognize these hurdles early and implement solutions that make adoption smoother and more sustainable.
1. High Initial Investment
Automation equipment, robotics, and software often require significant upfront spending, which can deter smaller manufacturers. However, shorter return-on-investment (ROI) periods—sometimes as little as 1–3 years—make the investment more attractive.
Solution: Start with modular, scalable automation solutions that can expand as the business grows. Cloud-based manufacturing systems like Deskera MRP also reduce infrastructure costs while offering advanced automation features.
2. Workforce Upskilling Needs
Introducing automation can create skill gaps, as existing staff may not be familiar with operating and maintaining new technologies.
Solution: Offer ongoing training and certification programs, focusing on both technical skills (e.g., robotics operation, software use) and analytical abilities to interpret automation data. This turns employees into active participants in the automation process rather than passive operators.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Many manufacturers use a mix of legacy machines and modern tools, which can make automation integration complex.
Solution: Choose automation technologies that are compatible with existing infrastructure or opt for integration-ready ERP/MRP platforms. This ensures a smooth transition without requiring a complete overhaul of existing processes.
4. Cybersecurity Risks
Automation systems connected to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can be vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Solution: Implement strong cybersecurity measures, such as network segmentation, regular software updates, and real-time threat monitoring. Training employees on cybersecurity best practices is equally important.
5. Resistance to Change
Employees and even management may be hesitant to adopt automation due to fears of job loss or disruption to existing workflows.
Solution: Communicate the benefits clearly—emphasizing how automation enhances safety, reduces repetitive work, and creates opportunities for higher-value roles. Involve teams in planning and implementation to foster buy-in.
By approaching automation adoption as a gradual, well-structured process rather than an all-at-once overhaul, manufacturers can overcome these challenges and set the stage for long-term success. The focus should be on strategic implementation, ensuring that automation aligns with business goals, workforce capabilities, and market demands.
The Role of Emerging Technologies in Manufacturing Automation
Manufacturing automation has evolved far beyond mechanical machines and assembly lines. Today, a new wave of emerging technologies is transforming how products are designed, produced, and delivered.
These innovations not only enhance operational efficiency but also create smarter, more adaptive manufacturing environments capable of responding instantly to market changes.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are enabling automation systems to analyze vast amounts of production data, identify patterns, and make predictions in real time. This leads to smarter decision-making, such as optimizing production schedules, predicting equipment failures, and improving quality control. AI-driven vision systems, for example, can detect defects invisible to the human eye, ensuring consistent product quality.
2. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
IIoT connects machines, sensors, and devices across the production floor, allowing them to communicate and share data. This interconnected ecosystem enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and faster troubleshooting. Manufacturers can track every stage of the production process, reducing downtime and increasing overall efficiency.
3. Robotics and Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Robots have long been part of automation, but modern robotics takes it a step further. Cobots work alongside human operators, handling repetitive or dangerous tasks while humans focus on strategic and creative work. They can be easily reprogrammed for different tasks, making them valuable in flexible manufacturing environments.
4. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical product, process, or system. In manufacturing, it allows companies to simulate production processes, test changes, and predict outcomes without disrupting real operations. This reduces risk, accelerates innovation, and improves decision-making.
5. Cloud Computing and Advanced ERP/MRP Systems
Cloud-based manufacturing platforms, such as Deskera MRP, integrate production planning, inventory management, and real-time reporting into a single solution. They provide remote access, scalability, and advanced analytics—helping manufacturers leverage automation without heavy IT infrastructure investments.
By embracing these emerging technologies, manufacturers can go beyond basic automation and create smart factories—highly efficient, adaptive, and resilient production environments. This not only boosts productivity and quality but also positions businesses to thrive in a rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
How Deskera MRP Can Help You
To truly unlock the full potential of manufacturing automation, businesses need more than just machines—they need a smart, connected platform to manage, monitor, and optimize operations. Deskera MRP delivers exactly that, offering an all-in-one cloud-based system that empowers manufacturers of all sizes to streamline processes and make smarter decisions.
Key ways Deskera MRP supports manufacturing automation:
- Automated Production Planning – Schedule and manage production runs efficiently with minimal manual intervention.
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking – Maintain optimal stock levels and avoid costly shortages or overstocking.
- AI-Powered Assistant (David) – Get instant insights, reports, and optimization suggestions.
- Demand Forecasting – Predict production needs accurately based on sales data and trends.
- Bill of Materials (BOM) Management – Simplify the creation and tracking of multi-level BOMs.
- Machine Maintenance Scheduling – Prevent downtime with proactive maintenance alerts.
- Advanced Reporting Templates – Generate detailed reports for better decision-making.
- Cloud-Based Access – Monitor and manage operations from anywhere, on any device.
- Integrated Modules – Connect finance, sales, procurement, and inventory into one seamless system.
By combining Deskera MRP with modern manufacturing automation, businesses can achieve higher efficiency, reduce costs, improve accuracy, and adapt quickly to changing market demands.
Key Takeaways
- Manufacturing automation is no longer optional—it’s a strategic necessity for manufacturers of all sizes to boost productivity, reduce costs, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
- Fixed, programmable, and flexible automation each serve distinct needs—choosing the right type depends on production volume, product variety, and adaptability requirements.
- Automation enhances efficiency, reduces human error, optimizes resources, and enables manufacturers to meet market demands faster while maintaining high quality.
- Common barriers like high initial investment, workforce adaptation, and integration issues can be mitigated through proper planning, training, and phased implementation.
- AI, IoT, robotics, and cloud-based platforms are driving the next generation of smart manufacturing, enabling data-driven decision-making and predictive capabilities.
- Deskera MRP integrates production planning, inventory management, demand forecasting, and machine maintenance into a unified platform—empowering manufacturers to fully leverage automation for growth.
Related Articles